Abstract
Microorganisms have developed various mechanisms to deal with metals, thus providing numerous tools that can be used in biohydrometallurgical processes. “Biomining” processes—including bioleaching and biooxidation processes—facilitate the degradation of minerals, accompanied by a release of metals. These processes are especially attractive for low-grade ores and are used on an industrial scale mainly for sulfidic ores. In biosorption processes, biomass or certain biomolecules are used to bind and concentrate selected ions or other molecules from aqueous solutions. Biosorptive materials can be an environmentally friendly and efficient alternative to conventional materials, such as ion exchange resins. Other interesting mechanisms are bioaccumulation, bioflotation, bioprecipitation, and biomineralisation. Although these processes are well-known and have been studied in detail during the last decades, the recent strong progress of biotechnologies (e.g., genetic engineering and molecule design), as well as their combination with novel developments in material sciences (e.g., nanotechnologies) facilitate new strategies for the application of biotechnologies in mineral processing. The article gives a summary of current activities in this field that are being performed in our group.
1. Introduction
During their evolution, microorganisms have developed many mechanisms to deal with toxic metals or to capture essential trace elements, thus regulating the mobility of the metals in the environment. Enzymatically-catalyzed reductions are well-investigated—e.g., of U(VI) to U(IV) [1,2], biooxidation, dissolution of minerals by weathering processes, bioprecipitation, biosorption, and bioaccumulation. These processes are not only relevant to understanding biogeochemical cycles, but are attractive for their application in the mining sector, such as metal recovery as well as for the microbial-mediated decontamination of heavy-metal polluted environments [3,4]. The understanding of the role of microorganisms in the mobilisation or immobilization of metals, as well as the investigation of the underlying processes, are of great importance for such developments.
In the past, the interactions of microbes, metabolites, cell compounds, or biomolecules with minerals and/or metals have been applied in different resource technologies—such as mineral degradation (“biomining”), metal recovery (e.g., via biosorption or bioaccumulation), or bioflotation. The latter takes advantage of the ability of certain bacteria or biomolecules to specifically bind to mineral surfaces. Bioflotation processes have been used, for example, for the separation of calcite and magnesite where cells of Rhodococcus opacus had been used as collector [5]. Other researchers used microorganisms such as Mycobacterium phei, Bacillus subtilis, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, and Aspergillus niger for bioflotation of hematite and quartz, pyrite, chalcopyrite, and others [5,6,7]. Recently, Curtis et al. (2009) used bacteriophages carrying genetically engineered protein coatings designed for the binding of inorganic particles for the flotation of chalcopyrite and pyrite [8].
The term “Biomining” describes the use of microorganisms for degrading minerals that enables the recovery of target metals. Generally, biomining comprises two different processes—namely, “bioleaching” and “biooxidation” [9]. Both processes are attractive alternatives to conventional smelting processes, which discharge large amounts of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and various toxic materials such as arsenic.
In the case of bioleaching, the target metals are solubilized as a result of mineral dissolution. In the case of biooxidation, the valuable metal remains in the solid phase, but becomes enriched. Thus, it can be used as a pretreatment process to degrade minerals sulfides to obtain concentrates.
In our group at the Helmholtz-Institute Freiberg for Resource Technology, we are pursuing different novel concepts that use microorganisms, microbial metabolites or proteins, designed biomolecules, or bio-based hybrid nanomaterials for the extraction and recovery of metals from primary and secondary resources. The article gives an overview of current projects and ideas.
2. Bioleaching
The integrating of bioleaching into mining strategies provides different advantages. The technology enables the extraction of metals from low-grade ores, polymetallic ores of difficult refractory concentrates where traditional methods fail. Further, microbes can help to remove arsenic or other toxic elements from concentrates in an environmentally-stable form. Commercial bioleaching processes of sulphidic ores are well-established and at the same time are relatively easy and reliable with regard to maintenance and infrastructural costs. Bioleaching is therefore attractive, especially for smaller deposits and remote locations.
Industrial processes that are currently applied focus on the bioleaching of sulfidic ores (reviewed in [10]). These approaches mainly rely on the use of chemolithoautotrophic microorganisms such as Acidithiobacillus spp., Ferrimicrobium spp., and Leptospirillum spp. that are able to use ferrous iron and/or reduced inorganic sulfur sources as electron donor. In these reactions, sulfuric acid and ferric iron are produced as byproducts, thus contributing to mineral degradation. The organisms are acidophilic and mostly grow within the pH range 1.5–2.0.
Currently there are two main types of bioleaching processes that are commercially performed. Irrigation-type processes imply the percolation of leaching solutions through crushed ores or concentrates that have been stacked in columns, heaps, or dumps, whereas stirred tank-type processes involve the operation of continuously running stirred tank reactors [11].
Modern industrial bioleaching processes mostly aim at the recovery of copper and use irrigation-type processes. The majority of commercially used stirred tank processes are focused on pretreatment via a biooxidative process for the recovery of gold from recalcitrant arsenopyrite. In these ores, the gold is finely distributed in a mixture of pyrite/arsenopyrite and cannot easily be solubilized by classical processes such as cyanidation. The arseonopyrite can be degraded by microbial activities accompanied by the liberation of gold [10].
Another bioleaching approach that is especially attractive for complex ores and non-sulfidic minerals (phosphates, oxides, carbonates, silicates)—although not yet operated on industrial scale—is the use of heterotrophic bacteria (reviewed by [12]). These approaches are attractive for the recovery of valuable metals from low-grade ores and minerals as well as for the beneficiation of minerals or the recovery of metals from secondary resources such as waste products. Generally, aerobic microorganisms cannot gain energy from non-sulfidic ores. Leaching of these ores using heterotrophic microorganisms requires an organic carbon source for their growth and as a source of energy. During this consumption, the microorganisms produce metabolites such as organic acids, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), or complexing agents such as siderophores that may interact with the mineral surfaces and can solubilize the metals. In addition, microbial-mediated reduction processes, acidification, or alkanization can contribute to the dissolution of minerals. As an example, the bioreduction of MnO2 (e.g., from ocean manganese nodules) by a consortium of heterotrophic bacteria was studied at pilot scale [13]. Principally, the process was working and obtained 95%–100% of manganese extraction, but it was not cost-effective. However, such an economic calculation strongly depends on the actual market situation as well as on the element of interest.
In our group, we concentrate on the development of bioleaching approaches using heterotrophic microorganisms such as bacteria and yeast strains. These approaches are especially attractive for metal recovery from complex non-sulfidic ores and secondary resources. Major challenges are to achieve high recovery rates as well as the design of cost-efficient processes. These challenges can be met by a close cooperation between microbiologists, engineers, and chemists.
2.1. Example: Bioleaching of Copper Shale
Sulfidic Kupferschiefer deposits that have been explored and exploited in Germany and Poland are Europe’s largest copper reserve, with more than 60 million tons of Cu and additional associated metals such as Ag, Pb, Zn, and possibly other high-value metals [14,15]. Kupferschiefer is a calciferous, carbon-rich marly clay with finely dispersed sulphidic copper minerals—mainly chalcocite, bornite, and chalcopyrite. Furthermore, Kupferschiefer contains significant amounts of kerogen and arsenic, both penalizing current pyrometallurgical processes. Changes of ore characteristics—such as an increase of organic carbon and arsenic contents accompanied by a decrease of the copper content—complicate existing processing technologies, in particular the production of concentrates via flotation followed by smelting processing. Hydrometallurgy and more specifically bioleaching is considered an ecologically acceptable and yet economic alternative. Bioleaching processes are strongly influenced by ore composition and minerals. In Kupferschiefer, Cu occurs as bornite (Cu5FeS4), chalcocite (Cu2S), a small portion of covellite (CuS), and chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) in minor amounts [16]. Whereas chalcocite and bornite can be completely dissolved by bioleaching, chalcopyrite is especially recalcitrant to leaching, thus being the main limitation of biohydrometallurgy processes. In the past, several research projects (F6 Bioshale, FP7 ProMine) were carried out that aimed the biohydrometallurgical metal recovery from Kupferschiefer ores [17,18].
Most promising was the use of organic rich copper flotation concentrates as one of the first processing steps. Tank leaching was demonstrated to be a technical viable option [19]. The possibility of controlling the redox potential in these kind of processes forces the leaching of chalcopyrite. It was further proven that classical acidophilic microbial consortia (e.g., A. ferrooxidans, L. ferriphilum, Sulfolobus spp., and others) can process these compounds. A disadvantage of this method is the large amount of acid that is required to remove carbonate from the ores.
The exploitation of Kupferschiefer black shale has to deal with a number of bottlenecks influencing the whole value chain. The presence of fine particles and a high content of organic matter in the materials hamper flotation processes. On the other hand, a removal of organic matter for enhanced flotation hinders the recovery of significant portions of valuable metals and the removal of carbonates implies a high acid consumption [14].
In the current German–French project “EcoMetals” (further information is available at www.ecometals.org), researchers from 15 German and French institutions—supported by the Polish mining company KGHM Polska Miedž S.A.—try to overcome these limitations [14]. The project aims the development of innovative efficient bioleaching processing routes for metal extraction from primary and secondary mineral resources. These developments include the investigation and understanding of basic bioleaching mechanisms, development of analytical tools, design of a novel bioreactor, enhancement of pre-treatment processes, development of a complete downstream-strategy to maximize the recovery of valuable metals and to minimize the waste generated by the bioleaching process, modelling, and development of new Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and sustainability assessment tools.
Our lab investigates the use of heterotrophic bacteria for metal extraction as an alternative bioleaching strategy to conventional bioleaching with acidophilic microorganisms. Such microorganisms produce organic acids (e.g., citric acid or glutamic acid) that dissolve the metals by protonic attack of carboxyl groups [20] and work as complexing agents. Thereby, complexation of metal ions might include decarboxylation of acids [21]. Kostudis et al. investigated the influence of glutamic acid on metal release from Kupferschiefer ores in detail [16]. Kupferschiefer ore samples from the Polkowice Mine in Lubin, Poland, were crushed and milled, and particles 0.1–2 mm in size of were used for leaching experiments. The average copper recovery for glutamic acid was estimated as 43.6%. Mineral liberation analysis (MLA) was performed on ore samples as well as leaching residues to detect mineralogical changes. The feed sample contained significant quantities of four copper minerals—namely chalcocite (3.5 wt %), bornite (1.4 wt %), chalcopyrite (0.7 wt %), and covellite (0.2 wt %). The three minerals chalcocite, bornite, and chalcopyrite decrease in abundance in response to leaching by glutamic acid, whereas the content of covellite increased up to 1.1 wt % in the leach residue, suggesting the temporary formation of secondary covellite. Results showed further that the most prominent part in copper leaching was contributed by chalcocite, as its relative abundance decreased from 67.7 wt % to 42.5 wt %. Chalcopyrite—which is usually recalcitrant to bioleaching—was leached at a similar rate, but occurred only in minor amounts in the ore samples. Therefore, it did not contribute significantly to the copper recovery.
In a recent work, we compared the influence of glutamic acid and citric acid as bulk chemical as well as biotechnologically-produced on the liberation of copper and associated elements [22]. Generally, leaching rates were higher at pH 7 and 10 than at pH 4, whereby elemental solubilisation by bulk citric acid was higher than by bulk glutamic acid. These differences were explained by the presence of three carboxyl groups in the case of citric acid in comparison to only two carboxyl groups in the case of glutamic acid, thus providing more deprotonated reactive groups for copper complexation at neutral conditions. Aside from copper, being the most abundant metal in Kupferschiefer ore (2.9%–4.3%), significant amounts of zinc (abundance of 0.1%–0.4%), manganese (abundance of 0.2%–0.3%), and nickel (abundance of 200 ppm) were released. Most interestingly, solubilisation of manganese by treatment with biotechnologically-produced citric acid was significantly higher (up to 238.4 µg·L−1 at pH 10) in comparison to bulk citric acid (up to 23.5 µg·L−1 at pH 4). In the case of nickel, the best leaching rates for biotechnologically-produced citric acid were obtained at pH 7 (up to 135 µg·L−1) in comparison to pH 10 (up to 72 µg·L−1). Direct comparison of leaching results using bulk chemicals and biotechnologically-produced organic acids suggest that bio-approaches do not enhance leaching rate. For example, copper release was with up to 511.5 mg·L−1 at pH 7, about two times higher when using bulk citric acid than with biotechnologically-produced citric acid. However, in these approaches, 1% of bulk citric acid was added, whereas solutions of biotechnologically-produced citric acid contained only 0.05% citric acid. Increased efficiency of bio-produced organic acids in comparison to bulk chemicals at similar molar concentrations has already been reported [23,24,25]. However, these results were obtained in the presence of acid-producing microorganisms and bioaccumulation was assumed to be crucial for enhanced efficiency. Consequently, spent medium performed less strongly. As mere fresh medium showed leaching effects in all of these studies, it is highly probable that medium compounds benefit metal solubilisation. In this respect, phosphates and sulphates may compete with organic acids for metal ions [26], and thus increase leaching efficiency similarly to the bioaccumulation effect.
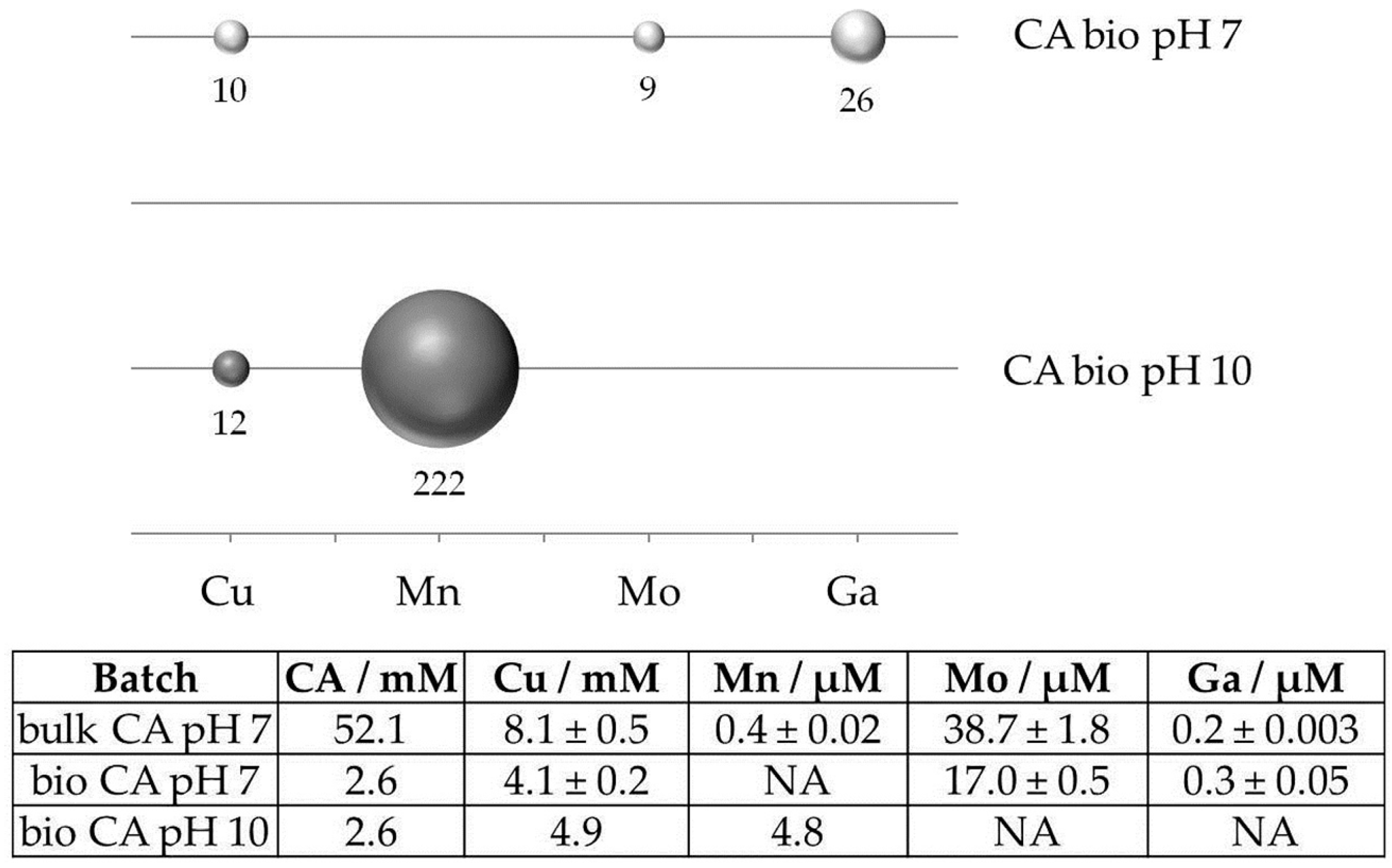
Leaching efficiency was calculated as the ratio of leached elements and citric acid available in the supernatant compared to the similar ratio in batches using bulk citric acid. In the case of manganese, this results in an up to 200-fold leaching efficiency (Figure 1) in bio-batches compared to bulk chemicals, whereas efficiency in the solubilisation of copper, molybdenum, and gallium was still increased by a factor of 9 to 26. This remarkable difference originates from the host minerals: In contrast to manganese which occurs mainly in the carbonate ankerite and clay minerals, copper, molybdenum and gallium are hosted by sulfidic minerals. Obviously, sulfidic minerals are less affected by leaching with citric acid in the complex supernatant at pH 10 than copper sulfides.
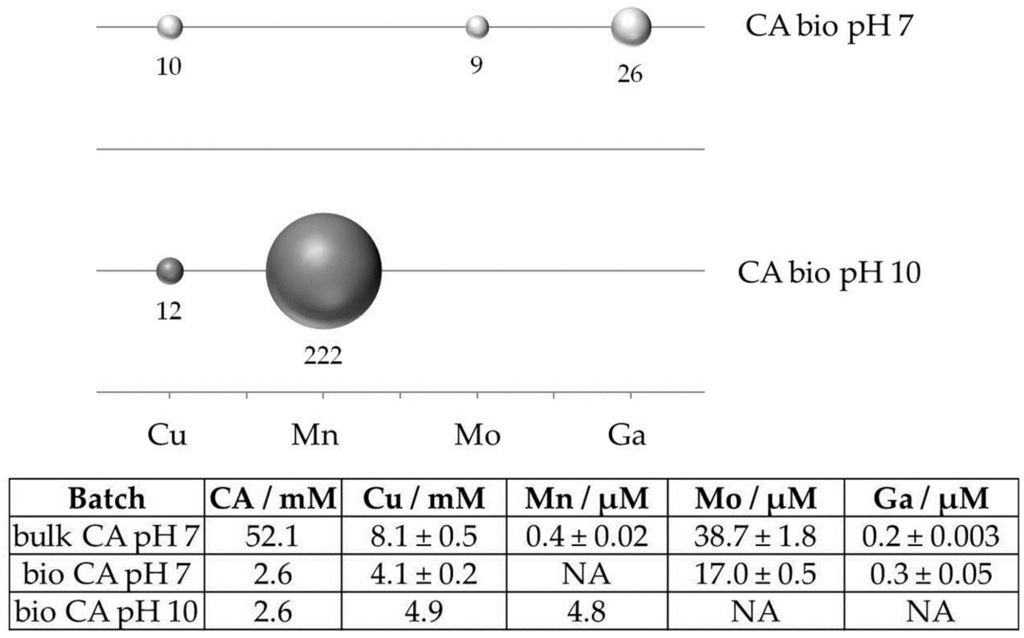
Figure 1.
Efficiency in solubilisation of Cu, Mn, Mo, and Ga from Kupferschiefer ore by biotechnologically-produced citric acid (CA) at pH 7 and 10 compared to bulk citric acid at pH 7. Ratios are calculated as molar concentrations of leached element per amount of citric acid available in the leaching supernatant (table). Elemental data were determined by ICP-MS. Values were not determined for Mn at pH 7 and Mo and Ga at pH 10.
In summary, these results show that leaching at neutral-to-basic conditions can be used for copper recovery, but also different associated elements from Kupferschiefer ores. Such approaches are attractive as they avoid pretreatment steps (such as dissolution of carbonates) that are required for bioleaching using acidophilic bacteria. Furthermore, variation of pH may enable the sequential mobilisation of different elements. Based on these results, our current research concentrates on the efficient and economic biotechnological production of glutamic acid and citric acid and the use of glutamic acid and citric acid-producing bacteria and yeasts for bioleaching.
2.2. Example: Bioleaching of Rare Earth Elements
Rare earth elements (REE) have been increasingly used in in different technologies, such as the fields of optics, permanent magnetism, electronics, superconductor technology, hydrogen storage, medicine, nuclear technology, secondary battery technology, and catalysis. Current mining technologies of REE consume high amounts of energy, water, and chemicals, accompanied by the release of radioactive elements and landscape destruction [27,28]. Innovative biotechnologies may contribute to the development of environmentally-friendly processes for the recovery of REE.
Although it can be expected that microorganisms play an important role in the biogeochemical cycle of REE, few studies describe the interactions of microorganisms with REE compounds. An early study of Schwartz (1980) reports the dissolution of commercial lanthanide oxides by different fungi—among them, different Aspergillus niger strains [29]. Although this study did not investigate the mechanism nor the determined bioleaching rates, this study demonstrated the principle accessibility of REE compounds for microbial reactions. Another study from 1988 investigated the possible biological degradation of highly-resistant Zircon mineral of the heavy metal soaps of the Baltic Sea using chemolitho-autotrophic bacteria such as A. ferrooxidans and heterotrophic bacteria such as Acetobacter spec. strains, which produce organic acids and complexing agents such as gluconic acid [30,31]. With both approaches, high leaching efficiencies were obtained, ranging from 43.6% (Er) to 91.6% (La) in the case of A. ferrooxidans and 58.6% (Lu) to 84.4% (Nd, Pr) in the case of Acetobacter methanolicus. Leaching efficiencies as well leaching rates depended on applied organisms, grain size, as well as on the monitored element, ranging from 0.04 mg/L·h (U) to 2.64 mg/L·h (Er) in the case of A. ferrooxidans and 0.019 mg/L·h (U) and 1.436 mg/L·h (Er) in the case of Acetobacter spec. Furthermore, the researchers described a preferential dissolution of the light REE compared to the heavy REE. In a more recent publication, researchers used fungal strains such as Aspergillus niger and Yarrowia lipolytica for bioleaching of Y and Sc from red mud [32]. In recent studies, several research groups investigated the bioleaching of REE from monazite ores. For example, Hassanien et al. (2014) used heterotrophic microorganisms such as Aspergillus ficuum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the bioleaching of REE from Egyptian monazite, reaching high leaching efficiencies of up to 60.6% and 52.6% by A. ficuum and P. aeruginosa, respectively [33]. In a very recent study, Shin et al. (2015) investigated the ability of different phosphate-solubilizing bacteria to leach REE from monazite-bearing ores. Although the bioleaching efficiencies were very low (up to 0.13% in case of Ce), the study proved the general suitability of phosphate-solubilising bacteria to degrade highly resistant monazite ores [34].
Aside from REE-bearing ores as primary resource, other secondary resources (“urban mine” products) might be another attractive source to contribute to the secure supply of REE in developed countries. Recycling strategies for REE from technical products have been not or only poorly developed. In a current project, we investigate the bioleaching of REE from fluorescent powder, which is collected as a distinct fraction during the recycling of fluorescent bulbs and energy-saving bulbs (compact fluorescent lamps) as a test case. Whereas chemolithoautotrophic acidophilic bacteria such as A. ferrooxidans are not suited as bioleaching organisms due to the buffering properties of the substrate, reasonable leaching rates—especially of Y2O3, which is a main REE component of the fluorescent powder—were obtained by using heterotrophic microorganisms.
We chose the tea “fungus” Kombucha for a more detailed analysis of REE leaching [35]. Kombucha is a symbiotic mixed culture consisting of yeasts (in our case Zygosaccharomyces lentus) and acetic bacteria (in our case Komagataeibacter hansenii). Normally Kombucha is used in households for the production of an allegedly wholesome beverage and it is known to produce high amounts of organic acids while being relatively stable against contaminants [36,37]. In our approach, the culture produced mainly acetic acid and gluconic acid. Entire Kombucha cultures as well as isolated microorganisms (Zygosaccharomyces lentus and Komagataeibacter hansenii) were used for bioleaching experiments. The different approaches showed best leaching rates for shaking cultures of entire Kombucha and its supernatants, with leaching rates of up to 7.9% of total REE. Comparing the leaching rate of the single elements, there was a clear tendency to preferred leaching of yttrium and europium (>12%). Therefore, yttrium oxide doped with europium (Y2O3:Eu3+, red dye) was primarily leached, probably due to a higher solubility of REE-oxides in comparison to REE-phosphates and aluminates. Although the obtained leaching rates were still too low for industrial applications, these results demonstrated the capability of microorganisms to extract REE from technical products, thus forming the basis for bio-based recycling applications.
3. Biosorption
Biosorption defines a process that allows the binding and concentration of selected ions or other molecules from aqueous solutions by biomass or certain biomolecules [38]. These techniques have been mainly applied for the removal of toxic metals from polluted waters, such as arsenic, chromate, cadmium, or uranium [39], but also for the recovery of valuable metals such as gold, platinum, palladium, or others from solutions [40,41]. Major challenges of all these procedures are selectivity, metal binding capacity, regenerability and stability of materials, and cost efficiency. There are several approaches that meet these challenges. Most studies concentrated on the use of bacterial cells, fungi, yeast [39], algae [42], or biocomponents such as crab shells [43], plant fibers [44], etc. as biosorptive components.
More recent developments concentrate on the direct engineering of improved microbes and enzymes—e.g., expression of metallothioneins, metal binding peptides, or other metal binding proteins and their display on cell surfaces (reviewed in [45,46]). A very promising novel approach is the selection of metal binding peptides by phage surface display. With this technique, peptides specific for several metallic surfaces or metal ions were selected [47,48,49].
The repeatable use of biomolecules for biosorption requires the immobilization of the molecules to an appropriate surface. The combination of bio-compounds with inorganic materials brings together advantages of both materials. In our group we use self-assembling S-layer proteins that form the outermost envelope of many bacteria as biocompound for the development of biosorptive composites.
3.1. Bacterial S-Layers
Proteinaceous surface layers (S-layers) of bacteria are one of the most common surface structures present in all major phylogenetic groups of bacteria and almost all archaea [50]. They are composed of protein or glycoprotein monomers of a molecular weight ranging from 40 to 200 kDa with the ability to self-assemble into two-dimensional paracrystalline arrays. Naturally, S-layers work as an interface between the cell and the environment. The protein layers provide numerous functional groups that interact with metals, such as COOH–, NH2–, OH–, PO4–, SO4– and SO–. In this way, S-layers can serve as ion traps, thereby preventing the uptake of toxic metals into the bacterial cell and making them an ideal barrier against toxic dissolved metal ions. Consequently, cells were protected from being seriously damaged by such metals. In addition, researchers have described the importance of binding metal complexes containing calcium, strontium, arsenic, or antimony with S-layers as an initial step of bio-mineralization [51,52,53]. For example, mineral phases such as gypsum, calcite, celestite, and strontianite were formed in this way on S-layers. In these instances, the S-layers provide crystallization nuclei and serve as a biomineralization template. Wang and Müller (2009) also discussed the involvement of S-layers in the formation of polymetallic nodules [54].
Another important aspect is the interaction with bivalent cations such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ that are crucial for the protein conformation of the single S-layer protein monomer, self-assembling, and the formation of the highly-ordered lattices. Based on preliminary results, there are at least two binding sites for these bivalent cations. Principally, Ca2+-binding proteins are well-known for their affinity for different lanthanides [55]. Therefore, it can be expected that S-layer proteins also interact with REE (mainly lanthanides). It is quite challenging to extract and separate REE, because many of them are similar in properties and are finely distributed in ores. A promising and “green” approach is the use of calcium-binding proteins such as S-layer proteins. We have shown in our lab that S-layer proteins are generally capable of binding Eu3+ via their Ca-binding sites (unpublished results). As a consequence, these proteins can be used for the recovery of at least some lanthanides from natural or industrial waters. Some possible applications for S-layer proteins include the recovery of REE from natural water, wastewater from mining operations, or wastewater in connection with the recycling of electrical and electronic equipment. It should also be noted that, in contrast to precious metals, the recovery of a bound lanthanide is possible by a pH shift, complexing agents, or elution with buffers possessing high salinity.
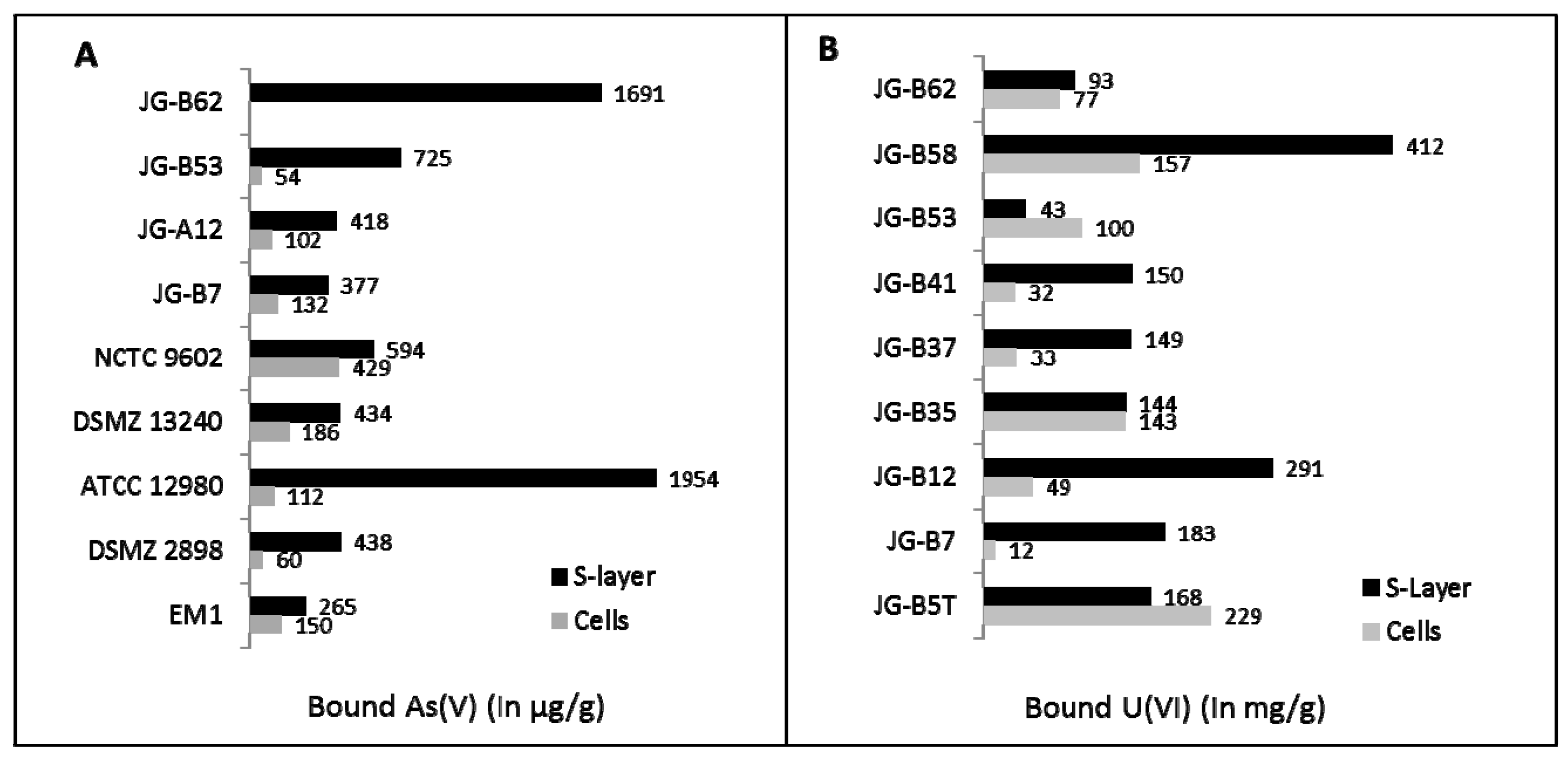
In our lab, we intensively investigated the S-layers of different bacterial strains that were isolated from uranium mining waste piles [41]. These S-layers interact with different heavy metals and metalloids such as uranium, lead, and arsenic, but also with precious metals such as palladium, platinum, or gold [56,57,58]. As shown in Figure 2, most investigated S-layers possess a higher binding capacity for toxic elements such as uranium or arsenic compared to intact cells. Especially the S-layer proteins and genes of the bacterial isolates Lysinibacillus sphaericus JG-A12 and L. sphaericus JG-B53, which were isolated from a uranium mining pile, have been extensively studied [56,57,58,59,60]. These proteins are able to bind high amounts of uranium (up to 20 mg U/g protein [61]) but also arsenic and precious metals such as Pd(II), Pt(II), and Au(III). Recent investigations by Quartz crystal micro balance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) showed that the sorption processes occur very rapidly [62,63].
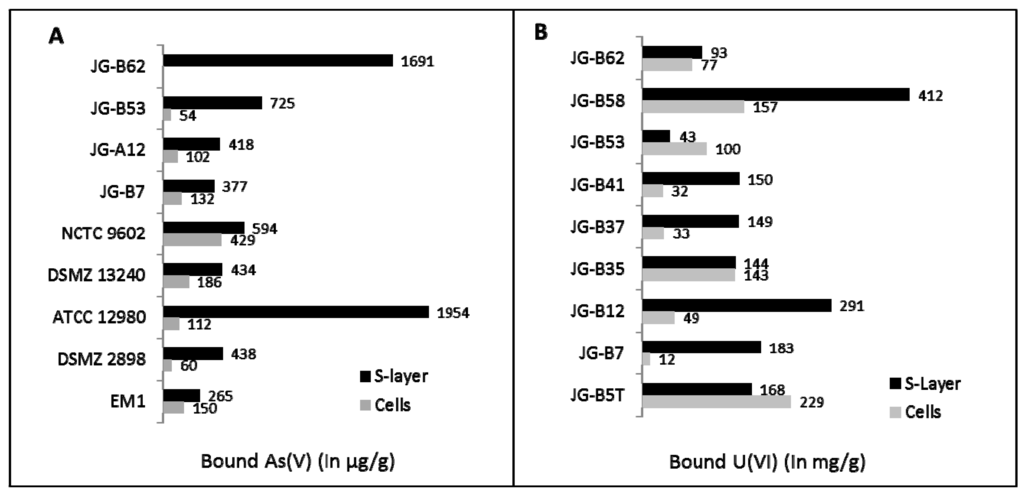
Figure 2.
(a) Arsenic and (b) uranium binding of cells and S-layers of several isolates recovered from a uranium mining waste pile nearby Johanngeorgenstadt (JG) and of several reference strains. The isolates JG-B62, JG-B53, JG-B7, JG-A12, and the reference strain NCTC 9602 are Lysinibacillus sphaericus strains, JG-B58 is a Viridibacillus arvi strain, and all other isolates are different Bacillus species. Used reference strains are Geobacillus stearothermophilus DSMZ 13240, Geobacillus stearothermophilus ATCC 12980, Lysinibacillus fusiformis DSMZ 2898, and Thermoanaerobacterium thermosulfurigenes EM1. Experiments were carried out with 200 mg U/L for cells and with 200 mg U/L for S-layers in 0.9% NaClO4 at pH 4.5 for 48 h or with 10 mg As(V)/L at pH 6.0 for 72 h.
These properties make S-layer proteins highly attractive for their utilization as biocomponents for the production of biosorptive filtration materials. Cells, spores, and S-layers of L. sphaericus JG-A12 were embedded in silica gels using an aqueous sol–gel process to produce a porous filter matrix (bioceramic, biocer) with a homogeneous structure and immobilized biocomponents [64,65]. The produced bioceramics were successfully used to remove copper and uranium from contaminated water.
However, current challenges for the industrial usage of S-layer proteins as filtration components are their cost efficient production and, in the case of precious metals, the desorption of metals from the protein bio-composite that would enable their reuse. Upscale can be achieved by heterologous expression of the proteins in host cells [66,67,68] or optimization of isolation procedures. The recovery of bound precious metals is currently only possible via thermal decomposition (fuming), which is also carried out for corresponding ion exchange materials.
3.2. Bio-Nanomaterials
Bacterial S-layer proteins are not only attractive for the removal of toxic elements or precious metals from aqueous solutions but can be used also for the synthesis and deposition of regular arranged nanoparticles of a defined size. These approaches use the regular charge clusters on the surface of the proteins, thus being capable of binding different ions. The bound metal ions can be converted to inorganic nanostructures and nanoparticles under appropriate conditions [69]. In previous projects, S-layer proteins have been used as template for the synthesis of Pd(0), Pt(0), or Au(0) nanoparticles and their interactions with the biological matrix have been studied in detail [56,57,62,63,70,71]. In comparison to bulk materials, such nanoparticles often show altered electrical, optical, or chemical properties. The use of S-layer proteins as a template allow a reliable immobilisation and arrangement of the nanoparticles into array structures. Due to their intrinsically high surface-to-volume ratio, such nanomaterials are attractive for catalytic or sensor applications [72,73,74,75].
Recently, Schmoock et al. (2014) described the use of photocatalytically active TiO2 and ZnO particles for the degradation of undesirable pharmaceutical compounds in water [76] and demonstrated in parallel the resistance of S-layers against reactive oxygen species. Further, we could synthesize Fe3O4 particles using S-layer proteins as template, thus producing a composite composed of S-layers and Fe3O4 [77]. Principally, such particles are well known for their ability to bind arsenic. For example, granulated ferric hydroxides such as FerroSorp® are commercially used for the removal of arsenic and uranium from contaminated waters. Keeping in mind that S-layer proteins alone exhibit remarkable As(V) binding capabilities, the question was whether a combination of S-layers and metal oxide particles may enhance these properties. Table 1 shows the capabilities of some S-layer/metal oxide composites. The material was used for the removal of pentavalent arsenic in a concentration range between 0.1 and 10 mg/L. It was found that the arsenic is bound more effectively by the composite material than by the adsorbent material FerroSorp® or the individual components of the S-layer protein, nanoscale titanium dioxide, or iron oxide. In our experiments, we could achieve a separation performance of up to 5.3 mg/g that was almost twice that of the commercial arsenic adsorbent FerroSorp®. To summarise, the binding ability was well beyond what was expected in the combination of these materials, thus making S-layer/metal oxide composites attractive for arsenic separation of contaminated waters.

Table 1.
Binding of As(V) by metal oxides and S-layer composites 1.
4. Conclusions
Nature provides numerous biochemical reactions and biomolecules that can be applied in mineral processing. The growing demand for sustainable technologies that enable a maximum metal recovery have caused a significant increased interest in such bio-based concepts. Recent developments in biotechnologies and material sciences—such as the design of molecules by bioengineering and nanotechnologies—open up new possibilities for innovative processes. The development and establishment of such technologies require close interdisciplinary cooperation between microbiologists, engineers, chemists, and geoscientists, which is the ambition of our institute.
Acknowledgments
The presented studies are supported by the German Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Germany (Grant 033RF001A (EcoMetals)), and the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU), Germany (Grant AZ 29758).
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to write the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J.P. Reduction of uranium by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J.P.; Gorby, Y.A.; Landa, E.R. Microbial reduction of uranium. Nature 1991, 350, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkay, T.; Schaefer, J. Metal and radionuclide bioremediation: Issues, coniderations and potentials. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, T.; Nasu, M. Current bioremediation practice and perspective. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero, A.E.C.; Torem, M.L.; de Mesquita, L.M.S. Fundamental studies of Rhodococcus opacus as a biocollector of calcite and magnesite. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.A.; Deo, N. Utility of microorganisms in mineral beneficiation. Met. Mater. Process. 1998, 10, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, P.; Natarajan, K.A. Microbially induced flocculation and flotation for separation of chalcopyrite from quartz and calcite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, S.B.; Hewitt, J.; MacGiliivray, R.T.A.; Dunbar, W.S. Biomining with bacteriophage: Selectivity of displayed peptides for naturally occurring sphalerite and chalcopyrite. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B. Development and application of biotechnologies in the metal mining industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7768–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, D.E. Heavy metal mining using microbes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, D.E. Biomining: Theory, Microbes and Industrial Processes; Springer/Landes Biosciences: Georgetown, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, N.; Sharma, D.K. Biohydrometallurgy for nonsulfidic minerals—A review. Geomicrobiol. J. 2004, 21, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veglio, F.; Beolchini, F.; Gasbarro, A.; Toro, L.; Ubaldini, S.; Abbruzzese, C. Batch and semi-continuous tests in the bioleaching of manganiferous minerals by heterotrophic mixed microorganisms. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 50, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutschke, S.; Guezennec, A.G.; Hedrich, S.; Schippers, A.; Borg, G.; Kamradt, A.; Gouin, J.; Giebner, F.; Schopf, S.; Schlomann, M.; et al. Bioleaching of Kupferschiefer blackshale—A review including perspectives of the Ecometals project. Miner. Eng. 2015, 75, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.; Piestrzynski, A.; Bachmann, G.; Püttmann, W.; Walther, S.; Fiedler, M. An overview of the European Kupferschiefer deposits. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2012, 16, 455–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kostudis, S.; Bachmann, K.; Kutschke, S.; Pollmann, K.; Gutzmer, J. Leaching of copper from Kupferschiefer by glutamic acid and heterotrophic bacteria. Miner. Eng. 2015, 75, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Hugues, P.; Norris, P.R.; Hallberg, K.B.; Sanchez, F.; Langwaldt, J.; Grotowski, A.; Chmielewski, T.; Groudev, S.; Consortium, B. Bioshale FP6 European project: Exploiting black shale ores using biotechnologies? Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Hugues, P.; Spolaore, P.; Consortium, B. Biohydrometallurgy applied to exploitation of black shale resources: Overview of bioshale FP6 European project. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolaore, P.; Joulian, C.; Gouin, J.; Ibanez, A.; Auge, T.; Morin, D.; d'Hugues, P. Bioleaching of an organic-rich polymetallic concentrate using stirred-tank technology. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G. The Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Serebryanaya, M.Z.; Petrova, L.N. Complexing as a mechanism of biodegradation of industrial waste, containing manganese dioxide. In Biohydrometallurgical Processing. Volume II; Jerez, C.A., Vargas, T., Tolado, H., Wiertz, J.V., Eds.; University of Chile Press: Santiago, Chile, 1995; pp. 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kostudis, S.; Kutschke, S.; Pollmann, K. Mobilisation of metals from Kupferschiefer sensu strictu in neutral to alkaline environment using bulk and biotechnologically-produced organic acids. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Biohydrometallurgy, Biohydrometallurgy 2016, Falmouth, UK, 20–22 June 2016.
- Aung, K.M.M.; Ting, Y.-P. Bioleaching of spent fluid catalytic cracking catalyst using aspergillus niger. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 116, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, A.; Ting, Y.-P. Bioleaching of spent hydrotreating catalyst by acidophilic thermophile acidianus brierleyi: Leaching mechanism and effect of decoking. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Ting, Y.-P. Metal extraction from municipal solid waste (MSW) incinerator fly ash—Chemical leaching and fungal bioleaching. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieuwerts, J.S.; Thornton, I.; Farago, M.E.; Ashmore, M.R. Factors influencing metal bioavailability in soils: Preliminary investigations for the development of a critical loads approach for metals. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 1998, 10, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golev, A.; Scott, M.; Erskine, P.D.; Ali, S.H.; Ballantyne, G.R. Rare Earths supply chains: Current status, constraints and opportunities. Resour. Policy 2014, 41, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, D.; Buchert, M.; Liu, R.; Dittrich, S.; Merz, C. Study on Rare Earths and Their Recycling; Öko-Institut e.V.: Freiburg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, W.; Naveke, R. Biological leaching of lowgrade ores with heterotrophic microorganisms. Metall 1980, 34, 847–850. [Google Scholar]
- Iske, U.; Glombitza, F. Possibilities for the application of biotechnological processes for the production of metals from ores, minerals and industrial-wastes. ChemInform 1988, 40, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, F.; Iske, U.; Bullmann, M. Mikrobielle Laugung von Seltenen Erdelementen und Spurenelementen. Bioengineering 1988, 4, 37–43. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Talasova, I.I.; Khavski, N.N.; Khairullina, R.T.; Karavaiko, G.L.; Dudeney, A.W.L. Red mud leaching with fungal metabolites. In Biohydrometallurgical Processing, Volume II; Jerez, C.A., Vargas, T., Tolado, H., Wiertz, J.V., Eds.; University of Chile Press: Santiago, Chile, 1995; pp. 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanien, A.G.; Desouky, O.A.N.; Hussien, S.S.E. Bioleaching of some Rare Earth Elements from Egyptian monazite using Aspergillus ficuum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 809–823. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.S.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.C. Use of phosphate solubilizing bacteria to leach Rare Earth Elements from monazite-bearing ore. Minerals 2015, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfe, S.; Flemming, K.; Lehmann, F.; Möckel, R.; Kutschke, S.; Pollmann, K. Leaching of rare earth elements from fluorescent powder using the tea fungus Kombucha. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Jayabalan, R.; Malini, K.; Sathishkumar, M.; Swaminathan, K.; Yun, S.-E. Biochemical characteristics of tea fungus produced during Kombucha fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.J.; O'Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequence-based analysis of the bacterial and fungal compositions of multiple Kombucha (tea fungus) samples. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption and me. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volesky, B.; Holan, Z.R. Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnol. Prog. 1995, 11, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N. Recovery of precious metals through biosorption—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, K.; Raff, J.; Merroun, M.; Fahmy, K.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Metal binding by bacteria from uranium mining waste piles and its potential applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.S.; Chen, J.P. A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: Materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubert, L.N.; Brennan, R.A. Passive remediation of acid mine drainage using crab shell chitin. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 24, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamun, N.; Triwahyono, S.; Jalil, A.A.; Matsuura, T.; Salleh, N.F.M. Acid-vacuo heat treated low cost banana stems fiber for efficient biosorption of Hg(II). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14129–14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M. Engineering of microorganisms towards recovery of rare metal ions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Bruhlmann, F.; Richins, R.D.; Mulchandani, A. Engineering of improved microbes and enzymes for bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 1999, 10, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, R.; Kim, D.S.; Thuong, N.; Tan, L.H.; Kim, C.W.; Yoo, I.K.; Choe, W.S. Chromatographic biopanning for the selection of peptides with high specificity to Pb2+ from phage displayed peptide library. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5940–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Rosi, N.L. Peptide-based methods for the preparation of nanostructured inorganic materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1924–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarikaya, M.; Tamerler, C.; Jen, A.K.Y.; Schulten, K.; Baneyx, F. Molecular biomimetics: Nanotechnology through biology. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sára, M.; Sleytr, U.B. S-layer proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultze-Lam, S.; Harauz, G.; Beveridge, T.J. Participation of a cyanobacterial S-layer in fine-grain mineral formation. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 7971–7981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phoenix, V.R.; Renaut, R.W.; Jones, B.; Ferris, F.G. Bacterial S-layer preservation and rare arsenic-antimony-sulphide bioimmobilization in siliceous sediments from champagne pool hot spring, Waiotapu, New Zealand. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2005, 162, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze-Lam, S.; Beveridge, T.J. Nucleation of celestite and strontianite on a cyanobacterial S-layer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Schröder, H.; Schlossmacher, U.; Müller, W.E.G. Organized bacterial assemblies in manganese nodules: Evidence for a role of S-layers in metal deposition. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, I.; Gelis, I.; Katsaros, N.; Luchinat, C.; Provenzani, A. Tuning the affinity for lanthanides of calcium binding proteins. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 8011–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, K.; Merroun, M.; Pollmann, K.; Raff, J.; Savchuk, O.; Hennig, C.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Secondary structure and Pd(II) coordination in S-layer proteins from Bacillus sphaericus studied by infrared and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, U.; Merroun, M.L.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Fahmy, K. S-layer protein from Lysinibacillus sphaericus JG-A12 as matrix for Au(III) sorption and Au-nanoparticle formation. Spectrosc-Int. J. 2010, 24, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merroun, M.; Raff, J.; Rossberg, A.; Hennig, C.; Reich, T.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Complexation of uranium by cells and S-layer sheets of Bacillus sphaericus JG-A12. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5532–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, F.L.; Weinert, U.; Guenther, T.J.; Raff, J.; Weiss, S.; Pollmann, K. Identification of multiple putative S-layer genes partly expressed by Lysinibacillus sphaericus JG-B53. Microbiology 2013, 159, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollmann, K.; Raff, J.; Schnorpfeil, M.; Radeva, G.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Novel surface layer protein genes in Bacillus sphaericus associated with unusual insertion elements. Microbiology 2005, 151, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raff, J.; Merroun, M.; Rossberg, A.; Soltmann, U.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Interactions of the U Mining Waste Pile Isolate Bacillus sphaericus JG-A12 with U. In Water rock interaction; Wanty, R.B., Seal, R.R., Eds.; Balkema Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Suhr, M.; Raff, J.; Pollmann, K. Au-interaction of Slp1 polymers and monolayer from Lysinibacillus sphaericus JG-B53—QCM-D, ICP-MS and AFM as tools for biomolecule-metal studies. JoVE 2016, 107, e53572–e53572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhr, M.; Unger, N.; Viacava, K.E.; Gunther, T.J.; Raff, J.; Pollmann, K. Investigation of metal sorption behavior of Slp1 from Lysinibacillus sphaericus JG-B53: A combined study using QCM-D, ICP-MS and AFM. BioMetals 2014, 27, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raff, J.; Soltmann, U.; Matys, S.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Boettcher, H.; Pompe, W. Biosorption of uranium and copper by biocers. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltmann, U.; Raff, J.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Matys, S.; Pompe, W.; Böttcher, H. Biosorption of heavy metals by sol-gel immobilized Bacillus sphaericus cells, spores and S-layers. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2002, 26, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, F.L.; Günther, T.; Raff, J.; Pollmann, K. E. coli filament formation induced by heterologous S-layer expression. Bioeng. Bugs 2011, 2, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, F.L.; Günther, T.J.; Flemming, K.; Raff, J.; Fahmy, K.; Springer, A.; Pollmann, K. Heterologous expression of the surface-layer-like protein Sllb induces the formation of long filaments of Escherichia coli consisting of protein-stabilized outer membrane. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3584–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollmann, K.; Matys, S. Construction of an S-layer protein exhibiting modified self-assembling properties and enhanced metal binding capacities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleytr, U.B.; Schuster, B.; Egelseer, E.M.; Pum, D. S-layers: Principles and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 823–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merroun, M.; Rossberg, A.; Hennig, C.; Scheinost, A.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Spectroscopic characterization of gold nanoparticles formed by cells and S-layer protein of Bacillus sphaericus JG-A12. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, R.; Mertig, M.; Raff, J.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Pompe, W. Electron-beam induced formation of highly ordered palladium and platinum nanoparticle arrays on the S-layer of Bacillus sphaericus NCTC9602. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, N.; Mikheenko, I.; Yong, P.; Deplanche, K.; Sanyahumbi, D.; Wood, J.; Pollmann, K.; Merroun, M.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Macaskie, L. Novel supported Pd hydrogenation bionanocatalyst for hybrid homogeneous/heterogeneous catalysis. Catal. Today 2007, 128, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, N.J.; Deplanche, K.; Snape, T.J.; Mikheenko, I.P.; Yong, P.; Samyahumbi, D.; Wood, J.; Pollmann, K.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Macaskie, L.E. A biogenic catalyst for hydrogenation, reduction and selective dehalogenation in non-aqueous solvents. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 94, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollmann, K.; Merroun, M.; Raff, J.; Hennig, C.; Selenska-Pobell, S. Manufacturing and characterization of Pd-nanoparticles formed on immobilized bacterial cells. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, M.; Matys, S.; Raff, J.; Pompe, W. Colorimetric As(V) detection based on S-layer functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 144, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoock, C.; Bornick, H.; Vogel, M.; Lehmann, F.; Kutschke, S.; Raff, J.; Dittmar, T.; Worch, E. S-layer proteins as possible immobilization matrix for photocatalysts-OH radical scavenging capacity and protein stability. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 277, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raff, J.; Pollmann, K.; Günther, T.; Marquard, A.; Katzschner, B.; Matys, S.; Pompe, W. Verwendung eines Biokompositmaterials zur Entfernung von Arsenverunreinigungen aus Wasser und Verfahren. Patent DE102011006753B3, 24 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).