A Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Double Hierarchy Linguistic Term Set
2.2. Double Hierarchy Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Set
2.3. The Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language
3. A Consensus Model for Large Group Decision-Making Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language
3.1. The Expert Clustering Algorithm Based on Similarity Measure
3.2. The Determination Method of Subjective and Objective Comprehensive Weight
3.3. The Consensus Degrees
4. A Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language
4.1. Reaching a Consensus within the Group
4.2. The Information Integration for Large Group Decision-Making
4.3. The Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method
5. The Case Study
- The self-confident single hierarchy interval hesitant fuzzy language (SC-SHIHFL). The second hierarchy LTS is deleted, and only the first hierarchy LTS is retained;
- The static self-confident double hierarchy interval hesitant fuzzy language (SSC-DHIHFL). Self-confidence is fixed, i.e., the value of self-confidence will not change with the group decision-making process;
- Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy language based on TOPSIS [12] (DHHFL-TOPSIS). The DHHFL-TOPSIS method ranks alternatives by measuring their closeness to an idealized goal;
- Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy language based on MULTIMOORA [11] (DHHFL-MULTIMOORA). The DHHFL-MULTIMOORA method analyzes the pros and cons of the scheme through three dimensions;
- Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy language based on consensus model handling minority opinions and non-cooperative behaviors in LGDM [23] (DHHFL-Consensus Model in LGDM).
| Number | Methods | Sort |
|---|---|---|
| Method 1 | SC-DHIHFL | |
| Method 2 | SC-SHIHFL | |
| Method 3 | SSC-DHIHFL | |
| Method 4 | DHHFL-TOPSIS | |
| Method 5 | DHHFL-MULTIMOORA | |
| Method 6 | DHHFL-Consensus Model in LGDM |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Expert | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
References
- Xu, X.H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, X.H. Dynamic Evolution Research on Emergency Decision Quality of Large Group Based on the Public Preferences Big Data. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2022, 30, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, I.; Martinez, L.; Herrera, F. A Consensus Model to Detect and Manage Noncooperative Behaviors in Large-Scale Group Decision Making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Ren, P.J. A Survey of Decision Making with Hesitant Fuzzy Preference Relations: Progress and Prospect. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2020, 40, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. The Concept of a Linguistic Variable and Its Application to Approximate Reasoning-I. Inf. Sci. 1975, 8, 199–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.M.; Martínez, L.; Herrera, F. Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Sets for Decision Making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K.T.; Gargov, G. Interval Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1989, 31, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, V. Hesitant Fuzzy Sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2010, 25, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S. A Method Based on Linguistic Aggregation Operators for Group Decision Making with Linguistic Preference Relations. Inf. Sci. 2004, 166, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.C.; Zhang, G.Q.; Hong, W.C.; Yu, S. Linguistic Computational Model Based on 2-Tuples and Intervals. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 21, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.J.; Liao, H.C.; Xu, Z.S.; Herrera, F. Double Hierarchy Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Set and MULTIMOORA Method: A Case of Study to Evaluate the Implementation Status of Haze Controlling Measures. Inf. Fusion 2017, 38, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Yang, F.X.; Fan, H.Y.; Yu, Q. Evaluation of Fog and Haze Governance Based on TOPSIS Method of Double-Layer Hesitation Fuzzy Language. Stat. Decis. 2019, 35, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Gou, X.J.; Xu, Z.S. Assessment of Traffic Congestion with ORESTE Method under Double Hierarchy Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Environment. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.D.; Shen, M.J.; Teng, F.; Zhu, B.Y.; Rong, L.L.; Geng, Y.S. Double Hierarchy Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Entropy-Based TODIM Approach using Evidential Theory. Inf. Sci. 2021, 547, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.C.; Xu, Z.S.; Gou, X.J. ELECTRE II Method Based on the Cosine Similarity to Evaluate the Performance of Financial Logistics Enterprises under Double Hierarchy Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Environment. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2023, 22, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Jiang, S.; Luo, G.; Liu, H.C. Identification of Key Performance Indicators for Hospital Management using an Extended Hesitant Linguistic DEMATEL Approach. Healthcare 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Yin, X.P.; Zhong, X.Y.; Wan, Q.F.; Yang, Z. Summary of Research on Theory and Methods in Large-Group Decision-Making: Problems and Challenges. Inf. Control. 2021, 50, 54–64+74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.C.; Zhang, H.J.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Integrating Experts’ Weights Generated Dynamically into the Consensus Reaching Process and Its Applications in Managing Non-Cooperative Behaviors. Decis. Support Syst. 2016, 84, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Luo, D.; Wei, B.L. Method for Large Group Decision-Making with Uncertain Linguistic Assessment Information Based on MC-EMD. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2017, 25, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, C.X.; Xue, H.F.; Lu, J. The Expert Synthesis and Integration Research Method Based on Hesitant Fuzzy Language. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2021, 41, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.B.; Xu, J.P. A Consensus Model for Large-Scale Group Decision Making with Hesitant Fuzzy Information and Changeable Clusters. Inf. Fusion 2018, 41, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Sarangi, A.; Mishra, D.; Mallick, P.K.; Shafi, J.; Srinivasu, P.N.; Ijaz, M.F. Automatic Data Clustering by Hybrid Enhanced Firefly and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithms. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.J.; Xu, Z.S.; Liao, H.C.; Herrera, F. Consensus Model Handling Minority Opinions and Noncooperative Behaviors in Large-Scale Group Decision-Making under Double Hierarchy Linguistic Preference Relations. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Shang, K.; Herrera, F. Social Network Analysis-Based Conflict Relationship Investigation and Conflict Degree-Based Consensus Reaching Process for Large Scale Decision Making using Sparse Representation. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.H. Large Group Risk Emergency Decision-Making Method Based on Group Pressure. J. Syst. Eng. 2022, 37, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.J.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, X.X.; Liao, H.C. Managing Consensus Reaching Process with Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Linguistic Preference Relations in Group Decision Making. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2021, 20, 51–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, X.J.; Xu, Z.S. Double Hierarchy Linguistic Term Set and Its Extensions: The State-of-the-Art Survey. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 832–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.; Nguyen, N.A.T.; Nguyen, V.T.T.; Dang, L.T.H. A Two-Stage Multi-Criteria Supplier Selection Model for Sustainable Automotive Supply Chain under Uncertainty. Axioms 2022, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


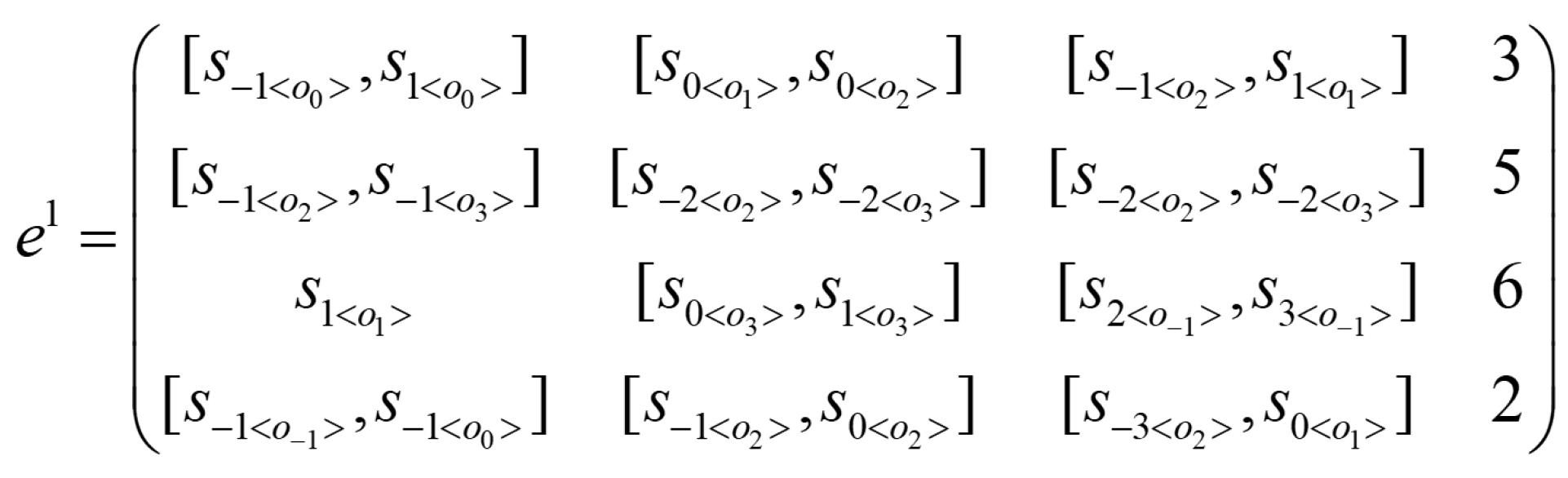
| Numerical Value | Semantic Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | Extremely low self-confidence |
| 2 | Very low self-confidence |
| 3 | Low self-confidence |
| 4 | Medium self-confidence |
| 5 | High self-confidence |
| 6 | Very high self-confidence |
| 7 | Extremely high self-confidence |
| Group | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [0.479, 0.631] | [0.417, 0.568] | [0.588, 0.769] | [0.366, 0.548] | |
| [0.595, 0.774] | [0.590, 0.758] | [0.642, 0.741] | [0.675, 0.873] | |
| [0.192, 0.466] | [0.360, 0.608] | [0.653, 0.787] | [0.558, 0.800] | |
| [0.056, 0.500] | [0.369, 0.395] | [0.408, 0.649] | [0.350, 0.410] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Cao, M.; Wang, L. A Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language. Axioms 2023, 12, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12060511
Zhang W, Cao M, Wang L. A Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language. Axioms. 2023; 12(6):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12060511
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenyu, Mengyao Cao, and Lei Wang. 2023. "A Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language" Axioms 12, no. 6: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12060511
APA StyleZhang, W., Cao, M., & Wang, L. (2023). A Two-Stage Large Group Decision-Making Method Based on a Self-Confident Double Hierarchy Interval Hesitant Fuzzy Language. Axioms, 12(6), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12060511









