A Method for Analyzing the Performance Impact of Imbalanced Binary Data on Machine Learning Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
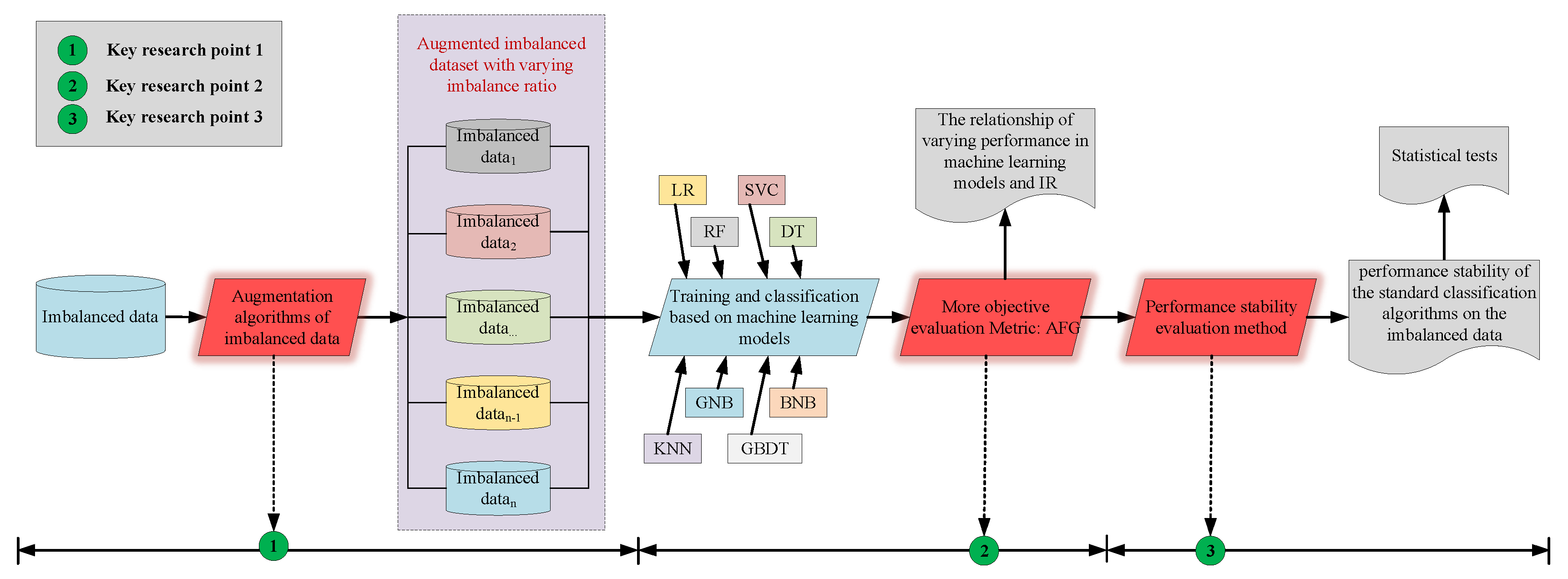
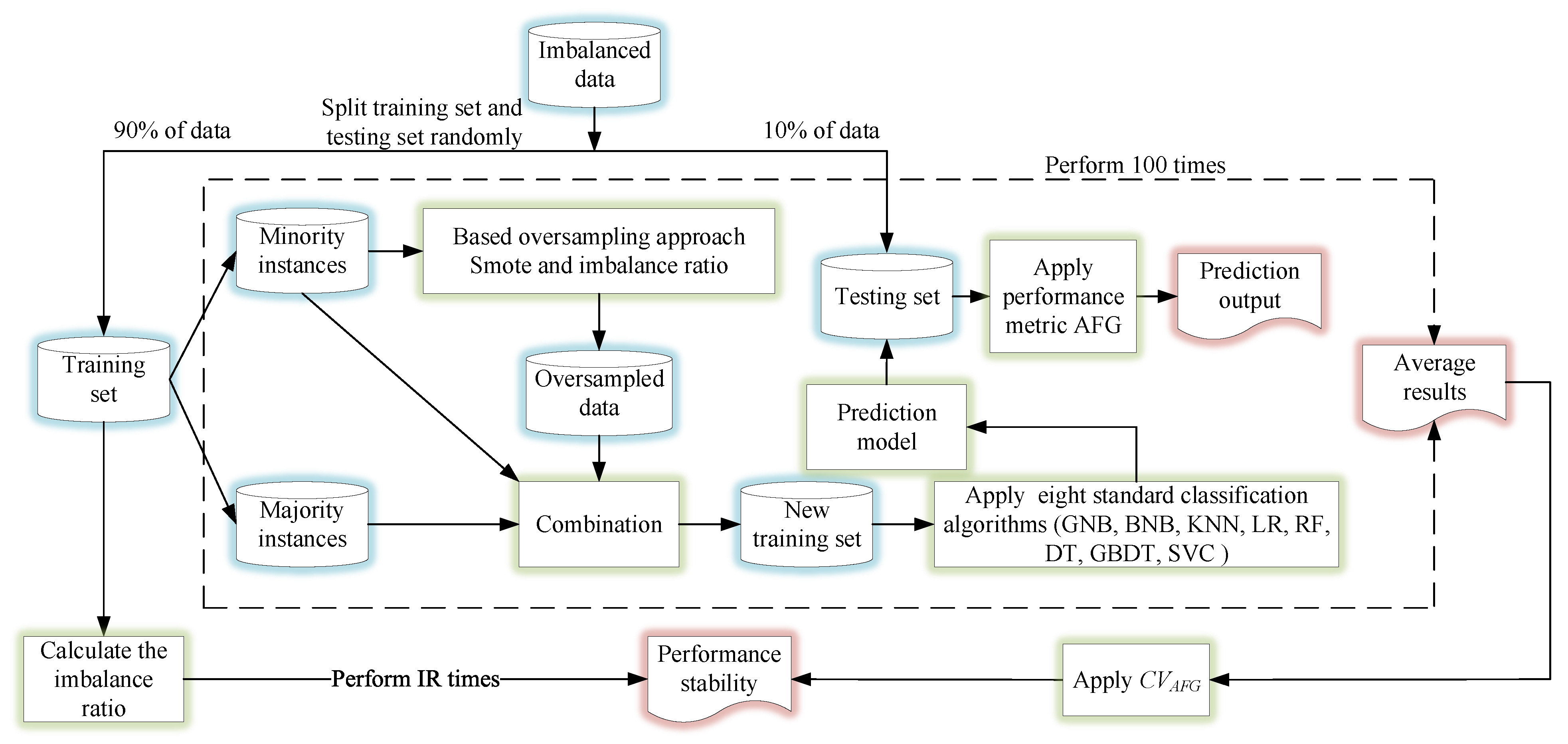
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Imbalanced Data Augmentation Algorithms
| Algorithm 1 Oversampling-based imbalanced data augmentation |
| Input:T: Original imbalanced data. |
| Output: Taugment: Augmented imbalanced dataset. |
| Procedure Begin |
|
| Algorithm 2 Undersampling based imbalanced data augmentation |
| Input:T: Original imbalanced data. |
| Output: Taugment: Augmented imbalanced dataset. |
| Procedure Begin |
|
| Algorithm 3 Hybrid sampling based imbalanced data augmentation |
| Input:T: Original imbalanced data. |
| Output: Taugment: Augmented imbalanced dataset. |
| Procedure Begin |
|
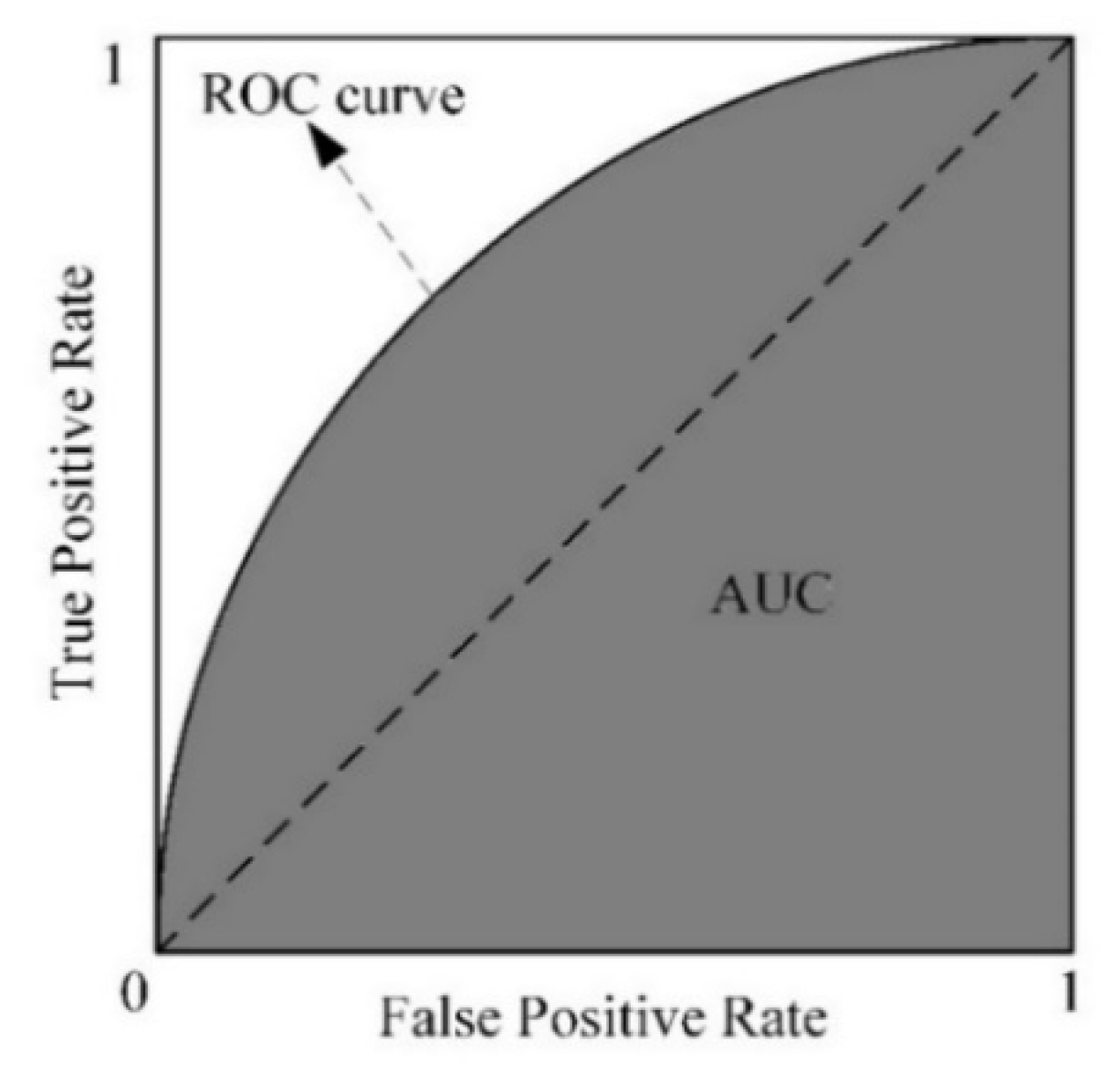
2.2. Performance Evaluation Metric
2.3. Performance Stability Evaluation Method
3. Experiment Settings
3.1. Benchmark Dataset
3.2. Machine Learning Models
3.3. Experimental Flow Design
3.4. Statistical Test Method
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
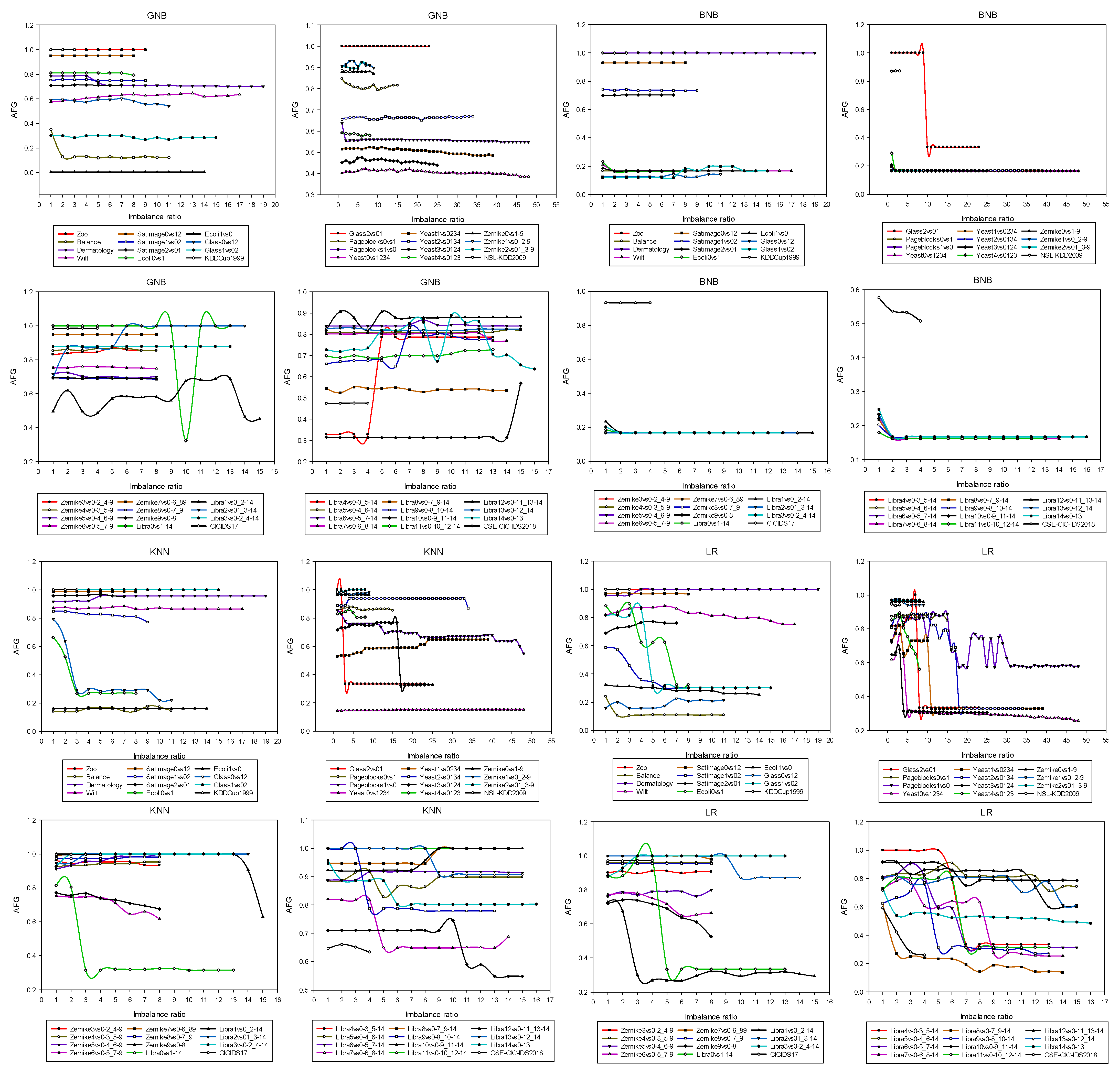
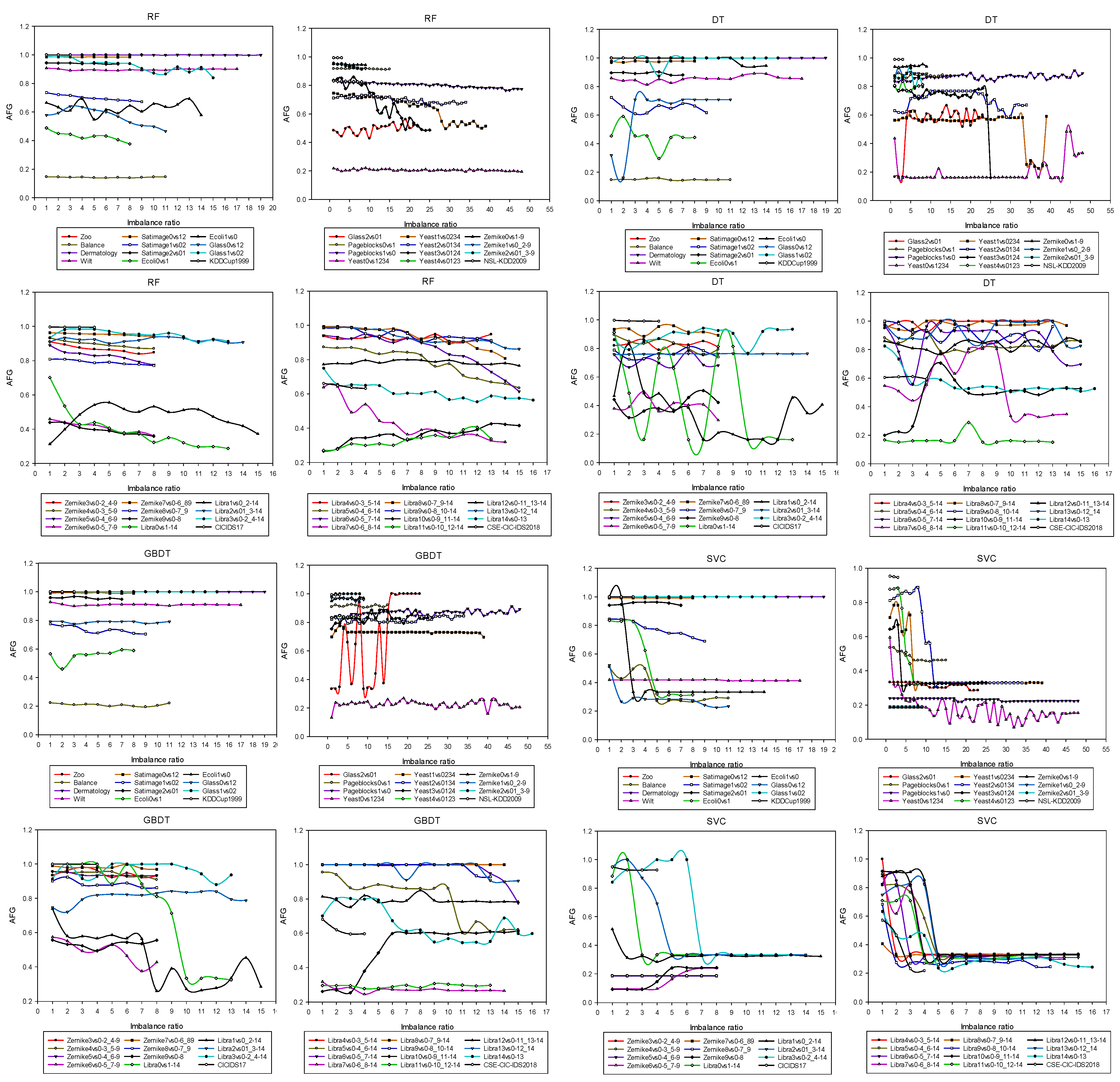
4.1. Relationship between Varying Performance in Machine Learning Models and IR
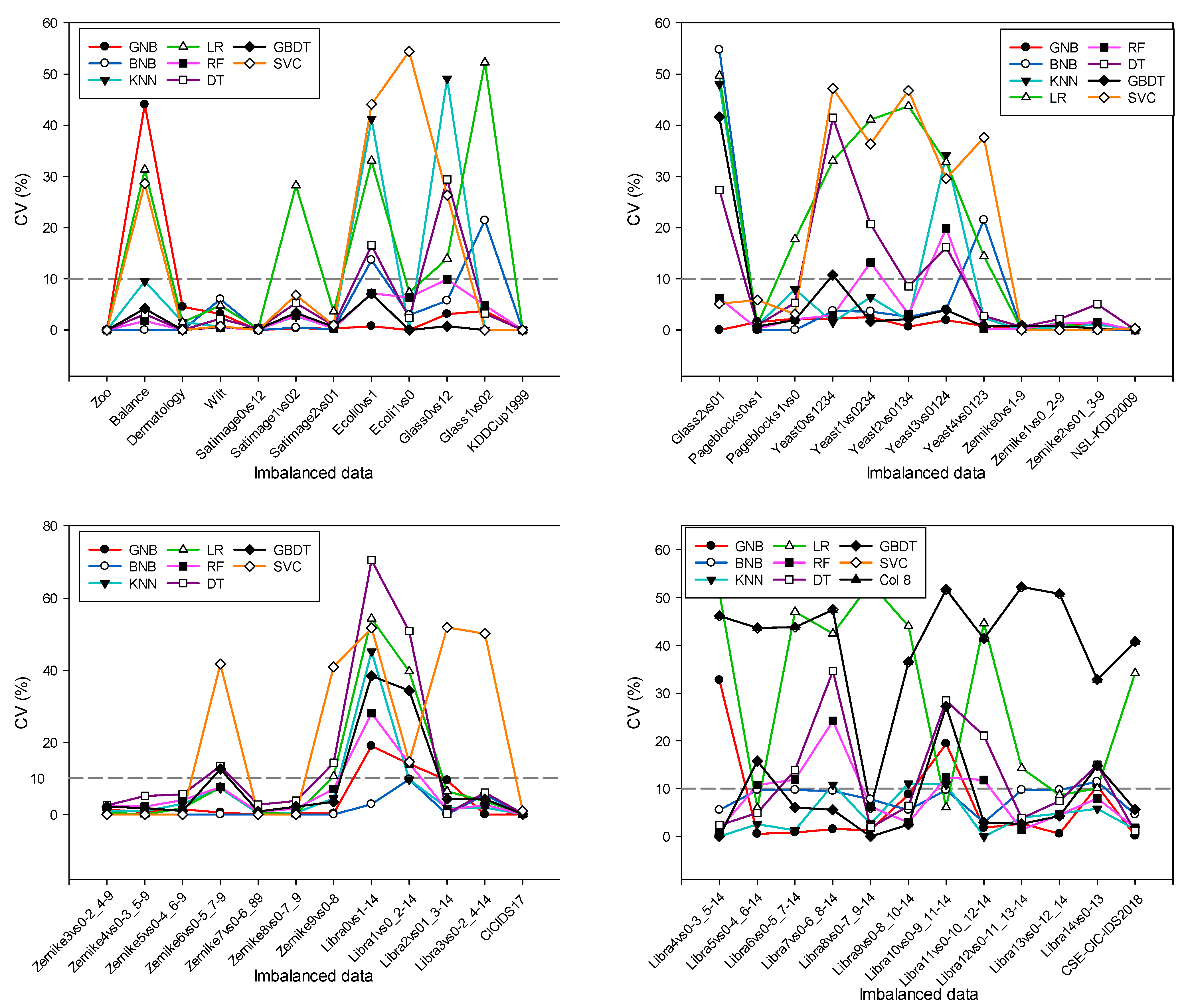
4.2. Performance Stability Results
4.3. Statistical Test Results
5. Related Works
- MFs indicates whether this approach is validated on the imbalanced data from multiple fields, yes (Y), no (N).
- EMs indicates whether this approach uses multiple evaluation metrics to obtain more objective experimental results, yes (Y), no (N).
- BDs indicates whether the experiment uses imbalanced data with more than 10,000 observations, yes (Y), no (N).
- CAs indicates how many machine learning models are used in the experiment.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, X.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Wu, F.; You, X.; Gao, Y.; Shan, S.; Yang, J.-Y. Multiset feature learning for highly imbalanced data classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Li, T.; Zhu, R.; Tang, Y.; Tang, M.; Lin, L.; Ma, Z. Conditional Wasserstein generative adversarial network-gradient penalty-based approach to alleviating imbalanced data classification. Inf. Sci. 2020, 512, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, T.; Zheng, X.; Yu, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhou, D.; Lv, C.; Yang, W. UFFDFR: Undersampling framework with denoising, fuzzy c-means clustering, and representative sample selection for imbalanced data classification. Inf. Sci. 2021, 576, 658–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Yi, B.; Cao, W.; Zheng, Q. Exploring ensemble oversampling method for imbalanced keyword extraction learning in policy text based on three-way decisions and SMOTE. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 188, 116051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Sohn, S.Y. Hybrid neural network with cost-sensitive support vector machine for class-imbalanced multimodal data. Neural Netw. 2020, 130, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardon, N.; Menardi, G.; Torelli, N. ROSE: A Package for Binary Imbalanced Learning. R J. 2014, 6, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al, S.; Dener, M. STL-HDL: A new hybrid network intrusion detection system for imbalanced dataset on big data environment. Comput. Secur. 2021, 110, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, B.S.; Shukla, S. SMOTE based class-specific extreme learning machine for imbalanced learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 187, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, H.; Fujita, H.; Fu, B.; Ai, W. Class-imbalanced dynamic financial distress prediction based on Adaboost-SVM ensemble combined with SMOTE and time weighting. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Yang, J. Learning imbalanced datasets based on SMOTE and Gaussian distribution. Inf. Sci. 2020, 512, 1214–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Susan, S. VGGIN-Net: Deep Transfer Network for Imbalanced Breast Cancer Dataset. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, R.; Ye, H.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D. A Cognitive Driven Ordinal Preservation for Multi-Modal Imbalanced Brain Disease Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cai, L.; Liao, B.; Zhu, W.; Xu, J. A Robust Oversampling Approach for Class Imbalance Problem with Small Disjuncts. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douzas, G.; Bacao, F. Self-Organizing Map Oversampling (SOMO) for imbalanced data set learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 82, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Qian, J. The impact study of class imbalance on the performance of software defect prediction models. Chin. J. Comput. 2018, 41, 809–824. [Google Scholar]
- Forkman, J. Estimator and tests for common coefficients of variation in normal distributions. Commun. Stat.—Theory Methods 2009, 38, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, E.R.; de Carvalho, A.C.; Yao, X. Ensemble of classifiers based on multiobjective genetic sampling for imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019, 32, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cheung, Y.; Tang, Y.Y. Bayes Imbalance Impact Index: A Measure of Class Imbalanced Data Set for Classification Problem. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 3525–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leski, J.M.; Czabański, R.; Jezewski, M.; Jezewski, J. Fuzzy Ordered c-Means Clustering and Least Angle Regression for Fuzzy Rule-Based Classifier: Study for Imbalanced Data. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 28, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, R.M.; Ferreira, J.A.; Machado, L.S. A New Bayesian Network Based on Gaussian Naive Bayes with Fuzzy Parameters for Training Assessment in Virtual Simulators. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 23, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S. Naive bayes and text classification i-introduction and theory. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1410.5329. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.; Cao, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. A Reinforced k-Nearest Neighbors Method with Application to Chatter Identification in High Speed Milling. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 10844–10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, E.; Li, X.; Kwon, D.; Zhang, Y.; Pohl, K. Logistic regression confined by cardinality-constrained sample and feature selection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 1713–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Z.; Zhao, C. Enhanced random forest with concurrent analysis of static and dynamic nodes for industrial fault classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, M.; Aparicio, J.; Rabasa, A.; Rodriguez-Sala, J.J. Efficiency analysis trees: A new methodology for estimating production frontiers through decision trees. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 162, 113783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Shi, J.; He, B.; Chen, J.; Ramamohanarao, K.; Li, Q. Exploiting GPUs for efficient gradient boosting decision tree training. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2019, 30, 2706–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Sonbhadra, S.K.; Agarwal, S.; Nagabhushan, P. One-class support vector classifiers: A survey. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 196, 105754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; He, H.; Li, J. Entropy-based Sampling Approaches for Multi-class Imbalanced Problems. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 32, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Habas, P.A.; Zurada, J.M.; Lo, J.Y.; Baker, J.A.; Tourassi, G.D. Training neural network classifiers for medical decision making: The effects of imbalanced datasets on classification performance. Neural Netw. 2008, 21, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loyola-González, O.; Martínez-Trinidad, J.F.; Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A.; García-Borroto, M. Study of the impact of resampling methods for contrast pattern based classifiers in imbalanced databases. Neurocomputing 2016, 175, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, A.; Carrasco, A.; Martín, A.; de las Heras, A. The impact of class imbalance in classification performance metrics based on the binary confusion matrix. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 91, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, G. An empirical comparison and evaluation of minority oversampling techniques on a large number of imbalanced datasets. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 83, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabtah, F.; Hammoud, S.; Kamalov, F.; Gonsalves, A. Data imbalance in classification: Experimental evaluation. Inf. Sci. 2020, 513, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, A.; Lettieri, N.; Malandrino, D.; Zaccagnino, R.; Capo, C. Adam or Eve? Automatic users’ gender classification via gestures analysis on touch devices. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 18473–18495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

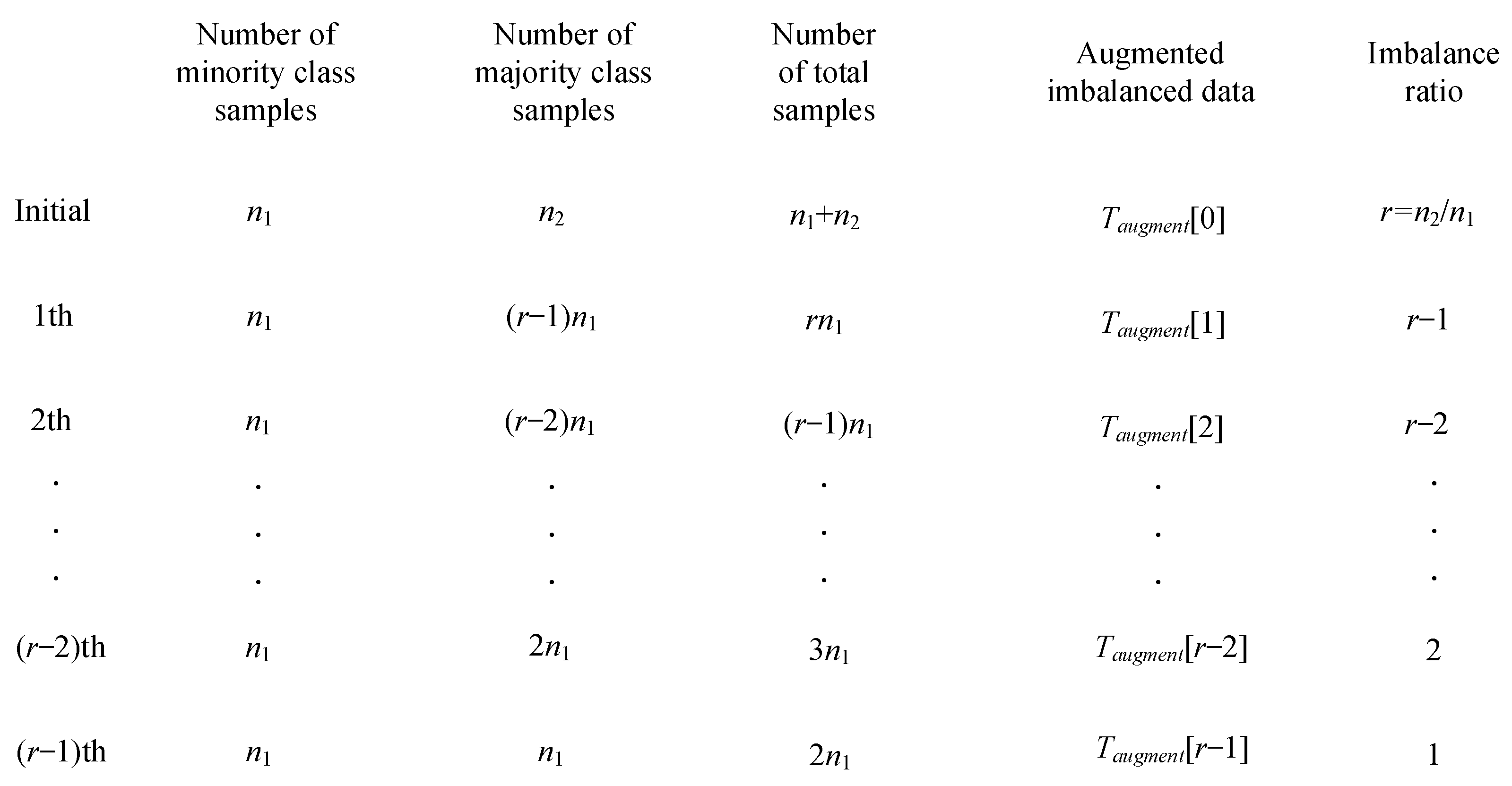
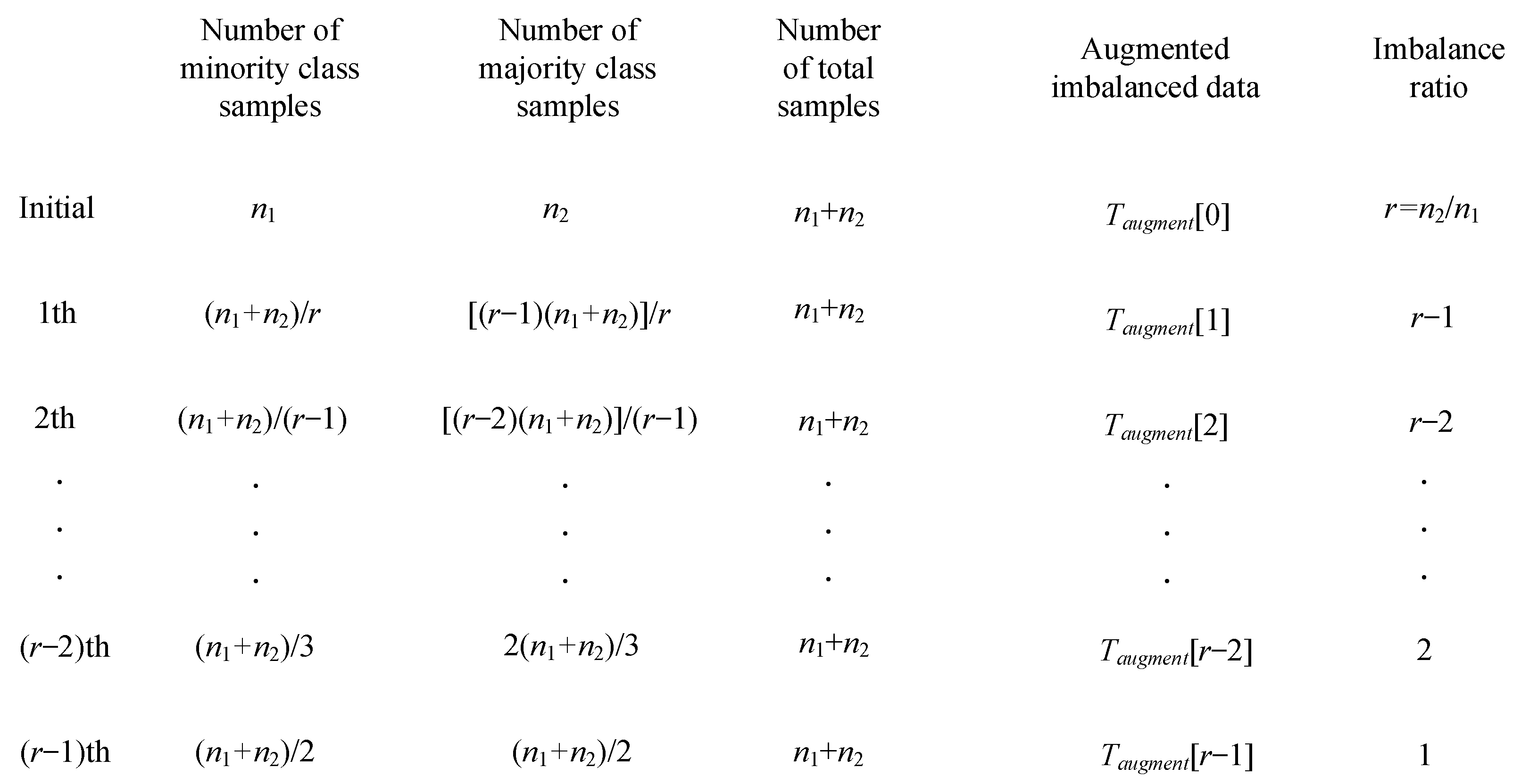
| Predicted Positive | Predicted Negative | |
| Actual positive | True positives (TP) | False negatives (FN) |
| Actual negative | False positives (FP) | True negatives (TN) |
| ID | Dataset | Instances | Features | Minority Class | Majority Class | Minority Instances | Majority Instances | IR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zoo | 101 | 17 | 7 | all other | 10 | 91 | 9.1 |
| 2 | Balance | 625 | 4 | B | all other | 49 | 576 | 11.755 |
| 3 | Dermatology | 358 | 34 | 6 | all other | 20 | 338 | 16.9 |
| 4 | Wilt | 4839 | 5 | w | n | 261 | 4578 | 17.540 |
| 5 | Satimage0vs12 | 6430 | 36 | 2 | all other | 703 | 5727 | 8.147 |
| 6 | Satimage1vs02 | 6430 | 36 | 4 | all other | 625 | 5805 | 9.288 |
| 7 | Satimage2vs01 | 6430 | 36 | 5 | all other | 707 | 5723 | 8.095 |
| 8 | Ecoli0vs1 | 336 | 7 | imU | all other | 35 | 301 | 8.6 |
| 9 | Ecoli1vs0 | 336 | 7 | om | all other | 20 | 316 | 15.8 |
| 10 | Glass0vs12 | 214 | 9 | 3 | all other | 17 | 197 | 11.588 |
| 11 | Glass1vs02 | 214 | 9 | 5 | all other | 13 | 201 | 15.462 |
| 12 | Glass2vs01 | 214 | 9 | 6 | all other | 9 | 205 | 22.778 |
| 13 | Pageblocks0vs1 | 5473 | 10 | 2 | all other | 329 | 5144 | 15.635 |
| 14 | Pageblocks1vs0 | 5473 | 10 | 5 | all other | 115 | 5358 | 46.591 |
| 15 | Yeast0vs1234 | 1484 | 8 | VAC | all other | 30 | 1454 | 48.467 |
| 16 | Yeast1vs0234 | 1484 | 8 | EXC | all other | 35 | 1449 | 41.4 |
| 17 | Yeast2vs0134 | 1484 | 8 | ME1 | all other | 44 | 1440 | 32.727 |
| 18 | Yeast3vs0124 | 1484 | 8 | ME2 | all other | 51 | 1433 | 28.098 |
| 19 | Yeast4vs0123 | 1484 | 8 | ME3 | all other | 163 | 1321 | 8.104 |
| 20 | Zernike0vs1-9 | 2000 | 47 | 1 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 21 | Zernike1vs0_2-9 | 2000 | 47 | 2 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 22 | Zernike2vs01_3-9 | 2000 | 47 | 3 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 23 | Zernike3vs0-2_4-9 | 2000 | 47 | 4 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 24 | Zernike4vs0-3_5-9 | 2000 | 47 | 5 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 25 | Zernike5vs0-4_6-9 | 2000 | 47 | 6 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 26 | Zernike6vs0-5_7-9 | 2000 | 47 | 7 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 27 | Zernike7vs0-6_89 | 2000 | 47 | 8 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 28 | Zernike8vs0-7_9 | 2000 | 47 | 9 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 29 | Zernike9vs0-8 | 2000 | 47 | 10 | all other | 200 | 1800 | 9 |
| 30 | Libra0vs1-14 | 360 | 90 | 1 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 31 | Libra1vs0_2-14 | 360 | 90 | 2 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 32 | Libra2vs01_3-14 | 360 | 90 | 3 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 33 | Libra3vs0-2_4-14 | 360 | 90 | 4 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 34 | Libra4vs0-3_5-14 | 360 | 90 | 5 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 35 | Libra5vs0-4_6-14 | 360 | 90 | 6 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 36 | Libra6vs0-5_7-14 | 360 | 90 | 7 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 37 | Libra7vs0-6_8-14 | 360 | 90 | 8 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 38 | Libra8vs0-7_9-14 | 360 | 90 | 9 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 39 | Libra9vs0-8_10-14 | 360 | 90 | 10 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 40 | Libra10vs0-9_11-14 | 360 | 90 | 11 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 41 | Libra11vs0-10_12-14 | 360 | 90 | 12 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 42 | Libra12vs0-11_13-14 | 360 | 90 | 13 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 43 | Libra13vs0-12_14 | 360 | 90 | 14 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 44 | Libra14vs0-13 | 360 | 90 | 15 | all other | 24 | 336 | 14 |
| 45 | KDDCup1999 | 13,228 | 41 | all other | normal | 3228 | 10,000 | 3.098 |
| 46 | NSL-KDD2009 | 13,158 | 41 | all other | normal | 3158 | 10,000 | 3.167 |
| 47 | CSE-CIC-IDS2018 | 12,403 | 78 | all other | normal | 2403 | 10,000 | 4.161 |
| 48 | CICIDS17 | 12,180 | 78 | all other | normal | 2180 | 10,000 | 4.587 |
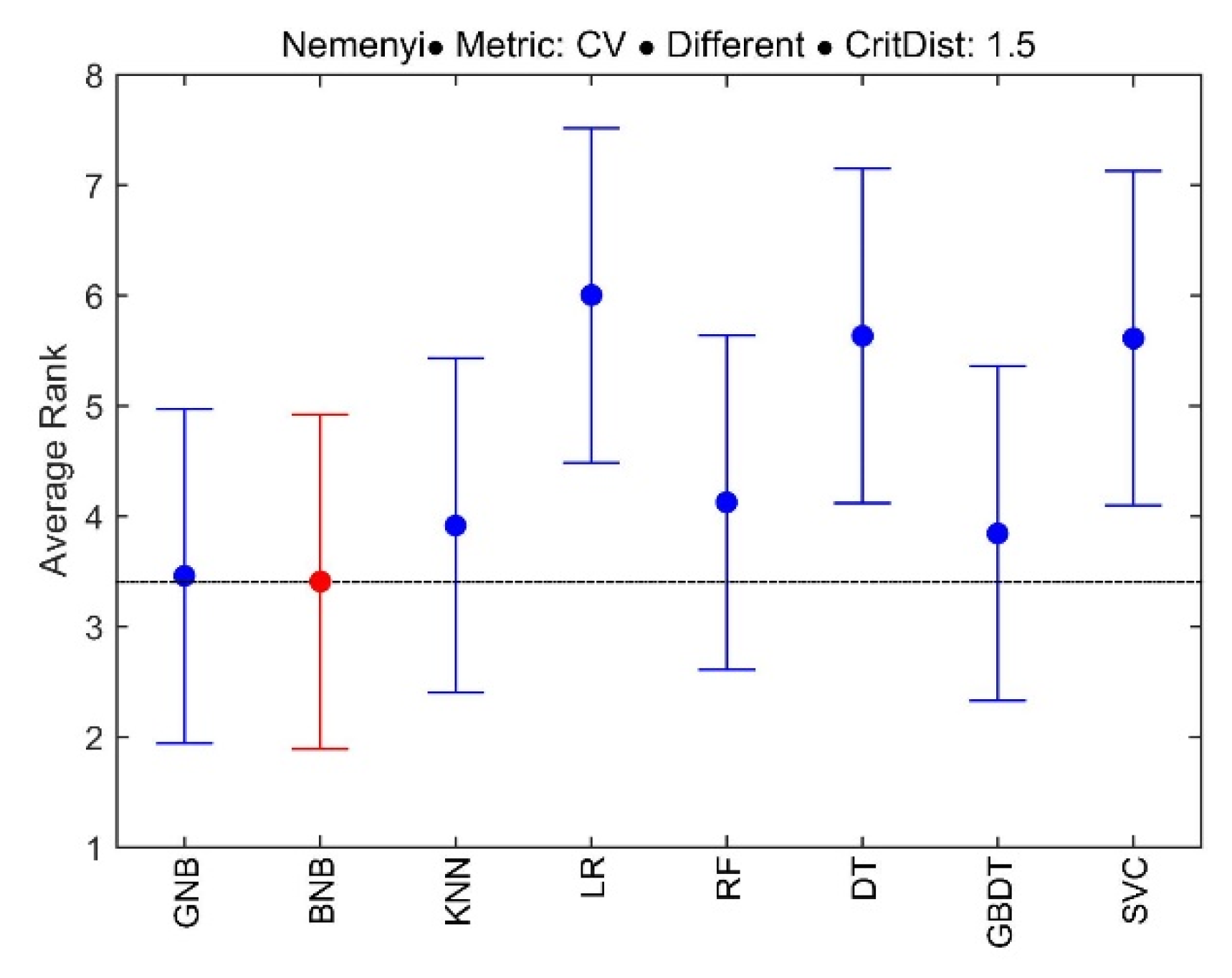
| Algorithms | GNB | BNB | KNN | LR | RF | DT | GBDT | SVC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVAFG | 3.4583 | 3.4063 | 3.9167 | 6.0000 | 4.1250 | 5.6354 | 3.8438 | 5.6146 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, M.; Wang, F.; Hu, X.; Miao, Y.; Cao, H.; Tang, M. A Method for Analyzing the Performance Impact of Imbalanced Binary Data on Machine Learning Models. Axioms 2022, 11, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110607
Zheng M, Wang F, Hu X, Miao Y, Cao H, Tang M. A Method for Analyzing the Performance Impact of Imbalanced Binary Data on Machine Learning Models. Axioms. 2022; 11(11):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110607
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Ming, Fei Wang, Xiaowen Hu, Yuhao Miao, Huo Cao, and Mingjing Tang. 2022. "A Method for Analyzing the Performance Impact of Imbalanced Binary Data on Machine Learning Models" Axioms 11, no. 11: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110607
APA StyleZheng, M., Wang, F., Hu, X., Miao, Y., Cao, H., & Tang, M. (2022). A Method for Analyzing the Performance Impact of Imbalanced Binary Data on Machine Learning Models. Axioms, 11(11), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11110607






