Study on Efficient Separation of Amorphous Silica from High-Alumina Coal Gangue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Calcination Test
2.3. Alkaline Leaching Test
2.4. Thermodynamic Analysis
2.5. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Thermal Behavior and Thermodynamic Analysis of High-Alumina Coal Gangue During Calcination
3.2. Separation of Amorphous Silica
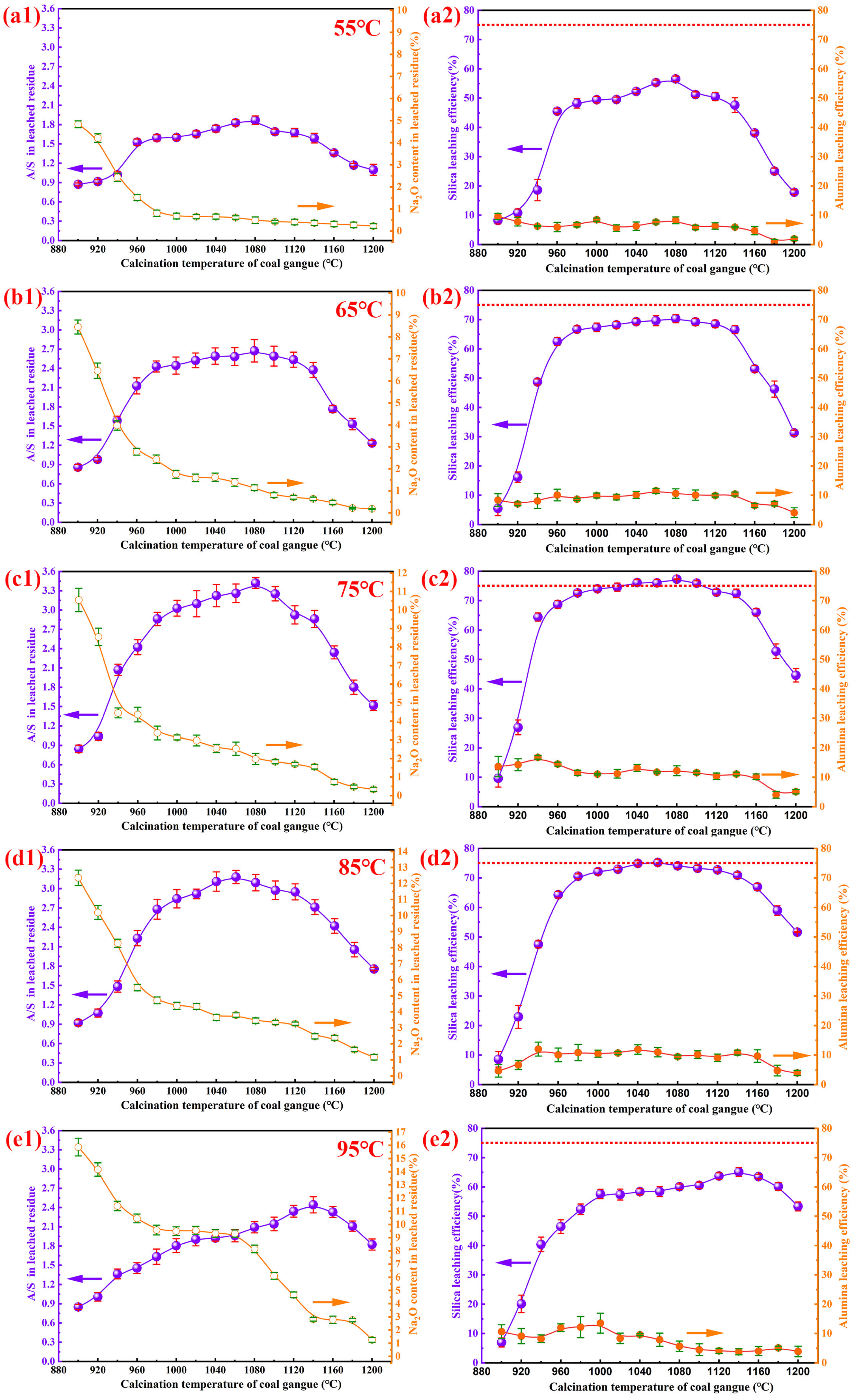
3.2.1. The Impact of Calcination Temperature on Desilication Efficiency
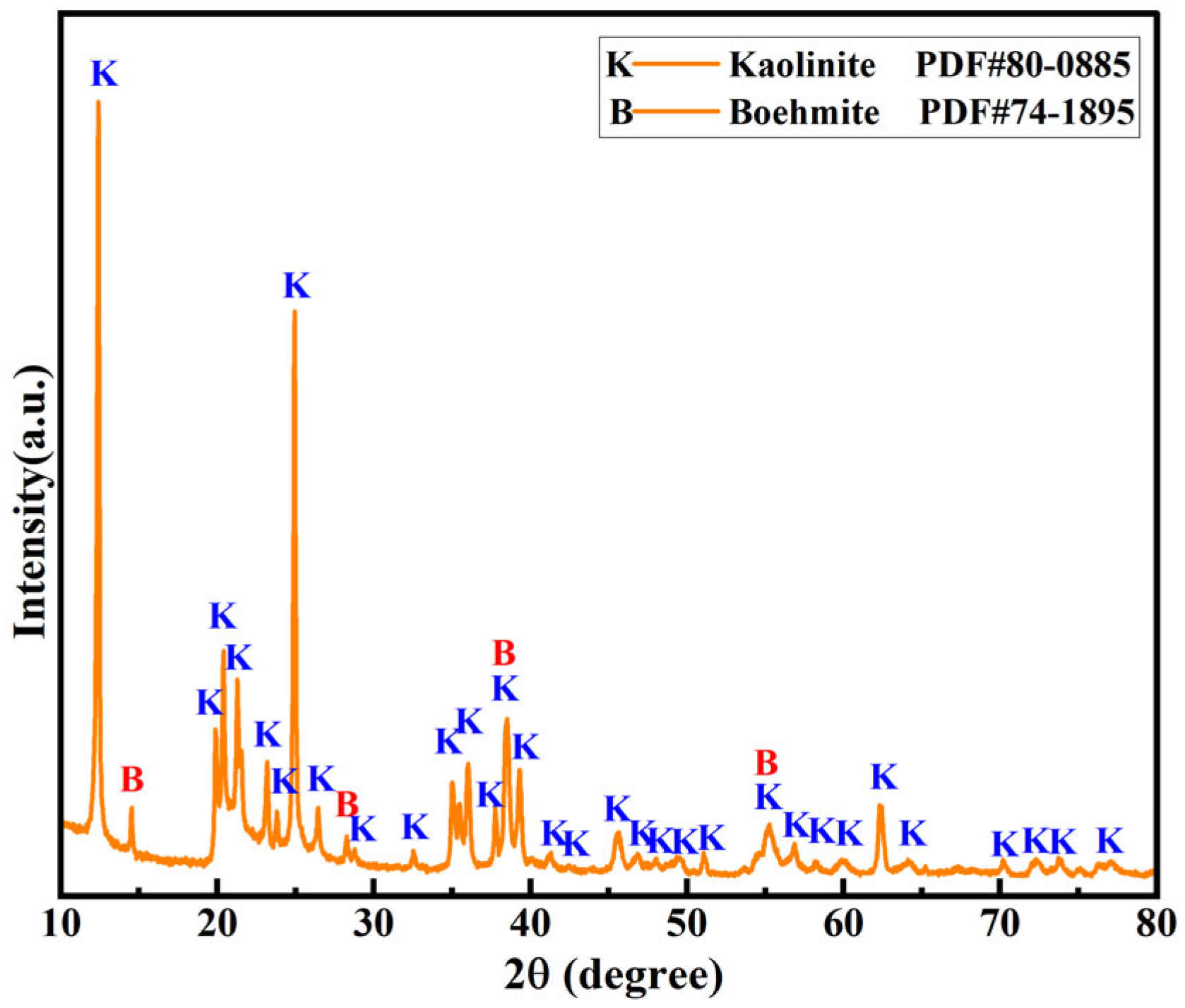
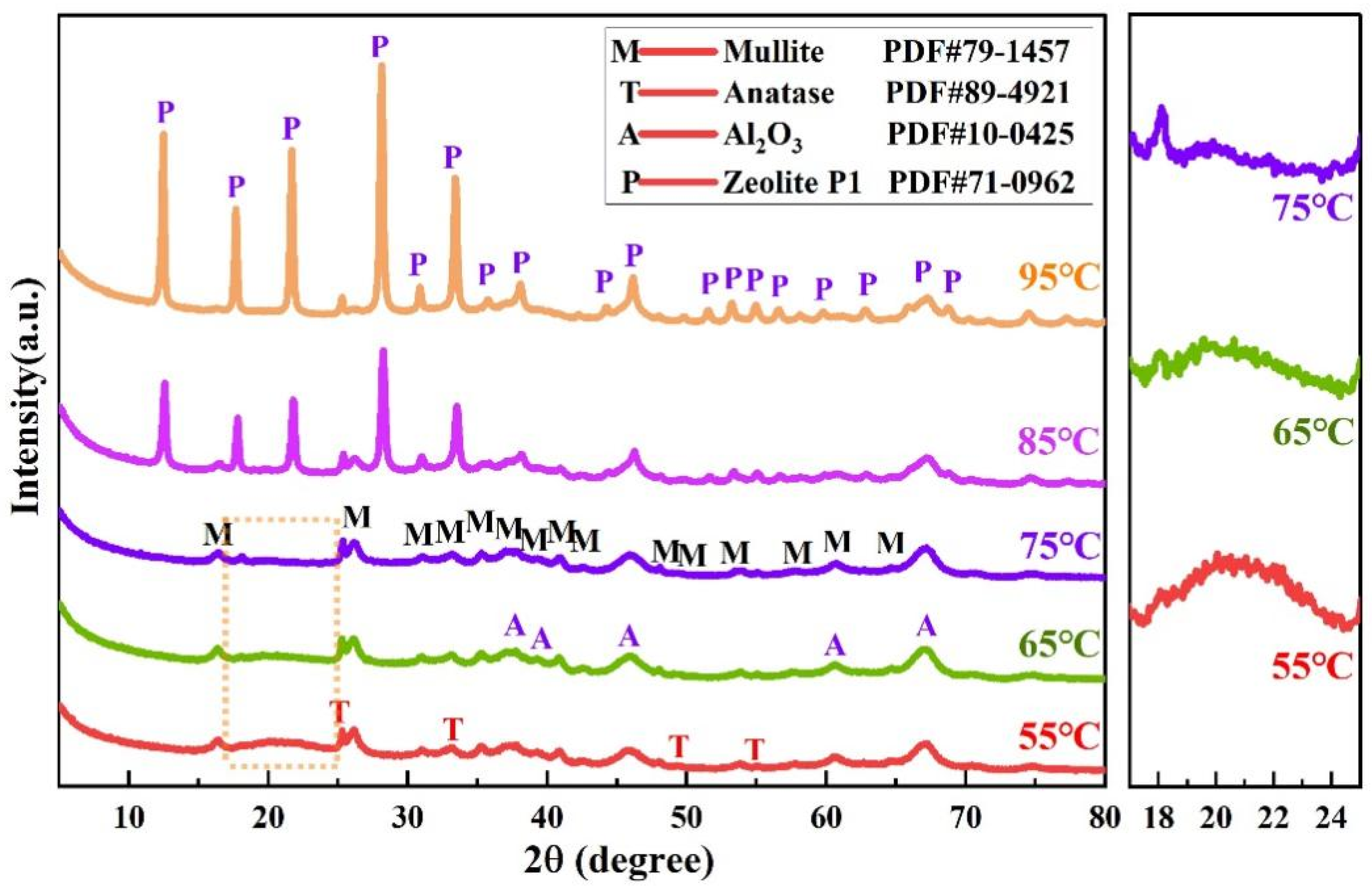
3.2.2. XRD Analysis
3.2.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.2.4. SEM-EDS Analysis
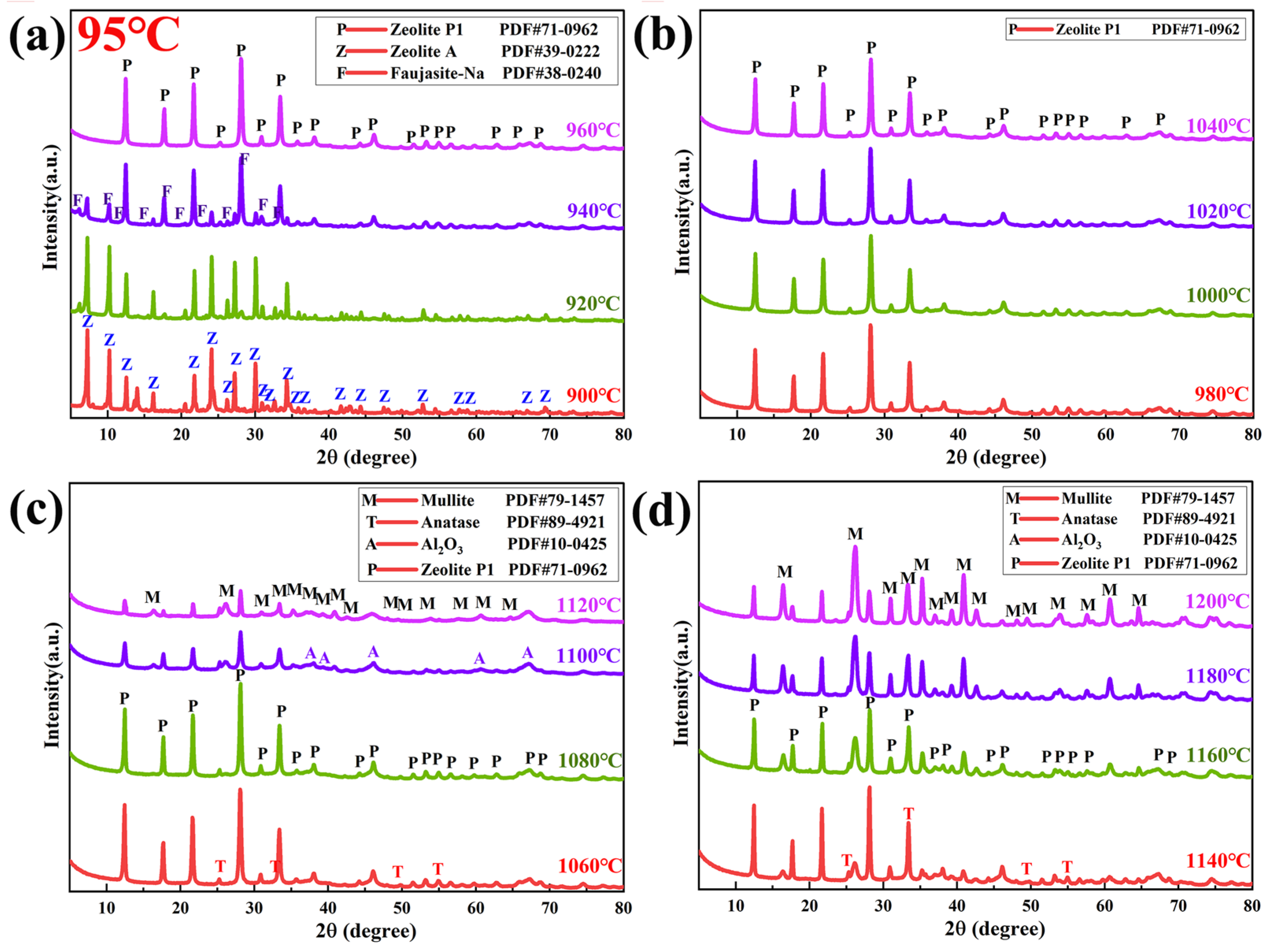
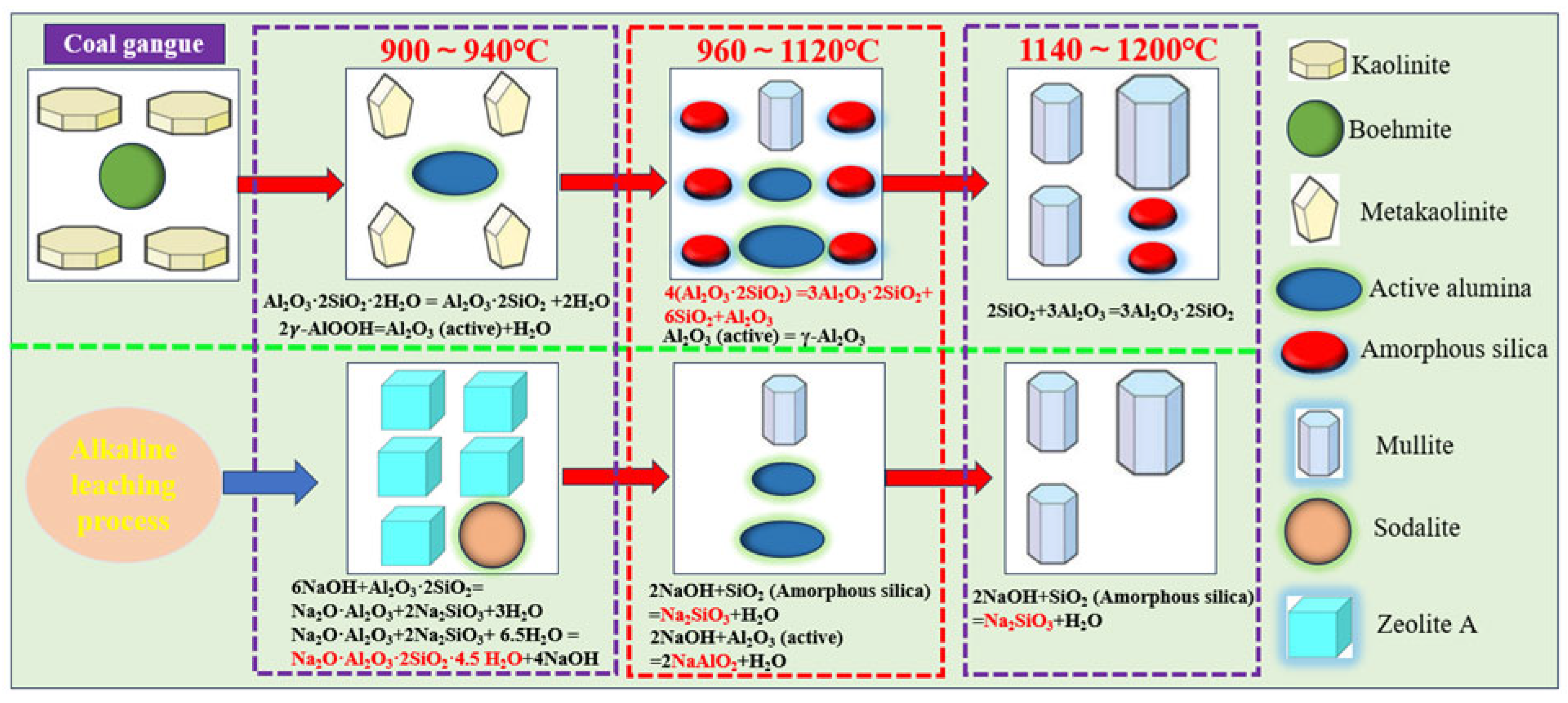
3.3. Mineral Phase Transformation of Coal Gangue During Calcination and Alkaline Leaching
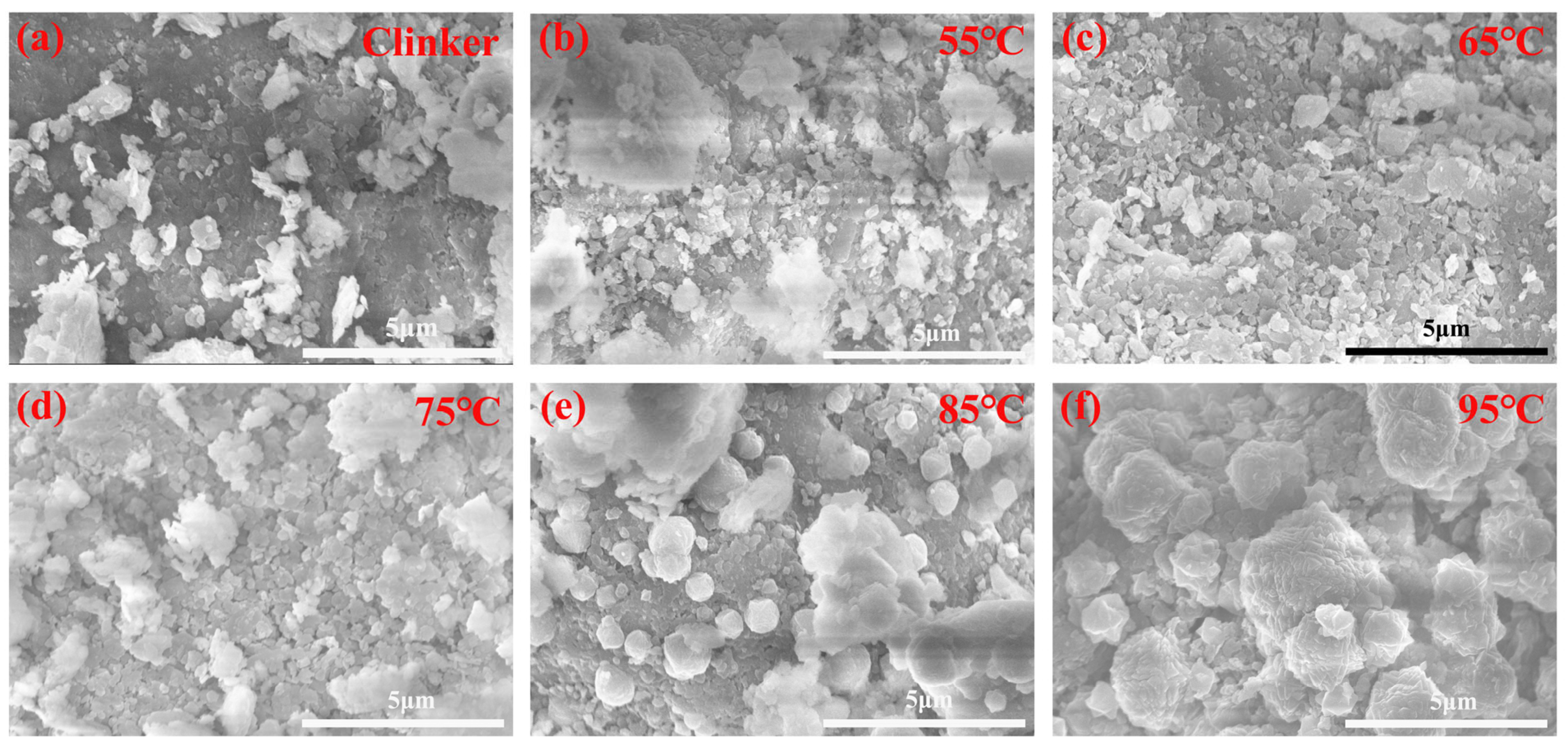
3.4. Microscopic Morphological Changes of the Leached Residues After Alkaline Leaching
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.M.; Cheng, F.C.; Zhang, D.K. Interactions of coal gangue and pine sawdust during combustion of their blends studied using differential thermos-gravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C. Effect of calcination condition on the microstructure and pozzolanic activity of calcined coal gangue. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 146, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Mei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Xie, D.; Xia, J.; Nie, Y. Novel desulfurization technology by employing coal gangue slurry as an absorbent: Performance and mechanism study. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946–117963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Zhong, Q.; Bao, H.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. Separation of aluminum and silica from coal gangue by elevated temperature acid leaching for the preparation of alumina and SiC. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z. Efficient separation of silica and alumina in simulated CFB slag by reduction roasting-alkaline leaching process. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, X.; Du, F.; Tan, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, C. Three-dimensional distribution and oxidation degree analysis of coal gangue dump fire area: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Lv, Z.; Mao, M. Evaluating the distribution and potential ecological risks of heavy metal in coal gangue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18604–18615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wan, J.; Sun, H.; Li, L. Investigation on the activation of coal gangue by a new compound method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, L. Study on the release characteristics of chlorine in coal gangue under leaching conditions of different pH values. Fuel 2018, 217, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wen, Q.; Hu, L.; Gong, M.; Tang, Z. Feasibility study on the application of coal gangue as landfill liner material. Waste Manag. 2017, 63, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Environmental investigation on co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal gangue: SO2, NOx and trace elements emissions. Waste Manag. 2016, 50, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Lee, N.K.; Lee, H.K. Circulating fluidized bed combustion ash as controlled low-strength material (CLSM) by alkaline activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, G.; Wu, S.; Lam, P.K.S. The environmental characteristics of usage of coal gangue in bricking-making: A case study at Huainan, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Bian, Z.; Dong, J.; Lei, S. Soil properties in reclaimed farmland by filling subsidence basin due to underground coal mining with mineral wastes in China. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.; Gao, J. Performance of microwave-activated coal gangue powder as auxiliary cementitious material. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2799–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, M. Preparation of solid-waste-based pervious concrete for pavement: A two-stage utilization approach of coal gangue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 125962–125975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lü, G.; Zhang, T.; Gong, Y. Kinetics of alumina extraction from coal gangue by hydrochloric acid leaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Li, G.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Rao, M.; Jiang, T. Extraction and value-added utilization of alumina from coal fly ash via one-step hydrothermal process followed by carbonation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 323, 129174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, K.; Cui, L.; Cheng, F. Improved extraction of alumina from coal gangue by surface mechanically grinding modification. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Lv, H.; Yang, X.; Cheng, F. AlCl3·6H2O recovery from the acid leaching liquor of coal gangue by using concentrated hydrochloric inpouring. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, T.; Peng, Z.; Rao, M.; Zhang, Y. Conversion of coal gangue into alumina, tobermorite and TiO2-rich material. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Deng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, C.; Shi, C.; Zeng, M. Extraction of alumina from alumina rich coal gangue by a hydro-chemical process. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 7, 192132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Ma, X. Reaction behaviour of Al2O3 and SiO2 in high alumina coal fly ash during alkali hydrothermal process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; He, X.; Shi, S.; Long, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C. Study on modes of occurrence and selective leaching of lithium in coal gangue via grinding-thermal activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, F. Novel process of alumina extraction from coal fly ash by pre-desilicating—Na2CO3 activation—Acid leaching technique. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, F.; Tan, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, P.; Miao, S. Digesting high-aluminum coal fly ash with concentrated sulfuric acid at high temperatures. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 180, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemi, A.; Ndlovu, S.; Sibanda, V.; van Dyk, L.D. Extraction of alumina from coal fly ash using an acid leach-sinter-acid leach technique. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 157, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Ji, X.; Sarker, P.K.; Tang, J.; Ge, L.; Xia, M.; Xi, Y. A comprehensive review on the applications of coal fly ash. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Teng, W.; Wang, X.; Qin, J.; Xu, P.; Li, P. Alkali desilicated coal fly ash as substitute of bauxite in lime-soda sintering process for aluminum production. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xia, M.; Sarker, P.K.; Chen, T. A review of the alumina recovery from coal fly ash, with a focus in China. Fuel 2014, 120, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Ma, S.; Shen, S.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Research and industrialization progress of recovering alumina from fly ash: A concise review. Waste Manag. 2016, 60, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Y. Efficient separation of alumina and silica in reduction-roasted kaolin by alkali leaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Y. Reaction behavior of kaolinite with ferric oxide during reduction roasting. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Jiang, T.; Li, G.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z. Activation and removal of silicon in kaolinite by thermochemical process. Scand. J. Metall. 2004, 33, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. The processing of high silica bauxites -Review of existing and potential processes. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xie, M.; Yu, G.; Ke, C.; Zhao, H. Study on calcination catalysis and the desilication mechanism for coal gangue. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10318–10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gong, C.; Li, D. Study on structural characteristic and mechanical property of coal gangue in activation process. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 32, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, K.; Cui, L.; Cheng, F.; Lou, H.H. Effect of Na2CO3 additive on the activation of coal gangue for alumina extraction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 131, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liu, S.; Jing, Y. Microwave activation of coal gangue for Al compound. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 592, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barin, I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 1995; ISBN 3527287450. [Google Scholar]
- Souri, A.; Golestani-Fard, F.; Naghizadeh, R.; Veiseh, S. An investigation on pozzolanic activity of Iranian kaolins obtained by thermal treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 103, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Long, X.; He, X.; Shi, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C. Study on the leaching behavior differences of rare earth elements from coal gangue through calcination-acid leaching. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 344, 127222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Thermal kinetics analysis of coal-gangue selected from Inner Mongolia in China. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 131, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Ma, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y. Extraction of valuable components from coal gangue through thermal activation and HNO3 leaching. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Min, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y. Improved holding and releasing capacities of coal gangue toward phosphate through alkali-activation. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.; Turturro, A.; Riani, P.; Montanari, T.; Finocchio, E.; Ramis, G.; Busca, G. Bulk and surface properties of commercial kaolins. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Li, X.; Xu, P.; Liu, Q. Thermal activation and structural transformation mechanism of kaolinitic coal gangue from jungar coalfield, inner mongolia, China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 223, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Tao, Q.; Fan, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; He, H.; Chen, T. A combined study by XRD, FTIR, TG and HRTEM on the structure of delaminated Fe-intercalated/pillared clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 324, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Frost, R.L. Delamination of kaolinite–potassium acetate intercalates by ball-milling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Ma, S.; Frost, R.L. The thermal behavior of kaolinite intercalation complexes—A review. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 545, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Frost, R.L. Thermal behavior and decomposition of kaolinite–potassium acetate intercalation composite. Thermochim. Acta 2010, 503–504, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | Na2O | TiO2 | MgO | K2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal gangue | 37.28 | 42.72 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 18.18 |
| Clinker | 45.77 | 52.39 | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.75 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.02 |
| Calcination Temperature | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | Na2O | TiO2 | MgO | K2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900 °C | 33.83 | 40.34 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 10.54 | 0.53 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 14.32 |
| 960 °C | 60.22 | 24.84 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 4.28 | 0.99 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 6.89 |
| 1020 °C | 67.14 | 21.33 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 2.90 | 1.07 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 5.78 |
| 1080 °C | 70.63 | 20.64 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 1.94 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 3.13 |
| 1140 °C | 68.79 | 24.11 | 0.55 | 0.49 | 1.56 | 1.05 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 2.26 |
| 1200 °C | 57.87 | 38.25 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.91 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 1.22 |
| Coal Gangue Band (cm−1) | Clinker Band (cm−1) | Leached Residue Band (cm−1) | Bond Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3689/3650/3619 | - | - | OH− |
| 1116 | 1078 | 1109 | Si-O (Si-O-Si/Si-O-Al) |
| 1030/1009 | - | - | Si-O-Si/Si-O-Al |
| - | - | 967 | Si-O-Al |
| 939/913 | - | - | Al-O-H |
| 738/750/680/645 | 802/726 | 826/724 | Si-O-Si/Si-O-Al |
| 537/461/429 | 552/451/418 | 535/420 | Si-O/Al-O |
| Desilication Temperature | Al2O3 | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | Na2O | TiO2 | MgO | K2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 55 °C | 61.47 | 33.56 | 0.50 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.99 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 1.02 |
| 65 °C | 68.02 | 25.52 | 0.58 | 0.30 | 1.11 | 1.10 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 1.87 |
| 75 °C | 70.63 | 20.64 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 1.94 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 3.13 |
| 85 °C | 67.11 | 21.74 | 0.54 | 0.25 | 3.46 | 1.05 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 4.87 |
| 95 °C | 54.98 | 26.43 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 8.11 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 8.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, J.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Yi, N. Study on Efficient Separation of Amorphous Silica from High-Alumina Coal Gangue. Minerals 2025, 15, 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121317
Hong J, Ma W, Zhang H, Yi N. Study on Efficient Separation of Amorphous Silica from High-Alumina Coal Gangue. Minerals. 2025; 15(12):1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121317
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Jingnan, Weibing Ma, Hongwei Zhang, and Naihe Yi. 2025. "Study on Efficient Separation of Amorphous Silica from High-Alumina Coal Gangue" Minerals 15, no. 12: 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121317
APA StyleHong, J., Ma, W., Zhang, H., & Yi, N. (2025). Study on Efficient Separation of Amorphous Silica from High-Alumina Coal Gangue. Minerals, 15(12), 1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121317






