Abstract
The phase diagrams of NaCO and KCO have been determined with multianvil (MA) and diamond anvil cell (DAC) techniques. In MA experiments with heating, -NaCO is stable up to 12 GPa and above this pressure transforms to /mcm-phase. At 26 GPa, NaCO-/mcm transforms to the new phase with a diffraction pattern similar to that of the theoretically predicted NaCO-/m. On cold compression in DAC experiments, -NaCO is stable up to the maximum pressure reached of 25 GPa. KCO shows a more complex sequence of phase transitions. Unlike -NaCO, -KCO has a narrow stability field. At 3 GPa, KCO presents in the form of the new phase, called KCO-III, which transforms into another new phase, KCO-IV, above 9 GPa. In the pressure range of 9–15 GPa, another new phase or the mixture of phases III and IV is observed. The diffraction pattern of KCO-IV has similarities with that of the theoretically predicted KCO-/m and most of the diffraction peaks can be indexed with this structure. Water has a dramatic effect on the phase transitions of KCO. Reconstruction of the diffraction pattern of -KCO is observed at pressures of 0.5–3.1 GPa if the DAC is loaded on the air.
1. Introduction
Natural occurrence of alkaline carbonates NaCO and KCO is in the form of rare minerals natrite NaCO [1] and gregoryite (Na,K,Ca)CO [2,3] and as a constituent part of double carbonates: Nyerereite and zemkorite (Na,K)Ca(CO) [4,5,6,7,8], shortite NaCa(CO) [9], eitelite NaMg(CO) [10] and polymorphs of KCa(CO) butchelite and fairchildite [11]. Other than these minerals, a number of double Na-Ca, Na-Fe and K-Mg carbonates were synthesised experimentally at pressures up to 6 GPa: NaCa(CO), NaCa(CO), NaCa(CO), NaCa(CO), NaFeCO, KMg(CO) [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
Despite a relatively small number of findings of simple alkaline and double alkaline–alkaline-earth carbonates, gregoryite together with nyerereite form the main part of unique natrocarbonatites rocks of the Oldoinyo-Lengai volcano (Tanzania) [6]. Nahcolite (NaHCO), eitelite and nyerereite were also found in carbonatitic inclusions in diamonds from the Juina, Mato Grosso State, Brazil [21,22]. The summary of other findings of double alkaline–alkaline-earth carbonates can be found elsewhere [5]. All these findings gave rise to intensive experimental investigation of NaCO and KCO melting curves in the pressure range of the upper mantle and transition zone of the Earth [19,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. The melting curve of NaCO was found to be smooth in the range of 3–18 GPa [23], while on the melting curve of KCO, two kinks, at 5 and 9 GPa, have been found at 2–20 GPa [24,25]. High-pressure transitions in solid phases of NaCO and KCO have been investigated only in one work, published as a PhD thesis [24]. In this work, three high pressure phases of KCO, new phase 1, new phase 2 and new phase 3 have been revealed. Crystal structures of these phases have not been determined and are still unknown.
Theoretically, phase transitions of alkaline carbonates have been investigated by Čančarevič and co-authors [30] and in our recent work [31]. Here, we report the results of in situ X-ray diffraction experiments with both multianvill (MA) and diamond anvil cell (DAC) techniques on the determination of NaCO and KCO P-T phase diagrams and the results of the indexing of high-pressure diffraction patterns with theoretically predicted structures.
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Techniques
The high-pressure high-temperature behaviour of KCO and NaCO have been investigated with in situ X-ray diffraction experiments. For both compounds, large volume multianvil apparatus and DAC experiments have been performed. DAC experiments were of three different types: (1) NaCO, without heating and pressures up to 25 GPa, performed at Advanced Photon Source (APS); (2) KCO, with laser heating and pressures up to 50 GPa, also performed at APS; (3) KCO, without heating and pressures in the range of 0.5–7 GPa, at the Siberian Synchrotron and Teraherts Radiation Centre (SSTRC). The first two types of experiments we will designate as DAC-APS and the last one as DAC-SSTRC.
Synthetic reagents of KCO and NaCO produced by Wako Co Ltd. (Wakayama, Japan) (99.99%, MA and DAC-SSTRC experiments) and Fischer Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA, USA) (>99.5%, DAC-APS experiments) have been used as the starting materials.
2.1.1. MA Experiments
The in situ X-ray diffraction experiments M964, M965, M967 and M1128 were conducted at the Spring-8 synchrotron radiation facility (Hyogo Prefecture, Japan), using a Kawai-type high-pressure apparatus, “SPEED-MkII”, installed at a bending magnet beam line BL04B1 [32]. An energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction technique was used for the in situ measurements. The incident X-rays were collimated to form a thin beam with dimensions of 0.05 mm in the horizontal direction and 0.1 mm in the vertical direction by tungsten carbide slits and directed to the sample through a pyrophyllite gasket and X-ray windows in the cell. A Ge solid-state detector with a 4096-channel analyzer was used, which was calibrated by using characteristic X-rays of Cu, Mo, Ag, La, Ta, Pt, Au and Pb. The diffraction angle (2) was approximately 5.5, calibrated before compression, using the known d-values of X-ray diffraction peaks of Au (note volumes used in the beam line software: = 67.847 Å), with an uncertainty of less than 0.0005. In order to obtain diffraction patterns with a reasonable number of lines, a special oscillation system to rotate the press from −3 to +6 has been employed [32]. We used ultra-hard 26 mm WC anvils (“Fujilloy,” TF-05) with a truncated edge length of 2.0 mm to compress a Co-doped MgO pressure medium shaped in form of octahedron with grinded edges and corners with edge length of 6.2 mm. Pyrophyllite gaskets with 2.0 mm thickness and 3.4 mm width were used to support anvil flanks. A TiB tubular heater, 1.7/1.1 mm in outer/inner diameter and 2.0 mm length was employed to heat the sample. WRe thermocouple, 0.05 mm in diameter, with junction placed just above the sample capsule was used to control temperature. To avoid thermocouple cut during compression, thicker thermocouple wires (0.15 + 0.10 mm) were inserted through the gaskets into the pressure medium. The sample, reagent grade NaCO or KCO powder, was blended with Au powder in 10:1 weight ratio in an agate mortar under acetone. The powder was compressed to a cylinder, 0.5 mm in height and 0.9 mm in diameter and then dried at 300 C for two hours. The sample was loaded into a h-BN capsule with wall thickness of 0.15 mm. The materials with low X-ray absorption were placed on the way of X-ray beam, namely, MgO cylinders, 1.0 mm in diameter and 0.5 mm in thickness were inserted from outside and a 5-m diamond powder was loaded into the hall 0.7 mm in diameter and 1.0 mm in length inside.
The cell assembly was first compressed to nearly the maximum press load at ambient temperature. Thereafter, we followed a complex P-T-path with several heating cycles while continuously taking diffraction patterns. Exposure times for collecting diffraction data were 200 s. The experimental pressures at high temperatures were calculated from the unit cell volume of Au using the equation of state reported in [33] with <0.05 GPa deviation. Typically, 4 of the diffraction lines (111), (200), (220) and (311) of Au were used to calculate the pressure and 7–10 major diffraction lines were used to calculate the volume of NaCO.
2.1.2. DAC-APS
In DAC-APS experiments we used symmetric DACs equipped with 300 m brilliant-cut diamonds. Rhenium gaskets were preindented to a thickness of ∼40 m and laser-cut in the center of the indentation in order to create a sample chamber of ∼100 m in diameter. To prevent sample contamination with water, NaCO or KCO reagents were annealed at 250 C for 30 h, sealed and transported to an Ar glovebox for DAC loadings. Upon sample loading, the minute amount of Pt/Au powder was mixed into the KCO/NaCO samples. Neon was gas-loaded as a pressure medium at 0.2 GPa.
Compression runs were performed at the 13ID-D undulator beamline of GeoSoilEnviroCARS, Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory. The X-ray beam ( = 0.3344 Å) was focused to a ∼3 × 5 m spot size. High temperatures (up to 2600 K) were achieved through double-sided Nd:YLF laser-heating system with a 20 m diameter focused laser beam [34] coupled to Pt powder. Temperature was measured by spectroradiometry simultaneously with XRD measurements. Collected spectra were fit to blackbody radiation function using T-Rax software (developed by C. Prescher). The uncertainty in temperature measurement is assumed to be typical of laser-heated DACs (∼150 K). Overall heating duration was about 10–20 min. After quenching, the samples were mapped with the X-ray. Every sample was heated in at least two areas.
2.1.3. DAC-SSTRC
Three different experiments have been performed as SSTRC: (1) With silicon oil as pressure transmitting medium and loading in a glovebox; (2) with silicon oil and loading on the air; (3) with methanol as a pressure transmitting medium and also loading on the air. The results of experiment (2) have been published in [35] and here we use them only for comparison.
Sample of KCO was preliminarily annealed in a vacuum oven at 200 C for 2 h, then ground in an agate mortar and mixed with pressure transmitting medium in a ratio of 1:4. This mixture was loaded in a 400 m hole in a stainless steel gasket of 100 m thickness under ambient conditions or in an Ar glovebox. Mao-Bell DACs were used to generate pressures up to 7 GPa.
In situ X-ray diffraction experiments were conducted at the beamline #4 of the VEPP-3 storage ring of the SSTRC (Novosibirsk, Russia) ( = 0.3685 Å) [36]. MAR345 imaging plate detector (pixel dimension 100 m) was used for data collecting. FIT2D [37] program was used to integrate the two-dimensional images to a maximum 2 value of 25. The pressure was measured by displacement of fluorescence line of SrBO:Sm [38] with PRL (BETSA) spectrometer with accuracy of ∼0.05 GPa.
2.2. Details of Ab Initio Calculations
For indexing of experimental diffraction patterns, structural models of -NaCO, NaCO-/mcm, NaCO-/m, -KCO and KCO- [31] were optimised with density functional theory (DFT). Incommensurate modulations of -NaCO structure [39] have not been considered. Optimisations have been performed using the plane wave basis set and the projector augmented wave method [40], as implemented in VASP code [41,42,43]. Exchange-correlation effects were taken into account within LDA (local density approximation) and GGA (generalised gradient approximation) with Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof functional [44]. LDA pseudopotentials with and valence electrons and GGA pseudopotentials with and electrons have been used for K, Na, O and C, respectively. A plane-wave basis set cutoff energy were set to 520 eV. The Brillouin zone was sampled using uniform -centred k-point meshes with a k-point grid of 2× 0.025 Å spacing. The iterative relaxation of atomic positions was stopped when all forces acting on atoms were smaller than 0.001 eV Å. After optimisation, symmetry of the structures were analysed with FINDSYM program [45]. VESTA software [46] have been used for the structure visualisation.
To take into account the temperature effect and calculate monovariant boundaries on P-T diagrams, we used the method of lattice dynamics within the quasi-harmonic approximation (QHA). The phonon frequencies and phonon dispersion curves were calculated with the PHONOPY 2.3 package [47]. The energy cut-off in this case was increased to 800 eV. Real-space force constants were calculated using supercell method and finite difference method as implemented in PHONOPY, with a supercell for NaCO-, NaCO-/mcm, NaCO-/m, KCO-/m, KCO-, -KCO, a supercell for -NaCO and a supercell for -KCO. Helmholtz free energies were computed for all structures at seven volumes starting from 0 GPa to 60 GPa, then corrected for thermal expansion using the quasiharmonic approximation.
2.3. Indexing
For unbiased comparison of diffraction patterns with that of theoretical structures, we used cell parameters directly from DFT calculations without any refinement. In the case of unambiguous correspondence, Pawley and Rietveld refinements have been performed. As LDA pseudopotential slightly underestimates, whereas GGA overestimates unit cell volume, we used structures with cell parameters averaged between LDA and GGA optimisations. As we will show below, such a simple technique gives the cell parameters that sufficiently better reproduce experimental values than LDA or GGA optimisations.
The phase identification and preliminary analysis of all the diffraction patterns have been performed with “PDIndexer” software [48]. For analysis of diffraction patterns recorded at Spring8 “XRayAnalysis" software, provided by the beamline, have been also used. Pawley and Rietveld refinements were performed with GSAS-II software [49]. The uncertainties in the unit cell volume of Au, determined by a least-squares fit, give typically less than 0.1 GPa uncertainty in pressure.
3. Results And Discussion
3.1. NaCO
In MA experiments, -NaCO is stable from 1 atm to 12 GPa and then two phase transitions at 12 GPa and at 26 GPa take place, see Figure 1a. In room temperature DAC-APS experiments, substantial changes in -NaCO diffraction patterns are not observed up to the maximum reached pressure of 25 GPa (Figure 1). Splitting of (40) diffraction peak, marked on Figure 1b with a star, can be explained by the the increasing of intensities of (400) and (200) reflections of -NaCO or by the some structural changes of -NaCO.
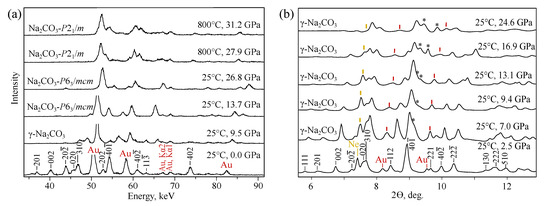
Figure 1.
Diffraction patterns of NaCO obtained in MA (a) and DAC (b) experiments.
The pressures of phase transitions in MA experiments are consistent with theoretical predictions [31]. According to calculations [31], NaCO undergoes two phase transitions in the pressure range of 0–40 GPa, first at 5 GPa from - to /mcm-phase and another at 35 GPa, from /mcm- to /m-phase.
As can be seen from Figure 2a,c theoretical diffraction peaks of - and /mcm-structures exactly reproduce experimental ones. The Pawley fit has been performed with the following R-factors (Figure 2b,d): -NaCO: R-bkg = 7.54%, wR-bkg = 13.49%, /mcm: R-bkg = 10.80%, wR-bkg = 19.95%. The difference between cell parameters before and after refinement does not exceed 0.07 Å for and 0.03 Å for /mcm structures. For the LDA and GGA optimised /mcm structure (without averaging) these deviations are sufficiently higher and reach 0.92 Å and 0.71 Å, respectively. This illustrates the efficiency of the technique when the structure averaged between LDA and GGA optimisations is used for the indexing (Figure S1). For a /mcm structure, the Rietveld refinement has also been performed, see Figure S2. It also confirms the consistency of the /mcm structure with the obtained diffraction pattern.
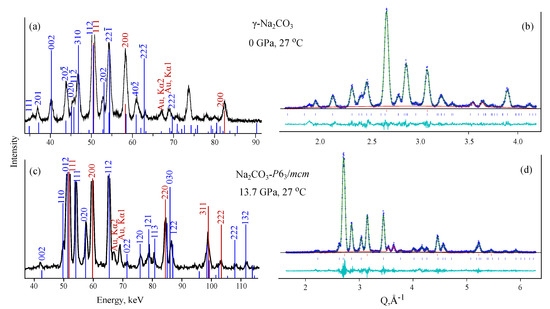
Figure 2.
Indexing of diffraction patterns with - (a) and /mcm (c) structures of NaCO and corresponding Pawley refinements (b,d). Blue bars correspond to the theoretical peaks of -NaCO (a,b) and NaCO-/mcm, red bars-to the peaks of Au.
Indexing of diffraction patterns, recorded above 27 GPa, with /m structure are ambiguous (Figure 3). The quality and number of diffraction peaks is not enough to perform the reliable Pawley fit. However, most of the experimental peaks can be indexed with /m structure (Figure 3). Based on this we consider /m structure as the structure of high-pressure polymorph of NaCO observed above 26 GPa.
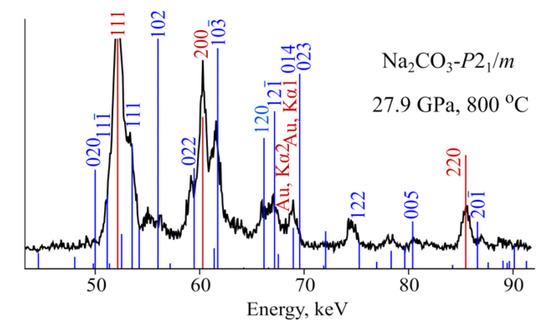
Figure 3.
Indexing of experimental diffraction pattern recorded at 27.9 GPa with /m structure of NaCO.
The obtained P-T diagram (Figure 4) is consistent with available experimental data on the melting curve of NaCO. According to these data, the melting temperature of NaCO is 1980 K at 17 GPa and up to this pressure the melting curve has no kinks [23]. Extrapolation of the phase boundary between - and /mcm phases (Figure 4) to the melting temperatures shows, the first kink on the melting curve appears at 18–19 GPa. This is consistent with the smooth character of the melting curve up to 17 GPa observed in the experiment [23].
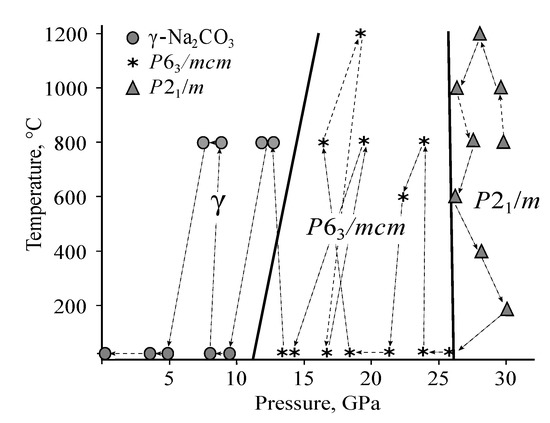
Figure 4.
Phase diagram of NaCO according to MA experiments.
In our previous work [50], we suggested the transition from -NaCO to -NaCO at 1–2 GPa. Both phases have similar structures, complicated by the incommensurate modulations in the case of -NaCO [39]. Distinguishing these two phases in our MA energy-dispersive diffraction patterns is problematic and here we designate both of them as -NaCO, assuming that this can be - or -phase.
The unit cell parameters and atomic coordinates of /mcm- and /m-phases are shown in Table 1, dependencies of the cell parameters on pressure for - and /mcm determined in MA experiments-in Table 2 and for -phase determined in DAC experiments—in Table S1.

Table 1.
Structural data for high-pressure phases of NaCO used for indexing and refinements. Cell parameters of /mcm- and phases according to Pawley refinement, other structural data according to DFT calculations.

Table 2.
Unit cell parameters of - and /mcm-phases of NaCO according to MA experiments.
3.2. KCO
3.2.1. MA and DAC-APS Results
Both DAC and MA experiments show consistent results on phase transitions of KCO. The same phase transitions are observed in both experiments and differences in pressures of the transitions do not exceed 3 GPa. Below we give pressures of phase transitions according to the MA experiment.
In both DAC-APS and MA experiments three high-pressure phase transitions are observed (Figure 5); the first takes place at less than 3 GPa, the second-at 10 and the third-at 15 GPa. The phase stable below 3 GPa, in the range of 3–10 GPa and above 15 GPa we will designate as KCO-II, KCO-III and KCO-IV, respectively. The existence of the phase KCO-II is assumed based on the experimental data of Li [24]. In the range of 10–15 GPa, the mixture of KCO-III and KCO-IV or another new phase, KCO-IIIb, is observed. KCO-IV has low-temperature and high-temperature forms, -KCO-IV and -KCO-IV, respectively. The changes of diffraction pattern during - to phase transformation is illustrated in Figure S3. Comparison of diffraction patterns of phases III and IV was obtained in DAC and MA settings, see Figures S4 and S5.
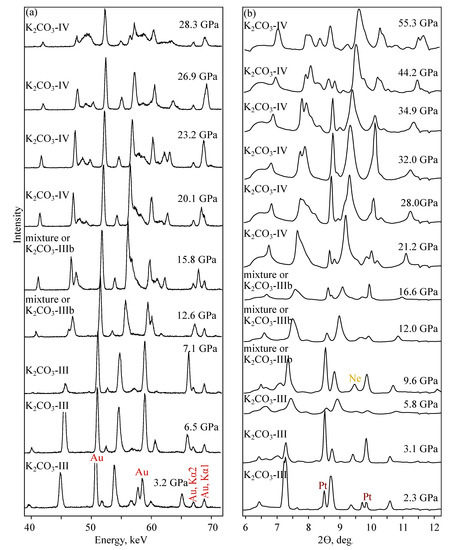
Figure 5.
Diffraction patterns of KCO collected in MA (a) and DAC-APS (b) experiments at room temperature.
The obtained phase diagrams according to MA and DAC-APS experiments are shown in Figure 6. The phase diagrams from these two experimental settings are consistent with each other. They are also consistent with available data on melting curves and high-pressure phase transitions of KCO [24,25,26], suggesting one phase transition at 3 GPa and another-in the range of 13–25 GPa.
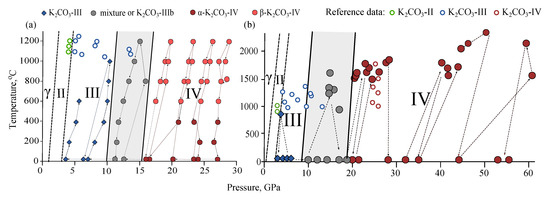
Figure 6.
Phase diagrams of KCO from MA (a) and DAC-APS (b) experiments. Empty circles-reference the data of Li [24].
3.2.2. Indexing of Experimental Diffraction Patterns
According to theoretical predictions [31], -KCO undergoes transition to KCO-P at 12 GPa. KCO- is the structural analogue of NaCO-/m. We mentioned this structural similarity in our previous work [31]; within the present investigation we analyse the pseudosymmetry of KCO- and find out that atomic shifts less than 0.07 Å increase the symmetry of the structure to /m. Below we will use KCO-/m structure instead of KCO- for indexing of experimental diffraction patterns.
Most of the peaks of -KCO-IV diffraction pattern can be satisfactorily indexed with KCO-/m structure, except of several intense ones (Figure 7). Structural data of KCO-/m used for indexing of experimental diffraction patterns are shown in Table S2. Based on the similarity of the experimental and theoretical diffraction patterns, phase IV can be considered as some structural analogue of KCO-/m. In this case, unindexed peaks are explained by the structural difference of /m and IV phases. However, they can be also explained by the presence of /m phase in the mixture with the second phase with a similar structure. In this case, the changing of diffraction peak intensities observed in MA experiments (Figure S3) is due to the changing of the ratio of these two phases.
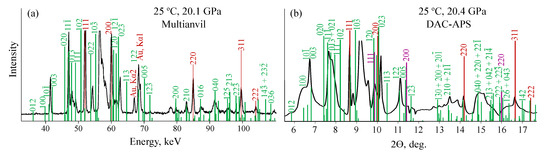
Figure 7.
Indexing of diffraction patterns of -KCO-IV from MA (a) and DAC-APS (b) experiments with KCO-/m structure. The peaks of KCO-/m are shown in green, peaks of Au pressure marker-in red and that of Ne-in yellow.
None of the high pressure diffraction patterns of KCO can be indexed with /mcm structure, observed for NaCO and LiCO [54]. Thus, stability field of /mcm structure shrinks with increasing of cation radius. For LiCO [54] it is observed in the range of 10–25 GPa, for NaCO-in the range of 12–26 GPa and for KCO it is not observed at all.
3.2.3. The Effect of Water
To estimate the effect of water on the high-pressure transitions of KCO we have performed two DAC experiments, (I) with loading in a glovebox and (II) with loading in the air. Silicone oil was used as the pressure transmitting medium in both cases. These experiments have been performed at SSTRC. DAC used in these experiments has a larger working chamber than in the experiments performed at APS and it is better suited for the studying of low-pressure phase transitions. All SSTRC experiments have been performed at room temperature.
In dry experiment (I), -KCO is stable up to the maximum reached pressure of 6.8 GPa. The observed amorphization, starting from 3 GPa, is due to non-hydrostatic compression in silicon oil [55]. In wet experiment (II), the new phase or phases are observed above 3.1 GPa (Figure 8). The diffraction pattern of this phase is different from diffraction patterns of KCO-III obtained in MA and DAC-APS experiments at nearly the same pressures (Figure S4).
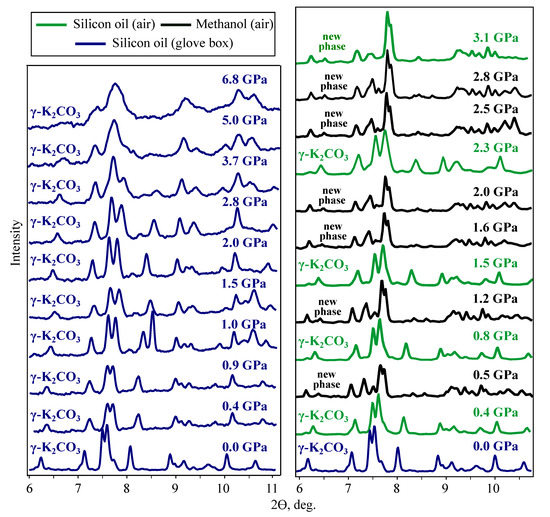
Figure 8.
Diffraction patterns recorded in DAC-SSTRC experiments. Results of experiment (I) are shown in green, of experiment (II) in black and of experiment (III) in blue.
The catalytic activity of KCO in the transesterification reaction of fatty acid glycerides with alcohols, used for the production of biodiesel from food grade vegetable oils [56], was the motivation for us to perform the third (III) experiment with methanol as a pressure transmitting media. The loading has been done on the air to make experimental conditions similar to those in the production of bio-diesel. The result of this experiment is surprising. At the first pressure point, 0.5 GPa, we observed the diffraction pattern of the same phase, which was synthesised in experiment (II) at 3.1 GPa (Figure 8). This phase (or phases) can be one of the hydrated form of KCO, one of the KCO high-pressure phases or a mixture of hydrate and high-pressure phase.
4. Theoretical P-T Diagrams and Stability of The Phases
Calculated phonon dispersion curves show dynamical instability of - and -phases for both NaCO and KCO. This is consistent with the unquenchable character of these phases ([57,58] and references therein). The average structure of -NaCO is also unstable (Figure S6a). The last fact is not surprising. The real structure of -phase is incommensurately modulated, with amplitudes of modulations reaching 0.4 Å [39]. The modulations likely stabilise the structure and the average structure without them became unstable. Other structures revealed in experiments, NaCO-/mcm, NaCO-/m, -KCO and KCO-/m, are dynamically stable (Figures S6 and S7).
The calculated values of unit cell volumes for -NaCO and NaCO-/mcm closely reproduce experimental V(P) dependance (Figure 9). As GGA pseudopotentials slightly overestimates volume, theoretical points lie higher than experimental ones. The fact that experimental points of -NaCO at 8.6 and 9.6 GPa lie higher than theoretical ones is due to the uncertainty in experimental determination of unit cell volume of -phase at high pressures. Parameters of the Vinet equation of state [59] for - and /mcm-phases determined by the theoretical points are the following:
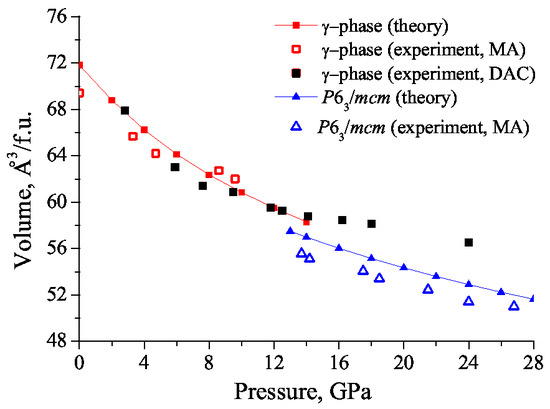
Figure 9.
Theoretical and experimental pressure V(P) dependencies for - and /mcm phases of NaCO. Solid red and blue lines correspond to the EOSs of and /mcm phases determined by the theoretical points.
-NaCO: =−148.046 eV, = 37.56 GPa, = 5.504, = 288.299 Å,
NaCO-/mcm: = −73.773 eV, = 44.33 GPa, = 5.73, = 137.505 Å.
The calculated P-T boundaries for /mcm and /m equilibriums correctly reproduce experimental results on phase transitions of NaCO (Figure 10a). According to calculations, both /mcm and /m structures are stable within all of the investigated temperature range, likely up to the melting temperatures. The upper stability boundary of structure of NaCO, revealed in our previous calculations [31], is restricted to nearly 0 C (Figure 10). Due to sufficient structural difference between and phases, the transformation is hindered by the kinetic of the process.
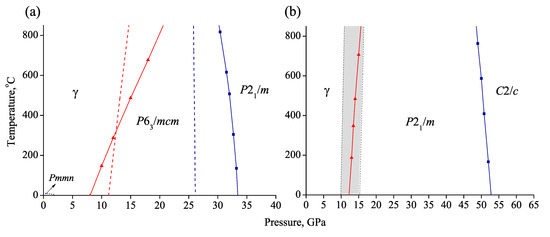
Figure 10.
Theoretical P-T diagrams of NaCO (a) and KCO (b). Theoretical phase boundaries are shown in solid lines, experimental in dashed lines.
The calculated stability field of KCO-/m spreads from ∼10 GPa to ∼55 GPa. At higher pressure /m structure transforms into structure (Figure 10b). According to obtained experimental data, phase IV of KCO was observed within the same P-T field. This is consistent with the assumption about structural similarity or even isostructurality of /m and IV phases of KCO.
5. Discussion
For both KCO and NaCO, -phases are characterised by the same NiIn type of cation array and differ only in the tilt of CO triangles [60]. Our results show quite a wide stability field of -NaCO and very narrow stability field of -KCO (Figure 11). This can be explained by the sufficient difference in the size of Na and K ions. Na ion fits better to NiIn type than the big K [61]. As a result, -KCO readily transforms to another structural type (phases II, III and IV) at relatively small compression. Li is, in turn, too small and does not adopt NiIn type at all, its form is of CaF type [60].
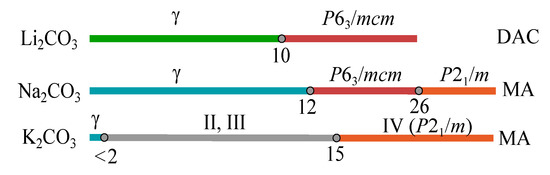
Figure 11.
Scheme, summarising experimental data on high-pressure phase transitions of LiCO [54], NaCO (this work) and KCO (this work). Numbers show pressures oh phase transitions in GPa. Similar crystal structures are shown in the same colours.
Comparison of high-pressure phase transitions of alkaline carbonates, LiCO, NaCO and KCO is presented on Figure 11. It shows that there are two main high-pressure structures of alkaline carbonates, /mcm and /m. /m structure is characterised by the higher coordination numbers, cations of alkaline metal in this structure are surrounded by seven or eight oxygens, disposed in the vertices of the deformed cube or two-capped trigonal prism, while in /mcm structure the coordination of alkaline metal by oxygen equals six and the coordination polyhedron is octahedron (Figure S8). As a result, the stability fields of /mcm-phases shrink with an increase in cation radius from Li to K, while stability fields of /m structures, assuming KCO-IV as the analogue of KCO-/m, expands.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/9/10/599/s1, Figure S1: Experimental diffraction patterns at 13.7 GPa (a) and at 27.9 GPa (b) with theoretical peaks of Na2CO2- (a) and Na2CO3- (b) structures. Peaks of the structure optimised with LDA are shown with thin blue lines, with GGA–with turquoise thin lines, and of the averaged structure–with thick violet lines; Figure S2: Rietveld refinement of Na2CO3- structure with MA diffraction pattern recorded at 13.7 GPa and 27 °C, R-factor = 27%; Figure S3: Changes of diffraction pattern on heating at pressures 26.9–28.8 GPa according to MA setting; Figure S4: Diffraction patterns in DAC-SSTRC (a), DAC-APS (b), and multianvil (c) settings at 2.3–3.6 GPa. Grey bands are shown for the convenience of visual comparison; Figure S5: Diffraction patterns of K2CO3-IV recorded in DAC-APS (a) and multianvil (b) settings; Figure S6: Phonon dispersion curves of Na2CO3 phases, at 0 GPa (a), at 12 GPa (b), and at 24 GPa (c) and at 36 GPa (d); Figure S7: Phonon dispersion curves of K2CO3 phases, at 0 GPa (a), at 1 GPa (b), at 36 GPa (c) and at 60 GPa (d); Figure S8: Na-O polyhedrons in (a) and (b) crystal structures of Na2CO3. Table S1: Unit cell parameters of -Na2CO3 from DAC-APS experiments; Table S2: Structural data of K2CO3- used for indexing of experimental diffraction pattern (according to DFT calculations, without refinement).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.N.G, A.S. and K.D.L.; methodology, P.N.G., A.S., S.S.L., K.D.L., A.Y.L., A.F.G., and I.S.S.; software, S.V.R.; validation, A.B. and S.V.R.; formal analysis, A.B., S.V.R., D.S., N.S., and A.Y.L.; investigation, P.N.G., A.B., D.S., and N.S.; resources, V.B.P., and Y.H.; writing–original draft preparation, P.N.G.; writing–review and editing, P.N.G. and K.D.L.; visualization, P.N.G. and A.B.; supervision, K.D.L., and A.F.G.
Funding
This research was funded by Russian Science Foundation (project No 14-17-00609-P). SSL was supported by Helmholtz Young Investigators Group CLEAR (VH-NG-1325).
Acknowledgments
We thank the Information Technology Centre of Novosibirsk State University for providing access to the cluster computational resources. A.F.G. and K.D.L. acknowledge support from Alfred P. Sloan Foundation via the Deep Carbon Observatory program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zubkova, N.; Pushcharovsky, D.Y.; Ivaldi, G.; Ferraris, G.; Pekov, I.; Chukanov, N. Crystal structure of natrite, γ-Na2CO3. Neues Jahrb. FÜR-Mineral. Monatshefte 2002, 2002, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittins, J.; McKie, D. Alkalic carbonatite magmas: Oldoinyo Lengai and its wider applicability. Lithos 1980, 13, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.; Keller, J.; Spratt, J.; Jeffries, T.; Sharygin, V. Chemical composition of nyerereite and gregoryite from natrocarbonatites of Oldoinyo Lengai volcano, Tanzania. Geol. Ore Depos. 2009, 51, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotina, N.B.; Gavryushkin, P.N.; Korsakov, A.V.; Rashchenko, S.V.; Seryotkin, Y.V.; Golovin, A.V.; Moine, B.N.; Zaitsev, A.N.; Litasov, K.D. Incommensurately modulated twin structure of nyerereite Na1.64K0.36Ca(CO3)2. Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2017, 73, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavryushkin, P.N.; Thomas, V.G.; Bolotina, N.B.; Bakakin, V.V.; Golovin, A.V.; Seryotkin, Y.V.; Fursenko, D.A.; Litasov, K.D. Hydrothermal synthesis and structure solution of Na2Ca(CO3)2:“synthetic analogue” of mineral nyerereite. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKie, D.; Frankis, E. Nyerereite: A new volcanic carbonate mineral from Oldoinyo Lengai, Tanzania. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 1977, 145, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, A.V.; Sharygin, I.S.; Korsakov, A.V. Origin of alkaline carbonates in kimberlites of the siberian craton: Evidence from melt inclusions in mantle olivine of the Udachnaya-East pipe. Chem. Geol. 2017, 455, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, K.; Ushchapovskaia, Z.; Kashaev, A.; Bogdanov, G.; Sizykh, I.I. Zemkorite-a new carbonate from yakutian kimberlites. Akad. Nauk. SSSR Dokl. 1988, 301, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Dickens, B.; Hyman, A.; Brown, W. Crystal structure of Ca2Na2(CO3)3 (shortite). J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. Sec. A Phys. Chem. 1971, 75, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, A. The crystallography structure of eitelite, Na2Mg(CO3)2. Am. Mineral. 1973, 58, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Pertlik, F. Structural investigations of synthetic fairchildite, K2Ca(CO3)2. Z. Kristallogr. 1981, 157, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, K.-F.; Simons, B. Crystal structure of synthetic K2Mg(CO3)2. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 1982, 161, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatskiy, A.; Rashchenko, S.V.; Ohtani, E.; Litasov, K.D.; Khlestov, M.V.; Borzdov, Y.M.; Kupriyanov, I.N.; Sharygin, I.S.; Palyanov, Y.N. The system Na2CO3-FeCO3 at 6 GPa and its relation to the system Na2CO3-FeCO3-MgCO3. Am. Mineral. 2015, 100, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavryushkin, P.N.; Bakakin, V.V.; Bolotina, N.B.; Shatskiy, A.F.; Seryotkin, Y.V.; Litasov, K.D. Synthesis and crystal structure of new carbonate Ca3Na2(CO3)4 homeotypic with orthoborates M3Ln2(BO3)4 (M=Ca, Sr and Ba). Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 4610–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatskiy, A.; Gavryushkin, P.N.; Litasov, K.D.; Koroleva, O.N.; Kupriyanov, I.N.; Borzdov, Y.M.; Sharygin, I.S.; Funakoshi, K.; Palyanov, Y.N.; Ohtani, E. Na-Ca carbonates synthesized under upper-mantle conditions: Raman spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction studies. Eur. J. Mineral. 2015, 27, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatskiy, A.; Sharygin, I.S.; Litasov, K.D.; Borzdov, Y.M.; Palyanov, Y.N.; Ohtani, E. New experimental data on phase relations for the system Na2CO3-CaCO3 at 6 GPa and 900–1400 °C. Am. Mineral. 2013, 98, 2164–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashchenko, S.V.; Bakakin, V.V.; Shatskiy, A.F.; Gavryushkin, P.N.; Seryotkin, Y.V.; Litasov, K.D. Noncentrosymmetric Na2Ca4(CO3)5 carbonate of “M13M23XY3Z” structural type and affinity between borate and carbonate structures for design of new optical materials. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 6079–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhao, D.; Peng, G.; Lin, C.; Ye, N. Explorations of new UV nonlinear optical materials in the Na2CO3-CaCO3 system. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 8758–8764. [Google Scholar]
- Podborodnikov, I.V.; Shatskiy, A.; Arefiev, A.V.; Rashchenko, S.V.; Chanyshev, A.D.; Litasov, K.D. The system Na2CO3–CaCO3 at 3 GPa. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2018, 45, 773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashchenko, S.V.; Shatskiy, A.F.; Arefiev, A.V.; Seryotkin, Y.V.; Litasov, K.D. Na4Ca(CO3)3: A novel carbonate analog of borate optical materials. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 5228–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, F.V.; Wirth, R.; Schreiber, A. Carbonatitic inclusions in deep mantle diamond from Juina, Brazil: new minerals in the carbonate-halide association. Can. Mineral. 2013, 51, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, F.; Matzel, J.; Jacobsen, B.; Hutcheon, I.; Wirth, R. Isotopic fractionation of oxygen and carbon in decomposed lower-mantle inclusions in diamond. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 110, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.; Lange, R.; Liu, J.; Militzer, B. Determination of calcium carbonate and sodium carbonate melting curves up to Earth’s transition zone pressures with implications for the deep carbon cycle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 457, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Melting and Structural Transformations of Carbonates and Hydrous Phases in Earth’s Mantle. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Inoue, T.; Li, B.; Pottish, S.; Wood, J.; Yang, C.; Tao, R. The K2CO3 fusion curve revisited: New experiments at pressures up to 12 GPa. J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 2016, 111, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tenner, T.J.; Lange, R.A. Do carbonate liquids become denser than silicate liquids at pressure? Constraints from the fusion curve of K2CO3 to 3.2 GPa. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2007, 153, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, W., Jr.; Cohen, L.H. Solid-solid and solid-liquid transitions in K2CO3, Na2CO3 and Li2CO3: Investigations to ≥5 kbar by differential thermal analysis; thermodynamics and structural correlations. Berichte Bunsenges. FÜR Phys. Chem. 1975, 79, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatskiy, A.; Sharygin, I.S.; Gavryushkin, P.N.; Litasov, K.D.; Borzdov, Y.M.; Shcherbakova, A.V.; Higo, Y.; Funakoshi, K.-I.; Palyanov, Y.N.; Ohtani, E. The system K2CO3-MgCO3 at 6 GPa and 900–1450 °C. Am. Mineral. 2013, 98, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefiev, A.V.; Shatskiy, A.; Podborodnikov, I.V.; Rashchenko, S.V.; Chanyshev, A.D.; Litasov, K.D. The system K2CO3–CaCO3 at 3 GPa: Link between phase relations and variety of K–Ca double carbonates at ≤0.1 and 6 GPa. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čančarevič, Ž.; Schön, J.; Jansen, M. Alkali metal carbonates at high pressure. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2006, 632, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavryushkin, P.N.; Behtenova, A.; Popov, Z.I.; Bakakin, V.V.; Likhacheva, A.Y.; Litasov, K.D.; Gavryushkin, A. Toward analysis of structural changes common for alkaline carbonates and binary compounds: Prediction of high-pressure structures of Li2CO3, Na2CO3 and K2CO3. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 5612–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, T.; Funakoshi, K.-I.; Kubo, A.; Nishiyama, N.; Tange, Y.; Sueda, Y.-I.; Kubo, T.; Utsumi, W. A large-volume high-pressure and high-temperature apparatus for in situ X-ray observation,‘SPEED-Mk. II’. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2004, 143, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, T.S.; Dorogokupets, P.I.; Dymshits, A.M.; Danilov, B.S.; Litasov, K.D. Microsoft excel spreadsheets for calculation of P–V–T relations and thermodynamic properties from equations of state of MgO, diamond and nine metals as pressure markers in high-pressure and high-temperature experiments. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 94, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakapenka, V.; Kubo, A.; Kuznetsov, A.; Laskin, A.; Shkurikhin, O.; Dera, P.; Rivers, M.; Sutton, S. Advanced flat top laser heating system for high pressure research at gsecars: Application to the melting behavior of germanium. High Press. Res. 2008, 28, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavryushkin, P.; Rashenko, S.; Shatskiy, A.; Litasov, K.; Ancharov, A. Compressibility and phase transitions of potassium carbonate at pressures below 30 kbar. J. Struct. Chem. 2016, 57, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piminov, P.; Baranov, G.; Bogomyagkov, A.; Berkaev, D.; Borin, V.; Dorokhov, V.; Karnaev, S.; Kiselev, V.; Levichev, E.; Meshkov, O.; et al. Synchrotron radiation research and application at VEPP-4. Phys. Procedia 2016, 84, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammersley, A.; Svensson, S.; Hanfland, M.; Fitch, A.; Hausermann, D. Two-dimensional detector software: From real detector to idealised image or two-theta scan. Int. J. High Press. Res. 1996, 14, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashchenko, S.V.; Kurnosov, A.; Dubrovinsky, L.; Litasov, K.D. Revised calibration of the sm: SrB4O7 pressure sensor using the sm-doped yttrium-aluminum garnet primary pressure scale. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 145902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, M.; Chapuis, G.; Meyer, M.; Petricek, V. Sodium carbonate revisited. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci 2003, 59, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, H.T.; Hatch, D.M. FINDSYM: Program for identifying the space-group symmetry of a crystal. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2005, 38, 237–238. [Google Scholar]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togo, A.; Oba, F.; Tanaka, I. First-principles calculations of the ferroelastic transition between rutile-type and CaCl2-type SiO2 at high pressures. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 134106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, Y. Development of a software suite on X-ray diffraction experiments. Rev. High Press. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. Gsas-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatskiy, A.; Gavryushkin, P.N.; Sharygin, I.S.; Litasov, K.D.; Kupriyanov, I.N.; Higo, Y.; Borzdov, Y.M.; Funakoshi, K.; Palyanov, Y.N.; Ohtani, E. Melting and subsolidus phase relations in the system Na2CO3-MgCO3 ± H2O at 6 GPa and the stability of Na2Mg(CO3)2 in the upper mantle. Am. Mineral. 2013, 98, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, M.; Hanfland, M.; Crichton, W. CaCO3-III and CaCO3-VI, high-pressure polymorphs of calcite: Possible host structures for carbon in the Earth’s mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 333, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavryushkin, P.N.; Martirosyan, N.S.; Inerbaev, T.M.; Popov, Z.I.; Rashchenko, S.V.; Likhacheva, A.Y.; Lobanov, S.S.; Goncharov, A.F.; Prakapenka, V.B.; Litasov, K.D. Aragonite-II and CaCO3-VII: New high-pressure, high-temperature polymorphs of CaCO3. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 6291–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litasov, K.D.; Shatskiy, A.; Gavryushkin, P.N.; Bekhtenova, A.E.; Dorogokupets, P.I.; Danilov, B.S.; Higo, Y.; Akilbekov, A.T.; Inerbaev, T.M. PVT equation of state of CaCO3 aragonite to 29 GPa and 1673 K: In situ x-ray diffraction study. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2017, 265, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzechnik, A.; Bouvier, P.; Farina, L. High-pressure structure of Li2CO3. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 173, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, S.; Chervin, J.; Munsch, P.; Le Marchand, G. Hydrostatic limits of 11 pressure transmitting media. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 075413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malins, K. The potential of K3PO4, K2CO3, Na3PO4 and Na2CO3 as reusable alkaline catalysts for practical application in biodiesel production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 179, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, A.; Ryan, J.; Walker, P. Structural phase transitions in K2CO3 (raman scattering study). J. Phys. Solid State Phys. 1981, 14, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainson, I.; Dove, M.; Harris, M.J. Neutron powder diffraction study of the ferroelastic phase transition and lattice melting in sodium carbonate, Na2CO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1995, 7, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, P.; Ferrante, J.; Rose, J.; Smith, J. Compressibility of solids. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1987, 92, 9319–9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatov, V.A. Crystal structures of inorganic oxoacid salts perceived as cation arrays: A periodic-graph approach. In Inorganic 3D Structures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 31–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D.; Prewitt, C.T. Revised values of effective ionic radii. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1970, 26, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).