Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Tuff in Zhongliangshan Mine, Chongqing, Southwestern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
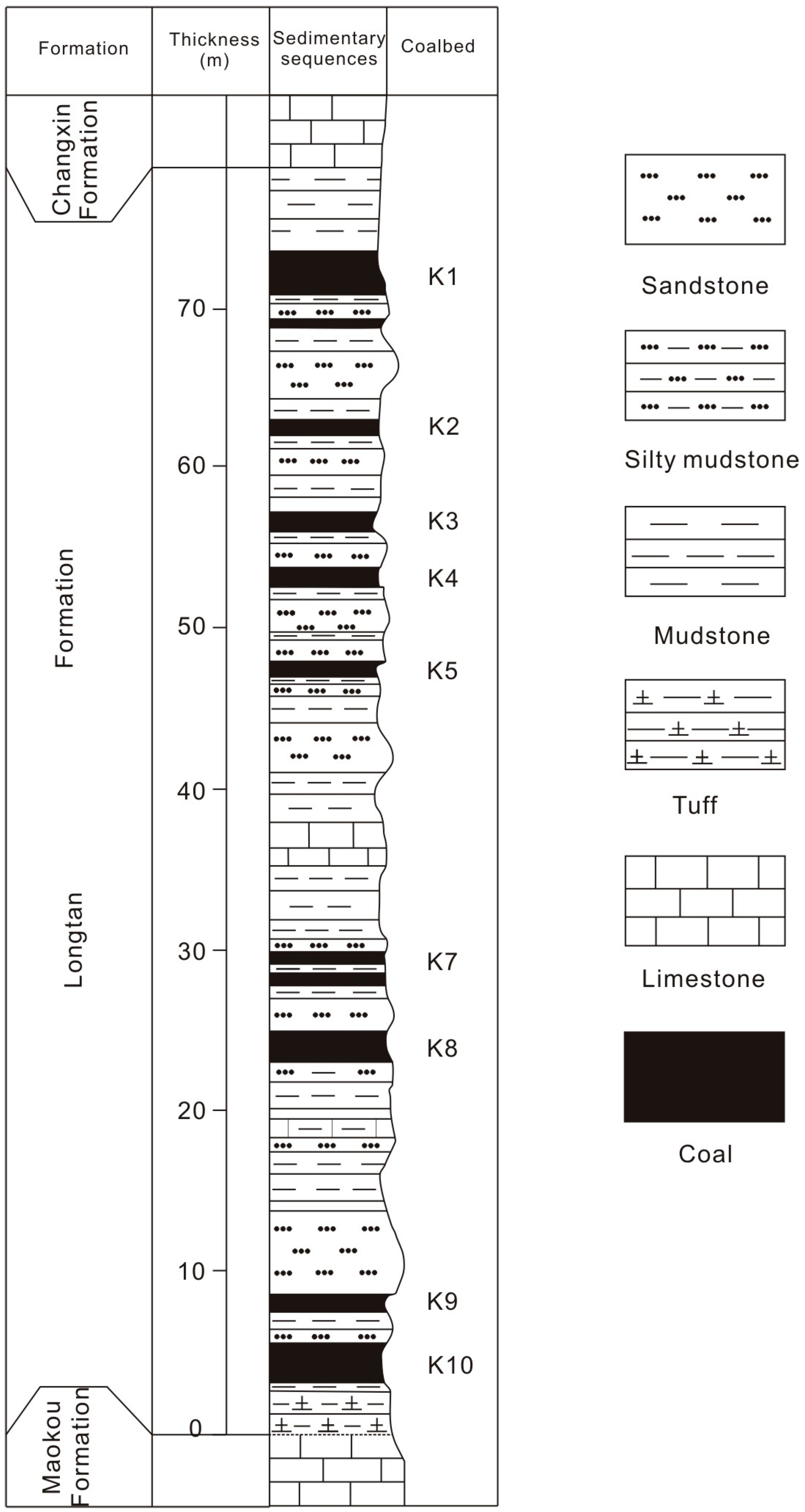
2. Geological Setting
3. Samples and Analytical Procedures
4. Results
4.1. Minerals
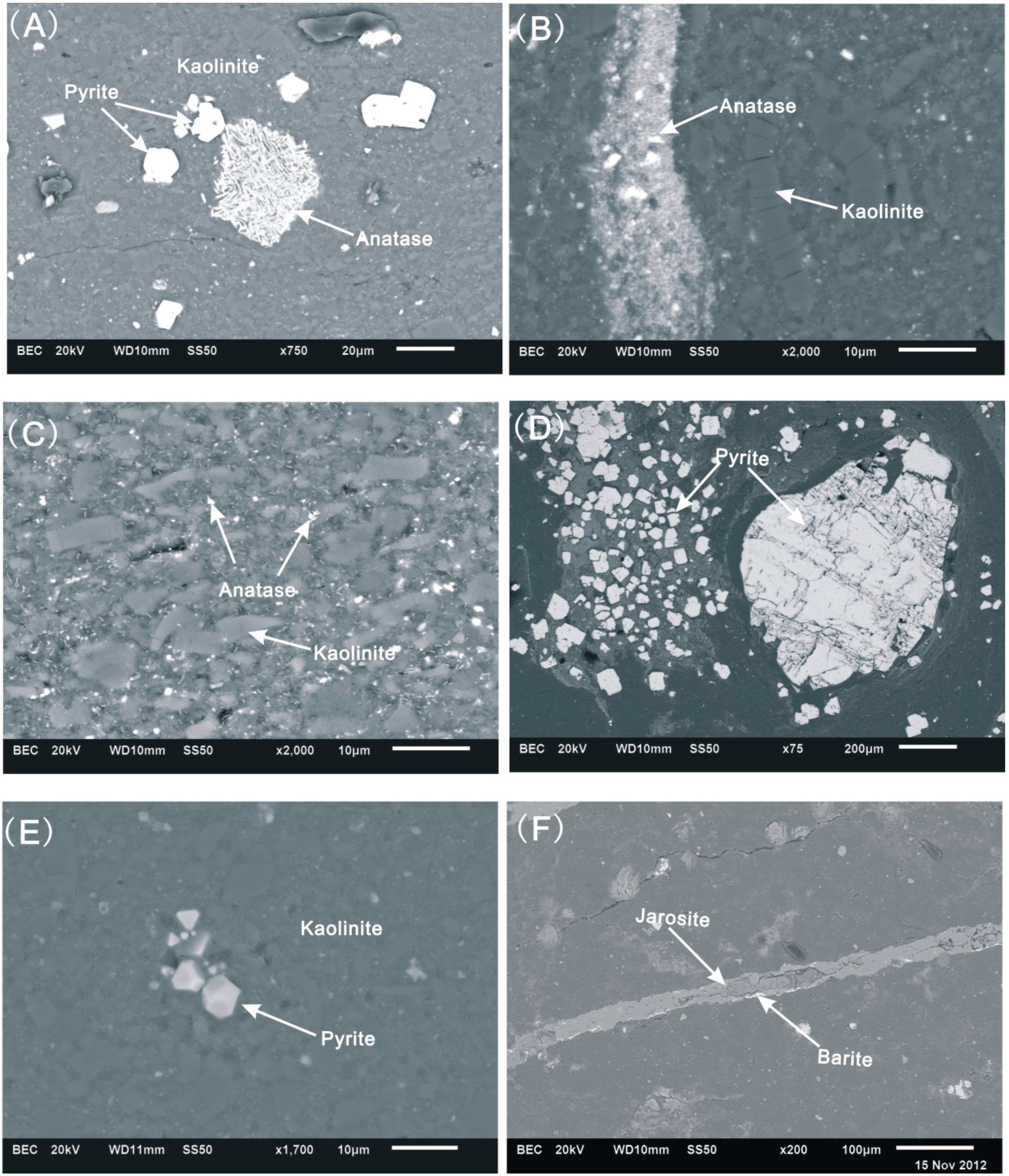
4.1.1. Kaolinite and Illite
4.1.2. Pyrite, Jarosite and Barite
4.1.3. Anatase
4.1.4. Calcite and Gypsum
4.1.5. Zircon and Florencite
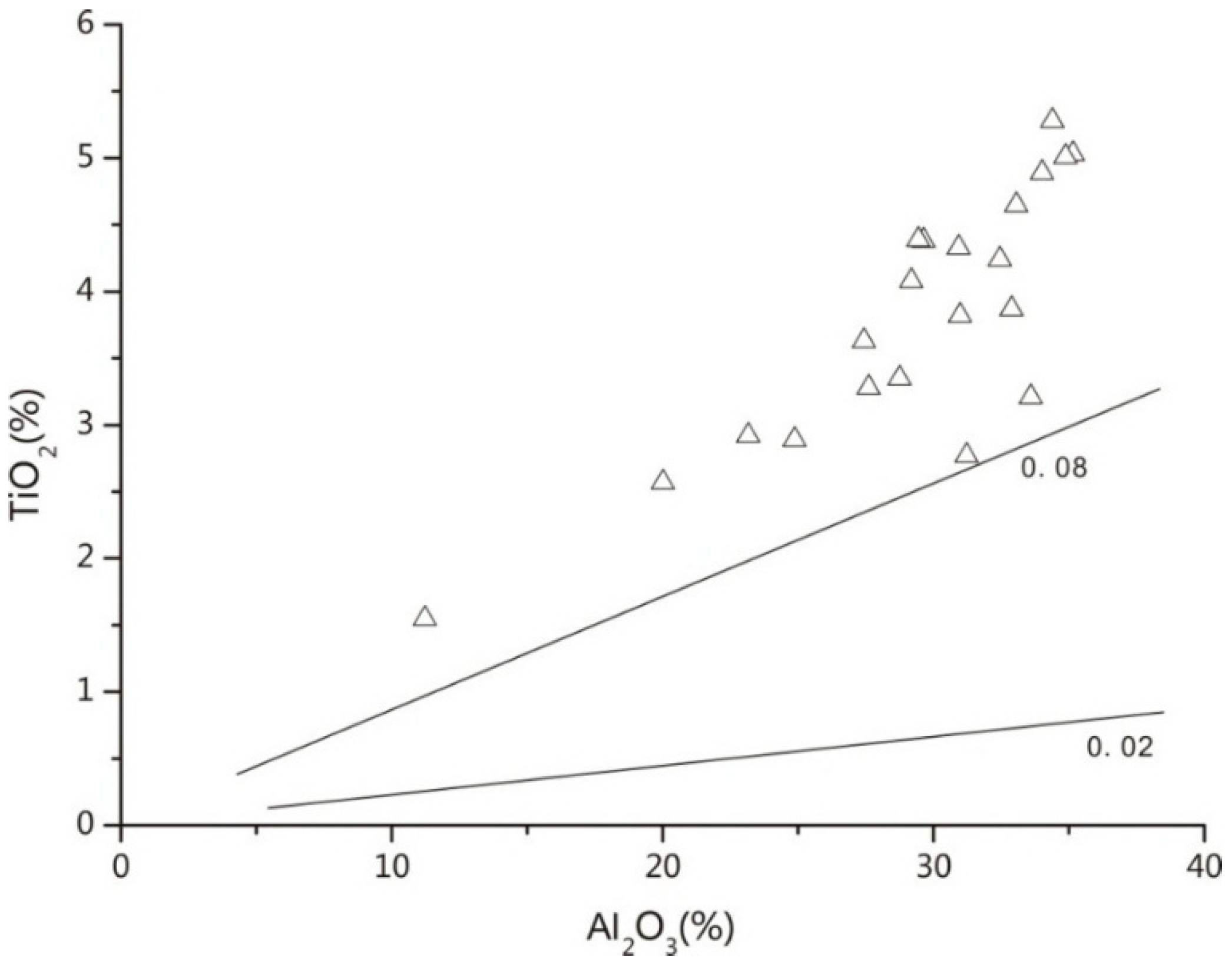
4.2. Major Elements
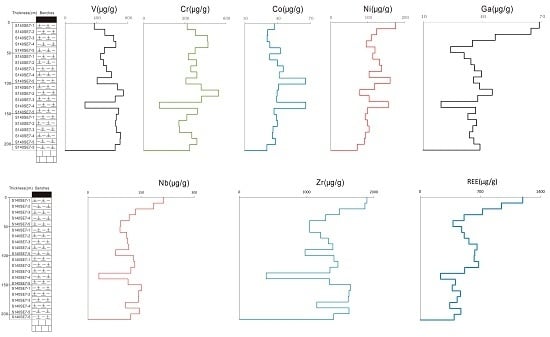
4.3. Trace Elements
4.3.1. Scandium
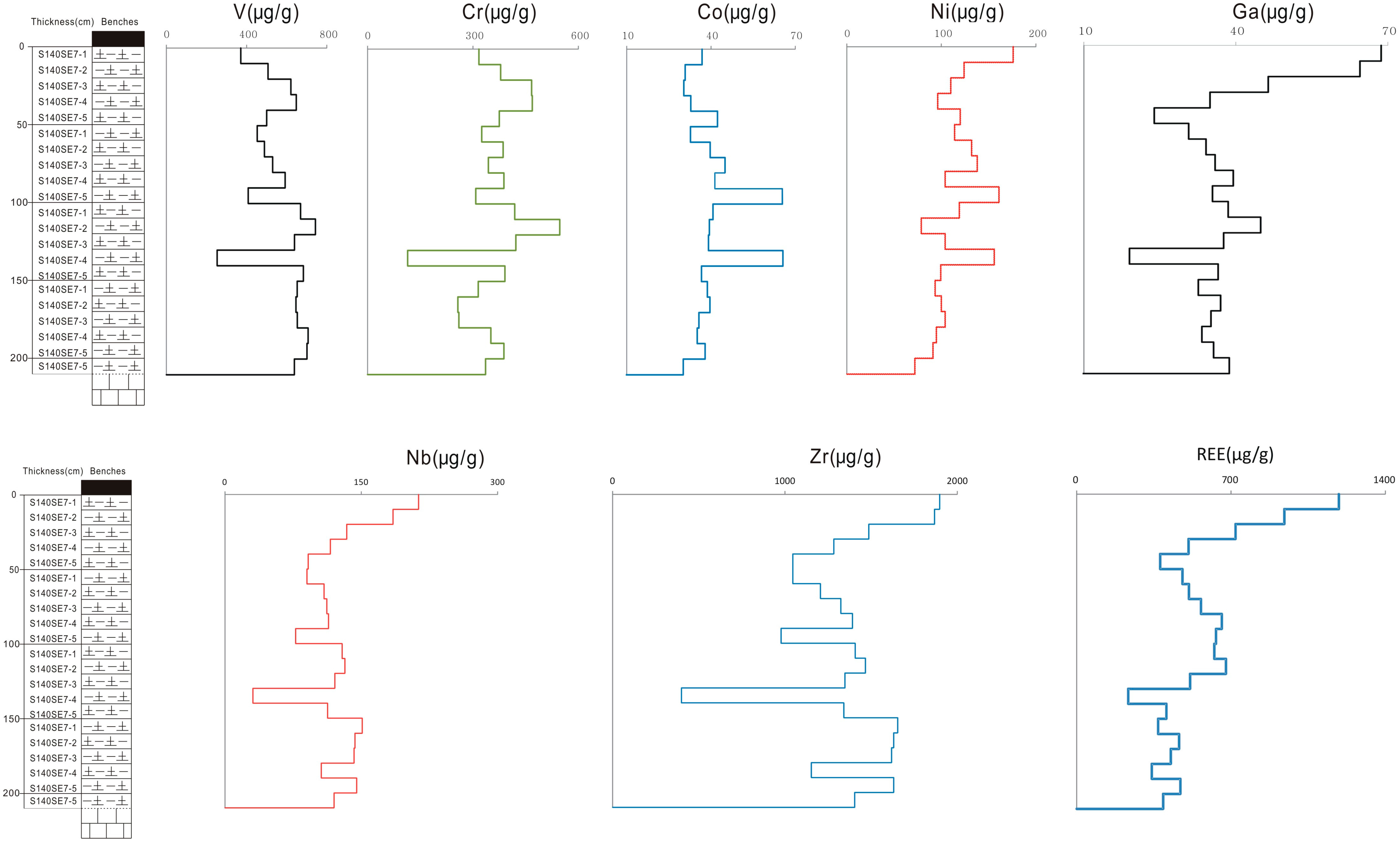
4.3.2. Vanadium, Cr, Co and Ni
4.3.3. Niobium, Ta, Zr and Hf
4.3.4. Gallium
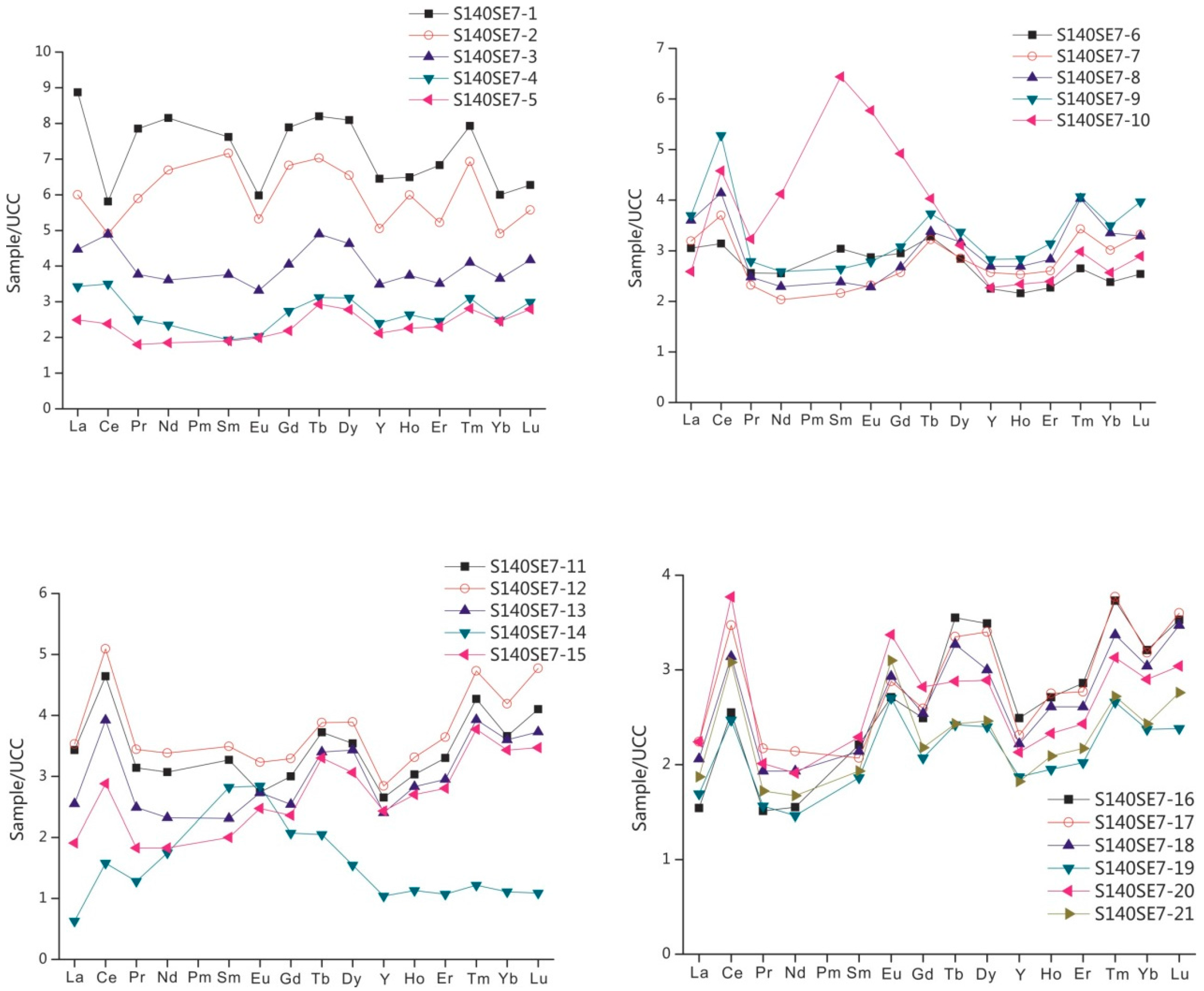
4.4. Rare Earth Elements (REE)
5. Discussion
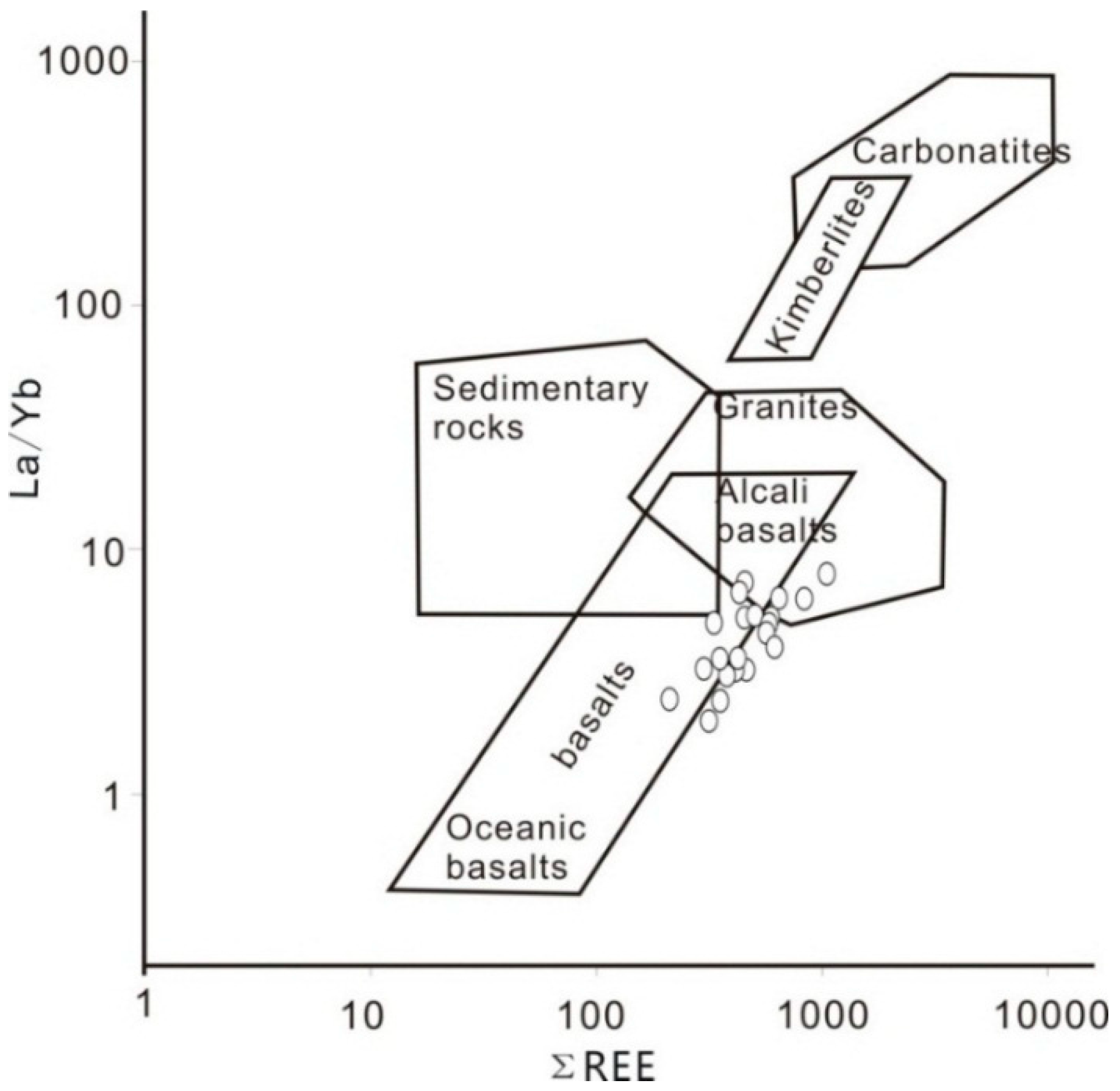
5.1. Origin of Tuff
5.2. Hydrothermal Solution
5.3. Preliminary Evaluation of Rare Metals
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.-L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y.P. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Granite, E.J.; Mayfield, D.B.; Lewis, A.S.; Finkelman, R.B. Notes on Contributions to the Science of Rare Earth Element Enrichment in Coal and Coal Combustion Byproducts. Minerals 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Chekryzhov, I.Y.; Seredin, V.V.; Nechaev, V.P.; Graham, I.T.; Hower, J.C.; Ward, C.R.; Ren, D.Y.; Wang, X.B. Metalliferous coal deposits in East Asia (Primorye of Russia and South China): A review of geodynamic controls and styles of mineralization. Gondwana Res. 2016, 29, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Wang, P.P.; Ward, C.R.; Tang, Y.G.; Song, X.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Hower, J.C.; Li, T.; Seredin, V.V.; Wagner, N.J.; et al. Elemental and mineralogical anomalies in the coal-hosted Ge ore deposit of Lincang, Yunnan, southwestern China: Key role of N2-CO2-mixed hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 152, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.N.; Hower, J.C.; Dai, S.; Wang, P.; Xie, P.; Liu, J. Petrology and Geochemistry of the Harlan, Kellioka, and Darby Coals from the Louellen 7.5-Minute Quadrangle, Harlan County, Kentucky. Minerals 2015, 5, 894–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Finkelman, R.B. Metalliferous coals: A review of the main genetic and geochemical types. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 253–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.F. Coal deposits as potential alternative sources for lanthanides and yttrium. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.F.; Sun, Y.Z.; Chekryzhov, I.Y. Coal deposits as promising sources of rare metals for alternative power and energy-efficient technologies. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Jiang, J.H.; Hower, J.C.; Song, X.L.; Jiang, Y.F.; Wang, X.B.; Gornostaeva, T.; Li, X.; et al. Composition and modes of occurrence of minerals and elements in coal combustion products derived from high-Ge coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V. From coal science to metal production and environmental protection: A new story of success. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 90–91, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, M.Q.; Wang, X.B.; Wang, J.M.; Song, X.L.; Jiang, Y.F.; Luo, Y.B.; Song, Z.T.; Yang, Z.; et al. A new type of Nb (Ta)–Zr(Hf)–REE–Ga polymetallic deposit in the late Permian coal-bearing strata, eastern Yunnan, southwestern China: Possible economic significance and genetic implications. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 83, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Xing, Y.W.; Zhang, W.G.; Song, W.J.; Wang, P.P. Enrichment of U-Se-Mo-Re-V in coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: Geochemical and mineralogical data from the Late Permian Guiding Coalfield, Guizhou, China. Miner. Deposita 2015, 50, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Eble, C.F.; O’Keefe, J.M.K.; Dai, S.F.; Wang, P.P.; Xie, P.P.; Liu, J.J.; Ward, C.R.; French, D. Petrology, Palynology, and Geochemistry of Gray Hawk Coal (Early Pennsylvanian, Langsettian) in Eastern Kentucky, USA. Minerals 2015, 5, 592–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhao, L.; Hower, J.C.; Johnston, M.N.; Song, W.J.; Wang, P.P.; Zhang, S.F. Petrology, mineralogy, and chemistry of size-fractioned fly ash from the Jungar power plant, Inner Mongolia, China, with emphasis on the distribution of rare earth elements. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.G.; Su, S.C.; Xiao, M.G.; Li, J.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the Late Permian coals in the Huayingshan coal-bearing area, Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Yang, J.Y.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Liu, H.D.; Garrison, T.M.; French, D.; O’Keefe, J.M.K. Geochemical and mineralogical evidence for a coal-hosted uranium deposit in the Yili Basin, Xinjiang, northwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Coal Geology Bureau. Sedimentary Environments and Coal Accumulation of Late Permian Coal Formation in Western Guizhou, Southern Sichuan and Eastern Yunnan, China; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 1996. (In Chinese)
- Dai, S.F.; Liu, J.J.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; French, D.; Jia, S.H.; Hood, M.M.; Garrison, T.M. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of Late Permian coals and host rocks from the Guxu Coalfield, Sichuan Province, China, with emphasis on enrichment of rare metals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Sampling of Coal Seams; Chinese Standard GB/T 482–2008; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- ASTM International. Test Method for Ash in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke from Coal; ASTM D3174–11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.C. Computer programs for standardless quantitative analysis of minerals using the full powder diffraction profile. Powder Diffr. 1991, 6, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.R.; Spears, D.A.; Booth, C.A.; Staton, I.; Gurba, L.W. Mineral matter and trace elements in coals of the Gunnedah Basin, New South Wales, Australia. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 40, 281–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.R.; Matulis, C.E.; Taylor, J.C.; Dale, L.S. Quantification of mineral matter in the Argonne Premium coals using interactive Rietveld-based X-ray diffraction. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2001, 46, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.D.; Ward, C.R. Quantitative X-ray powder diffraction analysis of clay minerals in Australian coals using Rietveldmethods. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 21, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.H.; Yan, M.C. Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Ren, Y.L. Element gochemistry of volcanic ash derived tonsteins in late Permian coal-bearing formation of eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou, China. Acta Sedimentol Sin. 1994, 12, 123–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Bohor, B.F.; Ren, Y.L. Trace element geochemistry of altered volcanic ash layers (tonsteins) in late Permian coal-bearing formations of eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou provinces, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2000, 44, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichuan Bureau of Coal Geology; Sichuan Institute of Coal Geology. Sedimentary Environment and Coal Accumulating Regulations of Late Permian Coal-Bearing Formation in Southern Sichuan; Guizhou Sceinece and Technology Press: Guiyang, China, 1994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Chou, C.-L.; Yue, M.; Luo, K.L.; Ren, D.Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of a Late Permian coal in the Dafang Coalfield, Guizhou, China: Influence from siliceous and iron-rich calcic hydrothermal fluids. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 61, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Zhou, Y.P.; Chou, C.-L.; Wang, X.B.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X.W. Mineralogy and geochemistry of a superhigh-organic-sulfur coal, Yanshan Coalfield, Yunnan, China: Evidence for a volcanic ash component and influence by submarine exhalation. Chem. Geol. 2008, 255, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DZ/T 0203–2002. Geology Mineral Industry Standard of P.R. China: Specifications for Rare Metal Mineral Exploration; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mineral Resources Industry Requirements Manual Editorial Board. Mineral Resources Industry Requirements Manual; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Graham, I.T.; Chou, C.-L.; Ward, C.R. A review of anomalous rare earth elements and yttrium in coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 159, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.W.; Zhao, Z.H. Geochemistry of mineralization with exchangeable REY in the weathering crusts of granitic rocks in South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2008, 33, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Li, D.; Chou, C.-L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, D.Y.; Ma, Y.W.; Sun, Y.Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of boehmite-rich coals: New insights from the Haerwusu Surface Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 74, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskenazy, G.M. Rare earth elements in a sampled coal from the Pirin Deposit, Bulgaria. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1987, 7, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, S.S.; Stanton, R.W.; Ryer, T.A. The effects of volcanic ash on the maceral and chemical composition of the C coal bed, Emery Coal Field, Utah. Org. Geochem. 1989, 14, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Ruppert, L.F.; Eble, C.F. Lanthanide, yttrium, and zirconium anomalies in the fire Clay coal bed, Eastern Kentucky. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 39, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.-L.; Li, S.S.; Jiang, Y.F. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the No. 6 coal (Pennsylvanian) in the Jungar Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Li, T.J.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Sun, J.H.; Liu, J.J.; Song, H.J.; Wei, J.P.; Li, Q.Q.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the Pennsylvanian coal in the Hailiushu Mine, Daqingshan Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China: Implications of sediment-source region and acid hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 137, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, R.; Harrison, R.K.; Land, D.H.; Young, B.R.; Davis, A.E.; Smith, T.K. Volcanogenic tonsteins from tertiary coal measures, East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1983, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, K.; Zhou, Y.P.; Ren, D.Y. Petrography and geochemistry of tonsteins from the 4th Member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in southern Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhang, W.G.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Song, W.J.; Wang, X.B.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Kang, H.; et al. Factors controlling geochemical and mineralogical compositions of coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: A case study from the Heshan Coalfield, southern China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 109–110, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zhang, W.G.; Ward, C.R.; Seredin, V.V.; Hower, J.C.; Li, X.; Song, W.J.; Wang, X.B.; Kang, H.; Zheng, L.C.; et al. Mineralogical and geochemical anomalies of Late Permian coals from the Fusui Coalfield, Guangxi Province, southern China: Influences of terrigenous materials and hydrothermal fluids. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 105, 60–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.Y.; Zhao, F.H.; Dai, S.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Luo, K.L. Geochemistry of Trace Elements in Coal; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Ren, Y.L. Distribution of arsenic in coals of Yunnan Province, China, and its controlling factors. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1992, 20, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Chou, C.-L. Occurrence and origin of minerals in a chamosite-bearing coal of Late Permian age, Zhaotong, Yunnan, China. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Dai, S.F.; Chou, C.-L.; Zhang, M.Q.; Wang, J.M.; Song, X.L.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.P.; Ren, D.Y. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Late Permian coals from the Taoshuping Mine, Yunnan Province, China: Evidences for the sources of minerals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 96–97, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Tian, L.W.; Chou, C.-L.; Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, M.Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Cao, H.Z.; Ren, D.Y. Mineralogical and compositional characteristics of Late Permian coals from an area of high lung cancer rate in Xuan Wei, Yunnan, China: Occurrence and origin of quartz and chamosite. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of Occurrence of Trace Elements in Coal; US Geological Survey Open-File Report; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1981; No. 81–99; p. 322. [Google Scholar]
- The U.S. Department of Energy. Available online: http://www.energy.gov/fe/articles/doe-selects-projects-enhance-its’s-research-recovery-rare-earth-elements-coal-and-coal.2015 (accessed on 2 December 2015).
- DZ/T 0208–2002. Geology Mineral Industry Standard of P.R. China: Specifications for Placer (Metallic Mineral) Exploration; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- DZ/T 0204–2002. Geology Mineral Industry Standard of P.R. China: Specifications for Rare Earth Mineral Exploration; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

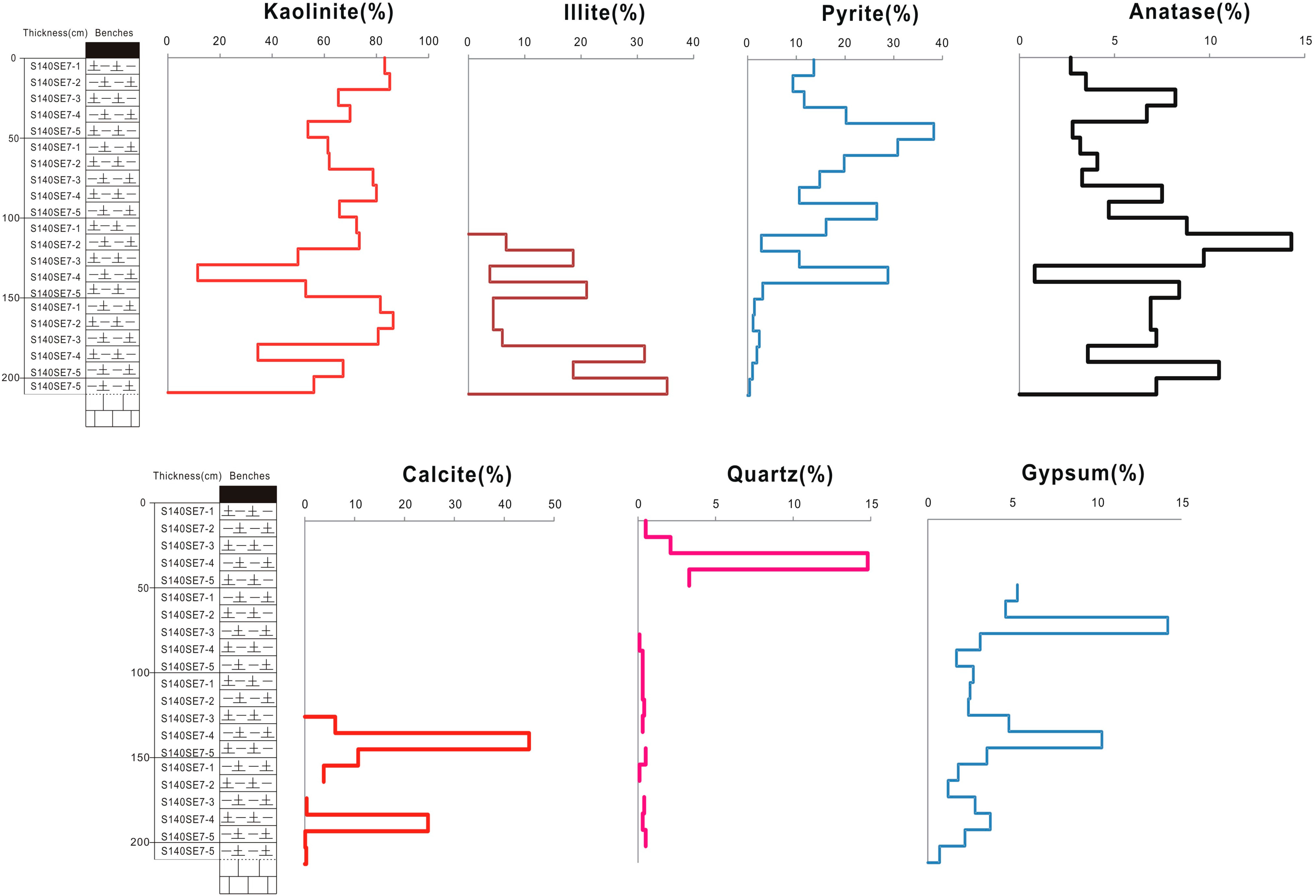

| Sample | Kaolinite | Illite | Pyrite | Anatase | Calcite | Quartz | Gypsum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S140SE7-1 | 83.2 | - | 13.6 | 2.7 | - | 0.5 | - |
| S140SE7-2 | 85.1 | - | 9.3 | 3.5 | - | 2.1 | - |
| S140SE7-3 | 65.4 | - | 11.6 | 8.2 | - | 14.8 | - |
| S140SE7-4 | 69.9 | - | 20.2 | 6.7 | - | 3.3 | - |
| S140SE7-5 | 53.7 | - | 38.2 | 2.8 | - | - | 5.3 |
| S140SE7-6 | 61.4 | - | 30.8 | 3.2 | - | - | 4.6 |
| S140SE7-7 | 61.9 | - | 19.8 | 4.1 | - | - | 14.2 |
| S140SE7-8 | 78.7 | - | 14.8 | 3.3 | - | 0.1 | 3.1 |
| S140SE7-9 | 80 | - | 10.6 | 7.5 | - | 0.3 | 1.7 |
| S140SE7-10 | 65.8 | - | 26.5 | 4.7 | - | 0.3 | 2.7 |
| S140SE7-11 | 72.4 | - | 16.1 | 8.8 | - | 0.3 | 2.5 |
| S140SE7-12 | 73.4 | 6.7 | 2.8 | 14.3 | - | 0.4 | 2.4 |
| S140SE7-13 | 49.9 | 18.6 | 10.6 | 9.7 | 6.1 | 0.3 | 4.8 |
| S140SE7-14 | 11.4 | 3.8 | 28.8 | 0.8 | 45 | - | 10.3 |
| S140SE7-15 | 52.9 | 21 | 3.1 | 8.4 | 10.7 | 0.5 | 3.5 |
| S140SE7-16 | 81.5 | 4.4 | 1.4 | 6.9 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 1.8 |
| S140SE7-17 | 86.4 | 4.4 | 1.1 | 6.9 | - | - | 1.2 |
| S140SE7-18 | 80.7 | 6 | 2.4 | 7.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 2.8 |
| S140SE7-19 | 34.5 | 31.3 | 1.9 | 3.6 | 24.7 | 0.3 | 3.7 |
| S140SE7-20 | 67.2 | 18.6 | 1 | 10.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 2.2 |
| S140SE7-21 | 56 | 35.3 | 0.4 | 7.2 | 0.3 | - | 0.7 |
| Average | 65.30 | 15.01 | 12.62 | 6.24 | 11.39 | 1.61 | 3.97 |
| Sample | LOI | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | FeO | SiO2/Al2O3 | TiO2/Al2O3 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Zr | Nb | Mo | Cd | In | Sb | Cs | Ba | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S140SE7-1 | 19.87 | 36.25 | 2.77 | 31.23 | 9.1 | 0.012 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.1 | 0.075 | 0.6 | 1.16 | 0.09 | 454 | 9.46 | 33.4 | 371 | 317 | 36.8 | 176 | 247 | 237 | 68.7 | 3.98 | 292 | 1898 | 213 | 3.4 | 3.13 | 0.615 | 4.22 | 1.17 | 146 | 57.6 | 15.9 | 4.02 | 0.042 | 0.11 | 58.1 | 1.41 | 50.3 | 25.7 |
| S140SE7-2 | 17.87 | 38.9 | 3.21 | 33.6 | 5.52 | 0.009 | 0.26 | 0.1 | 0.31 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.55 | 1.16 | 0.10 | 445 | 9.91 | 38 | 507 | 379 | 30.8 | 124 | 243 | 190 | 64.5 | 2.86 | 190 | 1868 | 185 | 2.12 | 2.04 | 0.654 | 2.82 | 1.15 | 113 | 51.4 | 14.6 | 3.52 | 0.02 | 0.058 | 40.4 | 1.21 | 49.7 | 24.5 |
| S140SE7-3 | 18.15 | 36.84 | 3.82 | 30.98 | 9.52 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.1 | 0.051 | 0.5 | 1.19 | 0.12 | 349 | 7.55 | 31.8 | 621 | 467 | 30.3 | 110 | 245 | 143 | 46.4 | 2.96 | 282 | 1487 | 134 | 1.73 | 0.952 | 0.587 | 3.51 | 1.48 | 141 | 37.7 | 8.88 | 4.44 | 0.018 | 0.085 | 39 | 1.62 | 33.4 | 9.83 |
| S140SE7-4 | 19.66 | 32.69 | 3.63 | 27.44 | 15.46 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.1 | 0.051 | 0.8 | 1.19 | 0.13 | 367 | 6.33 | 29.1 | 648 | 469 | 32.8 | 96.2 | 259 | 123 | 34.9 | 3.52 | 256 | 1284 | 116 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.719 | 3.7 | 1.4 | 122 | 33.4 | 8.29 | 3.44 | 0.013 | 0.087 | 47.4 | 1.63 | 28.2 | 9.71 |
| S140SE7-5 | 23.56 | 24.78 | 2.57 | 20.01 | 28.09 | 0.015 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.085 | 0.037 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.13 | 337 | 5.66 | 25.6 | 500 | 375 | 42.3 | 120 | 258 | 107 | 23.9 | 3.2 | 166 | 1046 | 91.6 | 1.56 | 1.46 | 0.457 | 4.13 | 1.07 | 92 | 26 | 6.91 | 3.16 | 0.014 | 0.207 | 61.3 | 1.22 | 23.8 | 8.11 |
| S140SE7-6 | 21.65 | 28.05 | 2.92 | 23.17 | 23 | 0.015 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.094 | 0.046 | 0.6 | 1.21 | 0.13 | 299 | 5.42 | 24 | 453 | 325 | 32.7 | 114 | 235 | 100 | 30.7 | 2.03 | 191 | 1046 | 90.2 | 1.22 | 1.31 | 0.437 | 4.23 | 0.892 | 89.6 | 27.1 | 5.96 | 2.75 | 0.007 | 0.24 | 53.5 | 1.15 | 23.4 | 8.97 |
| S140SE7-7 | 19.52 | 32.7 | 3.28 | 27.62 | 16.08 | 0.012 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.043 | 0.4 | 1.18 | 0.12 | 421 | 6.95 | 28.2 | 489 | 386 | 39.7 | 132 | 286 | 109 | 34.1 | 3.69 | 188 | 1206 | 109 | 0.985 | 1.22 | 0.494 | 3.41 | 1.1 | 101 | 30.7 | 7.6 | 2.83 | 0.006 | 0.103 | 49.3 | 1.35 | 27.9 | 11.4 |
| S140SE7-8 | 19.06 | 33.86 | 3.35 | 28.75 | 14.17 | 0.013 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.048 | 0.4 | 1.18 | 0.12 | 401 | 6.61 | 32.4 | 530 | 344 | 45 | 138 | 278 | 124 | 35.9 | 3.1 | 232 | 1324 | 112 | 1.04 | 1.31 | 0.541 | 3.91 | 1.1 | 115 | 33.8 | 7.82 | 3.66 | 0.009 | 0.189 | 55.2 | 1.51 | 29 | 13.2 |
| S140SE7-9 | 16.45 | 38.23 | 3.87 | 32.89 | 7.81 | 0.008 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.049 | 0.35 | 1.16 | 0.12 | 442 | 7.11 | 33.3 | 592 | 388 | 41.4 | 104 | 251 | 115 | 39.5 | 2.66 | 194 | 1392 | 114 | 1.03 | 1.5 | 0.519 | 2.23 | 1.05 | 99.3 | 36.9 | 8.57 | 3.67 | 0.006 | 0.058 | 34 | 1.48 | 30.4 | 16.6 |
| S140SE7-10 | 20.62 | 29.97 | 2.89 | 24.88 | 20.9 | 0.011 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.55 | 1.20 | 0.12 | 311 | 4.87 | 24.7 | 408 | 308 | 65.4 | 161 | 282 | 103 | 35.4 | 2.46 | 154 | 978 | 77.7 | 1.45 | 1.83 | 0.516 | 6.79 | 0.927 | 79.1 | 25.4 | 5.68 | 2.8 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 75.2 | 1.14 | 21.7 | 12.6 |
| S140SE7-11 | 17.82 | 35.72 | 4.38 | 29.64 | 11.54 | 0.004 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.066 | 0.5 | 1.21 | 0.15 | 321 | 7.34 | 33.2 | 669 | 419 | 40.7 | 119 | 316 | 192 | 38.5 | 5.34 | 287 | 1408 | 129 | 1.54 | 2.77 | 0.6 | 2.73 | 1.94 | 127 | 36.1 | 8.79 | 3.88 | 0.006 | 0.093 | 44 | 1.73 | 30 | 16 |
| S140SE7-12 | 15.42 | 40.12 | 4.65 | 33.07 | 5.18 | 0.007 | 0.2 | 0.26 | 0.49 | 0.43 | 0.086 | 0.25 | 1.21 | 0.14 | 248 | 7.59 | 36.5 | 743 | 547 | 39.4 | 78.8 | 330 | 178 | 44.9 | 14.9 | 325 | 1467 | 132 | 1.68 | 4.45 | 0.572 | 1.71 | 5.03 | 141 | 37.9 | 8.98 | 4.05 | 0.013 | 0.118 | 23.6 | 2.06 | 31.8 | 17.7 |
| S140SE7-13 | 17.93 | 35.93 | 4.39 | 29.44 | 9.57 | 0.008 | 0.2 | 1.56 | 0.3 | 0.43 | 0.067 | 0.6 | 1.22 | 0.15 | 219 | 6.48 | 30.7 | 639 | 422 | 39.1 | 104 | 266 | 161 | 37.6 | 12.5 | 341 | 1348 | 121 | 1.67 | 5.14 | 0.627 | 2.21 | 3.52 | 137 | 33.2 | 8.27 | 3.41 | 0.006 | 0.134 | 33.8 | 1.69 | 28.5 | 14 |
| S140SE7-14 | 18.09 | 15.54 | 1.55 | 11.23 | 31.32 | 0.039 | 0.43 | 20.38 | 0.16 | 0.65 | 0.017 | 1.75 | 1.38 | 0.14 | 31.5 | 2.16 | 12.6 | 253 | 114 | 65.6 | 156 | 146 | 108 | 19 | 14.9 | 503 | 400 | 30.7 | 0.712 | 18.4 | 0.211 | 3.32 | 1.66 | 60.3 | 9.45 | 2.28 | 1.7 | 0.008 | 0.292 | 34.9 | 0.595 | 8.57 | 5.46 |
| S140SE7-15 | 15.61 | 38.45 | 4.33 | 30.94 | 5.28 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 3.4 | 0.53 | 0.82 | 0.05 | 0.85 | 1.24 | 0.14 | 170 | 6.3 | 31.3 | 683 | 391 | 36.6 | 99.4 | 188 | 148 | 36.5 | 23.7 | 404 | 1342 | 113 | 1.37 | 6.96 | 0.501 | 2.08 | 5.27 | 143 | 34.9 | 7.88 | 3.69 | 0.006 | 0.156 | 26.9 | 1.52 | 28.7 | 14.2 |
| S140SE7-16 | 14.89 | 40.64 | 5.28 | 34.4 | 1.94 | 0.006 | 0.16 | 1.52 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.4 | 1.18 | 0.15 | 254 | 7.2 | 35.7 | 652 | 315 | 38.7 | 93.4 | 265 | 170 | 32.6 | 6.83 | 279 | 1654 | 151 | 1.78 | 3.52 | 0.628 | 1.27 | 1.96 | 131 | 41.3 | 10.4 | 4.61 | 0.018 | 0.071 | 19.6 | 1.34 | 34 | 17.4 |
| S140SE7-17 | 14.91 | 41.58 | 5.03 | 35.15 | 1.99 | 0.004 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.49 | 0.37 | 0.056 | 0.35 | 1.18 | 0.14 | 299 | 6.89 | 34.8 | 646 | 257 | 39.6 | 100 | 255 | 166 | 37 | 9.09 | 261 | 1631 | 143 | 0.996 | 4 | 0.567 | 1.68 | 2.37 | 131 | 41.4 | 10.1 | 3.76 | 0.025 | 0.08 | 23.8 | 1.36 | 32.2 | 18.5 |
| S140SE7-18 | 15.35 | 40.55 | 4.89 | 34.01 | 3.47 | 0.004 | 0.24 | 0.4 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.059 | 0.85 | 1.19 | 0.14 | 258 | 6.31 | 33.1 | 653 | 260 | 35.7 | 104 | 265 | 147 | 35.1 | 12.1 | 286 | 1619 | 142 | 1.4 | 3.55 | 0.531 | 1.99 | 2.25 | 137 | 39.8 | 9.76 | 3.74 | 0.013 | 0.08 | 26.1 | 1.39 | 32 | 19.5 |
| S140SE7-19 | 15.5 | 37.44 | 4.08 | 29.19 | 4.03 | 0.013 | 0.59 | 6.57 | 0.72 | 1.47 | 0.045 | 0.9 | 1.28 | 0.14 | 153 | 5.66 | 25 | 707 | 351 | 35.1 | 94.7 | 199 | 139 | 33.3 | 39.5 | 387 | 1153 | 106 | 1.49 | 6.92 | 0.505 | 2.42 | 5.33 | 160 | 28.8 | 7.07 | 3.48 | 0.036 | 0.287 | 21.8 | 1.39 | 27 | 20.1 |
| S140SE7-20 | 13.94 | 42.07 | 5.01 | 34.88 | 1.83 | 0.003 | 0.32 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.76 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 1.21 | 0.14 | 246 | 6.79 | 32.1 | 701 | 388 | 37.9 | 91.2 | 281 | 174 | 35.6 | 19.8 | 322 | 1631 | 145 | 1.6 | 4.14 | 0.578 | 1.76 | 3.18 | 158 | 41.4 | 9.92 | 4.05 | 0.009 | 0.164 | 23 | 1.55 | 34 | 26.4 |
| S140SE7-21 | 15.82 | 40.92 | 4.24 | 32.45 | 3.12 | 0.004 | 0.46 | 1.12 | 0.53 | 1.26 | 0.055 | 1.3 | 1.26 | 0.13 | 168 | 5.58 | 26.8 | 638 | 336 | 30.1 | 72 | 193 | 153 | 38.7 | 31.1 | 323 | 1405 | 120 | 1.48 | 3.47 | 0.526 | 1.5 | 4.24 | 165 | 35 | 8.39 | 3.43 | 0.015 | 0.236 | 25.2 | 1.27 | 29 | 23.8 |
| Average | 17.70 | 35.30 | 3.82 | 29.28 | 10.90 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 1.80 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.66 | 1.21 | 0.13 | 295 | 6.58 | 30.1 | 576 | 360 | 39.8 | 114 | 252 | 147 | 38.2 | 10.5 | 279 | 1361 | 123 | 1.53 | 3.80 | 0.54 | 2.93 | 2.29 | 123 | 35.2 | 8.67 | 3.53 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 38.9 | 1.41 | 30.2 | 15.9 |
| UCC | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 20 | 3 | 11 | 60 | 35 | 10 | 20 | 25 | 71 | 17 | 112 | 350 | 190 | 25 | 1.5 | 0.1 | nd | 0.2 | 3.7 | 550 | 5.8 | 2.2 | 2 | 0.0004 | 0.8 | 20 | nd | 10.7 | 2 |
| CC | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 14.7 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 4.0 | 5.7 | 10.1 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 7.2 | 4.9 | 1.0 | 38.0 | nd | 14.7 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 6.1 | 3.9 | 1.8 | 35.7 | 0.2 | 1.9 | nd | 2.8 | 7.9 |
| Sample | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Y | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S140SE7-1 | 266 | 372 | 55.7 | 212 | 34.3 | 5.38 | 30 | 4.92 | 28.3 | 142 | 5.19 | 15.7 | 2.38 | 13.2 | 1.88 |
| S140SE7-2 | 180 | 314 | 41.8 | 174 | 32.2 | 4.79 | 25.9 | 4.22 | 22.9 | 111 | 4.79 | 12 | 2.08 | 10.8 | 1.67 |
| S140SE7-3 | 134 | 313 | 26.8 | 93.9 | 16.9 | 2.99 | 15.4 | 2.94 | 16.2 | 76.8 | 2.99 | 8.08 | 1.23 | 8.02 | 1.25 |
| S140SE7-4 | 103 | 224 | 17.8 | 61.1 | 8.7 | 1.83 | 10.4 | 1.87 | 10.9 | 52.7 | 2.11 | 5.66 | 0.929 | 5.45 | 0.897 |
| S140SE7-5 | 74.6 | 152 | 12.8 | 48.1 | 8.55 | 1.79 | 8.32 | 1.76 | 9.73 | 46.7 | 1.81 | 5.28 | 0.843 | 5.4 | 0.837 |
| S140SE7-6 | 91.5 | 201 | 18.2 | 66.4 | 13.7 | 2.58 | 11.2 | 1.97 | 9.95 | 49.5 | 1.73 | 5.21 | 0.796 | 5.23 | 0.763 |
| S140SE7-7 | 95.7 | 237 | 16.5 | 52.9 | 9.71 | 2.09 | 9.78 | 1.93 | 9.99 | 56.6 | 2.02 | 5.97 | 1.03 | 6.63 | 0.996 |
| S140SE7-8 | 108 | 265 | 17.6 | 59.6 | 10.7 | 2.05 | 10.2 | 2.03 | 11.1 | 59.1 | 2.15 | 6.5 | 1.21 | 7.37 | 0.986 |
| S140SE7-9 | 111 | 338 | 19.8 | 67.4 | 11.9 | 2.5 | 11.7 | 2.24 | 11.8 | 62.2 | 2.27 | 7.23 | 1.22 | 7.69 | 1.19 |
| S140SE7-10 | 77.7 | 293 | 22.9 | 107 | 29 | 5.19 | 18.7 | 2.42 | 10.9 | 50 | 1.87 | 5.5 | 0.895 | 5.65 | 0.866 |
| S140SE7-11 | 103 | 297 | 22.3 | 79.7 | 14.7 | 2.47 | 11.4 | 2.23 | 12.4 | 58.3 | 2.42 | 7.58 | 1.28 | 8.05 | 1.23 |
| S140SE7-12 | 106 | 326 | 24.4 | 87.8 | 15.7 | 2.91 | 12.5 | 2.33 | 13.6 | 62.5 | 2.65 | 8.38 | 1.42 | 9.21 | 1.43 |
| S140SE7-13 | 76.5 | 251 | 17.7 | 60.4 | 10.4 | 2.46 | 9.64 | 2.04 | 12 | 52.7 | 2.26 | 6.79 | 1.18 | 7.91 | 1.12 |
| S140SE7-14 | 18.9 | 101 | 9.12 | 45.4 | 12.7 | 2.56 | 7.86 | 1.23 | 5.44 | 22.9 | 0.907 | 2.45 | 0.367 | 2.45 | 0.326 |
| S140SE7-15 | 57.3 | 184 | 13 | 47.7 | 9 | 2.22 | 8.96 | 1.98 | 10.7 | 53.5 | 2.16 | 6.45 | 1.13 | 7.54 | 1.04 |
| S140SE7-16 | 46.2 | 163 | 10.7 | 40.3 | 9.95 | 2.44 | 9.47 | 2.13 | 12.2 | 54.7 | 2.17 | 6.58 | 1.12 | 7.07 | 1.06 |
| S140SE7-17 | 67.2 | 222 | 15.4 | 55.7 | 9.3 | 2.59 | 9.83 | 2.01 | 11.9 | 50.8 | 2.2 | 6.38 | 1.13 | 6.99 | 1.08 |
| S140SE7-18 | 61.8 | 201 | 13.7 | 50.2 | 9.63 | 2.64 | 9.67 | 1.96 | 10.5 | 48.9 | 2.09 | 6 | 1.01 | 6.68 | 1.04 |
| S140SE7-19 | 50.7 | 158 | 11.1 | 37.9 | 8.35 | 2.43 | 7.86 | 1.45 | 8.4 | 41.1 | 1.56 | 4.65 | 0.799 | 5.21 | 0.714 |
| S140SE7-20 | 67.3 | 241 | 14.3 | 49.6 | 10.3 | 3.03 | 10.7 | 1.73 | 10.1 | 46.8 | 1.86 | 5.59 | 0.939 | 6.37 | 0.913 |
| S140SE7-21 | 56.1 | 197 | 12.2 | 43.3 | 8.68 | 2.79 | 8.27 | 1.46 | 8.61 | 40 | 1.67 | 4.98 | 0.817 | 5.35 | 0.827 |
| Average | 93.0 | 240 | 19.7 | 73.4 | 14.0 | 2.84 | 12.3 | 2.23 | 12.3 | 58.99 | 2.33 | 6.81 | 1.13 | 7.06 | 1.05 |
| Sample | REE (µg/g) | LREE (µg/g) | MREE (µg/g) | HREE (µg/g) | L/M | L/H | M/H | (La/Lu)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Lu)N | δCe | δEu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S140SE7-1 | 1189 | 940 | 211 | 38.4 | 4.46 | 24.51 | 5.49 | 1.41 | 1.16 | 1.26 | 0.70 | 0.77 |
| S140SE7-2 | 942 | 742 | 169 | 31.3 | 4.40 | 23.68 | 5.39 | 1.08 | 0.84 | 1.22 | 0.83 | 0.76 |
| S140SE7-3 | 721 | 585 | 114 | 21.6 | 5.11 | 27.10 | 5.30 | 1.07 | 1.19 | 0.97 | 1.19 | 0.85 |
| S140SE7-4 | 507 | 415 | 77.7 | 15.0 | 5.34 | 27.56 | 5.16 | 1.15 | 1.78 | 0.92 | 1.19 | 0.88 |
| S140SE7-5 | 379 | 296 | 68.3 | 14.2 | 4.33 | 20.89 | 4.82 | 0.89 | 1.31 | 0.78 | 1.12 | 0.98 |
| S140SE7-6 | 480 | 391 | 75.2 | 13.7 | 5.20 | 28.47 | 5.48 | 1.20 | 1.00 | 1.16 | 1.12 | 0.96 |
| S140SE7-7 | 509 | 412 | 80.4 | 16.6 | 5.12 | 24.74 | 4.83 | 0.96 | 1.48 | 0.78 | 1.36 | 0.99 |
| S140SE7-8 | 564 | 461 | 84.5 | 18.2 | 5.46 | 25.30 | 4.64 | 1.10 | 1.51 | 0.82 | 1.39 | 0.90 |
| S140SE7-9 | 658 | 548 | 90.4 | 19.6 | 6.06 | 27.96 | 4.61 | 0.93 | 1.40 | 0.78 | 1.64 | 0.97 |
| S140SE7-10 | 632 | 530 | 87.2 | 14.8 | 6.07 | 35.83 | 5.90 | 0.90 | 0.40 | 1.70 | 1.58 | 1.02 |
| S140SE7-11 | 624 | 517 | 86.8 | 20.6 | 5.95 | 25.13 | 4.22 | 0.84 | 1.05 | 0.73 | 1.41 | 0.88 |
| S140SE7-12 | 677 | 560 | 93.8 | 23.1 | 5.97 | 24.25 | 4.06 | 0.74 | 1.01 | 0.69 | 1.46 | 0.95 |
| S140SE7-13 | 514 | 416 | 78.8 | 19.3 | 5.28 | 21.60 | 4.09 | 0.68 | 1.10 | 0.68 | 1.56 | 1.13 |
| S140SE7-14 | 234 | 187 | 40.0 | 6.5 | 4.68 | 28.79 | 6.15 | 0.58 | 0.22 | 1.90 | 1.75 | 1.18 |
| S140SE7-15 | 407 | 311 | 77.4 | 18.3 | 4.02 | 16.98 | 4.22 | 0.55 | 0.96 | 0.68 | 1.54 | 1.14 |
| S140SE7-16 | 369 | 270 | 80.9 | 18.0 | 3.34 | 15.01 | 4.50 | 0.44 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 1.67 | 1.15 |
| S140SE7-17 | 465 | 370 | 77.1 | 17.8 | 4.79 | 20.79 | 4.34 | 0.62 | 1.08 | 0.72 | 1.57 | 1.24 |
| S140SE7-18 | 427 | 336 | 73.7 | 16.8 | 4.57 | 20.00 | 4.38 | 0.59 | 0.96 | 0.73 | 1.58 | 1.26 |
| S140SE7-19 | 340 | 266 | 61.2 | 12.9 | 4.34 | 20.57 | 4.74 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 1.52 | 1.38 |
| S140SE7-20 | 471 | 383 | 72.4 | 15.7 | 5.29 | 24.41 | 4.62 | 0.74 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 1.77 | 1.33 |
| S140SE7-21 | 392 | 317 | 61.1 | 13.6 | 5.19 | 23.25 | 4.48 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 1.72 | 1.51 |
| Average | 548 | 441 | 88.6 | 18.4 | 5.00 | 24.13 | 4.83 | 0.85 | 1.05 | 0.94 | 1.41 | 1.06 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, J.; Tian, H.; Li, T. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Tuff in Zhongliangshan Mine, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals 2016, 6, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020047
Zou J, Tian H, Li T. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Tuff in Zhongliangshan Mine, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals. 2016; 6(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Jianhua, Heming Tian, and Tian Li. 2016. "Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Tuff in Zhongliangshan Mine, Chongqing, Southwestern China" Minerals 6, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020047
APA StyleZou, J., Tian, H., & Li, T. (2016). Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Tuff in Zhongliangshan Mine, Chongqing, Southwestern China. Minerals, 6(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020047