Eco-Friendly Leaching of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass Using a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent System Based on Choline Chloride, Glycolic Acid, and Ascorbic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization of Black Mass
2.3. Preparation of DES Solutions
2.4. Leaching Experiments
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of DES
3.2. Leaching of Black Mass
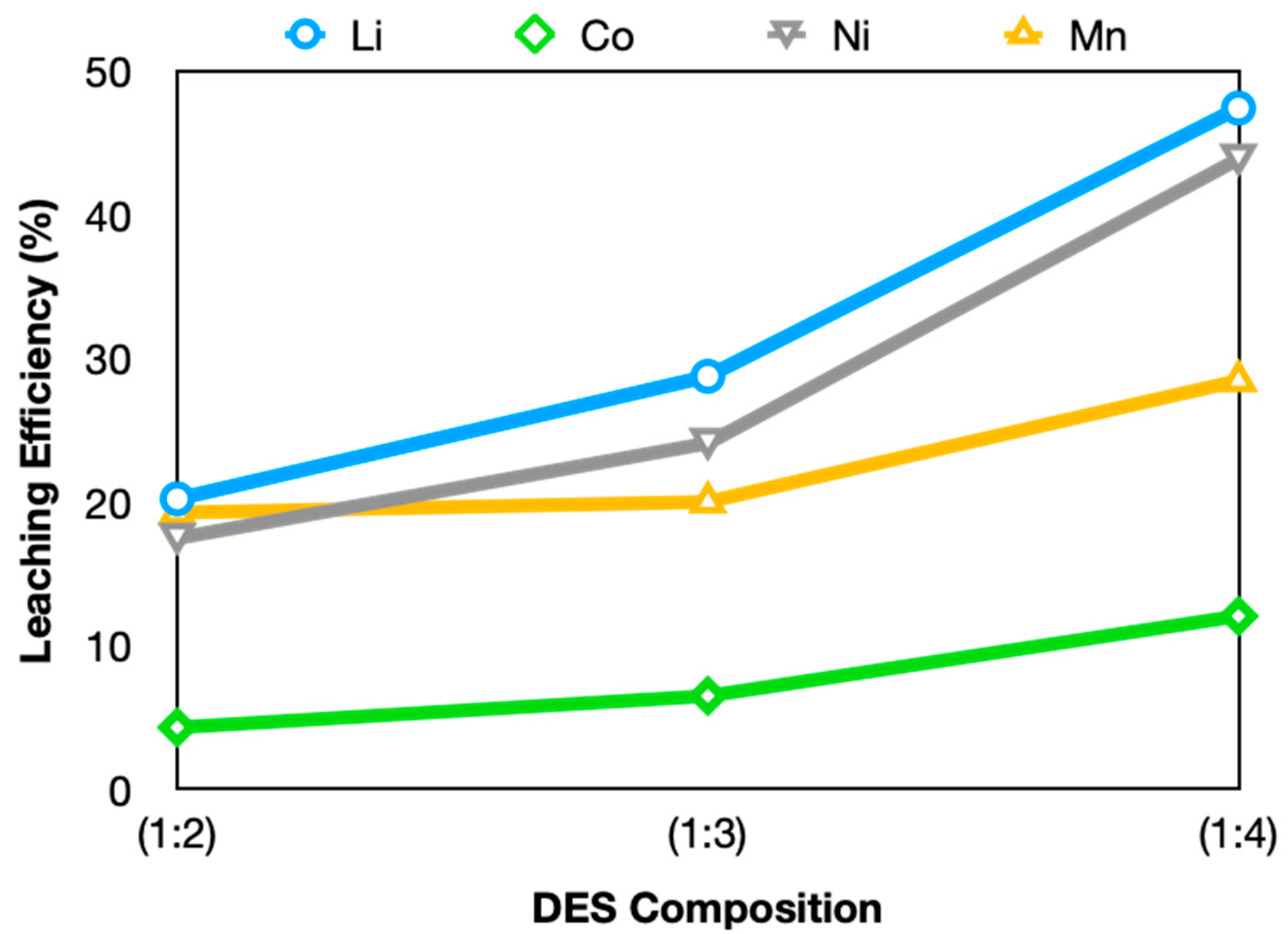
3.2.1. Effect of GLY Mole Ratio on Leaching Efficiency
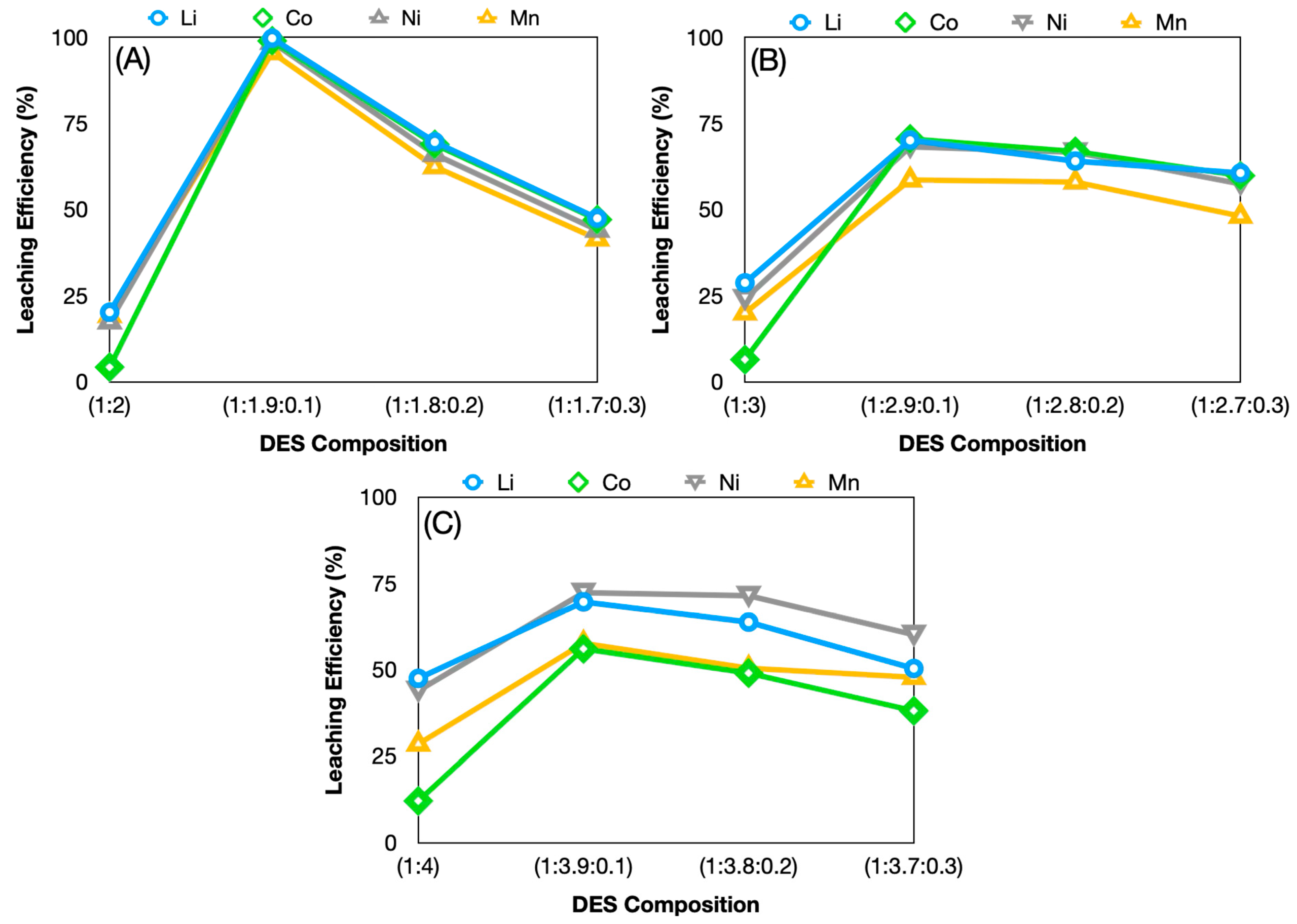
3.2.2. Effect of Ternary System Mole Ratios on Leaching Efficiency
3.2.3. Effect of Time on Leaching Efficiency
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature on Leaching Efficiency
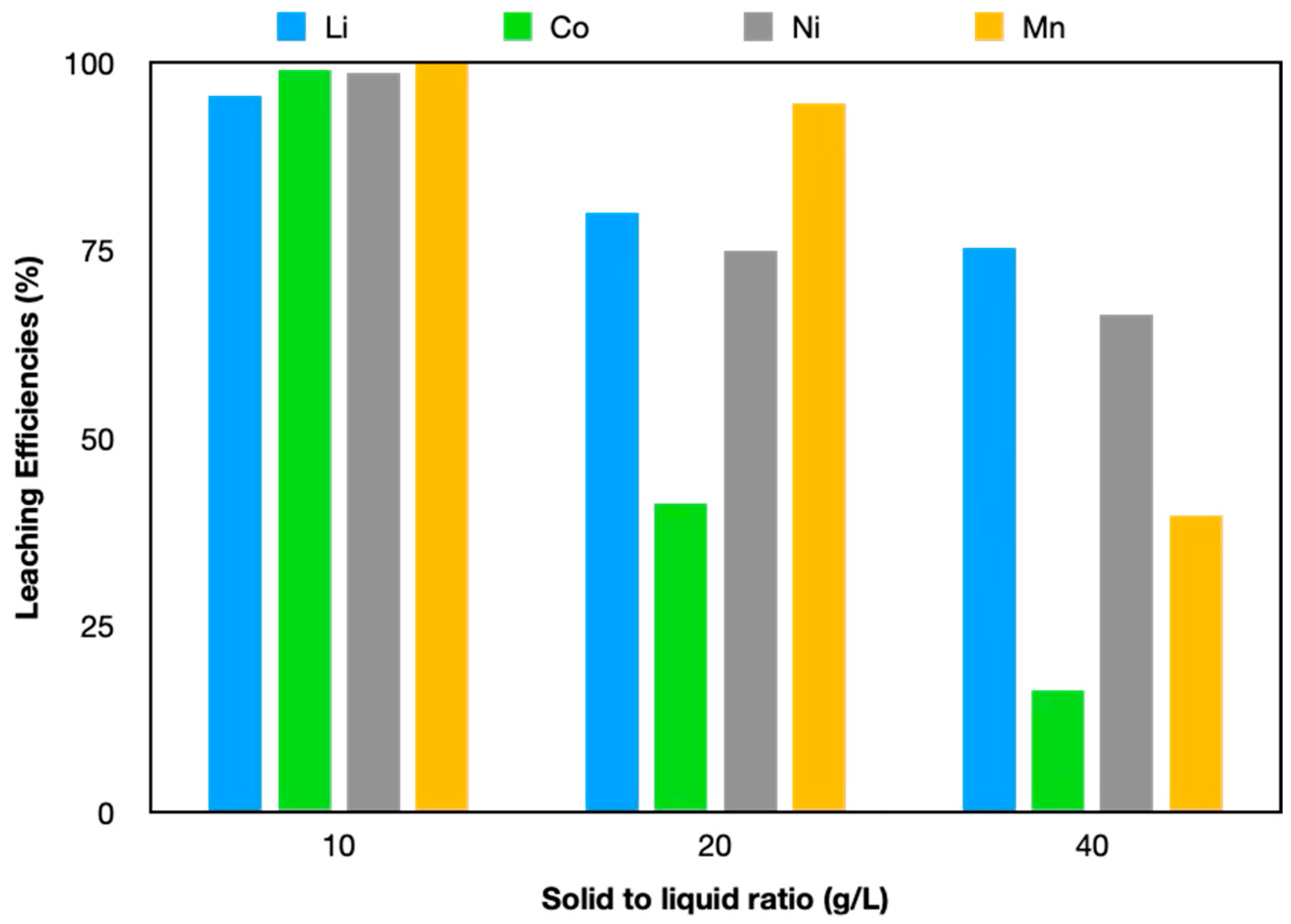
3.2.5. Effect of Solid to Liquid Ratio on Leaching Efficiency
3.2.6. Leaching Kinetics
3.2.7. Leaching Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Golmohammadzadeh, R.; Faraji, F.; Rashchi, F. Recovery of Lithium and Cobalt from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries (LIBs) Using Organic Acids as Leaching Reagents: A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.T.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Cathode Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, F.; Tedjar, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Houlachi, G.; Bouchard, P.; Demopoulos, G.P.; Zaghib, K. Progress and Status of Hydrometallurgical and Direct Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond. Materials 2020, 13, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, A.M.; de Souza, R.G. Review of Life Cycle Assessment on Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs) Recycling. Next Sustain. 2024, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, C.; Pham, H.D.; Jadhav, S.; Do, T.T.; Nerkar, J.; Hoang, L.T.M.; Kumar Nanjundan, A.; Mundree, S.G.; Dubal, D.P. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Green Approach for Cathode Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2022, 3, 2100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garole, D.J.; Hossain, R.; Garole, V.J.; Sahajwalla, V.; Nerkar, J.; Dubal, D.P. Recycle, Recover and Repurpose Strategy of Spent Li-Ion Batteries and Catalysts: Current Status and Future Opportunities. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3079–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, P.; Teng, L.; Rohani, S.; He, M.; Meng, F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W. Acid-Free Extraction of Valuable Metal Elements from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Waste Copperas. Waste Manag. 2023, 165, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X. Novel Electrochemically Driven and Internal Circulation Process for Valuable Metals Recycling from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Lin, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Lithium Carbonate Recovery from Cathode Scrap of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery: A Closed-Loop Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, P.; Mishra, S. Optimization of Leaching of Lithium and Cobalt from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by the Choline Chloride-Citric Acid/Malonic Acid DES Using Response Surface Methodology. Environ. Res. 2025, 269, 120917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegemann, L.; Gutscha, M. Environmental Impacts of Pyro- and Hydrometallurgical Recycling for Lithium-Ion Batteries—A Review. J. Bus. Chem. 2025, 22, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Shi, M.; Wu, C. Deep Eutectic Solvent for Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Comparison with Inorganic Acid Leaching. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 19029–19051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichowska-Kopczyńska, I.; Nowosielski, B.; Warmińska, D. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties and Applications in CO2 Separation. Molecules 2023, 28, 5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical Recovery of Cobalt from Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials Using Deep-Eutectic Solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Svärd, M.; Forsberg, K. Recycling Cathode Material LiCo1/3Ni1/3Mn1/3O2 by Leaching with a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Metal Recovery with Antisolvent Crystallization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, S.; Davey, K.; Mao, J.; Guo, Z. Green Recycling of Spent Li-Ion Battery Cathodes via Deep-Eutectic Solvents. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 867–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Shafaie, S.Z.; Abdollahi, H.; Entezari-Zarandi, A. Green Recycling of Spent Li-Ion Batteries by Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs): Leaching Mechanism and Effect of Ternary DES. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 109014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svigelj, R.; Dossi, N.; Grazioli, C.; Toniolo, R. Deep Eutectic Solvents (Dess) and Their Application in Biosensor Development. Sensors 2021, 21, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Zhou, F.; Mu, W.; Ling, C.; Mu, T.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Deep Insights into the Viscosity of Deep Eutectic Solvents by an XGBoost-Based Model plus SHapley Additive exPlanation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 26029–26036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem Glycolic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/757 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Emel’Yanenko, V.N.; Verevkin, S.P.; Stepurko, E.N.; Roganov, G.N.; Georgieva, M.K. Thermodynamic Properties of Glycolic Acid and Glycolide. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 84, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Rajani, N.; Kumawat, P.; Singh, N.; Kushwaha, J.P. Performance and Mechanism of Dye Extraction from Aqueous Solution Using Synthesized Deep Eutectic Solvents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem Ascorbic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/54670067 (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Opinion, S. Scientific Opinion on the Safety and Efficacy of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid, Sodium Ascorbate, Calcium Ascorbate, Ascorbyl Palmitate, Sodium Calcium Ascorbyl Phosphate and Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate) as a Feed Additive for All Animal Species Based on a Dossi submitted by DSM Nutritional Products Ltd. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ascorbic Acid. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garshin, A.P.; Shvaiko-Shvaikovskii, V.E. Mechanism of Oxidation of β-BN. Sov. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 1992, 31, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, E.; Dursun, H.N.; Kaya, F.; Burat, F.; Gürmen, S. Recycling of EoL Batteries with Ultrasonic Assisted Nitric-Ascorbic Acid Leaching: Experimental Design and Process Optimization. Min. Metall. Explor. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surel, A.S.; Gul, M.F.; Uysal, E.; Yesiltepe-Ozcelik, D.; Gurmen, S. Pulse Ultrasonication Leaching Approach for Selective Li Leaching from Spent LFP Cathode Material. Can. Metall. Q. 2024, 63, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F.; Wennmohs, F.; Becker, U.; Riplinger, C. The ORCA Quantum Chemistry Program Package. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 224108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, R.; Ludwig, M.; Webber, G.B.; Atkin, R.; Page, A.J. Nanostructure, Hydrogen Bonding and Rheology in Choline Chloride Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Function of the Hydrogen Bond Donor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuzlin, A.F.; Saadiah, M.A.; Yao, Y.; Nagao, Y.; Samsudin, A.S. Enhancing Proton Conductivity of Sodium Alginate Doped with Glycolic Acid in Bio-Based Polymer Electrolytes System. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmalia, W.; Shofiyani, A.; Sutiknyawati, Y.; Septiani, S. Simple Green Routes for Metal-Bixin Complexes Synthesis Using Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. Indones. J. Chem. 2022, 22, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.K.U.; Chan, Y.S.; Nandong, J.; Chin, S.F.; Ho, B.K. Formulation of Choline Chloride/Ascorbic Acid Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent: Characterization, Solubilization Capacity and Antioxidant Property. LWT 2020, 133, 110096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Du, R.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhou, D.; Wang, S.; Li, C. High-Efficiency Leaching of Valuable Metals from Waste Li-Ion Batteries Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Bian, X.; Han, W.; Cao, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, K.; Wang, S. The Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: A Comprehensive Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ou, L.; Yin, C. High-Efficiency Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Double Closed-Loop Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Marrucho, I.M. Insights into the Synthesis and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Cholinium Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svärd, M.; Ma, C.; Forsberg, K.; Schiavi, P.G. Addressing the Reuse of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Li-Ion Battery Recycling: Insights into Dissolution Mechanism, Metal Recovery, Regeneration and Decomposition. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202400410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Yu, J. Ascorbic Acid and Choline Chloride: A New Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent for Extracting Tert-Butylhydroquinone Antioxidant. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Influence of the Molecular Structure of Constituents and Liquid Phase Non-Ideality on the Viscosity of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Li, T.; Yan, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; An, N.; Huang, W.; Guo, Q.; Ge, X. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) with a Regulated Rate-Determining Step for Efficient Recycling of Lithium Cobalt Oxide. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11452–11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Deng, R.; Gao, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q. Sustainable Recovery of Metals from E-Waste Using Deep Eutectic Solvents: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 47, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, A.; Birol, B.; Saridede, M.N.; Kaplan, Ş.S.; Sönmez, M.Ş. Direct Microwave Leaching Conditions of Rare Earth Elements in Fluorescent Wastes. J. Rare Earths 2024, 42, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Rodriguez, N.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Kollau, L.J.B.M.; Kroon, M.C.; Binnemans, K. Degradation of Deep-Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11521–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’am, A.C.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chen, S.-W.; You, S.-J. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Waste Permanent Magnet (WPMs) via Selective Leaching Using the Taguchi Method. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Rashchi, F.; Mostoufi, N. Kinetics of Leaching: A Review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2022, 38, 113–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.B.; Gambardella, J.; Castellanos, V.; Trimarco, V.; Santulli, G. Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaltonen, M.; Peng, C.; Wilson, B.; Lundström, M. Leaching of Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Recycling 2017, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Ascorbic-Acid-Assisted Recovery of Cobalt and Lithium from Spent Li-Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porvali, A.; Shukla, S.; Lundström, M. Low-Acid Leaching of Lithium-Ion Battery Active Materials in Fe-Catalyzed Cu-H2SO4 System. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gu, S.; Guo, Y.; Dai, X.; Zeng, L.; Wang, K.; He, C.; Dodbiba, G.; Wei, Y.; Fujita, T. Leaching of Cathode Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Using a Mixture of Ascorbic Acid and HNO3. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 205, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; He, X.; Di, S.; Liu, K.; Li, D.; Du, J. Comparative of Malonic Acid Aqueous Solution and Malonic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent for LiCoO2 Cathode Materials Recovery: Leaching Efficiency and Mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
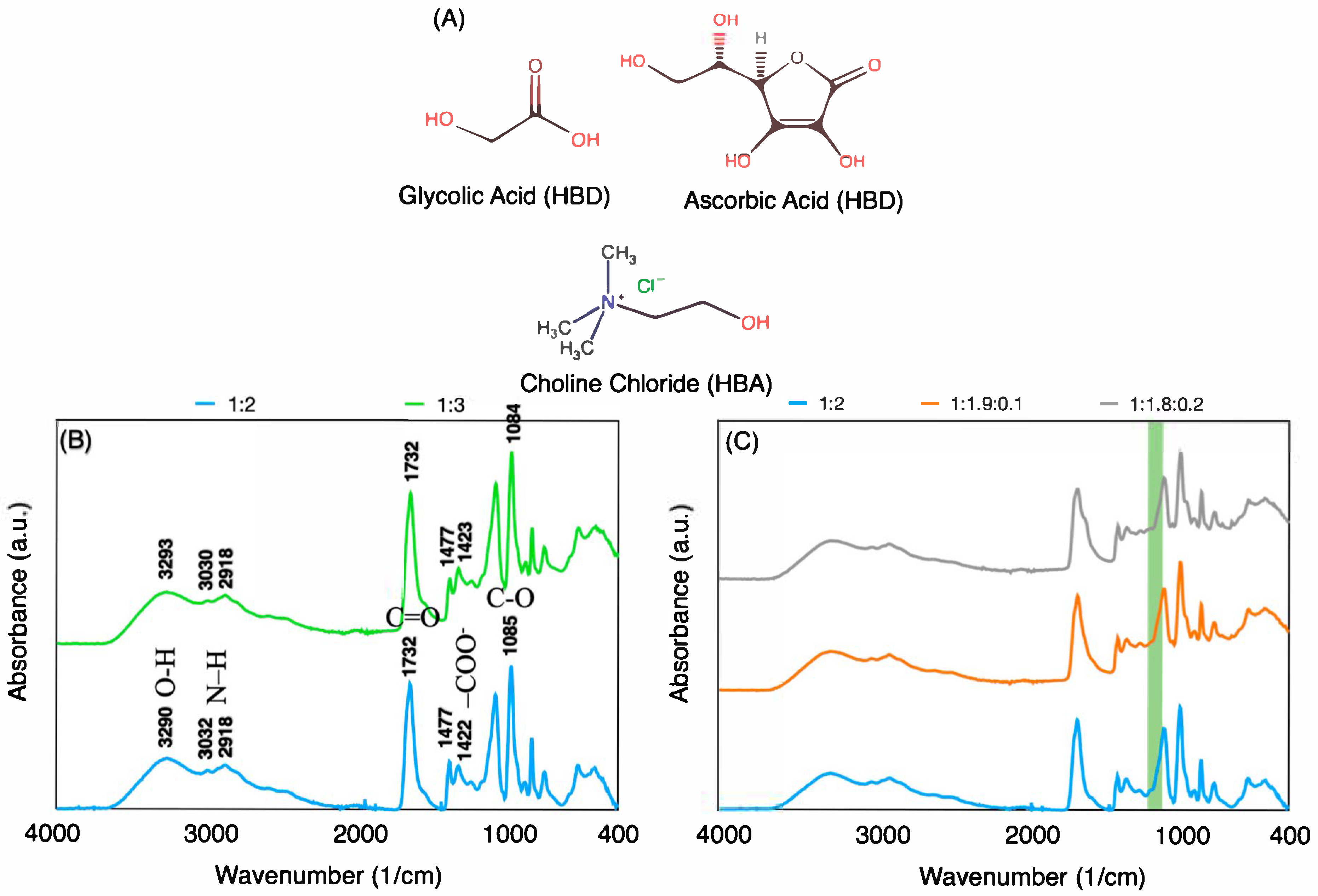





| DES Codes | Choline Chloride Ratio (Mole) | Glycolic Acid Ratio (Mole) | Ascorbic Acid Ratio (Mole) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:2 ChCl:GLY | 1 | 2 | - |
| 1:1.9:0.1 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| 1:1.8:0.2 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 1.8 | 0.2 |
| 1:1.7:0.3 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 1.7 | 0.3 |
| 1:3 ChCl:GLY | 1 | 3 | - |
| 1:2.9:0.1 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 2.9 | 0.1 |
| 1:2.8:0.2 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 2.8 | 0.2 |
| 1:2.7:0.3 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 2.7 | 0.3 |
| 1:4 ChCl:GLY | 1 | 4 | - |
| 1:3.9:0.1 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 3.9 | 0.1 |
| 1:3.8:0.2 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 3.8 | 0.2 |
| 1:3.7:0.3 ChCl:GLY:AA | 1 | 3.7 | 0.3 |
| DES Compositions | Leaching Efficiencies (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | Co | Ni | Mn | |
| (1:2) | 20.24 | 4.31 | 17.50 | 19.28 |
| (1:1.9:0.1) | 99.68 | 98.95 | 98.59 | 95.56 |
| (1:1.8:0.2) | 69.62 | 68.92 | 66.05 | 62.45 |
| (1:1.7:0.3) | 47.47 | 47.09 | 44.09 | 41.49 |
| (1:3) | 28.78 | 6.51 | 24.12 | 20.03 |
| (1:2.9:0.1) | 70.09 | 70.52 | 68.25 | 58.63 |
| (1:2.8:0.2) | 64.08 | 66.88 | 66.67 | 58.01 |
| (1:2.7:0.3) | 60.63 | 59.85 | 57.48 | 48.13 |
| (1:4) | 47.47 | 12.07 | 43.92 | 28.48 |
| (1:3.9:0.1) | 69.62 | 56.01 | 72.31 | 57.64 |
| (1:3.8:0.2) | 63.77 | 48.98 | 71.43 | 50.43 |
| (1:3.7:0.3) | 50.32 | 38.06 | 60.14 | 47.78 |
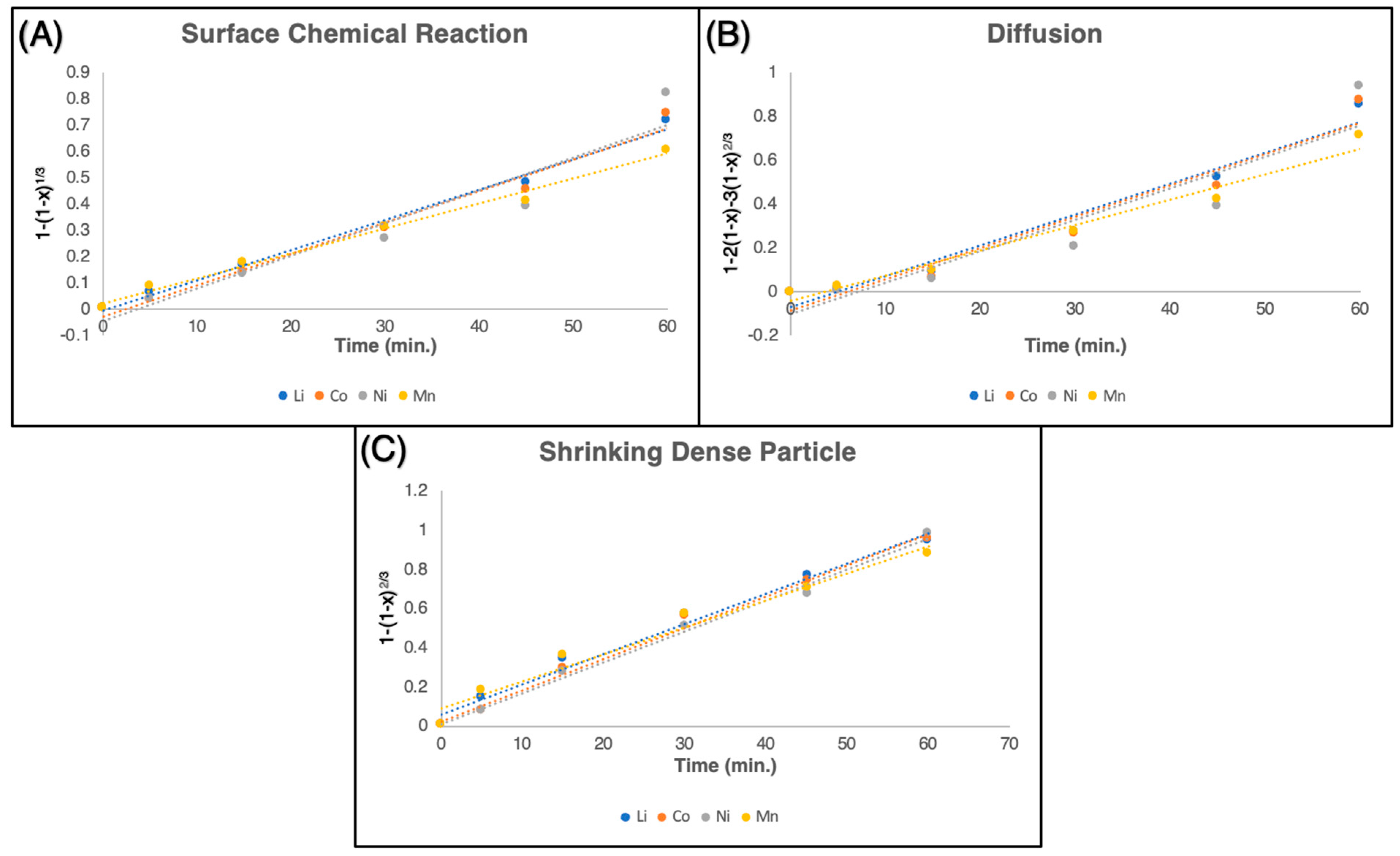
| Metals | Surface Chemical Reaction | Diffusion | Shrinking Dense Particle | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation | R2 | Equation | R2 | Equation | R2 | |
| Li | y = 0.0116x − 0.0067 | 0.9917 | y = 0.0141x − 0.0716 | 0.9625 | y = 0.0154x + 0.0602 | 0.9854 |
| Co | y = 0.012x − 0.0282 | 0.9806 | y = 0.0142x − 0.0859 | 0.9416 | y = 0.016x + 0.0234 | 0.9914 |
| Ni | y = 0.0124x − 0.0459 | 0.9231 | y = 0.0143x − 0.1032 | 0.8676 | y = 0.0158x + 0.0099 | 0.9935 |
| Mn | y = 0.0095x + 0.0215 | 0.9907 | y = 0.0116x − 0.0423 | 0.9735 | y = 0.0138x + 0.0907 | 0.966 |
| Metals | Arrhenius Model Constant | |
|---|---|---|
| Equation | R2 | |
| Li | y = −5.7804x + 14.154 | 0.8975 |
| Co | y = −8.5464x + 22.587 | 0.8222 |
| Ni | y = −8.2663x + 21.844 | 0.9061 |
| Mn | y = −7.8235x + 20.77 | 0.8708 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazlı, F.; Hasdemir, I.; Uysal, E.; Dursun, H.N.; Gezici, U.O.; Özçelik, D.Y.; Burat, F.; Gürmen, S. Eco-Friendly Leaching of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass Using a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent System Based on Choline Chloride, Glycolic Acid, and Ascorbic Acid. Minerals 2025, 15, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080782
Nazlı F, Hasdemir I, Uysal E, Dursun HN, Gezici UO, Özçelik DY, Burat F, Gürmen S. Eco-Friendly Leaching of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass Using a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent System Based on Choline Chloride, Glycolic Acid, and Ascorbic Acid. Minerals. 2025; 15(8):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080782
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazlı, Furkan, Işıl Hasdemir, Emircan Uysal, Halide Nur Dursun, Utku Orçun Gezici, Duygu Yesiltepe Özçelik, Fırat Burat, and Sebahattin Gürmen. 2025. "Eco-Friendly Leaching of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass Using a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent System Based on Choline Chloride, Glycolic Acid, and Ascorbic Acid" Minerals 15, no. 8: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080782
APA StyleNazlı, F., Hasdemir, I., Uysal, E., Dursun, H. N., Gezici, U. O., Özçelik, D. Y., Burat, F., & Gürmen, S. (2025). Eco-Friendly Leaching of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass Using a Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent System Based on Choline Chloride, Glycolic Acid, and Ascorbic Acid. Minerals, 15(8), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080782









