Enhancement of Biofilm Formation on Pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
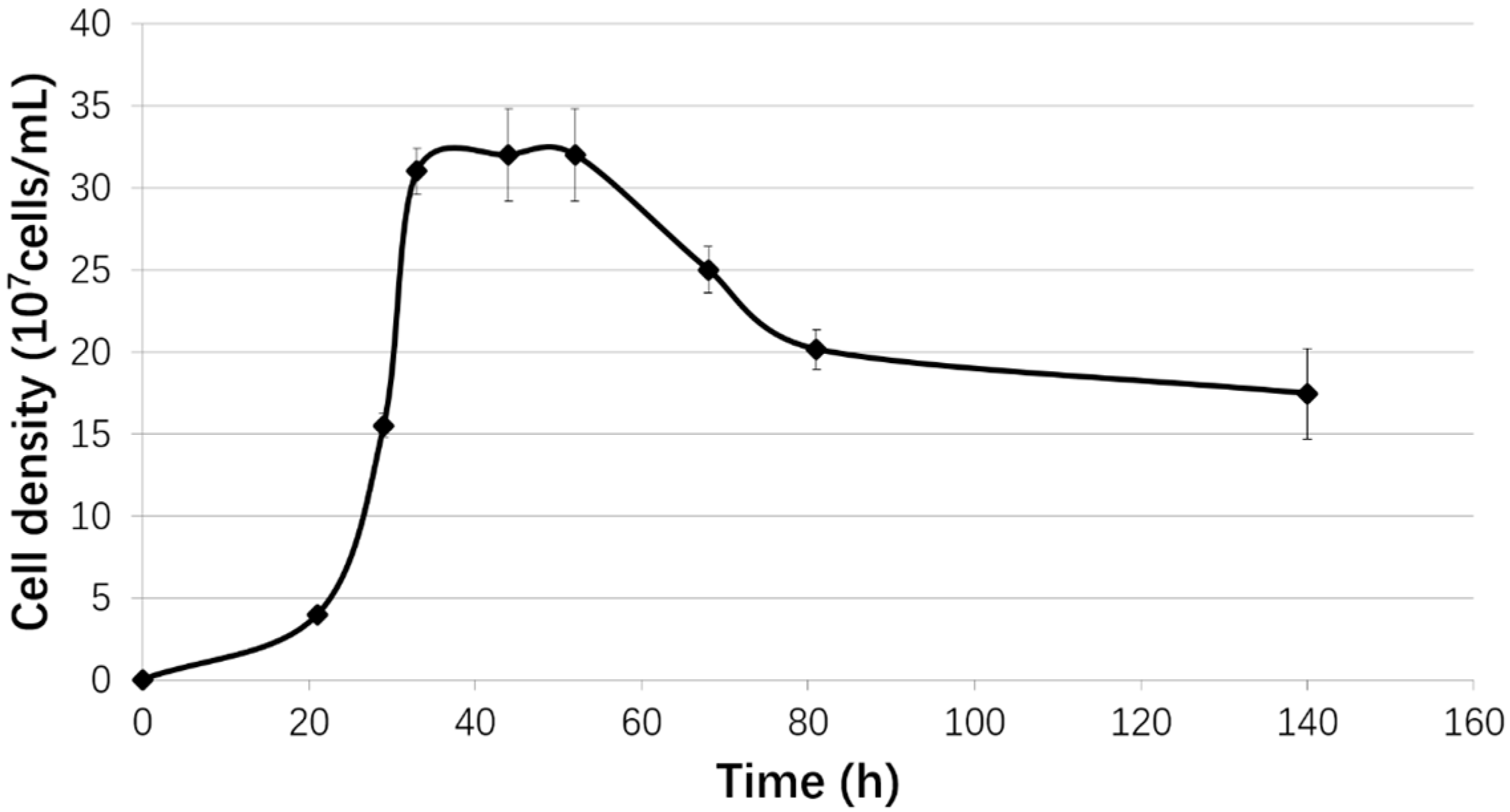
2.1. Strain and Growth Conditions
2.2. Preparation of Pyrite Grains and Pyrite Slices
2.3. Strategies for Enhancing Biofilm Formation
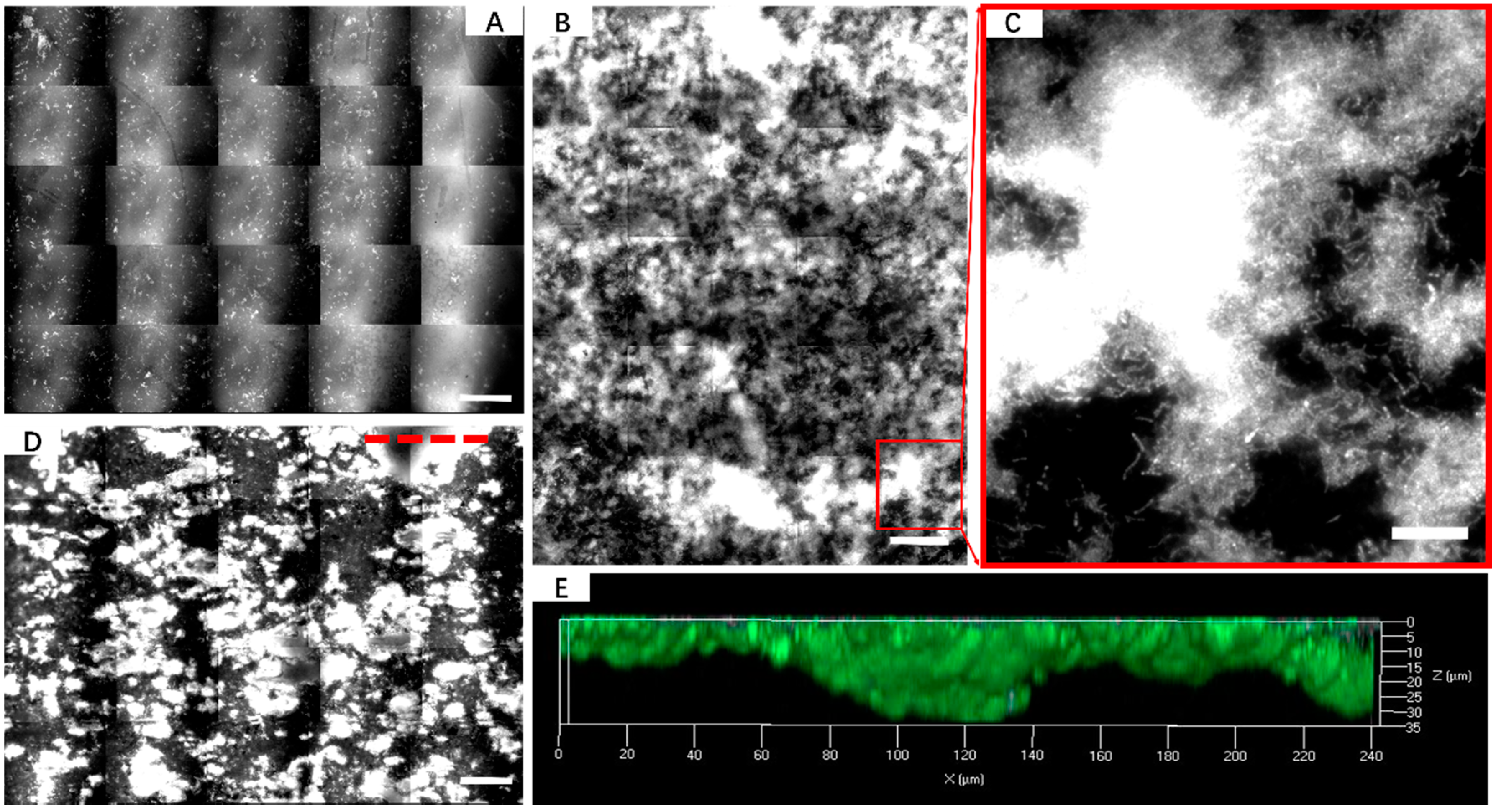
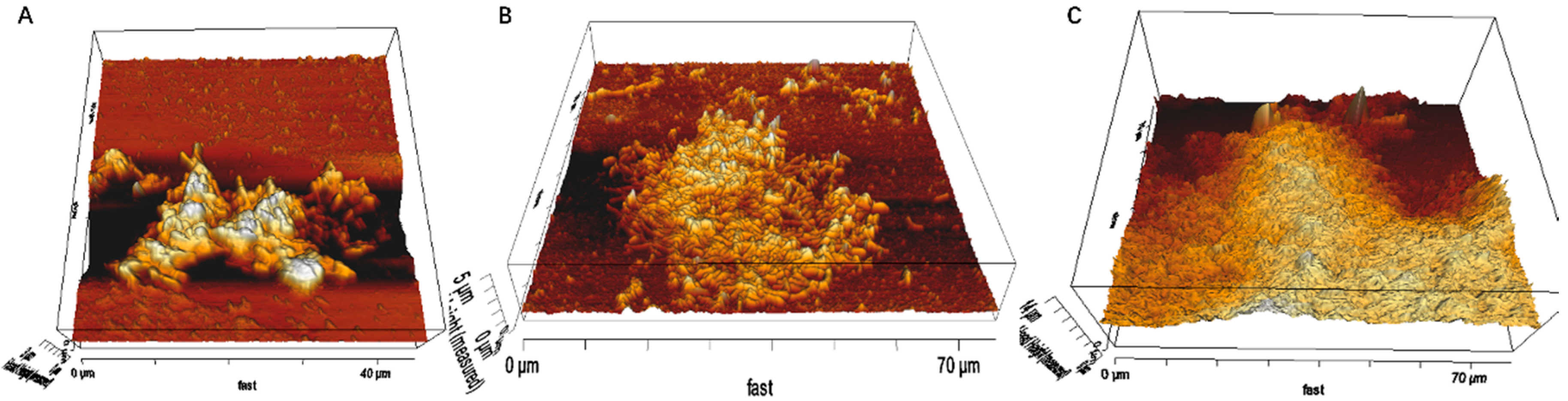
2.4. AFM, EFM and CLSM
3. Results and Discussion
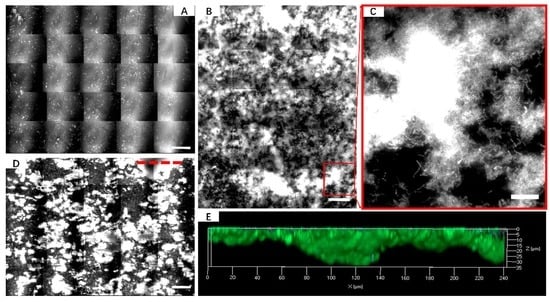
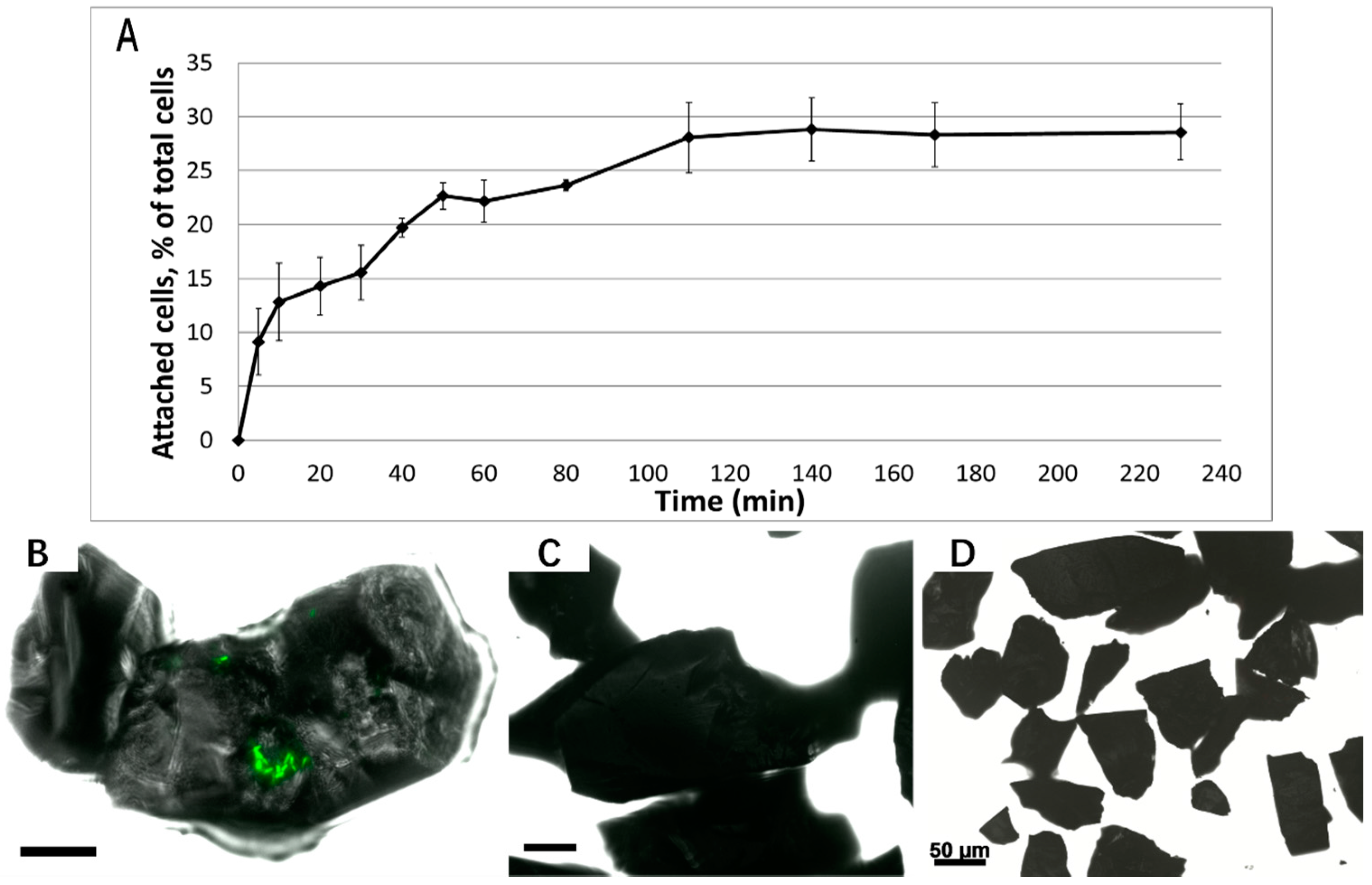
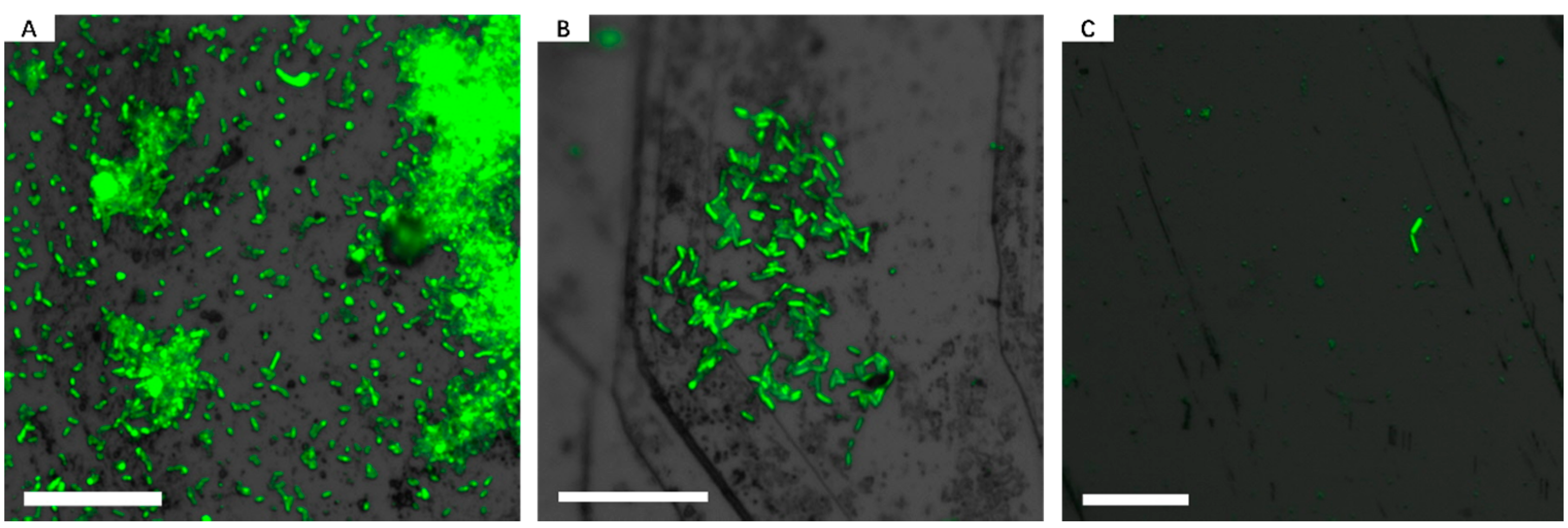
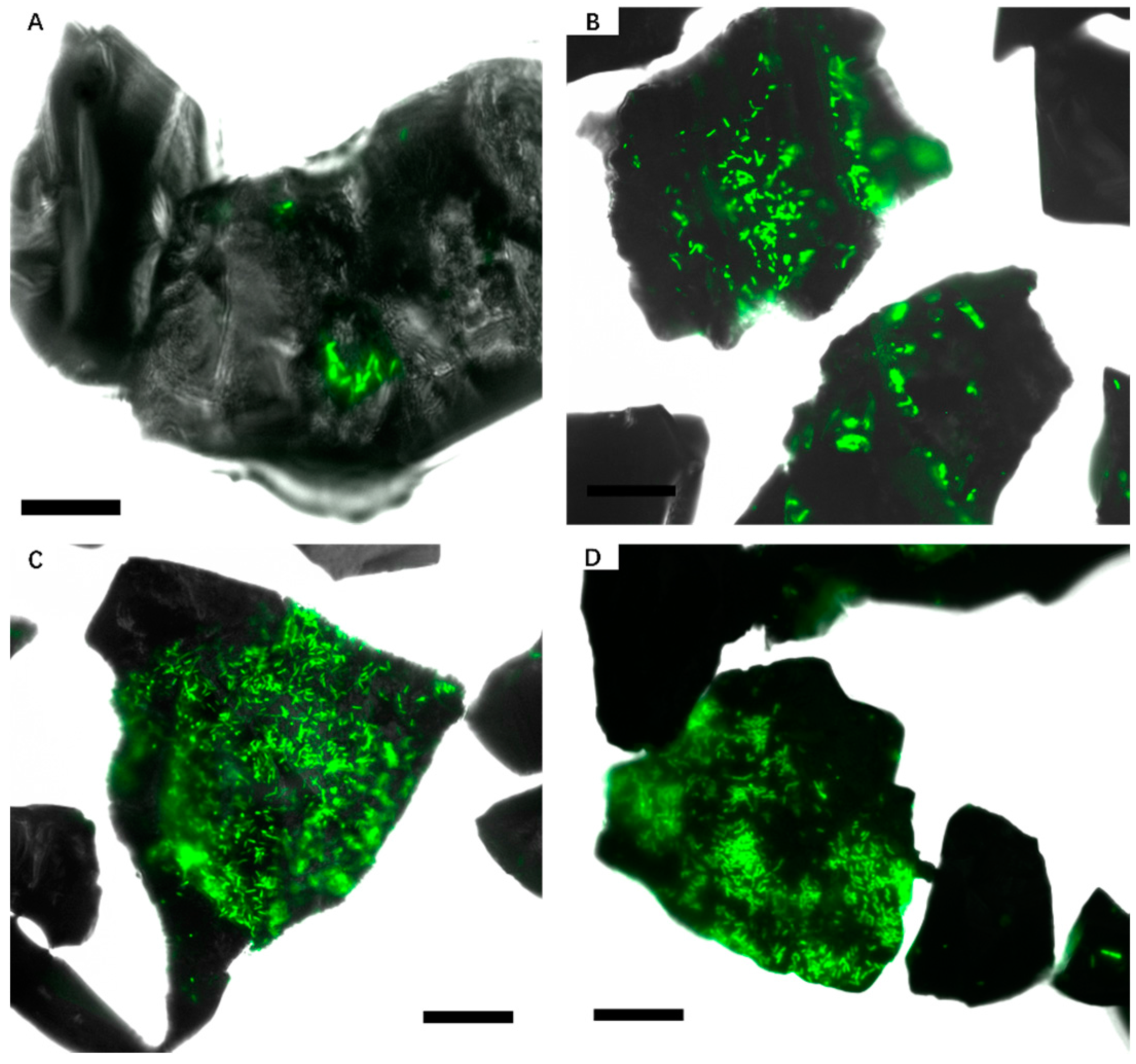
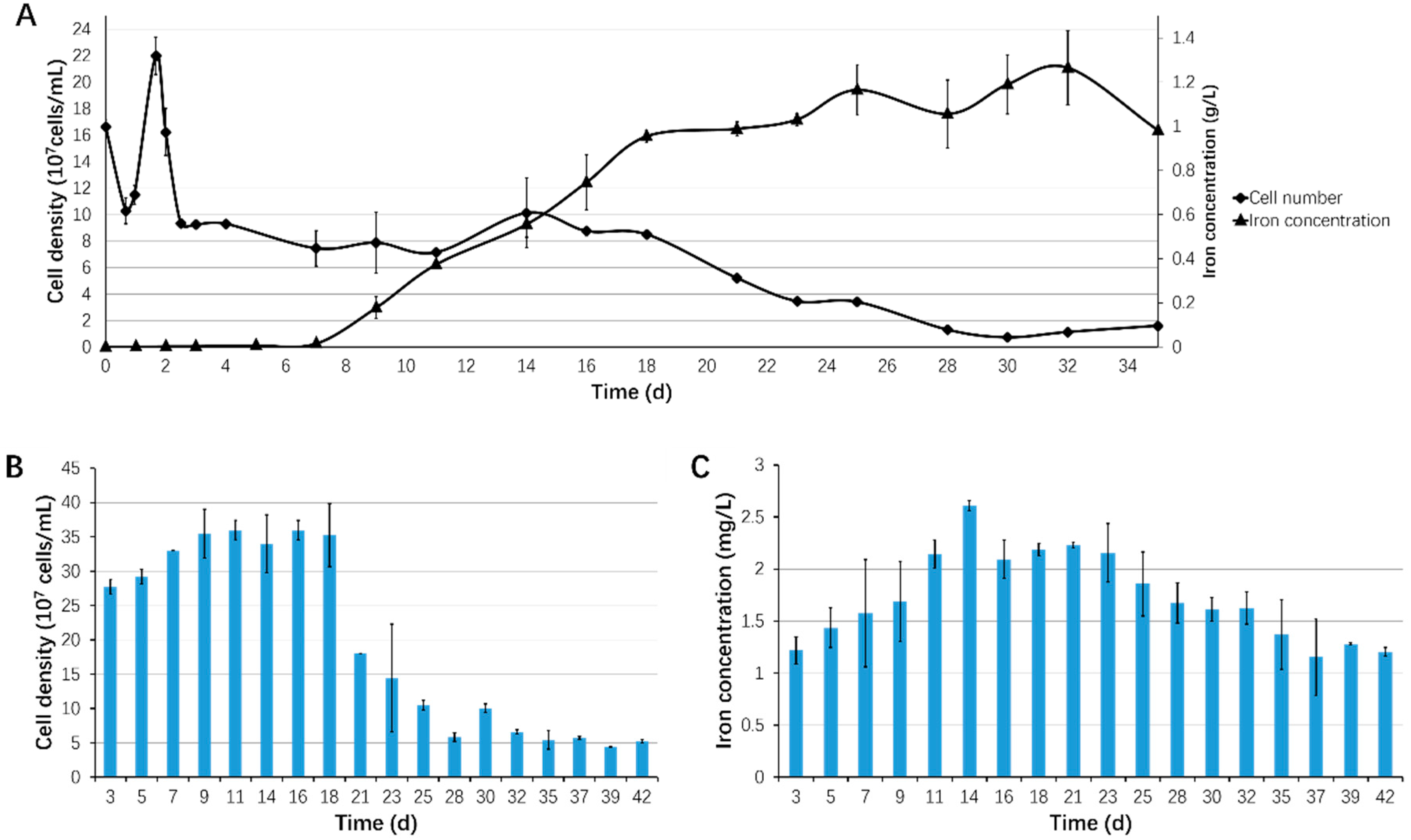
3.1. Biofilm Formation of Sb. thermosulfidooxidans on Pyrite under Standard Conditions
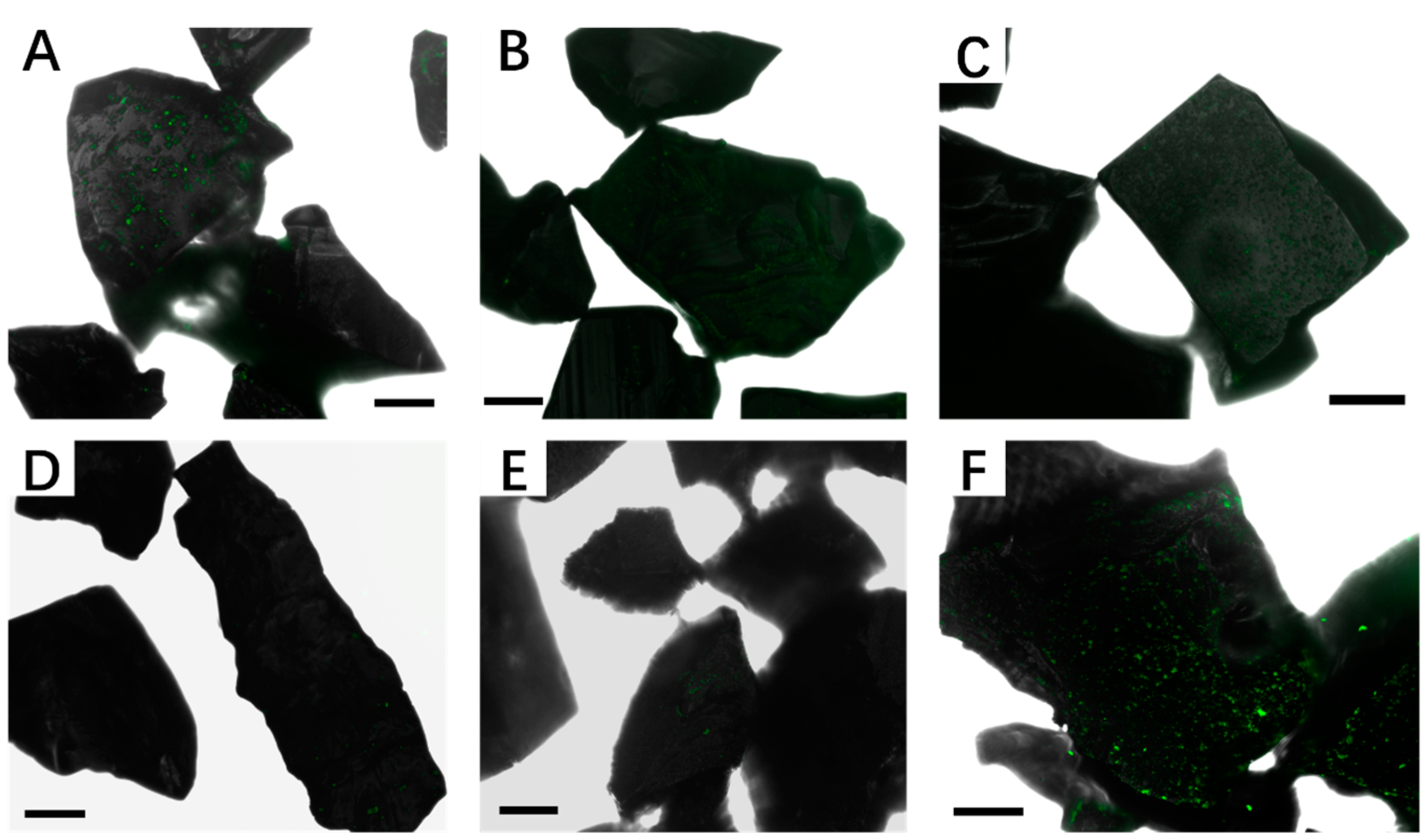
3.2. Effect of Different Strategies on Enhancement of Biofilm Formation by Sb. thermosulfidooxidans on Pyrite
3.3. Bioleaching of Sb. thermosulfidooxidans under Biofilm-Favoring Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohwerder, T.; Gehrke, T.; Kinzler, K.; Sand, W. Bioleaching review part A: Progress in bioleaching: Fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 63, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watling, H. Microbiological advances in biohydrometallurgy. Minerals 2016, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, W.; Gehrke, T.; Jozsa, P.G.; Schippers, A. (Bio)chemistry of bacterial leaching—Direct vs. Indirect bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, T.; Telegdi, J.; Thierry, D.; Sand, W. Importance of extracellular polymeric substances from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for bioleaching. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2743–2747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brierley, C.L.; Brierley, J.A. Progress in bioleaching: Part B: Applications of microbial processes by the minerals industries. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7543–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkin, E.; Keeling, S.; Perrot, F.; Shiers, D.; Palmer, M.-L.; Watling, H. Metals tolerance in moderately thermophilic isolates from a spent copper sulfide heap, closely related to Acidithiobacillus caldus, Acidimicrobium ferrooxidans and Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okibe, N.; Gericke, M.; Hallberg, K.B.; Johnson, D.B. Enumeration and characterization of acidophilic microorganisms isolated from a pilot plant stirred-tank bioleaching operation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, M.; Galleguillos, P.; Ghorbani, Y.; Tapia, P.; Contador, Y.; Velásquez, A.; Espoz, C.; Pinilla, C.; Demergasso, C. Variation in microbial community from predominantly mesophilic to thermotolerant and moderately thermophilic species in an industrial copper heap bioleaching operation. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 150, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovacheva, R.; Karavaĭko, G. Sulfobacillus, a new genus of thermophilic sporulating bacteria. Mikrobiologiia 1978, 47, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, D.E.; Johnson, D.B. The microbiology of biomining: Development and optimization of mineral-oxidizing microbial consortia. Microbiology 2007, 153, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolaore, P.; Joulian, C.; Gouin, J.; Morin, D.; d’Hugues, P. Relationship between bioleaching performance, bacterial community structure and mineralogy in the bioleaching of a copper concentrate in stirred-tank reactors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucher, S.; Battaglia-Brunet, F.; d’Hugues, P.; Clarens, M.; Godon, J.; Morin, D. Evolution of the bacterial population during the batch bioleaching of a cobaltiferous pyrite in a suspended-solids bubble column and comparison with a mechanically agitated reactor. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.; Gorham, N.; Shiers, D.; Watling, H. In situ imaging of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans on pyrite under conditions of variable pH using tapping mode atomic force microscopy. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, P.; Sauer, K.; Davies, D.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Jiao, W.; Jiang, H.; Sand, W.; Xia, J.; Liu, X.; Qin, W.; Qiu, G.; Hu, Y. Adhesion forces between cells of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans or Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and chalcopyrite. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 94, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrene, Y.F. Sticky microbes: Forces in microbial cell adhesion. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Li, Q.; Gan, M.; Jiang, H.; Qin, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, G. Insights into the relation between adhesion force and chalcopyrite-bioleaching by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 126, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackintosh, M. Nitrogen fixation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1978, 105, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, A.; Jozsa, P.; Sand, W. Sulfur chemistry in bacterial leaching of pyrite. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Bellenberg, S.; Neu, T.R.; Sand, W.; Vera, M. The biofilm lifestyle of acidophilic metal/sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms. In Biotechnology of Extremophiles: Advances and Challenges; Rampelotto, H.P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 177–213. [Google Scholar]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Kolter, R. Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 30, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, J.J.; Therit, B.; Melville, S.B. Type IV pili and the CcpA protein are needed for maximal biofilm formation by the gram-positive anaerobic pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdany, S.; Lashkari, K. Effect of pH on sporulation of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 30, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watling, H.R.; Perrot, F.A.; Shiers, D.W. Comparison of selected characteristics of Sulfobacillus species and review of their occurrence in acidic and bioleaching environments. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenberg, S.; Barthen, R.; Boretska, M.; Zhang, R.; Sand, W.; Vera, M. Manipulation of pyrite colonization and leaching by iron-oxidizing Acidithiobacillus species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sand, W.; Gerke, T.; Hallmann, R.; Schippers, A. Sulfur chemistry, biofilm, and the (in)direct attack mechanism—A critical evaluation of bacterial leaching. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 43, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R.C.; Shute, E.A.; Howard, G.T. Solubilization of minerals by bacteria: Electrophoretic mobility of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in the presence of iron, pyrite, and sulfur. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Kim, J.; Danhorn, T.; Merritt, P.M.; Fuqua, C. Phosphorus limitation increases attachment in Agrobacterium tumefaciens and reveals a conditional functional redundancy in adhesin biosynthesis. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellenberg, S.; Leon-Morales, C.-F.; Sand, W.; Vera, M. Visualization of capsular polysaccharide induction in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 129–130, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Boyd, C.D.; O’Toole, G.A.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Single-molecule analysis of Pseudomonas fluorescens footprints. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errington, J. Regulation of endospore formation in Bacillus subtilis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 1, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, D.; Mielke, R.; Southam, G.; Porter, T. Scanning force microscopy studies of the colonization and growth of A. ferrooxidans on the surface of pyrite minerals. Scanning 2005, 27, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Sand, W.; Zhang, R. Enhancement of Biofilm Formation on Pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. Minerals 2016, 6, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6030071
Li Q, Sand W, Zhang R. Enhancement of Biofilm Formation on Pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. Minerals. 2016; 6(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qian, Wolfgang Sand, and Ruiyong Zhang. 2016. "Enhancement of Biofilm Formation on Pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans" Minerals 6, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6030071
APA StyleLi, Q., Sand, W., & Zhang, R. (2016). Enhancement of Biofilm Formation on Pyrite by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. Minerals, 6(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6030071