Integrated Petrophysics and 3D Modeling to Evaluate the Role of Diagenesis in Permeability of Clastic Reservoirs, Belayim Formation, Gulf of Suez
Abstract
1. Introduction
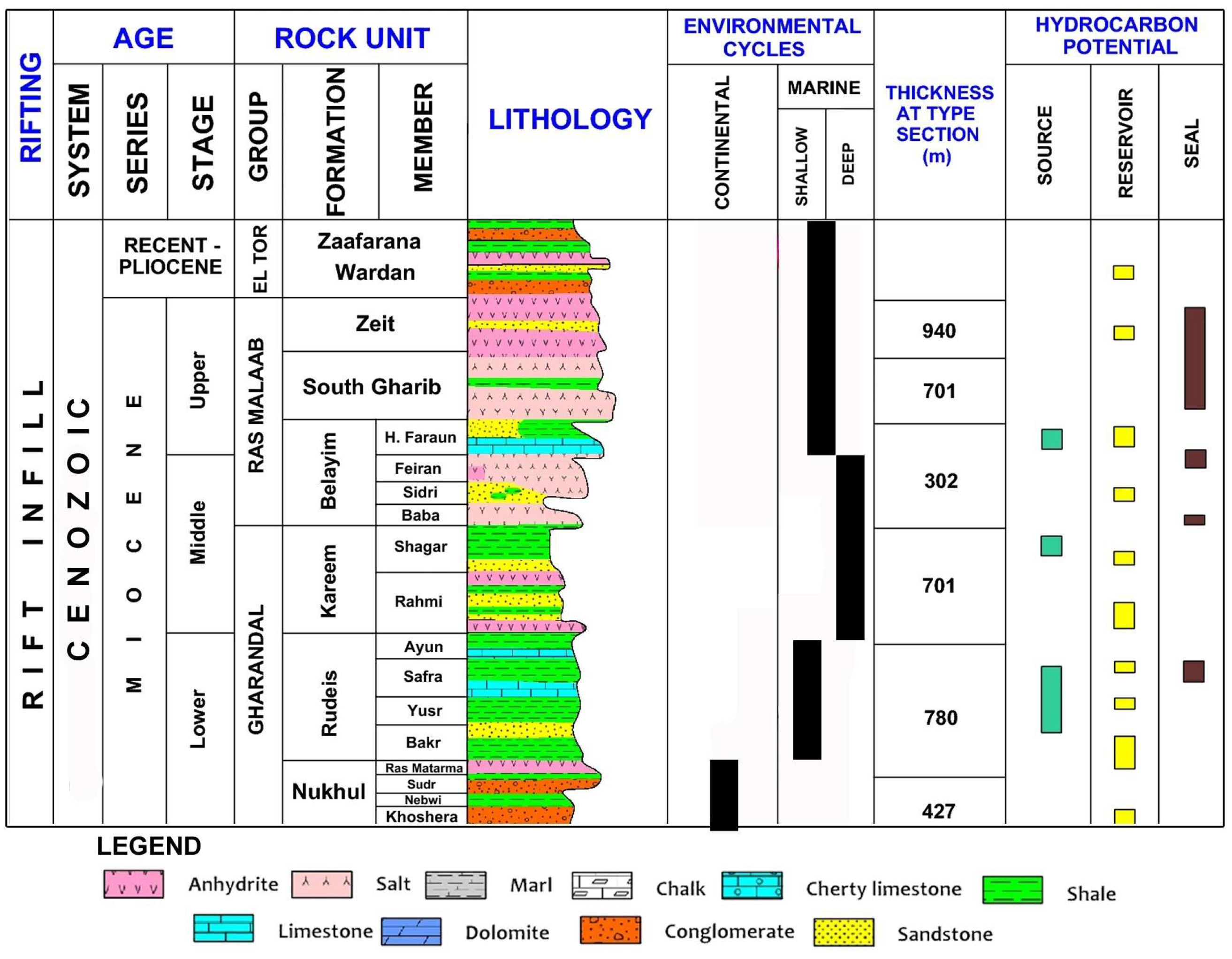
2. Geological Setting
2.1. Regional Tectono-Stratigraphic Framework
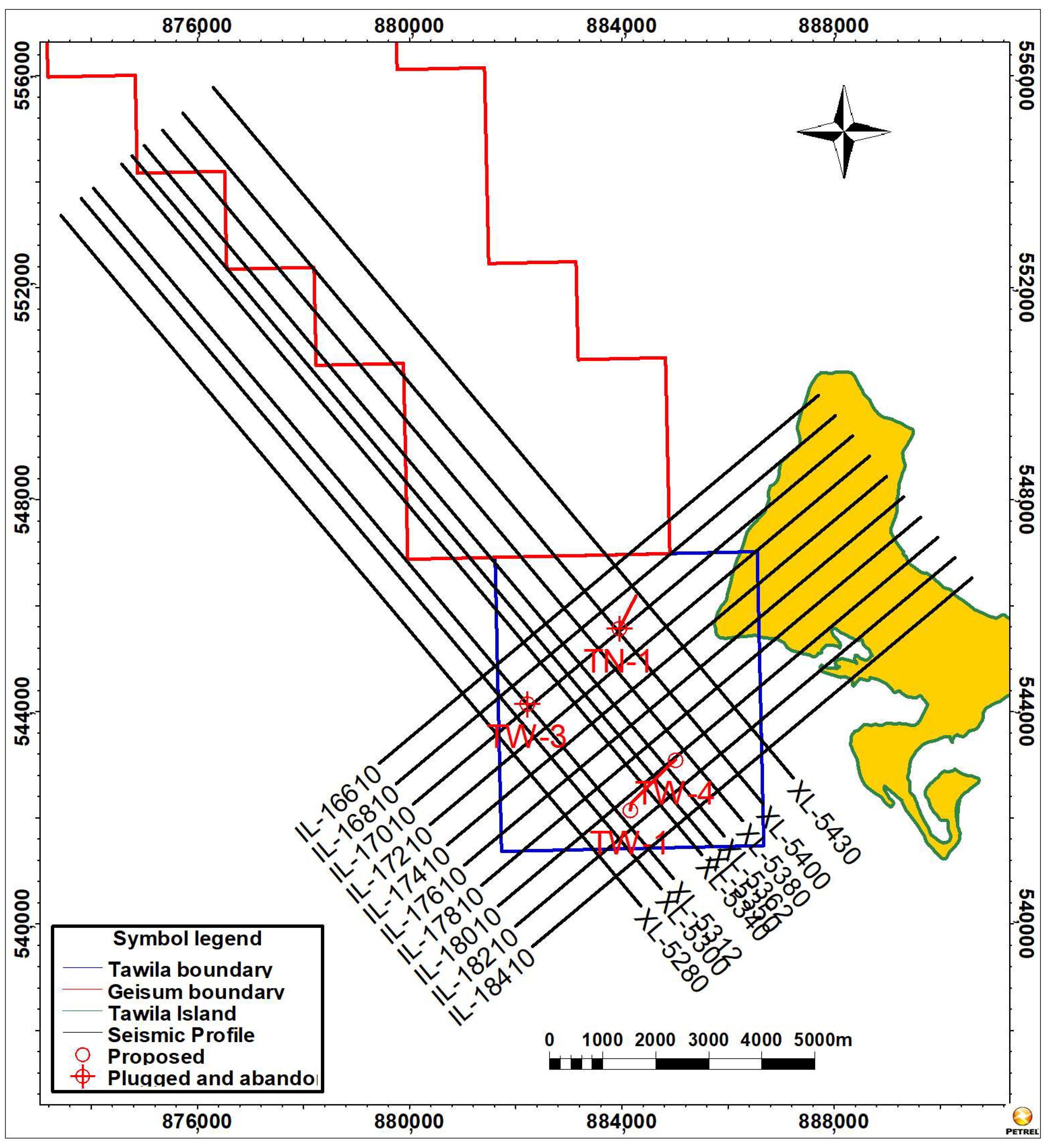
2.2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Petrophysical Workflow
3.2.1. Lithology and Diagenetic Mineral Identification
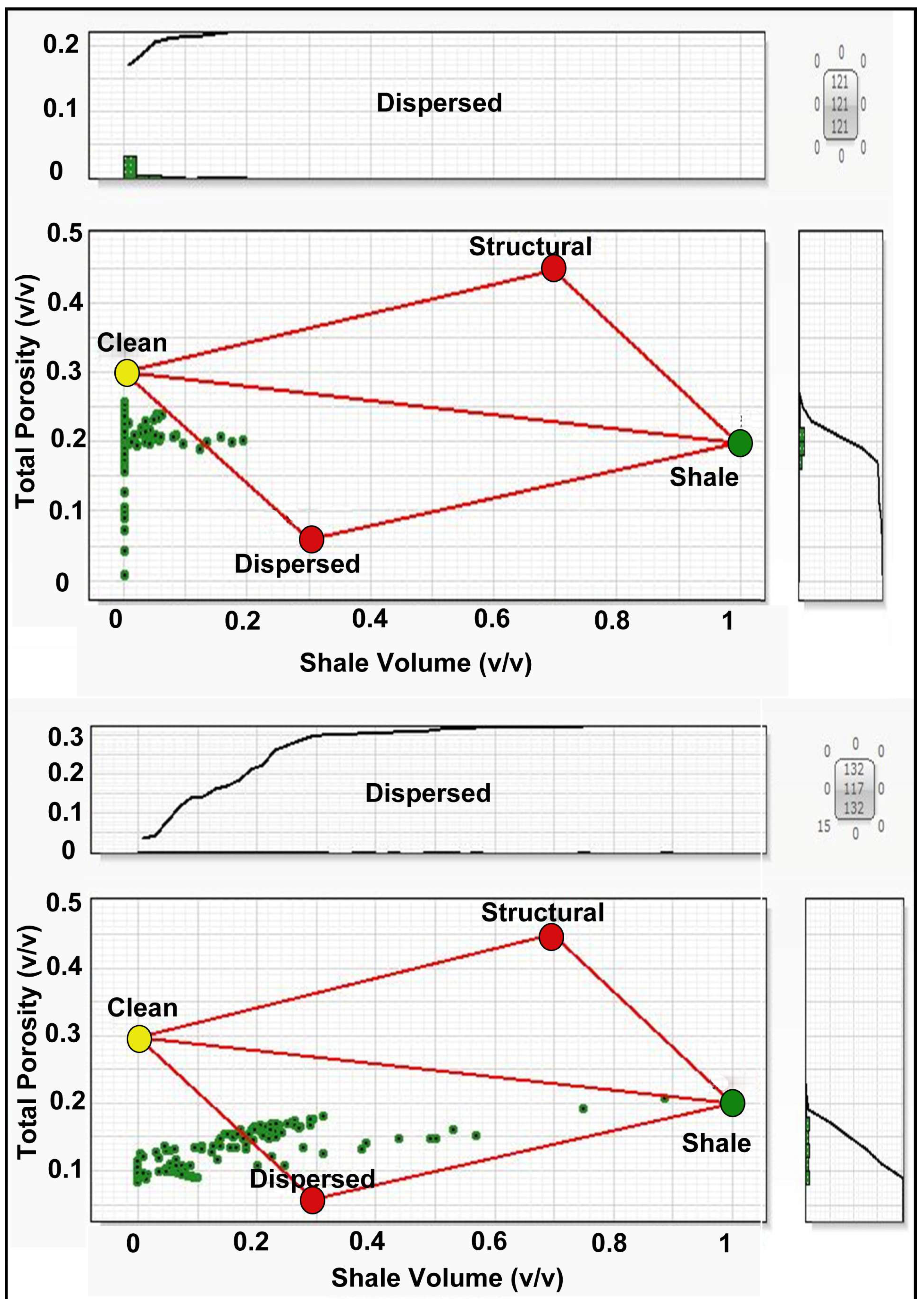
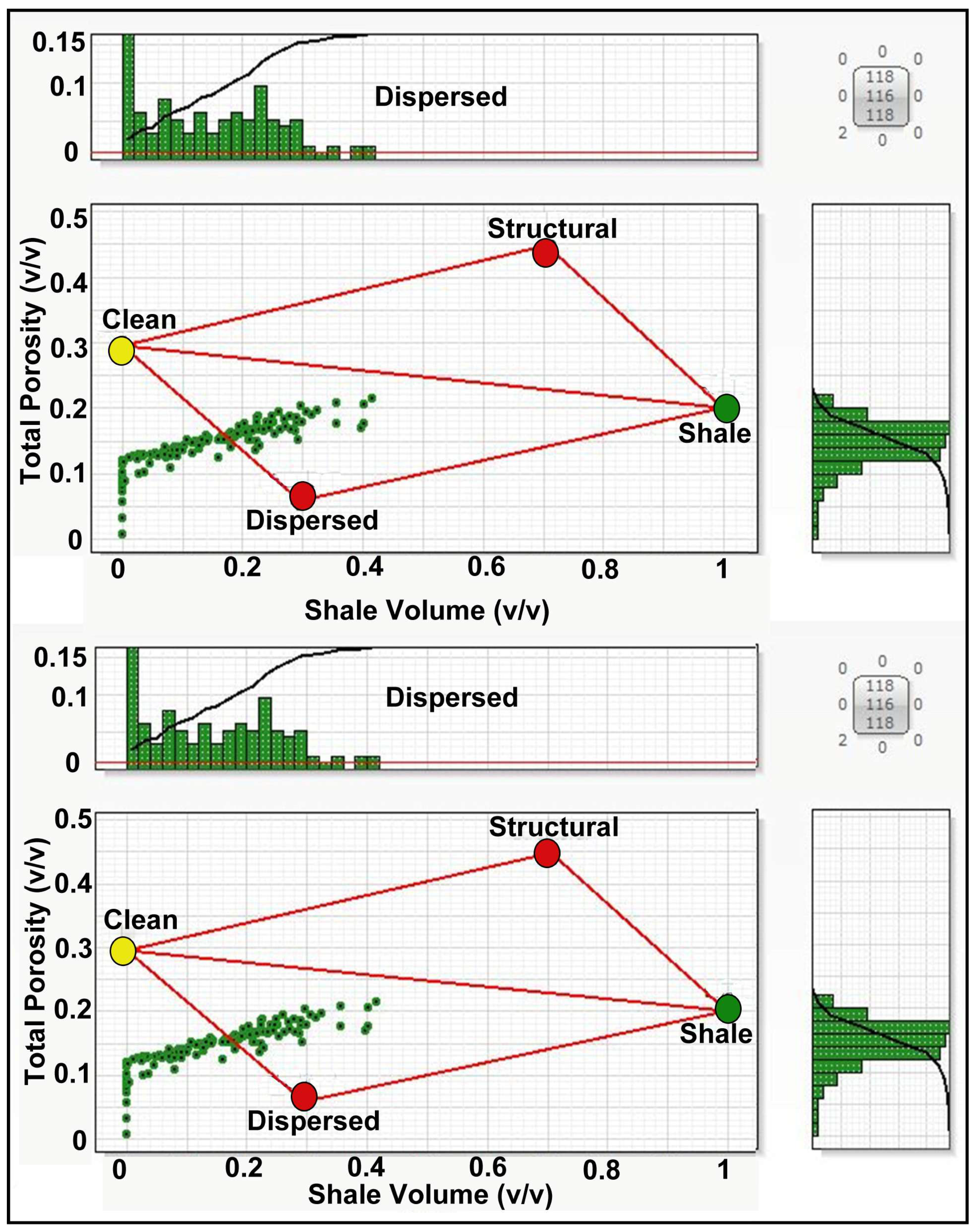
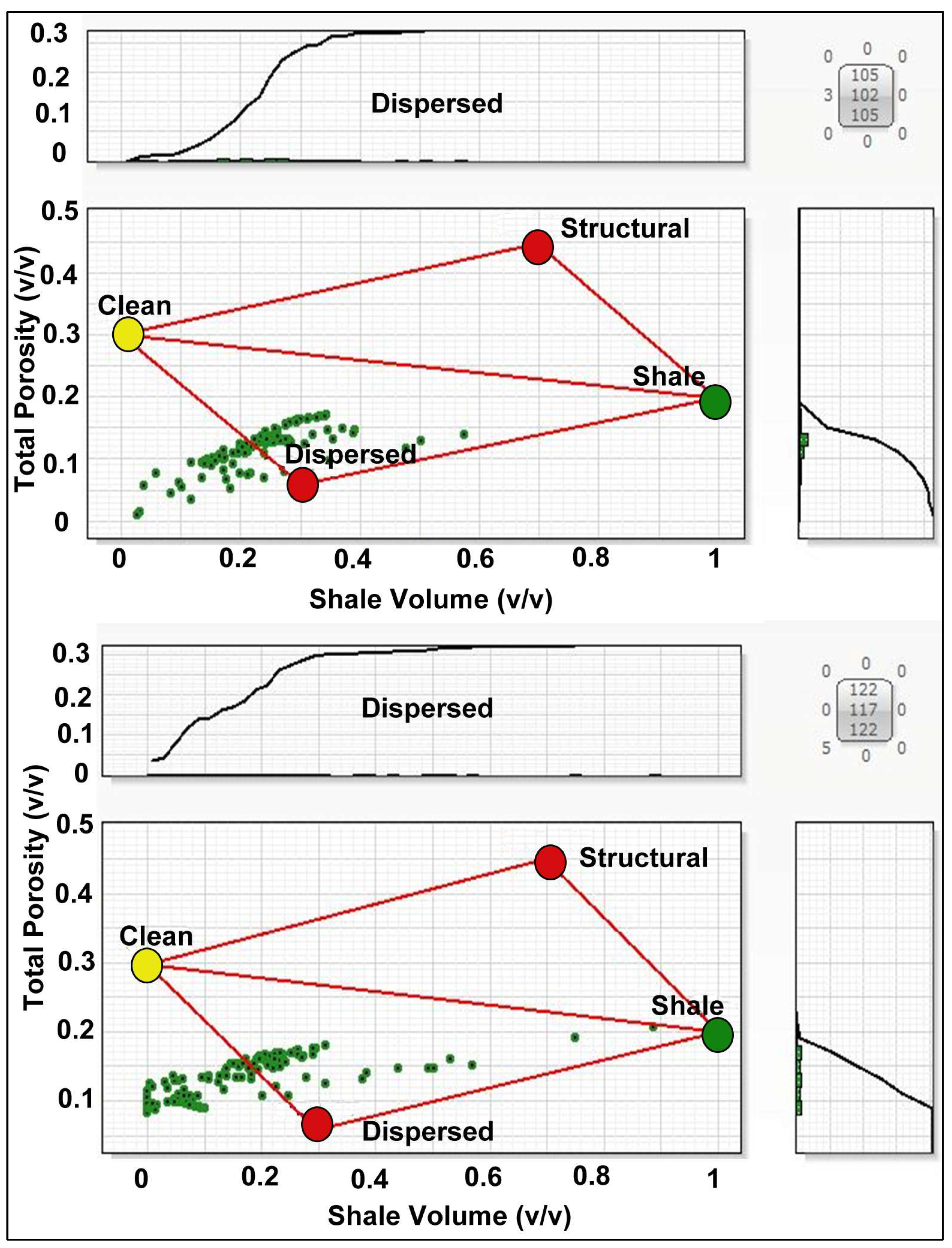
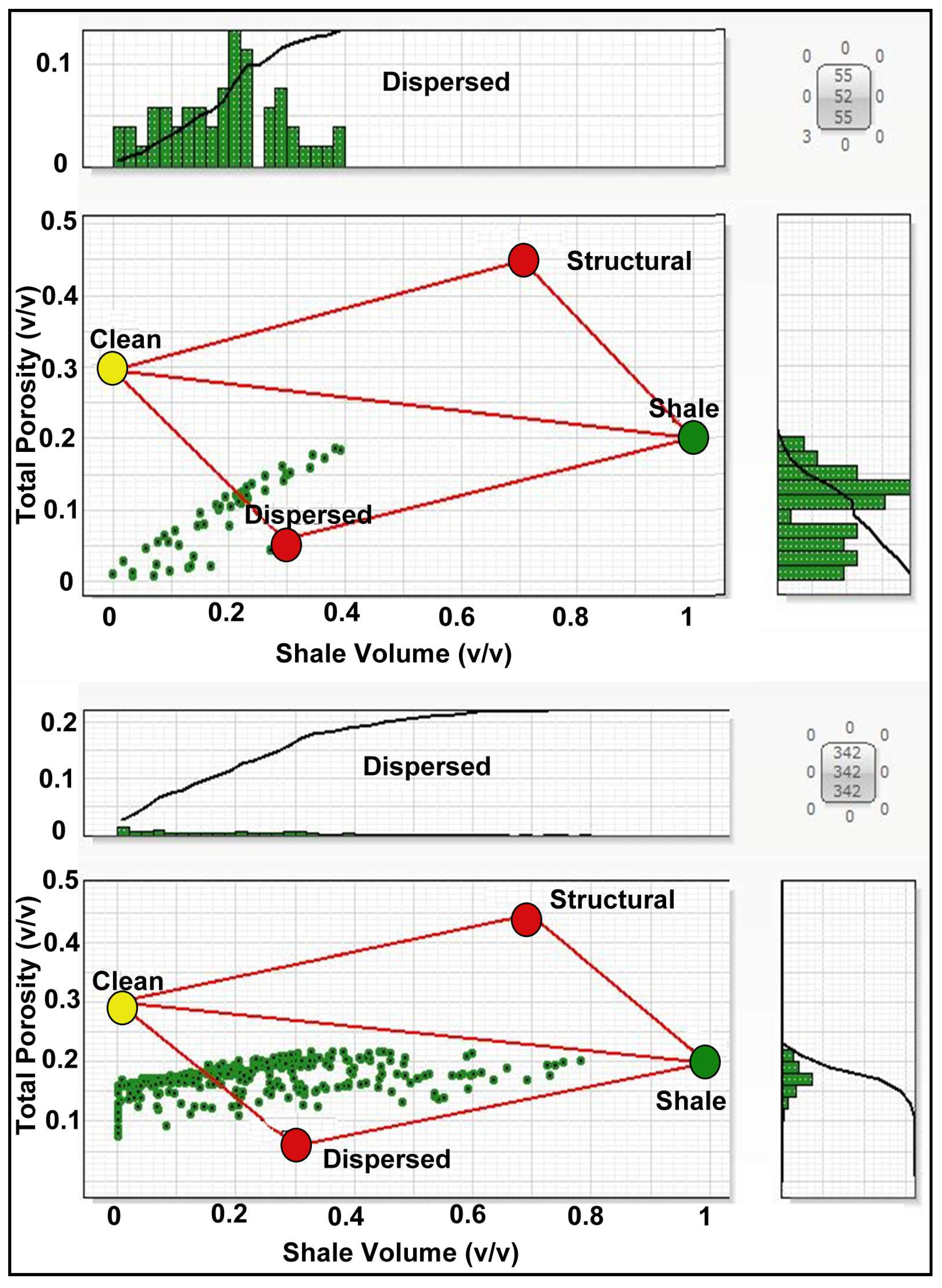
3.2.2. Shale Distribution Modeling
- -
- Laminated shale only:
- -
- Dispersed shale only:
- -
- Structure shale only:
- -
- Material equilibrium for shales:
3.2.3. Saturation and Flow Unit Analysis
3.2.4. Permeability Derivation and Anisotropy Analysis
3.3. Three-Dimensional Static Modeling
4. Results
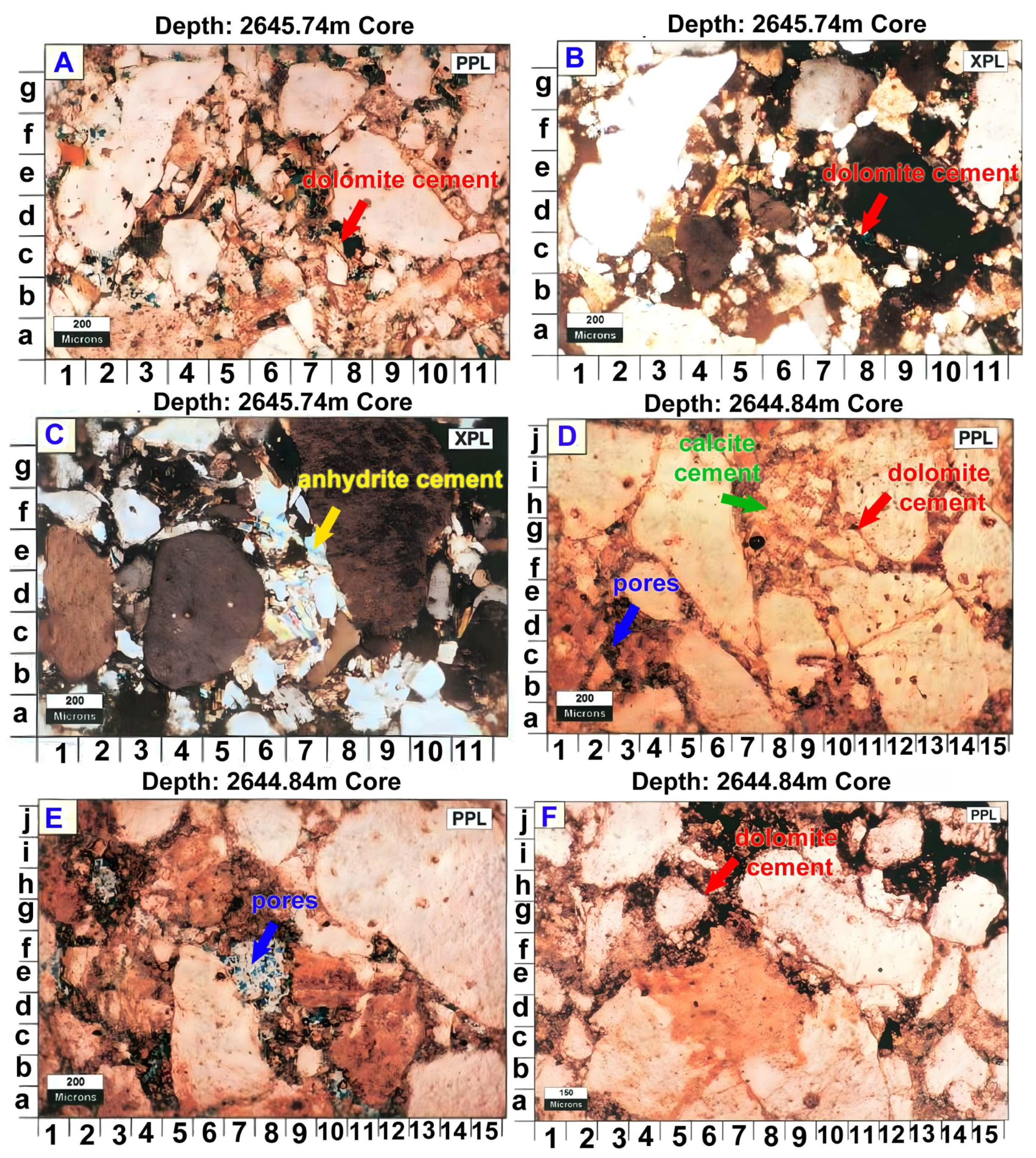
4.1. Diagenetic Facies and Their Petrophysical Signature
4.1.1. M-N Crossplot Analysis
4.1.2. Impact on Reservoir Properties
4.2. Quantifying the Baffles: Shale Distribution and Pore Occlusion
4.2.1. Thomas–Stieber Model Results
4.2.2. Porosity Destruction
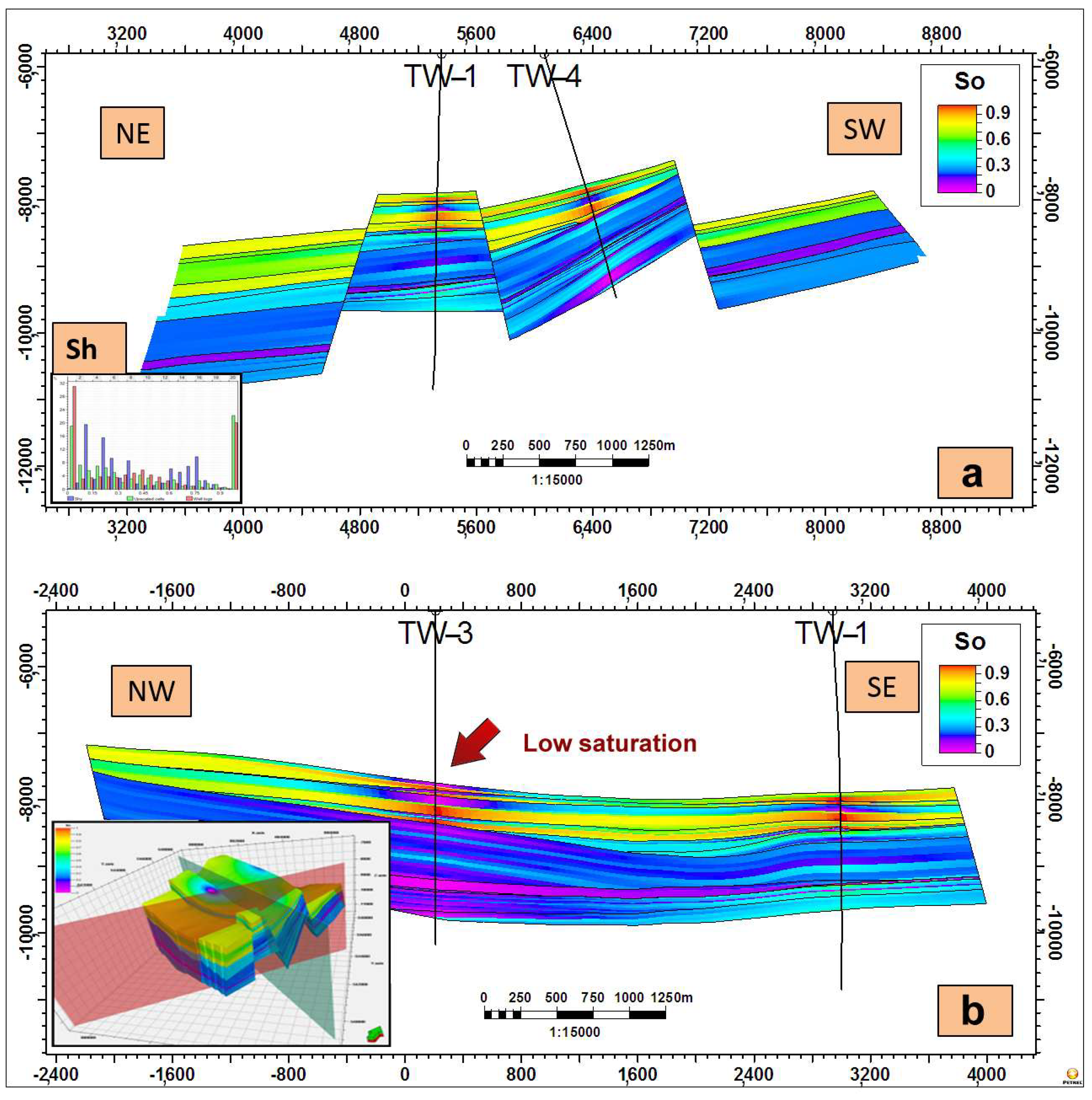
4.3. Hydraulic Flow Units and Saturation Characteristics
4.3.1. Defining Flow Units
4.3.2. The Movable vs. Residual Hydrocarbon Concept
4.4. Spatial Distribution of Shale Volume and Its Impact on Reservoir Quality
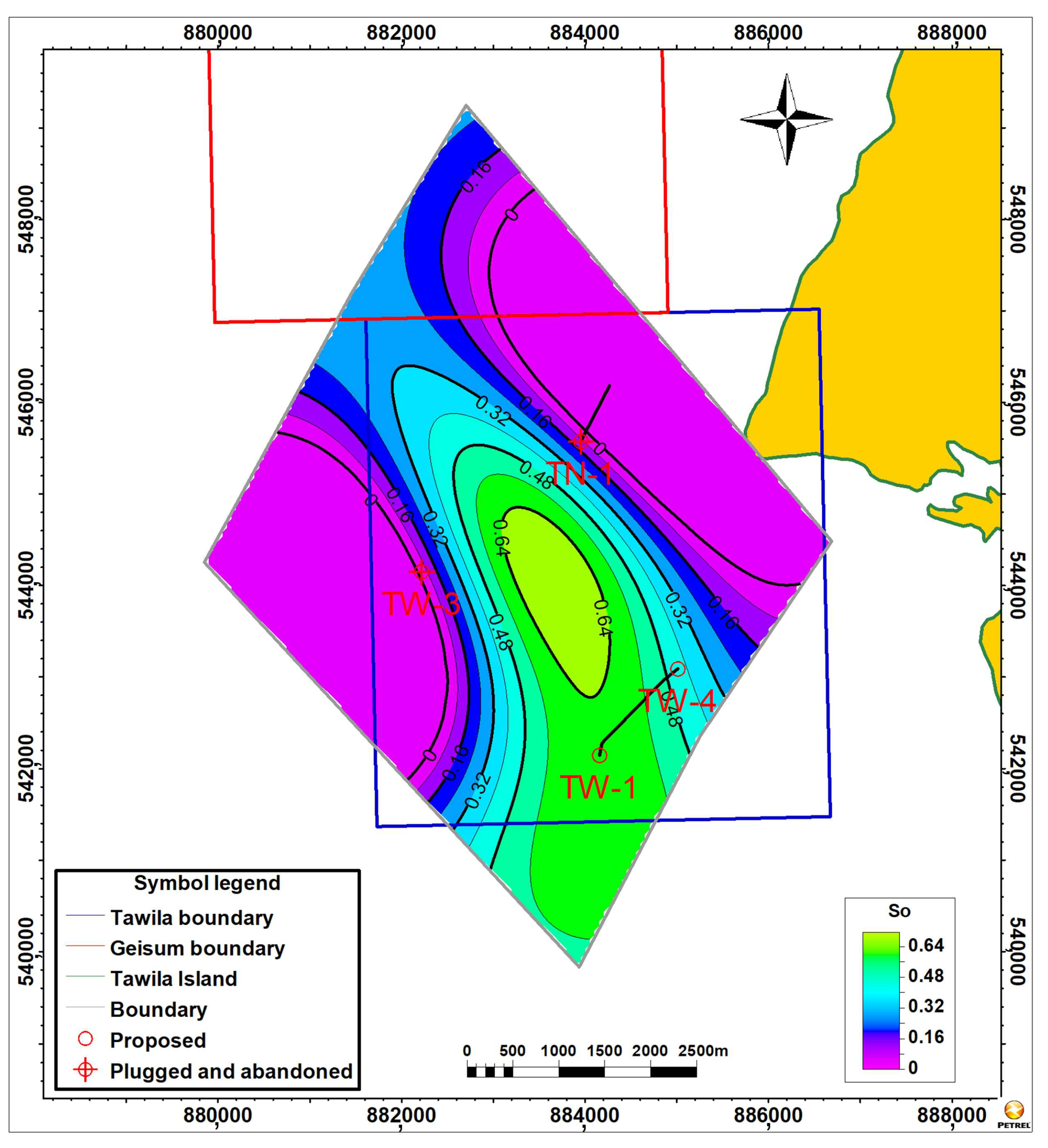
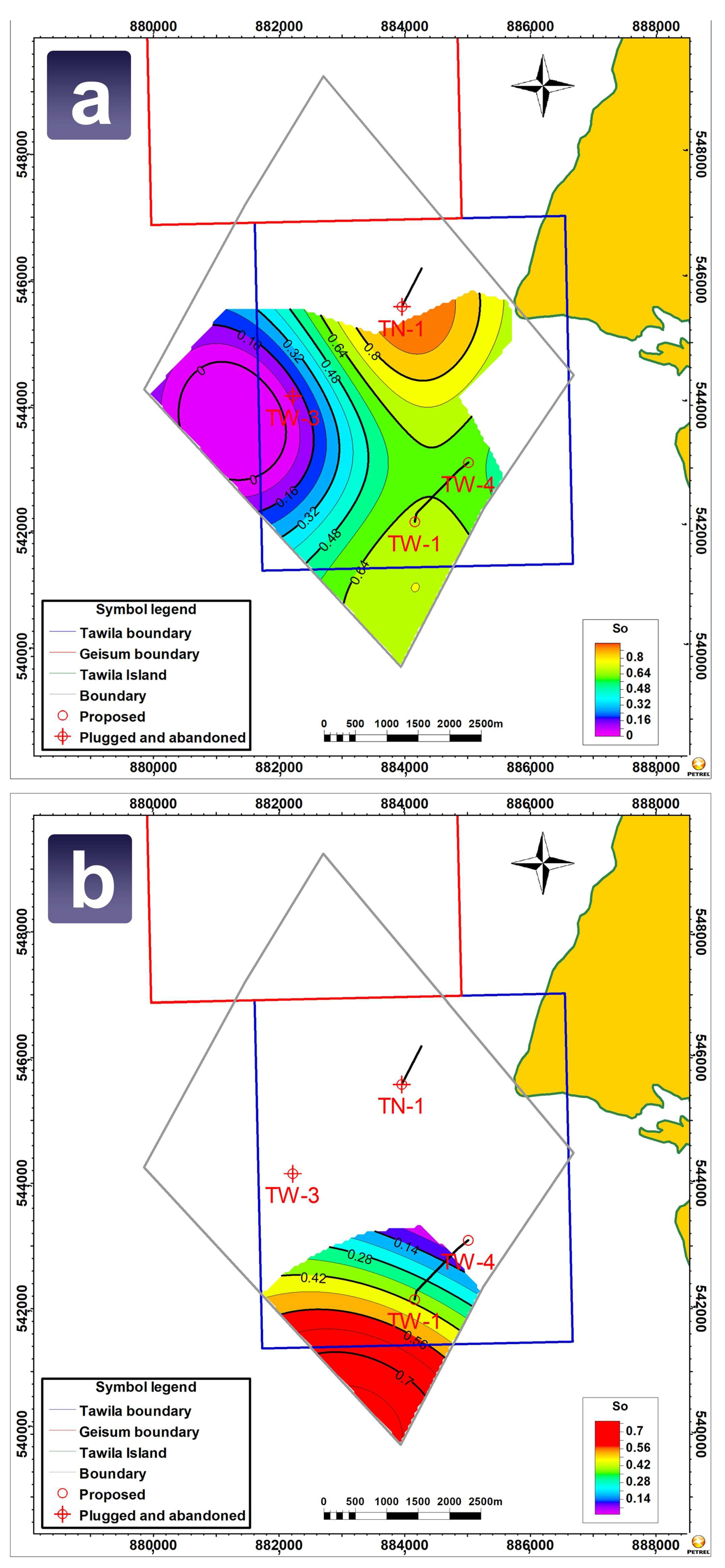
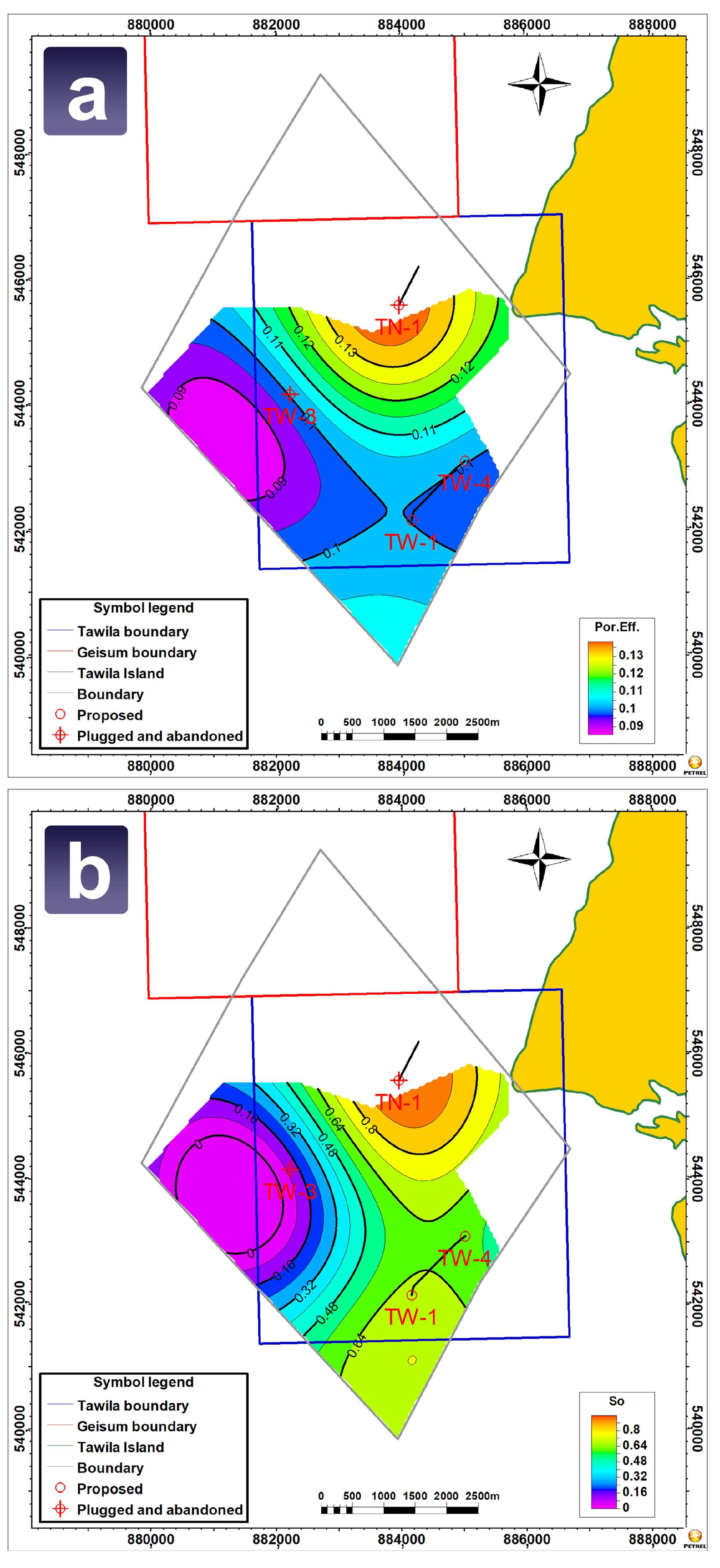
4.4.1. Petrophysical Contour Maps
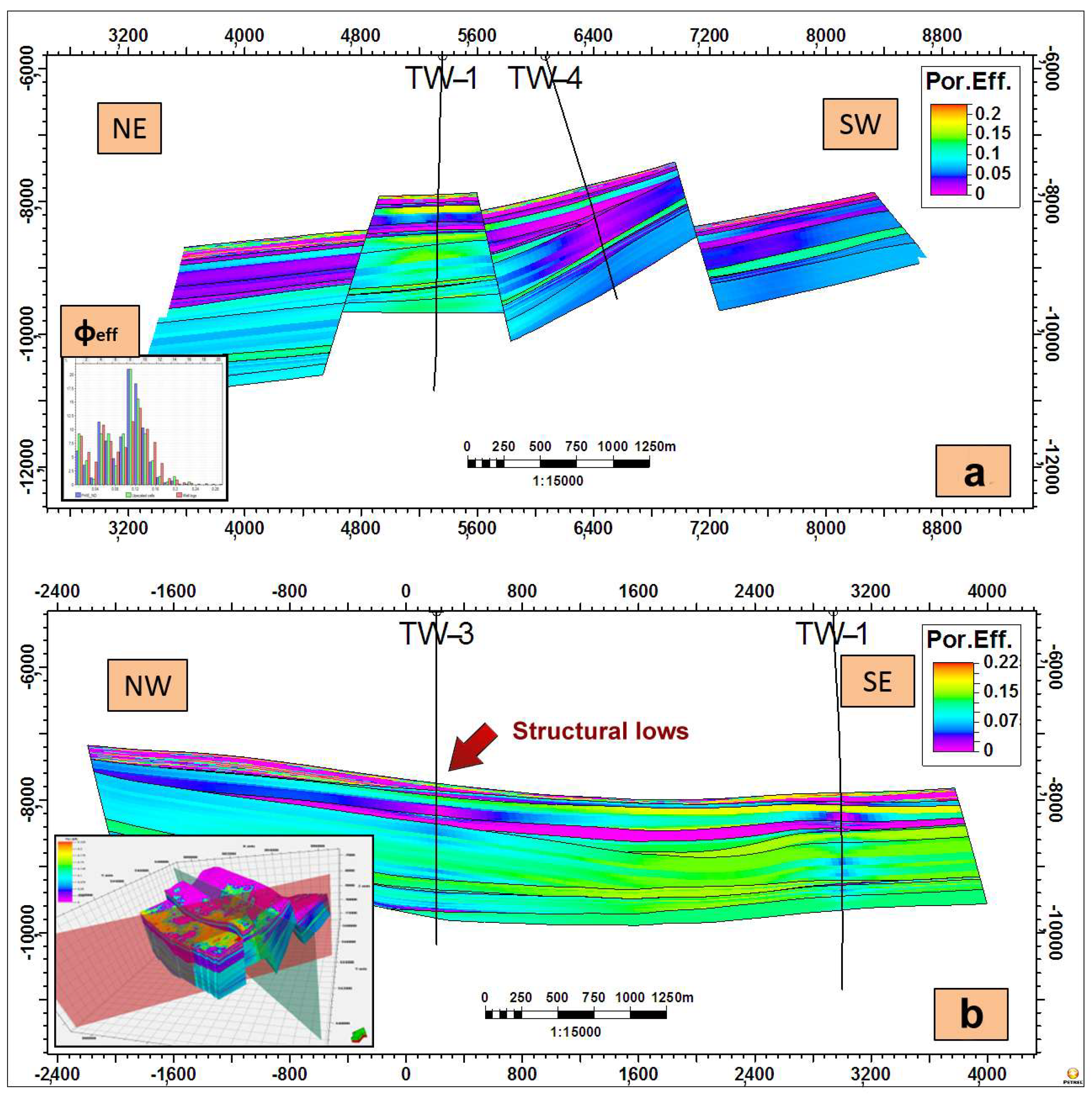
4.4.2. Three-Dimensional Property Models
5. Discussion
5.1. The Diagenetic Overprint: Dominant Control on Permeability
5.2. Flow Unit Architecture: Explaining Production Anomalies
5.3. Integrated Model: Synthesis of Structure and Diagenesis
5.4. Implications for Global Rift Basins
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.-F.; Qian, G.; Zhao, M.; Gao, Y.-F.; Su, W.; Xu, Y.-H. Sediment supply mechanism and its influence on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Paleogene of the northern Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2023, 12, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emishaw, L.; Katumwehe, A.; Leseane, K.; Demissie, Z.; Mickus, K.; Abdelsalam, M. The legacy of the East African rift system in understanding continental rifts worldwide from geophysical studies (with emphasis on gravity and magnetic studies). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2025, 226, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.E.d.S.; Leite, C.d.M.M.; Barbosa, J.S.F.; Corrêa-Gomes, L.C. The influence of the structural framework on the sedimentation of the Maracangalha Formation in the southern compartment of the Recôncavo Basin. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2025, 164, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, V.; Olagundoye, O.; Chizea, C.; Pellettier, J.; Onyeanuna, C.; Parsa, A.; Joubert, T.; Fashanu, M.; Enuma, C.; Ifihan, J.J.; et al. Unravelling the impact of geological heterogeneities in the reservoir management. An integrated study of the deep-water Akpo field (Niger delta). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 150, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; McCaly, K. Structural and stratigraphic evolution of the Gulf of Suez rift, Egypt: A synthesis. In Peri-Tethyan Rift/Wrench Basins and Passive Margins; Ziegler, P.A., Cavazza, W., Robertson, A.H.F., Crasquin-Soeau, S., Eds.; Mémoire Musee Histoire Naturelle, PeriTethys Memoir 6; Publ. sc. du Muséum: Paris, France, 2001; Volume 186, pp. 567–606. [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa, A.R. Controls on the Geometry of Transfer Zones in the Suez Rift and Northwest Red Sea: Implications for the Structural Geometry of Rift Systems. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2002, 86, 979–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Ayyad, H.M.; Abd El-Moghny, M.W.; Gameel, O. Sequence stratigraphy and biozonation of the Upper Eocene Anqabiya Formation, Gebel Anqabiya, Egypt. Geosci. J. 2019, 23, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.G.; Alsharhan, A.S. The Miocene Kareem Formation in the southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt: A review of stratigraphy petroleum geology. J. Pet. Geol. 1997, 20, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharhan, A.S. Petroleum geology and potential hydrocarbon plays in the Gulf of Suez rift basin, Egypt. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2003, 87, 143–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hewaidy, A.G.A.A.G.A.; Farouk, S.; Ayyad, H.M.H.M. Nukhul formation in wadi baba, southwest sinai peninsula, Egypt. GeoArabia 2012, 17, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, H.M.; Bazeen, Y.S.; Samir, A.; Ghanem, S.G.; Ali, A.H.; Gaafar, A.T.; Abdel-Gawad, A. Foraminiferal Proxies Reveal Miocene Climatic Shifts in the Gulf of Suez: Insights from the Rudeis and Kareem Formations on Lithostratigraphic Ambiguities and Central Paratethys Climatic Linkages During Burdigalian-Langhian Intervals. Geol. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawad, E.A.; Fathy, M.; Reda, M.; Ewida, H. Source rock evaluation of the Central Gulf of Suez, Egypt: A 1D basin modelling and petroleum system analysis. Geol. J. 2021, 56, 3850–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, H.M.; Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Farouk, S.; Samir, A.; Bazeen, Y.S. Sequence stratigraphy of the upper Oligocene–middle Miocene succession in west–central Sinai, Egypt. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Farouk, S.; Ayyad, H.M. Foraminifera and sequence stratigraphy of Burdigalian—Serravallian successions on the eastern side of the Gulf of Suez, southwestern Sinai, Egypt. Neues Jahrb. Geol. Palaontol.—Abh. 2013, 270, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, H.M.; Semary, H.E.; Fathy, M.; Hassan, A.H.; Ben Ghorbal, A.; Reda, M. Multifactorial Controls on Carbonate–Clastic Sedimentation in Rift Basins: Integrated Foraminiferal, Sequence Stratigraphic, and Petrophysical Analysis, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Minerals 2025, 15, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EGPC. Oligocene and Miocene Rock Stratigraphy of the Gulf of Suez Region; Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (EGPC): Cairo, Egypt, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Farouk, S.; Ayyad, H.M. Integrated biostratigraphy of the upper Oligocene-middle Miocene successions in west central Sinai, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 100, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, B.S.; El Sharawy, M.S. Hydrocarbon potential, structural setting and depositional environments of Hammam Faraun Member of the Belayim Formation, Southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 112, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhagaza, A.A.; Kassab, M.A.; Wanas, H.A.; Teama, M.A. Reservoir quality and rock type zonation for the Sidri and Feiran members of the Belayim Formation, in Belayim Land Oil Field, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 181, 104242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSSC. Miocene rock stratigraphy of Egypt. Egypt J. Geol. 1976, 18, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A. Coastal to Shallow Marine Miocene Facies in Zeit Bay area, Gulf of Suez. In Proceedings of the 8th EGPC, Exploration Seminar, Cairo, Egypt; 1986; Volume 1, pp. 344–359. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyad, H.M.; El-Sharnoby, A.A.; El-Morsy, A.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; El-Deeb, A.A. Quantitative reconstruction of paleoenvironmental conditions in the Gulf of Suez during the Burdigalian-Langhian (early to middle Miocene) using benthic foraminifera. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 503, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, M.; Salem, T.; Abdel-Fattah, M.I.; Fathy, M.; Farouk, S.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Gentzis, T. Petroleum system analysis of the Ras Ghara oil Field: Geochemical evaluation and 2D basin modelling of pre-rift and syn-rift formations in the southern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2025, 180, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, W.; Khalil, S.; Clare, A.; Comisky, J.; Abdelal, H.; Reed, T.; Kokkoros, G. Integration of outcrop and subsurface data during the development of a naturally fractured Eocene carbonate reservoir at the East Ras Budran concession, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2014, 374, 333–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.R.; Abdeen, M.M. Structural setting of the Hammam Faraun block, eastern side of the Suez rift. J. Univ. Kuwait 1992, 19, 291–309. [Google Scholar]
- Bosworth, W. A high-strain rift model for the southern Gulf of Suez (Egypt). Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1995, 80, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.M.; McClay, K.R. Structural control on syn-rift sedimentation, northwestern Red Sea margin, Egypt. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.; McClay, K. Extensional hard linkages, eastern Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Geology 1998, 26, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfunkel, Z.; Bartov, Y. The tectonics of the Suez Rift. Geol. Surv. Isr. Bull. 1977, 71, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.; Arthur, M.A. The Gulf of Suez-northern Red Sea neogene rift: A quantitive basin analysis. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1988, 5, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, T.L.; Moustafa, A.R.; Nelson, R.A.; Abdine, S.A. Tectonic Evolution and Structural Setting of the Suez Rift. In Interior Rift Basins; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994; pp. 9–55. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.A.A.; Fathy, M.; Hashem, M.E. Three-dimensional static reservoir modelling of Kareem sandstone reservoir, Tawilla Oil Field, at the southern region of Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Geol. J. 2024, 59, 3258–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.L. Neogene tectonic and stratigraphic events in the Gulf of Suez rift area, Egypt. Tectonophysics 1988, 153, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, H.; Hewaidy, A.G.; Hewaidy, A. Chattian-Aquitanian calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy of the Nukhul Formation in Wadi Baba Section, West Central Sinai, Egypt. Stratigraphy 2016, 13, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Abdelfadil, K.M.; Hasebe, N.; Tamura, A.; Abdelrahman, K.; Gharib, M.A.; Fnais, M.S.; Shehata, A.A. Thermochronological Constraints on the Tectonic History of the Arabian–Nubian Shield’s Northern Tip, Sinai, Egypt. Minerals 2024, 14, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, I. Assessment of the distribution of shale, porosity and hydrocarbon saturation in shaly sands. In Proceedings of the 10th European Formation Evaluation Symposium Transactions, Aberdeen, UK, 22–25 April 1986; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.C.; Stieber, S.J. The distribution of shale in sandstones and its effect upon porosity. In Proceedings of the SPWLA Annual Logging Symposium, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–7 June 1975; p. SPWLA-1975. [Google Scholar]
- Simandoux, P. Dielectric Measurements on Porous Media: Application to Measurement of Water Saturation. Study of the Behaviour of Argillaceous Formatio; SPWLA: Houston, TX, USA, 1963; pp. 97–124. [Google Scholar]
- Amaefule, J.O.; Altunbay, M.; Tiab, D.; Kersey, D.G.; Keelan, D.K. Enhanced Reservoir Description: Using Core and Log Data to Identify Hydraulic (Flow) Units and Predict Permeability in Uncored Intervals/Wells. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 October 1993; pp. 205–220. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, C.V.; Journel, A.G. GSLIB Geostatistical Software Library and User’s Guide, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, M.K.; Byrnes, A.P.; Bohling, G.C.; Seals, S.C.; Doveton, J.H. Statistically-based lithofacies predictions for 3-D reservoir modeling: Examples from the Panoma (Council Grove) Field, Hugoton Embayment, Southwest Kansas. In Proceedings of the American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 11–14 May 2003; Volume 12, p. A44. [Google Scholar]
- Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Ayyad, H.M.; Abdallah, A. Subsurface lower–middle Miocene biostratigraphy of Ras El Ush oil field, G. Zeit Area, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Al Azhar Bull. Sci. 2018, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyad, H.M.; Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Al-Labaidy, N.A. Sequence stratigraphy of the Miocene siliciclastic–carbonate sediments in Sadat Area, north-west of Gulf of Suez: Implications for Miocene eustasy. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 2255–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, H.M.; Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Omar, M.; Fathy, M. Sequence stratigraphy and reservoir quality of the Gulf of Suez syn-rift deposits of the Nukhul formation: Implications of rift initiation and the impact of eustacy and tectonic on deposition. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 156, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hasebe, N.; Abdelrahman, K.; Fnais, M.S.; Tamura, A. Reconstructing the Tectonic History of the Arabian–Nubian Shield in Sinai: Low-Temperature Thermochronology Implications on Wadi Agar Area. Minerals 2023, 13, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.; Fagelnour, M.; Zaky, A.S.; Arafat, M.; Salama, A.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Gentzis, T.; Jovane, L. Petroleum System Evaluation: Hydrocarbon Potential and Basin Dynamics in Abu Darag Sub-Basin, Northern Gulf of Suez (Egypt). Minerals 2024, 14, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, G.M.; Kamar, M.S.; Khaleal, F.M.; Azer, M.K.; Nasr, T.; Lasheen, E.S.R. Petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of tourmaline- bearing leucogranites, Sikait area, Southeastn desert of Egypt utilizing mineralogical and bulk rock analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 20191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walderhaug, O. Modeling Quartz Cementation and Porosity in Middle Jurassic Brent Group Sandstones of the Kvitebjørn Field, Northern North Sea. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 2000, 84, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan Niazi, A.M.; Jahren, J.; Mahmood, I.; Javaid, H. Reservoir quality in the Jurassic sandstone reservoirs located in the Central Graben, North Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 102, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azerêdo, A.C.; Duarte, L.V.; Silva, A.P. The challenging carbonates from the Pre-Salt reservoirs offshore Brazil: Facies, palaeoenvironment and diagenesis. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2021, 108, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Jiang, H.; Duc Nguyen, A. In situ U-Pb dating and geochemical characterization of multi-stage dolomite cementation in the Ediacaran Dengying Formation, Central Sichuan Basin, China: Constraints on diagenetic, hydrothermal and paleo-oil filling events. Precambrian Res. 2022, 368, 106481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, H.; Nguyen, A.D.; Sun, P. Temporal constraints on hydrothermal circulation associated with strike-slip faulting in the Permian Maokou carbonates, central Sichuan Basin (SW China). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wignall, B.; Freeman, K.H.; Summons, R.E. Early Cretaceous marine incursions into South Atlantic rift basins originated from the south. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




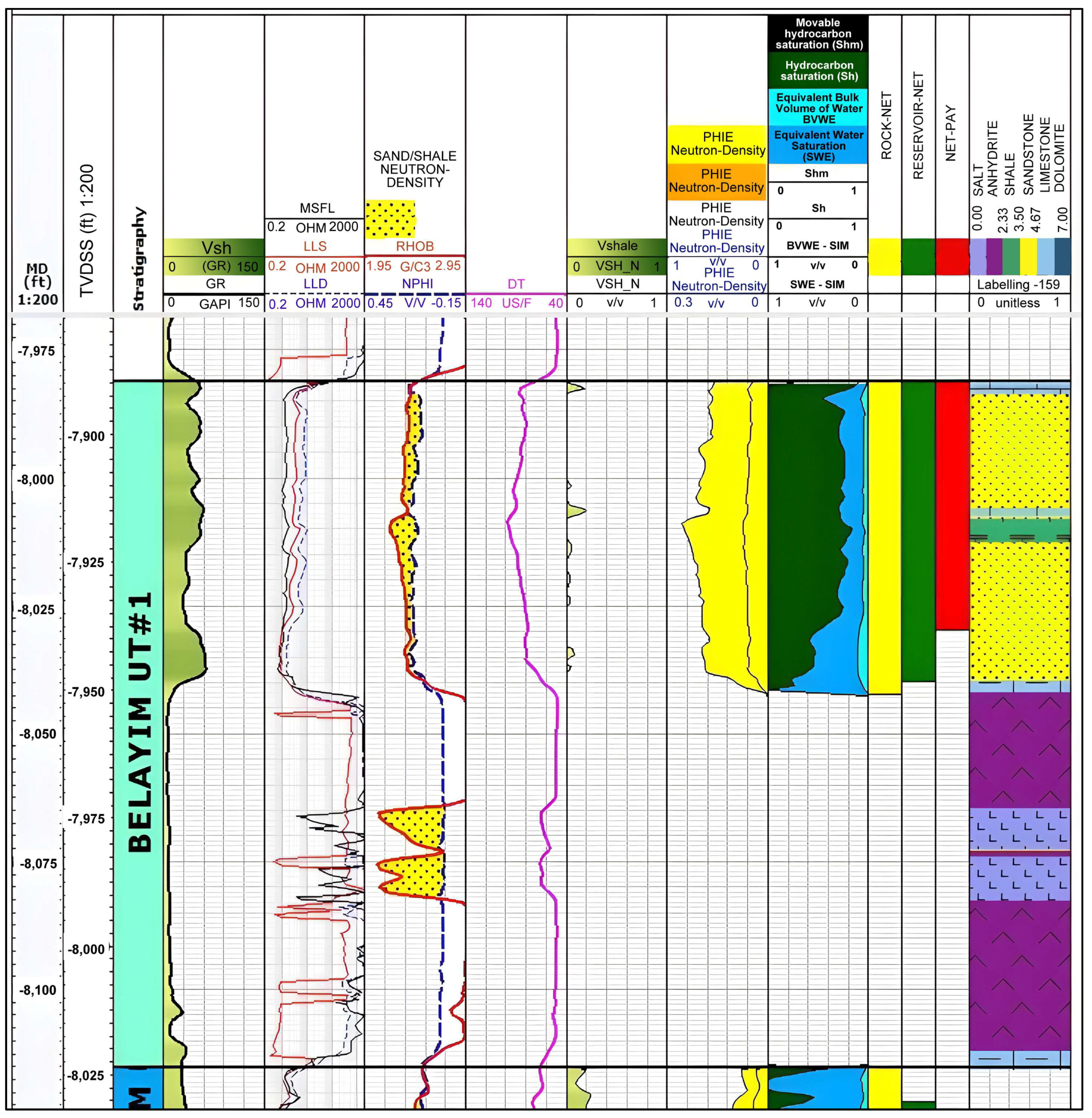



| Well Name | Reservoir Name | Gross (ft) | Net Reservoir (ft) | Net-Pay (ft) | Vsh (%) | ϕe (%) | Sw (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW-3 | Baba unit-1 | 55 | 51.5 | 0 | 14.4 | 14.8 | 100 |
| Baba unit-4 | 54 | 13 | 0 | 13.4 | 9 | 90 |
| Well Name | Reservoir Name | Gross (ft) | Net Reservoir (ft) | Net-Pay (ft) | Vsh (%) | ϕe (%) | Sw (%) | K (md) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW-1 | Baba unit-1 | 61 | 58.5 | 48.5 | 1.6 | 19 | 34.7 | >100 |
| Baba unit-4 | 48 | 24.005 | 24.005 | 22.1 | 7.5 | 33.1 | 5–20 | |
| Shagar unit-1 | 139 | 107.996 | 21.5 | 14.9 | 13.1 | 57.9 | 5–50 |
| HFU | Porosity Range (%) | Permeability Range (mD) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | >20 | >100 | High-quality, clean sandstone |
| 2 | 16–20 | 50–100 | Good reservoir quality |
| 3 | 14–18 | 10–50 | Moderate reservoir quality |
| 4 | 12–16 | 1–10 | Fair reservoir quality, some dispersed clay |
| 5 | 10–14 | 0.1–1 | Poor reservoir quality, significant diagenetic occlusion |
| 6 | 8–12 | 0.01–0.1 | Tight, non-reservoir |
| 7 | <8 | <0.01 | Fully cemented, non-reservoir |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fathy, M.; Abdelwahab, M.M.; Ayyad, H.M. Integrated Petrophysics and 3D Modeling to Evaluate the Role of Diagenesis in Permeability of Clastic Reservoirs, Belayim Formation, Gulf of Suez. Minerals 2025, 15, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101092
Fathy M, Abdelwahab MM, Ayyad HM. Integrated Petrophysics and 3D Modeling to Evaluate the Role of Diagenesis in Permeability of Clastic Reservoirs, Belayim Formation, Gulf of Suez. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101092
Chicago/Turabian StyleFathy, Mohamed, Mahmoud M. Abdelwahab, and Haitham M. Ayyad. 2025. "Integrated Petrophysics and 3D Modeling to Evaluate the Role of Diagenesis in Permeability of Clastic Reservoirs, Belayim Formation, Gulf of Suez" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101092
APA StyleFathy, M., Abdelwahab, M. M., & Ayyad, H. M. (2025). Integrated Petrophysics and 3D Modeling to Evaluate the Role of Diagenesis in Permeability of Clastic Reservoirs, Belayim Formation, Gulf of Suez. Minerals, 15(10), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101092







