Synthesis of Lithium Fluoride from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leaching Assays
2.2. Recovery Assays
3. Results
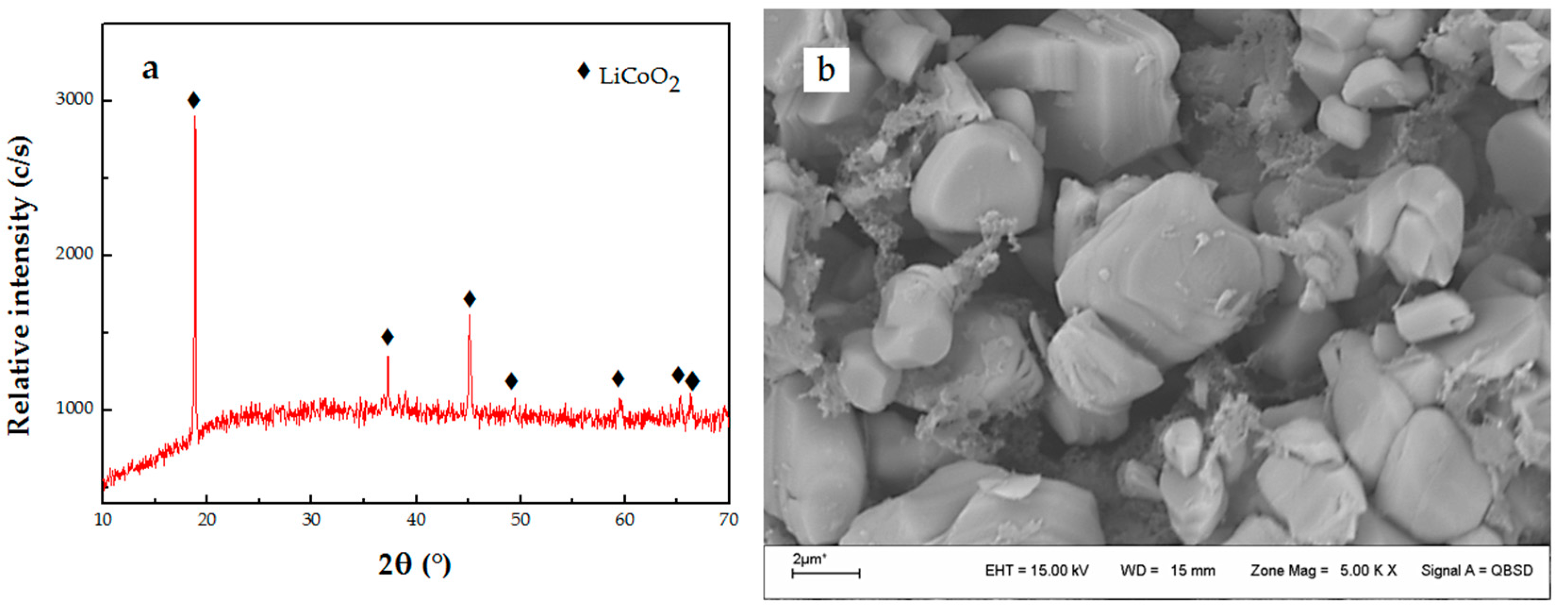
3.1. Dissolution of LiCoO2 with HF
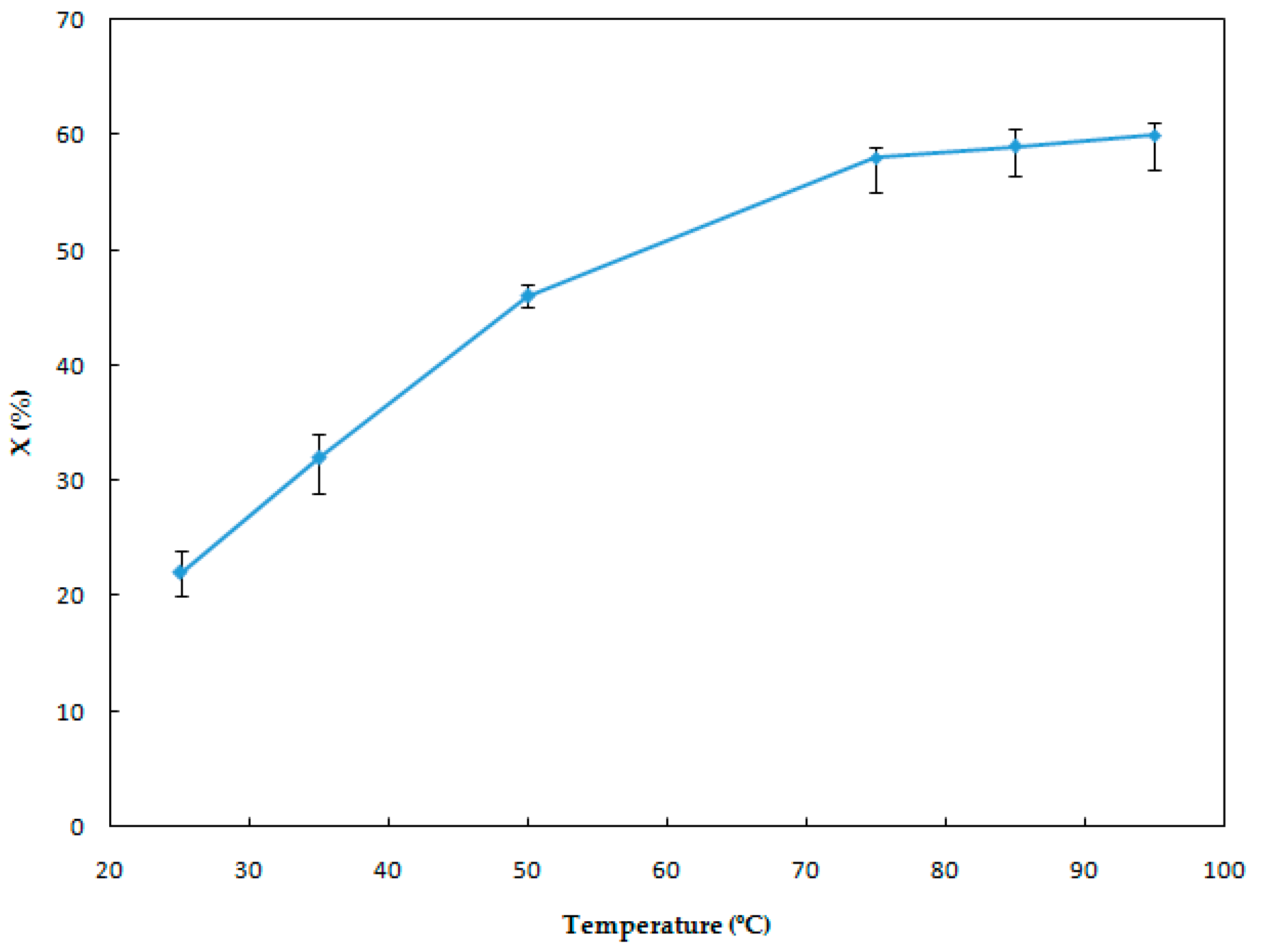
3.1.1. Effect of the Leaching Temperature
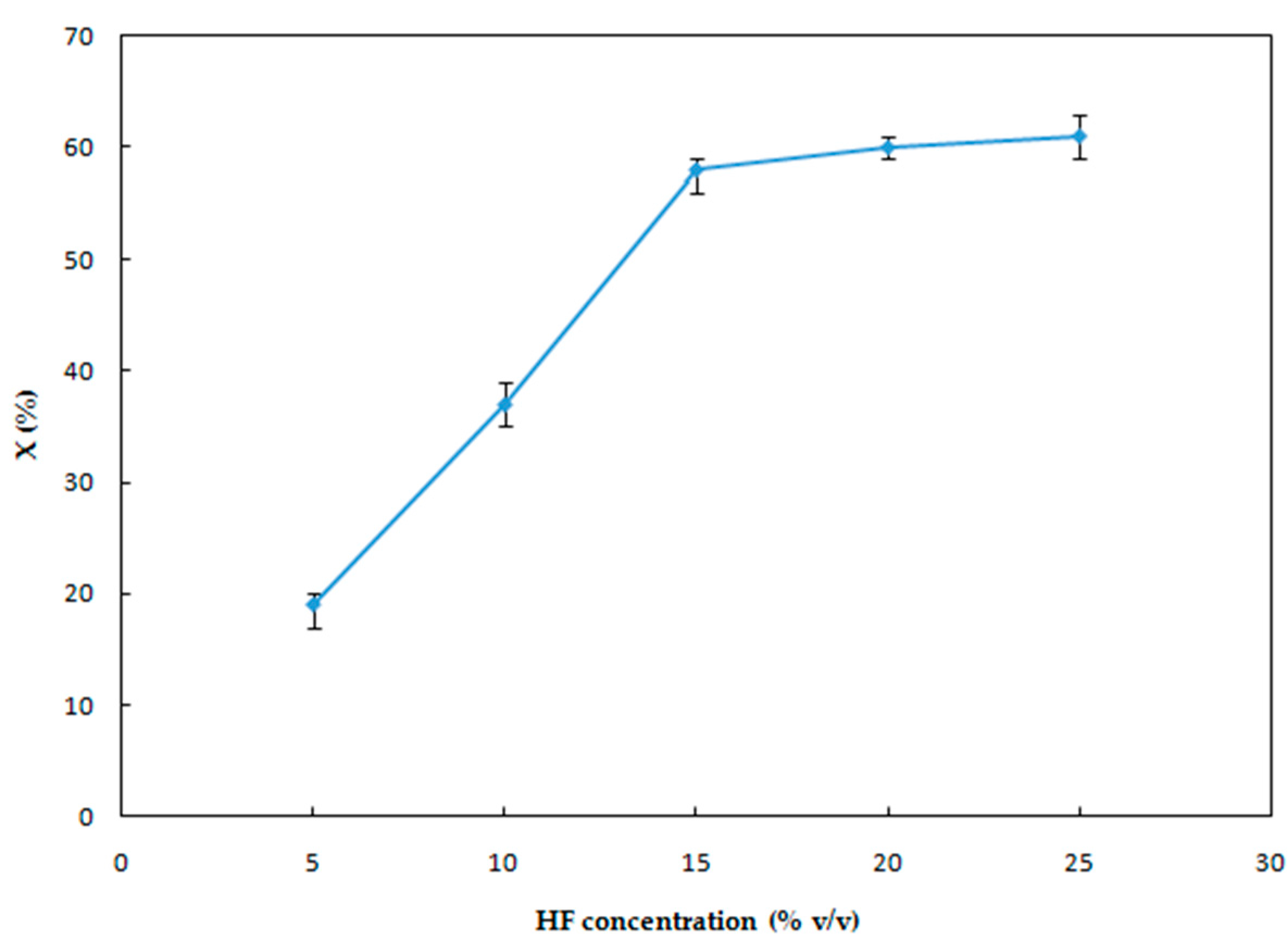
3.1.2. Effect of HF Concentration
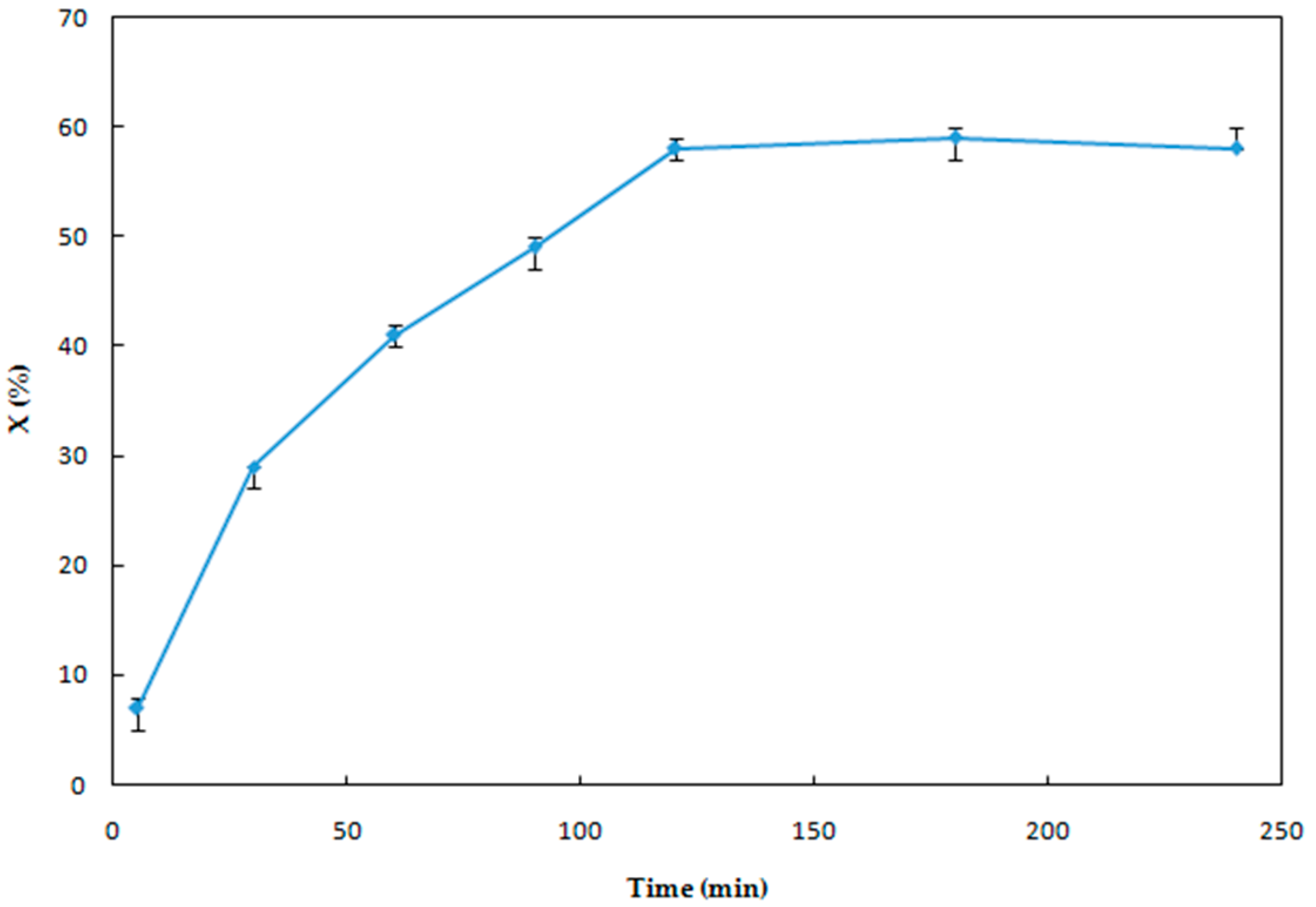
3.1.3. Effect of Reaction Time
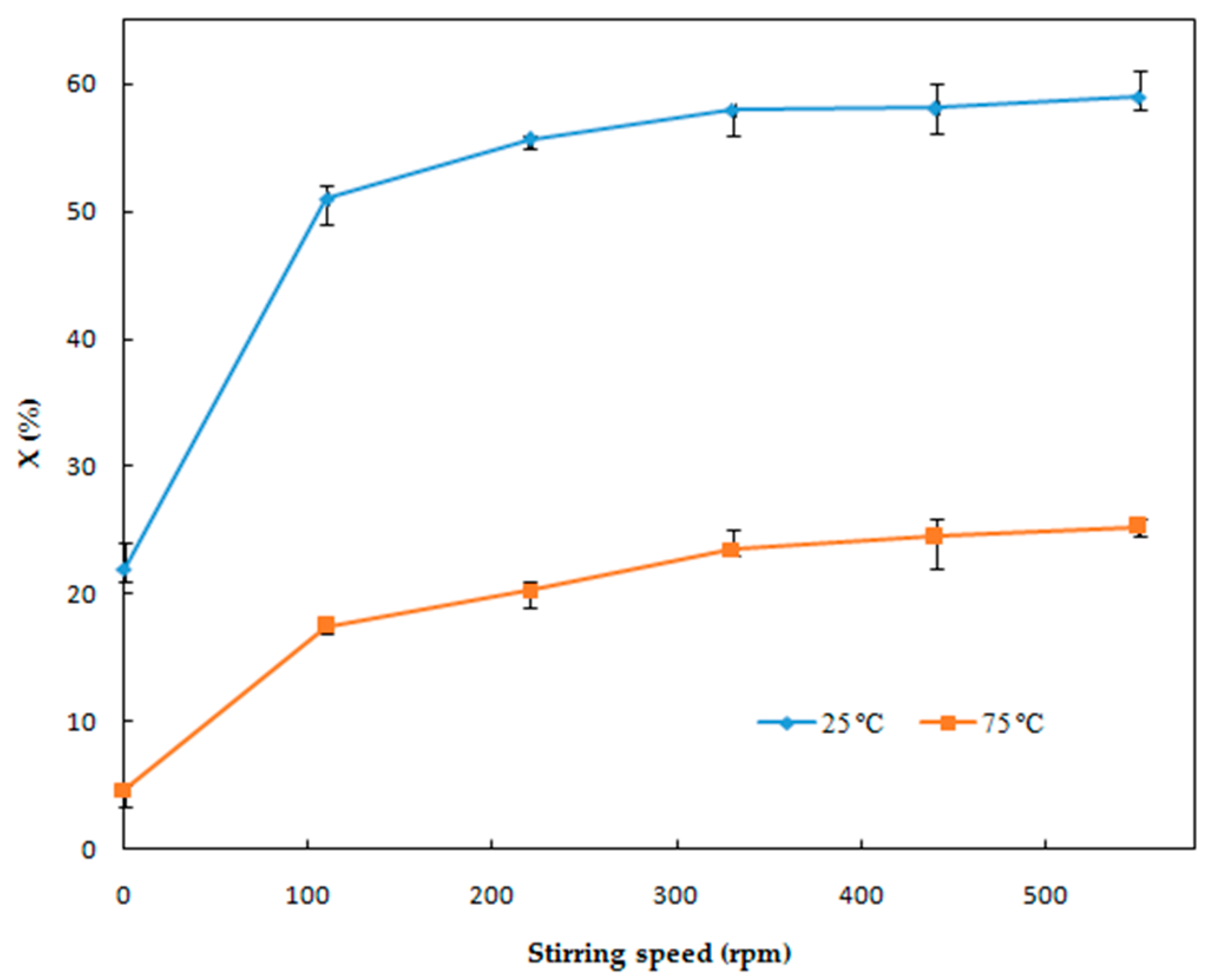
3.1.4. Effect of Stirring Speed
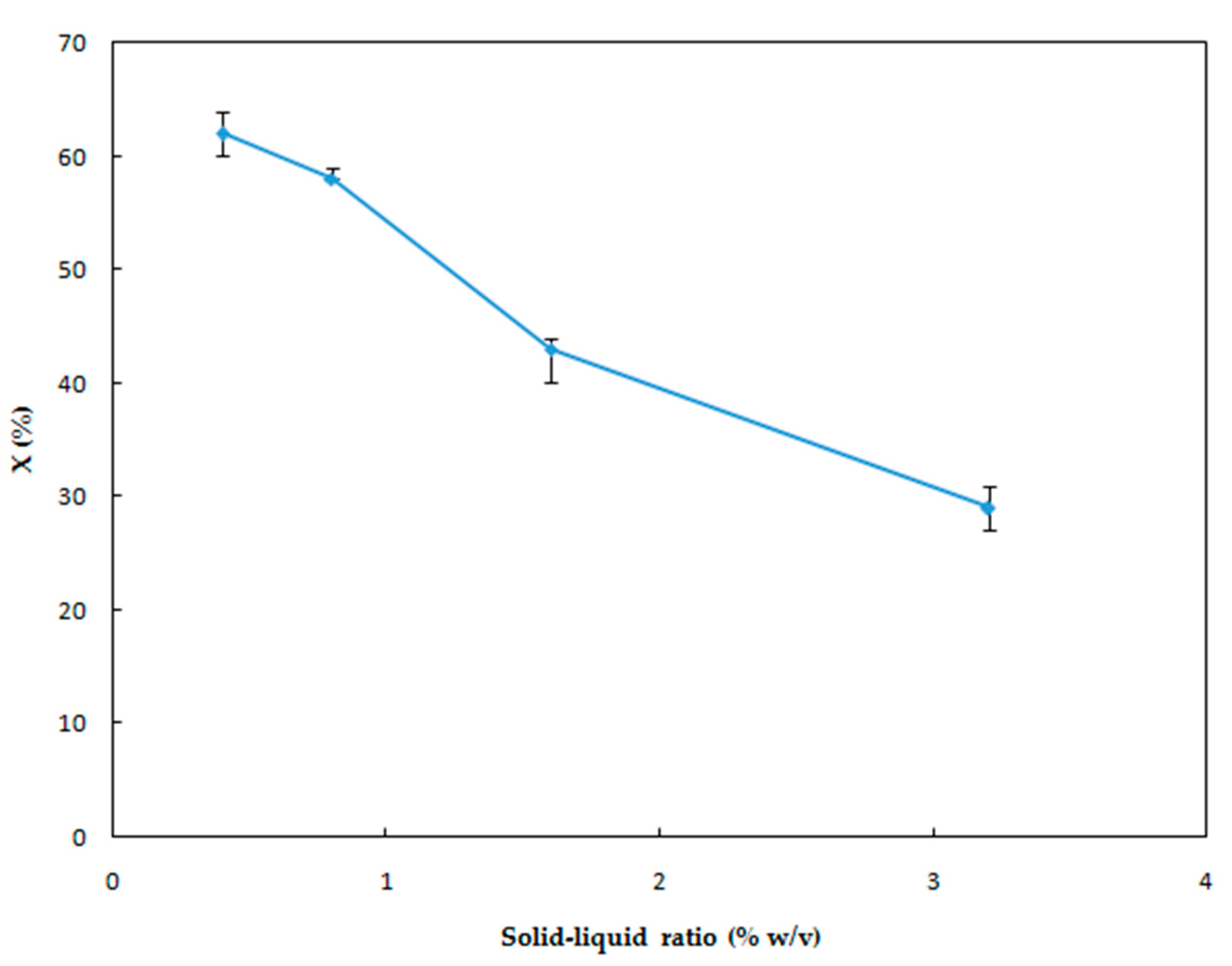
3.1.5. Effect of Solid-Liquid Ratio
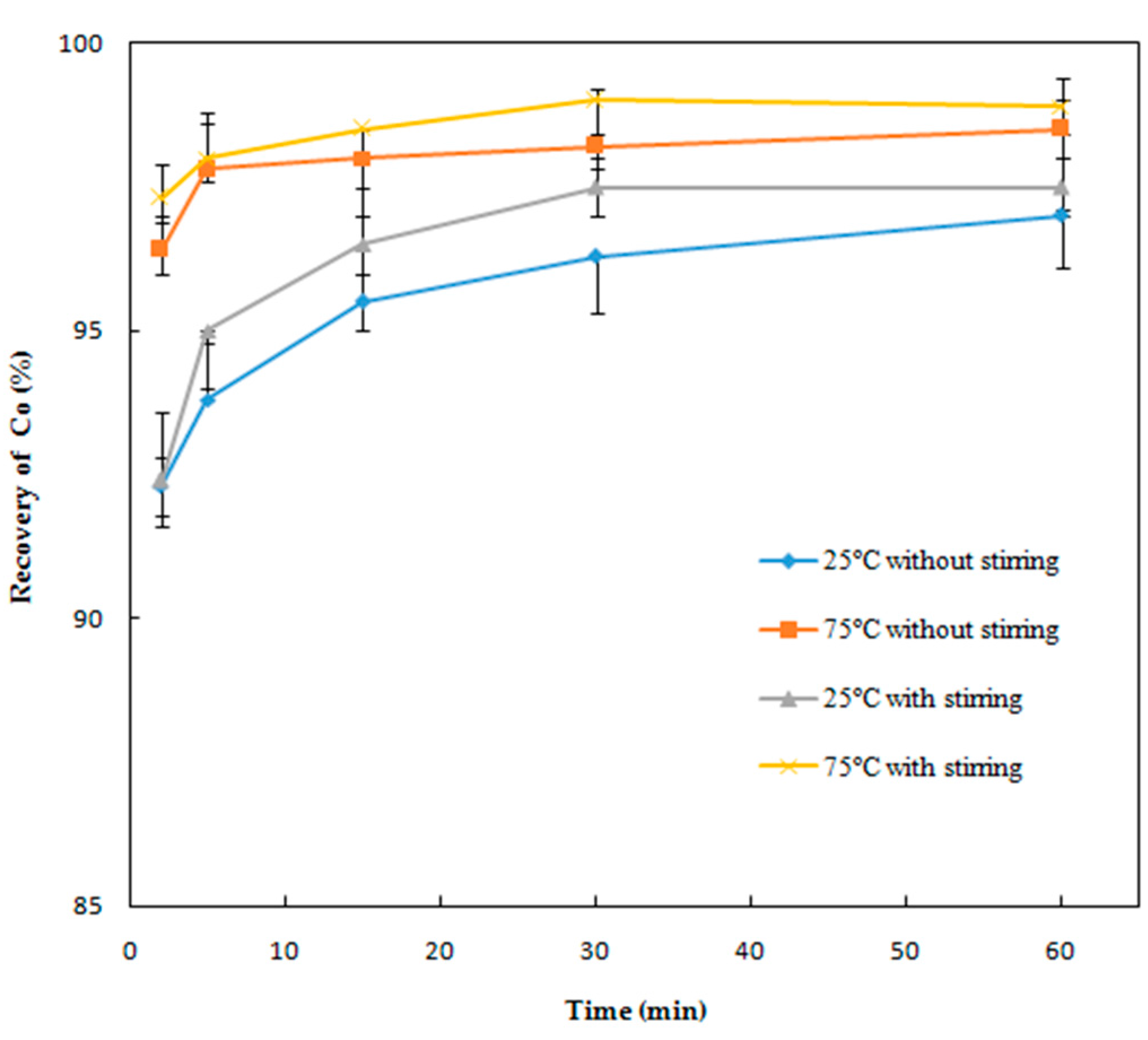
3.2. Recovery of Co and Li
3.2.1. Recovery of Co
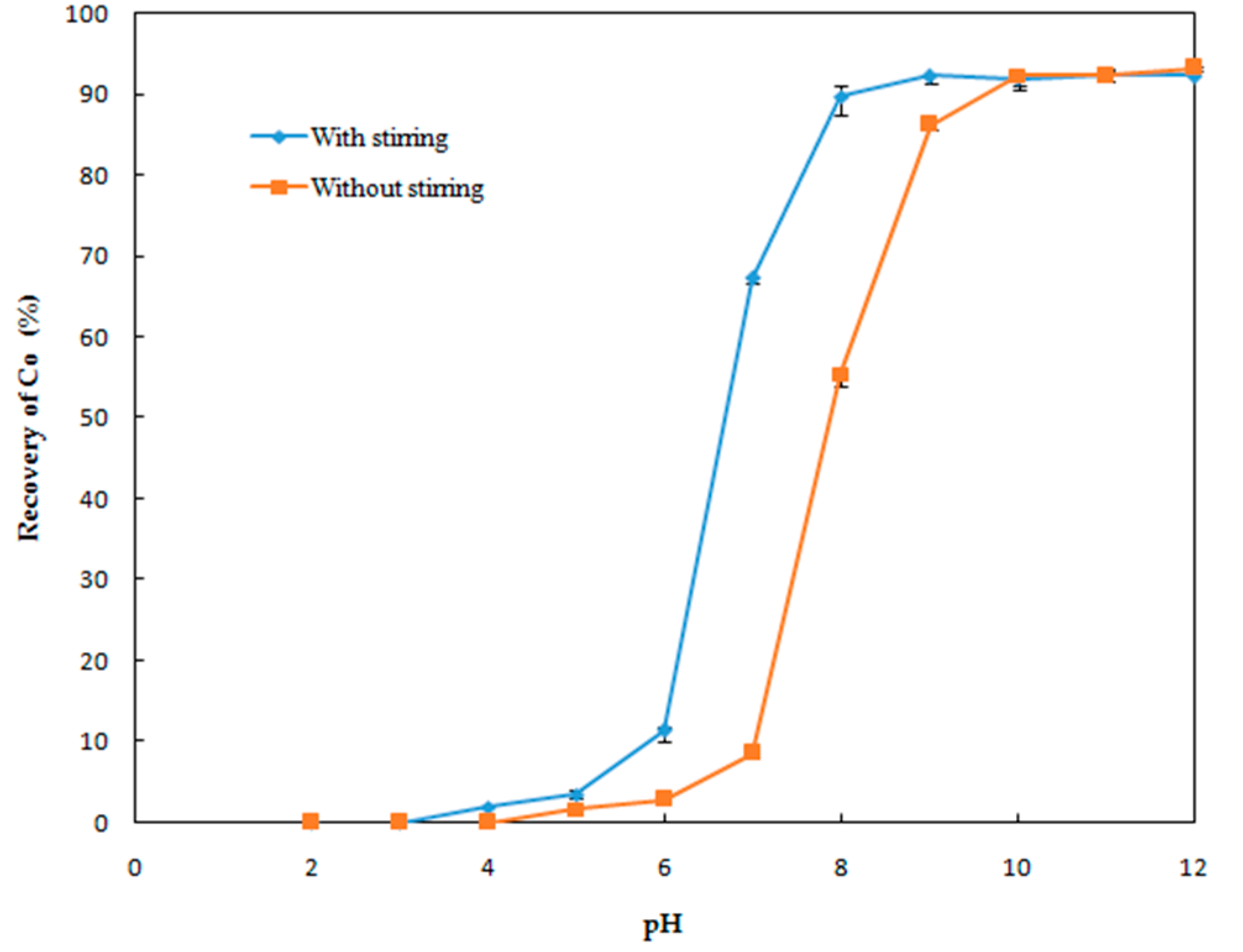
Effect of pH
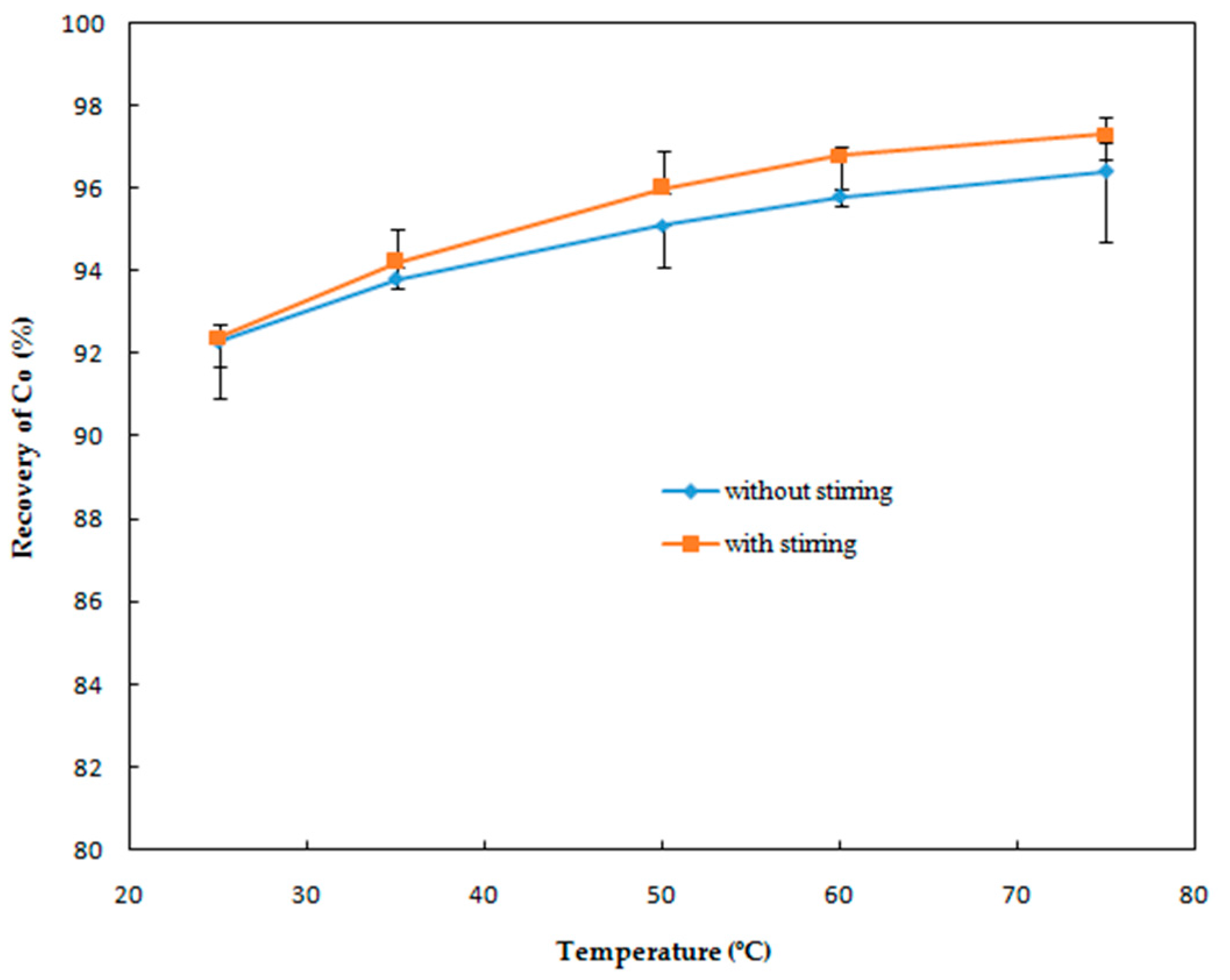
Effect of Temperature
Effect of Reaction Time
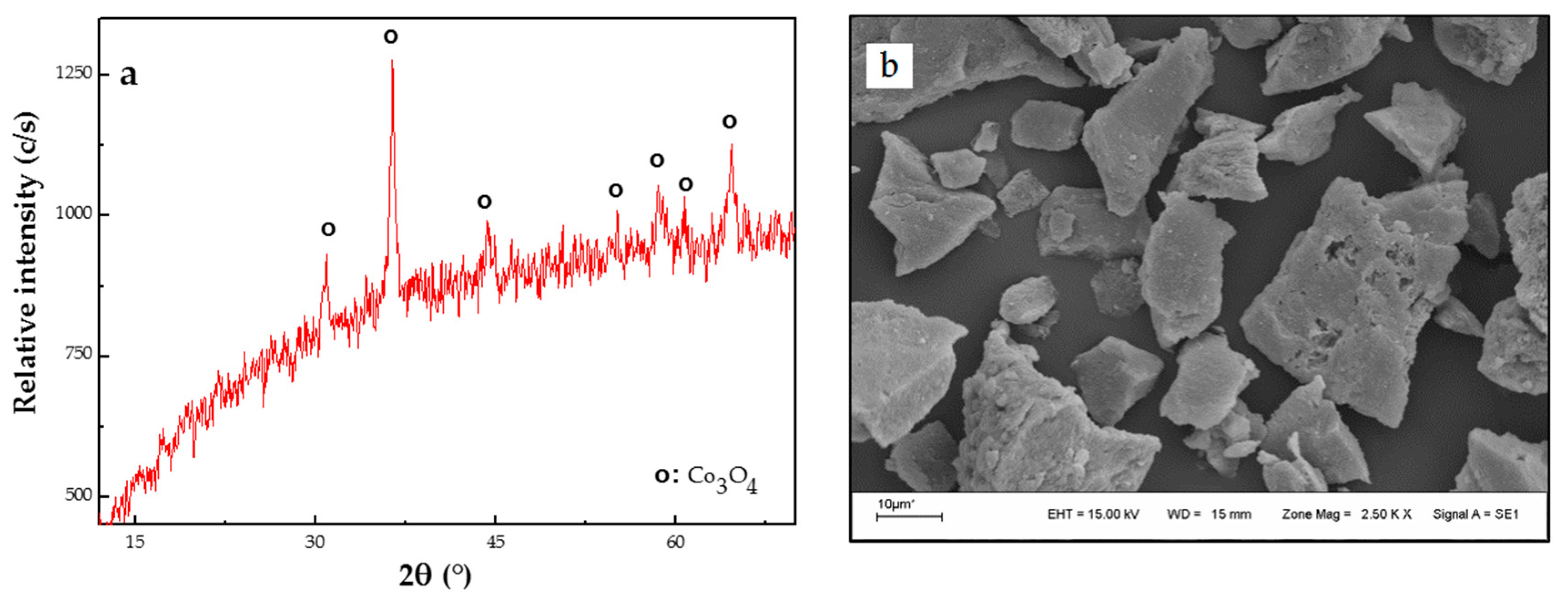
Synthesis of Co3O4
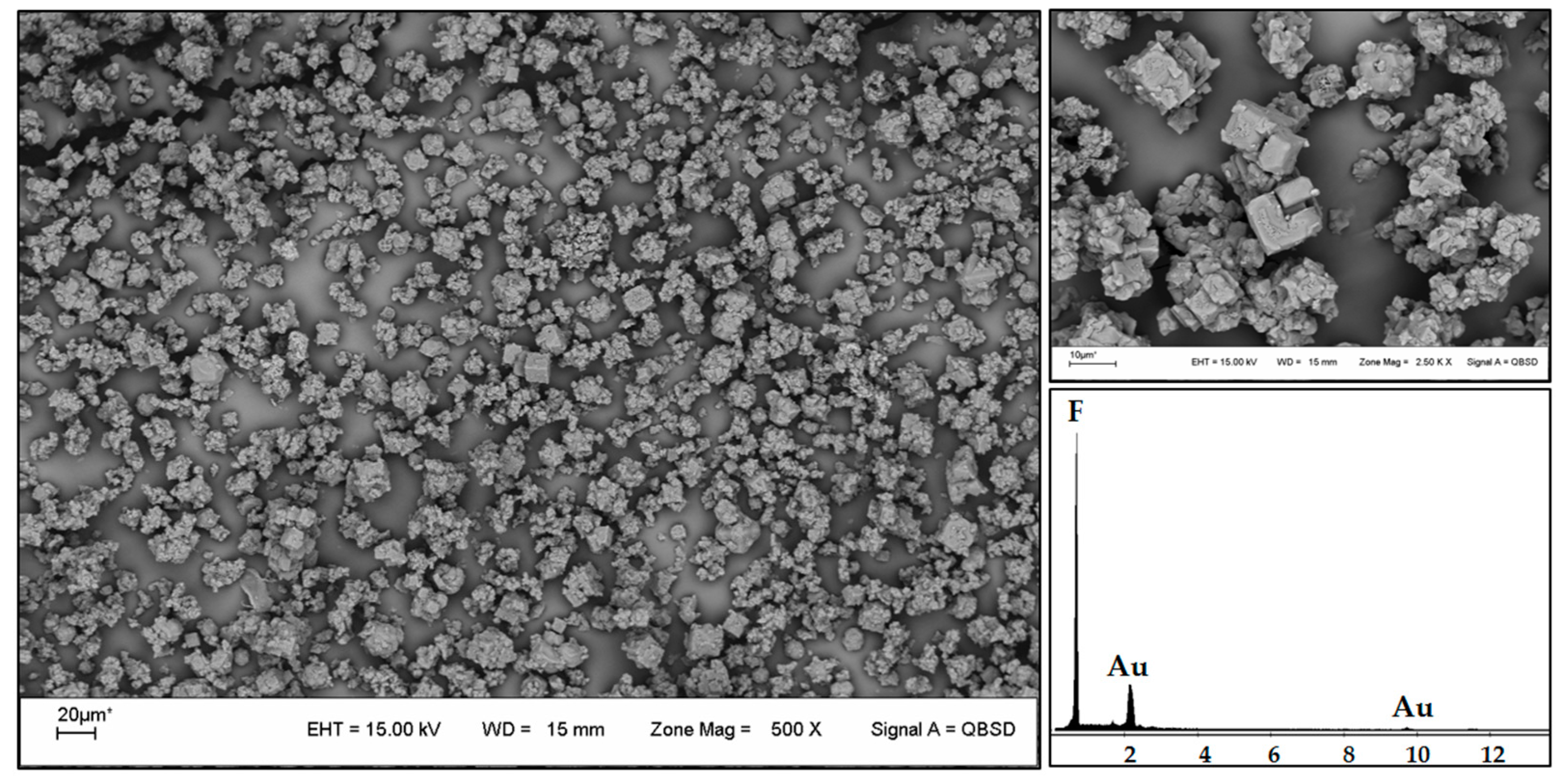
3.2.2. Recovery of Li
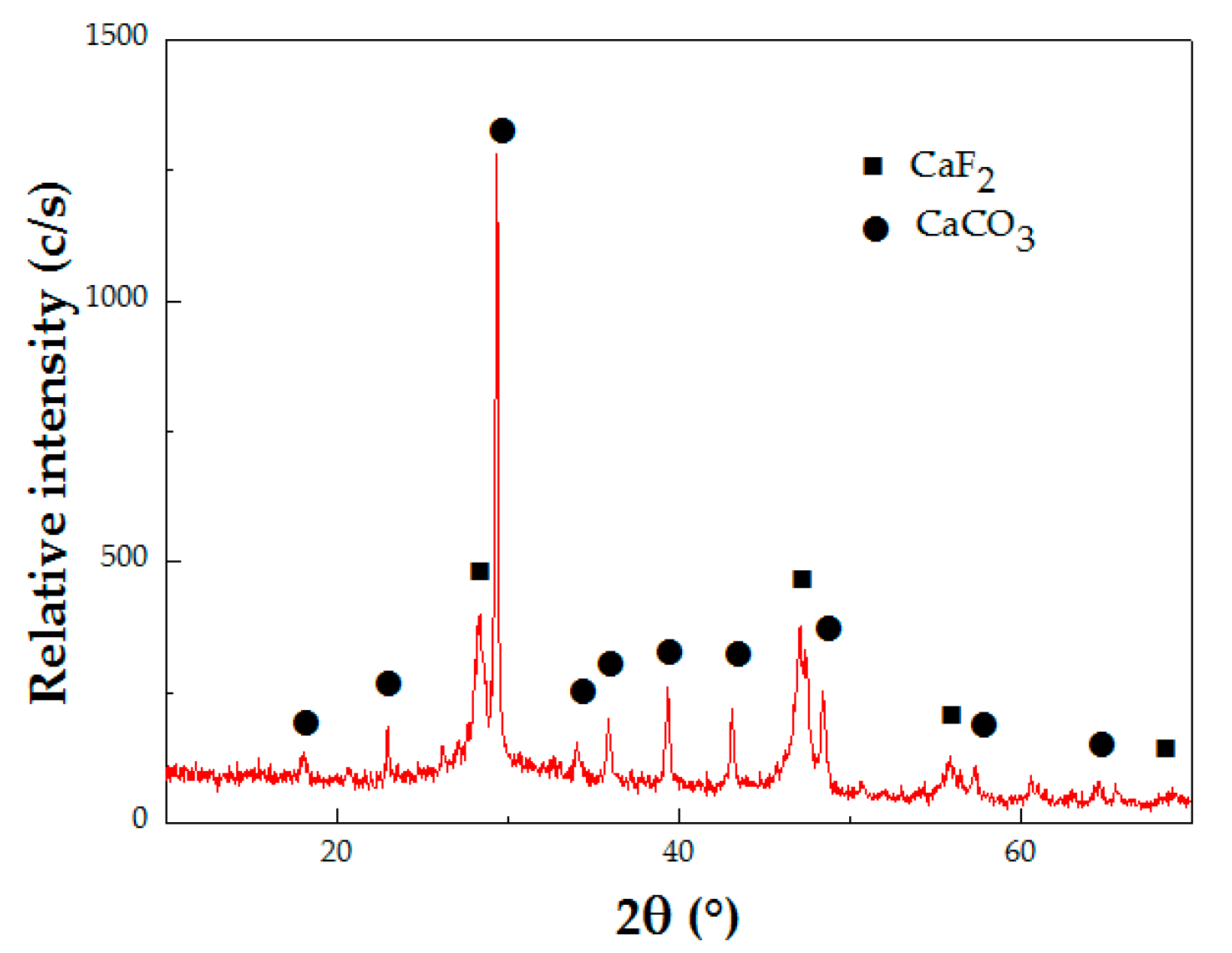
3.3. Elimination of F− Ion as CaF2
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habashi, F. Handbook of Extractive Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 1997; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- USGS National Minerals Information Center. Cobalt Statics and Information. Available online: http//minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/cobalt/ (accessed on 14 April 2017).
- Ra, D.; Han, K.S. Used lithium ion rechargeable battery recycling using Etoile-Rebatt technology. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F. Handbook of Extractive Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 1997; Volume IV. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, J.; Han, D.; Zuo, X. Recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion batteries with chemical deposition and solvent extraction. J. Power Sources 2005, 152, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Environmental friendly leaching reagent for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conard, B.R. The role of hydrometallurgy in achieving sustainable development. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 30, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, S.H. A novel recovery process of metal values from the cathode active materials of the lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Q.; Thomas, H.R.; Francis, R.W.; Lumb, K.R.; Wang, J.; Liang, B. A review of processes and technologies for the recycling of lithium-ion secondary batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, M.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B. A laboratory-scale lithium-ion battery recycling process. J. Power Sources 2001, 92, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantuano, D.; Dorella, G.; Elias, C.; Mansur, M. Analysis of a hydrometallurgical route to recover base metals from spent rechargeable batteries by liquid-liquid extraction with Cyanex 272. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, S.; Ansart, F.; Laberty-Robert, C.; Portal, J. Advances in the recovery of spent lithium battery compounds. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Rhee, K. Preparation of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yokoyama, T.; Itabashi, O.; Suzuki, T.M.; Inoue, K. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 47, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dunn, J.; Zhang, X.; Gaines, L.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Recovery of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries with organic acids as a leaching reagents and environmental assessment. J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacova, Z.; Havlik, T.; Kukurugya, F.; Orac, D. Cobalt and lithium recovery from active mass of spent Li-ion batteries: Theoretical and experimental approach. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, E.G.; Ruiz, M.C.; Ojeda, M.W.; Rodriguez, M.H. Cathodes of spent Li-ion batteries: Dissolution with phosphoric acid and recovery of lithium and cobalt from leach liquors. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Rhee, K.I. Reductive leaching of cathodic active materials from lithium ion batteries wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 68, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Kumari, A.; Jha, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Hait, J.; Pandey, B.D. Recovery of lithium and cobalt from waste lithium ion batteries of mobile phone. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayl, A.A.; Elkhashab, R.A.; Badawy, S.M.; El-Khateeb, M.A. Acid leaching of mixed spent Li-ion batteries. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; He, W.; Li, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J. Recovery of Co and Li from spent lithium-ion batteries by combination method of acid leaching and chemical precipitation. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Senanayake, G.; Sohn, J.; Shin, S.M. Recovery of cobalt sulfate from spent lithium ion batteries by reductive leaching and solvent extraction with Cyanex 272. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 100, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorella, G.; Mansur, M.B. A study of the separation of cobalt from Li-ion battery residues. J. Power Sources 2007, 170, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Sohn, J.S.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Development of a metal recovery process from Li-ion battery wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 79, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, B.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, G.H.; Sohn, J.S. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of cobalt from waste cathodic active material generated during manufacturing of lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, P.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chang, C.C. A combined recovery process of metals in spent lithium-ion batteries. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Qiu, K. Organic oxalate as leachant and precipitant for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Fan, S. Hydrometallurgical recovery of metal values from sulfuric acid leaching liquor of spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, J.; Han, D.; Yang, M.; Cui, M.; Hou, X. Recovery of metal values from a mixture of spent lithium-ion batteries and nickel-metal hydride batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 84, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, G.; Ruiz, M.C.; Rodriguez, M. Novel process for the extraction of lithium from β-spodumene by leaching with HF. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 147–148, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandová, J.; Dvořák, P.; Vu, H. Processing of zinnwaldite waste to obtain Li2CO3. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garret, D.E. Part 1-Lithium. In Handbook of Lithium and Natural Calcium Chloride; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.; Pohl, A.; Chakravadhanula, V.S.K.; Kübel, C.; Fichtner, M. LiF/Fe/V2O5 nanocomposite as high capacity cathode for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 267, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemnitz, E.; Scholz, G.; Rüdiger, S. Functionalized Inorganic Fluorides Synthesis: Characterization & Properties of Nanostructured Solids; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fasel, D.; Tran, M.Q. Availability of lithium in the context of the future D-T fusion reactors. Fusion Eng. Des. 2005, 75–79, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, G.; Ruiz, M.C.; Rodriguez, M. Alkaline metal fluorides synthesis as subproduct of β-spodumene leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 139, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontino, P.J.; Busnardo, N.G.; Afonso, J.C. Recovery of valuable elements from spent Li-batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 843–849. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroga, O.D.; Avanza, J.R.; Fusco, A.J. Modelado Cinético de las Transformaciones Fluido-Sólido Reactivo, 1st ed.; EUDENE: Corrientes, Argentina, 1996. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Habashi, F. Principles of Extractive Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
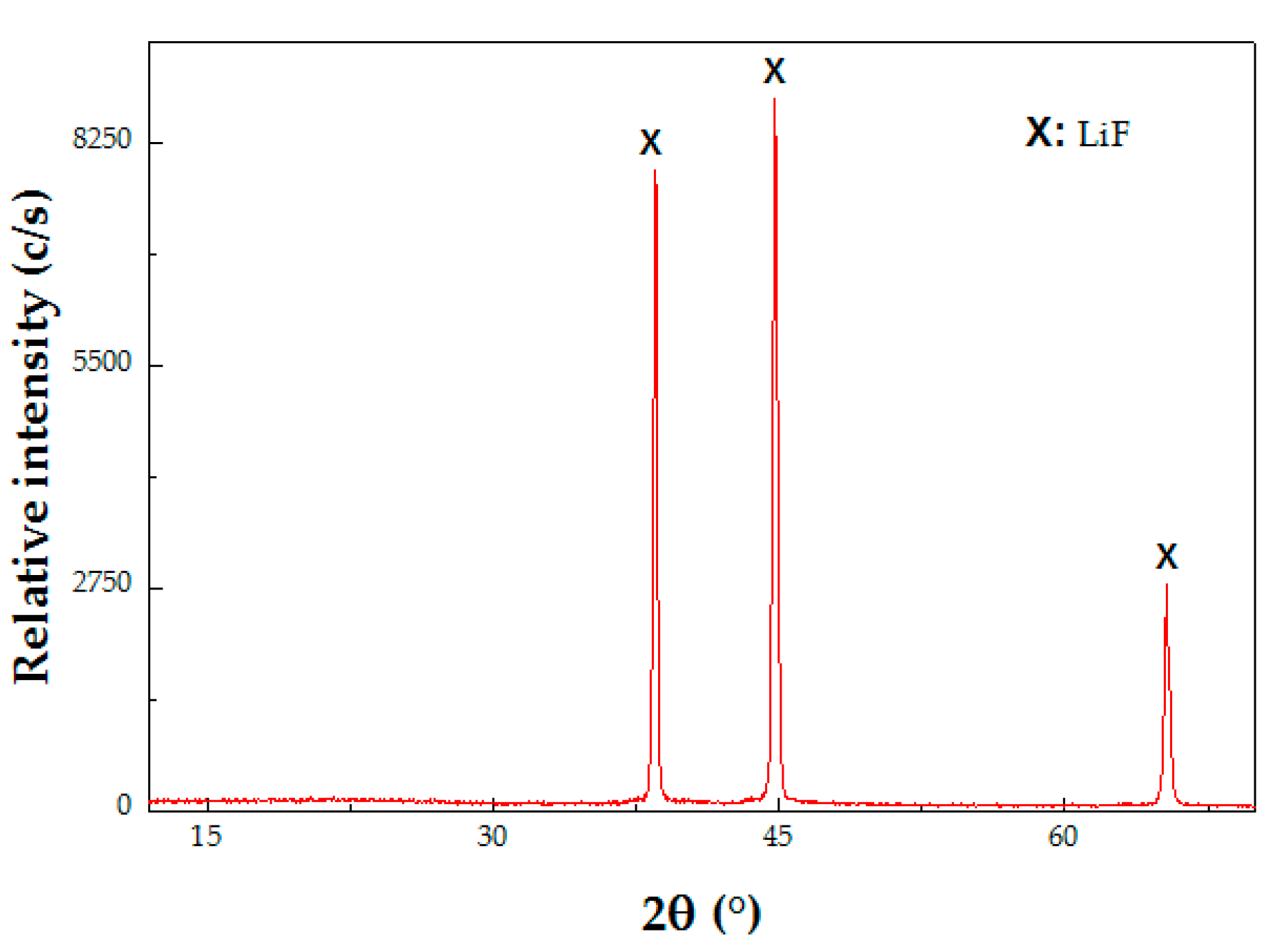

| Purity of LiF (wt %) | Elemental Composition (wt %) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | F | Na | K | Ca | Al | Others | |
| 98.4 | 26.5 | 71.9 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.78 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suarez, D.S.; Pinna, E.G.; Rosales, G.D.; Rodriguez, M.H. Synthesis of Lithium Fluoride from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. Minerals 2017, 7, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050081
Suarez DS, Pinna EG, Rosales GD, Rodriguez MH. Synthesis of Lithium Fluoride from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. Minerals. 2017; 7(5):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050081
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuarez, Daniela S., Eliana G. Pinna, Gustavo D. Rosales, and Mario H. Rodriguez. 2017. "Synthesis of Lithium Fluoride from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries" Minerals 7, no. 5: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050081
APA StyleSuarez, D. S., Pinna, E. G., Rosales, G. D., & Rodriguez, M. H. (2017). Synthesis of Lithium Fluoride from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. Minerals, 7(5), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7050081





