YOLO-EDH: An Enhanced Ore Detection Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Our model replaces conventional convolution with advanced deformable convolution operators, enabling the superior handling of complex morphological features while significantly improving the model’s generalization capacity and robustness;
- By integrating optimized dynamic convolution with the C3k2 module, our approach automatically adjusts the convolutional operations according to the input characteristics, thereby dramatically enhancing both the accuracy and adaptability in complex mining scenarios;
- The proposed framework incorporates a hierarchical guided attention fusion (HGAF) module [10], which boosts the detection performance through intelligent multi-scale feature fusion and adaptive weighting mechanisms.
2. Related Works
3. Methods
3.1. The Original YOLOv11 Network
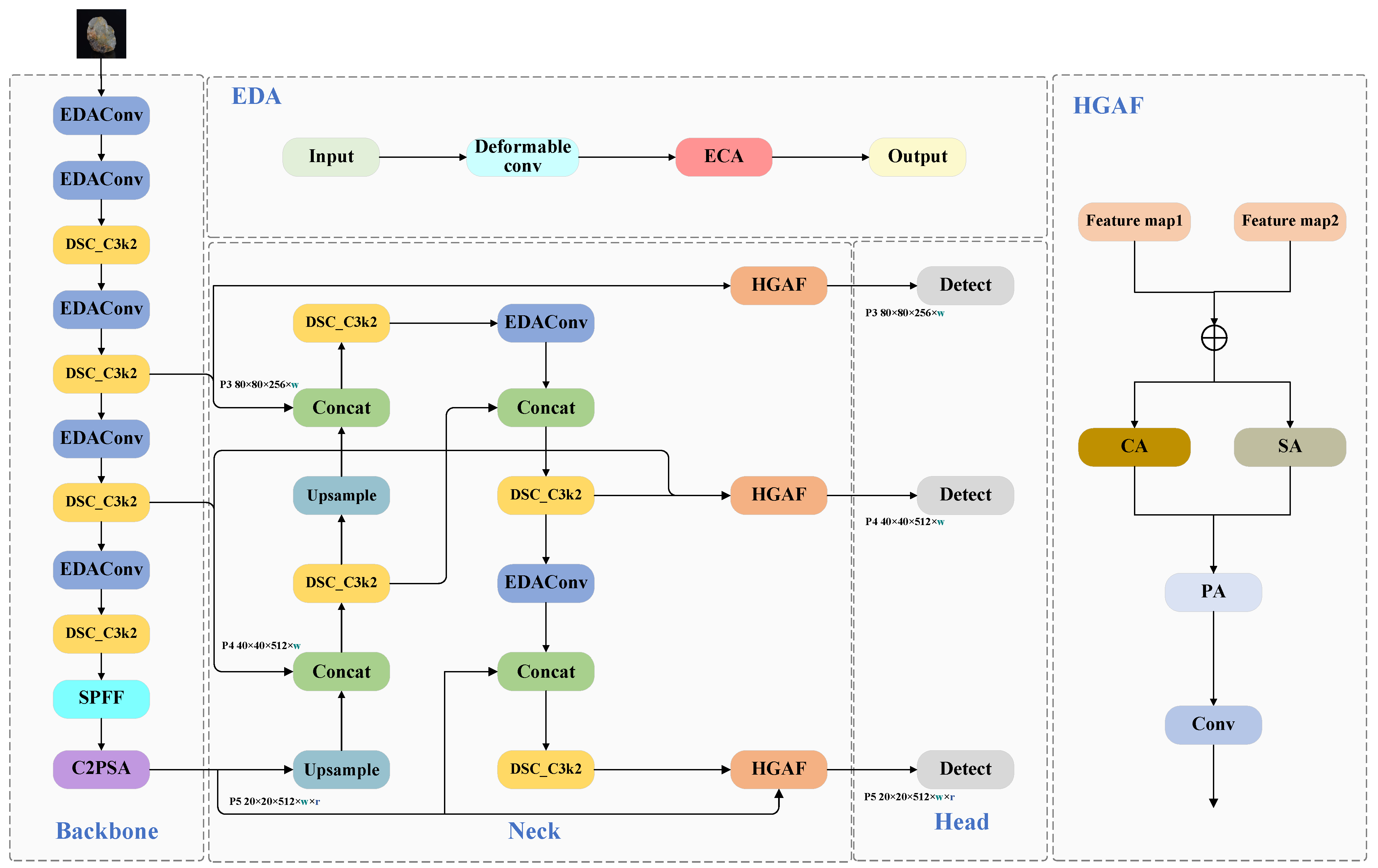
3.2. The Improved YOLO-EDH Network
3.3. EDA Module
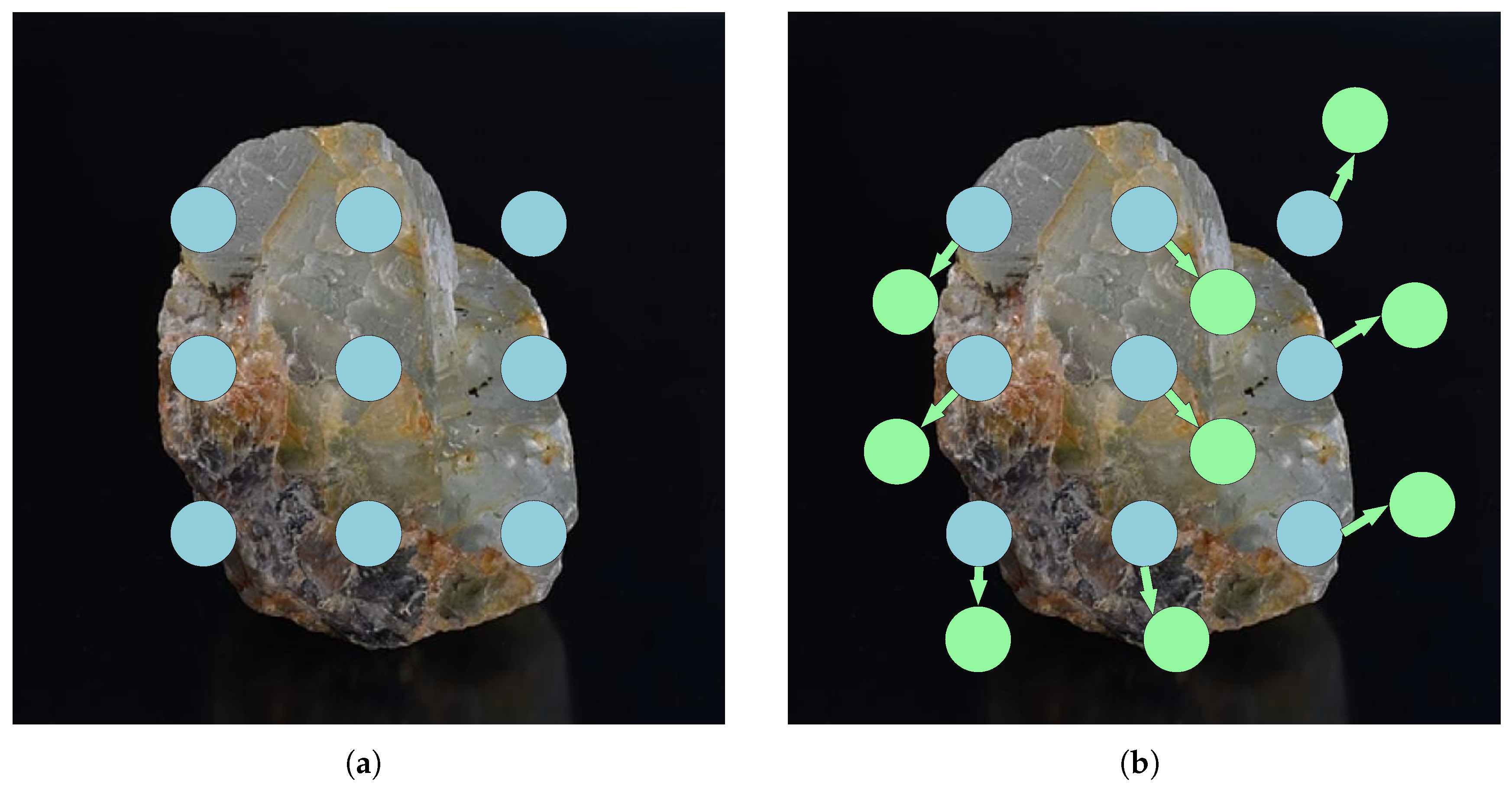
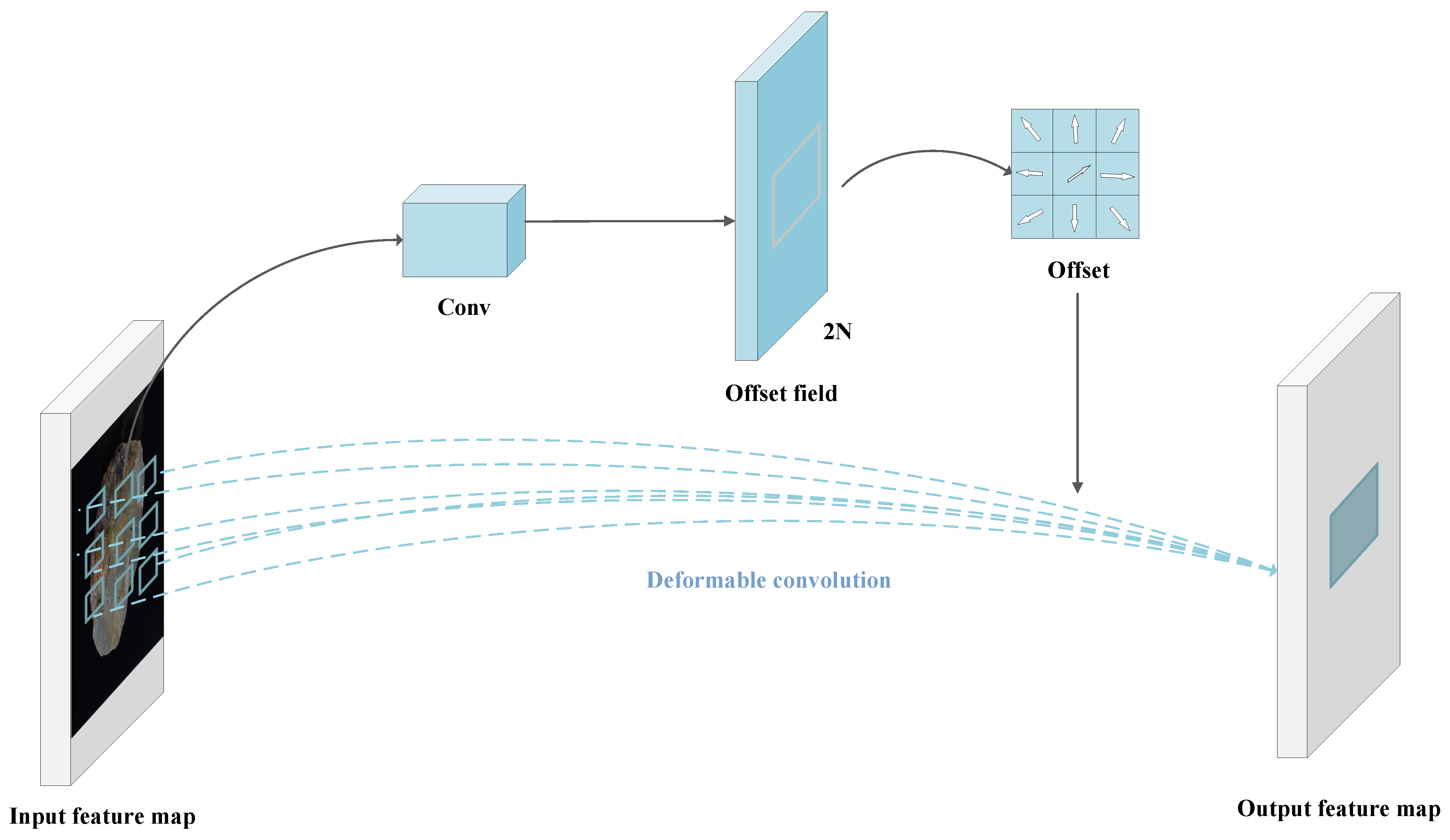
3.3.1. Deformable Convolution
- Offset generation: By applying a standard convolutional layer to the input feature map, the learnable offset is generated, determining the dynamic offset direction and magnitude of the convolution sampling points.
- Adaptive sampling: For each convolution position, the corresponding offset is used to adjust the sampling point coordinates. Since the offset sampling positions are mostly non-integer, bilinear interpolation is applied to compute the feature values at these positions, ensuring sampling accuracy.
- Convolution Operation: After obtaining the offset , a standard convolution operation is performed on the input feature map, integrating the dynamically sampled positions guided by the offset with conventional convolution computation. Since is typically learned as floating-point data, the value at needs to be determined via bilinear interpolation, as follows:
3.3.2. Augmented Deformable Convolution
3.4. DSC Module
3.4.1. Dynamic Convolution
3.4.2. Augmented Dynamic Convolution
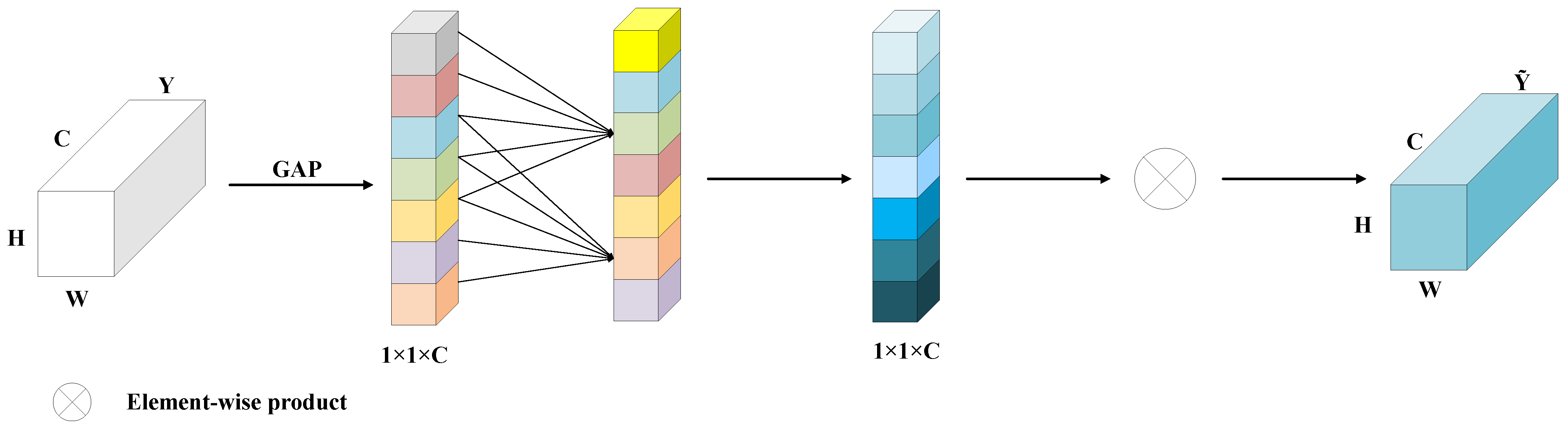
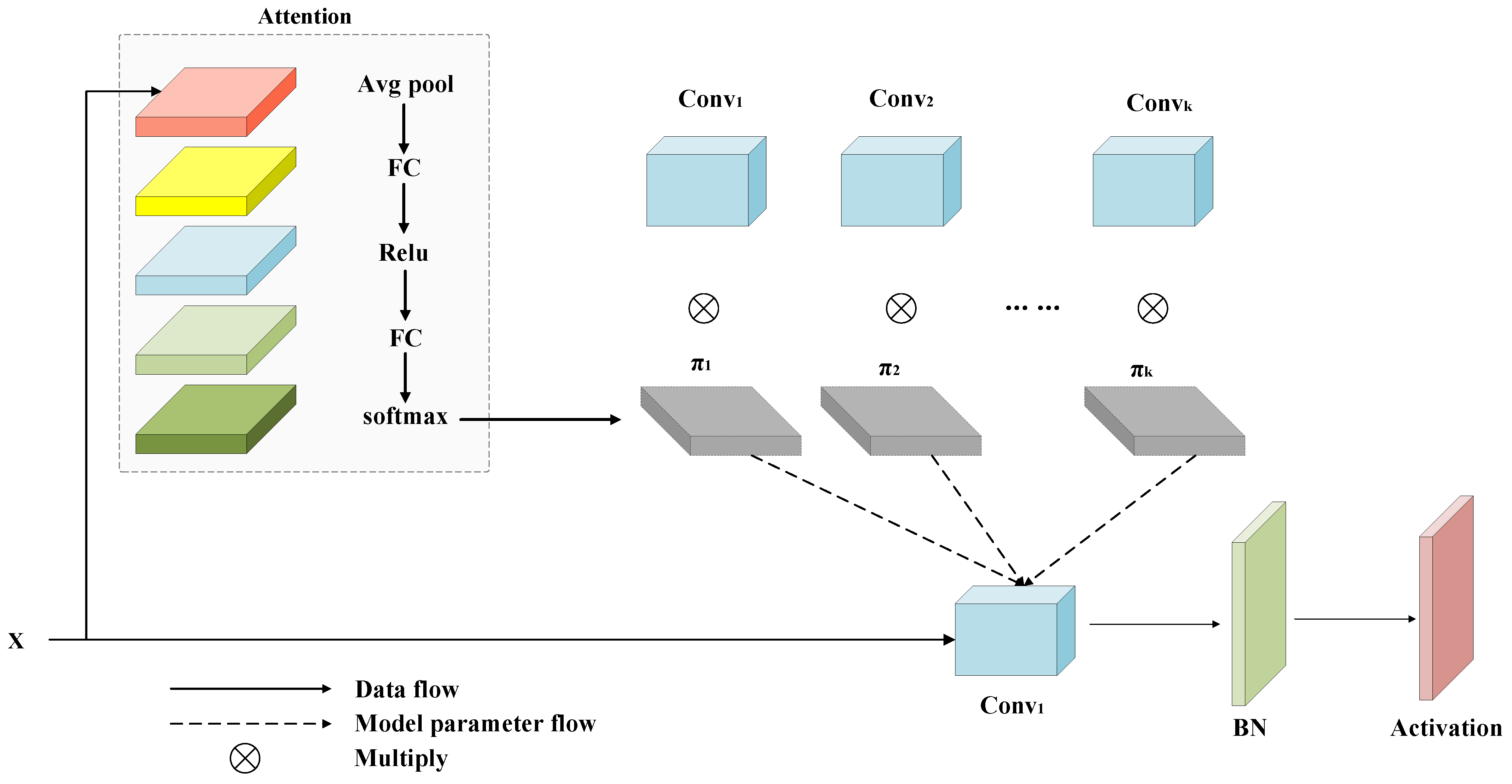
3.5. HGAF Module
4. Data and Experimental Preparation
4.1. Experimental Data
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
5. Experiments
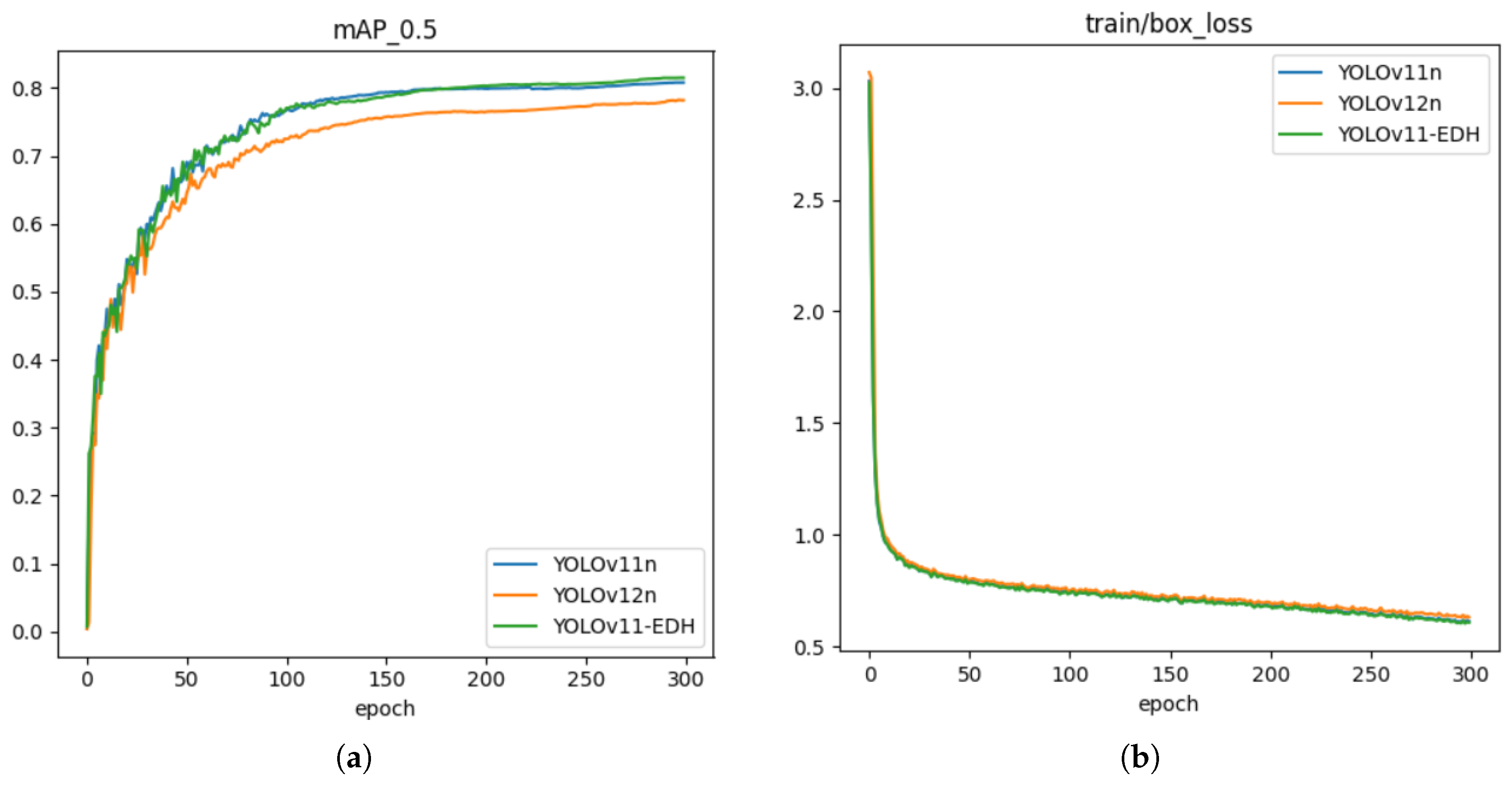
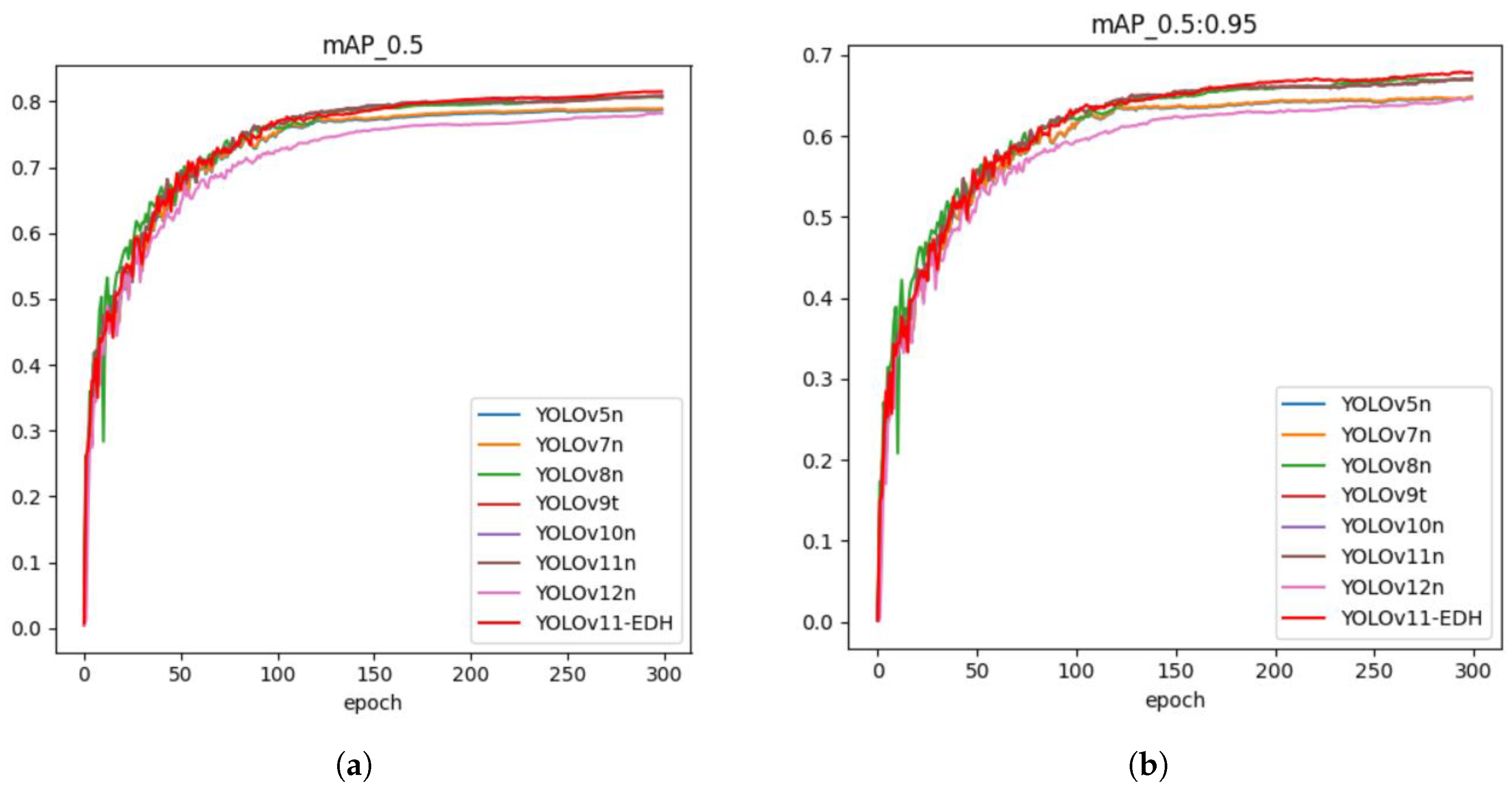
5.1. Model Training
5.2. Ablation Study
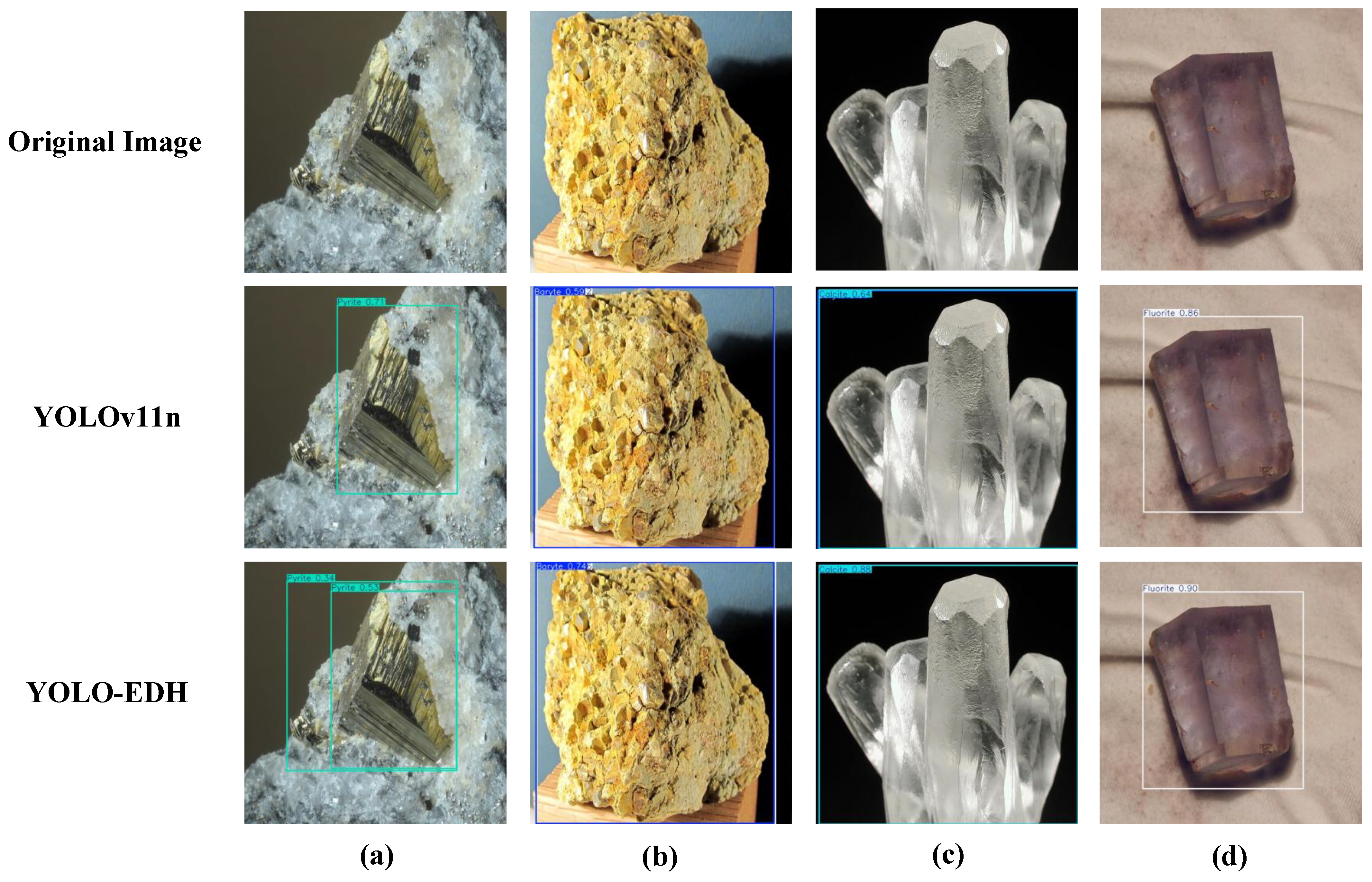
5.3. Visualization Experiments
5.4. Visualization of Classification Validation
5.5. Generalization Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C3k2 | Cross-Stage Partial Bottleneck with Convolution 3 and Kernel Size 2 |
| SPPF | Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast |
| C2PSA | Convolutional Block with Parallel Spatial Attention |
| C2f | CSPDarknet53 with 2 Fusion Layers |
References
- Al-Batah, M.S.; Isa, N.A.M.; Zamli, K.Z.; Sani, Z.M.; Azizli, K.A. A novel aggregate classification technique using moment invariants and cascaded multilayered perceptron network. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 92, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F.; Starck, J.L. Wavelet and curvelet moments for image classification: Application to aggregate mixture grading. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2008, 29, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, J.; Duchesne, C.; Bartolacci, G. A machine vision approach to on-line estimation of run-of-mine ore composition on conveyor belts. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskoi, E.; Suthers, S.; Campbell, J.; Raynlyn, T. Modelling and optimization of hydrocyclone for iron ore fines beneficiation—Using optical image analysis and iron ore texture classification. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2008, 87, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, J.; Tolley, W.; Rice, D. The development of a color sensor system to measure mineral compositions. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, J.T.; Auret, L. Machine learning applications in minerals processing: A review. Miner. Eng. 2019, 132, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jooshaki, M.; Nad, A.; Michaux, S. A systematic review on the application of machine learning in exploiting mineralogical data in mining and mineral industry. Minerals 2021, 11, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Xie, S.; Song, S. Surface iso-transformation and floatability of calcite and fluorite. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, Z.; Lu, Z.M. DEA-Net: Single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Yurtsever, E.; Lambert, J.; Carballo, A.; Takeda, K. A survey of autonomous driving: Common practices and emerging technologies. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58443–58469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.; Bizi, A.M.; Lee, J.A.; Bakouri, S.; Crespo, M.L. Real-time object detection, tracking, and monitoring framework for security surveillance systems. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, Y. Artificial convolutional neural network in object detection and semantic segmentation for medical imaging analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 638182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, Y. YOLOv11-BSS: Damaged Region Recognition Based on Spatial and Channel Synergistic Attention and Bi-Deformable Convolution in Sanding Scenarios. Electronics 2025, 14, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Qian, P. An Optimized YOLOv11 Framework for the Efficient Multi-Category Defect Detection of Concrete Surface. Sensors 2025, 25, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, M.; Banerjee, S.; Chaudhuri, S.S. Faster r-cnn and yolo based vehicle detection: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1442–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Torre, V.; Poggio, T.A. On edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, 8, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Stellar-YOLO: A Graphite Ore Grade Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11. Symmetry 2025, 17, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Dynamic convolution: Attention over convolution kernels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11030–11039. [Google Scholar]
- Attallah, Y. Minerals Identification & Classification. 2023. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/youcefattallah97/minerals-identification-classification (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Jiang, T.; Zhong, Y. ODverse33: Is the New YOLO Version Always Better? A Multi Domain benchmark from YOLO v5 to v11. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.14314. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Miao, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Improved foreign object tracking algorithm in coal for belt conveyor gangue selection robot with YOLOv7 and DeepSORT. Measurement 2024, 228, 114180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, Z. YOLOv8-Coal: A coal-rock image recognition method based on improved YOLOv8. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Yeh, I.H.; Mark Liao, H.Y. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. Yolov12: Attention-centric real-time object detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Meivel, S.; Devi, K.I.; Subramanian, A.S.; Kalaiarasi, G. Remote sensing analysis of the lidar drone mapping system for detecting damages to buildings, roads, and bridges using the faster cnn method. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2025, 53, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shao, Y. Weed detection in paddy field using an improved RetinaNet network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Scott, M.R.; Huang, W. Tood: Task-aligned one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE Computer Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3490–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 16965–16974. [Google Scholar]
- Open Source Toolkit. Rock Classification Dataset. 2023. Available online: https://gitcode_com.jxust.opac.vip/open-source-toolkit/7d489 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Ghasrodashti, E.K.; Adibi, P.; Karshenas, H.; Kashani, H.B.; Chanussot, J. Multimodal Image Classification Based on Convolutional Network and Attention-Based Hidden Markov Random Field. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, W.; Lu, K.; Xiao, B. An overview of multi-modal medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 215, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
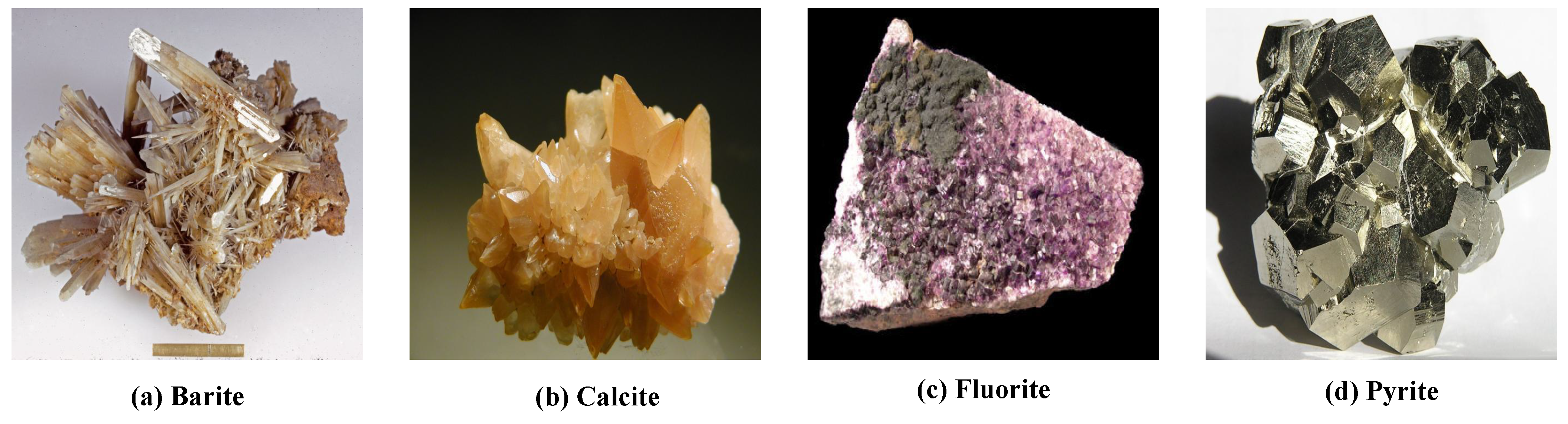



| Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Training Epochs | 300 |
| Learning Rate | 0.01 |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Optimizer Momentum | 0.937 |
| Optimizer Weight Decay | 0.0005 |
| Input Size |
| EDA | DSC | HGAF | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | F1 Score (%) | Params (/106) | Inference (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | 78.2 | 70.7 | 80.8 | 67.1 | 74.27 | 2.6 | 4.7 |
| ✓ | × | × | 78.6 | 71.3 | 81.5 | 67.6 | 74.77 | 2.7 | 5.1 |
| × | ✓ | × | 78.8 | 71.5 | 81.7 | 67.8 | 74.97 | 2.8 | 4.6 |
| × | × | ✓ | 78.4 | 71.0 | 81.2 | 67.4 | 74.52 | 2.6 | 4.9 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 79.1 | 72.3 | 82.4 | 67.9 | 75.55 | 3.2 | 5.2 |
| Algorithm | Precision (P) | Recall (R) | mAP (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | F1-Score | Params (/106) | Inference (ms) | FLOPS | Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n [24] | 78.7 | 69.3 | 78.7 | 64.7 | 73.71 | 2.50 | 3.1 | 7.2 | 262 |
| YOLOv7n [25] | 77.9 | 70.1 | 79.8 | 65.8 | 73.81 | 3.12 | 3.2 | 6.9 | 250 |
| YOLOv8n [26] | 75.7 | 71.9 | 80.5 | 67.0 | 73.76 | 3.01 | 3.1 | 6.8 | 245 |
| YOLOv9t [27] | 78.5 | 71.2 | 81.0 | 67.4 | 74.70 | 2.65 | 11.8 | 10.8 | 1212 |
| YOLOv10n [28] | 78.1 | 70.5 | 80.2 | 66.5 | 74.13 | 2.70 | 4.3 | 8.2 | 368 |
| YOLOv11n | 78.2 | 70.7 | 80.8 | 67.1 | 74.27 | 2.58 | 4.7 | 6.7 | 319 |
| YOLOv12n [29] | 68.1 | 77.9 | 78.2 | 64.6 | 72.71 | 2.85 | 8.1 | 7.0 | 497 |
| YOLO-EDH | 79.1 | 72.3 | 82.4 | 67.9 | 75.55 | 3.20 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 386 |
| Algorithm | Input Size | Precision (P) | Recall (R) | mAP (%) | F1-Score | Params (M) | FLOPS (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN [31] | 600 × 600 | 72.3 | 68.5 | 75.2 | 70.36 | 42.6 | 370.2 |
| RetinaNet [32] | 600 × 600 | 75.0 | 72.5 | 81.1 | 73.7 | 19.7 | 134.1 |
| TOOD [33] | 1024 × 1024 | 80.5 | 73.6 | 82.8 | 76.8 | 31.4 | 172.1 |
| RT-DETR-L [34] | 1024 × 1024 | 79.8 | 72.8 | 82.3 | 76.1 | 33.8 | 103.4 |
| YOLOv11n | 640 × 640 | 78.2 | 70.7 | 80.8 | 74.27 | 2.58 | 6.7 |
| YOLO-EDH | 640 × 640 | 79.1 | 72.3 | 82.4 | 75.55 | 3.20 | 6.7 |
| Algorithm | Precision (P) | Recall (R) | mAP (%) | F1-Score | Params (/106) | FLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv11n | 65.8 | 56.5 | 65.3 | 60.8 | 2.6 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv11s | 69.2 | 60.8 | 65.6 | 64.7 | 9.4 | 21.3 |
| YOLOv12n | 67.8 | 55.7 | 65.4 | 61.2 | 2.5 | 6.2 |
| YOLO-EDH | 68.8 | 56.0 | 66.5 | 61.7 | 3.1 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, L.; Huang, X.; Qiu, Z. YOLO-EDH: An Enhanced Ore Detection Algorithm. Minerals 2025, 15, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090952
Wan L, Huang X, Qiu Z. YOLO-EDH: An Enhanced Ore Detection Algorithm. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090952
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Lei, Xueyu Huang, and Zeyang Qiu. 2025. "YOLO-EDH: An Enhanced Ore Detection Algorithm" Minerals 15, no. 9: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090952
APA StyleWan, L., Huang, X., & Qiu, Z. (2025). YOLO-EDH: An Enhanced Ore Detection Algorithm. Minerals, 15(9), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090952






