Surface Properties and Beneficiation of Quartz with Flotation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Surface Properties of Quartz
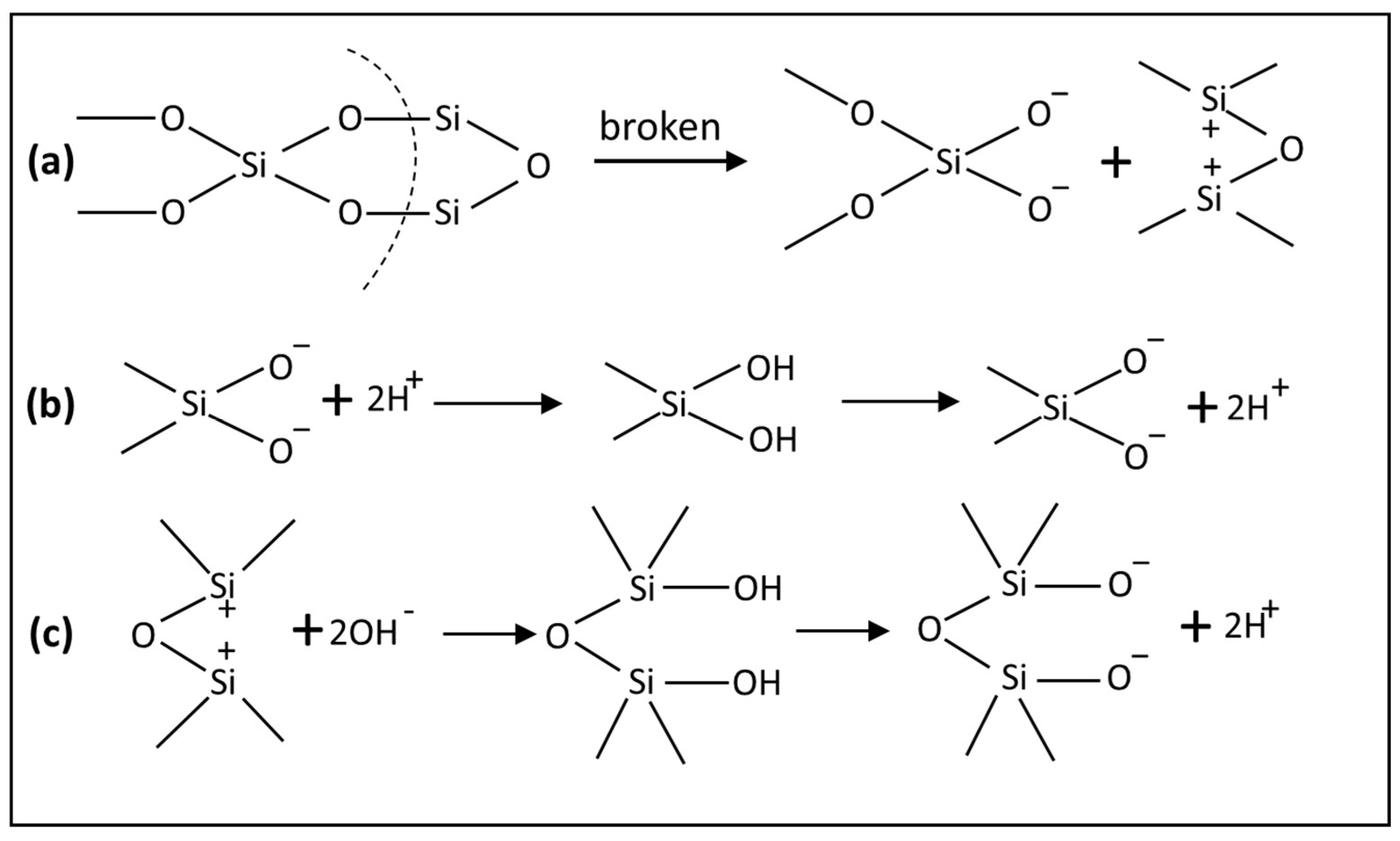
2.1. Surface Roughness and Heterogeneity of Quartz
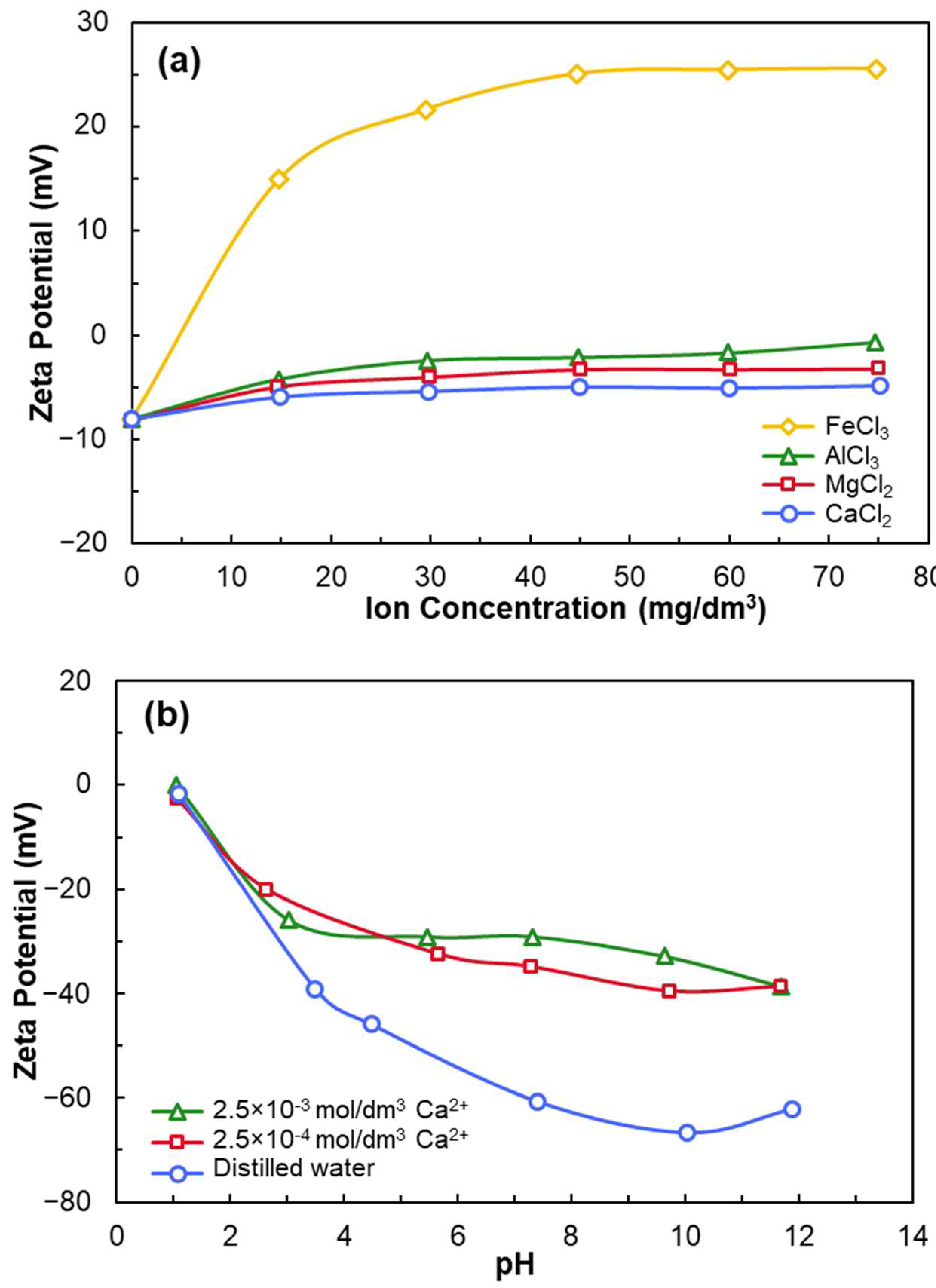
2.2. Electrochemical Properties
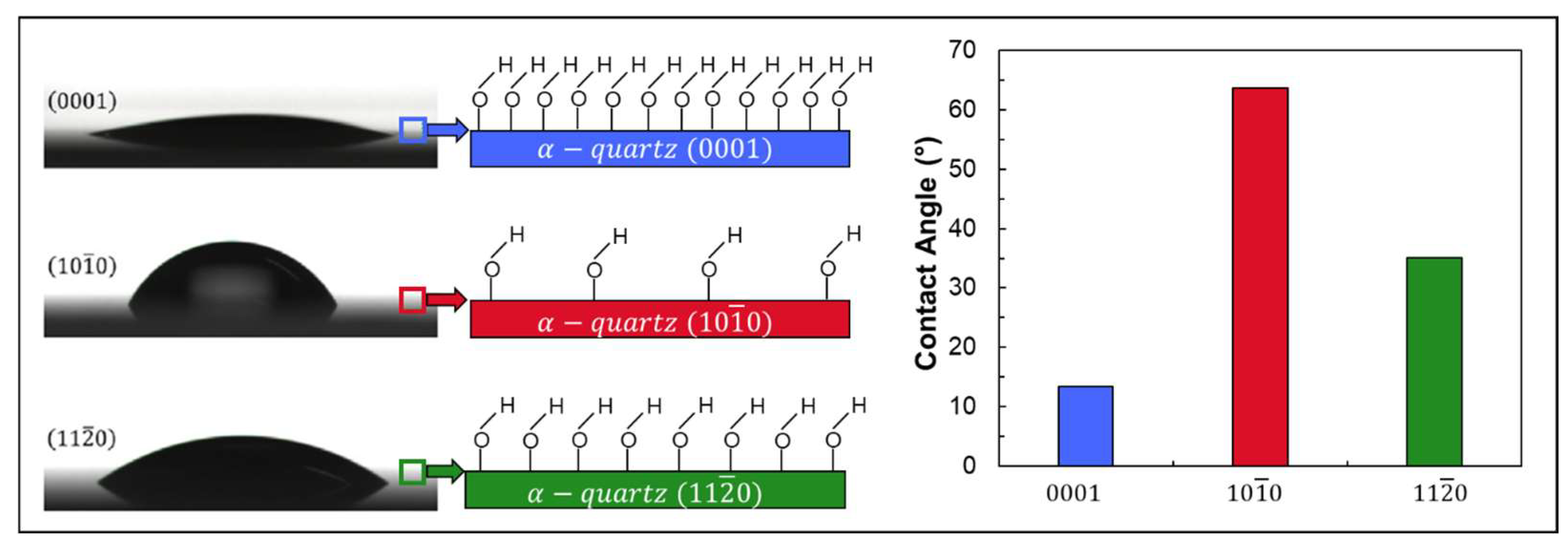
2.3. Wettability
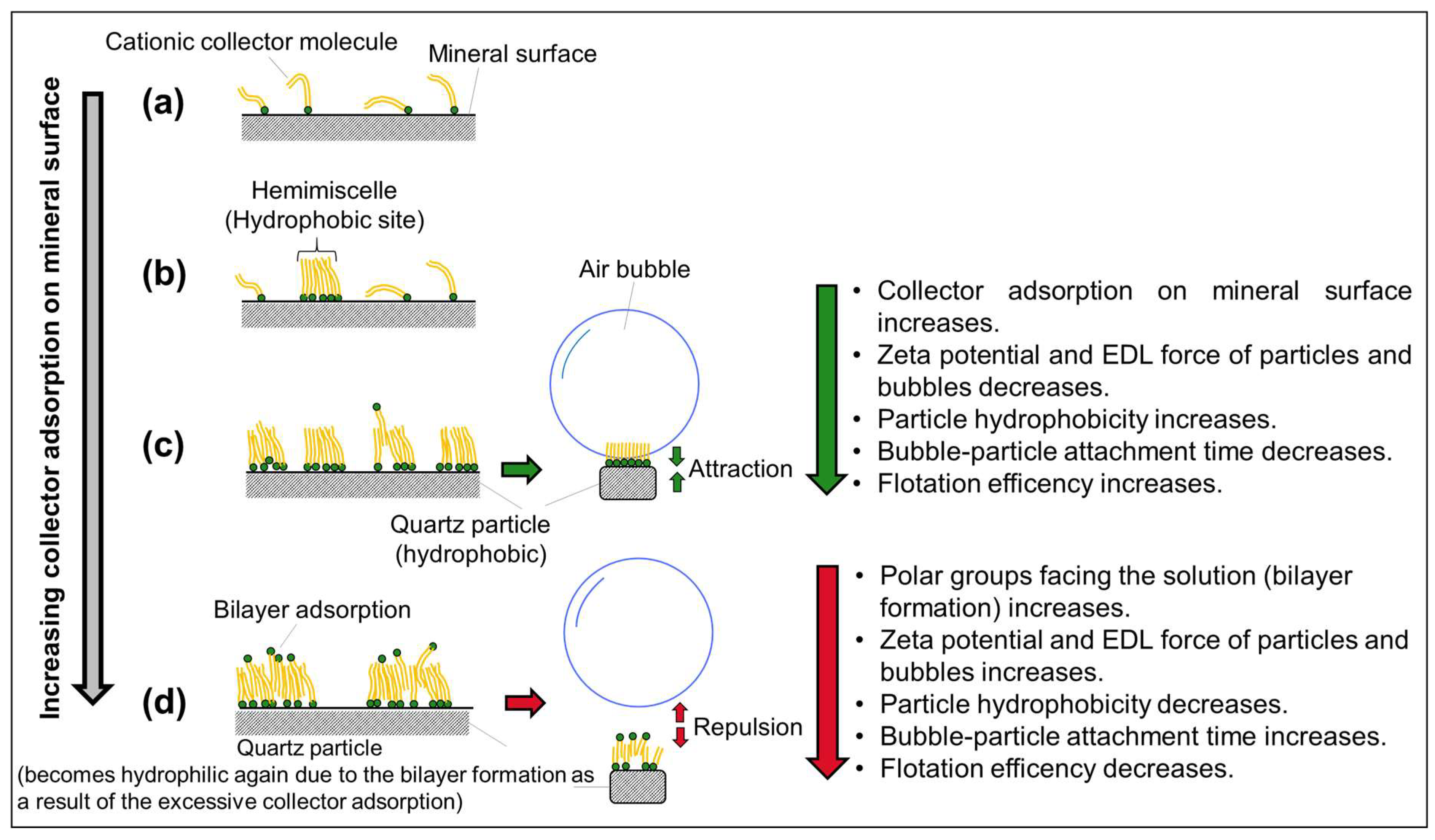
2.4. Bubble–Particle Interactions
3. Mineral Processing Technology
3.1. Pre-Concentration of Quartz with Physical Beneficiation Techniques
3.2. Flotation of Quartz
3.2.1. Cationic Flotation of Quartz
3.2.2. Anionic Flotation of Quartz
3.2.3. Selectivity in Quartz Flotation
3.3. High-Purity Quartz Processing Technology
3.4. Present Challenges, Recent Advancements, and Future Perspectives in Quartz Flotation
4. Conclusions
- The purity of quartz determines its industrial use and economic value.
- Physical separation methods (desliming, magnetic separation) are partially effective; flotation is usually used for final beneficiation.
- Grinding breaks Si–O bonds, causing quartz surfaces to become negatively charged at most pH levels (IEP ≈ pH 2).
- Depending on measurement methods, a hydrophilic surface with a contact angle of 10–45° is obtained.
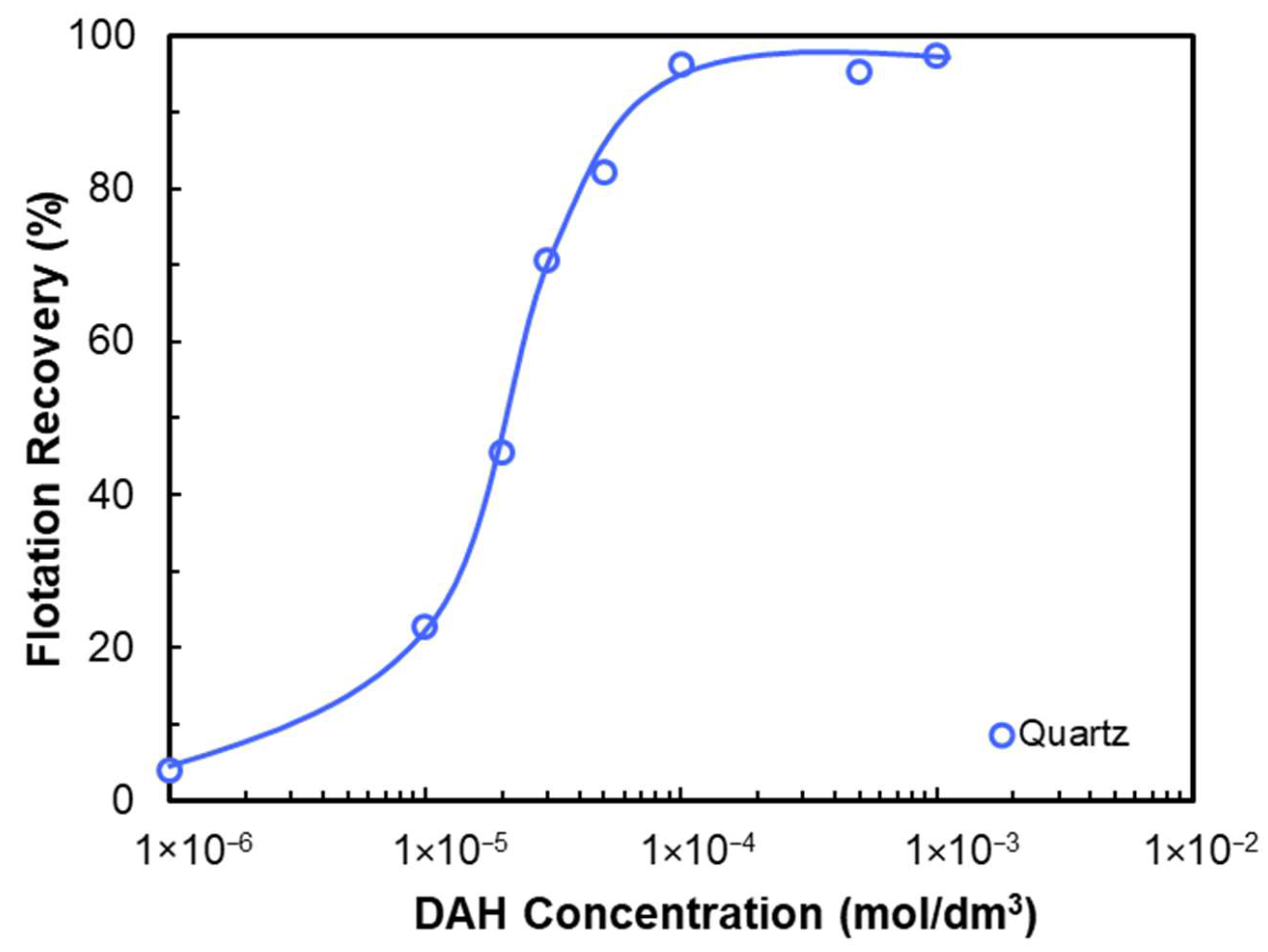
- Reduced attachment time (via increased hydrophobicity via collector adsorption) increases flotation recovery.
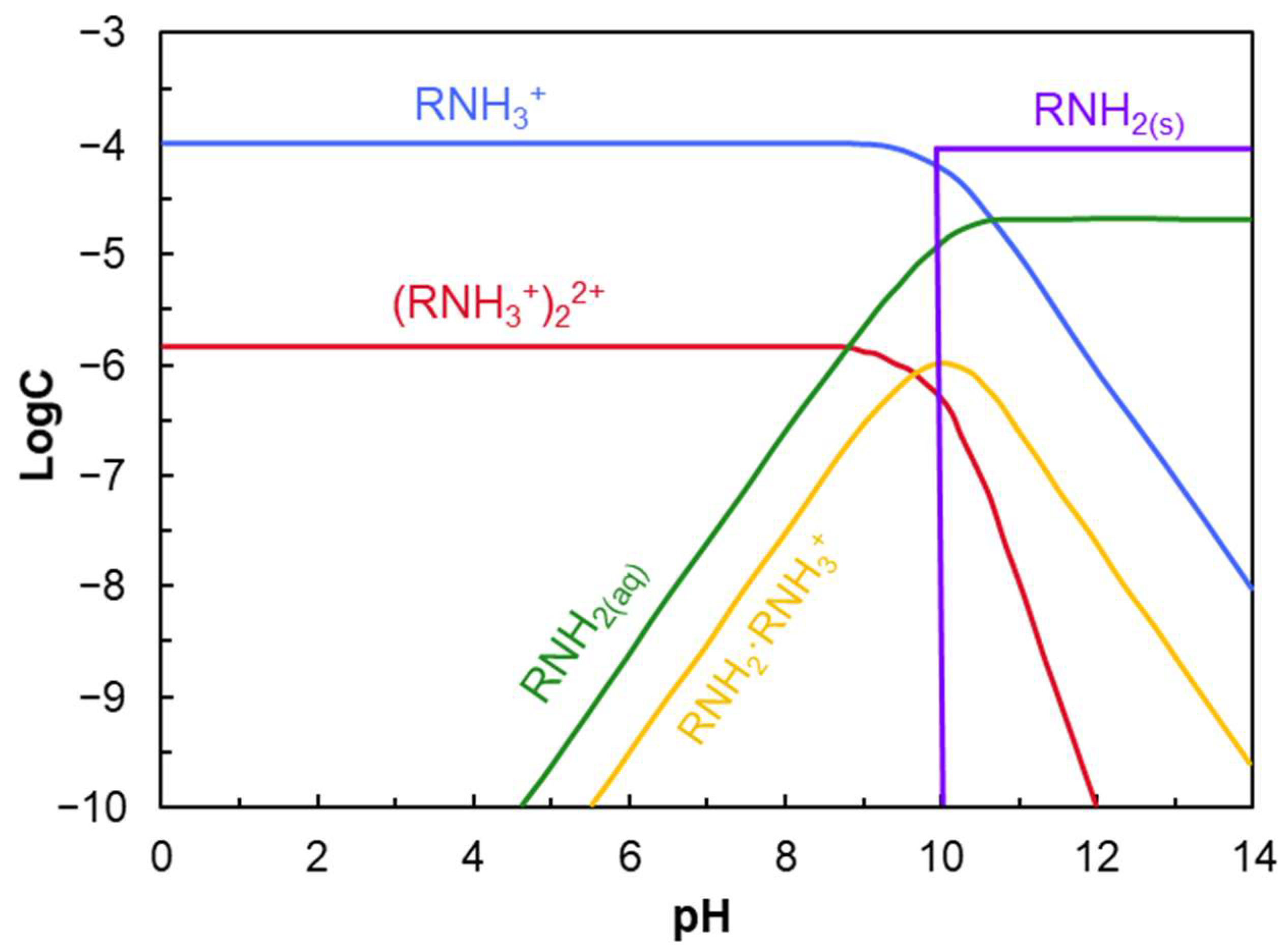
- Cationic amine collectors (C12–C18) adsorb onto quartz surfaces above IEP via physical adsorption and hemimicelle formation.
- At high concentrations, collector bilayers may form, reducing efficiency.
- Amines precipitate (as RNH2(s)) above pH 10 and inhibit adsorption.
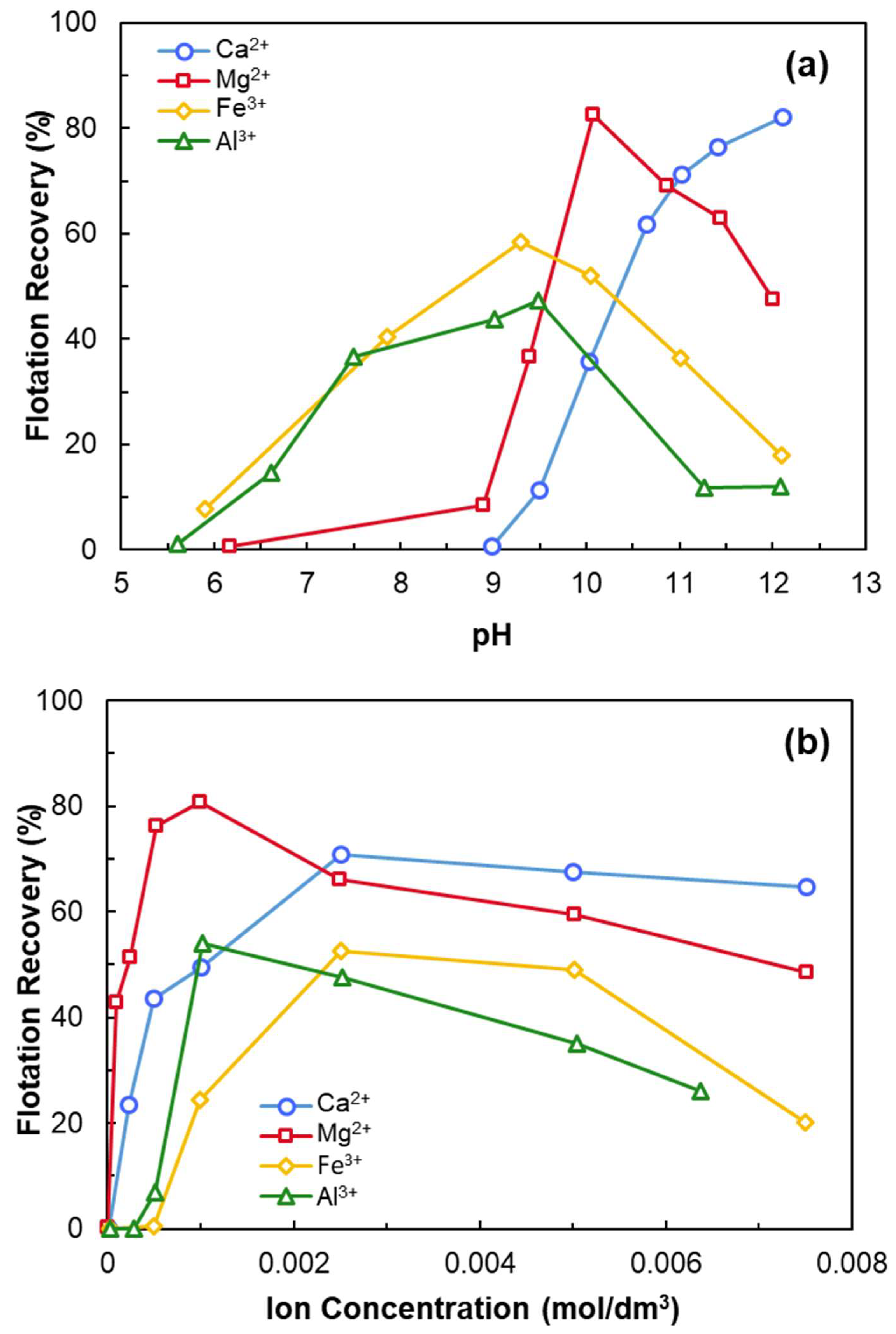
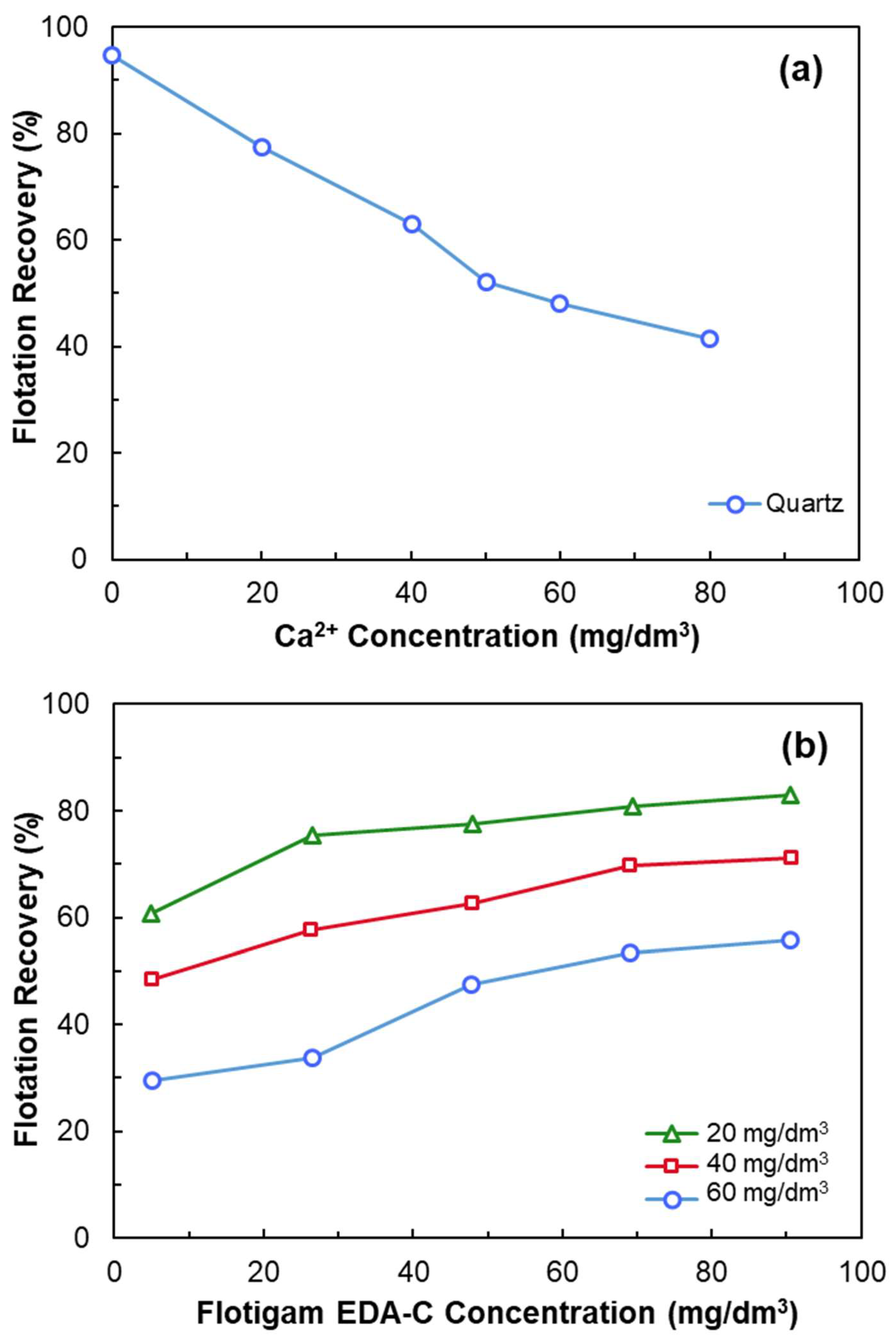
- Anionic collectors (e.g., NaOL) are ineffective on negatively charged quartz unless activated with multivalent cations such as Ca2+.
- At a certain pH, CaOH+ forms chemisorption sites through surface dehydration and oxygen binding.
- Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and starch selectively depress magnesite and hematite in quartz flotation.
- It is effective when quartz is the major component; impurities are floated while quartz is depressed.
- Fluoride ions, cationic polymers, and starch are common quartz depressants.
- pH control is critical to prevent quartz activation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, R.L.; Morse, J.G.; Morse, K.W. Main Group Elements. In Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, P.; Li, P.; Ding, J.; Sun, C.; Zhai, C.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Z.; Dang, W. Quartz types, formation mechanism, and its effect on shale oil and gas enrichment: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2025, 261, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, D.; Ma, C.; Wei, F.; Zhang, H. A New Insight into the Influence of Fluid Inclusions in High-Purity Quartz Sand on the Bubble Defects in Quartz Glass: A Case Study from Vein Quartz in the Dabie Mountain. Minerals 2024, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götze, J.; Pan, Y.; Müller, A. Mineralogy and mineral chemistry of quartz: A review. Mineral. Mag. 2021, 85, 639–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapiaggi, M.; Pagliari, L.; Pavese, A.; Sciascia, L.; Merli, M.; Francescon, F. The formation of silica high temperature polymorphs from quartz: Influence of grain size and mineralising agents. J. Eur. Ceram. 2015, 35, 4547–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Y. Resource, characteristic, purification and application of quartz: A review. Miner. Eng. 2022, 183, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddiaf, S.; Chihi, S.; Leghrieb, Y. The determination of some crystallographic parameters of quartz, in the sand dunes of Ouargla, Algeria. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 106, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungoren, C.; Ozdemir, O.; Wang, X.; Ozkan, S.G.; Miller, J.D. Effect of ultrasound on bubble-particle interaction in quartz-amine flotation system. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 52, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Wang, Q.; Ku, J.; Shang, H.; Shen, Z. Purification Technologies for High-Purity Quartz: From Mineralogy to Applications. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, S. Industrial Sand and Sandstone. In Industrial Minerals and Rocks: Commodities, Markets, and Uses; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Yi, Y.; Tan, Q.; Liu, L. Characteristics of high-purity quartz raw materials for crucibles and exploration of key purification technologies. Miner. Eng. 2025, 231, 109446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, G. The Influence of Grinding Media on the Grinding Effect of Granite Pegmatite-Type Quartz. Minerals 2025, 15, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, X.; Yu, B.; Sha, J.; Gao, R.; Qi, M.; Huang, Y.; Peng, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; et al. Flotation separation of quartz and feldspar under weak alkaline conditions using amine ether as a novel collector. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 315, 121873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Pan, B.; Xia, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, L.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Diao, Z. Purification of Vein Quartz Using a New Fluorine-Free Flotation: A Case from Southern Anhui Province, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, C.; Ni, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X. Research Status and Challenges of High-Purity Quartz Processing Technology from a Mineralogical Perspective in China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Yang, X.; Hou, Z. Preparation of High-Purity Quartz Sand by Vein Quartz Purification and Characteristics: A Case Study of Pakistan Vein Quartz. Minerals 2010, 14, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaram, V. Recent developments in analytical techniques for characterization of ultra pure materials—An overview. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2005, 28, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatalis, K.I.; Charalambides, G.; Benetis, N.P. Market of High Purity Quartz Innovative Applications. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 24, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippin, R.B.; Huiatt, H.L.; Butts, D. Silicate mineral and potash flotation. In Advances in Flotation Technology; Parekh, B.K., Miller, J.D., Eds.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Wei, K.; Ma, W. Effect of quartz crystal structure transformations on the removal of iron impurities. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 204, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatalis, K.I.; Charalampides, G.; Platias, S.; Benetis, N.P. Market Developments and Industrial Innovative Applications of High Purity Quartz Refines. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 14, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Ren, B. A Review on Removal of Iron Impurities from Quartz Mineral. Minerals 2023, 13, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Xie, J.; Duan, T.; Gao, M.; Wu, X.; He, H. Application of mixed collectors on quartz-feldspar by fluorine-free flotation separation and their interaction mechanism: A review. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2021, 57, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, A.; Mahmoud, M.; Arif, M.; Aljawad, M.S.; Kamal, M.S. Influence of Surface Cleaning on the Wettability of Quartz/Oil/Brine Systems. Energ. Fuel. 2023, 37, 12744–12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervo-Hansen, S.; Heyda, J.; Lund, M.; Matubayasi, N. Anion-cation contrast of small molecule solvation in salt solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 3238–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zhu, D.; Pan, J.; Li, S.; Yang, C.; Guo, Z. Advanced Processing Techniques and Impurity Management for High-Purity Quartz in Diverse Industrial Applications. Minerals 2024, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, P.T.L.; Smith, L.K. The effect of stirring speed and induction time on flotation. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, P.T.L.; Hao, F.P.; Smith, L.K.; Chau, T.T.; Bruckard, W.J. The effect of particle shape and hydrophobicity in flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 93, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: London, UK, 1992; p. 291. [Google Scholar]
- Derjaguin, B.; Landau, L. Theory of the stability of strongly charged lyophobic sols an of the adhesion of strongly charged particles in solutions of electrolytes. Acta Phys. Chim. 1941, 14, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1948; p. 218. [Google Scholar]
- Drelich, J.; Wang, Y.U. Charge heterogeneity of surfaces: Mapping and effects on surface forces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashley, R.M. Hydration forces between mica surfaces in aqueous electrolyte solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1981, 80, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Forces between surfaces in liquids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1982, 16, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjaguin, B.V. Structural and thermodynamic peculiarities of the boundary layers of liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 1980, 52, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churaev, N.V.; Deryagin, B.V. Inclusion of structural forces in the theory of stability of colloids and films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1985, 103, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.H.; Mao, L.Q. Application of extended DLVO theory. 4. Derivation of flotation rate equation from first principles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 181, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.H.; Ravishankar, S.A. Long-Range Hydrophobic Forces between Mica Surfaces in Dodecylammonium Chloride Solutions in the Presence of Dodecanol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 179, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, O.; Celik, M.S.; Drelich, J.W. Flotation of methylated roughened glass particles and analysis of particle–bubble energy barrier. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Miller, J.D. Dodecyl amine adsorption at different interfaces during bubble attachment/detachment at a silica surface. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2018, 54, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, B.; Guven, O.; Ozdemir, O.; Çelik, M.S. Analysis of flotation and aggregation characteristics of muscovite particles through the extended DLVO theory. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2022, 58, 151789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijk, A.; van Blaaderen, A.; Imhof, A. Synthesis of Monodisperse, Rodlike Silica Colloids with Tunable Aspect Ratio. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2346–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Flores, A.; Bradford, S.A.; Hwang, G.; Choi, S.; Tong, M.; Kim, H. Shape and orientation of bare silica particles influence their deposition under intermediate ionic strength: A study with QCM–D and DLVO theory. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 599, 124921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Flores, A.; Bradford, S.A.; Hwang, G.; Heyes, G.W.; Kim, H. Particle–bubble interaction energies for particles with physical and chemical heterogeneities. Miner. Eng. 2020, 155, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo, E.; Moreno, E.; Cabrera, I.; Cordoba, A.; Sala, S.; Veciana, J.; Ventosa, N. Liposomes and other vesicular systems: Structural characteristics, methods of preparation, and use in nanomedicine. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011, 104, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W.; Pradip. Zeta potentials in the flotation of oxide and silicate minerals. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 114–115, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Basics of Electrical Double Layer; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 7–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi-Jam, S.; Greenwood, R.W.; Waters, K.E. An overview of the temperature dependence of the zeta potential of aqueous suspensions. Results Eng. 2025, 27, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno-Tokunaga, A.; Pérez-Garibay, R.; Martínez-Carrillo, D. Zeta potential of air bubbles conditioned with typical froth flotation reagents. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 140, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdy, A.M.; Mirnezami, M.; Finch, J.A. Zeta potential of air bubbles in presence of frothers. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2008, 89, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X. Effect of secondary amino on the adsorption of N-Dodecylethylenediamine on quartz surface: A molecular dynamics study. Powder Technol. 2019, 351, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, A.V.; Zhang, M.; Wei, P.; Long, Q. Effects of alkyl ether amine and calcium ions on fine quartz flotation and its guidance for upgrading vanadium from stone coal. Powder Technol. 2018, 338, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-L.; Deng, H.-B.; Chen, C. Flotation separation of andalusite from quartz using sodium petroleum sulfonate as collector. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjargal, K.; Guven, O.; Ozdemir, O.; Boylu, F.; Pural, Y.E.; Celik, M.S. Correlation of Flotation Recoveries and Bubble–Particle Attachment Time for Dodecyl Ammonium Hydrochloride/Frother/Quartz Flotation System. Minerals 2023, 13, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyadhar, A.; Kumari, N.; Bhagat, R.P. Adsorption Mechanism of Mixed Cationic/Anionic Collectors in Quartz–Hematite Flotation System. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2014, 35, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, C. Collecting Agent–Mineral Interactions in the Reverse Flotation of Iron Ore: A Brief Review. Minerals 2020, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, B.; Ye, J.; Mao, S.; Li, X. Flotation separation of quartz from collophane using an amine collector and its adsorption mechanisms. Powder Technol. 2017, 318, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.W.; Akhtar, S. Cationic Flotation of Oxides and Silicates. In Flotation; Fuerstenau, M.C., Ed.; American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 1, pp. 87–116. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, H.; Li, D.; Xu, X. Wettability Alteration of the Quartz Surface in the Presence of Metal Cations. Energ. Fuel. 2013, 27, 7354–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, F.; Chi, R. Effects of Metal Ions on the Flotation of Apatite, Dolomite and Quartz. Minerals 2018, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungoren, C.; Kursun Unver, I.; Ozdemir, O. Introduction to mineral research. In Advances in Minerals Research; Ikhmayies, S.J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, T.T.; Bruckard, W.J.; Koh, P.T.L.; Nguyen, A.V. A review of factors that affect contact angle and implications for flotation practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 150, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczuk, P.B. Flotation and hydrophobicity of quartz in the presence of hexylamine. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 140, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P.B.; Drzymala, J. Contact Angle of Bubble with an Immersed-in-Water Particle of Different Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 4207–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, J. Mineral Processing, Foundations of Theory and Practice of Minerallurgy; Wroclaw University of Technology: Wroclaw, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Rao, S.; Liang, Y.; Lu, H. Crystal face dependent wettability of alpha-quartz: Elucidation by time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry techniques combined with molecular dynamics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, A.; Gholami, H.; Ozkan, S.G.; Niedoba, T.; Surowiak, A. Effect of Power Ultrasound on Wettability and Collector-Less Floatability of Chalcopyrite, Pyrite and Quartz. Minerals 2021, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Q. Exploring the behavior of an alcoholic amine grinding aid in grinding-flotation system: Separation of quartz from magnesite. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 411, 125783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Feng, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Bayoundoula, J. Selective flotation separation of spodumene and quartz with carboxylated chitosan as depressant. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpilowski, K. Influence of the ambient temperature on water and diiodomethane contact angle with quartz surface. Ann. Univ. Marie Curie Sklodowska 2015, 70, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wan, J.; Li, W.; Song, Y. Water contact angles on quartz surfaces under supercritical CO2 sequestration conditions: Experimental and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 42, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, W.; Mei, G.; Yu, M.; Yang, S.; He, Z. Flotation separation of quartz from phosphorite using an imidazole ionic liquid collector and its adsorption mechanism. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2022, 58, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, W. Adsorption behavior of mixed cationic/anionic surfactants and their depression mechanism on the flotation of quartz. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawala, J.; Karaguzel, C.; Wiertel, A.; Sahbaz, O.; Malysa, K. Kinetics of the bubble attachment and quartz flotation in mixed solutions of cationic and non-ionic surface-active substances. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 523, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, O.; Karaguzel, C.; Nguyen, A.V.; Celik, M.S.; Miller, J.D. Contact angle and bubble attachment studies in the flotation of trona and other soluble carbonate salts. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, B.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, S.; Shen, Y. Parameters of Collision and Adhesion Process Between a Rising Bubble and Quartz in Long-Chain Amine Solution and Their Correlation with Flotation. Minerals 2024, 14, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, S.G.; Baktarhan, Y.; Gungoren, C.; Demir, I. Effect of conventional and microwave thermal treatments on floatability of low- and high-rank lignites. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 42, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albijanic, B.; Amini, E.; Wightman, E.; Ozdemir, O.; Nguyen, A.V.; Bradshaw, D.J. A relationship between the bubble–particle attachment time and the mineralogy of a copper–sulphide ore. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Qu, J.; Tao, X.; He, H. Exploration on the mechanism of enhancing low-rank coal flotation with cationic surfactant in the presence of oily collector. Fuel 2018, 227, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, L.; Gao, H.; Zhao, L. The relationship among contact angle, induction time and flotation recovery of coal. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2018, 41, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.; Yordan, J.L. Induction Time Measurements for the Quartz-Amine Flotation System. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 141, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albijanic, B.; Ozdemir, O.; Nguyen, A.V.; Bradshaw, D. A review of induction and attachment times of wetting thin films between air bubbles and particles and its relevance in the separation of particles by flotation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, R.H.; Luttrell, G.H. The Effect of Bubble Size on Fine Particle Flotation. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1989, 5, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albijanic, B.; Ozdemir, O.; Hampton, M.A.; Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, A.V.; Bradshaw, D. Fundamental aspects of bubble–particle attachment mechanism in flotation separation. Miner. Eng. 2014, 65, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malayoglu, U.; Ozkan, S.G. Effects of Ultrasound on Desliming Prior to Feldspar Flotation. Minerals 2019, 9, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, S.; Gou, H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, L. Efficient recovery of feldspar, quartz, and kaolin from weathered granite. Minerals 2024, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Selim, A.Q.; Hagrass, A.A. Gravity Separation of Silica Sands for Value Addition. Part. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banza, A.N.; Quindt, J.; Gock, E. Improvement of the quartz sand processing at Hohenbocka. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 79, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, C.; Langlois, R.; Kökkılıç, O.; Zhou, M.; Williams, H.; Awais, M.; Rowson, N.A.; Waters, K.E. A design of experiments investigation into the processing of fine low specific gravity minerals using a laboratory Knelson Concentrator. Miner. Eng. 2019, 135, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroznikova, L.; Klutke, C.; McKnight, S.; Hall, S. The use of low-toxic heavy suspensions in mineral sands evaluation and zircon fractionation. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2008, 108, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Sun, N.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, W. Systematic review of feldspar beneficiation and its comprehensive application. Miner. Eng. 2018, 128, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nota, D.J.G.; Bakker, A.M.G. Identification of soil minerals using optical characteristics and specific gravity separation. Meded. Landbouwhogesch. Wagening. Ned. 1960, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, L.C.; André, F.P.; Miceli, H.; Neumann, R.; Tavares, L.M. Manufactured Feldspar-quartz Sand for Glass Industry from Gneiss Quarry Rock Fines Using Dry Rare-earth Magnetic Separation. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2019, 40, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Pan, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, P. Pre-concentration of quartz from sea sand through superconducting high gradient magnetic separation technology. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 58, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, L. Effect of sodium hexametaphosphate on the separation of fine quartz-magnetite by magnetic separation: A study of dispersion properties and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, S.K.; Dwari, R.K. Separation of the coal-quartz mixture using tribo-electrostatic separator: Effect of surface pretreatment. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 3361–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Z. Triboelectric characteristics and separation of magnesite and quartz. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2024, 124, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretti, R.; Serci, A.; Zucca, A. Electrostatic K-Feldspar/Na-Feldspar and Feldspar/Quartz Separation: Influence of Feldspar Composition. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2012, 33, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, O.; Ozdemir, O.; Karaagaclioglu, I.E.; Çelik, M.S. Surface morphologies and floatability of sand-blasted quartz particles. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaran, P.; Zhang, L.; Healy, T.W.; Ducker, W.; Herrera-Urbina, R.; Fuerstenau, M.C. Adsorption of surfactants and its influence on the hydrodynamics of flotation. In Froth Flotation A Century of Innovation; Fuerstenau, M.C., Yoon, R.-H., Eds.; SME: Littleton, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 179–225. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, B.A. Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology, An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral Recovery, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 488. [Google Scholar]
- Somasundaran, P.; Lou, A. Oxide mineral flotation fundamentals. In Advances in Flotation Technology; Parekh, B., Miller, D., Eds.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, Inc.: Littleton, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zilin, D. Cationic Collector. In The ECPH Encyclopedia of Mining and Metallurgy; Kuangdi, X., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 225–226. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.H.; Forssberg, K.S.E. Mixed collector systems in flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 51, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Q.; Wen, Q.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the biological flotation reagent obtained from Paenibacillus amylolyticus in magnetite and phlogopite flotation system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 610, 125930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohry, A.; Dehghan, R.; Mohammadi-Manesh, H.; Filho, L.d.S.L.; Chelgani, S.C. Effect of Ether Mono Amine Collector on the Cationic Flotation of Micaceous Minerals—A Comparative Study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplan, F.F.; Fuerstenau, D.W. Principles of nonmetallic mineral flotation. In Froth Flotation; The American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1962; Volume 50, pp. 170–214. [Google Scholar]
- Fuerstenau, D.W.; Colic, M. Self-association and reverse hemimicelle formation at solid–water interfaces in dilute surfactant solutions. Colloids Surf. A 1999, 146, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Phenomena Associated with the Adsorption of Ionic Surfactants at Solid–Water Interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 256, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.S.; Guven, O.; Karaağaçlıoğlu, İ.E.; Ozdemir, O. Does hemimicelle concentration (HMC) coincide with critical aggregation concentration (CAC) in flotation? Miner. Eng. 2024, 215, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyadhar, A.; Rao, K.H.; Chernyshova, I.V.; Forssberg, K.S.E.; Pradip. Mechanisms of Amine–Quartz Interaction in the Absence and Presence of Alcohols Studied by Spectroscopic Methods. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 256, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novich, B.E.; Ring, T.A. A Predictive Model for the Alkylamine-Quartz Flotation System. Langmuir 1985, 1, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.W.; Scott, J.L. Mechanisms of Dodecylamine Flotation of Quartz. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1990, 7, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Evans, G.; Xie, G.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, C.; Ge, L. Removal of fine quartz from coal-series kaolin by flotation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, M.; Sahbaz, O.; Cınar, F.; Kelebek, S.; Oteyaka, B. Effect of Jameson cell operating variables and design characteristics on quartz-dodecylamine flotation system. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahbaz, O.; Ucar, A.; Oteyaka, B. Velocity gradient and maximum floatable particle size in the Jameson cell. Miner. Eng. 2013, 41, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Fan, J.-C.; Fan, M.-Q. Quantum chemical calculations and molecular dynamics simulations of amine collector adsorption on quartz (0 0 1) surface in the aqueous solution. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 134, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungoren, C.; Ozdemir, O.; Ozkan, S.G. Effects of temperature during ultrasonic conditioning in quartz-amine flotation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2017, 53, 687–698. Available online: https://www.journalssystem.com/ppmp/Effects-of-temperature-during-ultrasonic-conditioning-in-quartz-amine-flotation,66975,0,2.html (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Bleier, A.; Goddard, E.D.; Kulkarni, R.D. The structural effects of amine collectors on the flotation of quartz. In Flotation; Fuerstenau, M.C., Ed.; American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 117–144. [Google Scholar]
- Glembotski, V.A.; Klassen, V.I.; Plaksin, I.N. Flotation; Primary Sources: New York, NY, USA, 1963; p. 620. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhaei, F.; Irannajad, M. Reagents types in flotation of iron oxide minerals: A review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2017, 39, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, M.C. Anionic flotation of oxides and silicates. In Flotation; Fuerstenau, M.C., Ed.; American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 1, pp. 148–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Yin, W.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Chen, K.; Yang, B. The role of surface roughness in the wettability and floatability of quartz particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Pang, T.; Han, R.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z. Insight into anionic and cationic flotation discrepancy of quartz with altered surface roughness by acid etching. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 381, 121816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xing, H. Mechanism of Quartz Flotation Enhanced by Calcium Ion. JOM 2025, 77, 2656–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wen, S.; Wu, D.; Bai, S.; Liu, D. Determination of the concentrations of calcium and magnesium released from fluid inclusions of sphalerite and quartz. Miner. Eng. 2013, 45, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-g.; Yang, L.-f.; Hu, X.-x.; Zhang, X.-r.; Zheng, G.-b. Flotation separation of quartz from magnesite using carboxymethyl cellulose as depressant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 1623–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Kou, J.; Sun, C. Synergy Effect between Sodium Oleate and Alcohol Ethoxylates on the Reverse Flotation of Quartz. Minerals 2023, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, K.; Oliva, J.; Alfonso, P.; Sampaio, C.H.; Anticoi, H. A Comparative Study of Quartz and Potassium Feldspar Flotation Process Using Different Chemical Reagents. Minerals 2024, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjahed, S.; Kheloufi, A.; Bobocioiu, E.; Kefaifi, A.; Kerkar, F.; Lebbou, K. Quartz Ore Beneficiation by Reverse Flotation for Silicon Production. Silicon 2020, 14, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, Y.; Rao, F.; Liu, T.; Sun, H.; Yin, W. Role of citric acid in selective flotation of limonite from quartz using sodium oleate as collector. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 355, 129650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Yao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, C. Combined inhibitors of Fe3+, Cu2+ or Al3+ and sodium silicate on the flotation of fluorite and quartz. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 643, 128702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irannajad, M.; Ejtemaei, M.; Gharabaghi, M. The effect of reagents on selective flotation of smithsonite–calcite–quartz. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y. The separation of kyanite from quartz by flotation at acidic pH. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H.; Wu, F.; Song, Y. The Effects of Calcination-Water Quenching on Quartz Purification and Its Mechanism. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 2519–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Xia, Z.; Li, W.; Lei, S. Influences of Na2CO3 roasting and H3PO4 hot-pressure leaching on the purification of vein quartz to achieve high-purity quartz. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 218, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jiang, X.; Zuo, Q.; Li, J.; Ban, B.; Chen, J. Purification Mechanism of Quartz Sand by Combination of Microwave Heating and Ultrasound Assisted Acid Leaching Treatment. Silicon 2021, 13, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Zang, F.; Ji, M.; Yu, M. Prepare and Mechanism of High Purity Quartz by Alkali Corrosion and Acid Leaching Process Using Vein Quartz. Silicon 2022, 14, 12475–12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.K.; Dash, N.; Samal, A.K.; Misra, P.K. Competency of chlorination roasting coupled water leaching process for potash recovery from K-feldspar: Mechanism and kinetics aspects. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Luo, D.; Deng, J.; Sun, S.; Song, S.; Jiang, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, K. An environmentally friendly strategy for the preparation of high-purity quartz using combined collector reverse flotation coupled with acid-leaching technology. Miner. Eng. 2025, 227, 109274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgaroto, S.; Azevedo, A.; Rubio, J. Flotation of quartz particles assisted by nanobubbles. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 137, 6–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gungoren, C.; Ozdemir, O.; Ozkan, S.G. Surface Properties and Beneficiation of Quartz with Flotation. Minerals 2025, 15, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080846
Gungoren C, Ozdemir O, Ozkan SG. Surface Properties and Beneficiation of Quartz with Flotation. Minerals. 2025; 15(8):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080846
Chicago/Turabian StyleGungoren, Can, Orhan Ozdemir, and Safak Gokhan Ozkan. 2025. "Surface Properties and Beneficiation of Quartz with Flotation" Minerals 15, no. 8: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080846
APA StyleGungoren, C., Ozdemir, O., & Ozkan, S. G. (2025). Surface Properties and Beneficiation of Quartz with Flotation. Minerals, 15(8), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080846











