Metallogenic Controls of the Jurassic Arc, Xizang: Insights from Geochemistry, Zircon Chronology, Hf Isotopes, and In Situ Trace Elements
Abstract
1. Introduction
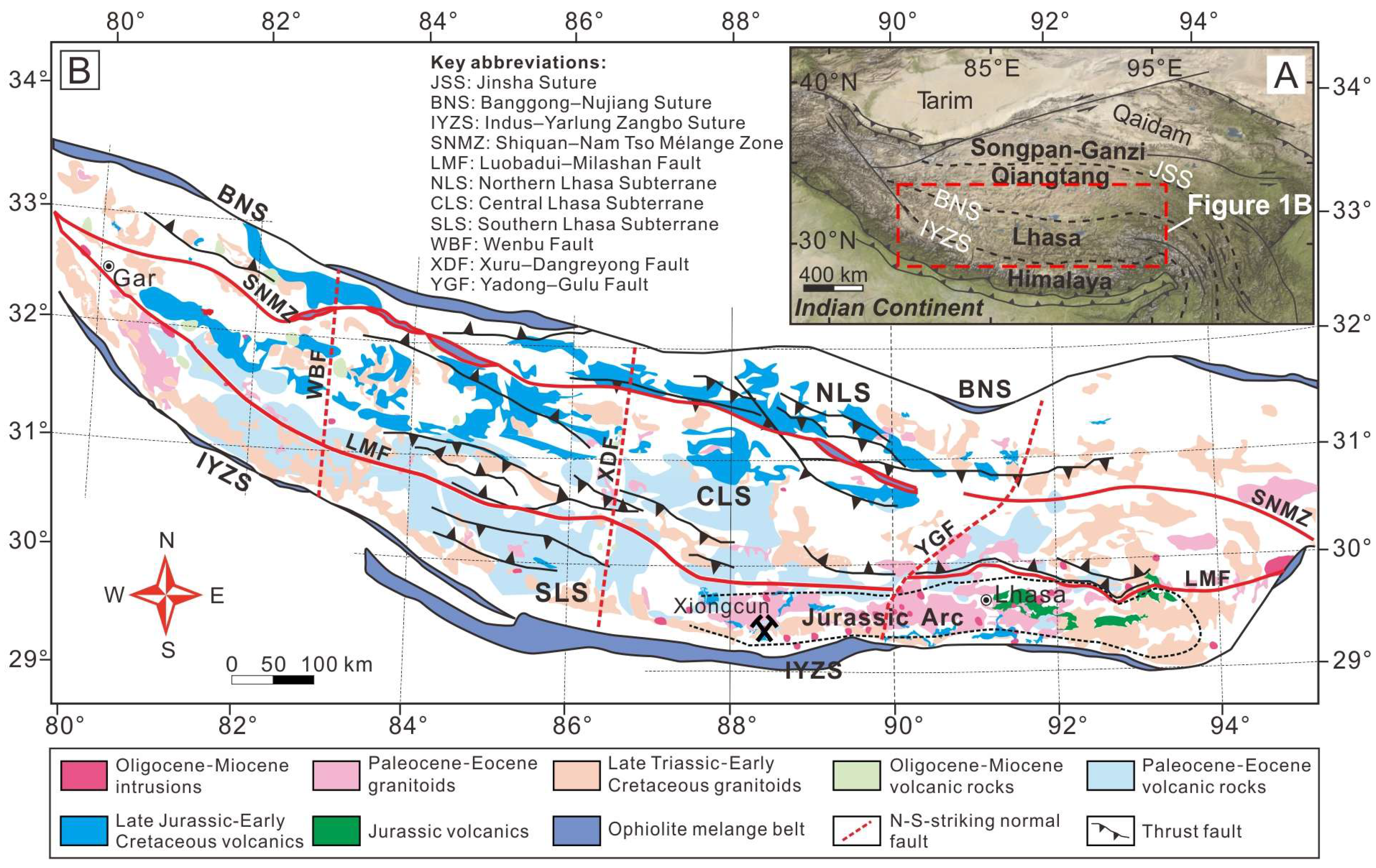
2. Geological Setting
2.1. Tectonic Framework
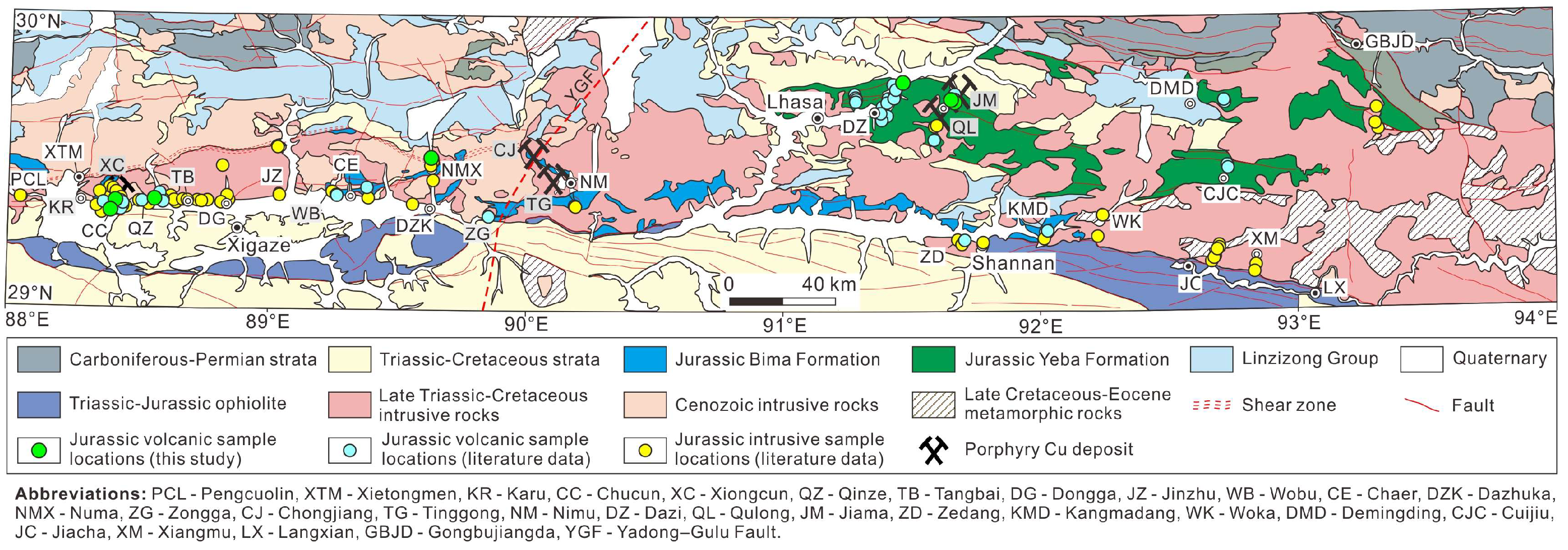
2.2. Regional Geology
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
3.1. Petrological Characteristics for the Jurassic Volcanic Samples
3.2. Analytical Methods
4. Results
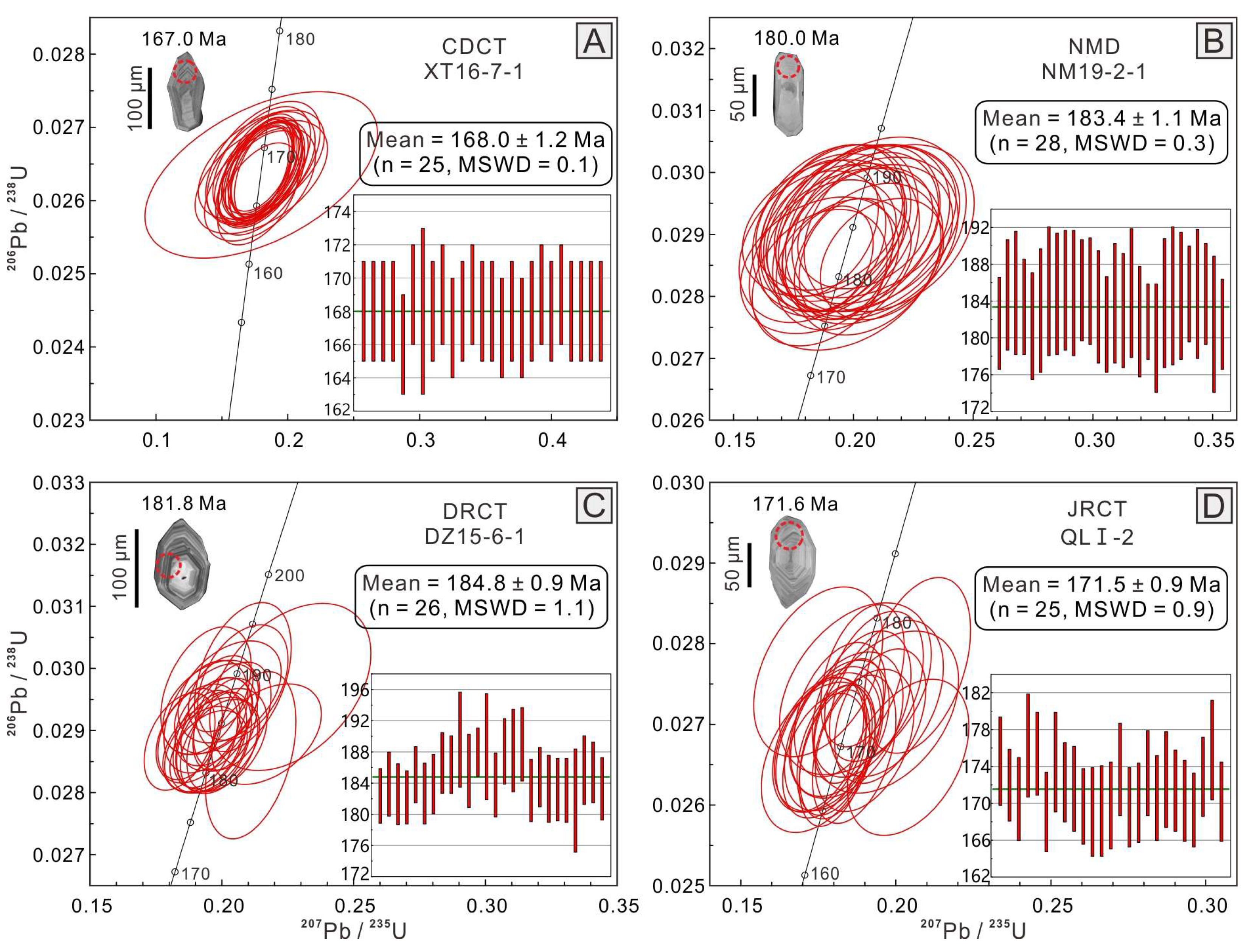
4.1. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Ages
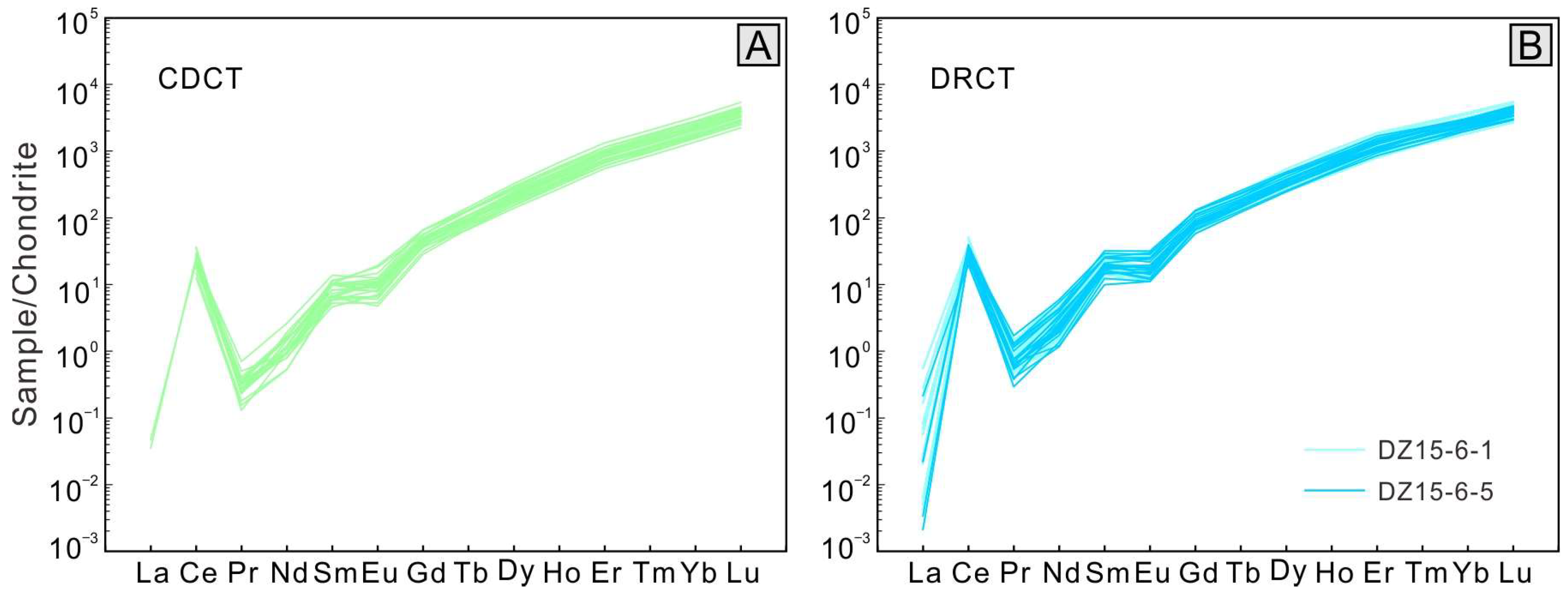
4.2. Zircon Trace Elements
4.3. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotopic Compositions
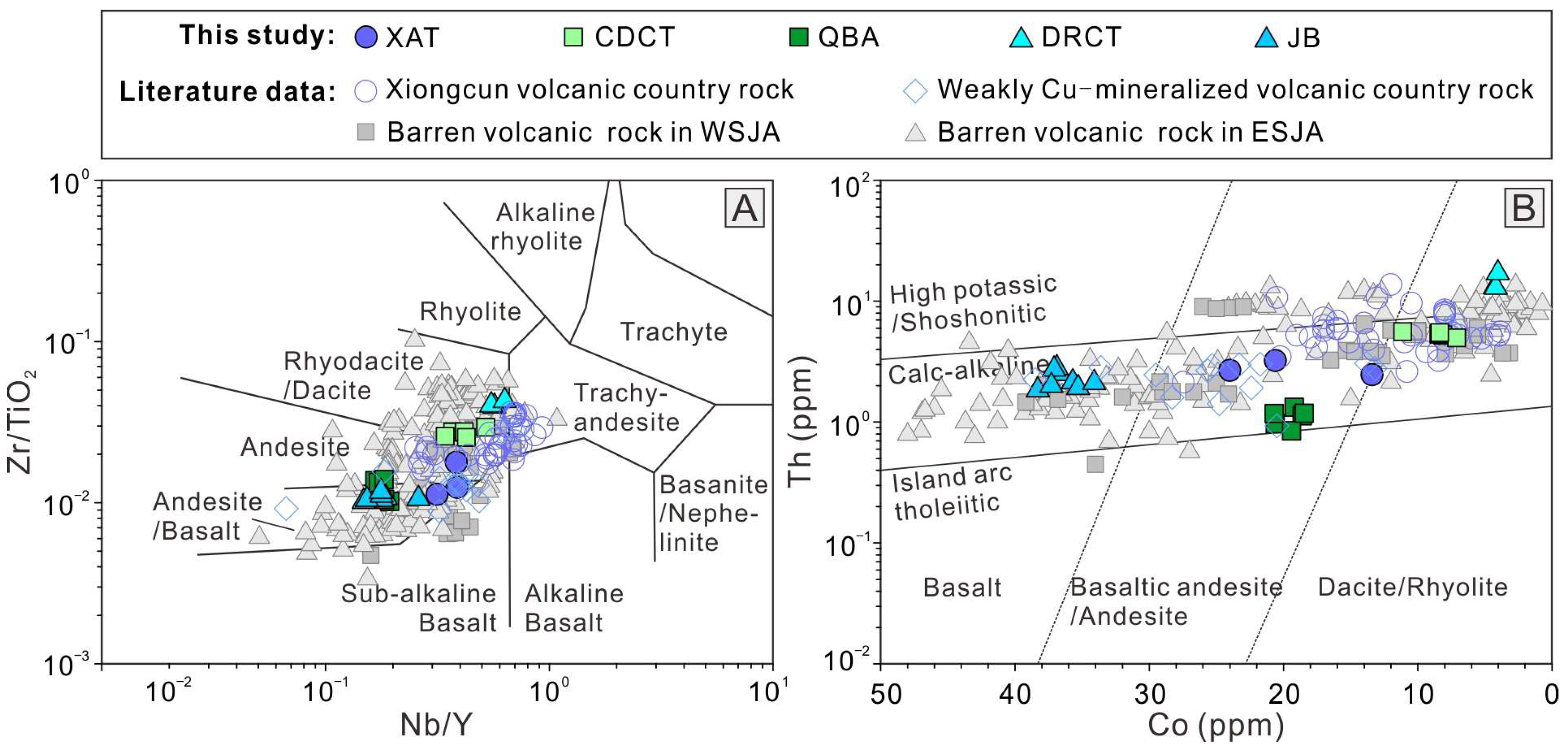
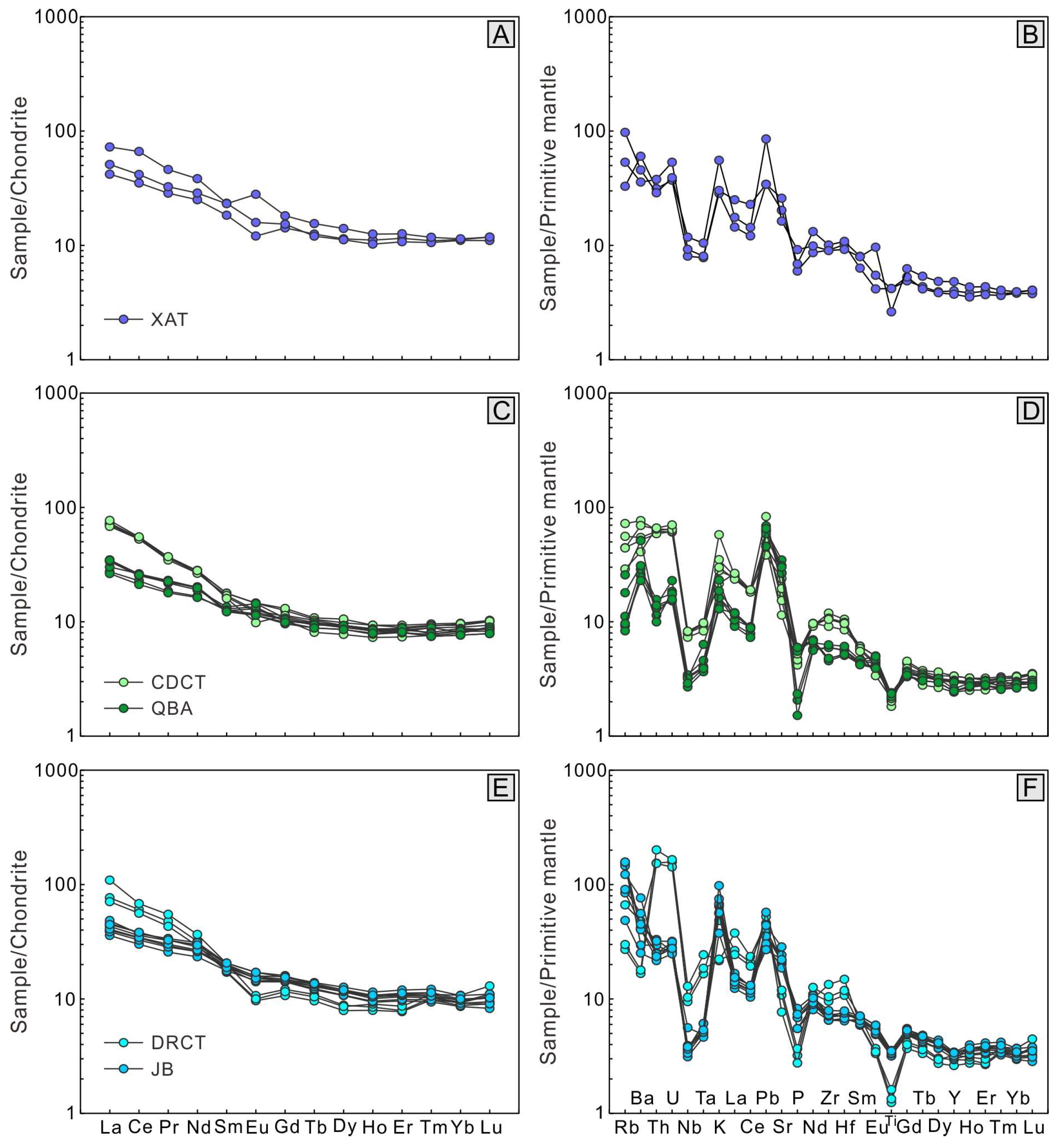
4.4. Whole-Rock Major and Trace Elements
5. Discussion
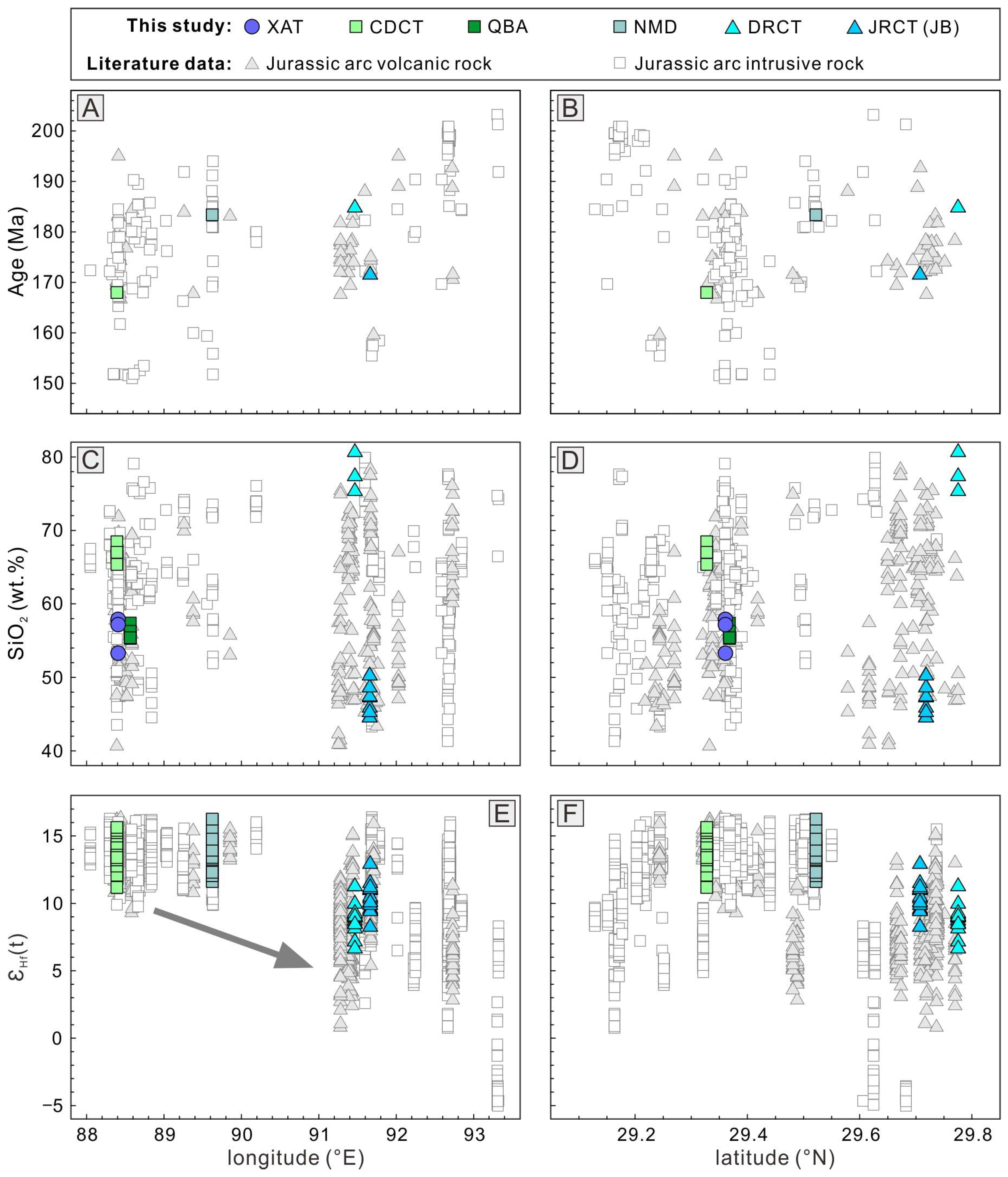
5.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of the Jurassic Arc
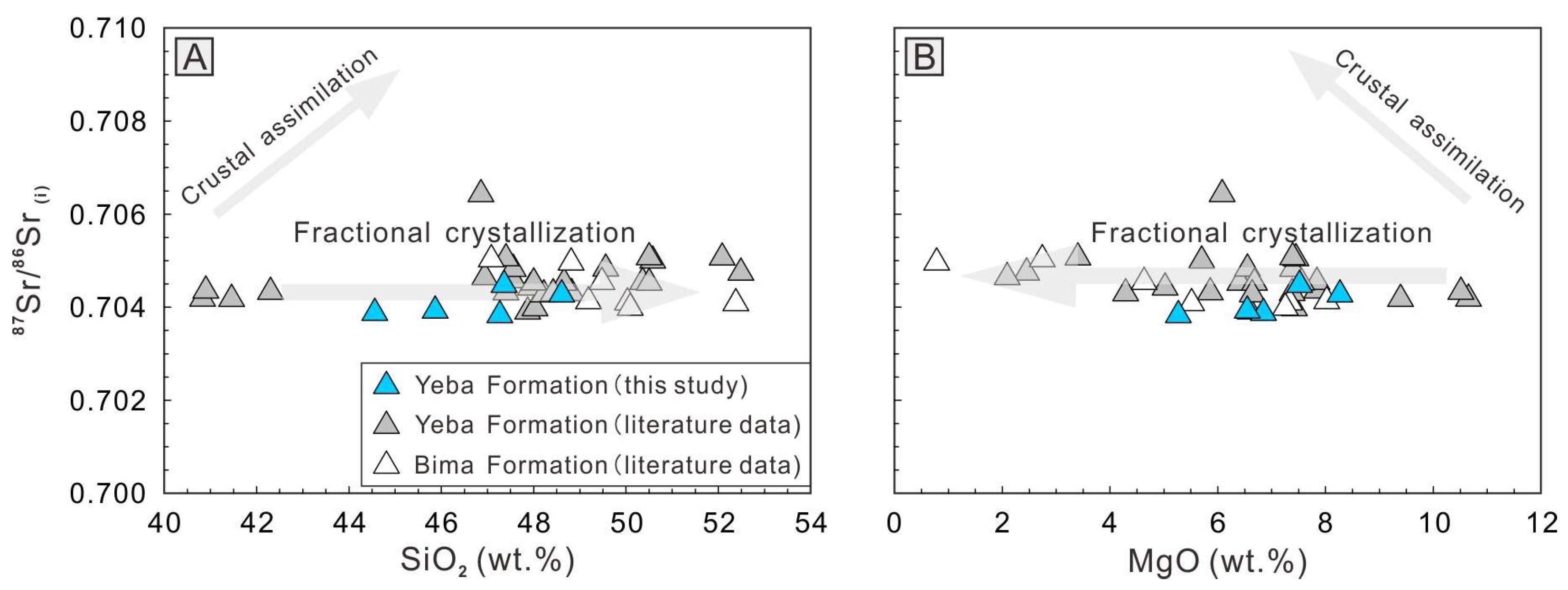
5.2. Petrogenesis of the Jurassic Arc Magmatic Rocks
5.2.1. Petrogenesis of the WSJA Magmatic Rocks
5.2.2. Petrogenesis of the ESJA Magmatic Rocks
5.2.3. Tectonic Setting
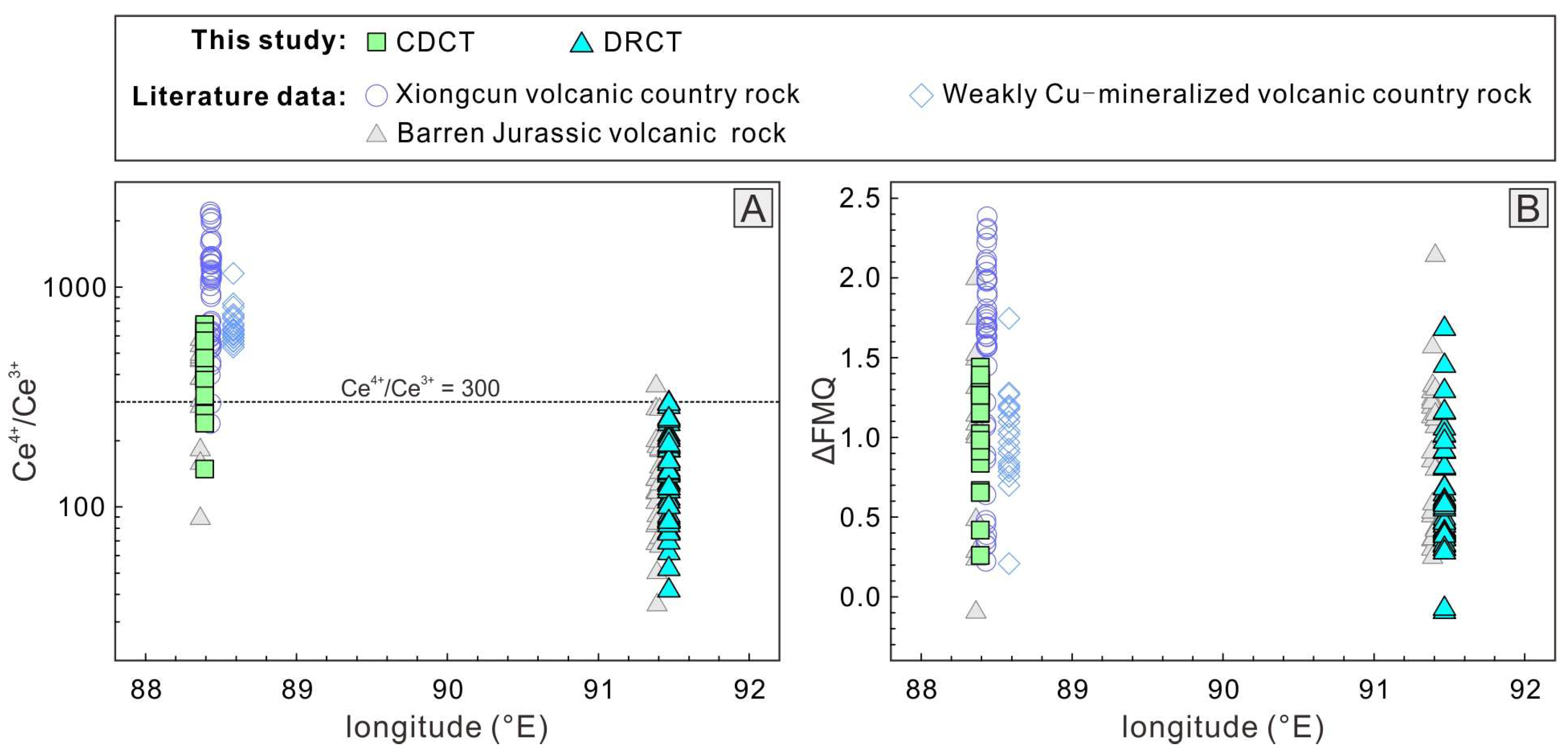
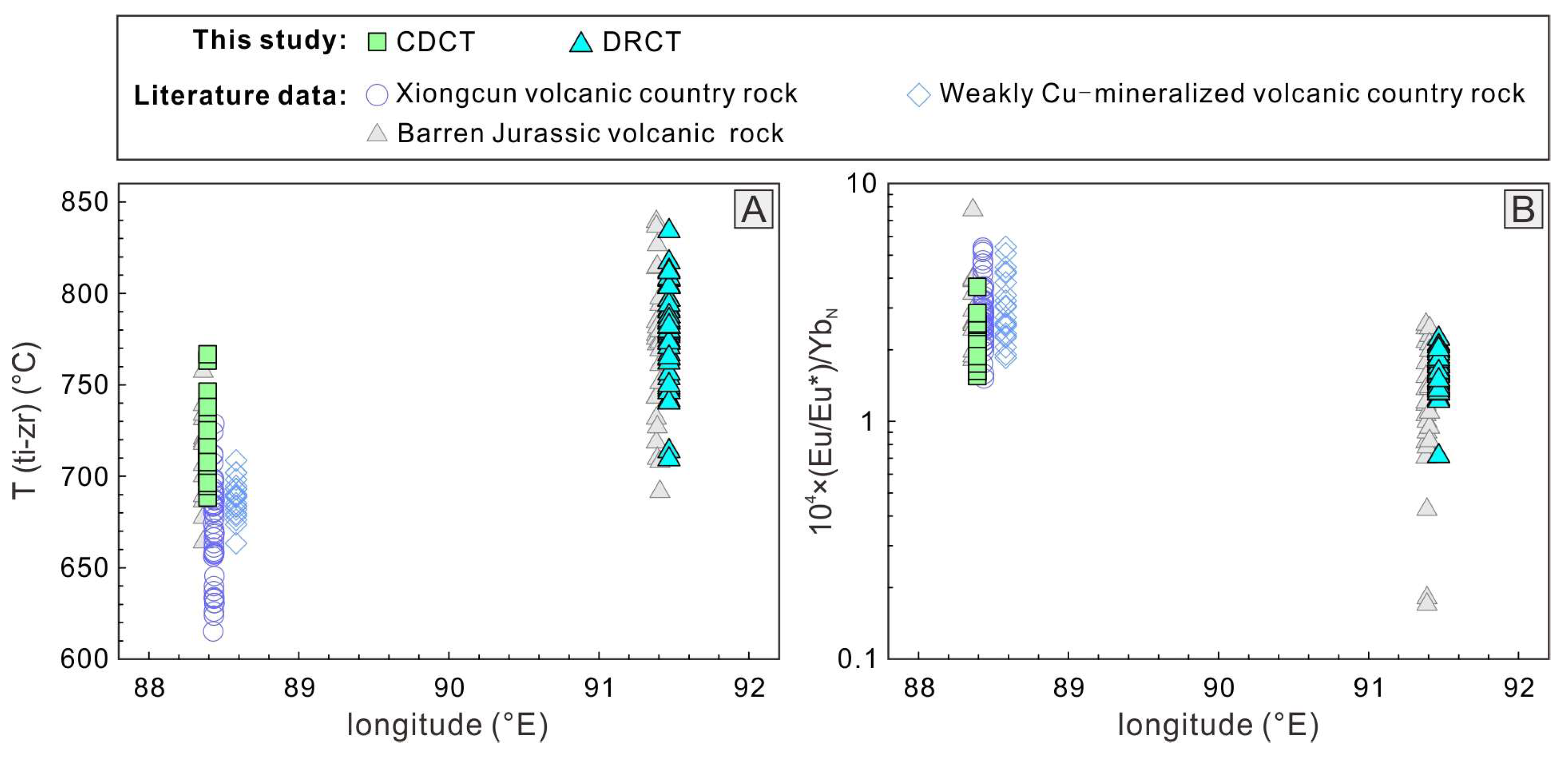
5.3. Key Factors Controlling the Jurassic Cu Mineralization in the Gangdese Belt
5.3.1. Factors Controlling Magmatic Fertibility of the Jurassic Arc
Magma Oxygen Fugacity
Magma Water Content
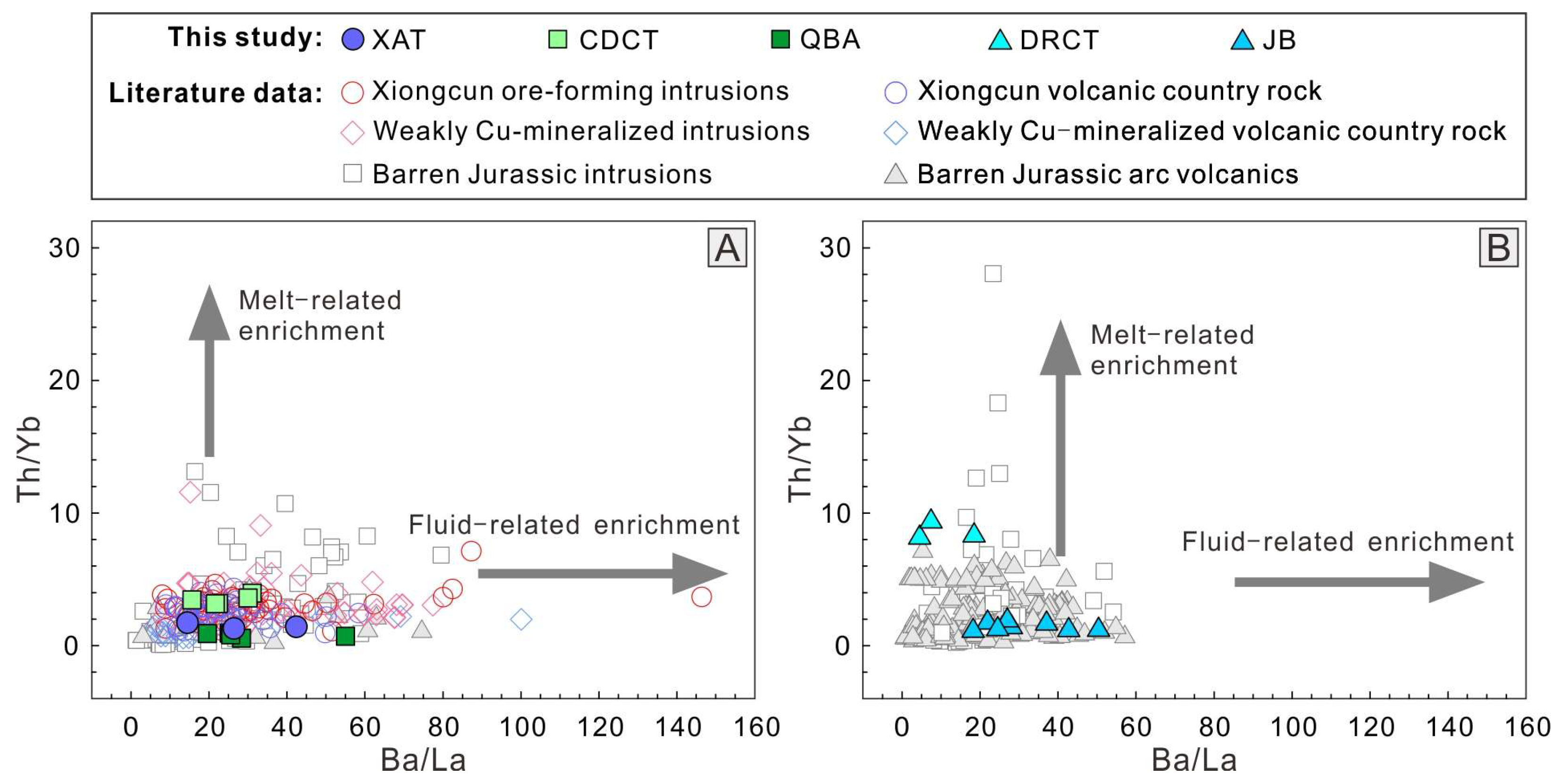
5.3.2. Differences in Deep Magmatic Processes Between the WSJA and ESJA
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the Gangdese belt, Jurassic magmatic rocks show a continuous temporal distribution, peaking at 170–185 Ma. These rocks are spatially concentrated within the longitudinal range of 88° E–94° E and the latitudinal range of 29° N–30° N. Zircon Hf isotopic data reveal significant E–W variations but minimal N–S differences, allowing the Jurassic Arc to be subdivided into WSJA and ESJA subzones.
- (2)
- The mafic volcanic rocks in both WSJA and ESJA derive from depleted mantle, but ESJA’s source shows heterogeneity due to ancient crustal remnants. Intermediate-acidic rocks formed via MASH at the lower crust base and AFC process during ascent. Both subzones developed in an arc setting linked to Neo-Tethyan Oceanic slab subduction.
- (3)
- The mineralization differences between WSJA and ESJA stem from varying fluid metasomatism in their source regions, leading to contrasts in magma oxygen fugacity and water content—key factors controlling porphyry Cu deposit formation. WSJA magmas show higher values in both, while ESJA lacks significant mineralization potential.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sillitoe, R.H. A Plate Tectonic Model for the Origin of Porphyry Copper Deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P. Tectono-Magmatic Precursors for Porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) Deposit Formation. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1515–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M.; Cooke, D.R. Porphyry copper deposits in China. SEG Spec. Publ. 2019, 22, 133–187. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, D.R.; Hollings, P.; Walshe, J.L. Giant porphyry deposits: Characteristics, distribution, and tectonic controls. Econ. Geol. 2005, 100, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.B.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhong, H.; Hu, R.Z.; Zhou, W.D.; Li, C. Re-Os molybdenite ages and zircon Hf isotopes of the Gangjiang porphyry Cu-Mo deposit in the Tibetan Orogen. Miner. Deposita 2013, 48, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.D.; Huang, R.F.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.B.; Zhang, C.C.; Sun, S.J.; Zhang, L.P.; Ding, X.; Li, C.Y.; Zartman, R.E.; et al. Porphyry deposits and oxidized magmas. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.C.; Chen, J.L.; Xu, J.F.; Lei, M.; Xiong, Q.W. Origin of Miocene Cu-bearing porphyries in the Zhunuo region of the southern Lhasa subterrane: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry. Gondwana Res. 2017, 41, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, Y.J.; McCuaig, T.C.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chang, H.F.; Guo, F.; Xu, L.J. Miocene Ultrapotassic, High-Mg Dioritic, and Adakite-like Rocks from Zhunuo in Southern Tibet: Implications for Mantle Metasomatism and Porphyry Copper Mineralization in Collisional Orogens. J. Petrol. 2018, 59, 341–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wu, C. Metallogenesis and major challenges of porphyry copper systems above subduction zones. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 899–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.C. Further discussion on porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit formation in Chinese mainland. Earth Sci. Front. 2020, 27, 20–44, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, D.C.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Zhao, Z.D.; Mo, X.X. Porphyry mineralization in the Tethyan orogen. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 2042–2067, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Wu, C.D.; Tian, S.H.; Hou, Z.Q.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, D.C. Magmatic and structural controls on the tonnage and metal associations of collision-related porphyry copper deposits in southern Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 122, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Qiu, C.X.; Wang, L.Q.; Feng, J.; Wu, S.S.; Wang, Y.Y. Application of ASTER Remote Sensing Data to Porphyry Copper Exploration in the Gondwana Region. Minerals 2023, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.D.; Park, J.W.; Zheng, Y.C.; Hwang, J. Role of chalcophile element fertility in the formation of the eastern Tethyan post-collisional porphyry Cu deposits. Miner. Deposita 2024, 59, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.K.; Xu, P.Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Sun, M.; Su, W.P. Significance of Adakitic Plutons for Mineralization in Wubaduolai Copper Deposit, Xizang: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb Age, Hf Isotope, and Geochemistry. Minerals 2025, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Lang, X.H.; Xie, F.W.; Gao, Y.M.; Li, Z.J.; Huang, Y.; Ding, F.; Yang, H.H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Jurassic No. I porphyry Cu-Au deposit in the Xiongcun district, Gangdese porphyry copper belt, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajacz, Z.; Candela, P.A.; Piccoli, P.M.; Sanchez-Valle, C. The partitioning of sulfur and chlorine between andesite melts and magmatic volatiles and the exchange coefficients of major cations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 89, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.R.; Fiorentini, M.L.; Henríquez, G.J. New magmatic oxybarometer using trace elements in zircon. J. Petrol. 2020, 61, egaa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, B.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L. In Situ Mineralogical Constraints on Magmatic Process for Porphyry Deposits in the Upper Crust: A Case from Tongchang–Chang’anchong Porphyry Deposits, SW China. Minerals 2023, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botcharnikov, R.E.; Holtz, F.; Behrens, H. Solubility and fluid-melt partitioning of H2O and Cl in andesitic magmas as a function of pressure between 50 and 500 MPa. Chem. Geol. 2015, 418, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucks, R.R.; Henríquez, G.J.; Fiorentini, M.L. Zircon and whole-rock trace element indicators of magmatic hydration state and oxidation state discriminate copper ore-forming from barren arc magmas. Econ. Geol. 2024, 119, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Zheng, Y.C.; Xu, B.; Hou, Z.Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, A.P.; Wang, L.; Wu, C.D.; Guo, Q.F. Mechanisms of fluid degassing in shallow magma chambers control the formation of porphyry deposits. Am. Mineral. 2024, 109, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.W.; Tang, J.X.; Lang, X.H.; Ma, D. The different sources and petrogenesis of Jurassic intrusive rocks in the southern Lhasa subterrane, Tibet: Evidence from the trace element compositions of zircon, apatite, and titanite. Lithos 2018, 314–315, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Liang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Sotiriou, P.; Huang, W.T.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.Q. Geochemical characteristics and magma fertility for the Jurassic arc rocks in the Gangdese belt, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Mo, X.X.; Yang, Z.M.; Wang, A.J.; Pan, G.T.; Qu, X.M.; Nie, F.J. Metallogeneses in the Collisional Orogen of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: Tectonic Setting, Tempo-Spatial Distribution and Ore Deposit Types. Geol. China 2006, 33, 340–351, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.T.; Mo, X.X.; Hou, Z.Q.; Zhu, D.C.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, G.M.; Zhao, Z.D.; Geng, Q.R.; Liao, Z.L. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 521–533, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.C.; Zhao, Z.D.; Niu, Y.L.; Mo, X.X.; Chung, S.L.; Hou, Z.Q.; Wang, L.Q.; Wu, F.Y. The Lhasa Terrane, Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Duan, L.F.; Lu, Y.J.; Zheng, Y.C.; Zhu, D.C.; Yang, Z.M.; Yang, Z.S.; Wang, B.D.; Pei, Y.R.; Zhao, Z.D.; et al. Lithospheric architectures of the Lhasa Terrane and its control on ore deposits in Himalayan–Tibetan orogen. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 1541–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.D.; Zheng, Y.C.; Xu, B.; Hou, Z.Q.; Chai, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y. Ultrapotassic enclaves in the Miocene adakitic granitoids, southern Tibet: Direct evidence for collision-related crust-mantle interaction and its implications. Lithos 2023, 442–443, 107052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Kemp, A.; Zheng, Y.C.; Li, Q.Y.; Tang, J.X.; Yang, Z.S.; Duan, L.F. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones. Geology 2015, 43, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.Q.; Chen, X.L.; Huang, W.T.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.Y.; Xu, J.F.; Chen, L. Identification of an Early–Middle Jurassic oxidized magmatic belt, south Gangdese, Tibet, and geological implications. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Lang, X.H.; Tang, J.X.; Deng, Y.L.; Cui, Z.W. Early–Middle Jurassic (182–170 Ma) Ruocuo adakitic porphyries, southern margin of the Lhasa terrane, Tibet: Implications for geodynamic setting and porphyry Cu-Au mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 173, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.Y.; Yang, Z.S.; Zheng, Y.C.; Hou, Z.Q.; Xu, B.; Wu, C.D.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, C. The spatiotemporal distribution, petrogenesis, and key ore-forming factors of the Jurassic magmatic arc in the Gangdese belt, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 186, 106865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.C.; Mo, X.X.; Niu, Y.L.; Zhao, Z.D.; Wang, L.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Wu, F.Y. Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa terrane, Tibet. Chem. Geol. 2009, 268, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.Q.; Xu, J.F.; Wilde, S.A.; Feng, Z.H.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, B.D.; Fu, W.C.; Pan, H.B. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Sangri Group Volcanic Rocks, Southern Lhasa Terrane: Implications for the early subduction history of the Neo-Tethys and Gangdese Magmatic Arc. Lithos 2014, 200–201, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.X.; Xu, Z.Q.; Chen, X.J.; Meert, J.G.; He, Z.Y.; Liang, F.H.; Meng, Y.K.; Ma, S.W. The origin and tectonic significance of the volcanic rocks of the Yeba Formation in the Gangdese magmatic belt, South Tibet. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Richards, J.P.; Liang, H.Y.; Zou, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.T.; Ren, L.; Wang, F.Y. Contrasting arc magma fertilities in the Gangdese belt, Southern Tibet: Evidence from geochemical variations of Jurassic volcanic rocks. Lithos 2019, 324–325, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.H.; Wang, X.H.; Deng, Y.L.; Tang, J.X.; Xie, F.W.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yin, Q.; Jiang, K. Early Jurassic volcanic rocks in the Xiongcun district, southern Lhasa subterrane, Tibet: Implications for the tectono-magmatic events associated with the early evolution of the Neo-Tethys Ocean. Lithos 2019, 340–341, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.H.; Deng, Y.L.; Wang, X.H.; Tang, J.X.; Yin, Q.; Xie, F.W.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.; He, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks of the Bima Formation, southern Lhasa subterrane, Tibet: Implications for early Neo-Tethyan subduction. Gondwana Res. 2020, 80, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Liu, C.Z.; Wu, F.Y.; Ji, W.Q.; Wang, J.G. Zedong terrane revisited: An intra-oceanic arc within Neo-Tethys or a part of the Asian active continental margin? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 80, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Xu, J.F.; Zeng, Q.G.; Wang, Q.; Mao, G.Z.; Li, J. Is there a Neo-Tethys’ subduction record earlier than arc volcanic rocks in the Sangri Group? Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 661–668, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Q.R.; Pan, G.T.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhu, D.C.; Liao, Z.L. Isotopic geochronology of the volcanic rocks from the Yeba Formation in the Gangdise zone, Xizang. Sediment. Geol. Tethy. Geol. 2006, 26, 1–7, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.C.; Pan, G.T.; Chung, S.L.; Liao, Z.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, G.M. SHRIMP Zircon Age and Geochemical Constraints on the Origin of Lower Jurassic Volcanic Rocks from the Yeba Formation, Southern Gangdese, South Tibet. Int. Geol. Rev. 2008, 50, 442–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Xu, J.F.; Chen, J.L.; Kang, Z.Q.; Dong, Y.H. Early Jurassic volcanic rocks from the Yeba Formation and Sangri Group: Products of continental marginal arc and intra-oceanic arc during the subduction of Neo-Tethys Ocean? Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 2089–2100, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q.W.; Chen, J.L.; Xu, J.F.; Huang, F.; Chen, X.F.; Zeng, Y.C.; Lei, M. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemical characteristics and genetic study of Yeba Formation lavas in Demingding area, southern Tibet. Geol. Bull. Chin. 2015, 34, 1645–1655, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.X.; Xu, Z.Q.; Meert, J.; Santosh, M. Early Jurassic intra—Oceanic arc system of the Neotethys Ocean: Constraints from andesites in the Gangdese magmatic belt, south Tibet. Isl. Arc 2017, 26, 12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Zhao, Z.D.; Niu, Y.L.; Zhu, D.C.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Z.Q.; Mo, X.X.; Wei, J.C. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Jurassic Yeba Formation volcanic rocks in southern Tibet: Initiation of back-arc rifting and crustal accretion in the southern Lhasa Terrane. Lithos 2017, 278–281, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.C.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, C.; Qiu, Z.L.; Wang, J.G.; Shen, X.L.; Deng, X.Q. Sequence and petrogenesis of the Jurassic volcanic rocks (Yeba Formation) in the Gangdese arc, southern Tibet: Implications for the Neo-Tethyan subduction. Lithos 2018, 312–313, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, I. Zircon morphology as a crystallogenetic indicator. Krist. Und Tech. 1973, 8, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Schaltegger, U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.R.; Palin, J.M.; Campbell, I.H. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce(IV)/Ce(III) in zircon: Application to porphyry copper deposits of northern Chile. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2002, 144, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, J.; Floyd, P. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chem. Geol. 1977, 20, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, A.R.; Kerr, A.C.; Pearce, J.A.; Mitchell, S.F. Classification of altered volcanic island arc rocks using immobile trace elements: Development of the Th-Co discrimination diagram. J. Petrol. 2007, 48, 2341–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tafti, R.; Hou, Z.Q.; Shen, Z.C.; Guo, N.; Evans, N.J.; Jeon, H.; Li, Q.Y.; Li, W.K. Across-arc geochemical variation in the Jurassic magmatic zone, Southern Tibet: Implication for continental arc-related porphyry Cu-Au mineralization. Chem. Geol. 2017, 451, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.H.; Wang, X.H.; Tang, J.X.; Deng, Y.L.; Cui, Z.W.; Yin, Q.; Xie, F.W.; Yang, Q.Y. Composition and age of Jurassic diabase dikes in the Xiongcun porphyry copper-gold district, southern margin of the Lhasa terrane, Tibet, China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Geol. J. 2017, 53, 1973–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hou, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y.C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.W.; Zhen, G.; Wu, C.D. Jurassic Hornblende Gabbros in Dongga, Eastern Gangdese, Tibet: Partial Melting of Mantle Wedge and Implications for Crustal Growth. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.S.; Wang, R.Q.; Zhao, J.L.; Yu, S.B. Petrogenesis of the Early Jurassic gabbro-granite complex in the middle segment of the Gangdese belt and its implications for tectonic evolution of Neo-Tethys: A case study of the Dongga pluton in Xigaze. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 3569–3580, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hildreth, W.; Moorbath, S. Crustal contributions to arc magmatism in the Andes of Central Chile. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 98, 455–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, X.F.; He, Z.Y.; Klemd, R.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, T.Y.; Yan, L.L. Early Jurassic adakitic rocks in the southern Lhasa sub-terrane; southern Tibet: Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications. Geol. Mag. 2017, 155, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Qiu, J.S.; Wang, R.Q.; Xu, H.; Hong, Y.F. Petrogenesis of the Early Jurassic-Eocene composite pluton in Siborongqu, Gyaca County, eastern segment of the Gangdese belt, and its tectonic implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 3020–3046, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, D.C.; Wang, Q.; Weinberg, R.F.; Wang, R.; Li, S.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, Z.D. Constructing the Early Mesozoic Gangdese crust in southern Tibet by hornblende-dominated magmatic differentiation. J. Petrol. 2019, 60, 515–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.C.; Liu, D.M.; Zeren, Z.X.; Nima, C.R. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of lavas in the Yeba Formation in the eastern part of the Gangdise belt. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2009, 39, 435–445, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Dong, X.; Shen, K.; Lu, X. Precambrian evolution of the Lhasa terrane, Tibet: Constraint from the zircon U-Pb geochronology of the gneisses. Precambrian Res. 2013, 237, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.M.; Niu, Y.L.; Tian, Z.L.; Zhang, L.L. Reworked Precambrian metamorphic basement of the Lhasa terrane, southern Tibet: Zircon/titanite U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and geochemistry. Precambrian Res. 2020, 336, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.Q.; Wu, F.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Liu, C.Z. Identification of Early Carboniferous Granitoids from Southern Tibet and Implications for Terrane Assembly Related to the Paleo-Tethyan Evolution. J. Geol. 2012, 120, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.M.; Liu, F.; He, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.H. Late Paleozoic intrusive rocks from the southeastern Lhasa terrane, Tibetan Plateau, and their Late Mesozoic metamorphism and tectonic implications. Lithos 2014, 198–199, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.M. Cambrian granitoids from the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: Research on petrology and zircon Hf isotope. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 1183–1199, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Peate, D.W. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1995, 23, 251–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesworth, C.J.; Turner, S.P.; McDermott, F.; Peate, D.W.; Calsteren, P.V. U-Th isotopes in arc magmas: Implications for element transfer from the subducted crust. Science 1997, 276, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.F.; Chung, S.L.; Song, B.; Liu, D.Y.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Pearson, N.J.; Ji, J.Q.; Wen, D.J. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on the Mesozoic tectonics and crustal evolution of southern Tibet. Geology 2006, 34, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.Q.; Wu, F.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Li, J.X.; Liu, C.Z. Zricon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet. Chem. Geol. 2009, 262, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.S.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, S.W.; Cawood, P.A.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, H.F. Petrogenesis of Early to Middle Jurassic granitoid rocks from the Gangdese belt, Southern Tibet: Implications for early history of the Neo-Tethys. Lithos 2013, 179, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Kapp, P.; Pullen, A.; Yue, Y.H. Petrogenesis of Middle–Late Triassic volcanic rocks from the Gangdese belt, southern Lhasa terrane: Implications for early subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic lithosphere. Lithos 2016, 262, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.A.; Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M.; Duerr, S.B.; Chen, Z.; Ryerson, F.J.; Kidd, W.S.F.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X. Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Tibetan plateau? Geology 1997, 25, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, Y. The subduction factory: How it operates in the evolving earth. GSA Today 2005, 15, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutscher, M.A. Andean subduction styles and their effect on thermal structure and interplate coupling. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2002, 15, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.M.; Watson, E.B. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 154, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, L.A.; Watson, E.B. Rutile saturation in hydrous siliceous melts and its bearing on Ti-thermometry of quartz and zircon. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 258, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Huang, H.Q.; Jiang, X.Y. Water-fluxed crustal melting produces Cordilleran batholiths. Geology 2016, 44, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.A.; Cottrell, E. Water and the oxidation state of subduction zone magmas. Science 2009, 325, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.M.; Xu, Y.G.; Xia, X.P.; Yang, J.H.; Huang, X.L.; Spencer, C.J.; Sun, J.F.; Cui, Z.X.; Li, M.J.; Zhang, W.F.; et al. Mantle induced hydration and oxidation of intracontinental granite sources in the North China Craton. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2025, 651, 119177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, P.; Kaegi, R.; Müntener, O. Experimentally derived intermediate to silica-rich arc magmas by fractional and equilibrium crystallization at 1.0 GPa: An evaluation of phase relationships, compositions, liquid lines of descent and oxygen fugacity. J. Petrol. 2018, 59, 11–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.D.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Bodnar, R.J.; Zhao, P.L.; Zajacz, Z.; Chou, I.M.; Mao, J.W. 2025. The role of magma differentiation in optimizing the fluid-assisted extraction of copper to generate large porphyry-type deposits. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadr8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.L.; Zajacz, Z.; Tsay, A.; Chu, X.; Cheng, Q.M.; Yuan, S.D. The partitioning behavior of Mo during magmatic fluid exsolution and its implications for Mo mineralization. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 339, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yang, Z.M.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Suo, M.S. Impact of laser focus on accuracy of U-Pb dating of zircons by LA-ICPMS. Miner. Deposits. 2019, 38, 21–28, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstwood, M.S.A.; Košler, J.; Gehrels, G.; Jackson, S.E.; McLean, N.M.; Paton, C.; Pearson, N.J.; Sircombe, K.; Sylvester, P.; Vermeesch, P.; et al. Community-Derived Standards for LA-ICP-MS U-(Th-)Pb Geochronology-Uncertainty Propagation, Age Interpretation and Data Reporting. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2016, 40, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Woodhead, J.D.; Hellstrom, J.C.; Hergt, J.M.; Maas, R. Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust downhole fractionation correction. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, Q0AA06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.M.; Wang, R.; Hou, Z.Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.W.; Qu, W.J. Hot Paleocene-Eocene Gangdese arc: Growth of continental crust in southern Tibet. Gondwana Res. 2018, 62, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.M.; Vervoort, J.D.; Hanchar, J.M. Guidelines for reporting zircon Hf isotopic data by LA-MC-ICPMS and potential pitfalls in the interpretation of these data. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Horstwood, M.S.A.; Morris, G.A.; Nasdala, L.; Norberg, N.; et al. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Lang, X.; Cui, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, X. Geology and geochemistry constraints on the genesis of the No. 2 porphyry copper-gold deposit in the Xiongcun district, Gangdese porphyry copper belt, Tibet, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 477–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.H.; Guo, W.B.; Wang, X.H.; Deng, Y.L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Xie, F.W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, K. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the ore-bearing porphyries in the Xiongcun district: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 2105–2123, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.M.; Xin, H.B.; Xu, W.Y. Petrogenesis of the ore-hosting volcanic rocks and their contribution to mineralization in Xiongcun superlarge Cu-Au Deposit, Tibet. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 964–971, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tafti, R. Metallogeny, Geochronology and Tectonic Setting of the Gangdese Belt, Southern Tibet, China. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.Q.; Yu, H.X.; Wang, B.D.; Huang, F.; Zeng, Y.C.; Huang, W.L.; Wen, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, Z.C.; Tan, R.Y. Petrogenesis and geological implications of Early Jurassic granodiorites in Renqinze area, central part of the southern Lhasa subterrane. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 2795–2810, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hou, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y.C.; Wang, R.; He, M.Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Wang, Z.X.; He, W.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y. In situ elemental and isotopic study of diorite intrusions: Implication for Jurassic arc magmatism and porphyry Cu-Au mineralization in southern Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 90, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.T.; Long, X.P.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, C. Mixing of Early Jurassic crustal and mantle-derived magmas induced by subduction of the Neo-Tethyan Ocean: Evidence from the Dongga dioritic pluton, South Tibet. Geochimica 2018, 47, 478–490, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.K.; Xu, Z.Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.H.; Sun, J.B.; Zhang, K.H. The determination of the Early Jurassic magmatism in the middle Gangdese Batholith, Southern Tibet and its tectonic significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 1196–1215, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.Q.; Wu, F.Y.; Liu, C.Z.; Chung, S.L. Geochronology and petrogenesis of granitic rocks in Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1240–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.K.; Dong, H.W.; Cong, Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Cao, H. The early-stage evolution of the Neo-Tethys ocean: Evidence from granitoids in the middle Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet. J. Geodyn. 2016, 94–95, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Xu, W.C.; Guo, J.Q.; Zong, K.Q.; Cai, H.M.; Yuan, H.L. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic composition of deformed granite in the southern margin of the Gangdese belt, Tibet: Evidence for early Jurassic subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic slab. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 1347–1353, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.M.; Hou, Z.Q.; Xia, D.X.; Song, Y.C.; Li, Z. Relationship between Western Porphyry and mineralization in Qulong copper deposit of Tibet and its enlightenment to further exploration. Miner. Deposits 2008, 27, 28–36, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.M. Genesis and tectonic significance of the Early Jurassic magmatic rocks from the southern Lhasa terrane. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 1933–1948, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, L.S.; Gao, L.E.; Tang, S.H.; Hu, G.Y. Remnant Jurassic intra-oceanic arc system in Southern Tibet: Geochemistry and tectonic implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 1741–1754, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shui, X.F.; He, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, T.Y. Magma origin of Early Jurassic tonalites in the eastern Gangdese magmatic belt, southern Tibet and its implications for the crustal evolution of the Lhasa terrane. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 3129–3152, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Ma, C.Q.; Bian, Q.J.; Hu, Y.Q.; Long, T.C.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, D.M.; Tu, J.H. Evidences from geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of volcanic rocks of Yeba Formation in Demingding area, the east of middle Gangdise, Tibet. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2009, 28, 31–40, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, B.; Zhao, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; et al. Metallogenic Controls of the Jurassic Arc, Xizang: Insights from Geochemistry, Zircon Chronology, Hf Isotopes, and In Situ Trace Elements. Minerals 2025, 15, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121228
Xu P, Zheng Y, Hou Z, Yang Z, Li X, Zhao X, Xu B, Zhao M, Wu C, Liu C, et al. Metallogenic Controls of the Jurassic Arc, Xizang: Insights from Geochemistry, Zircon Chronology, Hf Isotopes, and In Situ Trace Elements. Minerals. 2025; 15(12):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121228
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Peiyan, Yuanchuan Zheng, Zengqian Hou, Zhusen Yang, Xin Li, Xiaoyan Zhao, Bo Xu, Miao Zhao, Changda Wu, Chang Liu, and et al. 2025. "Metallogenic Controls of the Jurassic Arc, Xizang: Insights from Geochemistry, Zircon Chronology, Hf Isotopes, and In Situ Trace Elements" Minerals 15, no. 12: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121228
APA StyleXu, P., Zheng, Y., Hou, Z., Yang, Z., Li, X., Zhao, X., Xu, B., Zhao, M., Wu, C., Liu, C., & Ma, W. (2025). Metallogenic Controls of the Jurassic Arc, Xizang: Insights from Geochemistry, Zircon Chronology, Hf Isotopes, and In Situ Trace Elements. Minerals, 15(12), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121228








