Influence of pH and Contaminant Redox Form on the Competitive Removal of Arsenic and Antimony from Aqueous Media by Coagulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Solutions Preparation
2.2. Coagulation Experiments
2.2.1. Experimental Conditions
2.2.2. Jar Test Procedure
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherm Models
2.3. Other Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
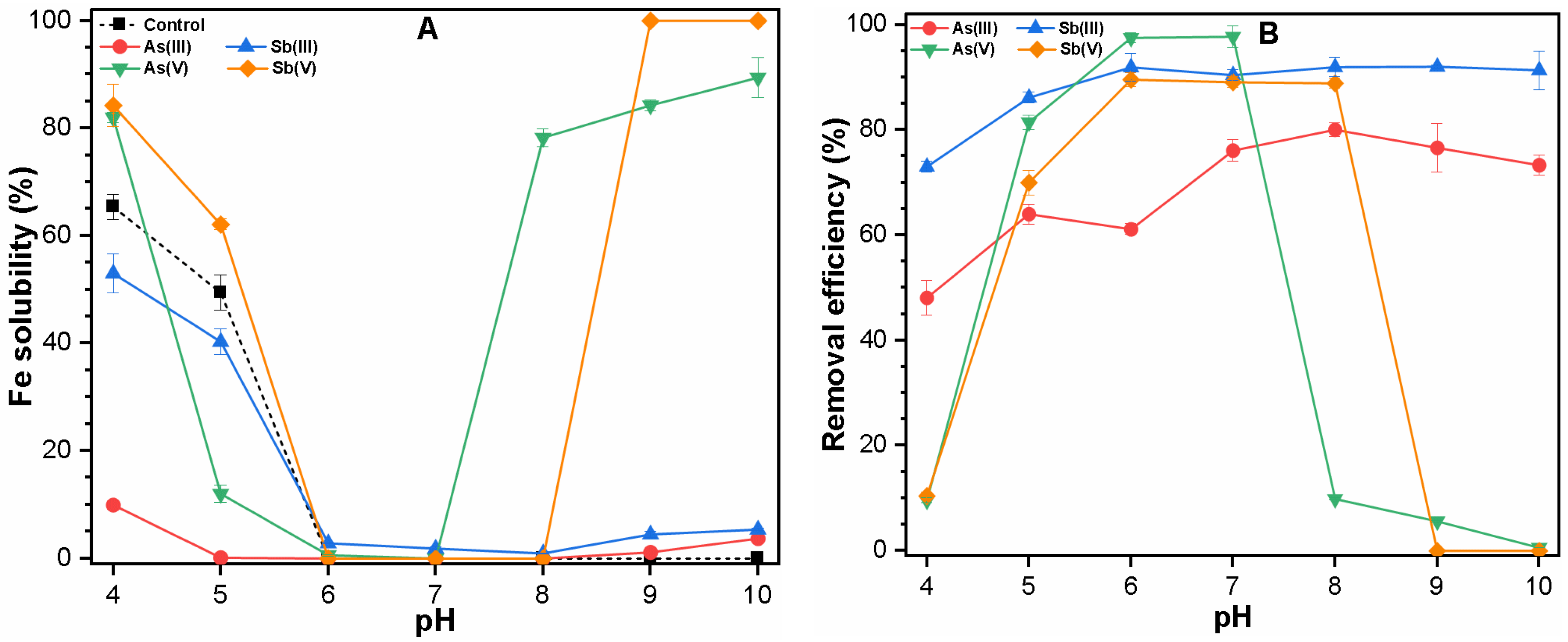
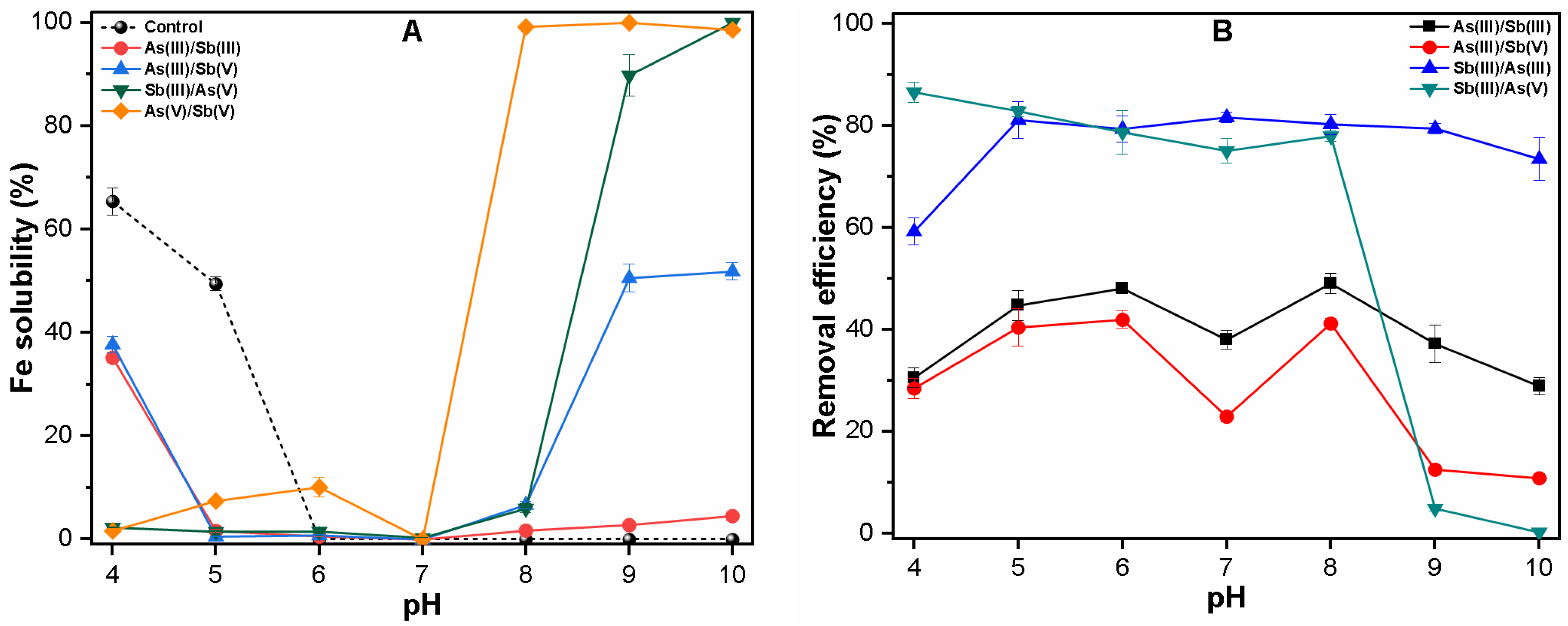
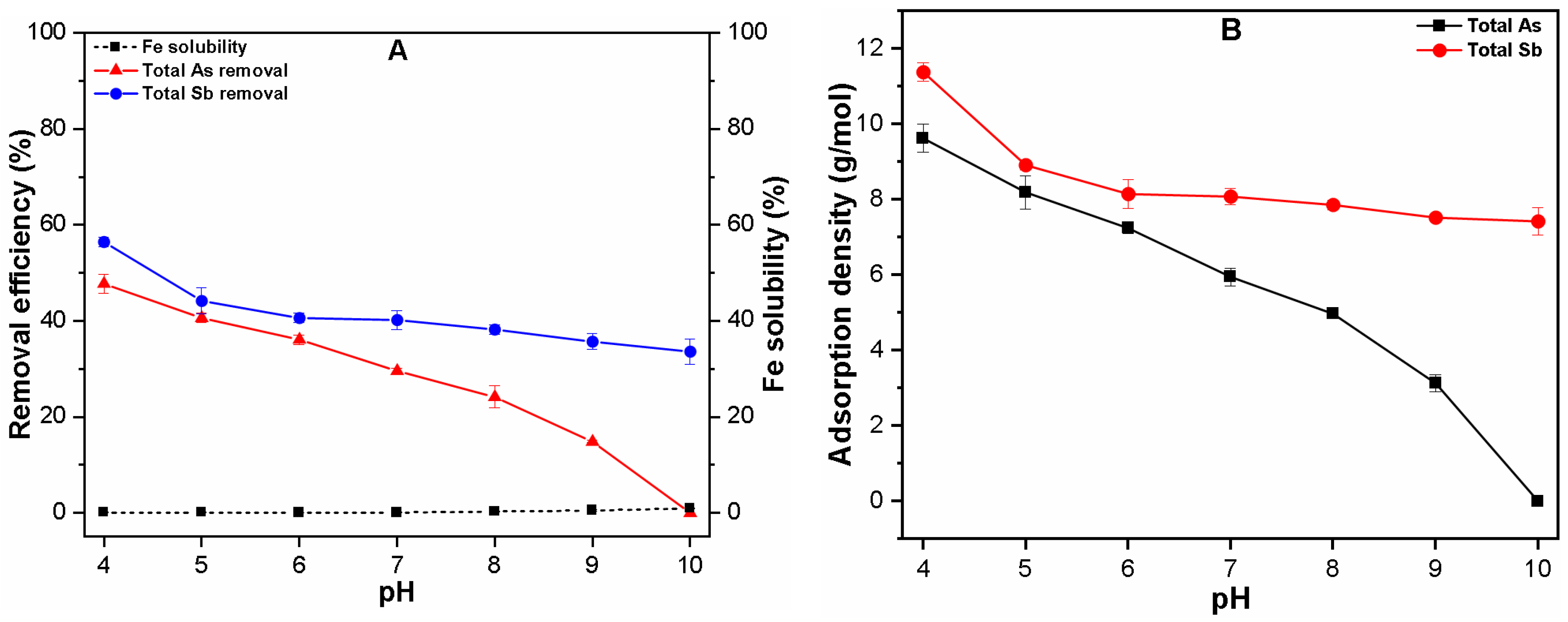
3.1. Effect of pH on Fe Solubility and As and Sb Removal by Coagulation
3.1.1. Single Solute System
3.1.2. Binary System
3.1.3. Quaternary System
3.2. Modeling As and Sb Coagulation Data by Isotherm Studies
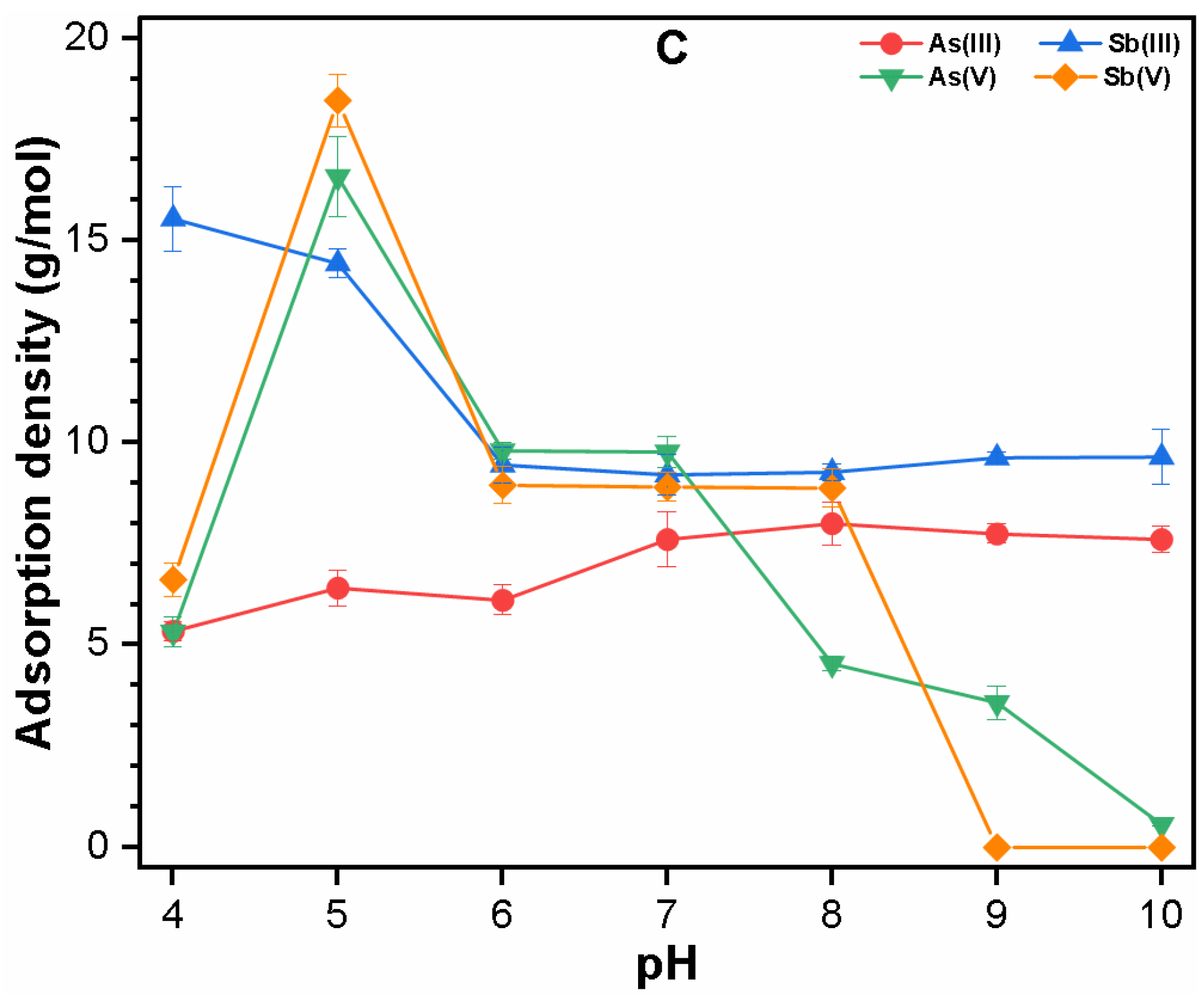
3.2.1. Single Solute System
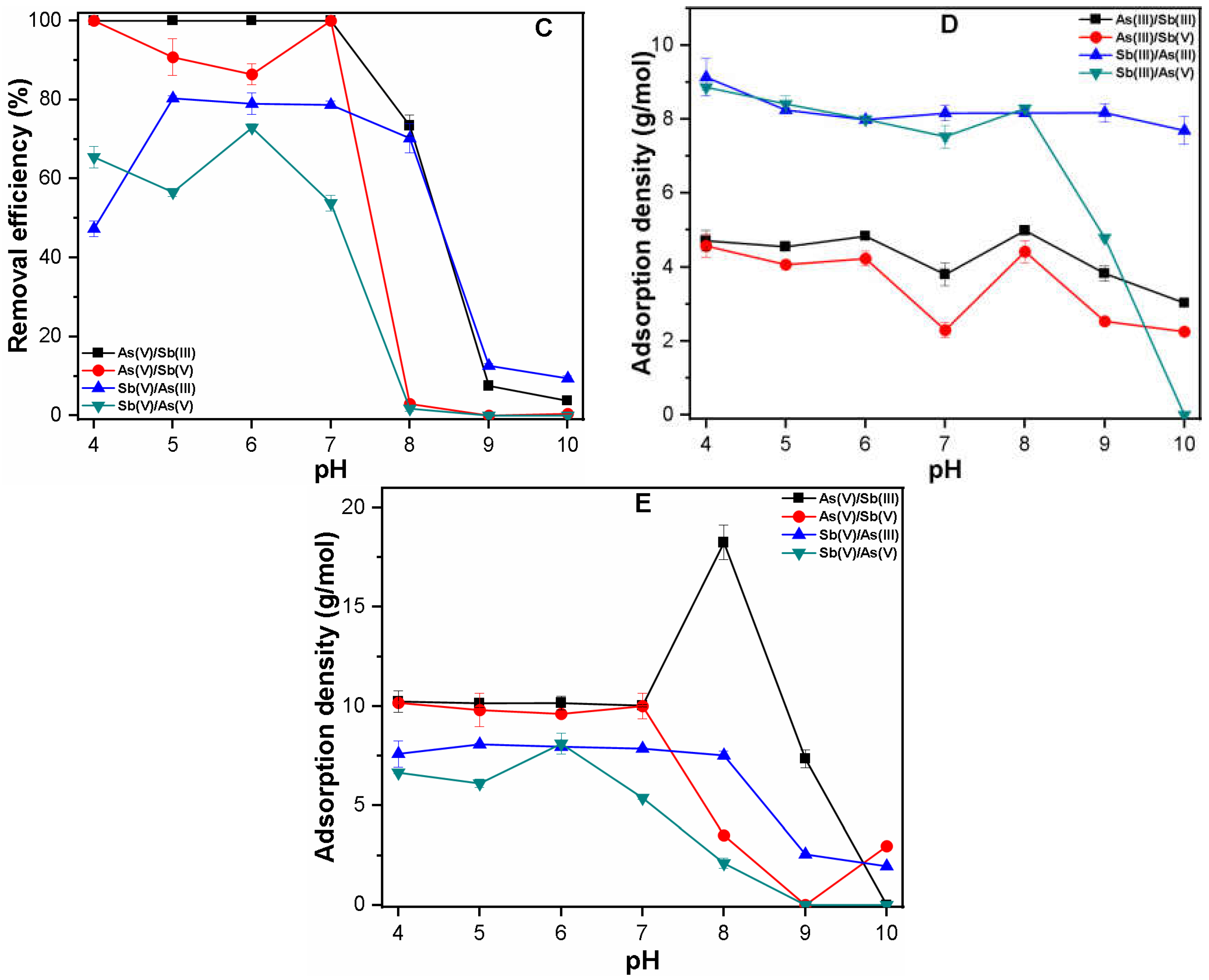
3.2.2. Binary System
3.2.3. Quaternary System
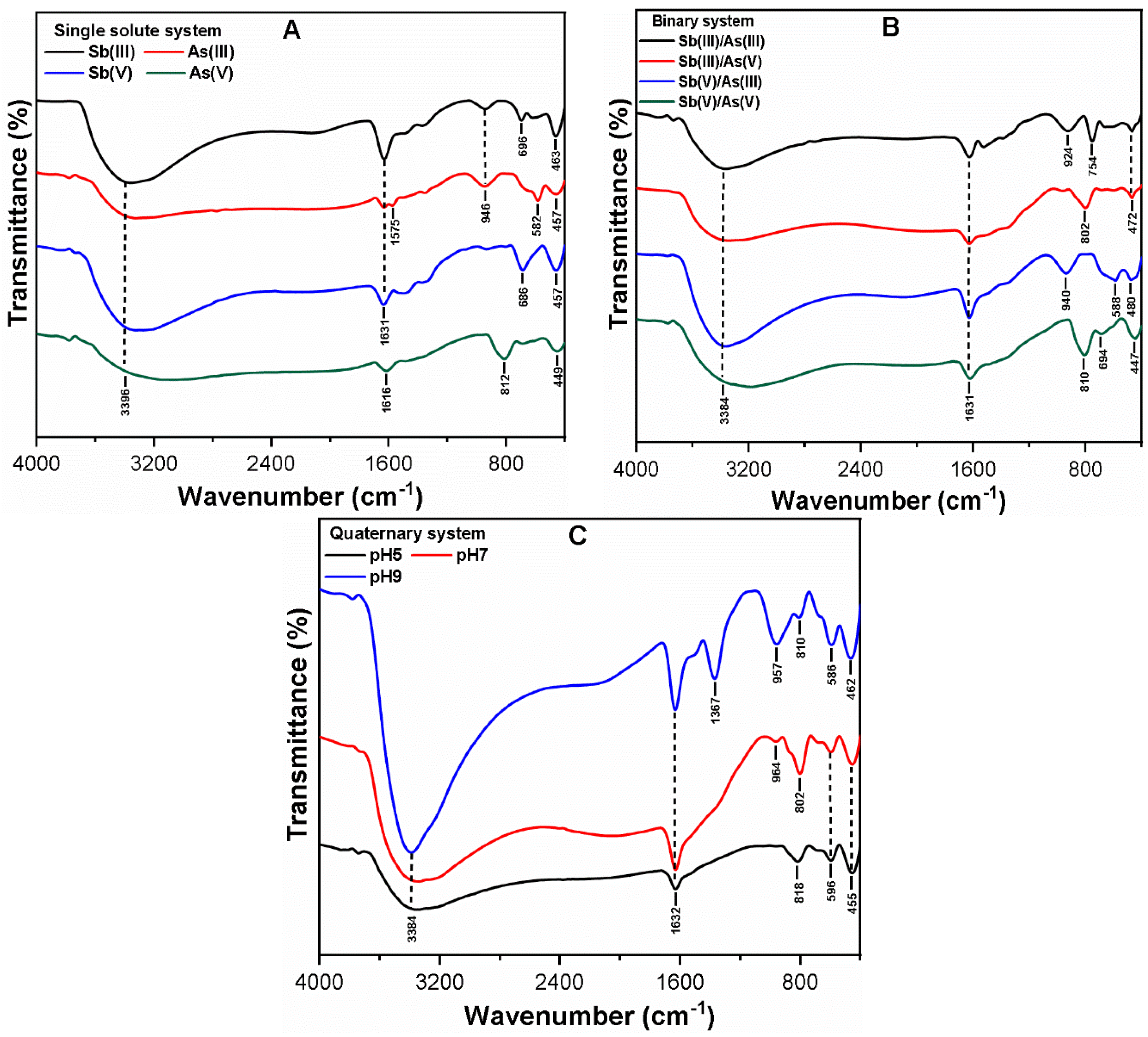
3.3. Mechanism of As and Sb Removal by FC Coagulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Sun, S.-P.; He, M.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.D.; Wu, W.D. As (V) and Sb (V) co-adsorption onto ferrihydrite: Synergistic effect of Sb (V) on As (V) under competitive conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14585–14594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarak, H.; Chai, L.-Y.; Mirza, N.; Yang, Z.-H.; Pervez, A.; Tariq, M.; Shaheen, S.; Mahmood, Q. Antimony (Sb)–pollution and removal techniques–critical assessment of technologies. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 1296–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.-W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters: I. Occurrence. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2002, 57, 125–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S.G.S. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2017: US Geological Survey; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2017.
- Hansell, C. All manner of antimony. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Saha, K.C.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Pati, S.; Dutta, R.N.; Roy, S.; Quamruzzaman, Q.; Rahman, M.; Chakraborti, D. Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bengal delta and its health effects. In Safe and Sustainable Use of Arsenic-Contaminated Aquifers in the Gangetic Plain; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 215–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Tsang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Adsorption capacities of poorly crystalline Fe minerals for antimonate and arsenate removal from water: Adsorption properties and effects of environmental and chemical conditions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, C.; Deng, Q.; Meng, W.; Giesy, J.P. Comparison of arsenic and antimony biogeochemical behavior in water, soil and tailings from Xikuangshan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiller, E.; Lalinská, B.; Chovan, M.; Jurkovič, Ľ.; Klimko, T.; Jankulár, M.; Hovorič, R.; Šottník, P.; Fľaková, R.; Ženišová, Z. Arsenic and antimony contamination of waters, stream sediments and soils in the vicinity of abandoned antimony mines in the Western Carpathians, Slovakia. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, M.; Xi, J.; Lu, X. Antimony distribution and mobility in rivers around the world’s largest antimony mine of Xikuangshan, Hunan Province, China. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M. Distribution and phytoavailability of antimony at an antimony mining and smelting area, Hunan, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2007, 29, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Salmon, K.; DuBow, M.S. A chromosomal ars operon homologue of Pseudomonas aeruginosa confers increased resistance to arsenic and antimony in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 1998, 144, 2705–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, M.A.; Khan, R.; Park, D.R.; Lee, Y.-W.; Yeom, I.T. Removal of Sb (III) and Sb (V) by Ferric Chloride Coagulation: Implications of Fe Solubility. Water 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; van Leeuwen, J.; Mulcahy, D. Removal of As (III) and As (V) by ferric salts coagulation–Implications of particle size and zeta potential of precipitates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuz, A.-K.; Mönch, H.; Johnson, C.A. Sorption of Sb (III) and Sb (V) to goethite: Influence on Sb (III) oxidation and mobilization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.C.; Lockwood, P.V.; Ashley, P.M.; Tighe, M. The chemistry and behaviour of antimony in the soil environment with comparisons to arsenic: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungureanu, G.; Santos, S.; Boaventura, R.; Botelho, C. Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: Overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, I.; Vithanage, M.; Bundschuh, J. Antimony as a global dilemma: Geochemistry, mobility, fate and transport Title. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOE. MOE Korea. 2015. Available online: http://www.me.go.kr/home/web/index.do?menuId=68 (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Antelo, J.; Avena, M.; Fiol, S.; López, R.; Arce, F. Effects of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of phosphate and arsenate at the goethite–water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkenhaug, G.; Zhu, Y.-G.; He, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mulder, J. Antimony (Sb) and arsenic (As) in Sb mining impacted paddy soil from Xikuangshan, China: Differences in mechanisms controlling soil sequestration and uptake in rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3155–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrence and Uses; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 167–168. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, H.D.; Postma, D.J.; Jakobsen, R.; Larsen, O. The Transformation of Fe (III) Oxides Catalysed by Fe2+ and the Fate of Arsenate during Transformation and Reduction of Fe (III) Oxides; DTU Environment: Lyngby, Denmark, 2006; ISBN 8791855020. [Google Scholar]
- Biber, M.V.; dos Santos Afonso, M.; Stumm, W. The coordination chemistry of weathering: IV. Inhibition of the dissolution of oxide minerals. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnamperuma, F.N. The chemistry of submerged soils. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Berlin, Germany, 1972; Volume 24, pp. 29–96. ISBN 0065-2113. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, T.D.; Morel, F.M.M. Photoreductive dissolution of colloidal iron oxides in natural waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1984, 18, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeMonte, J.J.; Stuckey, J.W.; Sanchez, J.Z.; Tappero, R.; Rinklebe, J.; Sparks, D.L. Sea level rise induced arsenic release from historically contaminated coastal soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5913–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohne, T.; Rinklebe, J.; Diaz-Bone, R.A.; Du Laing, G. Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: Impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony. Geoderma 2011, 160, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Ma, Z.; Tong, M. Efficient removal of trace antimony (III) through adsorption by hematite modified magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, P.; Alguacil, F.J. Adsorption of antimony and arsenic from a copper electrorefining solution onto activated carbon. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 66, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Srivastava, A. Reverse Engineering-Based Hardware Trojan Detection. In The Hardware Trojan War; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 269–288. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M. Removal of antimony (V) and antimony (III) from drinking water by coagulation–flocculation–sedimentation (CFS). Water Res. 2009, 43, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M.; Meng, X.; Jin, X.; Qiu, N.; Zhang, J. Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: Adsorption behavior and surface structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Pichler, T. Sequential and simultaneous adsorption of Sb (III) and Sb (V) on ferrihydrite: Implications for oxidation and competition. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Pichler, T. Competitive adsorption of As (III), As (V), Sb (III) and Sb (V) onto ferrihydrite in multi-component systems: Implications for mobility and distribution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Kang, Y.; Li, L. Aqueous arsenic (As) and antimony (Sb) removal by potassium ferrate. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kamei, T.; Magara, Y. Comparing polyaluminum chloride and ferric chloride for antimony removal. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Fu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, F.; Giesy, J.P. Removal of antimonate (Sb (V)) and antimonite (Sb (III)) from aqueous solutions by coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation (CFS): Dependence on influencing factors and insights into removal mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guan, X. Arsenate and arsenite removal by FeCl3: Effects of pH, As/Fe ratio, initial As concentration and co-existing solutes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 92, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Chen, P.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M.; Liang, S. Arsenic removal by ferric chloride. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1996, 88, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Chen, P.-Y.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M. Arsenic removal from drinking water during coagulation. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Uber Die Adsorption in Losungen. Z. Phys. Chem. (Leipz.) 1906, 57, 385–470. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Li, H.-J.; Cai, H.-Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.-C.; Yi, H.-B.; Min, X.-B. Microscopic insight into precipitation and adsorption of As (V) species by Fe-based materials in aqueous phase. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinder, B.; Furrer, G.; Stumm, W. The coordination chemistry of weathering: II. Dissolution of Fe(III) oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W. Reactivity at the mineral-water interface: Dissolution and inhibition. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 120, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.T.; Torrents, A.; Smolen, J.; Vasudevan, D.; Hadley, J. Adsorption of organic compounds possessing ligand donor groups at the oxide/water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.T. Reactions of extracellular organic ligands with dissolved metal ions and mineral surfaces. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1997, 35, 309–344. [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima, H. DLVO Theory of Colloid Stability. In Electrical Phenomena at Interfaces, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2018; pp. 119–136. [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, W. The Inner-Sphere Surface Complex. Adv. Chem. 1995, 244, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.-S.; Seong, H.J.; Chon, C.-M.; Park, J.H.; Nam, I.-H.; Yoo, K.; Ahn, J.S. Interaction of Sb (III) with iron sulfide under anoxic conditions: Similarities and differences compared to As (III) interactions. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauling, L. The formulas of antimonic acid and the antimonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, D.; Tsang, Y.F. Differences in Sb (V) and As (V) adsorption onto a poorly crystalline phyllomanganate (δ-MnO2): Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and mechanisms. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Yu, Q.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from wastewater by anion exchange resins: Effects of resin properties and solution chemistry. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5188–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Luo, J.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. The remarkable effect of the coexisting arsenite and arsenate species ratios on arsenic removal by manganese oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Qu, J. The mechanism of antimony (III) removal and its reactions on the surfaces of Fe–Mn binary oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.; Park, D.; Zam Zam, S.; Shin, S.; Khan, S.; Akram, M.; Yeom, I. Influence of Organic Ligands on the Colloidal Stability and Removal of ZnO Nanoparticles from Synthetic Waters by Coagulation. Processes 2018, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-S.; Qu, J.-H.; Liu, H.-J.; Liu, R.-P.; Li, G.-T. Removal mechanism of As (III) by a novel Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent: Oxidation and sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4613–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Zam, S.Z.; Park, D.R.; Yeom, I.T. Assessment of Key Environmental Factors Influencing the Sedimentation and Aggregation Behavior of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Aquatic Environment. Water 2018, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsunobu, S.; Muramatsu, C.; Watanabe, K.; Sakata, M. Behavior of antimony (V) during the transformation of ferrihydrite and its environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9660–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
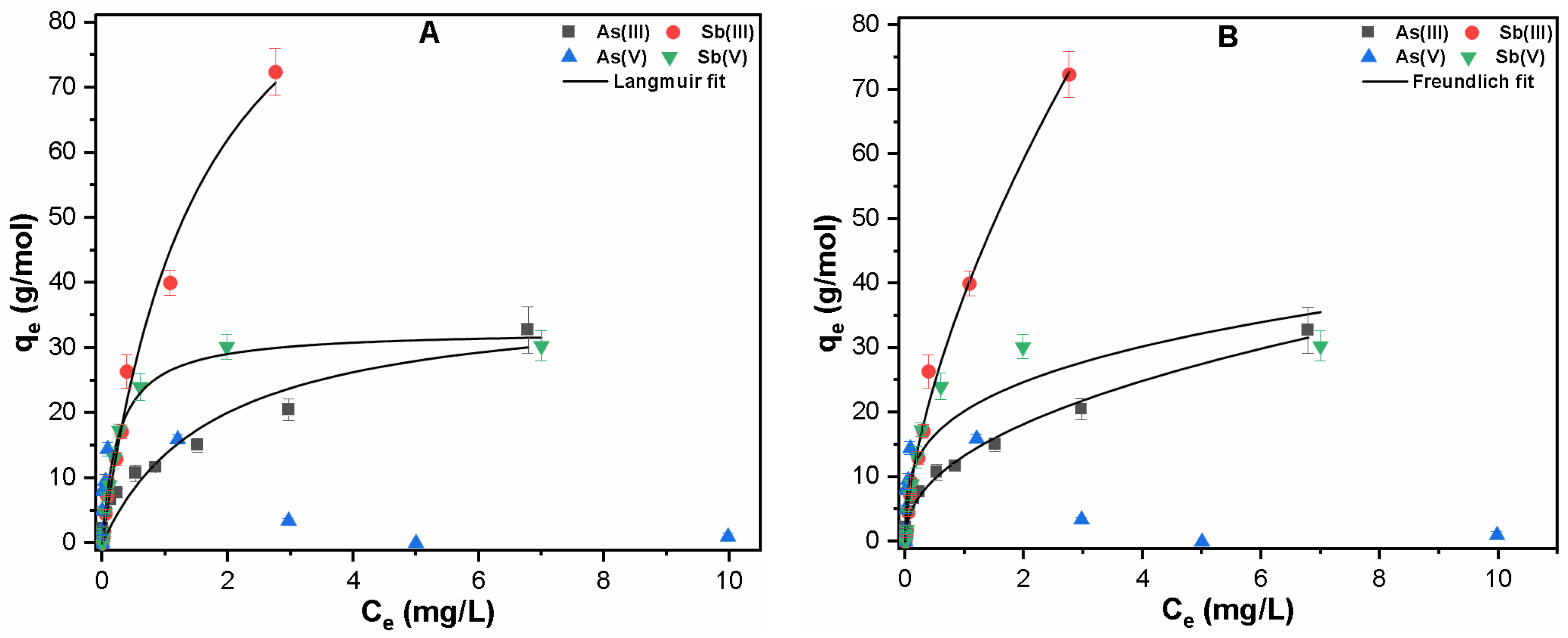
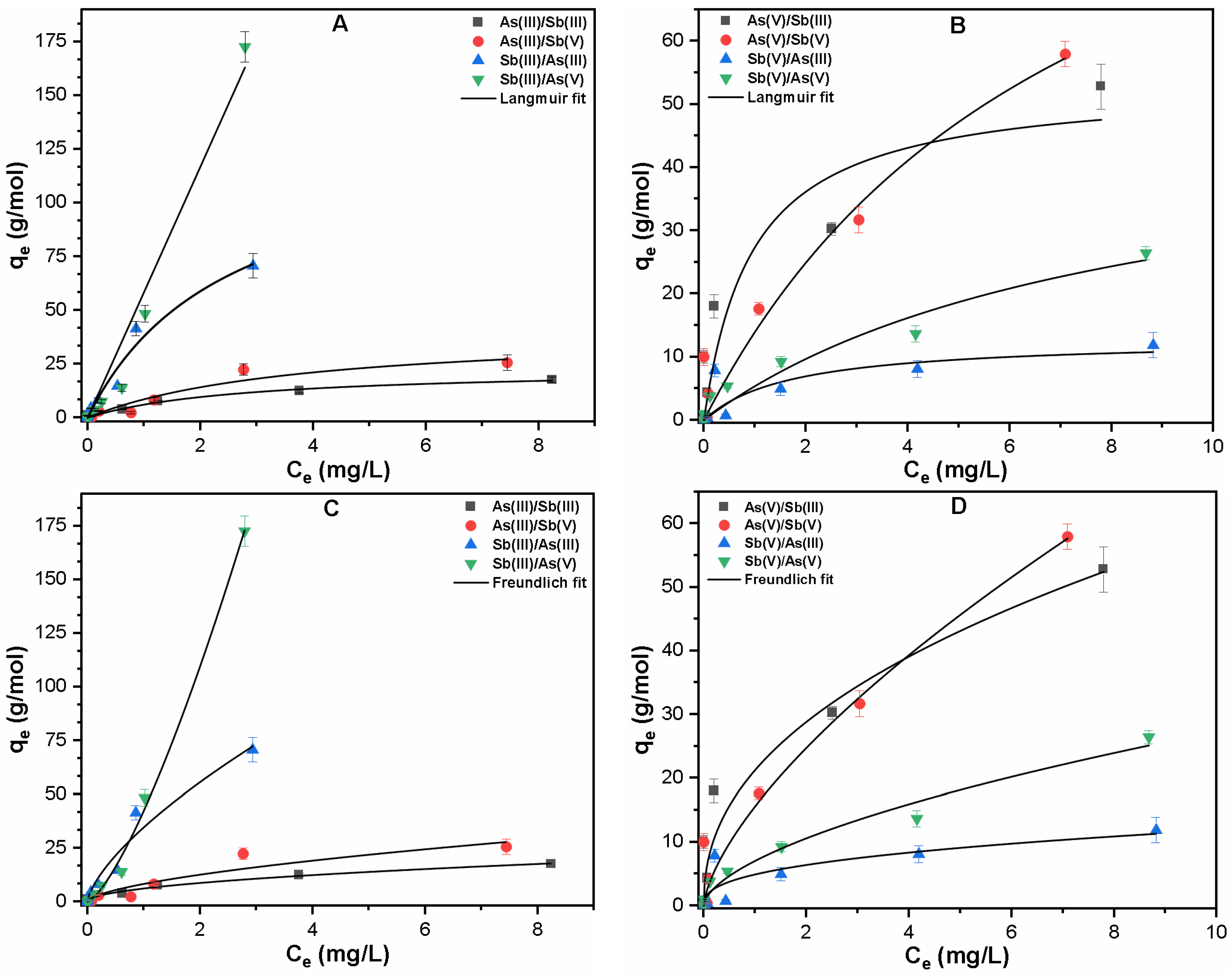
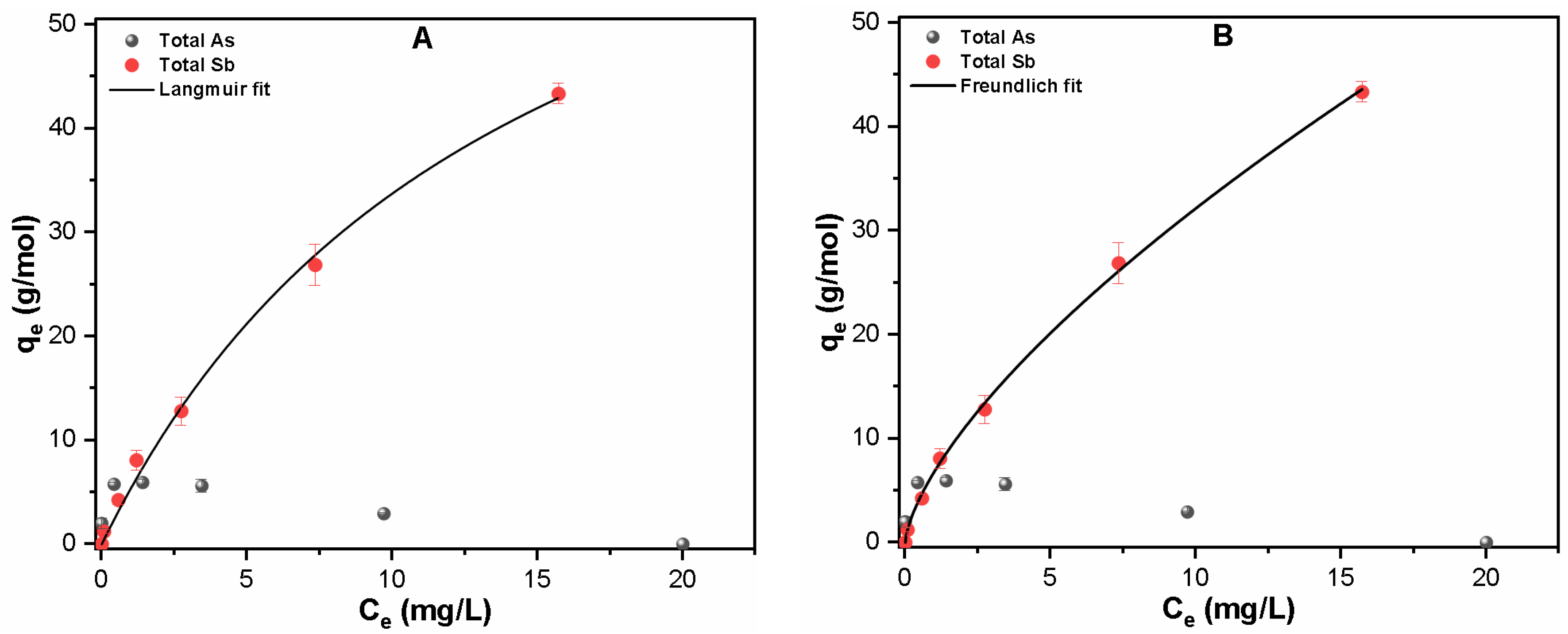
| Contaminants | Langmuir Fitting | Freundlich Fitting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | qm (g/mol) | R2 | KF (g/mol) (L/mg) | n | R2 | |
| As(III) | 0.559 | 38.01 | 0.917 | 13.346 | 2.221 | 0.984 |
| Sb(III) | 0.622 | 111.95 | 0.985 | 38.359 | 1.586 | 0.990 |
| Sb(V) | 3.961 | 32.74 | 0.994 | 20.255 | 3.457 | 0.852 |
| Sample | Solutes | Langmuir Fitting | Freundlich Fitting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | qm (g/mol) | R2 | KF (g/mol) (L/mg) | n | R2 | ||
| As(III)/Sb(III) | As(III) | 0.355 | 23.11 | 0.981 | 6.169 | 1.984 | 0.987 |
| Sb(III) | 0.400 | 132.29 | 0.962 | 34.666 | 1.465 | 0.950 | |
| As(III)/Sb(V) | As(III) | 0.264 | 40.99 | 0.908 | 8.308 | 1.661 | 0.861 |
| Sb(V) | 0.586 | 12.84 | 0.550 | 4.896 | 2.608 | 0.652 | |
| As(V)/Sb(III) | As(V) | 1.053 | 53.32 | 0.848 | 21.258 | 2.276 | 0.895 |
| Sb(III) | 0.00001 | 5771510 | 0.962 | 42.400 | 0.729 | 0.996 | |
| As(V)/Sb(V) | As(V) | 0.135 | 116.97 | 0.945 | 15.574 | 1.497 | 0.951 |
| Sb(V) | 0.122 | 49.19 | 0.928 | 7.028 | 1.696 | 0.967 | |
| Solutes | Langmuir Fitting | Freundlich Fitting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | qm (g/mol) | R2 | KF (g/mol) (L/mg) | n | R2 | |
| Sb(III, V) | 0.069 | 82.04 | 0.995 | 6.82 | 1.485 | 0.998 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inam, M.A.; Khan, R.; Park, D.R.; Ali, B.A.; Uddin, A.; Yeom, I.T. Influence of pH and Contaminant Redox Form on the Competitive Removal of Arsenic and Antimony from Aqueous Media by Coagulation. Minerals 2018, 8, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8120574
Inam MA, Khan R, Park DR, Ali BA, Uddin A, Yeom IT. Influence of pH and Contaminant Redox Form on the Competitive Removal of Arsenic and Antimony from Aqueous Media by Coagulation. Minerals. 2018; 8(12):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8120574
Chicago/Turabian StyleInam, Muhammad Ali, Rizwan Khan, Du Ri Park, Babar Aijaz Ali, Ahmed Uddin, and Ick Tae Yeom. 2018. "Influence of pH and Contaminant Redox Form on the Competitive Removal of Arsenic and Antimony from Aqueous Media by Coagulation" Minerals 8, no. 12: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8120574
APA StyleInam, M. A., Khan, R., Park, D. R., Ali, B. A., Uddin, A., & Yeom, I. T. (2018). Influence of pH and Contaminant Redox Form on the Competitive Removal of Arsenic and Antimony from Aqueous Media by Coagulation. Minerals, 8(12), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8120574







