An Enhanced Spatial Capture Model for Population Analysis Using Unidentified Counts through Camera Encounters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Employs a prior distribution for the essential parameter of the zero-inflated population;
- (2)
- Regularizes the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) by controlling the effective sample size;
- (3)
2. Methods
2.1. Hierarchical Spatial Capture–Recapture Model
2.2. Proposed Method
2.3. Sensitivity of the Model to
2.4. Autocorrelation Plot
2.5. Effective Sample Size
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCMC | Markov chain Monte Carlo |
| HSCR | Hierarchical spatial capture–recapture |
| Population size | |
| Estimated population size | |
| Sampling occasion | |
| Camera encounter history for individual , at camera , on occasion | |
| The encounter rate for individual at camera | |
| The baseline encounter rate | |
| Home range radius. | |
| The Euclidean distance between activity center and the camera location | |
| The number of camera encounters at camera on occasion | |
| The augmented parameter (the total number of hypothetical individuals) | |
| Probability of success, i.e., the probability that an individual in the occupancy model of size is a member of the original model of size | |
| and | Parameters of Beta probability distribution |
| ESS | The effective sample size |
| The number of zeros added to the model (data augmentation size) | |
| The autocorrelation between the current sample and kth preceding sample |
References
- Pollock, K.H. Capture-Recapture Models: A Review of Current Methods, Assumptions and Experimental Design. Stud. Avian Biol. 1981, 6, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, C.J.; Seber, G.A. Estimating Animal Abundance: Review III. Stat. Sci. 1999, 14, 427–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.D. Capture-Recapture Models. BioScience 1992, 42, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, K.H. A Capture-Recapture Design Robust to Unequal Probability of Capture. J. Wildl. Manag. 1982, 46, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, K.H.; Nichols, J.D.; Brownie, C.; Hines, J.E. Statistical Inference for Capture-Recapture Experiments. Wildl. Monogr. 1990, 48, 3–97. [Google Scholar]
- Karanth, K.U. Estimating Tiger Panthera Tigris Populations from Camera-Trap Data Using Capture—Recapture Models. Biol. Conserv. 1995, 71, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, A.F.; Nichols, J.D.; Karanth, K.U. Camera Traps in Animal Ecology: Methods and Analyses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 271. [Google Scholar]
- Jaber, M.; Woesik, R.V.; Kachouie, N.N. Probabilistic Detection Model for Population Estimation; Old Dominion University: Norfolk, VA, USA, 2018; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Distiller, G.; Borchers, D.L. A spatially explicit capture–recapture estimator for single-catch traps. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 5075–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeman, R.; Massei, G.; Sage, M.; Gentle, M.N. Monitoring Wild Pig Populations: A Review of Methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8077–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.A.; Young, K.V. A Hierarchical Model for Spatial Capture–Recapture Data. Ecology 2008, 89, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.A.; Karanth, K.U.; Gopalaswamy, A.M.; Kumar, N.S. Bayesian Inference in Camera Trapping Studies for a Class of Spatial Capture–Recapture Models. Ecology 2009, 90, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kery, M.; Gardner, B.; Stoeckle, T.; Weber, D.; Royle, J.A. Use of Spatial Capture-recapture Modeling and DNA Data to Estimate Densities of Elusive Animals. Conserv. Biol. 2011, 25, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, D. A Non-Technical Overview of Spatially Explicit Capture–Recapture Models. J. Ornithol. 2012, 152, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.A.; Chandler, R.B.; Sollmann, R.; Gardner, B. Spatial Capture-Recapture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 0-12-407152-X. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, B.; Reppucci, J.; Lucherini, M.; Royle, J.A. Spatially Explicit Inference for Open Populations: Estimating Demographic Parameters from Camera-trap Studies. Ecology 2010, 91, 3376–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royle, J.A.; Dorazio, R.M.; Link, W.A. Analysis of Multinomial Models with Unknown Index Using Data Augmentation. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2007, 16, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Liang, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Jin, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, F. Longitudinal Data Analysis Based on Bayesian Semiparametric Method. Axioms 2023, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, C.M. Markov Chain Monte Carlo and Gibbs Sampling. Lect. Notes EEB 2004, 581, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, R.; Nassar, M.; Elshahhat, A. Statistical Analysis of Inverse Lindley Data Using Adaptive Type-II Progressively Hybrid Censoring with Applications. Axioms 2023, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollmann, R.; Tôrres, N.M.; Furtado, M.M.; de Almeida Jácomo, A.T.; Palomares, F.; Roques, S.; Silveira, L. Combining Camera-Trapping and Noninvasive Genetic Data in a Spatial Capture–Recapture Framework Improves Density Estimates for the Jaguar. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 167, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, R.B.; Royle, J.A. Spatially explicit models for inference about density in unmarked or partially marked populatioins. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2013, 7, 936–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.A.; Dorazio, R.M. Parameter-Expanded Data Augmentation for Bayesian Analysis of Capture–Recapture Models. J. Ornithol. 2012, 152, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, O.F.; Roberts, G.O.; Sköld, M. Robust Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods for Spatial Generalized Linear Mixed Models. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2006, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanovska, I. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods in Biological Mechanistic Models. 2012. Available online: https://www.research-collection.ethz.ch/handle/20.500.11850/153590 (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Lewis, A. Efficient Sampling of Fast and Slow Cosmological Parameters. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, L.; Elvira, V.; Louzada, F. Effective Sample Size for Importance Sampling Based on Discrepancy Measures. Signal Process. 2017, 131, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabreti, L.G.; Höhna, S. Convergence Assessment for Bayesian Phylogenetic Analysis Using MCMC Simulation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, S. Investigating the Number of Monte Carlo Simulations for Statistically Stationary Model Outputs. Axioms 2023, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, M. A Spatiotemporal Bayesian Model for Population Analysis. 2022. Available online: https://repository.fit.edu/etd/880/ (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Martin, A.D.; Quinn, K.M.; Park, J.H. MCMCpack: Markov Chain Monte Carlo in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







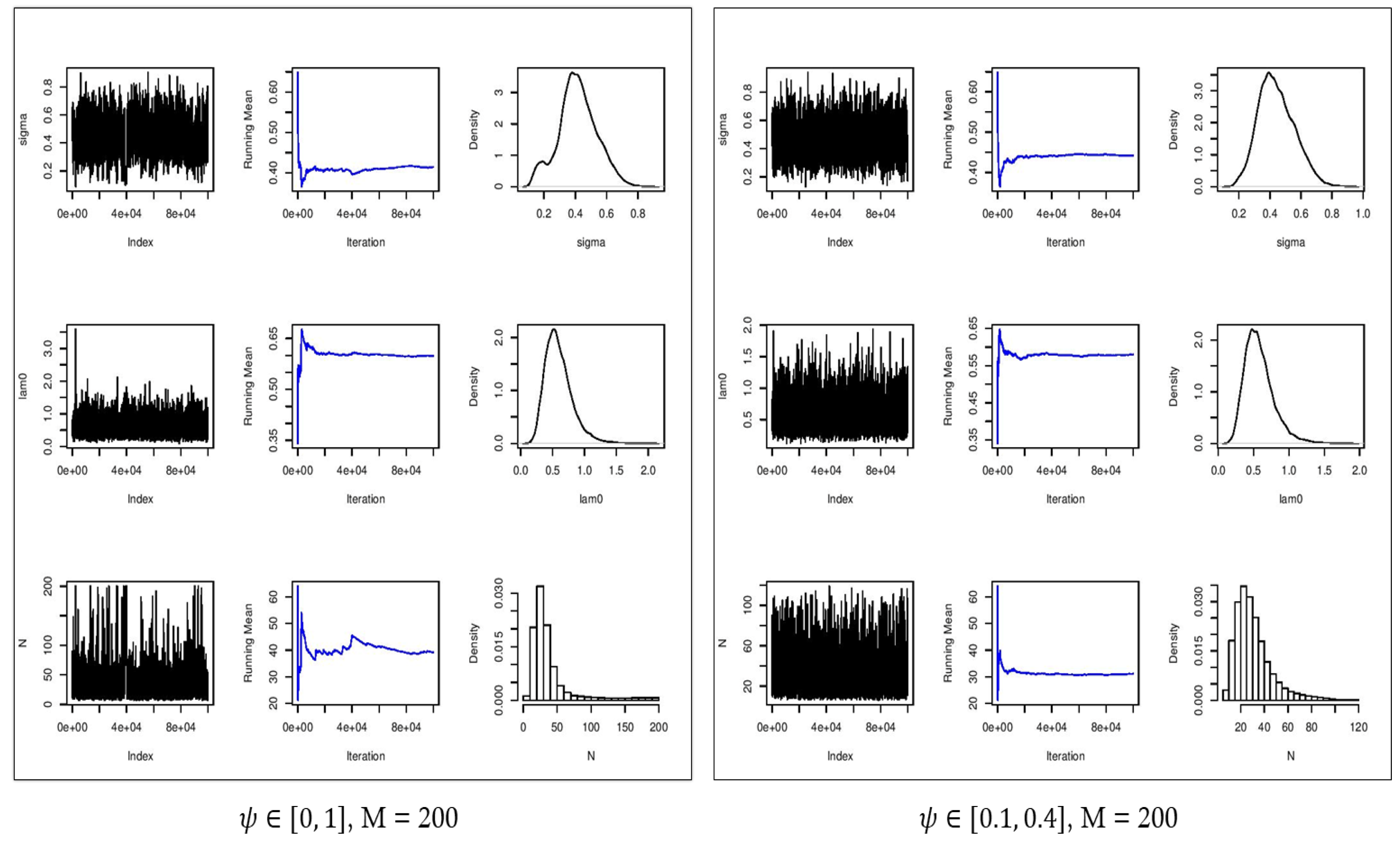
| 100 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.437 | 0.589 | 0.313 | 0.046 | 25.200 | 30.887 | 2.577 | 1113.2 | 1297.6 | 0.668 | 0.625 |
| 0.00–0.50 | 0.451 | 0.606 | 0.274 | 0.045 | 9.600 | 27.107 | 2.322 | 1850.8 | 2180.9 | 0.482 | 0.412 | |
| 0.10–0.40 | 0.465 | 0.585 | 0.253 | 0.043 | 1.200 | 25.255 | 2.185 | 2679.4 | 3232.7 | 0.403 | 0.324 | |
| 0.05–0.35 | 0.479 | 0.584 | 0.231 | 0.042 | 7.600 | 23.326 | 2.036 | 2505.5 | 3145.0 | 0.395 | 0.309 | |
| 0.10–0.35 | 0.471 | 0.589 | 0.237 | 0.043 | 5.200 | 23.862 | 2.077 | 2738.4 | 3681.9 | 0.352 | 0.260 | |
| 200 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.416 | 0.596 | 0.199 | 0.028 | 59.200 | 39.231 | 2.501 | 250.6 | 263.3 | 0.909 | 0.894 |
| 0.00–0.50 | 0.443 | 0.579 | 0.158 | 0.026 | 26.400 | 30.979 | 2.030 | 1066.8 | 1140.4 | 0.674 | 0.623 | |
| 0.10–0.40 | 0.415 | 0.579 | 0.174 | 0.027 | 39.200 | 33.433 | 2.192 | 2340.8 | 2727.2 | 0.496 | 0.431 | |
| 0.05–0.35 | 0.443 | 0.579 | 0.153 | 0.025 | 22.400 | 29.922 | 1.969 | 2082.8 | 2203.2 | 0.547 | 0.486 | |
| 0.10–0.35 | 0.411 | 0.592 | 0.173 | 0.027 | 38.400 | 33.340 | 2.184 | 3017.5 | 3701.7 | 0.446 | 0.375 |
| 100 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.560 | 0.497 | 0.323 | 29.200 | 31.943 | 1674.3 | 1862.4 | 0.635 | 0.593 |
| 0.00–0.50 | 0.563 | 0.546 | 0.273 | 9.200 | 27.173 | 3661.7 | 4368.0 | 0.393 | 0.334 | |
| 0.10–0.40 | 0.516 | 0.557 | 0.261 | 4.400 | 26.251 | 5987.0 | 7677.7 | 0.270 | 0.205 | |
| 200 | 0.00–1.00 | 0.546 | 0.527 | 0.170 | 36.000 | 33.321 | 1490.3 | 1778.8 | 0.670 | 0.620 |
| 0.00–0.50 | 0.527 | 0.564 | 0.158 | 26.400 | 31.026 | 2647.5 | 3152.3 | 0.528 | 0.473 | |
| 0.10–0.40 | 0.496 | 0.545 | 0.165 | 32.00 | 31.168 | 3880.0 | 4606.6 | 0.412 | 0.355 |
| 95% CI | 95% CI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 100 | 30.887 | 25.733 | 36.041 | 0.313 | 0.220 | 0.406 |
| 27.107 | 22.463 | 31.751 | 0.274 | 0.185 | 0.363 | |
| 25.255 | 20.886 | 29.624 | 0.253 | 0.166 | 0.340 | |
| 23.326 | 19.255 | 27.397 | 0.231 | 0.147 | 0.315 | |
| 23.862 | 19.707 | 28.017 | 0.237 | 0.152 | 0.322 | |
| = 200 | 39.231 | 34.230 | 44.232 | 0.199 | 0.143 | 0.255 |
| 30.979 | 26.919 | 35.039 | 0.158 | 0.106 | 0.210 | |
| 33.433 | 29.049 | 37.817 | 0.174 | 0.120 | 0.228 | |
| 29.922 | 25.984 | 33.860 | 0.153 | 0.102 | 0.204 | |
| 33.340 | 28.972 | 37.708 | 0.173 | 0.120 | 0.226 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaber, M.; Hamad, F.; Breininger, R.D.; Kachouie, N.N. An Enhanced Spatial Capture Model for Population Analysis Using Unidentified Counts through Camera Encounters. Axioms 2023, 12, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12121094
Jaber M, Hamad F, Breininger RD, Kachouie NN. An Enhanced Spatial Capture Model for Population Analysis Using Unidentified Counts through Camera Encounters. Axioms. 2023; 12(12):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12121094
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaber, Mohamed, Farag Hamad, Robert D. Breininger, and Nezamoddin N. Kachouie. 2023. "An Enhanced Spatial Capture Model for Population Analysis Using Unidentified Counts through Camera Encounters" Axioms 12, no. 12: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12121094
APA StyleJaber, M., Hamad, F., Breininger, R. D., & Kachouie, N. N. (2023). An Enhanced Spatial Capture Model for Population Analysis Using Unidentified Counts through Camera Encounters. Axioms, 12(12), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms12121094








