Experimental Investigation on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Sulfide Ores with Different Sulfur Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Samples and Method
2.1. Sulfide Ore Sample Preparation
2.2. Experimental Approach
2.2.1. Oxidation Weight Gain Test
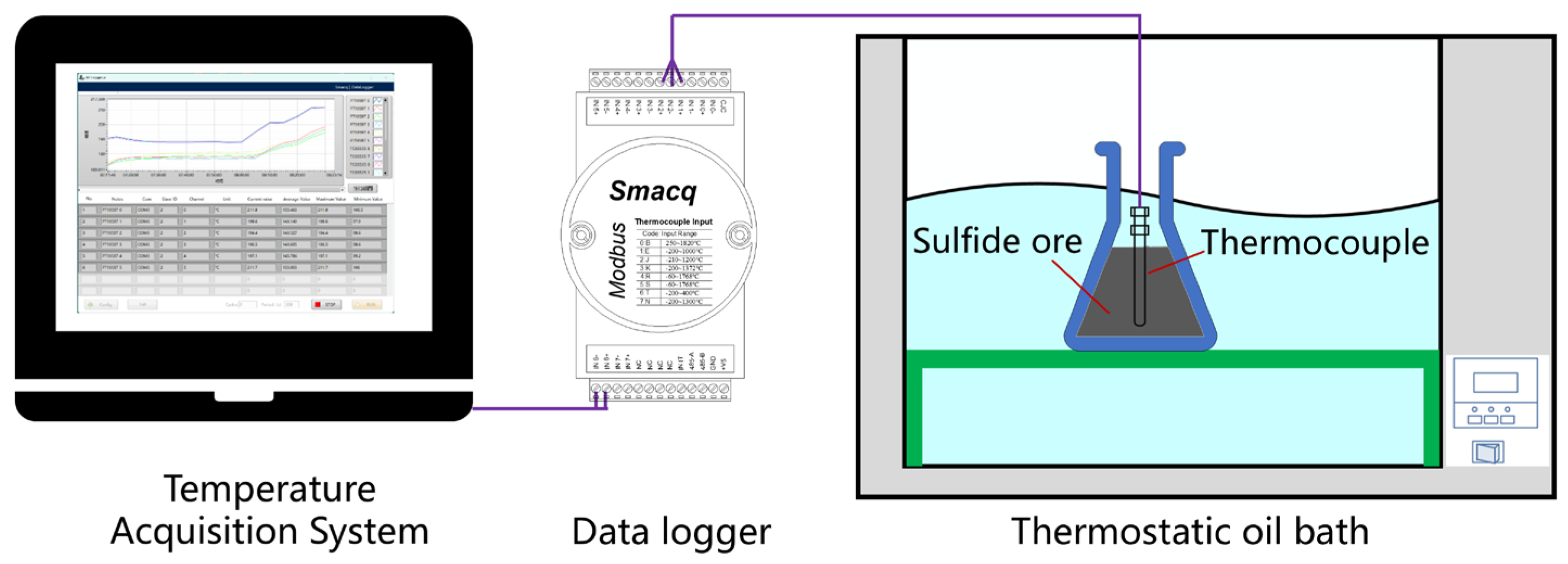
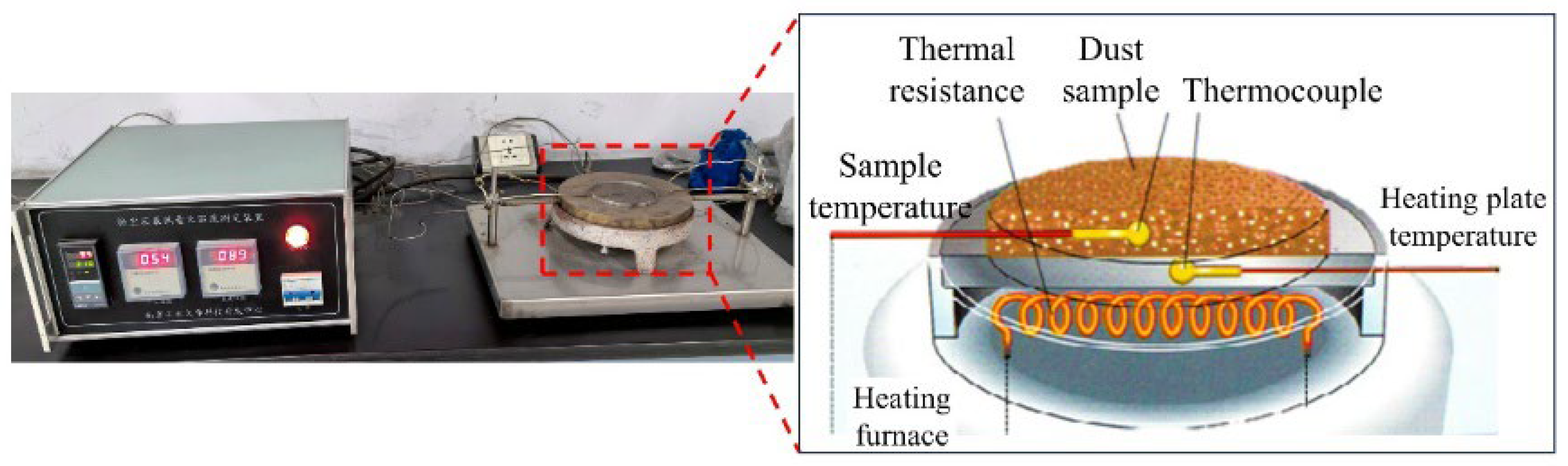
2.2.2. Self-Heating Temperature and Ignition Temperature Test
2.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weight Gain of Sulfide Ore Samples
3.2. Self-Heating Temperature and Ignition Temperature
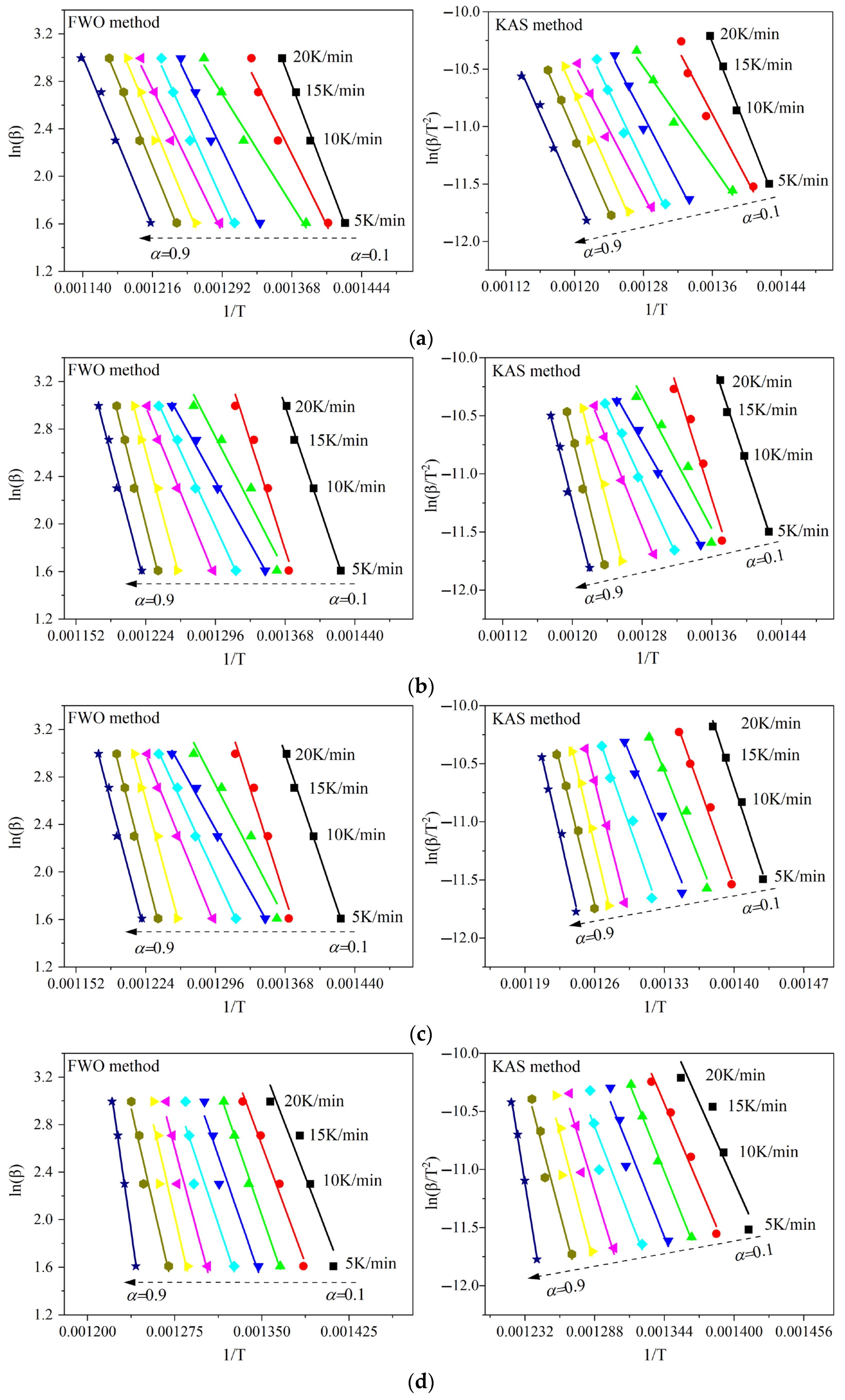
3.3. Kinetic Analysis of the Oxidation Reaction
3.3.1. Combustion Stage Division
3.3.2. Effects of Sulfur Content on Thermogravimetric Properties
3.3.3. Apparent Activation Energy
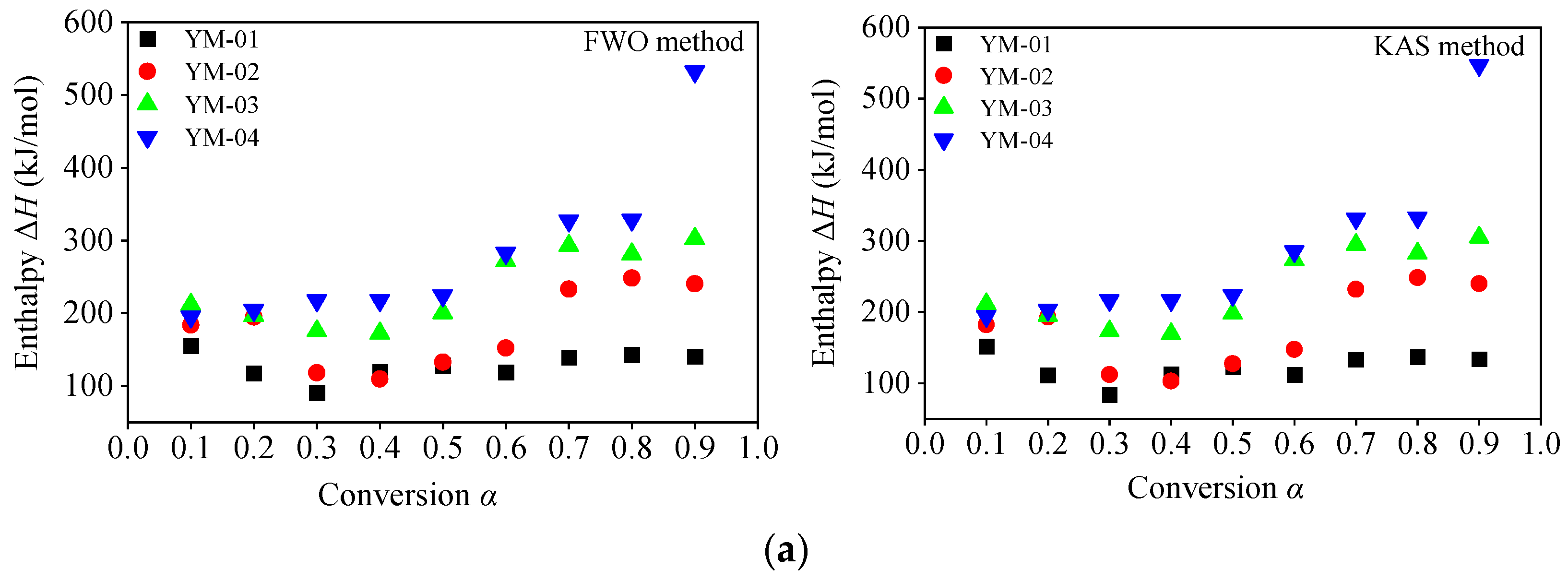
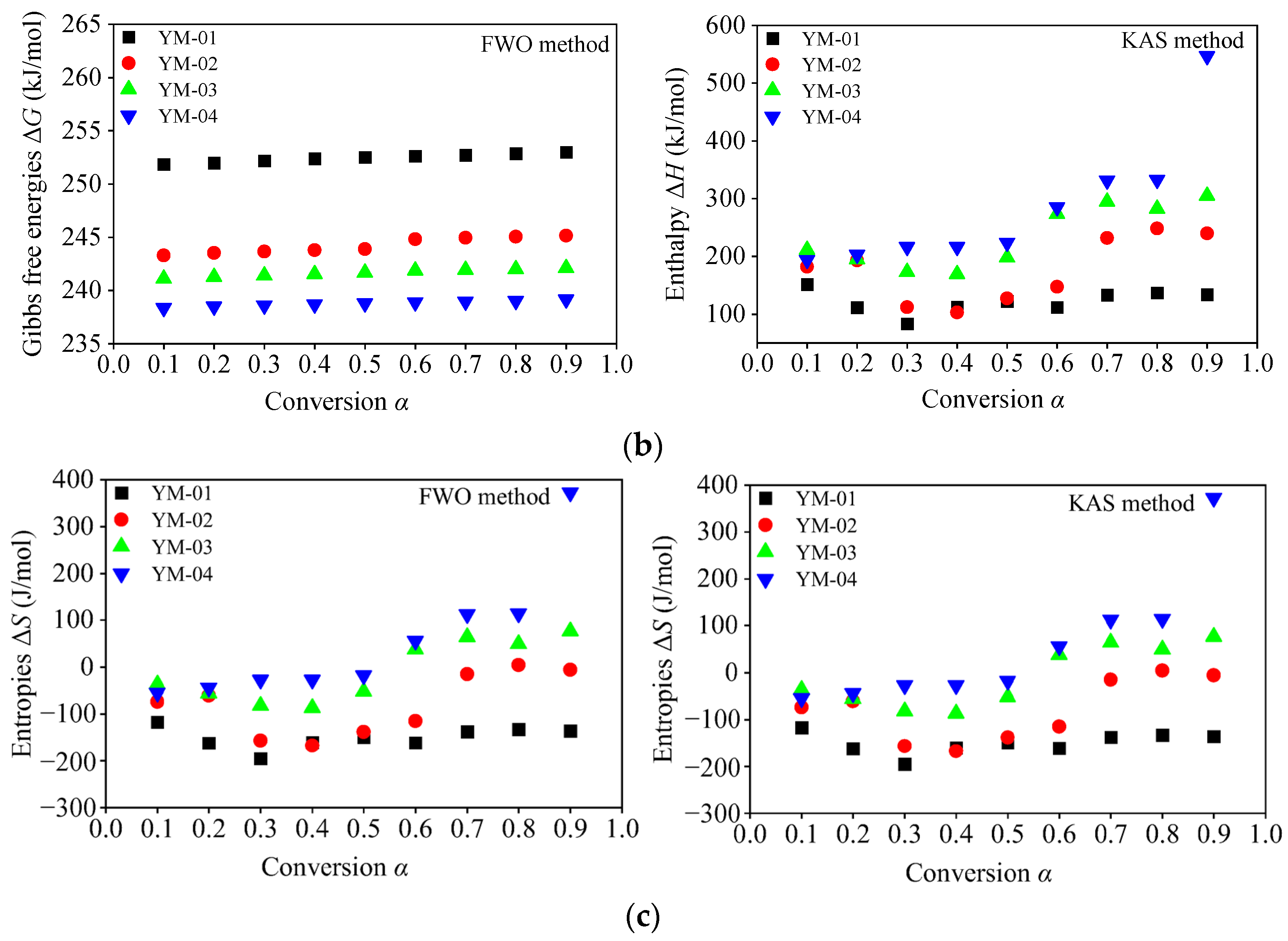
3.3.4. Thermodynamic Parameters
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The sulfide ore samples exhibited varying degrees of weight gain and agglomeration after oxidation under constant temperature and humidity for one month. The ranking of the oxidation weight gain rate was consistent with the ranking of the sulfur content for each sample. The self-heating temperatures were 135, 152.5, 162.5, and 176.9 °C, and the ignition temperatures were 425.3, 438.6, 455.4, and >500 °C for each sample, respectively. As the sulfur content of the samples increased, the self-heating and ignition temperatures decreased.
- (2)
- The thermogravimetric analysis of SCSO showed that the combustion process can be subdivided into three stages. Stage I is the low-temperature oxidation stage, during which trace mineral decomposition and oxygen absorption occurred. Stage II is the combustion decomposition stage, during which obvious mass loss occurred due to the decomposition and depolymerization reactions of the sulfide ore. Stage Ⅲ is the slow burnout stage, during which the non-decomposable or non-reacting substances remained until burnout, and the sample weight no longer changed. Otherwise, with an increase in the sulfur content, the enlargement in the temperature range became increasingly obvious, and the mass loss increased in stage II.
- (3)
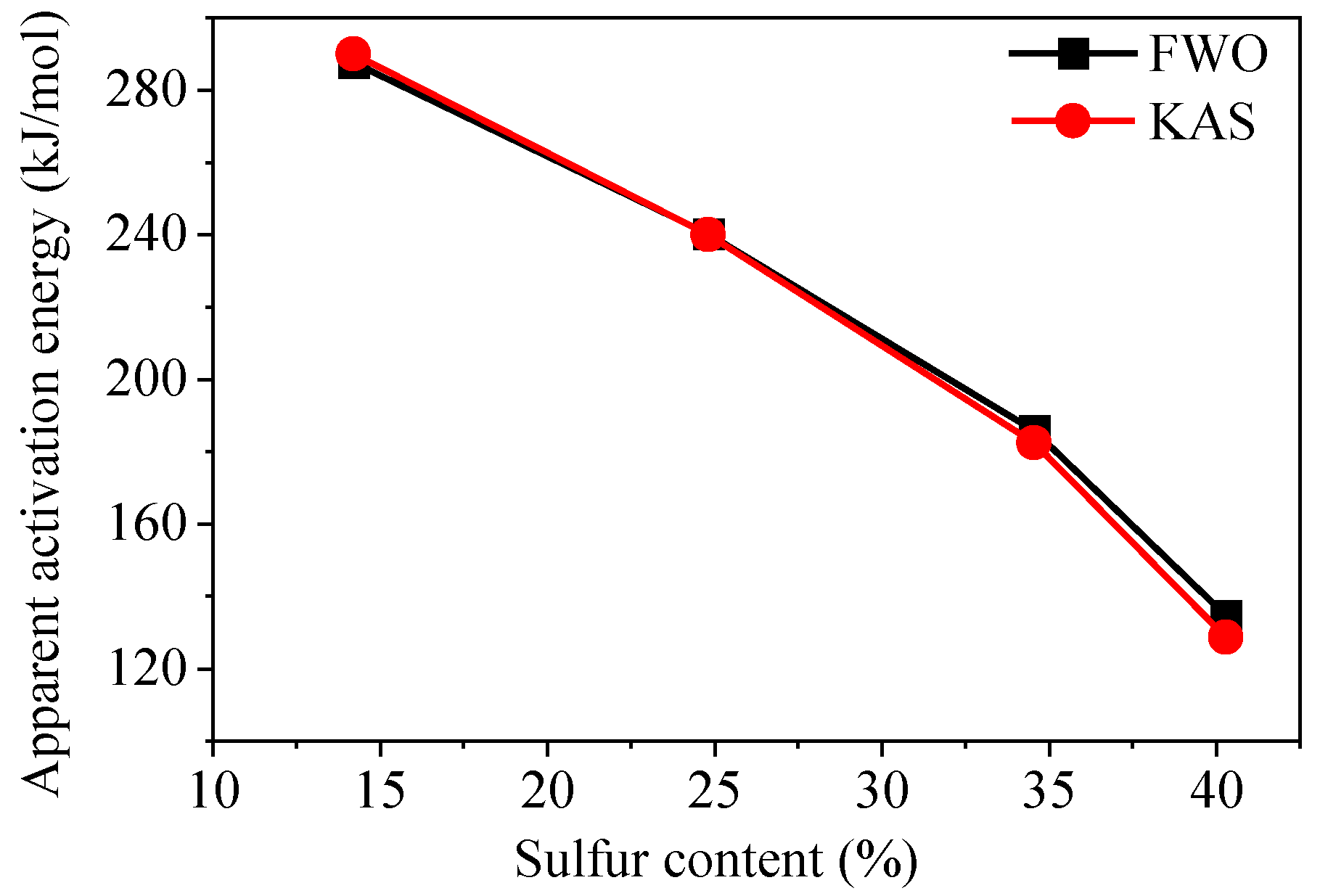
- For the combustion decomposition stage, the average activation energies of samples YM-01, YM-02, YM-03, and YM-04 calculated using the FWO method were 134.6, 185.8, 240.3, and 287.7 kJ/mol, respectively, and those calculated using the KAS method were 128.6, 182.5, 240.0, and 290.0 kJ/mol, respectively. Apparent activation energy decreased significantly with the increase in the sulfur content. This indicates that sulfide ores with high sulfur content show a stronger tendency for spontaneous combustion and are indispensable for the development of prevention and control measures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Wu, A.; Ai, C.; Li, X.; Miao, X. Inhibition of Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Ores by Thermopile Sulfide Oxidation. Miner. Eng. 2013, 49, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Yin, H.; Yang, F.; Hong, Y. Multi-Physics Modelling and Simulation on the Spontaneous Heating of Sulfide Ores. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 199, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somot, S.; Finch, J.A. Possible Role of Hydrogen Sulphide Gas in Self-Heating of Pyrrhotite-Rich Materials. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismayilov, R.T.; Karimov, V.M.; Zeynalova, S.A. Study of Spontaneous Combustion of the Main Industrial Types of Sulphide Ores of Sulphide- Polymetallic Deposits of Azerbaijan. J. Geol. Geogr. Geoecol. 2023, 32, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, F. Mining Safety Research in China: Understanding Safety Research Trends and Future Demands for Sustainable Mining Industry. Resour. Policy 2023, 83, 103632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pan, K.; Lang, Z.; Huang, R.; Sun, W.; Chu, H.; Ren, H.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Thermodynamics of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids for Inhibiting the Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Ore. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, S.; Yi, R.; Kang, Y. Simulation and Catastrophe Detection of Spontaneous Combustion Processes in Sulfide Ores. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, F.-Q.; Guo, Y.; Ren, X. Mapping Knowledge Domains for Mine Heat Hazard: A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends and Future Needs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 17076–17093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Liu, H.; Xiang, C.; Song, Y.; Lv, C. Visualization and Analysis of Mapping Knowledge Domain of Oxidation Studies of Sulfide Ores. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5809–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Liu, P.; Ping, P.; Chen, G. Evaluation of the Pyrophoric Risk of Sulfide Mineral in Storage. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2016, 44, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shang, Y.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Chen, X.F.; Niu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Study of Spontaneous Combustion Mechanism and Heat Stability of Sulfide Minerals Powder Based on Thermal Analysis. Powder Technol. 2017, 309, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wu, C.; Li, Z. Investigation of the Propensity of Sulfide Concentrates to Spontaneous Combustion in Storage. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2011, 24, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliyas, A.; Hawboldt, K.; Khan, F. Thermal Stability Investigation of Sulfide Minerals in DSC. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wu, C.; Cui, Y.; Lu, G. Apparent Activation Energy for Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Concentrates in Storage Yard. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliyas, A.; Hawboldt, K.; Khan, F. Kinetics and Safety Analysis of Sulfide Mineral Self-Heating: Part 1. Effect of Mineralogy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 106, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C. Thermal Roasting Behavior and Kinetics of African Cobalt-Rich Copper Sulfide Ore in Air Atmosphere. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 13469–13481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pan, K.; Xiang, C.; Ye, D.; Wang, H.; Gou, X. Mechanochemical Effect of Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Ore. Fuel 2022, 329, 125391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wu, C. Mechanism of Mechanical Activation for Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Minerals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yin, Z.; He, Y.; Huang, B. Mechanism of Mechanical Activation for Sulfide Ores. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, F.-Q.; Li, X. Effects of Water Immersion on the Pore Structure and Thermodynamic Properties of Sulfide Ores. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 7503–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wu, C.; Li, Z. Spontaneous Combustion Tendency of Fresh and Pre-Oxidized Sulfide Ores. J. Cent. South Univ. 2014, 21, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, K.; Xu, Y. Law of Characteristic Gases Production in the Low-Temperature Oxidation Stage of Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Ores. Fuel 2025, 380, 133195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, C.; Shi, Y. Locating Method of Fire Source for Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Ores. J. Cent. South Univ. T. 2011, 18, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, D.; Wu, C.; Wang, X. Infrared Thermography for Prediction of Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Ores. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gou, X.; Pan, K.; Huang, R.; Lang, Z.; Ye, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Thermodynamics and Inhibition Mechanism of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids for Inhibiting Spontaneous Combustion of Iron Sulfide. Fuel 2023, 338, 127335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, F.-Q.; Qiu, D.-Y.; Hong, Y. Inhibiting Effects of Inhibitors on Different Temperature Oxidation of Sulfide Ores. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2024, 196, 2460–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Ji, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship and Mechanism of Ionic Liquids Inhibiting Spontaneous Combustion of Ferrous Sulfide. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2025, 1244, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hong, Y.; Yang, F. A Risk Assessment Model of Spontaneous Combustion for Sulfide Ores Using Bayesian Network Combined with Grounded Theory. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 192, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wu, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of Spontaneous Combustion Tendency of Sulfide Ore Heap Based on Nonlinear Parameters. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 2431–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wu, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z. Oxidation Activity Evaluation of Sulfide Ores Based on Weight Gain Rate Fusion Under Different Oxidation Conditions. In Proceedings of the 11th International Mine Ventilation Congress, Xi’an, China, 14–20 September 2018; Chang, X., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 991–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Bouffard, S.C.; Senior, G.D. A New Method for Testing the Self-Heating Character of Sulphide Concentrates. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Pan, W.; Shen, X.; Cheng, S. Nonlinear Determination Method for Self-Heating Initiative Temperature of Sulfide Ores. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1709158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 16430-2018; Determination of the Minimum Ignition Temperature of Dust Layer. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Xi, Z.; Shan, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Analysis of Coal Spontaneous Combustion by Thermodynamic Methods. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2021, 193, 2305–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Liu, H.; Mu, J.; Lang, Z.; Wang, H.; Nie, R.; Kong, F. Thermodynamic Model and Kinetic Compensation Effect of Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfur Concentrates. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20618–20629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Xie, T. Oxidation Behavior and Kinetics Parameters of a Lean Coal at Low Temperature Based on Different Oxygen Concentrations. Minerals 2021, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, B. Investigation of Thermodynamic Parameters in the Pyrolysis Conversion of Biomass and Manure to Biochars Using Thermogravimetric Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan, R.; Zhang, D. Thermal Stability and Kinetics of Decomposition of Ammonium Nitrate in the Presence of Pyrite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wu, C. Prediction and Forecast of Spontaneous Combustion of Sulfide Minerals-Theory and Technology; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Turmanova, S.C.; Genieva, S.D.; Dimitrova, A.S.; Vlaev, L.T. Non-Isothermal Degradation Kinetics of Filled with Rise Husk Ash Polypropene Composites. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
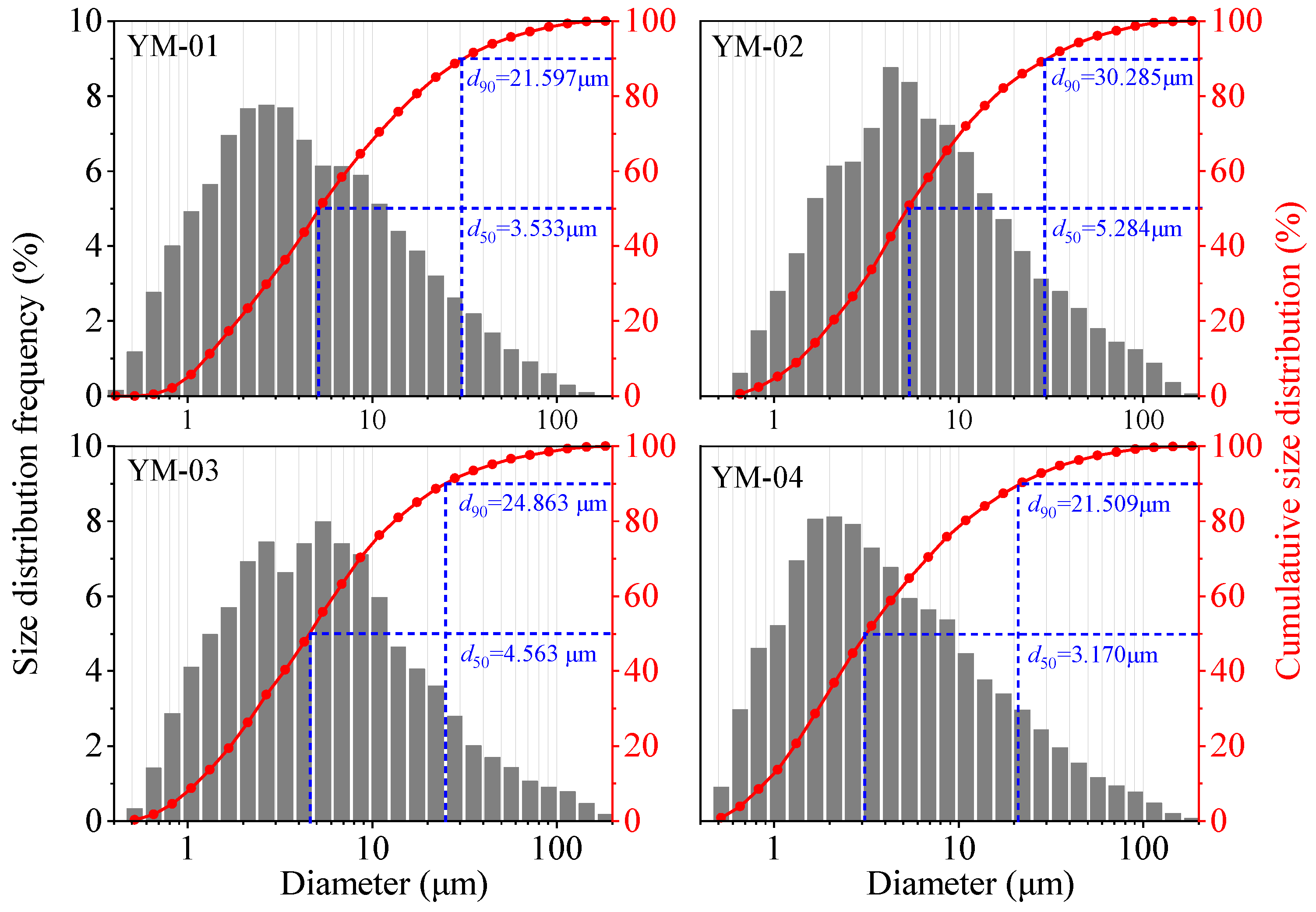
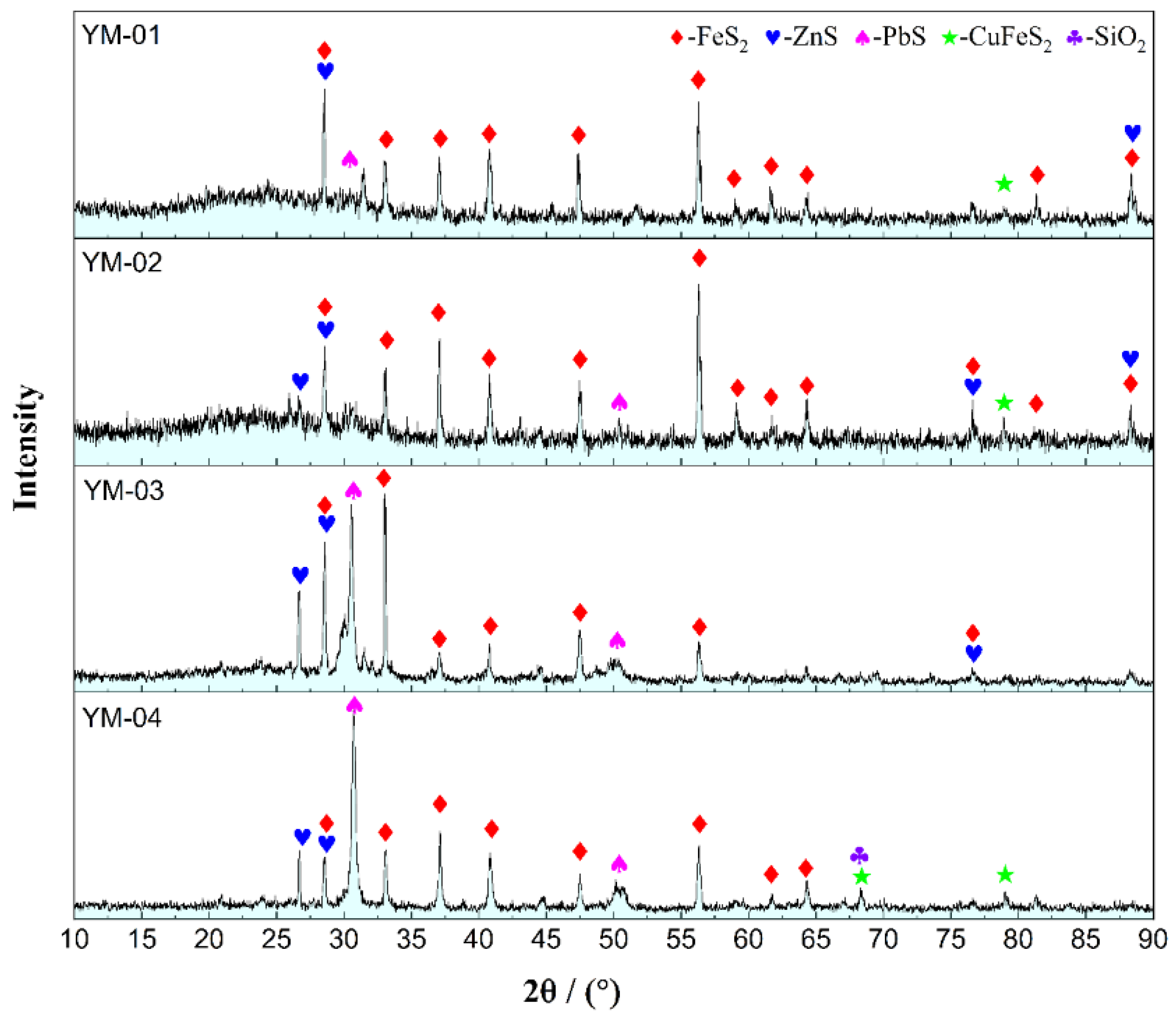
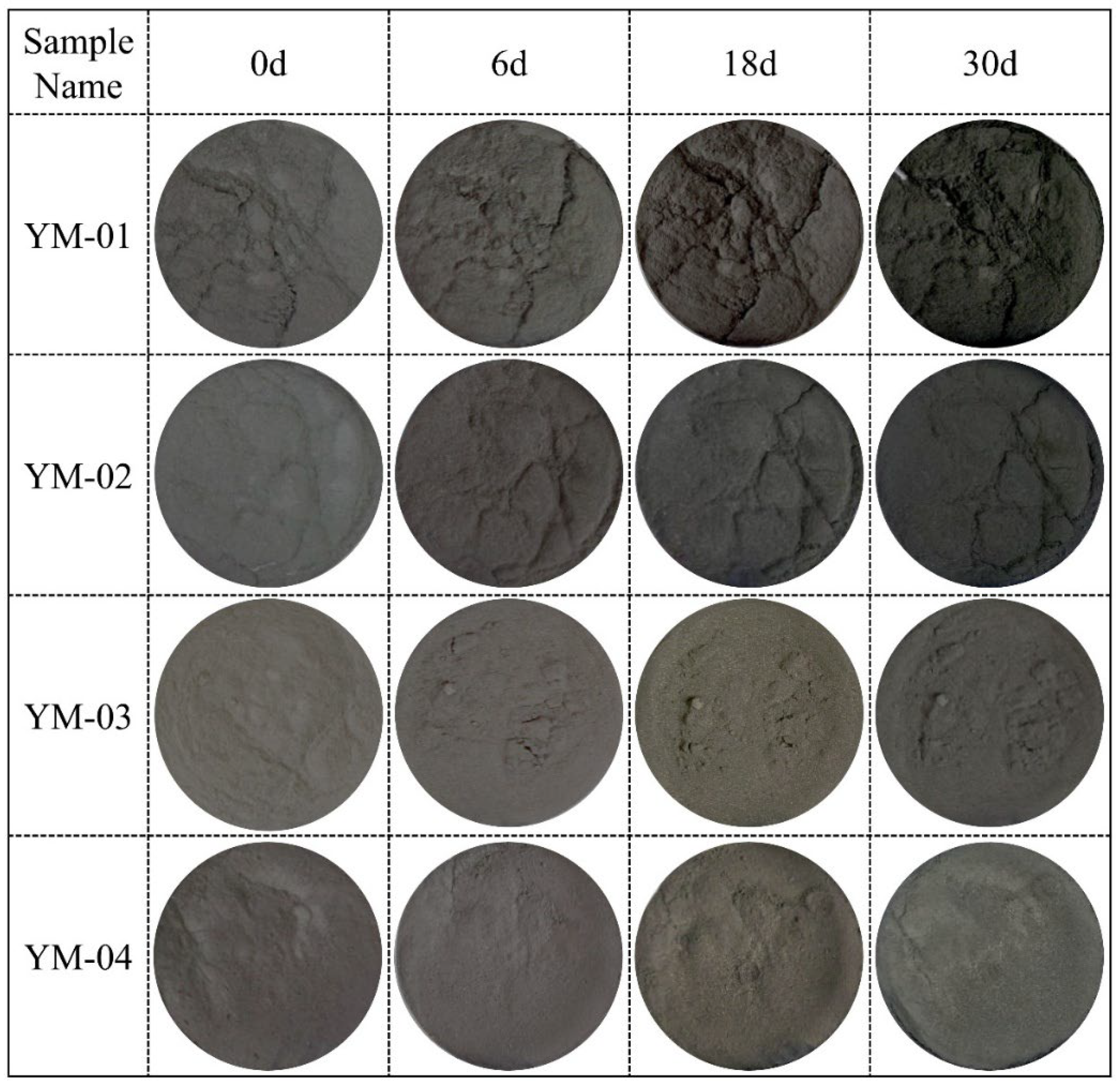




| Sample Name | Mass Fraction (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | Fe | Pb | Zn | Si | Mn | Al | Ca | Mg | Cu | |
| YM-01 | 40.29 | 10.61 | 0.998 | 0.459 | 4.54 | 7.17 | 3.24 | 2.22 | 0.581 | 0.012 |
| YM-02 | 34.56 | 36.59 | 0.579 | 1.27 | 1.68 | 2.01 | 1.14 | 1.37 | 0.461 | 0.01 |
| YM-03 | 24.81 | 25.72 | 1.81 | 3.2 | 2.07 | 1.47 | 0.526 | 4.78 | 1.47 | - |
| YM-04 | 14.2 | 22.25 | 6.2 | 16.28 | 3.55 | 3.34 | 3.07 | 10.15 | 2.93 | 0.015 |
| Compounds | YM-01 | YM-02 | YM-03 | YM-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeS2 | 36.63 | 32.59 | 24.81 | 18.25 |
| ZnS | 6.29 | 12.51 | 14.98 | 17.15 |
| PbS | 3.13 | 2.21 | 3.87 | 4.09 |
| CuFeS2 | 0.56 | 0.32 | - | 0.40 |
| Fe2O3 | 5.26 | 11.63 | 9.68 | 7.81 |
| SiO2 | 9.71 | 3.58 | 4.44 | 7.58 |
| Sample Name | Initial Temperature T1/°C | Final Temperature T2/°C | Mass Loss in Stage II/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 K/min | 10 K/min | 15 K/min | 20 K/min | Average Value | |||
| YM-01 | 402.5 | 610.3 | 27.3 | 26.1 | 23.6 | 20.8 | 24.5 |
| YM-02 | 402.7 | 591.7 | 27.0 | 25.2 | 23.2 | 21.5 | 24.2 |
| YM-03 | 401.6 | 570.4 | 20.2 | 21.6 | 20.4 | 19.0 | 20.3 |
| YM-04 | 401.9 | 558.2 | 16.7 | 15.2 | 14.8 | 13.4 | 15.0 |
| Conversion α | Apparent Activation Energy E (kJ/mol) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWO Method | KAS Method | |||||||
| YM-01 | YM-02 | YM-03 | YM-04 | YM-01 | YM-02 | YM-03 | YM-04 | |
| 0.1 | 161.0 | 190.1 | 217.9 | 201.4 | 157.4 | 188.0 | 217.4 | 199.9 |
| 0.2 | 123.6 | 200.9 | 202.5 | 210.6 | 117.9 | 199.0 | 200.9 | 209.3 |
| 0.3 | 97.0 | 124.5 | 181.8 | 223.9 | 89.6 | 118.3 | 178.9 | 223.2 |
| 0.4 | 125.7 | 115.9 | 178.9 | 224.1 | 119.4 | 109.1 | 175.6 | 223.2 |
| 0.5 | 135.1 | 139.5 | 206.5 | 231.3 | 129.0 | 133.7 | 204.3 | 230.6 |
| 0.6 | 125.5 | 159.0 | 278.5 | 289.5 | 118.7 | 154.1 | 279.9 | 291.7 |
| 0.7 | 146.0 | 239.7 | 299.1 | 334.2 | 140.0 | 238.7 | 301.4 | 338.5 |
| 0.8 | 149.8 | 255.4 | 287.8 | 335.3 | 143.8 | 255.0 | 289.3 | 339.4 |
| 0.9 | 147.7 | 247.6 | 309.3 | 539.3 | 141.2 | 246.6 | 311.8 | 553.9 |
| Average | 134.6 | 185.8 | 240.3 | 287.7 | 128.6 | 182.5 | 240.0 | 290.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Xu, B.; Feng, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Experimental Investigation on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Sulfide Ores with Different Sulfur Content. Minerals 2025, 15, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080880
Huang Q, Xu B, Feng J, Lu Y, Wang X, Liu Q. Experimental Investigation on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Sulfide Ores with Different Sulfur Content. Minerals. 2025; 15(8):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080880
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qisong, Bo Xu, Junjun Feng, Yugen Lu, Xiangyu Wang, and Qinglang Liu. 2025. "Experimental Investigation on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Sulfide Ores with Different Sulfur Content" Minerals 15, no. 8: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080880
APA StyleHuang, Q., Xu, B., Feng, J., Lu, Y., Wang, X., & Liu, Q. (2025). Experimental Investigation on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Sulfide Ores with Different Sulfur Content. Minerals, 15(8), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080880





