Abstract
This paper focuses on delineating and charactering of the magma crystallization conditions of the post-collision Lavarab Alkaline Basaltic Lavas in East Iran. The lavas consist mainly of alkali basalt and basanite, with subordinate trachybasalt. Olivine mostly shows forsterite, chrysolite and hyalo-siderite compositions. Clinopyroxenes are diopside and augite, belonging to peralkaline to subalkaline magmatic series within post-collisional tectonic settings. Estimates of temperature and pressure obtained from single clinopyroxene thermobarometers suggest that crystallization temperatures vary between approximately 1110 and 1260 °C, with pressures ranging from about 0.05 to 1.35 GPa, which correspond to depths of roughly 2 to 51 km at high oxygen fugacity in both the lower and upper continental crust. Olivine-liquid thermometry yields temperatures of ~1385 to ~1393 °C for basanites and ~1275 to ~1339 °C for alkali basalts, assuming a constant pressure of 1.4 GPa. The chemical compositions of phenocrysts in the studied basaltic lavas provide evidence of magma recharge, occurring through multiple pulses of new magma injected into the existing reservoir prior to eruptions. Petrographic evidence, including absorption features, rounded crystal morphologies, patchy zones in olivine, and sieve textures in clinopyroxene, support this interpretation. Additionally, microprobe analyses reveal oscillatory variations in crystal composition from core to rim, confirming the hypothesis of dynamic magma replenishment.
1. Introduction
Understanding the processes that govern magma generation, storage, and evolution in post-collisional tectonic settings remains poorly constrained in igneous petrology [1,2,3]. Relationships among mantle melting, trans-crustal magma plumbing systems, and geochemical diversity of alkaline basalts continue to be debated [4]. This gap is especially relevant in collisional orogens like the Alpine–Himalayan belt, where lithospheric thinning, crustal assimilation, and fault-guided magma ascent may collectively shape magmatic products. Addressing this topic not only enriches our understanding of mantle dynamics but also provides a robust framework for evaluating the continental lithosphere’s response to orogeny and subsequent extension.
The Neogene Lavarab Alkaline Basaltic Lavas (LABL), erupted within the Sistan Suture Zone following the closure of the Neo-Tethyan Ocean, record critical information about mantle dynamics, crustal interactions, and post-collisional volcanism following the closure of the Neo-Tethyan Ocean. The LABL lavas are located in the southern part of Sefidabeh Basin in the middle part of the Sistan Suture Zone, east Iran, and have formerly been interpreted as Oligocene-Miocene basalts [5,6,7]. Previous studies of this zone were focused on the characteristics, origin and tectonic setting of igneous rocks [8,9]. However, the identification of magmatic processes within the reservoir has not been addressed through the investigation of phenocrysts that crystallized in the magma chamber prior to eruption. Phenocryst mineral chemistry is a powerful tool to address this gap.
The chemistry of rock-forming minerals not only reflects the chemistry of the crystallizing melt but also can be used to investigate magma crystallization conditions. Minerals resistant against alteration and weathering, such as clinopyroxene, play a more significant role compared to other minerals. Olivine and pyroxene, normally crystallized during the early stages of magmatic systems, directly reflects the composition of the parental magma, the physicochemical conditions prevailing during crystallization in the magma chamber(s) and the tectonic environment (e.g., [10,11]). The composition of clinopyroxene is used to estimate the crystallization condition (temperature, pressure, and oxygen fugacity) during the crystallization of a magma through the various thermobarometers [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
On the other hand, phenocrysts in basalts indicate that their parent melts underwent a period of crystallization in one or more hypabyssal magma chambers during ascent from the mantle to the surface [23]. Therefore, by studying the minerals that formed in the magma chamber before eruption, it is possible to better understand these magma chamber processes.
The aim purpose of this paper is to investigate the mineral chemistry and geochemical signatures of LABL. This offers insights into not only the magmatic processes active in the Sistan Suture Zone but also the broader questions concerning mantle heterogeneity and post-collisional alkaline magmatism in the Alpine-Himalayan orogenic belt. Thus, this work advances the broader understanding of how continental lithosphere responds to collisional orogeny and subsequent extension by linking mineral-scale data to large-scale tectonic processes.
2. Geological Setting and Study Area
Iran is situated in the central part of the Alpine-Himalaya Orogen, which formed as a result of the convergence between the Eurasian and Gondwanan supercontinents. This extensive orogenic belt extends from western Europe and continues through Turkey, Iran, Afghanistan, to Tibet, and Indonesia [24,25].
The Sistan Suture Zone in eastern Iran provides a notable example of the tectonic evolution of the Alpine-Himalaya Orogen, where subduction did not result in the formation of a widespread magmatic arc. Instead, the rapid destruction of a narrow strip of oceanic lithosphere led to development of the Ratuk and Neh ophiolite complexes, which formed as accretionary prisms, and the Sefidabeh basin, a forearc basin. These geological features reflect the dynamic interplay between subduction, accretion, and basin formation within the evolving Alpine-Himalayan orogenic system.
Three phases of deformation affected the marine sediments of the Neh Complex and Sefidabeh basin [9]. The first two occurred between the Early Eocene and the Early Miocene, associated with regional metamorphism (within the greenschist facies and the biotite schist zone). The third phase of deformation formed large strike-slip faults and folding in the Pliocene-Quaternary and accompanied recent volcanism [26].
The age of the deep to shallow marine deposits in the Sefidabeh basin is Maastrichtian-Paleogene and comprises lavas, pyroclastics, and volcanoclastic derivatives with detrital and carbonate rocks [8], deposited in a forearc basin. Its eastern border with the Afghan block is formed by the Harirud fault and its lower contact with the basement is the Talkhab thrust [27]. The effusives in the Sefidabeh basin are aligned in three tracts in a nearly north-south trend (ca. 20 km long and max. 2 km broad). After the eruption of the LABL the depositional environment gradually deepened, and beds of marl were deposited alternating with clastic rocks [6]. Lava morphology and the interbedded detrital rocks indicate that the lavas erupted in a continental alluvial-fluvial or lacustrine environment.
The tectonic setting of the LABL is post-collisional. Their parent melts stem from a low degree partial melting of upwelling asthenosphere which was triggered by delamination of a thickened lithosphere root [28]. Asthenospheric upwelling and lithospheric thinning resulted in a tensional setting with reactivation of the Zahedan and Harirud faults that may have acted as conduits for ascending magmas [28].
3. Field Relations and Petrography
The LABL rocks form elongated outcrops parallel to and near the Zahedan dextral fault in the west (Figure 1). In the studied area, an asymmetric syncline with a north-south axis contains lavas exposed on both its western and eastern limbs, where they are concordant with interbedded Oligocene-Miocene sediments (Figure 2a). Two eruption stages can be recognized on the eastern limb. Following the first stage, a 20-m-thick sedimentary sequence was deposited which was followed by the second stage. The first stage produced thicker and more extensive volcanic rocks, which are also exposed on the western limb. Field observations reveal columnar structures and lava flows (Figure 2b,c). Eruption likely occurred in shallow water, at depths of up to 30 m, as indicated by the presence of Ostracoda (Cytherella sp. and Cytheridea sp.) in marl deposits stratigraphically underlying the lavas near Harmak (see Figure 1 and Figure 2d). The marls also contain benthic foraminifera such as Pararotalia sp., Elphidium sp., Osangularia sp., and Asterigerina sp., suggest that these marls belong to the Early Miocene.
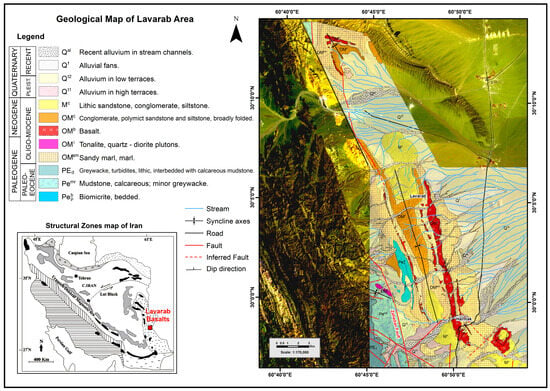
Figure 1.
Geological map of LABL and surrounding areas, based on our detailed field work and geological maps 1:250,000 [5,7] and 1:100,000 [6]. The Structural Zones map of Iran is modified after Berberian [25] in Rezaei-Kahkhaei et al. [29].
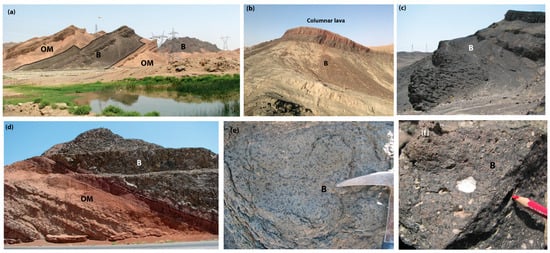
Figure 2.
(a) A view of the Oligocene-Miocene sediments (OM) and interbedded basalts (B) around Harmak village, westward dip view to the northwest.; (b) massive lavas at the bottom and columnar lavas at the top; (c) a view of Lavarab lava flow, view to the southwest; (d) Baked Oligocene-Miocene sandy marl (OM) below Oligocene-Miocene lavas (B), entrance of Harmak village, view to the east; (e) onion skin weathering and pyroxene phenocrysts in Lavarab lavas; (f) Vesicles of different sizes filled with zeolite.
Lavas forming an annular outcrop in the southeastern LABL probably erupted at the intersection of a NW-SE dextral fault with a NE-SW sinistral fault in a local extensional environment. These melanocratic to mesocratic lavas are porphyritic (relatively micro/phenocryst-rich) and vesicular (Figure 2e,f), and are classified into three main groups based on petrographic characteristics:
3.1. Trachybasalt
Trachybasalts are porphyritic or vesicular with a microlithic to aphanitic groundmass, containing micro- and phenocrysts (<3 mm in length, ca. 20 vol-%) of tabular plagioclase and ca. 10 vol-% euhedral to subhedral clinopyroxene (Figure 3a). Plagioclase commonly displays polysynthetic twinning, zonation and sieve textures. Few opaque minerals are observed which may initially have been amphibole. Vesicles are mostly filled by calcite. Accessory minerals are apatite and opaque minerals.
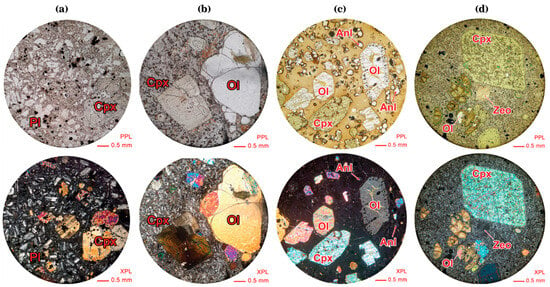
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs (in parallel-polarized and cross-polarized lights). (a) Plagioclase and clinopyroxene micro-phenocrysts/phenocrysts in trachybasalt; (b) Oscillatory zoning and hourglass twinning of clinopyroxene in alkali basalt; (c) Olivine and clinopyroxene phenocrysts and analcime micro-phenocrysts within a glassy groundmass in alkali basalt; (d) Clinopyroxene euhedral phenocryst with sieve texture, altered olivine, and a cavity is filled by zeolite in basanite. Abbreviations are: Cpx: clinopyroxene, Pl: plagioclase, Ol: olivine, Anl: analcime, Zeo: zeolite.
3.2. Alkali Basalt
The alkali basalts are porphyritic or vesicular with a microlithic or glassy groundmass, where vesicles are mostly filled with zeolite. These lavas contain 35%–45% micro- and phenocrysts (<1 cm in length) comprising ca. 20–30 vol-% clinopyroxene, 5–10 vol-% olivine, ca. 5 vol-% analcime, and minor Fe-Ti oxides (Figure 3b,c). Euhedral to subhedral pyroxene, subhedral to euhedral olivine, and euhedral analcime are present as both micro-phenocrysts and phenocrysts. Clinopyroxene crystals are typically euhedral and present in two generations: one exhibiting sieve texture and the second one lacking this. Clear oscillatory zoning and hourglass twinning can be observed in thin section (Figure 3b). Analcime occurs as rounded microcrysts and euhedral micro-phenocrysts scattered in the glassy groundmass, while olivine displays embayed crystal morphologies and skeletal growth (Figure 3c). Apatite inclusions are abundant in pyroxene and also form fine needles in the groundmass. Opaque minerals are present in fine-grained, cubic, and occasionally dendritic habit, occurring both within the groundmass and as inclusions in phenocrysts, particularly olivine.
3.3. Basanite
Basanites are porphyritic or vesicular with a fine-grain to microlithic, and occasionally glassy groundmass. The lavas contain 35%–40% phenocrysts, comprising 20–30 vol-% clinopyroxene, 10–15 vol-% olivine, ca. 5 vol-% analcime, with minor amounts of Fe-Ti oxides. In some samples, olivine crystals were altered to chlorite and iddingsite (Figure 3d). Clinopyroxene micro-phenocrysts and phenocrysts are mostly euhedral. An ultramafic sample (L.57) contains 15% phenocrysts (<1.5 mm in length), consisting of ca. 14 vol-% olivine, and minor clinopyroxene.
The groundmasses of both alkali basalts and basanites contain micro-phenocrysts (<10 to 100 µm in size) of the same phases and in the same relative abundances as found in the phenocryst population. Plagioclase microliths are commonly euhedral to subhedral, whereas the other phases show anhedral morphologies. Additionally, sanidine occurs within the fine-grained (~0.25 mm) groundmass.
4. Analytical Technique
4.1. Electron Probe Micro-Analyzer (EPMA)
One trachybasalt (L.10), four alkali basalt (L.38, L.51, L.61 and L.81), and two basanite (L.57 and L.65) samples were prepared for electron microprobe analyses. Backscattered electron (BSE) imaging of clinopyroxene and olivine was used to identify zonation patterns of the different crystal populations, and to identify mineral domains suitable for chemical microanalysis. Quantitative spot analyses were performed using a CAMECA SX 100 electron microprobe at the Micro-Area Analysis Laboratory, Polish Geological Institute (Warsaw, Poland), under operating conditions of 15 kV acceleration voltage, 20 nA current, a spot size of 5 μm and 10 s counting time at peak position.
4.2. Test for Equilibrium in Mineral-Liquid Geothermobarometry
The software MagMin_PT [30] was used to calculate KD(Fe-Mg)ol–liq using Equations (1) and (2) (originally suggested for olivine by Roeder and Emslie [31]) to test for equilibrium between olivine-liquid and between clinopyroxene-liquid.
MgOmin + FeOliq = MgOliq + FeOmin
KD(Fe-Mg)min-liq = XFeminXMgliq/XMgminXFeliq
4.3. Programs to Calculate Temperature and Pressure
MagMin_PT was also used to determine temperature based on glass or whole-rock composition, as well as for the olivine thermometry. For clinopyroxene the thermobarometric calculations following Soesoo [19] and were performed using an MS Excel spreadsheet, while those based on Putirka et al. [32,33] and Putirka [21] were carried out using WinPyrox [34] and MagMin_PT [30].
5. Results
5.1. Whole-Rock Composition
The LABL whole-rock geochemical characteristics indicate a dominant alkaline sodic nature ([Na2O + K2O] = 4.13–8.11 wt.% and K2O/Na2O = 0.13–1.62) (see Supplementary data). The LABL show low to moderate SiO2 contents (43.76–53.91 wt.%), high alkali contents (4–8 wt.%), and high CaO concentrations (7.39–10.83 wt.%). MgO contents range from 3.01 to 13.38 wt.%, with Mg# (Mg# = 100 Mg2+/[Mg2+ + Fe2+]) ranging from 53.60 to 83.24 (mean = 74.51). Al2O3 contents vary from 12.97 to 17.88 wt.%. TiO2 contents range from 0.47 1.79 wt.% (mean = 0.8 wt.%), classifying these rocks as low-Ti type [35,36]. These geochemical attributes suggest a close affinity with intraplate alkaline basalts and continental rift alkaline basalts [37]. The compatible trace element Ni shows a clear correlation with MgO contents, as well as the trend between Cr and MgO. The concentrations of Cr and Ni range from 59.6 to 690.3 ppm and 31.4 to 537.3 ppm, respectively.
The lava compositions are predominantly alkali basalt, basanite, and minor trachy-andesite after Winchester and Floyd [38] (Figure 4). For a more detailed account see [28].
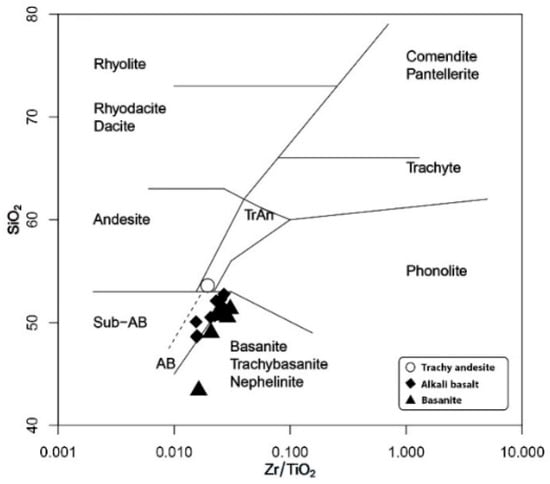
Figure 4.
SiO2 vs. Zr/TiO2 diagram showing the classification of the studied rocks [38].
5.2. Mineral Chemistry
In seven LABL samples, 950 points on 272 olivine and clinopyroxene crystals were analyzed ranging in size from mega-phenocrysts (0.5–1 cm), phenocrysts (0.5–5 mm), micro-phenocrysts (0.1–0.5 mm) to microcrysts (<0.1 mm; see Supplementary data).
5.2.1. Olivine
Olivine occurs in both basanites and alkali basalts, with forsterite contents ranging from Fo55 to Fo94, classified as forsterite, chrysolite, and hyalosiderite (Figure 5). Its chemical composition includes CaO (0.02–0.5 wt.%), NiO (0.03–0.53 wt.%), and MnO (0.05–0.84 wt.%). Based on petrographic observations, backscattered electron (BSE) imaging, and electron probe microanalysis (EPMA) data, olivine crystals are identified as both magmatic phenocrysts and mantle-derived xenocrysts.
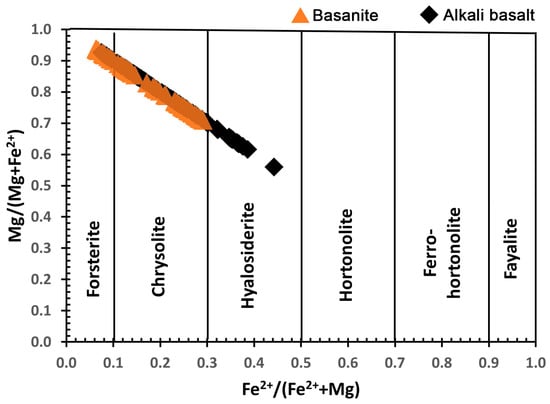
Figure 5.
LABL olivine classification.
Olivine xenocrysts commonly display broad, chemically homogeneous cores (Fo89–94), surrounded by thin rims characterized by sharp compositional discontinuities and lower forsterite contents (Fo71–89). Their chemical composition includes CaO (0.02–0.10 wt.%), NiO (0.30–0.54 wt.%), and MnO (0.05–0.20 wt.%). These crystals frequently exhibit resorptive textures, suggesting partial dissolution. The abrupt decrease in forsterite content at the crystal rims is indicative of interaction with the host melt, either during magma ascent or residence within the magma chamber [39].
Magmatic olivine phenocrysts have forsterite contents ranging from Fo70 to Fo89, with CaO (0.10–0.50 wt.%), NiO (0.30–0.40 wt.%), and MnO (0.10–0.80 wt.%). These crystals are euhedral to subhedral in shape, exhibit generally normal zoning, and only rarely display resorption textures (e.g., embayed margins) indicative of interaction with the melt. They commonly occur in association with clinopyroxene (diopside–augite) and analcime.
In basanite samples, olivine ranges from Fo70 Fa29 Tp0.8 to Fo94 Fa6 Tp0.05 (based on 24 crystals, n = 96), and in alkali basalt from Fo72 Fa27 Tp0.08 to Fo92 Fa7 Tp1 (based on 55 crystals, n = 195). A representative olivine xenocryst from a basanite sample (L.57) shows normal zoning, characterized by high Mg contents (Fo86–91), transitioning to outer rim zones with lower Mg concentrations (Fo71–76) (Figure 6a).
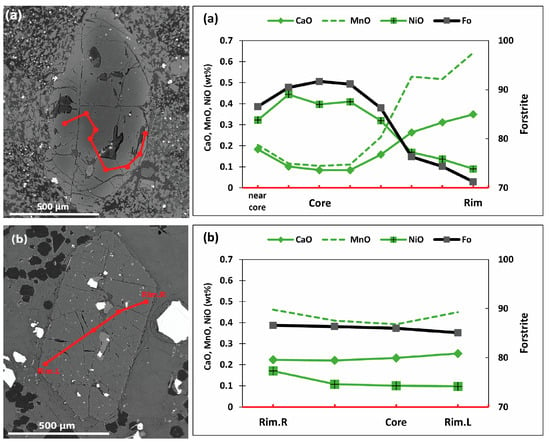
Figure 6.
Examples of BSE images and compositional traverses of olivine crystals from (a) Patchy-zoned, resorbed wide core and sharp normal zonation with low-Fo and NiO, but high-MnO rim overgrowth as a mantle xenocryst (basanite, L.57); (b) Generally, a euhedral homogenic magmatic phenocryst (alkali basalt, L.38). The red line and points on image show the location of geochemical traverse.
A representative olivine phenocryst from the alkali basalt (sample L.38) displays same texture and compositional characteristics, with core regions containing ~Fo86 and rims remaining invariant at Fo85–86.5. Rim-ward trends in minor element represents depletion in NiO, enrichment in MnO, and weak enrichment in CaO (Figure 6b).
Micro-phenocrysts of olivine (100–500 μm) in both rock groups are anhedral, unzoned and exhibit limited variation in Mg contents (ca. Fo70.4–87), with the exception of one alkali basalt sample (L.61). In this sample, olivine forsterite ranges from Fo55 to Fo88.5. The presence of micro-phenocrysts with low forsterite contents (Fo55–67), alongside phenocryst cores reaching up to Fo85, suggests significant magmatic differentiation or possible crustal contamination affecting the magma composition [37].
5.2.2. Clinopyroxene
Clinopyroxenes in the LABL are Ca-Mg-Fe rich [40] and classified as diopside and augite [41] in all rock types (Figure 7a,b). BSE images and compositional traverses of clinopyroxene crystals of each rock type are presented in Figure 8, highlighting the patchy-zoning and oscillatory zonation in the samples.
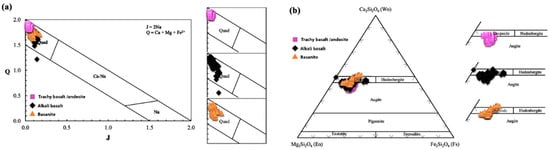
Figure 7.
(a) Q-J Diagram [40], Quad: Ca-Mg-Fe pyroxenes; (b) Pyroxene Classification [41] for all clinopyroxenes related to Lavarab lavas. Data from 206 crystals, n = 776.
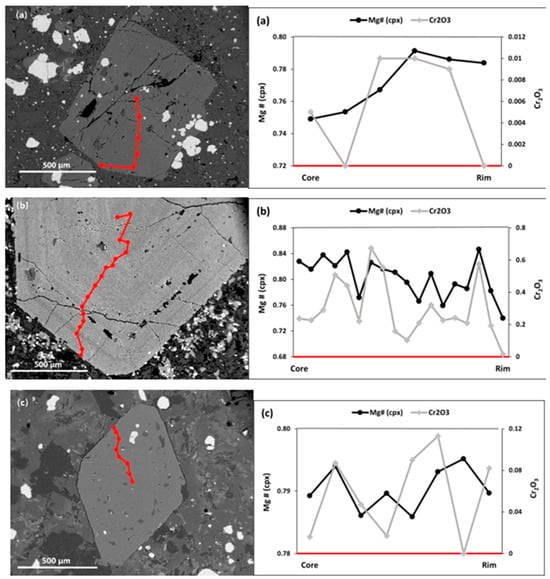
Figure 8.
Examples of compositional traverses of LABL clinopyroxene crystals. (a) Low-Mg and Cr reversed zoned clinopyroxene with a high-Mg and Cr rim (trachybasalt, L.10); (b) Oscillatory, generally normal zoned crystal lacking a prominent core with fluctuations in Mg and Cr values from core to rim (Alkali basalt, L.51); (c) Typical euhedral crystal with fluctuations in Mg and Cr contents from core to rim lacking a core (basanite, L.65). The red line and points on the image show the location of geochemical traverse.
In order to investigate magma evolution during ascent and cooling, one sample from each rock was selected: L.81 (SiO2 = 49.3 wt.%) from alkali basalts, L.57 (SiO2 = 42.3 wt.%) from basanite, and L.10 (SiO2 = 52.7 wt.%) from trachybasalt. According to the crystal size, the clinopyroxene mineral chemistry data from these samples are categorized into three groups, being micro-phenocrysts (30–500 µm), phenocrysts (0.5–5 mm), and mega-phenocrysts (5–10 mm).
- Clinopyroxene micro-phenocrysts
This group is observed in trachybasalt (L.10) and basanite (L.57), whereas they are absent in alkali basalt (L.81). In basanite, these crystals are Ca-Mg-Fe-rich, containing Ca- and Mg-pyroxene with diopside compositions (Wo47En33Fs8 to Wo52En45Fs15; data from 9 crystals, n = 22). According to Morimoto et al. [41], these pyroxene micro-phenocrysts are classified as augite and diopside.
In trachybasalt, pyroxene micro-phenocrysts are characterized by Ca- and Mg-rich compositions, with a higher abundance of augite and lower abundance of diopside components (Wo40En40Fs11 to Wo46En47Fs15).
- Clinopyroxene phenocrysts
Clinopyroxene phenocrysts are found in alkali basalt (L.81) and trachybasalt (L.10) whereas they are absent in basanite (L.57). According to the binary plot (Q-J), all clinopyroxene phenocrysts are in the range of Ca-Mg-Fe rich clinopyroxene. The alkali basalt clinopyroxene is diopside and augite (Wo42En42Fs5 to Wo46En51Fs12) as well as in the trachybasalt (Wo40En42Fs8 to Wo47En47Fs15) but with a higher abundance of augite (data from 5 crystals, n = 51 for alkali basalt, and 7 crystals, n = 57 for trachybasalt). Patchy-zoning or oscillatory-zoning are observed in the clinopyroxene.
- Clinopyroxene mega-phenocrysts
This group of crystals is found in alkali basalt (L.81), but is absent in basanite and trachybasalt. All data fall within the Ca-Mg-Fe-rich range, predominantly exhibiting diopside compositions (Wo44En42Fs8 to Wo46En47Fs12) (data from 4 crystals, n = 38).
The compositional differences of the investigated clinopyroxene crystals are shown in Figure 9.
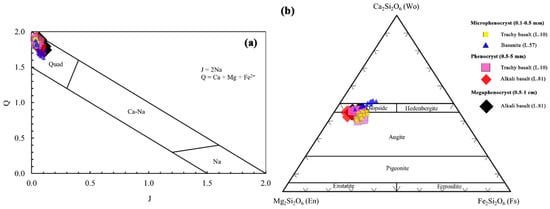
Figure 9.
(a) Q-J Diagram [40]; (b) Clinopyroxene classification [41] for micro-phenocrysts, phenocrysts and mega-phenocrysts in trachybasalt (L.10), alkali basalt (L.81) and basanite (L.57) of the LABL.
Examination of clinopyroxene structural behavior using the Na + AlIV versus AlVI + 2Ti + Cr diagram reveals that a significant portion of the basanite and alkali basalt samples plot above the Fe3+ = 0 line (Figure 10). This distribution indicates the relative amount of ferric iron present [14], reflecting more oxidizing conditions and high oxygen fugacity during pyroxene crystallization for LABL. In contrast, most clinopyroxenes from the trachybasalt samples plot near the Fe3+ = 0 line, indicating more reducing conditions and a negligible contribution of Fe3+ to their structural formula compared to those in basanite and alkali basalt samples.
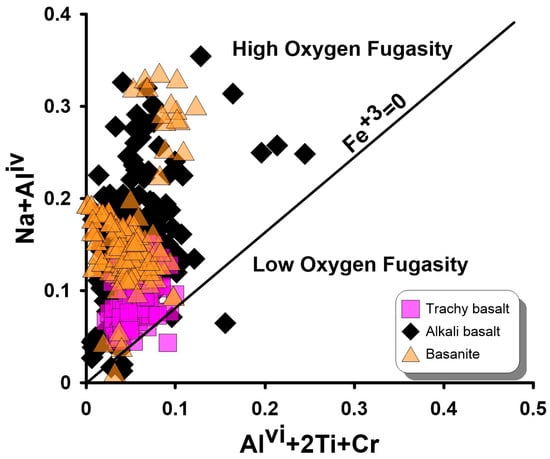
Figure 10.
Oxidizing conditions during pyroxene crystallization [14].
These differences in oxidation state not only confirm the variability of physicochemical conditions controlling mineral crystallization but also strengthen the reliability of the applied geothermobarometric models for the LABL volcanic rocks.
6. Discussion
6.1. Crystallization Conditions
Due to the impossibility of directly measuring intensive parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, and oxygen fugacity) during magma generation, movement and accumulation in magma chambers, as well as its crystallization and emplacement within the crust, geoscientists commonly use indirect methods to quantify these. One such method involves utilizing the equilibrium composition between coexisting minerals and the melt from which they were crystallized. Determining these conditions is based on the thermodynamic principles of a chemical mineral-melt equilibrium, achieved by characterizing the chemical properties of experimental products analogous to the compositions of igneous minerals and their coexisting melts [22,42].
Olivine compositions are widely used to constrain magmatic conditions such as temperature, oxygen fugacity, and H2Omelt. However, post-crystallization elemental diffusion may change the initial compositions, leading to large uncertainty in thermodynamic estimates [43]. Clinopyroxene is considered to be more resistant to post-growth alteration and is therefore an important mineral for thermo-barometric estimates, determination of oxygen fugacities, petrological interpretations, including the type of magma series, and the tectonic environment of magma formation [44]. Moreover, clinopyroxene is present in a wide range of rock types (from komatiite and picrite to basalt, andesite, dacite, and even some rhyolites) and occurs in diverse tectonic settings, including hot spots, intracontinental rifts, mid-ocean ridges, oceanic islands, arc islands, and continental margin magmatic arcs [21].
6.1.1. Whole Rock/Glass Geothermometry
Putirka [21] showed that, in spite of the simplicity and narrow calibration range, the Helz and Thornber [45] and Montierth et al. [46] thermometers work remarkably well for liquid (or glass) solidus thermometers. The formulations depend only upon the MgO content in the liquid (MgOliq): T (°C) = 20.1MgOliq + 1014 °C [45] and T (°C) = 23.0MgOliq + 1012 °C [46].
According to Helz and Thornber [45], the whole-rock thermometry for the LABL basanitic lavas is estimated to be 1237–1243 °C (avg = 1239 °C) and for the alkaline basaltic lavas to be 1151–1209 °C (avg = 1180 °C) independent of pressure. Moreover, the Putirka [21] Equations (13)–(16) can be applied to glass (liquid) thermometry and are valid for olivine-bearing volcanic rock over an extensive compositional and P-T range (P = 0.0001–14.4 GPa; T = 729–2000 °C; SiO2 = 31.5–73.64 wt.%; Na2O + K2O = 0–14.3 wt.%; H2Omelt = 0–18.6 wt.%). The Equation (16), which is similar to the Yang et al. [47] Equation (4), applies specifically to liquids that are in equilibrium with olivine+plagioclase+clinopyroxene. It performs less well when additional phases, such as spinel or other oxides, are present.
Using the Putirka [21] Equation (13): T (°C) = 26.3MgOliq + 994.4 °C), the whole-rock geothermometry estimates indicate that the basanites crystallized within a temperature range of 1286–1294 °C (avg = 1289 °C), whereas alkali basalts record temperatures between 1174–1250 °C with SEE of ±71 °C. Additionally, the glass thermometry for a group of alkali basalts with a hyalo groundmass (L.81, L.38) reveals an average temperature of 1056 °C using the Helz and Thornber [45] method and 1049 ± 71 °C using Putirka [21] Equation (13) (independent of pressure). The groundmass glass serves as an indicator of the composition of the residual melt from which crystals formed during the eruption; thus, its lower estimated solidus temperatures, in contrast to those derived from whole-rock analyses, provide insights into the cooling history of the residual melt before the eruption occurred.
6.1.2. Olivine Geothermometry
When using thermometers or barometers based on mineral-mineral or mineral-melt equilibria, it is crucial that equilibrium between the phases is achieved and maintained. Otherwise, any calculated pressure-temperature condition will be meaningless [21]. In the case of the olivine–liquid thermometer, the composition of either whole-rock or glass must be considered. If the liquid is in equilibrium with olivine, the Fe-Mg exchange coefficient between olivine and liquid is expected to be in the range of KD (Fe-Mg)ol-liq = 0.30 ± 0.03 [31,48], thereby confirming the applicability of the thermometer to the volcanic system.
The Fe-Mg distribution coefficients (KD) range from 0.11 to 0.69 in basanites and from 0.27 to 0.33 in alkali basalts. Based on the Rhodes diagram (Figure 11; [49]), olivine is not generally in equilibrium with the coexisting liquid in the LABL rocks, except in some samples. Petrographic evidence, including absorption features, rounded crystal morphologies, and patchy zoned olivine crystals (in back scattered image), confirm liquid disequilibrium between olivine and the surrounding melt.
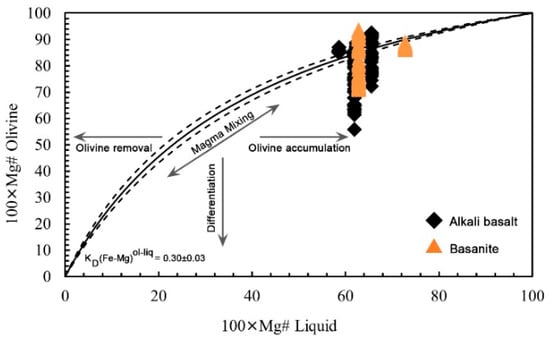
Figure 11.
Measured Mg# of Lavarab olivines verses melt Mg# of their host basalts (Rhodes diagram). Equilibrium curves are calculated from the Fe/Mg partition coefficient between olivine and melt. Melt compositions are based on LABL whole-rock analyses.
The thermometers of Putirka et al.’s [50] Equations (2) and (4), later improved in Putirka [21] Equations (21) and (22), provide the most reliable temperature estimates when water is present, with standard error of estimate (SEE) of ±53 °C and ±29 °C respectively.
Using both above equations and averaging the results at constant pressure (e.g., 1.4 GPa as the highest estimated pressure value for clinopyroxene of the LABL), the crystallization temperature of the Ol with KD(Fe-Mg)ol-liq ca. 0.30 ± 0.03 is calculated to be 1385-1393 °C for basanites (n = 7), and 1275–1339 °C for alkali basalts (n = 65).
6.1.3. Clinopyroxene Geothermobarometry
Determining the temperature and pressure conditions that control magma crystallization before eruption [21] is a crucial topic in igneous petrology, volcanology, and geochemistry. Due to its sensitivitfy to the temperature and pressure prevailing in magmatic systems, numerous thermobarometers have been developed and based on clinopyroxene-only [20,51,52] as well as clinopyroxene-liquid equilibria [21,32,53,54].
While both approaches provide critical insights into crystallization conditions, Wang et al. [42] emphasize that clinopyroxene-only thermobarometry is one of the most practical tools to reconstruct crystallization pressures and temperatures of clinopyroxene. Because it does not require any information about coexisting silicate melt or other co-crystallized mineral phases, it has been widely used to elucidate the physiochemical conditions of crystallizing magmas. In this section, we examine the application of clinopyroxene-based geothermobarometers to the LABL, assessing their effectiveness in constraining magmatic evolution.
In the Soesoo [19] method, which incorporates all the oxides present in the mineral, temperature estimation is performed based on the calculation of XPT and YPT indices. Accordingly, trachybasalt clinopyroxene crystallized at T = ca. 1150–1200 °C and P = ca. 0.3–0.6 GPa, alkali basalt clinopyroxene at T = ca.1165 to 1270 °C and P = ca. 0.4–1.4 GPa, and basanite Clinopyroxene at T = ~1170–1230 °C and P =~ 0.5 to 1.25 GPa (Figure 12).
Putirka’s [21] Equation (32d), based on the Nimis and Taylor [20] clinopyroxene-only thermometer model and Putirka’s [21] Equation (32b), delivers the following values for the intermediate part of LABL: trachybasalt, T = 1156 − 1223 ± 58 °C, with an average of 1190 ± 58 °C and P = 0.13 − 0.9 ± 0.26 GPa with an average of 0.51 ± 0.26 GPa. Similarly, for alkali basalts, the estimated crystallization T = 1135 − 1287 ± 58 °C (average = 1209 ± 58 °C) and P = 0.1 − 1.4 ± 0.26 GPa (average = 0.65 ± 0.26 GPa). In contrast, basanites show a wide crystallization temperature interval (T= 934 − 1278 ± 58 °C) with an average of 1200 ± 58 °C, accompanied by a P = 0.15 − 1.34 ± 0.26 GPa, averaging 0.71 ± 0.26 GPa. The results derived from various geothermobarometric calculations are presented in Table 1.
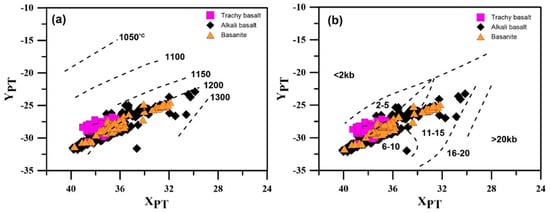
Figure 12.
XPT-YPT plot [19] of clinopyroxene crystallization (a) temperature conditions; (b) pressure conditions for Lavarab volcanic rocks.
XPT = 0.446SiO2 + 0.187TiO2 − 0.404Al2O3 + 0.346FeO(total) − 0.052MnO + 0.309MgO + 0.431CaO − 0.446Na2O
YPT = −0.369SiO2 + 0.535TiO2 − 0.317Al2O3 + 0.323FeO(total) + 0.235MnO − 0.516MgO − 0.167CaO − 0.153Na2O
Over the last thirty years, various geothermobarometric methods have been developed to estimate the crystallization conditions of magma chambers, among which the use of clinopyroxene-liquid equilibrium has been widely applied [21,53,54,55,56,57,58,59]. Although this thermobarometer provides valuable insights, it remains challenging due to the open nature of magmatic systems and several magmatic processes, including contamination, mixing and mingling of distinct magma batches.

Table 1.
P-T results of different Clinopyroxene-only geothermobarometry models for the investigated LABL rocks.
Table 1.
P-T results of different Clinopyroxene-only geothermobarometry models for the investigated LABL rocks.
| Clinopyroxene-Only Thermobarometry | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soesoo (1997) [19] | Putirka (2008) [21] RiMG | ||||
| Equation (32a) (SEE = ±0.26 GPa) | Equation (32b) (SEE = ±0.26 GPa) | Equation (32d) (SEE = ±58 °C) | |||
| T (°C) | P (GPa) | P (GPa) | P (GPa) | T(°C) | |
| Trachybasalt n = 93 | 1150–1200 | 0.3–0.6 | 0.12–0.9 (avg = 0.55) | 0.13–0.9 (avg = 0.51) | 1156–1223 (avg = 1190) |
| Alkali basalts n = 418 | 1165–1270 | 0.4–1.45 | 0.03–1.99 (avg = 0.74) | 0.1–1.4 (avg = 0.65) | 1135–1287 (avg = 1209) |
| Basanites n = 169 | 1170–1230 | 0.5–1.25 | 0.1–1.57 (avg = 0.8) | 0.15–1.34 (avg = 0.71) | 934–1278 (avg = 1200) |
Pressure is one of the key variables that controls magmatic phase equilibria. However, estimating magma chamber pressures from erupted products is challenging [53]. The successful application of this method requires not only the accurate knowledge of the mineral composition but also of the whole-rock or glass composition. Consequently, the method becomes unreliable if clinopyroxene and the bulk rock or glass composition are not in equilibrium. These issues can be assessed via the Fe-Mg exchange coefficients of clinopyroxene-liquid KD(Fe-Mg)cpx-liq. When KD(Fe-Mg)cpx-liq is close to or equal to 0.28 ± 0.08 [49], the values can be interpreted as indicating clinopyroxene-liquid equilibrium. However, based on the Rhodes diagram (Figure 13), the majority of the clinopyroxenes in each sample are not in equilibrium with the coexisting melt. This implies that the magmatic system was open, likely influenced by multiple melt injections or rapid magma ascent. Petrographic evidence such as sieve texture, absorption features, and oscillatory zonation within clinopyroxene crystals confirm an open magmatic system for the LABL.
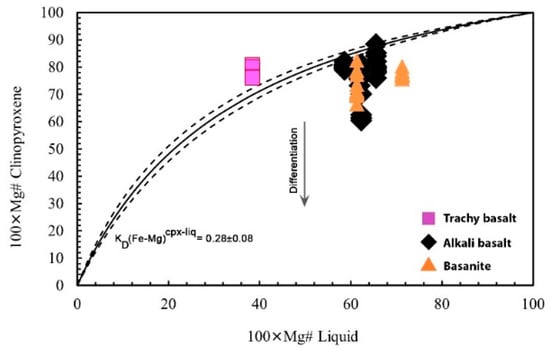
Figure 13.
The Rhodes diagram [49], showing the measured Mg# of LABL clinopyroxene versus the melt Mg# of their host basalts. Equilibrium curves are calculated from the Fe/Mg partition coefficient between clinopyroxene and melt. Melt compositions are based on LABL whole-rock.
The Fe-Mg exchange coefficients of clinopyroxene-only composition (KD(Fe-Mg)cpx) range from 0.24 to 0.31 for basanites. However, the corresponding KD(Fe-Mg)cpx-liq range from 0.3 to 1.0, indicating there is no reliable data to justify the usage of this method for the LABL basanites. In contrast, in alkali basalts, KD(Fe-Mg)cpx is from 0.28 to 0.29 and KD(Fe-Mg)cpx-liq is 0.24 to 0.3 which are thus in acceptable ranges to apply mineral-liquid thermobarometry. In trachybasalt, KD(Fe-Mg)cpx ranges from 0.25 to 0.27 and KD(Fe-Mg)cpx-liq is 0.1 to 0.26.
Here, the Putirka et al. [32] models are used to estimate the temperature and pressure conditions prevailing in the magma chamber during the crystallization. The crystallization temperature of clinopyroxene in alkali basalt ranges between 1071 and 1215 ± 0.61 °C at a pressure of 0.77 − 1.0 ± 0.48 GPa (see Table 2). Moreover, the Putirka [21] Equation (31) represents a barometer based on the partitioning of Al between clinopyroxene and liquid, providing further insights into the pressure conditions of crystallization. Accordingly, the estimated crystallization pressure of clinopyroxene within alkali basalt ranges from 0.63 to 1.06 ± 0.3 GPa. Additionally, utilizing the model presented in Equation (33) by Putirka [21], the crystallization temperature of clinopyroxene is projected to fall between 1132 and 1206 ± 0.46 °C, as detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
P-T results of different clinopyroxene-liquid equilibrium geothermobarometry models for LABL.
Figure 14 illustrates the P-T binary diagrams that model temperature and pressure for all rock types of the LABL, employing the clinopyroxene-only method using Mag-Min_PT.
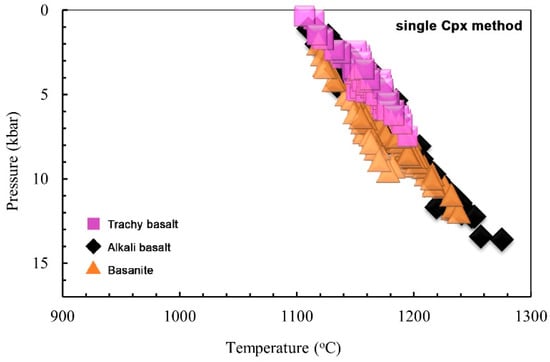
Figure 14.
P-T binary diagram [30], clinopyroxene-only thermobarometry modeling of Lavarab volcanic rocks.
Utilizing clinopyroxene-only thermobarometry the crystallization temperature of clinopyroxenes in the basanite ranges from T = 1120–1240 °C at P = 0.2–1.2 GPa, corresponding to depths of roughly 8–46 km. In the case of alkali basalt, the crystallization conditions are T = 1110–1260 °C and P = 0.1–1.35 GPa (corresponding to depths of about 9–51 km), while for the trachybasalt, the temperatures T = 1110 to 1190 °C under low to moderate pressures of 0.05 to 0.75 GPa (corresponding to depths of 2 to 29 km). Furthermore, thermobarometric analysis utilizing the clinopyroxene-melt method indicates that the crystallization temperature of magma in the alkali basalt ranges from T = 1071–1215 °C, at P = 0.55 and 1.05 GPa (depths of ~21–40 km).
Also, the temperature and pressure variations from the core to the rim of selected clinopyroxene phenocrysts in all three rock types (Figure 15) indicate new magma pulses into the magma reservoir.
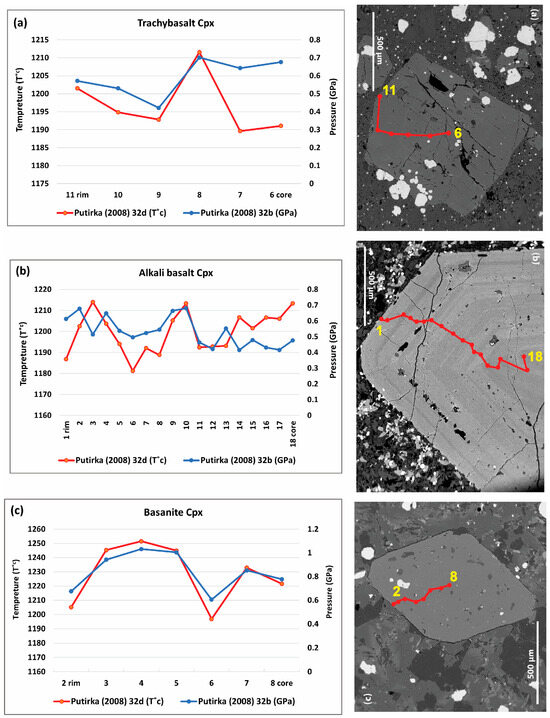
Figure 15.
P-T variations from the core to the rim of selected clinopyroxene phenocrysts in (a) trachybasalt, (b) alkali basalt, (c) basanite samples. The red line and points on the image show the location of geochemical traverse and the numbers indicate the starting and ending points of the analyzed path.
The overall geothermobarometric results derived from both clinopyroxene-only and clinopyroxene–melt equilibria suggest variable crystallization conditions across the LABL rock types, with basanites and alkali basalts forming under higher temperatures and pressures compared to trachybasalts. However, the structural and chemical features of the clinopyroxenes—such as sieve textures, oscillatory zoning, and absorption features—along with the deviation of many KD(Fe-Mg)cpx-liq values from the equilibrium range, indicate an open magmatic system.
The presence of ferric iron (Fe3+) in many basanitic and alkaline clinopyroxenes, as evidenced in the Na + AlIV vs. AlVI + 2Ti + Cr diagram, further supports crystallization under relatively oxidizing conditions, which can be linked to magma recharge [60] or crustal contamination [61]. These conditions can modify the redox state of the melt and influence Fe-Mg partitioning, leading to potential biases in thermobarometric estimates if Fe3+ is not considered. In contrast, trachybasaltic samples show clinopyroxene signatures consistent with more reducing environments, supporting more stable and equilibrium-driven crystallization pathways in those magmas.
Taken together, the combination of mineral chemistry, structural indicators, and Fe3+ distribution confirms that the LABL magmatic system experienced multiple pulses, dynamic crystallization conditions, and evolving oxidation states.
6.2. Thermobarometric Constraints and Limitations
The thermobarometric estimates presented in this study provide critical insights into the crystallization conditions of the LABL magmas. They analyzed clinopyroxenes record a ~0.1–1.4 GPa pressure range (Figure 14), suggesting crystallization from Moho depths (~30 km) to shallow crustal levels (~5 km). Moreover, core-to-rim P-T zoning in olivine and clinopyroxene (Figure 15) is consistent with recharge-driven thermal perturbations. This disequilibrium likely reflects open-system processes such as magma mixing, rapid ascent, or recharge events supported also by resorbed olivine cores and clinopyroxene sieve textures. However, there are also significant constraints and limitations inherent in the methods by (1) magma composition and mineral- melt equilibrium, (2) model-specific uncertainties and (3) redox conditions. Here, we evaluate these limitations and their implications for interpreting crystallization histories.
6.2.1. Magma Composition and Mineral-Melt Equilibrium Test
Magma Composition: Whole-rock compositions, often used as melt compositions, may not represent true equilibrium liquids due to cumulate entrainment or contamination of magma. Groundmass glass thermometry (e.g., 1056 °C vs. whole-rock 1289 °C in alkali basalts) highlights this difference, with glasses preserving late-stage, near-solidus conditions.
Olivine- melt Equilibrium: The large scatter in KD(Fe-Mg)ol-liq (0.12–1.43) in LABL samples (Figure 10) indicates mineral-melt disequilibrium, likely driven by magma mixing, rapid ascent, or syn-eruptive degassing. Notably, only a limited number of basanites and alkali basalts yield KD values within the equilibrium range (0.27–0.33), permitting reliable mineral-liquid thermobarometry.
Clinopyroxene- melt Equilibrium: While Putirka et al. [21] formulations (e.g., Equation (31)) are robust for equilibrium pairs, their application to LABL is restricted to limited number of trachybasalt and alkali basalts due to disequilibrium in other rocks. Even here, the ±0.3 GPa pressure uncertainty underscores the challenge of resolving mid-crustal (~0.5 GPa) vs. deep-crustal (~1.0 GPa) reservoirs.
6.2.2. Model-Specific Uncertainties
Olivine geothermometry: The inherent statistical uncertainty of olivine geothermometry arises from the specific empirical or thermodynamic calibration of the thermometer equation itself. For the model of Putirka et al. [31] Equation (2), the SEE is ±53 °C. The model represented by Putirka et al. [31] Equation (4), later refined as Equation (22) in Putirka [21], has an SEE of ±29 °C and is noted for its improved reliability in water-bearing systems. Crucially, even when mineral-melt equilibrium is perfectly maintained, these specific models carry an inherent uncertainty of at least ±29 °C or ±53 °C, respectively, due to limitations in their calibration.
Clinopyroxene-only thermobarometry: Methods like Putirka’s [21] Equation (32d) are sensitive to AlVI/AlIV partitioning, which varies with oxygen fugacity (fO2) and H2O content. The ±0.26 GPa pressure uncertainty (Putirka [21]), due to fO2 variations that influence Al partitioning in clinopyroxene [21], corresponds to depth errors of ~10 km, complicating precise magma storage estimates. The Soesoo [19] and Putirka [21] models yield overlapping but non-identical P-T ranges (Table 1), reflecting differences in calibration datasets (e.g., hydrous vs. anhydrous systems).
6.2.3. Redox Conditions and Their Thermobarometric Implications
Iron is the main element that is readily oxidized or reduced in response to the range of redox states experienced by crustal rocks [62,63,64,65,66]. The amount of ferric (Fe3+) iron is commonly a good indicator of the redox budget of a rock [67], and the ratio of ferric to ferrous (Fe2+) iron provides a first-order indication of its oxidation state [68]. Under such conditions, assuming total Fe as Fe2+ without correcting for Fe3+ content may lead to inaccurate Fe/Mg ratios, resulting in erroneous values for KD (Fe-Mg exchange coefficient), as well as over- or under-estimated crystallization temperatures and pressures. Therefore, incorporating Fe3+ estimates is essential to improve the accuracy of thermobarometric calculations.
6.3. Magma Type and Tectonic Setting Based on Clinopyroxene Composition
Numerous weathered or even slightly metamorphosed basalts exhibit fresh clinopyroxene crystals within the altered groundmass. The microprobe analysis of these relict grains can be used to identify the magma type of the host lava [11].
LeBas [69] indicated that the concentrations of Al and Ti in pyroxenes is influenced by the magma’s alkalinity. Utilizing Al2O3 and SiO2 contents in the chemical composition of pyroxenes allows for the differentiation of alkaline, peralkaline, and subalkaline types of magma (Figure 16a). The diagram illustrates that the clinopyroxenes from the LABL are categorized as peralkaline (specifically for basanite and certain alkali basalts) and alkaline-subalkaline (including alkali basalt and trachybasalt) as depicted in Figure 16a. In a Ti versus Na+Ca diagram [10], basanite and alkali basalt are situated within the alkali basalt field, whereas trachybasalt is positioned along the boundary between sub-alkali basalt and alkali basalt fields (Figure 16b).
Nisbet and Pearce [11] have indicated that pyroxenes found in within-plate alkali basalts have high Na and Ti and low Si contents, whereas pyroxenes of within-plate tholeiites and volcanic arc basalts contain more Ti, Fe and Mn. Tholeiitic basalts erupted within plates in oceanic islands or continental rifts (WPT samples), and alkali basalts erupted within plates (WPA samples) [11]. The pyroxene composition based on discriminant functions (F1-F2) well distinguishes between alkaline basalts in intra-plate settings (WPA), within-plate tholeiitic magmas (WPT), and volcanic arc basalts (VAB) from one another. However, a significant overlap was observed between within-plate tholeiites and oceanic floor basalts (WPT-OFB), as well as between volcanic arc basalts and oceanic floor basalts (VAB-OFB). In this diagram, the trachybasalt and alkali basalt fall within the volcanic arc basalts (VAB) field, whereas basanite plot in within-plate alkali basalt. Also, diagrams of pyroxene composition based on Na2O-MnO-TiO2 and TiO2-SiO2 provide the basis for visual discrimination [11]. In the Na2O-MnO-TiO2 diagram, basanite and alkali basalt are located within the WPA field and trachybasalt is plotted in the VAB+WPA field. In the TiO2-SiO2 discrimination diagram, trachybasalt, alkali basalt and basanite are located within the WPA and to some extent in the VAB (Figure 16c–e). According to Leterrier et al. [10], the clinopyroxenes found in the LABL trachybasalt and alkali basalt exhibit similarities to those from orogenic tholeiitic basalt when taking into account the Ti and Ca cations concentrations. Furthermore, the Ti and Ca contents in clinopyroxene from basanite are comparable to those in clinopyroxene derived from alkali basalt (Figure 16f). The local geology in eastern Iran indicates a subduction- and collision-dominated tectonic regime. Intrusive rocks include granodioritic and biotite granite plutons, monzodiorite to dacite porphyritic dykes, which are calc-alkaline, metaluminous, and I-type, with geochemical signatures of volcanic arc and post-collisional magmas [26]. Houshmand-Manavi et al. [28] demonstrated that the LABL is related to a post-collisional setting in the Oligocene-Miocene, through comprehensive field observations and whole-rock geochemical analysis. It is postulated that an extensional environment related to the activity of two dextral basement faults that trend north-south, situated to the east and west of the region provided a pathway for magma ascent. The geology is characterized by the presence of deep reaching basement faults that facilitated the ascent and eruption of magma, which can be associated with the Zahedan and Harriroud faults, as evidenced by the alignment of the lava, which run parallel to these faults and being situated in the intervening space between them. These lavas occasionally exhibit features indicative of a pseudo-active margin (VAB), attributed to mantle metasomatism caused by fluids released during the subduction of the Sistan oceanic lithosphere (Late Cretaceous-Middle Eocene, [9,26]). Moreover, the tectonic discrimination diagrams based on clinopyroxene and whole-rock [28] chemistry more likely reflect some inherited characteristics from a heterogeneous source, which prohibits to determine the true LABL tectonic setting. Therefore, the LABL is classified as post-collisional. However, it should be noted that recent studies have demonstrated the limitations of conventional clinopyroxene-based geochemical discrimination diagrams. In this regard, Li et al. [70] applied a machine learning approach using a global clinopyroxene dataset and achieved an accuracy of over 90% in distinguishing tectonic settings. Although the present study relies on traditional approaches, applying such ML-based methods in future work could provide more precise and reliable interpretations of the tectonic setting of the LABL basalts.
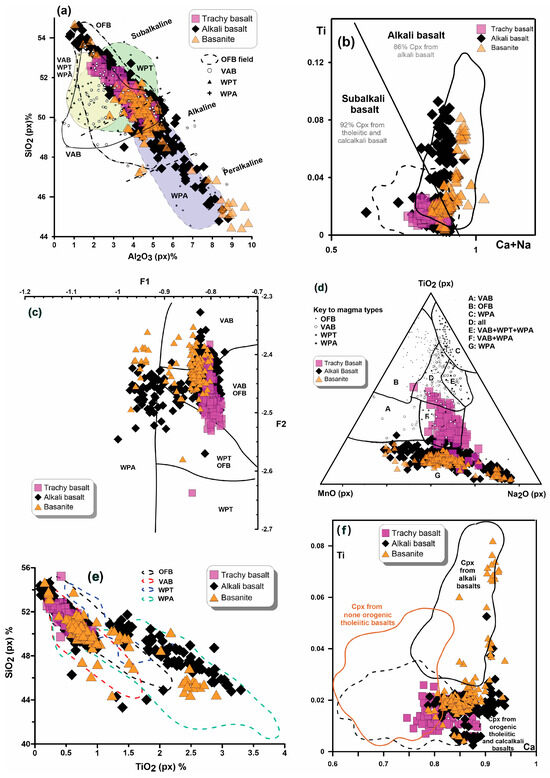
Figure 16.
(a) Al2O3 versus SiO2 diagram [11]; (b) Ti versus Na+Ca, discrimination diagram for clinopyroxene phenocrysts from alkali basalts and other basalts [10]; Various discrimination diagrams based on the compositional of clinopyroxenes from Nisbet and Pearce [11] for the basaltic lavas of Lavarab. (c) Diagram of F1-F2; (d) diagram of Na2O-MnO-TiO2; (e) diagram of TiO2-SiO2. (f) Diagram based on clinopyroxene Ca-Ti cations [10].
F1 = −0.012×SiO2− 0.0807×TiO2 + 0.0026×Al2O3 − 0.0012×FeO(total) − 0.0026×MnO + 0.0087×MgO − 0.0128×CaO − 0.0419×Na2O
F2 = −0.0469×SiO2 − 0.0818×TiO2 − 0.0212×Al2O3 − 0.0041×FeO(total) − 0.1435×MnO − 0.0029×MgO + 0.0085×CaO + 0.016×Na2O
6.4. Magma Crystallization and Evolution Modeling
A volcanism model of LABL is presented in the Sistan Suture Zone tectonic evolution sketch in Figure 17a. It shows the delamination of thickened oceanic lithosphere root which caused to generate LABL parent magma from low degrees of partial melting of the upwelled asthenosphere beneath the studied area [28]. Basaltic magma, due to its low viscosity and high temperature, exhibits significant mobility and begins to ascend immediately after generation in the mantle.
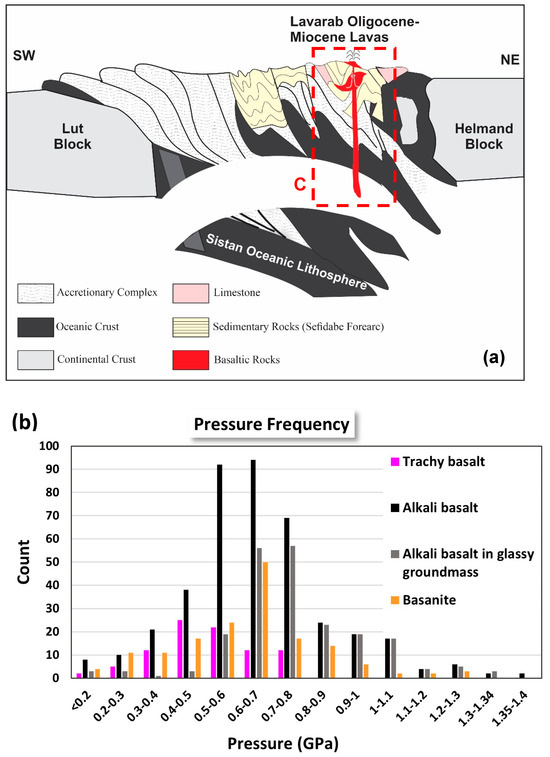
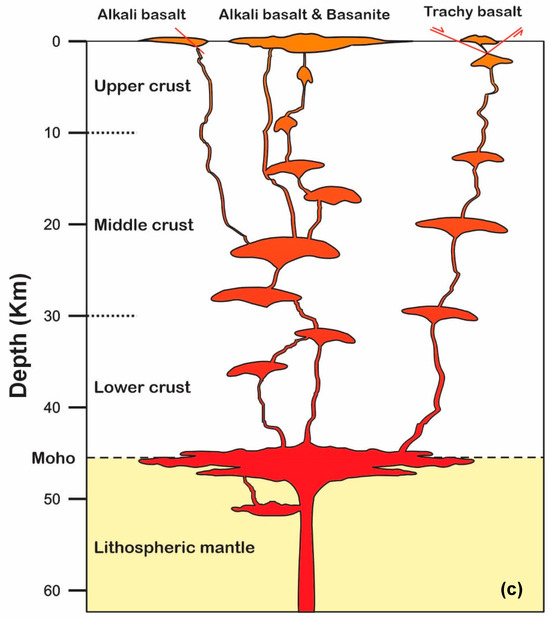
Figure 17.
(a) Volcanism model of Lavarab lavas in the tectonic evolution model of the Sistan Suture Zone [28]. (b) Frequency distribution of the estimated pressures of LABL based on clinopyroxene composition; (c) Schematic illustration of the magma plumbing system of the Lavarab lavas. Determination of magma chamber depths is limited to clinopyroxene pressure frequency. Pressure is calculated by Putirka Equation (32b) [21].
The calculated P-T ranges (0.1–1.4 GPa; ca 940–1290 °C) and petrographic evidence (e.g., sieve-textured clinopyroxene, resorbed olivine) collectively suggest the basaltic magma ascended after generation in the mantle and accumulated at depths exceeding ca. 45 km (Moho depth in East Iran [71,72]) in the lower crust, and subsequently initiated the crystallization. We propose a multi-tiered magma plumbing system beneath the LABL through a three-stage model:
- Deep Storage (1.0–1.4 GPa; ~38–51 km):
High-P clinopyroxene mega-phenocrysts (e.g., L.81) and Fo > 90 olivine cores crystallized in the lower crust/uppermost mantle, facilitated by localized heating during lithospheric delamination [39], supported by evidences such as coexisting high-Mg# clinopyroxene (Wo46En47) and olivine (Fo92) with Cr-spinel inclusions.
- Mid-Crustal Storage (0.3–0.8 GPa; ~11–30 km):
When fault reactivation (Zahedan/Harirud) opened pathways for magma ascent, the basaltic magma reached depths of 30–10 km (middle crust) leading to the crystallization of plagioclase and clinopyroxene. This is supported by the estimated pressures of clinopyroxene mega-phenocrysts in LABL basalts and basanites that most pressure frequency distribution represents P = 0.4–0.7 GPa, indicating periods of crystallization occurred in the middle crust magma chamber. The estimated pressure values, (P = 0.4–0.6 GPa) at depths of 15–20 km, are associated with trachybasalts (Figure 17b,c).
The mineral chemistry data also show that this mid-crustal storage refilled by deep-derived magma raised from the deep storage (1.0–1.4 GPa; ~38–51 km). The mixing between deep-derived and evolved melts, recorded by (a) reverse-zoned clinopyroxene (high-Mg rims; Figure 8a). (b) olivine with Mn-enriched rims (Figure 6a), indicating Fe-Mg exchange with fractionated melt.
- Shallow Conduits (<0.3 GPa; <11 km):
Eventually, the remaining magma, along with the phenocrysts, rises through fractures and faults to the surface. Trachybasalt crystallization (0.1–0.75 GPa) reflects rapid ascent through fractures created by a tensile mechanism resulting from the action of dextral Zahdan and Harriroud faults in the area (Figure 17b,c). This is supported by (a) Glassy groundmass (quenched melt), and (2) Lack of zoning in microlites that represent a short residence time.
In summary, this architecture explains the LABL’s chemical diversity: basanites represent deep, low-degree melts, while trachybasalts reflect shallow crustal assimilation.
In the following, sample L.81 from alkali basalts with glassy groundmass was selected to investigate the differences between crystallization temperature and pressure of clinopyroxene mega-phenocrysts and phenocrysts. As shown in Figure 18, the maximum temperature estimated for mega-phenocrysts is ~1200 °C at the maximum pressure of ~1 GPa, while the maximum temperature for phenocrysts is ~1190 °C at the maximum pressure of ~0.7 GPa, based on the clinopyroxene-only thermobarometer. In other words, the crystallization of clinopyroxene mega-phenocrysts and phenocrysts started at depths of ~38 km and ~26 km, in the lower and middle crust, respectively. There is no notable reduction in temperature during the pressure release of ca. 0.3 GPa, which indicates a continuous and rapid ascent from depths of approximately 11 km to the surface and quenching after eruption, leading to the formation of a glassy groundmass in this sample.
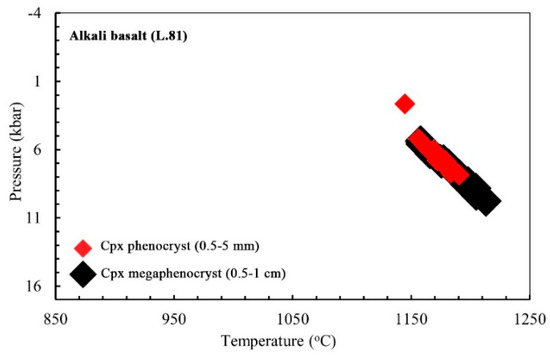
Figure 18.
Comparison of the conditions governing the crystallization of clinopyroxene mega-phenocrysts and phenocrysts from the alkali basaltic sample (L.81), based on only clinopyroxene thermobarometry.
7. Conclusions
The mineral chemistry of the LABL indicates a peralkaline to subalkaline magma nature, suggesting an origin in an intra-plate tectonic setting and volcanic arc environment. This contradicts the local geological situation. It is therefore important to note that these implied geotectonic settings probably originate in inherited traits from a heterogeneous mantle source. Therefore, based on the real tectonic regime during the Oligocene-Miocene in Iran and field observations, a more realistic post-collision tectonic environment is suggested for the LABL. Additionally, we propose that LABL magmas were stored in a trans crustal (through-crustal) plumbing system (2–51 km depth), with eruptions triggered by fault-mediated recharge from deep reservoirs. Petrographic and thermobarometric data reveal cyclic recharge-fractionation-eruption episodes, characteristic of the LABL post-collisional alkaline volcanism.
The application of multiple thermobarometric approaches (whole-rock, olivine, and clinopyroxene chemistry) consistently indicates that the studied basaltic lavas were generated and stored under high-temperature conditions. Basanites record the highest crystallization temperatures (up to ~1390 °C) at upper mantle depths (ca. 46 km at 1.2 GPa) to lower crustal levels (ca. 8 km at 0.2 GPa), whereas alkali basalts show slightly lower temperatures (~1170–1340 °C) over broader pressure and depth ranges (0.1–1.35 GPa; 4–51 km). Trachybasalts, in contrast, crystallized at comparatively lower temperatures (~1110–1190 °C) and at shallower levels (2–29 km), reflecting their confinement to middle–upper crustal reservoirs.
These results collectively demonstrate a polybaric magma plumbing system, in which basanites and alkali basalts were stored from the lower crust to near-surface levels, while trachybasalts were mainly restricted to mid- to upper-crustal chambers. Moreover, the chemical compositions of phenocrysts in the studied basaltic lavas provide evidence of magma recharge through multiple pulses of new magma injected into the existing reservoirs prior to eruptions. The eruption history of the LABL reflects the interplay between deep melt generation associated with lithospheric thinning and fault-controlled ascent, with the observed chemical diversity resulting from polybaric fractionation and crustal assimilation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15090915/s1, Table S1: Whole rock major and trace element compositions; Table S2: Lavarab EPMA data; Table S3: Olivine thermometry results; Table S4: Cpx-liq thermobarometry results; Table S5: Cpx compositions and thermobarometry results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.-M. and M.R.-K.; Data curation, S.H.-M.; Formal analysis, S.H.-M.; Investigation, S.H.-M. and H.G.; Methodology, S.H.-M., H.G. and U.K.; Software, S.H.-M.; Supervision, M.R.-K.; Visualization, S.H.-M.; Writing—original draft, S.H.-M.; Writing—review & editing, S.H.-M., M.R.-K. and U.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request. Requests can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study is a part of the first author’s PhD thesis. Hereby, the support of the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology of Iran is gratefully acknowledged. The authors appreciate the help of Fatemeh Vakili, Mehdi Norouzi and Hasan Narimani (Geological Survey of Iran, Tehran, Iran). We are also grateful to Ewa Krzemińska and Grzegorz Zieliński (Polish Geological Institute, Warsaw, Poland) for helping us with the EPMA and to Christian Ball (University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria) who helped with the SEM imaging. Thanks to Mohammad Goudarzi (University of Vienna) for his help with data-curation and software usage, and to Sima Houshmand-Manavi for the geological map preparation, data-curation and visualization. Thanks, are also due to the Editor-in-Chief of the journal, associated editor and reviewers of the journal for their review and handling of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LABL | Lavarab Alkaline Basaltic Lavas |
| GSI | Geological Survey of Iran |
| SEE | Standard error of estimate |
| RiMG | Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry |
| Quad | Ca-Mg-Fe pyroxenes |
| N/A | Not available |
References
- Xi, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Xian, H.; Pan, F.; Li, S.; Xue, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Reconstruction of Magma Plumbing System and Regional Magmatic Processes via Chemical and Structural Zoning of Biotite in Rhyolite from Long Valley, CA. JGR Solid Earth 2024, 129, e2024JB029205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundy, J.; Cashman, K. Petrologic Reconstruction of Magmatic System Variables and Processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 69, 179–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, C.; Blundy, J.D.; Sparks, R.S.J. The Genesis of Intermediate and Silicic Magmas in Deep Crustal Hot Zones. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 505–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.V.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Blundy, J.D. Vertically Extensive and Unstable Magmatic Systems: A Unified View of Igneous Processes | Science, 355(6331), Eaag3055. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.aag3055 (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Behruzi, A. Geological Quadrangle Map of Zahedan; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Aghanabati, A. Geological Map of Kuh-e Do Poshti; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Aghanabati, A. Geological Quadrangle Map of Daryacheh-Ye-Hamun; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Camp, V.E.; Griffis, R.J. Character, Genesis and Tectonic Setting of Igneous Rocks in the Sistan Suture Zone, Eastern Iran. Lithos 1982, 15, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirrul, R.; Bell, I.R.; Griffis, R.J.; Camp, V.E. The Sistan Suture Zone of Eastern Iran. GSA Bull. 1983, 94, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leterrier, J.; Maury, R.C.; Thonon, P.; Girard, D.; Marchal, M. Clinopyroxene Composition as a Method of Identification of the Magmatic Affinities of Paleo-Volcanic Series. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1982, 59, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, E.G.; Pearce, J.A. Clinopyroxene Composition in Mafic Lavas from Different Tectonic Settings. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1977, 63, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, B.J.; Banno, S. Garnet-Orthopyroxene and Orthopyroxene-Clinopyroxene Relationships in Simple and Complex Systems. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1973, 42, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.R.A. Pyroxene Thermometry in Simple and Complex Systems. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1977, 62, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, E.L.; Papike, J.J.; Bence, A.E. Statistical Analysis of Clinopyroxenes from Deep-Sea Basalts. Am. Mineral. 1979, 64, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, D.H. Pyroxene Thermometry. Am. Mineral. 1983, 68, 477–493. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, P.M. Thermodynamic Analysis of Quadrilateral Pyroxenes. Part 1: Derivation of the Ternary Nonconvergent Site-Disorder Model. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1985, 91, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.M.; Lindsley, D.H. Thermodynamic Analysis of Quadrilateral Pyroxenes. Part II: Model Calibration from Experiments and Applications to Geothermometry. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1985, 91, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, P.; Mercier, J.-C.C. The Mutual Solubility of Coexisting Ortho- and Clinopyroxene: Toward an Absolute Geothermometer for the Natural System? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1985, 76, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soesoo, A. A Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Clinopyroxene Composition: Empirical Coordinates for the Crystallisation PT-estimations. GFF 1997, 119, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P.; Taylor, W.R. Single Clinopyroxene Thermobarometry for Garnet Peridotites. Part I. Calibration and Testing of a Cr-in-Cpx Barometer and an Enstatite-in-Cpx Thermometer. Contrib Miner. Pet. 2000, 139, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D. Thermometers and Barometers for Volcanic Systems. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2008, 69, 61–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, P.E.; Kent, A.J.R.; Till, C.B.; Donovan, J.; Neave, D.A.; Blatter, D.L.; Krawczynski, M.J. Barometers Behaving Badly I: Assessing the Influence of Analytical and Experimental Uncertainty on Clinopyroxene Thermobarometry Calculations at Crustal Conditions. J. Petrol. 2023, 64, egac126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R. Igneous Rocks and Processes: A Practical Guide; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4443-3065-6. [Google Scholar]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; Altıner, D.; Cin, A.; Ustaömer, T.; Hsü, K.J. Origin and Assembly of the Tethyside Orogenic Collage at the Expense of Gondwana Land. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1988, 37, 119–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, M. Generalized Tectonic Map of Iran. In Berberian M (Ed) Continental Deformation in the Iranian Plateau; Geological Survey of Iran: Tehran, Iran, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei-Kahkhaei, M.; Corfu, F.; Galindo, C.; Rahbar, R.; Ghasemi, H. Adakite Genesis and Plate Convergent Process: Constraints from Whole Rock and Mineral Chemistry, Sr, Nd, Pb Isotopic Compositions and U-Pb Ages of the Lakhshak Magmatic Suite, East Iran. Lithos 2022, 426–427, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damani Gol, S.; Bagheri, S. Paleogene Thrust System in the Eastern Iranian Ranges; Kharazmi University: Tehran, Iran, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Houshmand-Mananvi, S.; Rezaei-Kahkhaei, M.; Ghasemi, H. Whole Rock Geochemistry and Tectonic Setting of Oligocene-Miocene Lavarab Lava (North Zahedan). Sci. Q. J. Geosci. 2024, 34, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei-Kahkhaei, M.; Esmaeily, D.; Sahraei, H. Evaluation of Impact Processes in the Formation of Neshveh Volcanic Rocks, NW Saveh. Sci. Q. J. Geosci. 2018, 28, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, M.; Asan, K. MagMin_PT: An Excel-Based Mineral Classification and Geothermobarometry Program for Magmatic Rocks. MinMag 2023, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, P.L.; Emslie, R.F. Olivine-Liquid Equilibrium. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1970, 29, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D.; Mikaelian, H.; Ryerson, F.; Shaw, H. New Clinopyroxene-Liquid Thermobarometers for Mafic, Evolved, and Volatile-Bearing Lava Compositions, with Applications to Lavas from Tibet and the Snake River Plain, Idaho. Am. Mineral. 2003, 88, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.; Ryerson, F.J.; Mikaelian, H. New Igneous Thermobarometers for Mafic and Evolved Lava Compositions, Based on Clinopyroxene + Liquid Equilibria. Am Miner. 2003, 88, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, F. WinPyrox: A Windows Program for Pyroxene Calculation Classification and Thermobarometry. Am. Mineral. 2013, 98, 1338–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peate, D.W.; Hawkesworth, C.J. Lithospheric to Asthenospheric Transition in Low-Ti Flood Basalts from Southern Paraná, Brazil. Chem. Geol. 1996, 127, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.B.; Sutton, S.R. Valences of Ti, Cr, and V in Apollo 17 High-Ti and Very Low-Ti Basalts and Implications for Their Formation. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2018, 53, 2138–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Winchester, J.A.; Floyd, P.A. Geochemical Discrimination of Different Magma Series and Their Differentiation Products Using Immobile Elements. Chem. Geol. 1977, 20, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.V.; Hofmann, A.W.; Kuzmin, D.V.; Yaxley, G.M.; Arndt, N.T.; Chung, S.L.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Elliott, T.; Frey, F.A.; Garcia, M.O.; et al. The Amount of Recycled Crust in Sources of Mantle-Derived Melts. Science 2007, 316, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Kitamura, M. Q-J Diagram for Classification of pyroxenes. J. Jpn. Assoc. Mineral. Petrol. Econ. Geol. 1983, 78, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, N.; Fabrise, J.; Ferguson, A.; Ginzburg, I.V.; Ross, M.; Seifert, F.A.; Zussman, J.; Akoi, K.; Gottardi, G. Nomenclature of Pyroxenes. Am. Mineral. 1988, 173, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hou, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, R.; Marxer, F.; Zhang, H. A New Clinopyroxene Thermobarometer for Mafic to Intermediate Magmatic Systems. Eur. J. Mineral. 2021, 33, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hong, L.-B.; Qian, S.-P.; He, P.-L.; He, M.-H.; Yang, Y.-N.; Wang, J.-T.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Ren, Z.-Y. The Effect of Elemental Diffusion on the Application of Olivine-Composition-Based Magmatic Thermometry, Oxybarometry, and Hygrometry: A Case Study of Olivine Phenocrysts from the Jiagedaqi Basalts, Northeast China. Am. Mineral. 2023, 108, 1449–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh Baniasadi, M.; Ghasemi, H.; Angiboust, S.; Rezaei Kahkhaei, M.; Papadopoulou, L. Application of clinopyroxene geothermobarometers on the gabbro/dioritic rocks associated with the Gowd-e-Howz (Siah-Kuh) granitoid stock, Baft, Kerman. Sci. Q. J. Geosci. 2024, 34, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helz, R.T.; Thornber, C.R. Geothermometry of Kilauea Iki Lava Lake, Hawaii. Bull Volcanol 1987, 49, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montierth, C.; Johnston, A.D.; Cashman, K.V. An Empirical Glass-Composition-Based Geothermometer for Mauna Loa Lavas. In Mauna Loa Revealed: Structure, Composition, History, and Hazards; American Geophysical Union (AGU): Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 207–217. ISBN 978-1-118-66433-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.-J.; Frey, F.A.; Clague, D.A.; Garcia, M.O. Mineral Chemistry of Submarine Lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: Implications for Magmatic Processes within Hawaiian Rift Zones. Contrib Miner. Pet. 1999, 135, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplis, M.J. The Thermodynamics of Iron and Magnesium Partitioning between Olivine and Liquid: Criteria for Assessing and Predicting Equilibrium in Natural and Experimental Systems. Contrib Miner. Pet. 2005, 149, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.M.; Dungan, M.A.; Blanchard, D.P.; Long, P.E. Magma Mixing at Mid-Ocean Ridges: Evidence from Basalts Drilled near 22° N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Tectonophysics 1979, 55, 35–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.D.; Perfit, M.; Ryerson, F.J.; Jackson, M.G. Ambient and Excess Mantle Temperatures, Olivine Thermometry, and Active vs. Passive Upwelling. Chem. Geol. 2007, 241, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P. A Clinopyroxene Geobarometer for Basaltic Systems Based on Crystal-Structure Modeling. Contrib Miner. Pet. 1995, 121, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P.; Ulmer, P. Clinopyroxene Geobarometry of Magmatic Rocks Part 1: An Expanded Structural Geobarometer for Anhydrous and Hydrous, Basic and Ultrabasic Systems. Contrib Miner. Pet. 1998, 133, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neave, D.A.; Putirka, K.D. A New Clinopyroxene-Liquid Barometer, and Implications for Magma Storage Pressures under Icelandic Rift Zones. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putirka, K.; Johnson, M.; Kinzler, R.; Longhi, J.; Walker, D. Thermobarometry of Mafic Igneous Rocks Based on Clinopyroxene-Liquid Equilibria, 0–30 Kbar. Contrib Miner. Pet. 1996, 123, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tormey, D.R.; Grove, T.L.; Bryan, W.B. Experimental Petrology of Normal MORB near the Kane Fracture Zone: 22°–25° N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 96, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, J.; Koepke, J.; Holtz, F. An Experimental Investigation of the Influence of Water and Oxygen Fugacity on Differentiation of MORB at 200 MPa. J. Petrol. 2005, 46, 135–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thy, P.; Lesher, C.E.; Nielsen, T.F.D.; Brooks, C.K. Experimental Constraints on the Skaergaard Liquid Line of Descent. Lithos 2006, 92, 154–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botcharnikov, R.E.; Koepke, J.; Holtz, F.; McCammon, C.; Wilke, M. The Effect of Water Activity on the Oxidation and Structural State of Fe in a Ferro-Basaltic Melt. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 5071–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husen, A.; Almeev, R.R.; Holtz, F. The Effect of H2O and Pressure on Multiple Saturation and Liquid Lines of Descent in Basalt from the Shatsky Rise. J. Petrol. 2016, 57, 309–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundermeyer, C.; Gätjen, J.; Weimann, L.; Wörner, G. Timescales from Magma Mixing to Eruption in Alkaline Volcanism in the Eifel Volcanic Fields, Western Germany. Contrib Miner. Pet. 2020, 175, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, I.S.E. The Redox States of Basic and Silicic Magmas: A Reflection of Their Source Regions? Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1991, 106, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinner, G.A. Pelitic Gneisses with Varying Ferrous/Ferric Ratios from Glen Clova, Angus, Scotland. J. Petrol. 1960, 1, 178–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumble, D. Fe-Ti Oxide Minerals from Regionally Metamorphosed Quartzites of Western New Hampshire. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1973, 42, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Sandiford, M. Sapphirine and Spinel Phase Relationships in the System FeO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-O2 in the Presence of Quartz and Hypersthene. Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 98, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.L.; Powell, R.; Guiraud, M. Low-Pressure Granulite Facies Metapelitic Assemblages and Corona Textures from MacRobertson Land, East Antarctica: The Importance of Fe203and TiOz in Accounting for Spinel-Bearing Assemblages. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1989, 7, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ague, J.J.; Baxter, E.F.; Eckert, J.O. JR High fO2 During Sillimanite Zone Metamorphism of Part of the Barrovian Type Locality, Glen Clova, Scotland. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 1301–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.A. Redox Decoupling and Redox Budgets: Conceptual Tools for the Study of Earth Systems. Geology 2006, 34, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, J.F.A.; Powell, R. Influence of Ferric Iron on the Stability of Mineral Assemblages. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2010, 28, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBas, M.J. The Role of Aluminium in Igneous Clinopyroxenes with Relation to Their Parentage. Am. J. Sci. 1962, 260, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Reichow, M.K.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Santosh, M. A Machine-Learning-Based Approach Using Clinopyroxene Data to Improve Accuracy and Efficiency in Predicting Tectonic Settings: Implications for Rodinia Supercontinent Breakup Triggered by Mantle Plume Events. Am. Mineral. 2025, 110, 996–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Zadeh, S. Estimation of Moho Depth in Iran by Combination of Gravity and Seismic Data; Institude for Advanced Studies in Basic Sceineces, Gava Zang: Znajan, Iran, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sepahvand, M.R. Variations of Moho Depth and Vp/Vs Ratio in Central and Eastern Iran Using the Zhu and Kanamori Method; Kerman Graduate University of Technology (KGUT): Kerman, Iran, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).