An Efficient Convolutional Neural Network with Supervised Contrastive Learning for Multi-Target DOA Estimation in Low SNR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Signal Model and Data Setting
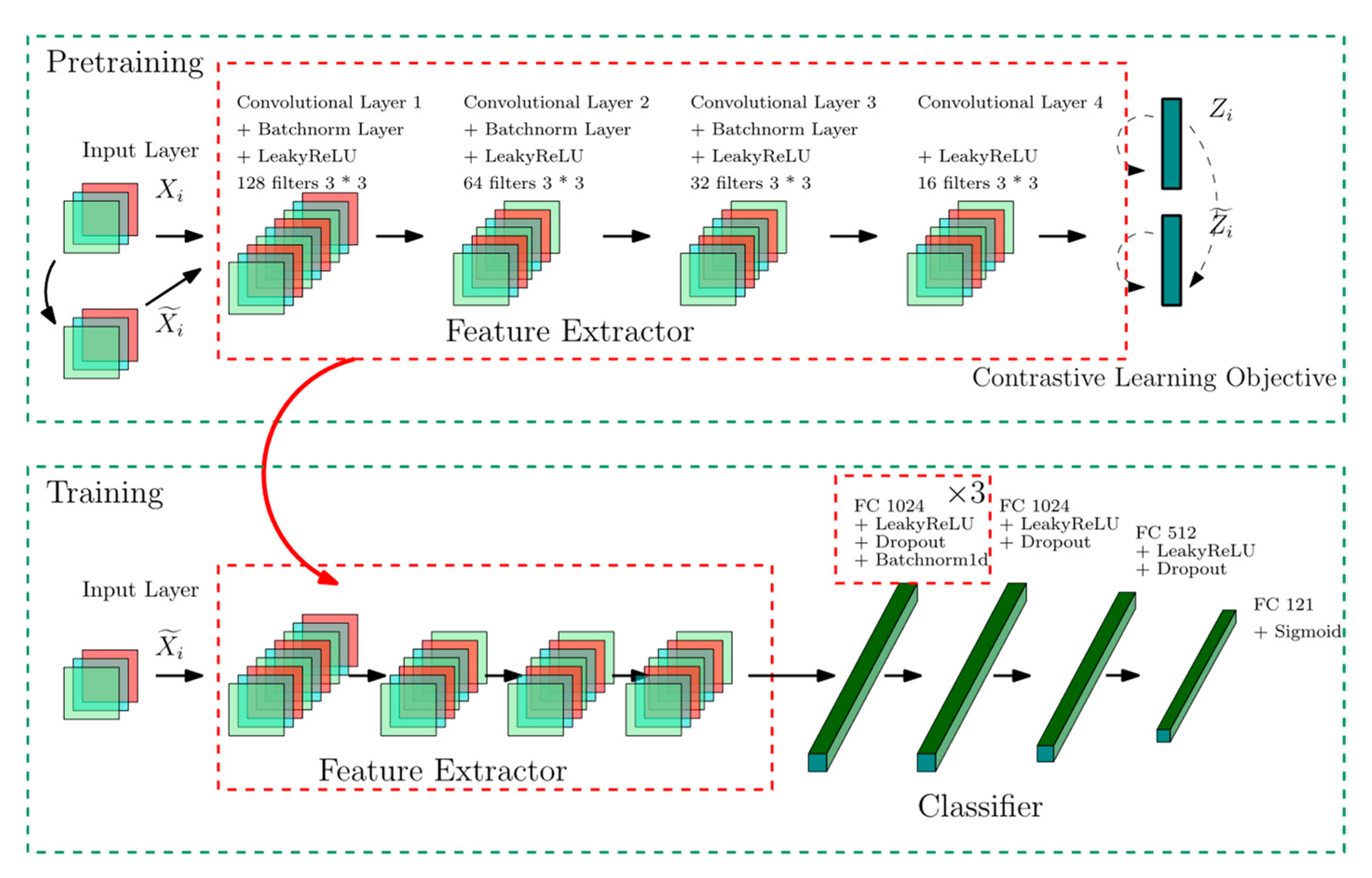
3. The Proposed Model
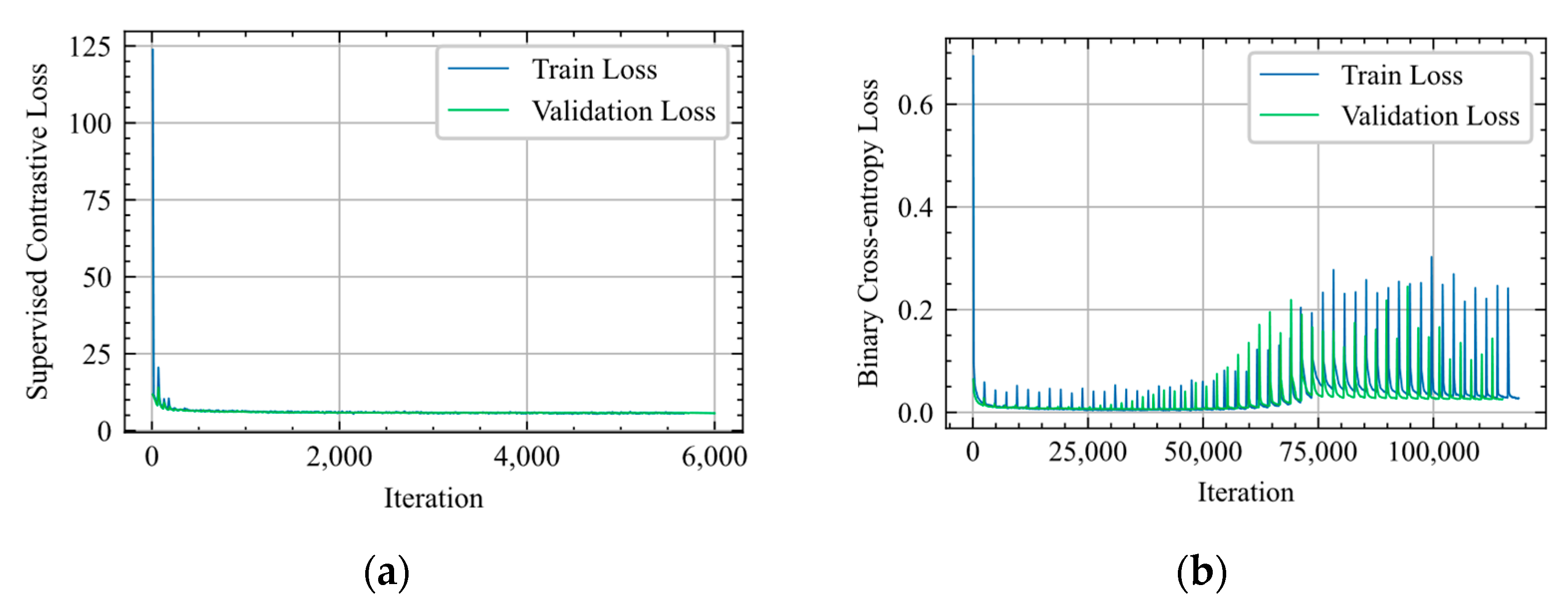
3.1. Pretraining Stage
3.2. Training Stage
4. Simulation Results
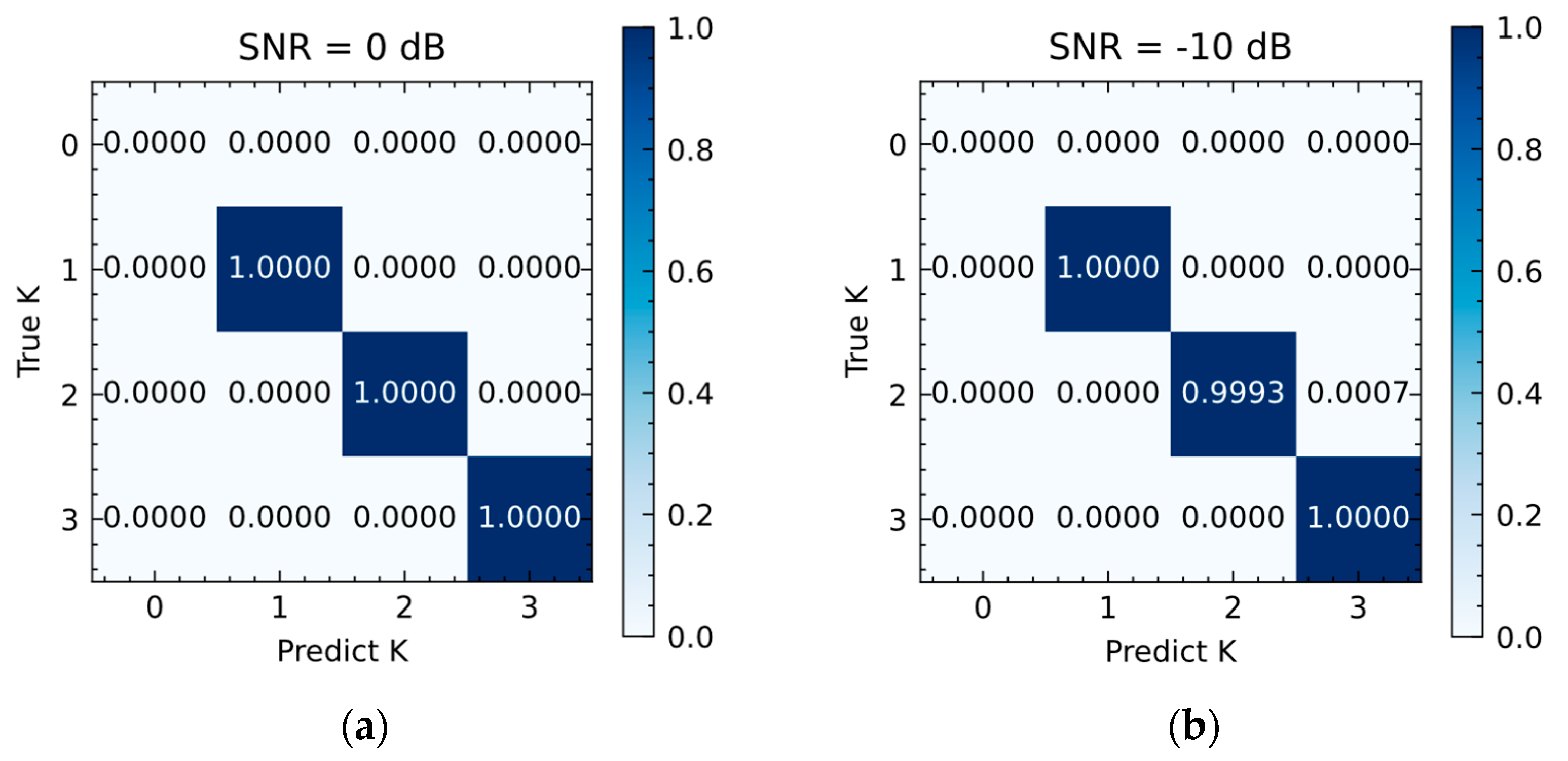
4.1. Unknown Number of Sources
4.2. Known Number of Sources
4.2.1. RMSE under Varying SNRs
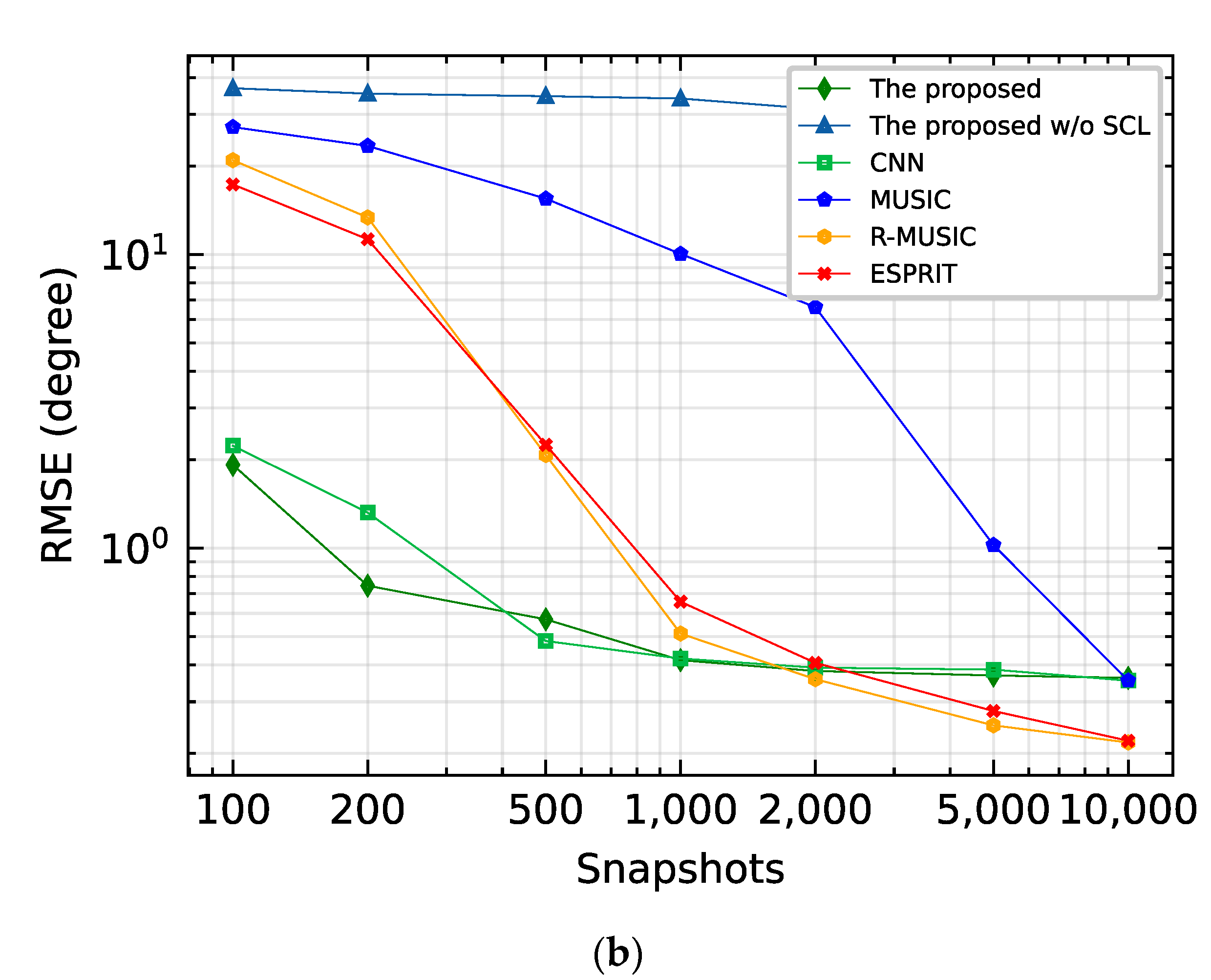
4.2.2. RMSE versus Varying Snapshots
5. Analysis
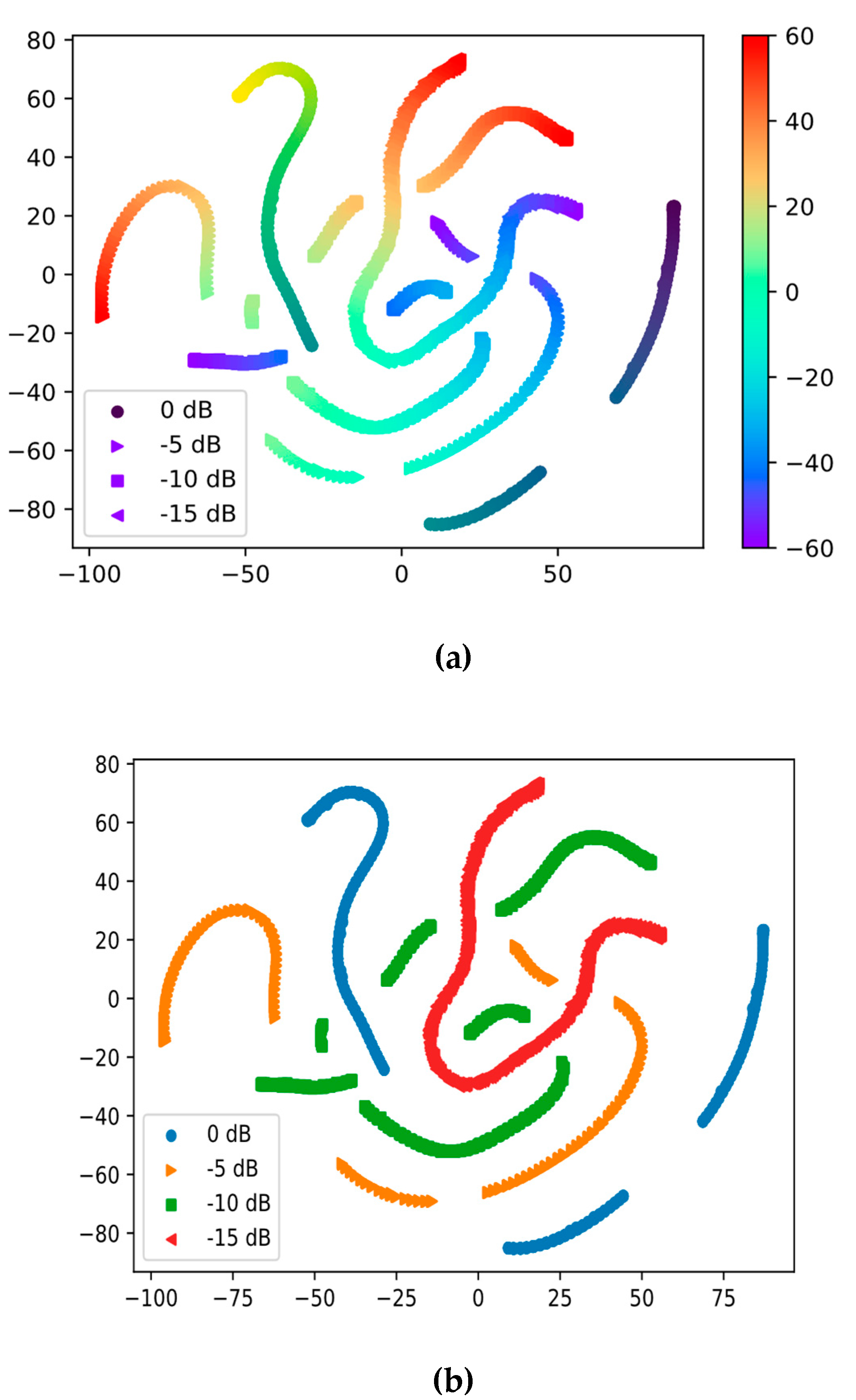
5.1. Latent Space Visualization
5.2. Feature Learning for Analysis
5.2.1. Preliminary and Ideal Model
- The label is generated as a Rademacher random variable.
- Given , each input include a feature patch and a noise patch , that are sampled as:where presenting the random variable taking value 1 with probability 1-x and −1 with probability x. and is usually constant, representing the invariant feature; and is usually uncertain with different data, representing the spurious feature with unreliable information.
- The noise vector conforms to the Gaussian distribution , indicating a noise orthogonal with both spurious and invariant features.
5.2.2. Theorem and Intuition
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.D.; Hari, K.V.S. Performance analysis of root-MUSIC. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Porosity reconstruction based on Biot elastic model of porous media by homotopy perturbation method. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 158, 112007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ding, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, W. Parameter Estimation for Nonlinear Diffusion Problems by the Constrained Homotopy Method. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Qi, Y. A nonlinear multigrid method for the parameter identification problem of partial differential equations with constraints. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ouyang, D.; Guo, L.; Qiu, R.; Qi, Y.; Xie, W.; Ma, Q.; Liu, C. Combination of Multigrid with Constraint Data for Inverse Problem of Nonlinear Diffusion Equation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Parameter estimation with the multigrid-homotopy method for a nonlinear diffusion equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 413, 114393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumchaiseemak, N.; Chatnuntawech, I.; Teerapittayanon, S.; Kotchapansompote, P.; Kaewlee, T.; Piriyajitakonkij, M.; Wilaiprasitporn, T.; Suwajanakorn, S. Toward Ant-Sized Moving Object Localization Using Deep Learning in FMCW Radar: A Pilot Study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Ohgane, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Kitayama, D.; Kishiyama, Y. DoA estimation of two targets with deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communications (WPNC), Bremen, Germany, 25–26 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.M.; Zhang, C.; Philip, S.Y. Direction-of-arrival estimation based on deep neural networks with robustness to array imperfections. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 7315–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.K.; Sellathurai, M.; Eldar, Y.C. Deep networks for direction-of-arrival estimation in low SNR. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3714–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Deep learning-aided coherent direction-of-arrival estimation with the FTMR algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Jia, X.; Tian, F. A gridless DOA estimation method based on convolutional neural network with Toeplitz prior. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oord, A.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03748. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Kuen, J.; Ma, L.; Shahroudy, A.; Shuai, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 77, 354–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlan, S.J.; Hinton, G.E. Simplifying neural networks by soft weight-sharing. Neural Comput. 1992, 4, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Mane, D.; Vasudevan, V.; Le, Q.V. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation policies from data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.09501. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, K.; Khasahmadi, A.H. Contrastive multi-view representation learning on graphs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Event, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 4116–4126. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Nitzberg, R. Constant-false-alarm-rate signal processors for several types of interference. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1972, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.M.; Zhang, Q.T.; Reilly, J.P.; Yip, P.C. On information theoretic criteria for determining the number of signals in high resolution array processing. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Nehorai, A. Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Adavanne, S.; Politis, A.; Virtanen, T. Direction of arrival estimation for multiple sound sources using convolutional recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1462–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y. Towards understanding ensemble, knowledge distillation and self-distillation in deep learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.09816. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Belkin, M.; Gu, Q. Benign overfitting in two-layer convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 25237–25250. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, K.; Bian, Y.; Han, B.; Cheng, J. Towards Understanding Feature Learning in Out-of-Distribution Generalization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.11327. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Srikant, R. Why deep neural networks for function approximation? arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.04161. [Google Scholar]
- Arjovsky, M.; Bottou, L.; Gulrajani, I.; Lopez-Paz, D. Invariant risk minimization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.02893. [Google Scholar]


| Number of Sources K 1 | (Degree) | (Degree) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNR = 0 dB | |||
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.2600 | 0.2600 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 0.2600 | 0.2600 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 0.2600 | 0.2600 |
| SNR = −10 dB | |||
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.2659 | 0.7400 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 0.2789 | 1.2600 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 0.3052 | 1.1200 |
| SNR = −15 dB | |||
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.4062 | 23.74 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 0.4737 | 15.11 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 0.7463 | 10.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, P.; Zhou, Z. An Efficient Convolutional Neural Network with Supervised Contrastive Learning for Multi-Target DOA Estimation in Low SNR. Axioms 2023, 12, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090862
Li Y, Zhou Z, Chen C, Wu P, Zhou Z. An Efficient Convolutional Neural Network with Supervised Contrastive Learning for Multi-Target DOA Estimation in Low SNR. Axioms. 2023; 12(9):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090862
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingchun, Zhengjie Zhou, Cheng Chen, Peng Wu, and Zhiquan Zhou. 2023. "An Efficient Convolutional Neural Network with Supervised Contrastive Learning for Multi-Target DOA Estimation in Low SNR" Axioms 12, no. 9: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090862
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhou, Z., Chen, C., Wu, P., & Zhou, Z. (2023). An Efficient Convolutional Neural Network with Supervised Contrastive Learning for Multi-Target DOA Estimation in Low SNR. Axioms, 12(9), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12090862






