Abstract
This paper reports the leaching of seafloor massive sulphides (SMS) from the Loki’s Castle area at the Arctic Mid-Ocean Ridge in sulphuric acid with manganese dioxide and sodium chloride. The results presented are of various leaching experiments conducted under different conditions in order to optimise the dissolution of copper and silver. It was shown that the main copper bearing minerals in the SMS were chalcopyrite and isocubanite, while silver could occur as an admixture in the crystallographic lattice of sulphides or as disseminated micro inclusions. Based on the results, the leaching mechanism was discussed and elucidated. It was shown that the dissolution of the SMS was mainly due to galvanic interactions between the primary marine minerals of SMS and manganese dioxide. Addition of sodium chloride promoted the extraction mechanism.
Keywords:
leaching; chalcopyrite; isocubanite; copper; silver; manganese dioxide; marine minerals; deep-sea mining 1. Introduction
The major copper-bearing mineral in the seafloor massive sulphides (SMS) from the Loki’s Castle area at the Arctic Mid-Ocean Ridge is isocubanite (CuFe2S3), rather than chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), which causes difficulties in flotation. Hence, hydrometallurgical processing appears to be an alternative method for efficient extraction of metals from the SMS. In our previous paper, we showed that copper and zinc can be effectively extracted by nitric acid leaching [1]. Nitric acid is a strong lixiviant and allows rapid extraction of primary metals of interest from the SMS, however, it is uneconomical due to its high price. Alternatives include the use of conventional industrial lixiviants, such as sulphuric acid. Several authors have investigated copper dissolution from sulphides in sulphuric acid (H2SO4), with manganese dioxide (MnO2) [2,3,4] and sodium chloride (NaCl) [5,6,7,8].
A potential source of MnO2 can also be from the deep seabed area, specifically polymetallic nodules (PN). The largest deposits of such ores are found in the Pacific Ocean between Hawaii, California, and around Polynesia, and, particularly, the eastern equatorial Pacific within the Clarion Clipperton Zone (CCZ) [9]. Several metallurgical methods were proposed to extract manganese and other base metals, such as silver, copper, zinc, and cobalt from the nodules. Direct hydrometallurgical processing of manganese nodules involves leaching with ammonia, hydrochloric, or sulphuric acid in the presence of other reductants, such as glucose, charcoal, and even sulphide minerals, including chalcopyrite, sphalerite, pyrrhotite, and pyrite [10,11,12].
Both the seafloor massive sulphides and the deep-sea polymetallic nodules can serve as potential sources of critical raw materials. Potential galvanic interactions between the primary marine minerals of the SMS and PN may allow extraction of the valuable metals from these resources. Addition of sodium chloride, i.e., also potentially from the sea (seawater evaporation), may even promote the extraction mechanism. For such a leaching system, no artificial introduction of air is needed.
In this study, we examined the feasibility of galvanic leaching of seafloor massive sulphides using manganese dioxide in H2SO4-NaCl media. The effects of temperature, as well as the dosage of H2SO4, MnO2, and NaCl, on the extraction of copper and silver were investigated. Based on the results, the leaching mechanism was discussed and elucidated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this work, the seafloor massive sulphide (SMS) rock samples from the Loki’s Castle hydrothermal vent field at the Artic Mid-Ocean Ridge were investigated. The SMS deposit was first reported by Pedersen et al. [13]. It occurs on an axial volcanic ridge adjacent to an ultraslow spreading plate margin, where active venting is observed at a depth of 2400 m. A series of black smoker chimneys cap two sulphide-bearing mounds, each approximately 150 m across and 30 m high. In 2016, the MarMine cruise recovered, via grab sampling, more than 200 kg of loose boulders from the mound flanks [14]. The location and areas of operation, as well as a method of sample storage, are described elsewhere [1,14]. Prior to the leaching experiments, the SMS samples were unpacked and dried at room temperature. Elemental and mineralogical analyses were accomplished using X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and optical microscopy. The elemental composition of the SMS rock samples from the Loki’s Castle is shown in our previous paper [1]. In this work, the sample with the relatively high content of copper (2.2%) and silver (15 ppm) was used in the leaching tests.
Mineralogical phases include silica, with minor barite (BaSO4), pyrite/marcasite (FeS2), sphalerite ((Zn,Fe)S), intergrowths of isocubanite (CuFe2S3) and chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), galena (PbS), and minor pyrrhotite (Fe(1−x)S (x = 0–0.17)) (Figure 1). Sulphide minerals were disseminated in variably intergrown and sub-angular throughout a fine-grained black groundmass with a grain size of 1–100 µm [1]. Sphalerite, chalcopyrite, and isocubanite showed complex intergrowth textures on the nano- to microscale (Figure 1). The lamellae of chalcopyrite, down to 20 nm, were observed in a matrix of isocubanite; in rare occasions, pure chalcopyrite rims the isocubanite/chalcopyrite intergrowths or exists as separate grains. The Cu-phases were intimately intergrown with sphalerite, showing typical “chalcopyrite disease” [15] on various scales (Figure 1C). In addition, homogeneous sphalerite may overgrow sphalerite with chalcopyrite disease (Figure 1B), isocubanite-chalcopyrite intergrowths may overgrow homogenous sphalerite, and sphalerite with or without chalcopyrite disease may overgrow the heterogeneous Cu phase (Figure 1C). Finally, homogenous sphalerite may contain anomalously high levels of Fe, which can be up to 20%. Isocubanite is closely associated with chalcopyrite. The silver phase was not detected by XRD due to its low content in the sample. Silver could occur as an admixture in the crystallographic lattice of sulphides or as disseminated micro inclusions.

Figure 1.
(A) Photomicrograph demonstrating sulphide mineralogy and textures: Cu is hosted in isocubanite (Icb) and chalcopyrite (ccp) intergrowths; Zn in sphalerite (Sp); Pb in galena (Gn) and pyrite (Py), highly altered in this sample. (B) Gradual decrease in chalcopyrite inclusions (upper arrow) in sphalerite (light grey), with the distance from the Cu-phase. Isocubanite (dark grey) host lamellae of chalcopyrite (lower arrow). (C) Various modes of sphalerite and chalcopyrite-iscocubanite textures. The centre yellow grain is an intergrowth of isocubanite and chalcopyrite. Several initial grains of sphalerite, with strong chalcopyrite disease, are rimmed by zones of homogenous sphalerite.
Despite featuring a relatively typical volcanogenic massive sulphide (VMS) mineralogy, these complex intergrowths provide challenges to conventional mineral processing methods, such as liberation by mechanical comminution and upgrading by flotation. Figure 1A illustrates that milling to approximately 10 s of µm would appear to liberate most of the sulphides. However, the ubiquitous sub-micron textures observed in both Cu+Fe- and Zn-bearing minerals may prevent total liberation by conventional grinding. Thus, discrete phases may not be accessed by flotation techniques. This inherent mineralogical characteristic, along with the high Fe content in sphalerite, has been a challenge in the attempts to upgrade a sulphide concentrate by removing pyrite.
Sample preparation prior to leaching involved crushing using a jaw crusher (Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany), followed by grinding in a disc mill (Retsch GmbH, Haan, Germany), and subsequent dry-sieving to obtain a particle size fraction that was below 50 µm, with a d80 of 35 µm. No significant changes in the particle size distribution were observed after leaching. Mili-Q water® and analytical grades of MnO2 in powdered form, H2SO4, and NaCl, were used in all experiments.
2.2. Methods
Leaching tests were carried out in aqueous solutions of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) as the primary lixiviant and additives, such as manganese dioxide (MnO2) and sodium chloride (NaCl). A known mass of a feed (2.15 ± 0.05 g), together with 70 cm3 of specific concentration of acid and additives, were added to 100 cm3 reaction flasks. The flasks were then placed in the Carousel 6 Plus reaction station from Radley’s Innovation Technology and heated to the target temperature under reflux. Mechanical agitation was set at 300 rpm.
Leaching was conducted for 24 h at the following parameters: Temperatures (30–80 °C), acid concentrations (0–1.5 M), MnO2 (0–19.5 g/dm3) and NaCl (0–1 M) dosages. Solution aliquots were collected periodically and analysed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Final leaching residues were dried and analysed using XRF (Thermo Scientific™, Waltham, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Manganese Dioxide and Sodium Chloride Addition
Dissolution of the economically significant metals, copper (XCu) and silver (XAg), from the seafloor massive sulphides (SMS) was investigated in 1 M H2SO4, with different dosages of MnO2 and NaCl at 80 °C. No extraction of either metals in the aqueous H2SO4 solution was observed in the absence of MnO2, either with or without NaCl (Figure 2 and Figure 3). This means that the oxidation of the copper and silver species did not happen.
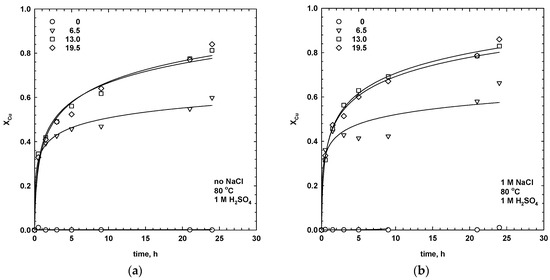
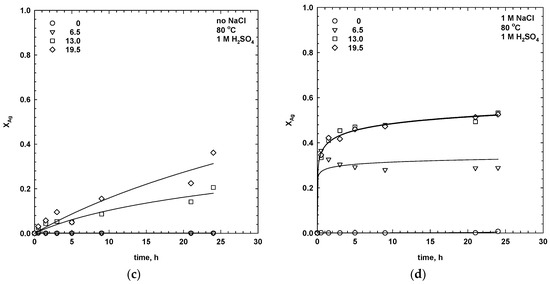
Figure 2.
Effect of MnO2 dosage (g/dm3) on the dissolution (X) of copper (a,b) and silver (c,d) in the absence (a,c) and presence (b,d) of chloride ions (80 °C, 1 M H2SO4, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm).
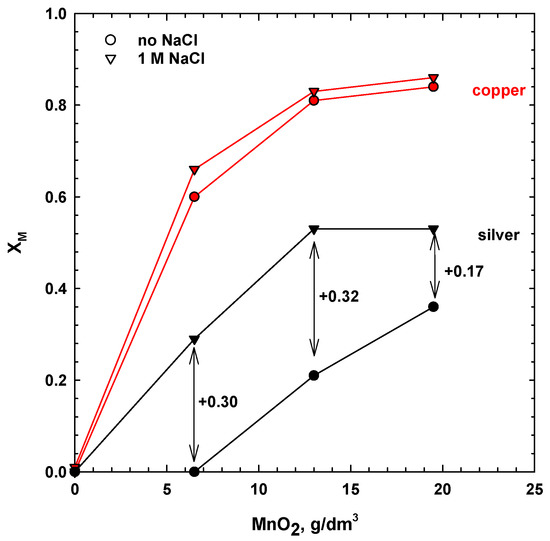
Figure 3.
Effects of the addition of manganese dioxide and sodium chloride on the ultimate extraction of copper and silver (80 °C, 1 M H2SO4, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm, leaching time 24 h).
Copper and silver only started to dissolve in the presence of MnO2. The leaching rate of chalcopyrite and isocubanite, the copper-bearing minerals present in the SMS sample, increased with the addition of MnO2. Initially, rapid leaching kinetics were achieved, exhibiting rapid extraction of copper (Figure 2). The results also indicate that the ultimate dissolution (i.e., extracted fraction X after 24 h) of copper increased from ca. 60%, with 6.5 g/dm3 MnO2, to ca. 80%, with 13 g/dm3 MnO2. Higher dosage of MnO2 only slightly enhanced copper extraction. In the case of silver, the leaching kinetics were linear and very slow, and only 35% of the silver was extracted, with 19.5 g/dm3 of MnO2, after 24 h. The kinetics curves indicate that a longer leaching time would facilitate the dissolution of the copper and silver (Figure 2).
In the given SMS sample, solubilisation of the sulphide minerals in the H2SO4 solution, with MnO2, can be explained by galvanic interactions between the copper and silver phases and the MnO2 [2,3,4]. Chalcopyrite and, most probably, isocubanite (no available data in the literature) have lower rest potentials than MnO2 and could act as a cathode against the anodic MnO2 forming a galvanic couple. Under galvanic contact, the rate of corrosion of the mineral-MnO2 is much higher than their individual self-corrosion rates [3,16].
Moreover, the rest potential of the mixed mineral matrices consisting of chalcopyrite and cubanite, a mineral with the same composition as isocubanite but different structure, as well as sphalerite and chalcopyrite, are lower than that of chalcopyrite alone [17]. With the copper phases composed predominantly of isocubanite/chalcopyrite and sphalerite/chalcopyrite intergrowths, this encouraged the relatively fast initial dissolution of copper, via the reduction of the primary oxidant MnO2 in the cathodic half-cell reaction:
MnO2 + 4H+ + 2e− → Mn2+ + 2H2O
Oxidative dissolution of chalcopyrite is electrochemical in nature, and follows the principle of corrosion where it corrodes anodically [3]:
CuFeS2 → Cu2+ + Fe2+ + 2S° + 4e−
The same electrochemical mechanism is proposed for isocubanite:
CuFe2S3 → Cu2+ + 2Fe2+ + 3S° + 6e−
Under investigated conditions, zinc dissolved rapidly and, for the clarity of this paper, the extraction data and leaching mechanism for zinc are not shown here.
The identified galvanic reactions indicate that the leaching in the H2SO4-MnO2 media resulted in the reduction of manganese(IV) to manganese(II), via electron transfer from the anodic corrosion of sulphide minerals [3]. Ferrous (Fe2+) ions could be oxidized to ferric (Fe3+) ions by manganese dioxide forming ferric sulphate in aqueous H2SO4 solution:
2Fe2+ + MnO2 + 4H+ → 2Fe3+ + Mn2+ + 2H2O
Electrochemical oxidation of the chalcopyrite by ferric ions has been demonstrated [18,19,20,21], and can be simplified in the anodic reaction:
and described as [18,22]:
Fe3+ + e− → Fe2+
CuFeS2 + 4Fe3+ = Cu2+ + 5Fe2+ + 2S°
In reaction (6), it has been generally understood that sulphates (cupric and ferrous) may form at the expense of the elemental sulphur; however, the presence of the resulting ferrous sulphate may retard the chalcopyrite oxidation with ferric ions [19]. This ferric-ferrous couple of reaction (5) could act as the secondary oxidant, which may also oxidize isocubanite following the same mechanism as chalcopyrite in the proposed reaction:
CuFe2S3 + 6Fe3+ = Cu2+ + 8Fe2+ + 3S°
Due to limited mass of the sample for leaching tests, XRD analyses of the residues could not be obtained, however, the XRF data showed an increased sulphur concentration that may be due to the formation of elemental sulphur during leaching under the investigated conditions. Some sulphur could also be further oxidized to sulphate ions in the presence of the oxidants in the acidic medium.
The non-linear shapes of the dissolution curves for copper (Figure 2) suggests the formation of a passivation layer on the chalcopyrite/isocubanite surfaces during leaching. Many studies have been undertaken to establish the type and structure of the passivation layer on the chalcopyrite surface. It was shown that the dissolution of chalcopyrite depended on the oxidation rate from the sulphide to elemental sulphur reaction [23,24,25,26].
Manganese dioxide can also act as the oxidizing agent for silver, although the results showed that leaching in the sulphate media was very slow and inefficient. This was consistent with the data presented by Jiang et al. [27]. Due to the relatively low concentration of silver in the sample, the silver phase was not detected by XRD, and we assume that it could occur as an admixture in the crystallographic lattice of the sulphides. Thus, the presence of manganese dioxide might cause the dissolution of silver according to the simplified reaction:
2Ag + MnO2 + 4H+ → 2Ag+ + Mn2+ + 2H2O
The results show that the leaching performance of silver and copper was strongly affected by the dosage of MnO2, while the addition of sodium chloride only influenced the dissolution rate of silver (Figure 2 and Figure 3). As seen, in the absence of chloride ions and at low dosages of manganese dioxide (6.5 g/dm3), the extraction of silver was negligible.
The addition of chloride ions, together with manganese dioxide, accelerated the process kinetics and increased the ultimate dissolution of silver by ca. 30%, with 6.5–13 g/dm3 MnO2 (Figure 3). Extraction of silver, with 13 g/dm3 MnO2, after 24 h was 53%. The effect was less pronounced at higher dosages of manganese dioxide (19.5 g/dm3), which was probably due to the limited solubility of the silver complexes.
A relatively fast silver dissolution rate was primarily attributed to the potential formation of dissolved chlorine gas in the reaction of MnO2 and NaCl in the acidic solution:
MnO2 + 2NaCl + 4H+ → Mn2+ + 2Na+ + Cl2 + 2H2O
However, no gas formation was noted during leaching, i.e., any formed chlorine may have been readily utilized in the redox reactions.
Silver can be leached out as chloride complexes of Ag(I):
AgCl + (n − 1)Cl− → [AgCln](1−n), n = 1, 2, 3, 4
Free chloride ions could redissolve the formed silver chloride precipitates due to the progressive formation of chloro-complexes of silver [AgCln]1−n, with a higher stability [24,28,29]. The proportion of complex ions depends on the concentration of chloride ions in the solution, and at 1 M NaCl the concentration of insoluble AgCl is very low [30].
Copper was also effectively dissolved during leaching with sodium chloride, however, the results showed that the addition of chloride ions did not effectively increase the dissolution rate in comparison to leaching without NaCl (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The influence of sodium chloride during the sulphuric leaching of the chalcopyrite is still under debate. The rate of the chalcopyrite dissolution in the presence of sodium chloride depends on many parameters, including the mineral origin, grain size, impurities, and stoichiometry [5]. To date, no paper has been published on the dissolution of isocubanite, which is the major copper-bearing mineral in the investigated sample. During the leaching of seafloor massive sulphides, chlorine gas could dissolve the chalcopyrite and isocubanite according to the reactions:
2CuFeS2 +5Cl2 → 2CuCl2 + 2FeCl3 + 4S°
CuFe2S3 +4Cl2 → CuCl2 + 2FeCl3 + 3S°
Leaching in the mixed sulphate-chloride media yielded mixed chloro-aquo copper complexes (green colour of the leach solution, [31]), elemental sulphur, which was proved by Parker et al. [32], and an increased content in the residue, as well as oxidation of ferrous to ferric ions. Dissolution of the chalcopyrite in ferric chloride can be represented as follows [33]:
while for isocubanite oxidation the proposed reaction is:
CuFeS2 + 4FeCl3 → CuCl2 + 5FeCl2 + 2S°
CuFe2S3 + 6FeCl3 → CuCl2 + 8FeCl2 + 3S°
Oxidative dissolution of the chalcopyrite [34,35] and isocubanite in the presence of cupric chloride was also possible according to reactions:
CuFeS2 + 3Cu2+ → 4Cu+ + Fe2+ + 2S°
CuFe2S3 + 5Cu2+ → 6Cu+ + 2Fe2+ + 3S°
The potential formation of cupric chloride may allow the existence of the Cu(II)|Cu(I) couple, acting as the oxidant in reactions (15) and (16). The presence of chlorides stabilized the Cu(I) species in the solution [31]. Resulting cuprous chloride complexes have a higher stability than cupric chloride complexes [36], hence, cupric ions tend to undergo reduction.
Al-Harahsheh et al. [37] reported the synergistic effect of ferric chloride and the resulting formation of cupric chloride in chalcopyrite leaching, noting that the latter is a stronger oxidant than the former. Moreover, agitation could sweep away the cupric chloride complexes formed. Unlike under stagnant conditions, cupric chloride complexes accumulate at the reaction interface, causing enhanced dissolution of copper.
The data from Figure 2, for 13 g/dm3 MnO2, were replotted to show the influence of the addition of chloride ions on the relationship between the dissolution of copper and silver. This type of curve is very helpful for the assessment of any separation results and has been used in mineral processing to show the process selectivity and kinetics [38]. As seen from Figure 4, in the absence of NaCl, the curve has a parabolic shape, which means that there was no simultaneous leaching of the copper and silver phases. Dissolution of the copper was very fast, while leaching of the silver was very slow. Silver started to dissolve slightly when most of the copper was leached out. It might indicate that the silver was finely disseminated in the sulphides and that their initial leaching was beneficial in exposing the silver phase. Sulphides are less noble than silver and dissolve first.
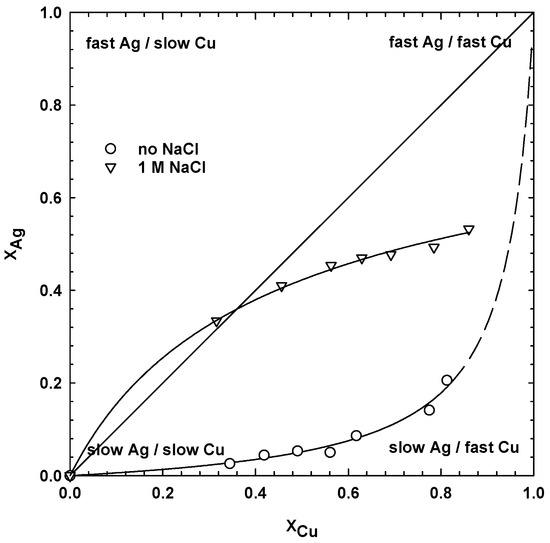
Figure 4.
Dissolution of silver (XAg) vs. dissolution of copper (XCu) curve (80 °C, 1 M H2SO4, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm, leaching time 24 h).
When chloride ions were used, instantaneous dissolution of the silver and copper at the initial stage of the process can be observed. Then, the leaching kinetics of the silver slowed down, while the copper continued. A similar dependency was observed for all dosages of manganese dioxide, but for the clarity of the figures, the data were not plotted.
Initial fast dissolution of copper and, especially, silver may be due to the formation of highly oxidizing chlorine, which could have oxidized the copper sulphides faster when compared to galvanic oxidation, primarily due to the Mn(IV)|Mn(II) couple in the chloride-free system. The oxidized species of copper and silver may have competed with the available chlorine, as well as free chloride. Silver dissolution in the aqueous solution may have been restricted by the available chlorine and limited solubility of the silver chloride complexes. On the other hand, continued leaching of the copper may be a result of:
- (i)
- Primary galvanic interactions between the chalcopyrite, isocubanite, and manganese oxide, or
- (ii)
- Synergistic effects of both the ferric chloride and cupric chloride leaching.
As indicated, the shape of the XAg vs. XCu curve (Figure 4) depends on the presence of chloride ions, therefore, two different mathematical equations were derived for the best approximation of the experimental points. The empirical formulae, obtained by using a nonlinear least-squares regression for one-adjustable parameter a, are:
- (i)
- For sulphate media leaching without NaCl
- (ii)
- For sulphate media leaching with 1 M NaClwhere a1 and a2 are the empirical constants for leaching in the absence and presence of chloride ions, respectively. The constants, a1 and a2, were calculated using the Sigma Plot software package. The constants assume values at different ranges, but both start from 0 for the dissolution of copper only, and increases when the dissolution of silver also increases. Thus, the higher the value of a1 and a2, the faster the dissolution of silver, and the slower the extraction rate of the copper. For simultaneous leaching of the copper and silver phases, the constant, a1, is equal to 1. The calculated values of the empirical constants, a1 and a2, for leaching tests, with different dosages of MnO2, are collected in Table 1. For leaching in the absence of NaCl, the constant, a1, was equal to zero in water and 6.5 mg/dm3 of MnO2, indicating that only copper was extracted. The values of a1 and a2 increased with the manganese dioxide dosage, which resulted in a higher extraction of silver.
 Table 1. Calculated values of the empirical constants a1 (Equation (17)) and a2 (Equation (18)), and ultimate dissolutions of copper XCu and silver XAg.
Table 1. Calculated values of the empirical constants a1 (Equation (17)) and a2 (Equation (18)), and ultimate dissolutions of copper XCu and silver XAg.
3.2. Effect of Acid Concentration
A series of experiments were performed to evaluate the effects of sulphuric acid concentration on the dissolution of copper and silver. The acid concentration varied from 0 to 1.5 M, while other conditions were kept constant (80 °C, with 1 M NaCl and 13 g/dm3 MnO2). As seen from Figure 5, there was no dissolution of the copper and silver in water. The leaching rates of copper and silver increased with an increase in the sulphuric acid concentration. The low concentrations of H2SO4 were not effective for copper and silver dissolution. Extraction of the copper and silver was significant at acid concentrations higher than 0.5 M, and further increases in the acid concentration only slightly improved the extraction of silver and copper. This indicates that hydrogen ions were involved in the leaching process and that the dissolution rates of copper and silver phases depended on the hydrogen ion strength, which had created more oxidizing conditions potentially favouring the proposed galvanic reactions.
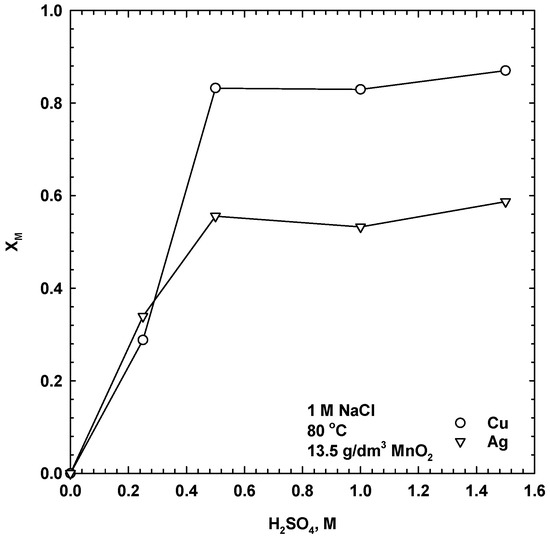
Figure 5.
Influence of acid concentration on dissolution of copper and silver (80 °C, 1 M NaCl, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm, leaching time 24 h).
3.3. Effect of Temperature
Temperature has a pronounced effect on the dissolution of metals from sulphides in the presence of sulphuric acid. The effect of temperature was studied in 1 M H2SO4, 1 M NaCl, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2 over the range 30–80 °C. The results are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. As seen, the extraction of copper and silver was very low at 30 °C. At low temperatures, the dissolution of chalcopyrite, and, thus, isocubanite, was prevented by the formation of passivation species on the surface [25]. Dutrizac and MacDonald [5] observed that, in the acidified ferric sulphate solution, the presence of NaCl accelerated the dissolution of chalcopyrite at temperatures above 50 °C. However, at lower temperatures, it may have an inhibiting effect. Furthermore, an increase in temperature could have favoured the forward reaction of the galvanic systems (both primary and secondary oxidation reactions) that resulted in an accelerated dissolution of both metals. After 24 h, the dissolution of copper and silver increased from 20 to 82% and from 10 to 53%, respectively, as temperature increased from 30 to 80 °C. Such results emphasize the dependence of the copper and silver dissolution from the SMS on temperature under the investigated conditions.
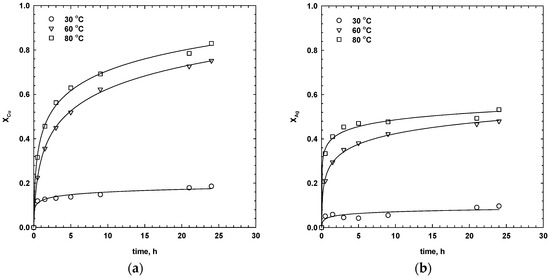
Figure 6.
Effect of temperature on the dissolution of copper (a) and silver (b) (1 M H2SO4, 1 M NaCl, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm).
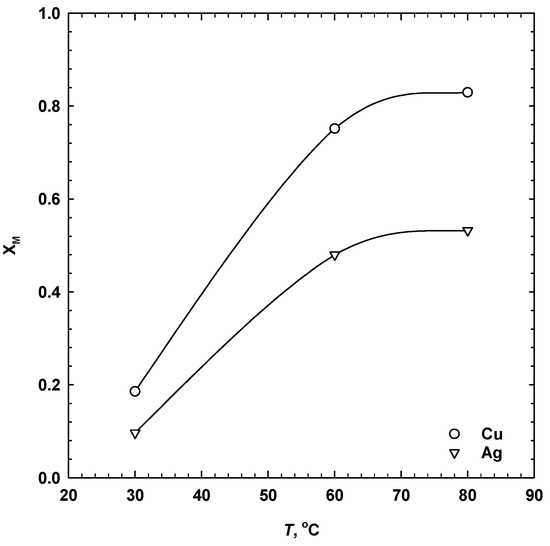
Figure 7.
Influence of temperature on the ultimate dissolution of copper (a) and silver (b) after 24 h (1 M H2SO4, 1 M NaCl, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm).
Temperature dependence can be used to estimate the apparent activation energy for the dissolution of copper and silver phases, and, thus, to determine the dominant leaching mechanism under the investigated conditions. The activation energy can be derived from the relationship between the dissolution kinetic rate constant and the temperature (Arrhenius plot). Several models have been developed to describe the leaching kinetics and among them the Elovich equation was found to successfully describe the dissolution kinetics of copper and silver from the investigated SMS sample. The Elovich equation is expressed as [39,40,41]:
where XM is the extracted fraction (dissolution) of the metal and t is the leaching time. The constant, k, represents the initial kinetic rate (h−1), while β is a measure of resistive forces that slows down the dissolution rate from an initial value to its maximum at XM = 1 [40]. When integrated, with respect to time, Equation (19) has the form:
Figure 6 shows that the experimental points fitted well to the Elovich equation. The empirical constants, k and β, were calculated using the Sigma Plot software package. For all tests, the lowest value of the determination coefficient was 0.97, while the error in the dissolution kinetics of copper and silver was obtained with the 95% confidence interval. As seen from Figure 8, there was a good correlation between the experimental and calculated values of copper and silver dissolution at different temperatures. It confirms the suitability of the Elovich equation for the description of sulphuric acid leaching of copper and silver phases from the SMS under the investigated conditions.
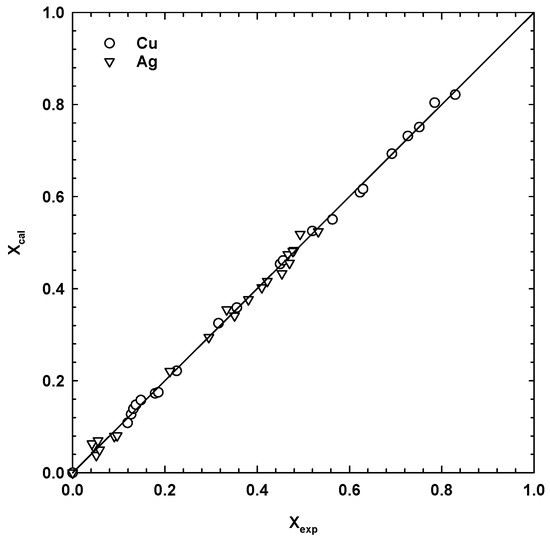
Figure 8.
Comparison of the calculated (Equation (20)) and experimental values of fraction of Cu extracted at different temperatures (1 M H2SO4, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2, 1 M NaCl, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm).
The Arrhenius equation, used to calculate the apparent activation energy, Ea (J∙mol−1), of the copper and silver phases’ leaching, has the form:
where A is the pre-exponential factor, R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J∙mol−1∙K−1), and T is the absolute temperature (K). The values of ln k were plotted against 1000/T, that is the Arrhenius plot shown in Figure 9, and the apparent activation energies were found to be 91 J∙mol−1, with R2 = 0.97 for copper and 101 J∙mol−1, with R2 = 0.84 for silver.
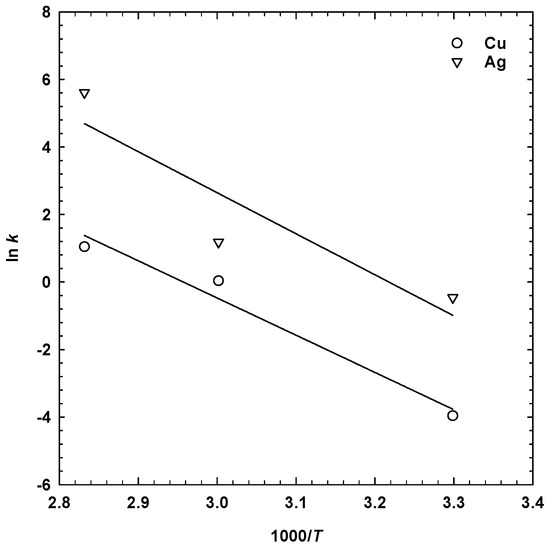
Figure 9.
Arrhenius plot for the dissolution of copper and silver from the seafloor massive sulphides (SMS) (1 M H2SO4, 13.5 g/dm3 MnO2, 1 M NaCl, 30 g/dm3 SMS, 300 rpm).
The relatively high values of the apparent activation energies suggests that electrochemical reactions were mainly responsible for the dissolution of copper [42] and silver from the seafloor massive sulphides during sulphuric acid leaching in the presence of manganese dioxide and sodium chloride.
4. Conclusions
It was shown that the dissolution of the SMS was mainly due to galvanic interactions between the primary marine minerals of the SMS and manganese dioxide. The results clearly indicate that deep-sea manganese nodules could be used as an oxidant for the leaching of seafloor massive sulphides from the Loki’s Castle area at the Artic Mid-Ocean Ridge. For such a system, no artificial introduction of either air or oxygen is needed. Addition of chloride ions also had a positive effect on the leaching rate and efficiency of copper and silver. Due to the reduced accessibility of freshwater in some countries and the high costs of hydrochloric acid, the mixed sulphate-chloride systems offer the possibility of economical leaching, particularly where seawater is easily available.
Author Contributions
P.B.K. conceived and designed experiments. P.B.K. conducted the leaching experiments and analysed the data. K.D., B.S. and K.A. collected and interpreted the mineralogical data. P.B.K. wrote the paper with significant contribution from D.O.M. and R.A.K. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The Norwegian Research Council (Norges Forskningsråd, NFR) is acknowledged for financing the project under grant no 247626/O30. The industrial partners are acknowledged for co-funding the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kowalczuk, P.B.; Snook, B.; Kleiv, R.A.; Aasly, K. Efficient extraction of copper and zinc from seafloor massive sulphide rock samples from the Loki’s Castle area at the Arctic Mid-Ocean Ridge. Miner. Eng. 2018, 115, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.B.; Madhuchhanda, M.; Rao, K.S.; Rath, P.C.; Paramguru, R.K. Oxidation of chalcopyrite in the presence of manganese dioxide in hydrochloric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 57, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantayat, B.P.; Rath, P.C.; Paramguru, R.K.; Rao, S.B. Galvanic interaction between chalcopyrite and manganese dioxide in sulphuric acid medium. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2000, 31B, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Jiao, C.; Guo, X. Extraction of valuable metals from manganese-silver ore. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 119–120, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E.; MacDonald, R.J.C. The effect of sodium chloride on the dissolution of chalcopyrite under simulated dump leaching conditions. Metall. Trans. 1971, 2, 2310–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Y.; Jeffrey, M.I.; Lawson, F. The effect of chloride ions on the dissolution of chalcopyrite in acidic solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 56, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, J.; Jana, R.K.; Kumar, V.; Sanyal, S.K. Some studies on sulphuric acid leaching of anode slime with additives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 6593–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.F.C.; Leao, V.A. The role of sodium chloride on surface properties of chalcopyrite leached with ferric sulfsulphate. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 87, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rona, P.A. Resources of the Sea Floor. Science 2003, 299, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.P.; Anand, S.; Das, S.C.; Jena, P.K. Leaching of manganese nodules in ammoniacal medium using glucose as reductant. Hydrometallurgy 1986, 16, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, S.B.; Jena, P.K. Reduction leaching of manganese nodules of Indian Ocean origin in dilute hydrochloric acid. Hydrometallurgy 1988, 21, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, G. Acid leaching of metals from deep-sea manganese nodules—A critical review of fundamentals and applications. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1379–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, R.B.; Rapp, H.T.; Thorseth, I.H.; Lilley, M.D.; Barriga, F.J.A.S.; Baumberger, T.; Flesland, K.; Fonseca, R.; Fruh-Green, G.L.; Jorgensen, S.L. Discovery of a black smoker vent field and vent fauna at the Arctic Mid-Ocean Ridge. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsen, M.; Aasly, K.; Ellefemo, S.; Hilario, A.; Ramirez-Llodra, E.; Søreide, F.; Falcon-Suarez, I.; Juliani, C.; Kieswetter, A.; Lim, A.; et al. NTNU Cruise Reports 2016 No 1 MarMine Arctic Mid Ocean Ridge 15.08.2016–05.09.2016; NTNU: Trondheim, Norway, 2016; ISSN 2535-2520. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, P.B., Jr.; Bethke, P.M. Chalcopyrite disease in sphalerite: Pathology and epidemiology. Am. Miner. 1987, 72, 451–467. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, H.; Hareyama, W. Galvanic leaching of chalcopyrite using manganese oxides in spent zinc-carbon batteries. Resour. Process. 2016, 63, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.A.; Iwasaki, I. Role of galvanic interactions in the bioleaching of Duluth gabbro copper-nickel sulphides. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1983, 18, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrizac, J.E.; MacDonald, R.J.C. Ferric ion as a leaching medium. Miner. Sci. Eng. 1974, 6, 59–100. [Google Scholar]
- Dutrizac, J.E. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in ferric sulfate and ferric chloride media. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1981, 12, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, P.C.; Paramguru, R.K.; Jena, P.K. Kinetics of dissolution of sulphide minerals in ferric chloride solution. I. Dissolution of galena, sphalerite and chalcopyrite. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 1988, 97, C150–C158. [Google Scholar]
- Winand, R. Chloride hydrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy 1991, 27, 285–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, E.M.; Muñoz, J.A.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Ballester, A. Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. Part I: General aspects. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, S.L.; Thomas, J.E.; Fornasiero, D.; Gerson, A.R. The evolution of surface layers formed during chalcopyrite leaching. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 4392–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.J.; Wen, S.M.; Deng, J.S.; Liu, J.; Nie, Q. Leaching chalcopyrite with sodium chlorate in hydrochloric acid solution. Can. Metall. Q. 2012, 51, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremaninezhad, A.; Dixon, D.G.; Asselin, E. Electrochemical and XPS analysis of chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) dissolution in sulfsulphuric acid solution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Harmer, S.; Chen, M. Synchrotron-based XPS and NEXAFS study of surface chemical species during electrochemical oxidation of chalcopyrite. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Qiu, G. Simultanous leaching of manganese and silver from manganese-silver ores at room temperature. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 69, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, B.; Javad, M. Chloride leaching of lead and silver from refractory zinc plant residue. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2011, 15, 473–480. [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewski, T.; Gibas, K.; Borowski, K.; Adamski, Z.; Wozniak, B.; Muszer, A. Chloride leaching of silver and lead from a solid residue after atmospheric leaching of flotation copper concentrates. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2017, 53, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, T.; Xia, X. Behaviour of silver and lead in selective chlorination leaching process of gold-antimony alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vreese, P.; Brooks, N.R.; Hecke, K.V.; Meervelt, L.V.; Matthijs, E.; Binnemans, K.; van Deun, R. Speciation of copper(II) complexes in an ionic liquid based on choline chloride and in choline chloride/water mixtures. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 4972–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, G.K.; Woods, R.; Hope, G.A. Raman investigation of chalcopyrite oxidation. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 318, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, M.L.; Liddell, L.C. Leaching of CuFeS2 by aqueous FeCl3, HCl, and NaCl: effect of solution composition and limited oxidant. Metall. Trans. B-Process Metall. 1987, 18, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. Chalcopyrite Its Chemistry and Metallurgy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrom, M.; Aromaa, J.; Forsen, O.; Hyvarinen, O.; Barker, M. Leaching of chalcopyrite in cupric chloride. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.M.; Winand, R. Solubilities, densities, and electrical conductivities of aqueous copper (I) and copper (II) chlorides in solutions containing other chlorides such as zinc, sodium, and hydrogen chlorides. Hydrometallurgy 1984, 12, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.; Kingman, S.; Al-Harahsheh, A. Ferric chloride leaching of chalcopyrite: synergistic effect of CuCl2. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 91, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, J. Mineral Processing. Foundation of Theory and Practice of Minerallurgy; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Wroclawskiej: Wroclaw, Poland, 2007; ISBN 978-83-7493-362-9. [Google Scholar]
- McLintock, I.S. The Elovich equation in chemisorption kinetics. Nature 1967, 216, 1204–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Yin, Z.; Hu, H.; Chen, Q. Dissolution kinetics of zinc silicate (hemimorphite) in ammoniacal solution. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.; He, J.; Li, H. Leaching kinetics of hemimorphite in ammonium chloride solution. Metals 2017, 7, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Montes, K.S.; Padilla, R. Chalcopyrite leaching in sulfate–chloride media at ambient pressure. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).