Radioactivity of Natural Nuclides (40K, 238U, 232Th, 226Ra) in Coals from Eastern Yunnan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
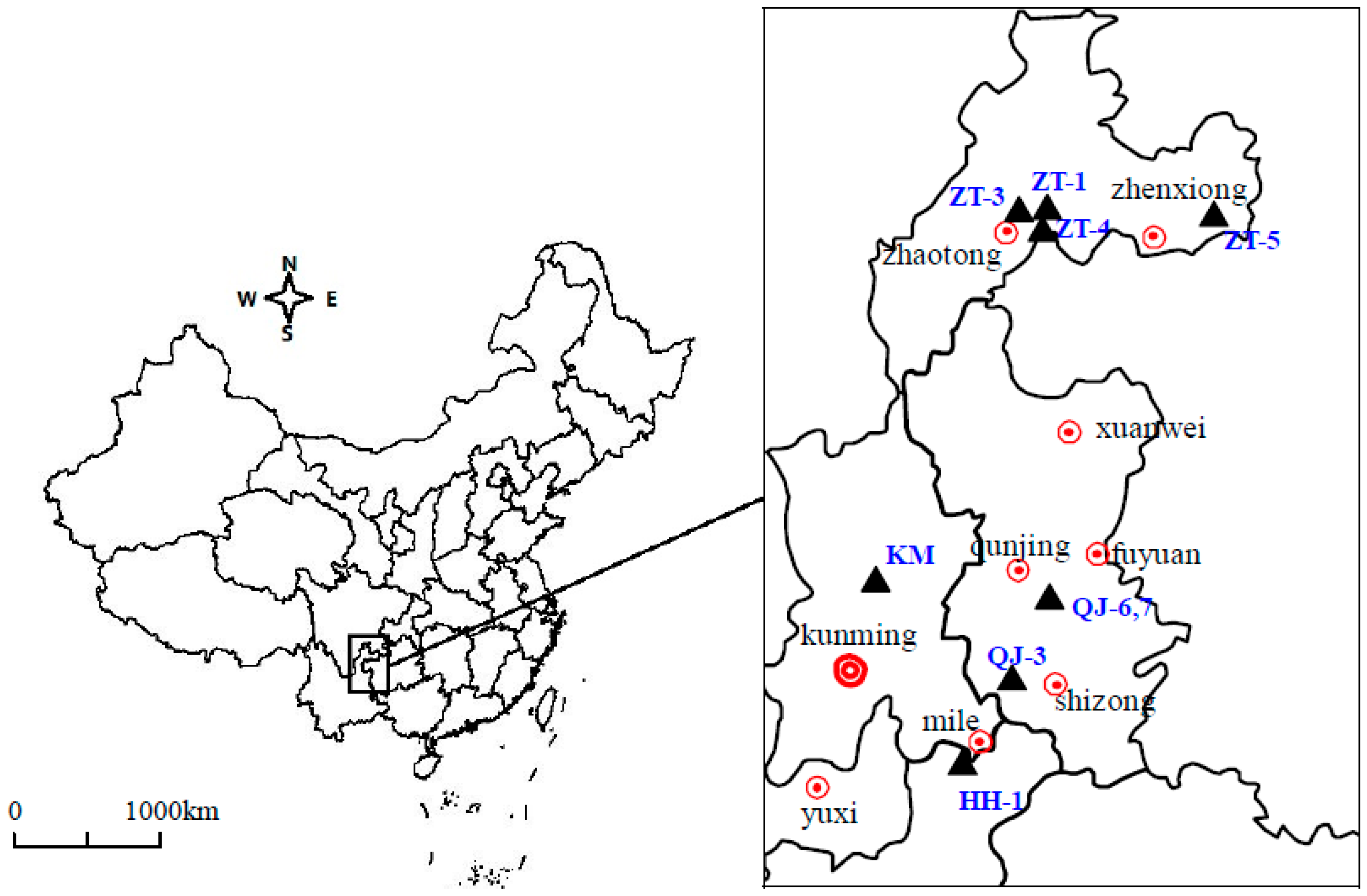
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Analysis
| Sample ID | Coal Mine | Coal Rank | Proximate Analysis | St,d | U | Th | Ra | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Ad | Vdaf | |||||||
| ZT-1 | Maoergou | Anthracite | 1.20 | 29.24 | 12.66 | 4.00 | 5.50 | 9.65 | 1.87 |
| KM | Kelang | Lignite | 9.97 | 15.46 | 56.34 | 1.95 | 7.32 | 2.71 | 2.49 |
| ZT-3 | Changsheng | Anthracite | 0.61 | 4.71 | 5.67 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 1.06 | 0.12 |
| ZT-4 | Xujiayuan | Anthracite | 0.47 | 9.47 | 7.00 | 1.68 | 0.54 | 1.93 | 0.18 |
| ZT-5 | Shizhuang | Anthracite | 0.82 | 32.12 | 12.42 | 3.22 | 3.72 | 7.59 | 1.26 |
| QJ-3 | Xingying | Coking coal | 0.62 | 14.04 | 19.96 | 0.46 | 1.54 | 3.46 | 0.52 |
| HH-1 | Tuobai | Coking coal | 0.55 | 22.81 | 17.99 | 4.15 | 4.76 | 8.41 | 1.62 |
| QJ-6 | Gongqing | Coking coal | 0.69 | 10.85 | 22.64 | 1.74 | 1.64 | 7.47 | 1.52 |
| QJ-7 | Coking coal | 0.75 | 19.81 | 20.48 | 0.93 | 1.74 | 3.78 | 0.59 | |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Coal Basic Parameters
4.2. Concentrations of U and Th in Coals
4.3. Levels of Radioactivity in Coals
| Sample ID | 238U | 232Th | 226Ra | 40K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT-1 | 84.90 | 36.00 | 46.40 | 165.00 |
| KM | 68.80 | 17.00 | 61.80 | 229.30 |
| ZT-3 | 17.70 | 10.30 | 3.10 | 30.60 |
| ZT-4 | 29.80 | 15.80 | 4.50 | 78.70 |
| ZT-5 | 92.30 | 37.10 | 31.30 | 134.20 |
| QJ-3 | 65.10 | 32.30 | 13.00 | 46.10 |
| HH-1 | 78.20 | 33.70 | 40.20 | 65.00 |
| QJ-6 | 59.30 | 11.10 | 37.80 | 54.90 |
| QJ-7 | 78.60 | 20.50 | 14.60 | 67.80 |
| mean | 63.86 ± 25 | 23.76 ± 11 | 28.09 ± 20 | 96.84 ± 66 |
| Yunnan a | 36.60 ± 31 | 16.50 ± 15 | 39.20 ± 4 | 36.10 ± 35 |
| China a | 64.90 ± 32 | 37.50 ± 18 | 49.40 ± 31 | 106.00 ± 27 |
| Poland b | 23.50 | 14.30 | 18.10 | 129.90 |
| Australia c | 25.00 | 24.00 | 21.00 | 75.00 |
4.4. Factors Influencing Radioactivity of Nuclides
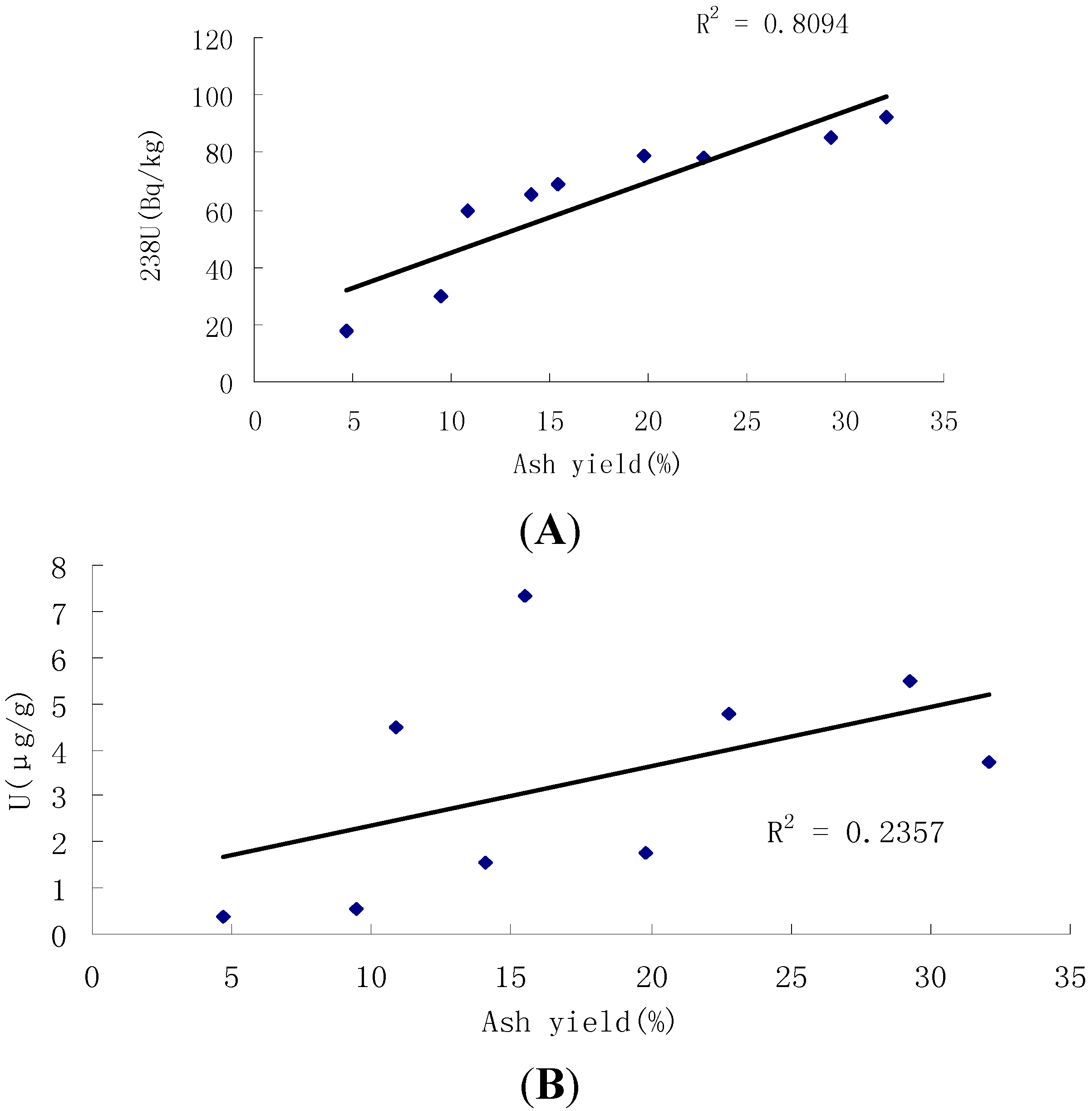
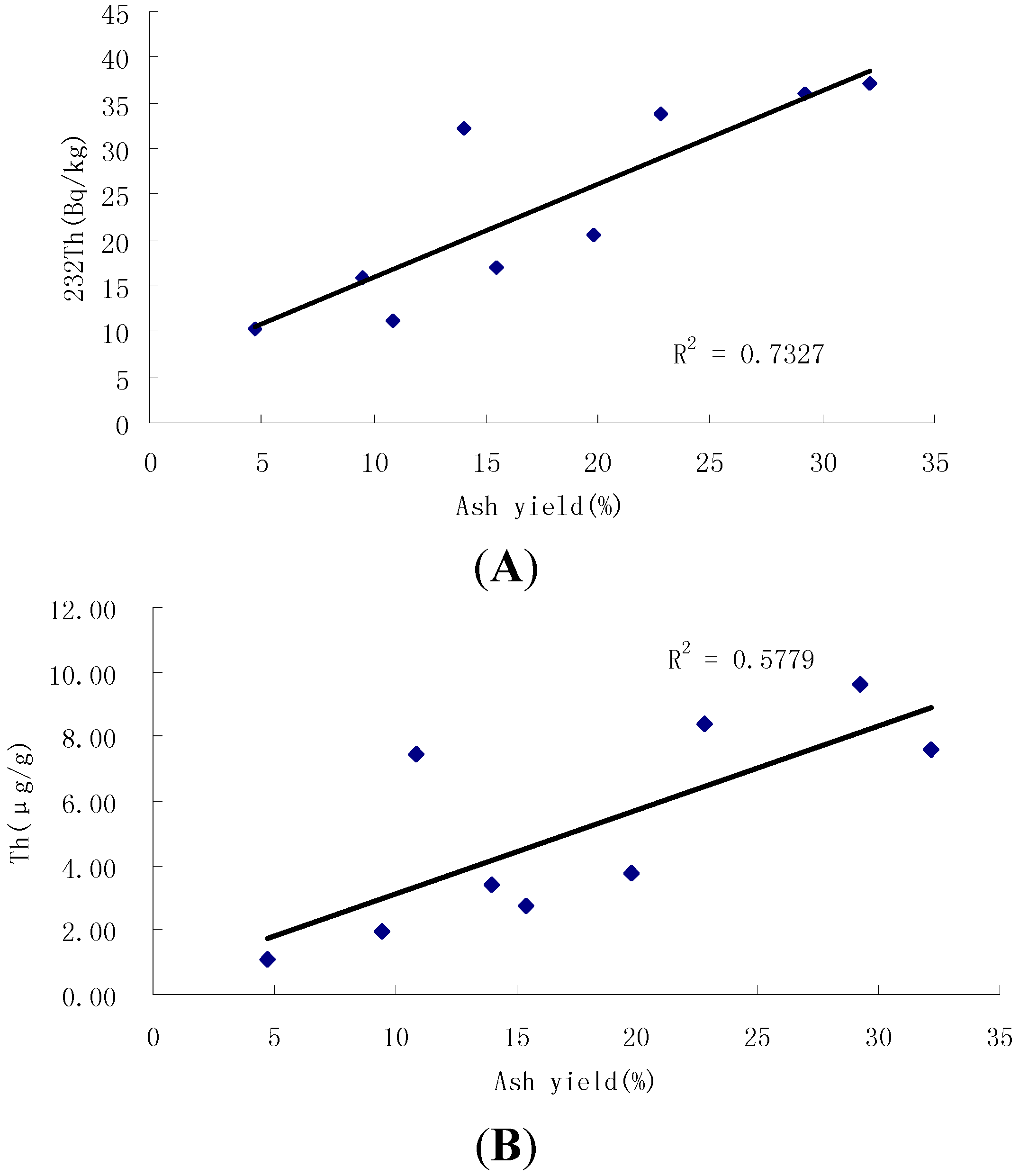
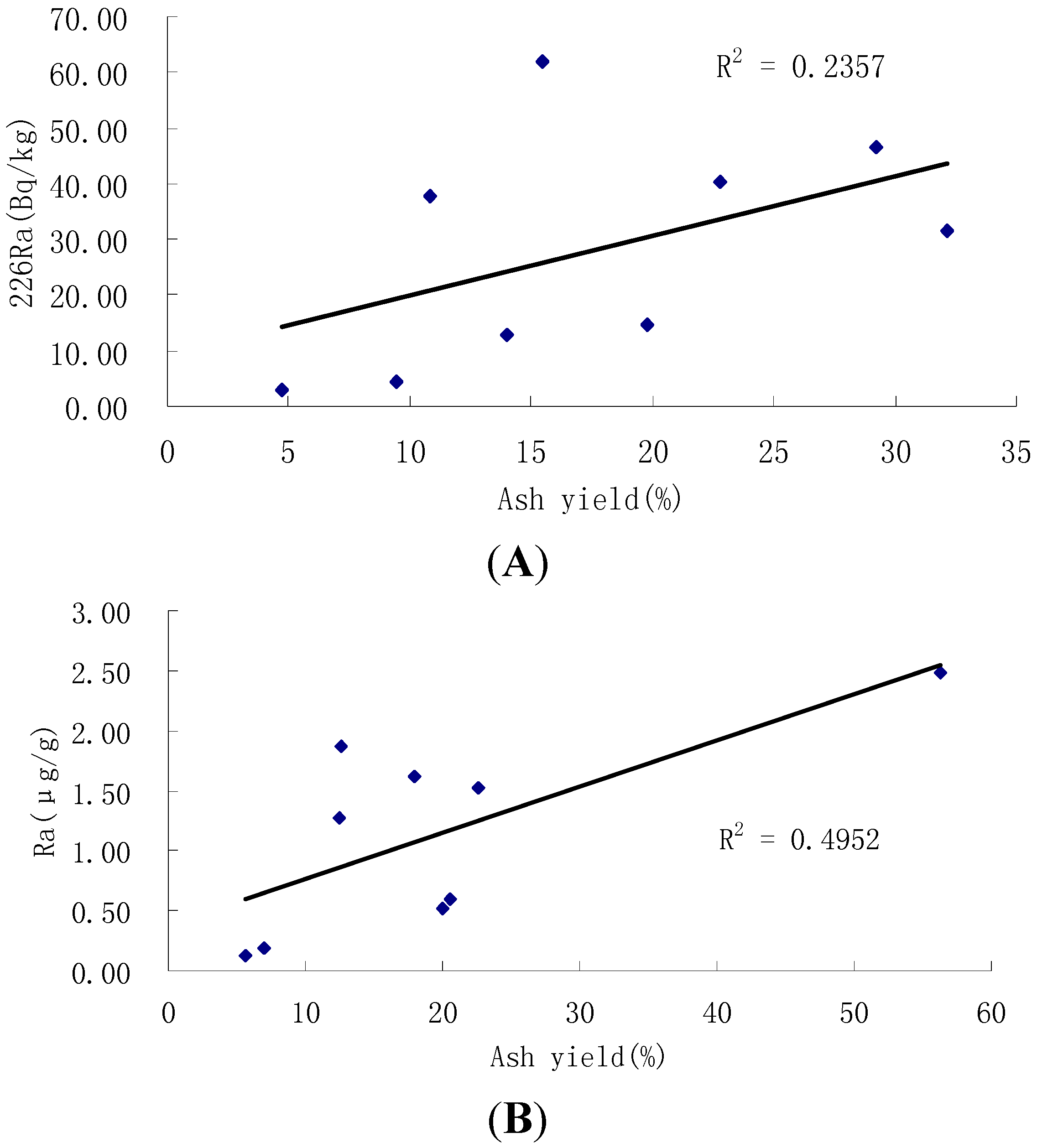
4.5. Radioactive Impacts of Nuclides
| Sample ID | Raeq | Ir | IRa | D (nGy/h) | AED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZT-1 | 110.59 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 50.06 | 61.40 |
| KM | 103.77 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 48.38 | 59.33 |
| ZT-3 | 20.19 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 8.93 | 10.95 |
| ZT-4 | 33.15 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 14.90 | 18.28 |
| ZT-5 | 94.69 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 42.47 | 52.08 |
| QJ-3 | 62.74 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 27.44 | 33.65 |
| HH-1 | 93.40 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 41.64 | 51.06 |
| QJ-6 | 57.90 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 26.46 | 32.45 |
| QJ-7 | 49.14 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 21.95 | 26.92 |
| mean | 69.51 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 31.36 | 38.46 |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Papastefanou, C. Escaping radioactivity from coal-fired power plants (CPPs) due to coal burning and the associated hazards: A review. J. Environ. Radioact. 2010, 101, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenbud, M.; Petrow, H.G. Radioactivity in the atmospheric effluents of power plants that use fossil fuels. Science 1964, 144, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworowski, Z.; Bilkiewicz, J.; Zylicz, E. 226Ra in contemporary and fossil snow. Health Phys. 1971, 20, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, H.; Merz, E.; Schiffers, A. Radioaktive emissionen aus mit rheinischer braunkohle befeuerten kraftwerksanlagen. Braunkohle 1974, 11, 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, D.E.; Giorgio, H.R. Gamma-ray activity in bituminous, sub-bituminous and lignite coals. Health Phys. 1977, 32, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papastefanou, C.; Charalambous, S. On the radioactivity of fly ashes from coal power plants. Z. Naturforschung A 1979, 34, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastefanou, C.; Charalambous, S. Hazards from radioactivity of fly ash from Greek coal power plants (CPP). In Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA), Jerusalem, Israel, 9–14 March 1980; Volume 3, pp. 161–165.
- Jiang, X.W.; Liu, Q.S.; Li, R.X.; Bai, G.; Lin, Z.C.; Liu, X.H.; Pan, S.; Gan, L.; Zhu, L. Level of natural radionuclides in coal in China. Radiat. Prot. 1989, 9, 181–188. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.D.; Pan, Z.Q.; Liu, S.L.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.H.; Liao, H.T.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, N.P. Investigation and analysis of the content of natural radionuclides at coal mines in China. Radiat. Prot. 2007, 27, 171–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Wang, P.; Ward, C.R.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Jiang, J.; Hower, J.C.; Li, T.; Seredin, V.V.; Wagner, N.J.; et al. Elemental and mineralogical anomalies in the coal-hosted Ge ore deposit of Lincang, Yunnan, southwestern China: Key role of N2-CO2-mixed hydrothermal solutions. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chou, C.L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, X. Mineralogy and geochemistry of a superhigh-organic-sulfur coal, Yanshan Coalfield, Yunnan, China: Evidence for a volcanic ash component and influence by submarine exhalation. Chem. Geol. 2008, 255, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, W.; Wang, P. Enrichment of U-Se-Mo-Re-V in coals preserved within marine carbonate successions: Geochemical and mineralogical data from the Late Permian Guiding Coalfield, Guizhou, China. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Wan, H.; Finkelman, R.B.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Z. Distribution of uranium in the main coalfields of China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2012, 30, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.S. The survey of uranium in coal in Yunnan province. Coal Geol. China 1992, 4, 22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P. The survey of some trace elements and toxic elements in Yunnan province. Sci. Technol. Yunnan Coal 1985, 3, 2–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.L. The survey of natural radioactivity level of coal mine in Yunnan. Chin. J. Radio Health 2007, 16, 196–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.W.; Yu, Y.L.; You, M.; Guo, C.L.; Zhou, S.K.; Yu, Z.X. Analysis of environment contamination from concomitant radioactivity of coal mine source. J. China Coal Soc. 2007, 32, 762–766, (In Chinese ). [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cao, D.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Tao, Z.G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z. Study on tectonic analysis of coal controlled structure mode in Yunnan province. Coal Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 100–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.G.; Cao, D.Y.; Li, J.; Shi, X.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, J. Study on coalfield structural framwork and coal measures hosting pattern in easthern Yunnan area. Coal Geol. China 2011, 23, 56–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.P. Distribution of arsenic in coal of Yunnan province, China and its controlling factors. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1992, 20, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.P.; Bohor, B.F.; Ren, Y.L. Trace element geochemistry of altered volcanic ash layers (tonsteins) in Late Permian coal-bearing formations of eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou Provinces, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2000, 44, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.C.; Pan, R.Q.; Liu, C.R. Sedimentary Environments and Coal Accumulation of Late Permian Coal Formation in Western Guizhou, Southern Sichuan, and Eastern Yunnan, China; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 1996; pp. 124–155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Q. Study on Gas Geology Condition of Coal Mines in Yunnan; Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 61–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Coal Standardization Technical Committee. Sampling of Coal Seams; GB/T482-2008 C.S.; Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- China’s Ministry of Coal Industry. Chinese Standard for Coal Classification; GB5751-86 C.S.; Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 1986. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Test Method for Moisture in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; D3173-11, A.S.; American Society for Testing and Materials International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Test Method for ash in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; D3174-11, A.S.; American Society for Testing and Materials International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; D3175-11, A.S.; American Society for Testing and Materials International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Test Methods for Total Sulfur in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke; D3177-02, A.S. (Reapproved 2007); American Society for Testing and Materials International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- National Standard Substance: Standard Substance for Rock Composition Analysis, No. GBW07114.
- Cevik, U.; Damla, N.; Koz, B.; Kaya, S. Radiological characterization around the Afsin-Elbistan coal-fired power plant in Turkey. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standard Substance: Natural Uranium and Thorium Ore Standard Material, No. GBW04127.
- National Standard Substance: Thorium Powder Standard Radioactive Source, No. GBW04325.
- National Standard Substance: Potassium-40 Powder Standard Radioactive Source, No. GBW04326.
- Ren, D.Y.; Zhao, F.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yang, S.J. Distributions of minor and trace elements in Chinese coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 40, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketris, M.P.; Yudovich, Y.E. Estimations of clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: World averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; Tang, Y.G.; Chen, K.; Deng, T.; Cheng, F.P.; Liu, D. Distribution of twelve toxic trace elements in coals from Southwest China. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2006, 35, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bem, H.; Wieczorkowski, P.; Budzanowski, M. Evaluation of technologically enhanced natural radiation near the coal-fired power plants in the Lodz region of Poland. J. Environ. Radioact. 2002, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardy, J.J.; McOrist, G.D.; Farrar, Y.J. Neutron activation analysis and radioactivity measurements of Australian coals and fly ashes. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1989, 133, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, D.G.; Ragainl, R.C.; Ondov, J.M. Behavior of natural radionuclides in western coal-fired power plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1978, 12, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Finkelman, R.B. Metalliferous coals: A review of the main genetic and geochemical types. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 253–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, H.W. Geochemistry of the Naturally Occuring Radioactive Series; National Technical Information Service: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1974; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of Occurrence of Trace Elements in Coal; United States Geological Survey Open-File Report; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1981; Volume 81–99, p. 322. [Google Scholar]
- Seredin, V.V. Metalliferous coals: Formation conditions and outlooks for development. In Coal Resources of Russia; Geoinformmark: Moscow, Russia, 2004; Volume 6, pp. 452–519. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Arbuzov, S.I.; Volostnov, A.V.; Rikhvanov, L.P.; Mezhibor, A.M.; Ilenok, S.S. Geochemistry of radioactive elements (U, Th) in coal and peat of northern Asia (Siberia, Russian Far East, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 86, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.P.; Moore, R.E.; Witherspoon, J.P.; Blanco, R.E. Radiological impact of airborne effluents of coal and nuclear plants. Science 1978, 202, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, G.; Wu, S.; Lam, P.K. The environmental characteristics of usage of coal gangue in bricking-making: A case study at Huainan, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papastefanou, C. Radiation impact from lignite burning due to 226Ra in Greek coal-fired power plants. Health Phys. 1996, 70, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, U.C. Environmental impact of coal industry and thermal power plants in India. J. Environ. Radioact. 2004, 72, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretka, J.; Mathew, P.J. Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Health Phys. 1985, 48, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Building Materials Academy. Building Materials Radionuclide Limited; GB/6566-2010, C.S.; Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Exposure to Radiation from the Natural Radioactivity in Building Materials; OECD Nuclear Energy Agency: Paris, France, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation: Sources; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Feng, Q.; Sun, R.; Liu, G. Radioactivity of Natural Nuclides (40K, 238U, 232Th, 226Ra) in Coals from Eastern Yunnan, China. Minerals 2015, 5, 637-646. https://doi.org/10.3390/min5040513
Wang X, Feng Q, Sun R, Liu G. Radioactivity of Natural Nuclides (40K, 238U, 232Th, 226Ra) in Coals from Eastern Yunnan, China. Minerals. 2015; 5(4):637-646. https://doi.org/10.3390/min5040513
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Qiyan Feng, Ruoyu Sun, and Guijian Liu. 2015. "Radioactivity of Natural Nuclides (40K, 238U, 232Th, 226Ra) in Coals from Eastern Yunnan, China" Minerals 5, no. 4: 637-646. https://doi.org/10.3390/min5040513
APA StyleWang, X., Feng, Q., Sun, R., & Liu, G. (2015). Radioactivity of Natural Nuclides (40K, 238U, 232Th, 226Ra) in Coals from Eastern Yunnan, China. Minerals, 5(4), 637-646. https://doi.org/10.3390/min5040513





