40Ar-39Ar Chronometry Supports Multi-Stage Tectonic Thermal Events in the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE Deposit
Abstract
1. Introduction
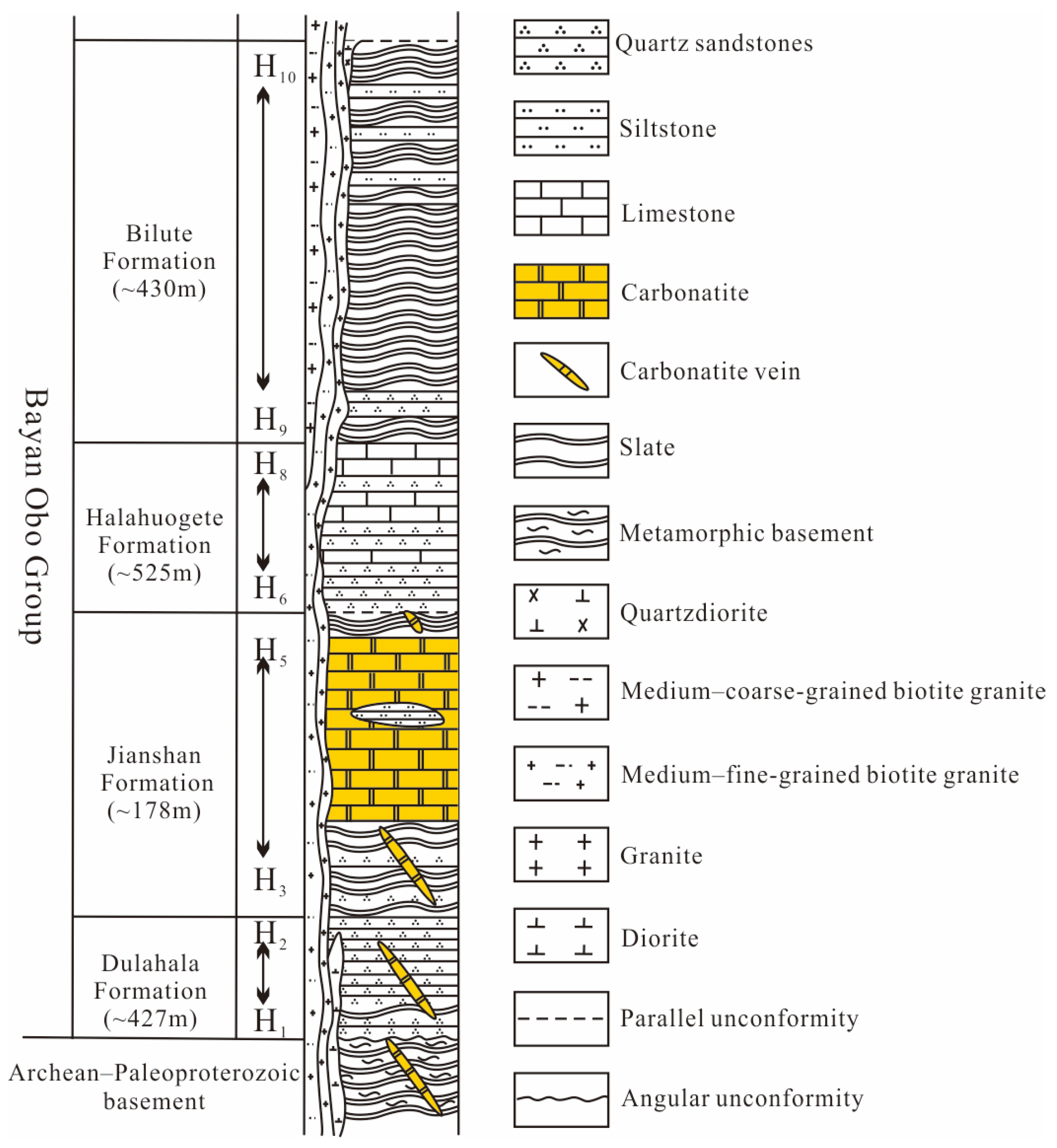
2. Regional Geological Background
2.1. Regional Geology
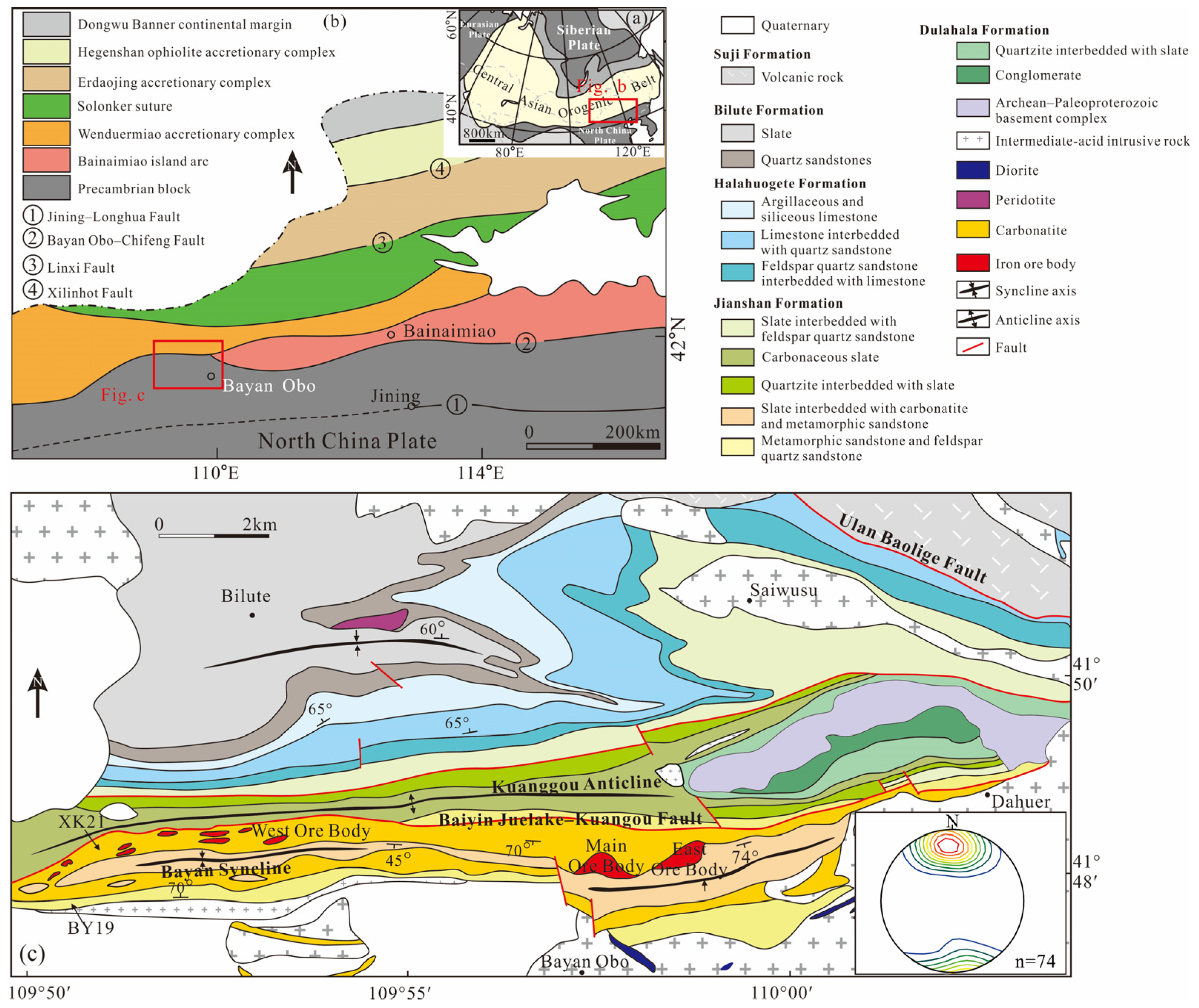
2.2. Geology of Ore Deposits
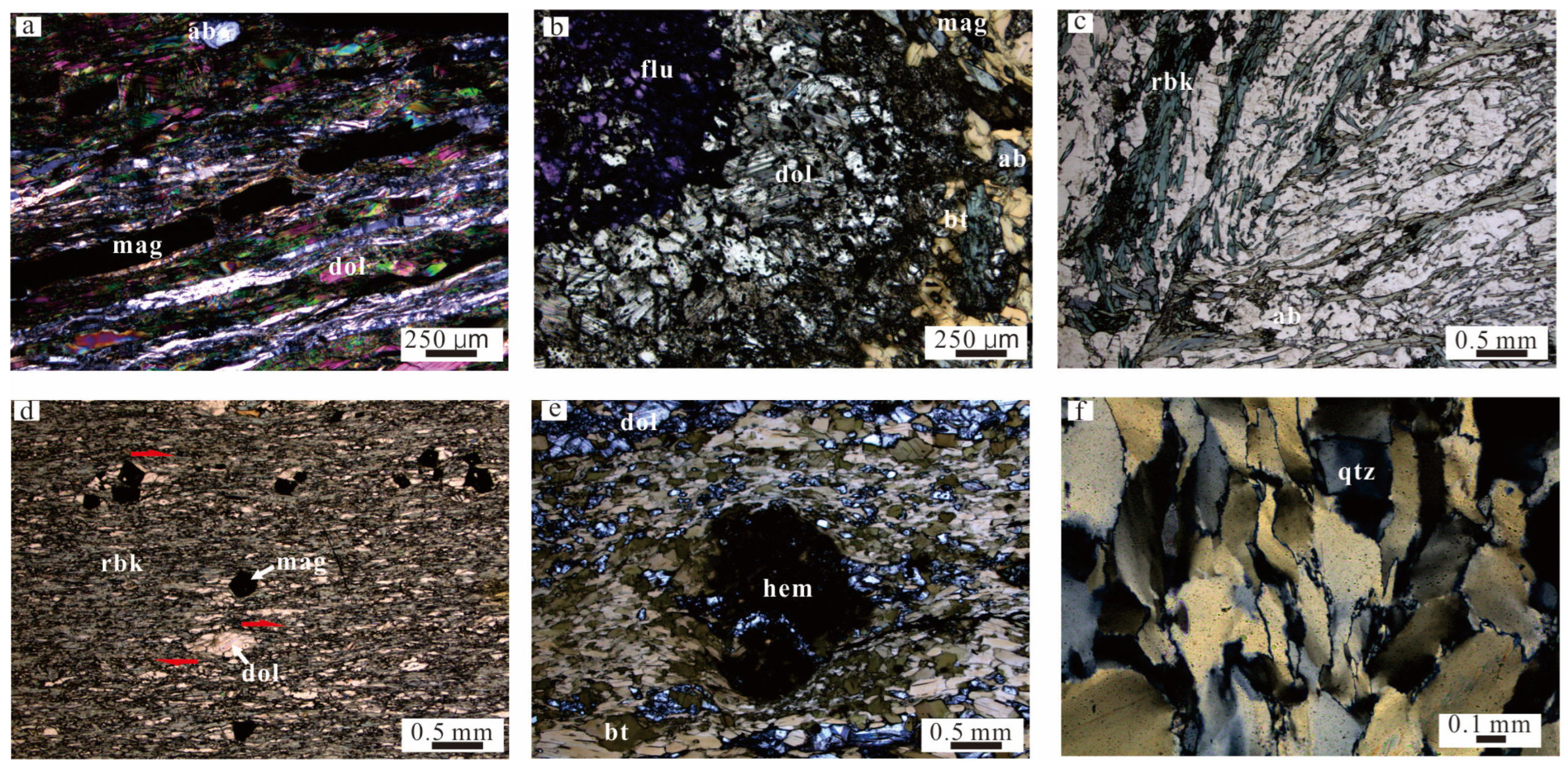
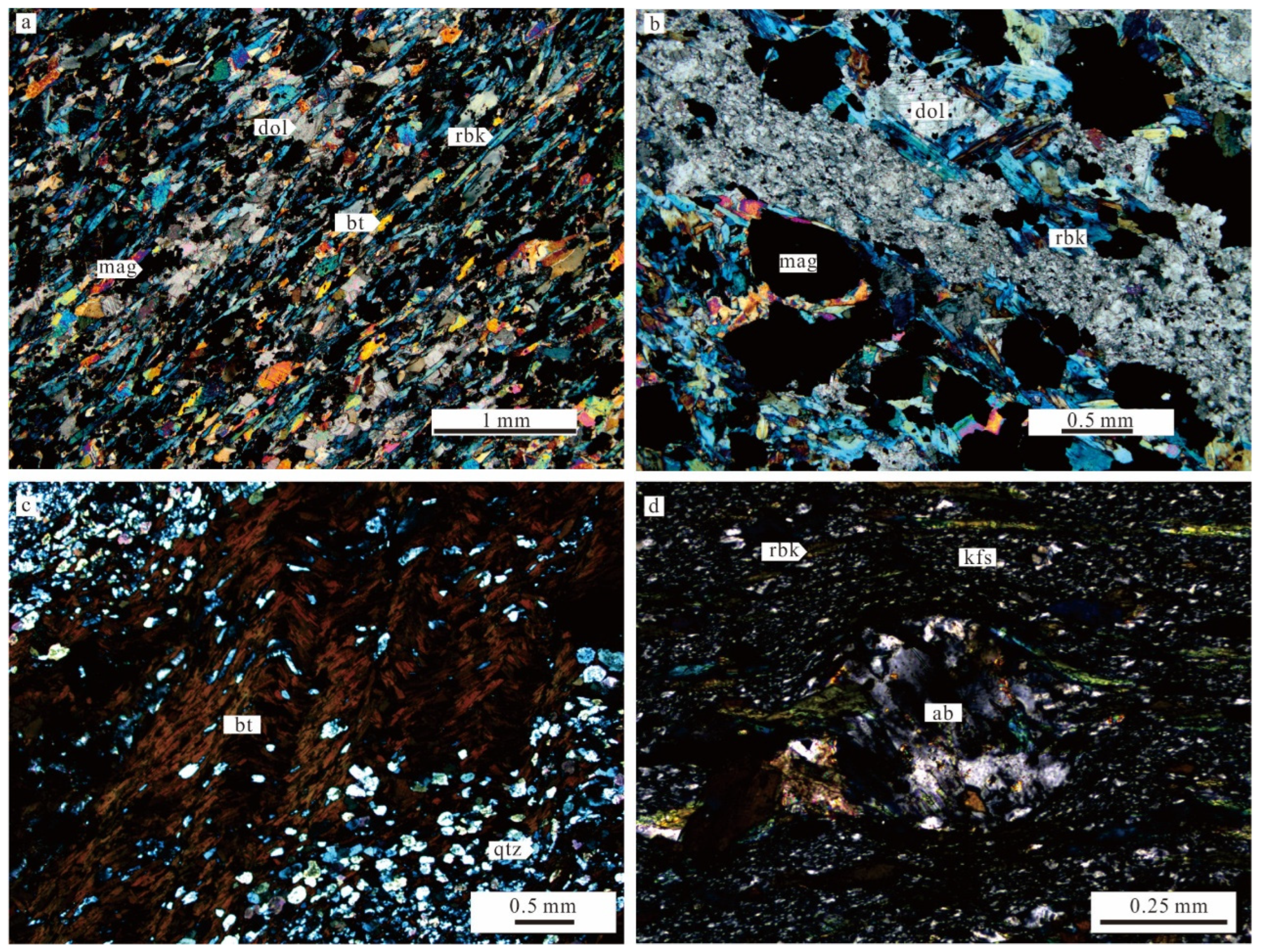
3. Deformation Characteristics
4. Sample Collection and Testing Methods
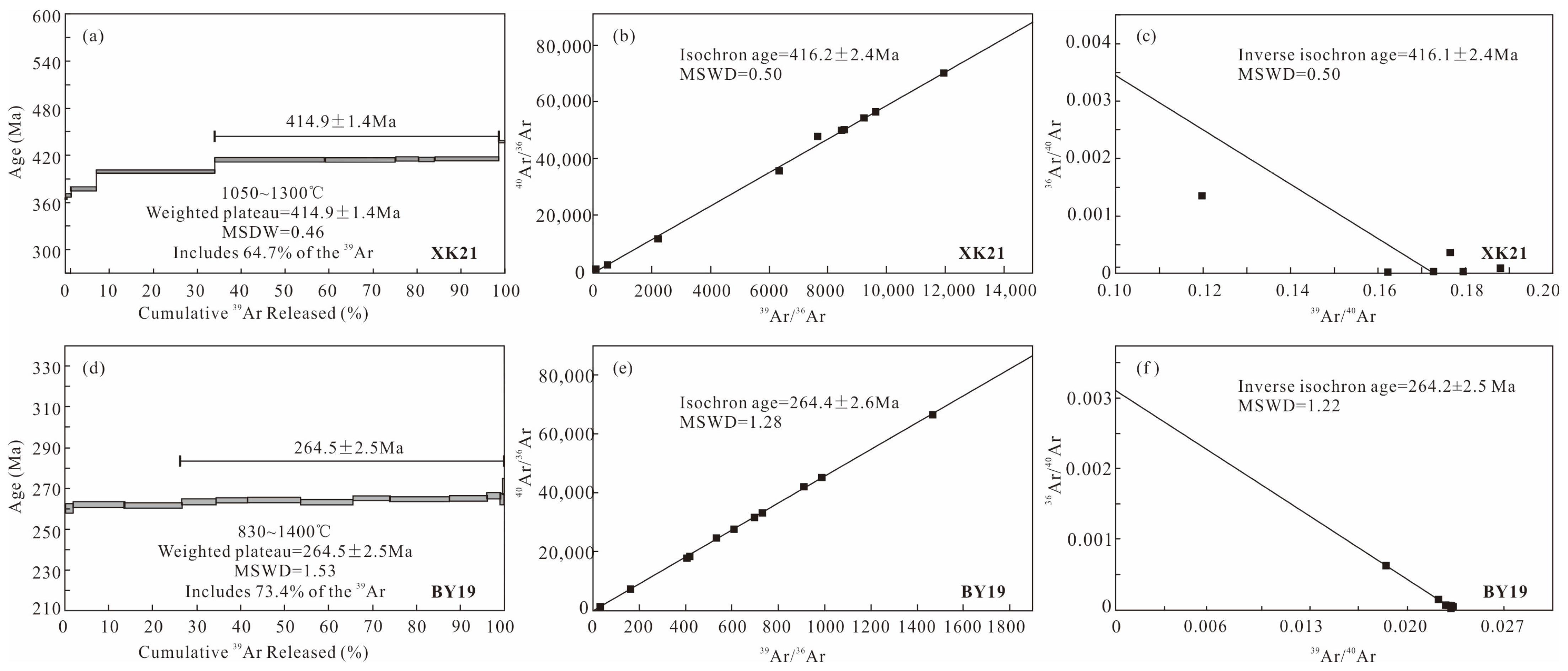
5. Analytical Results
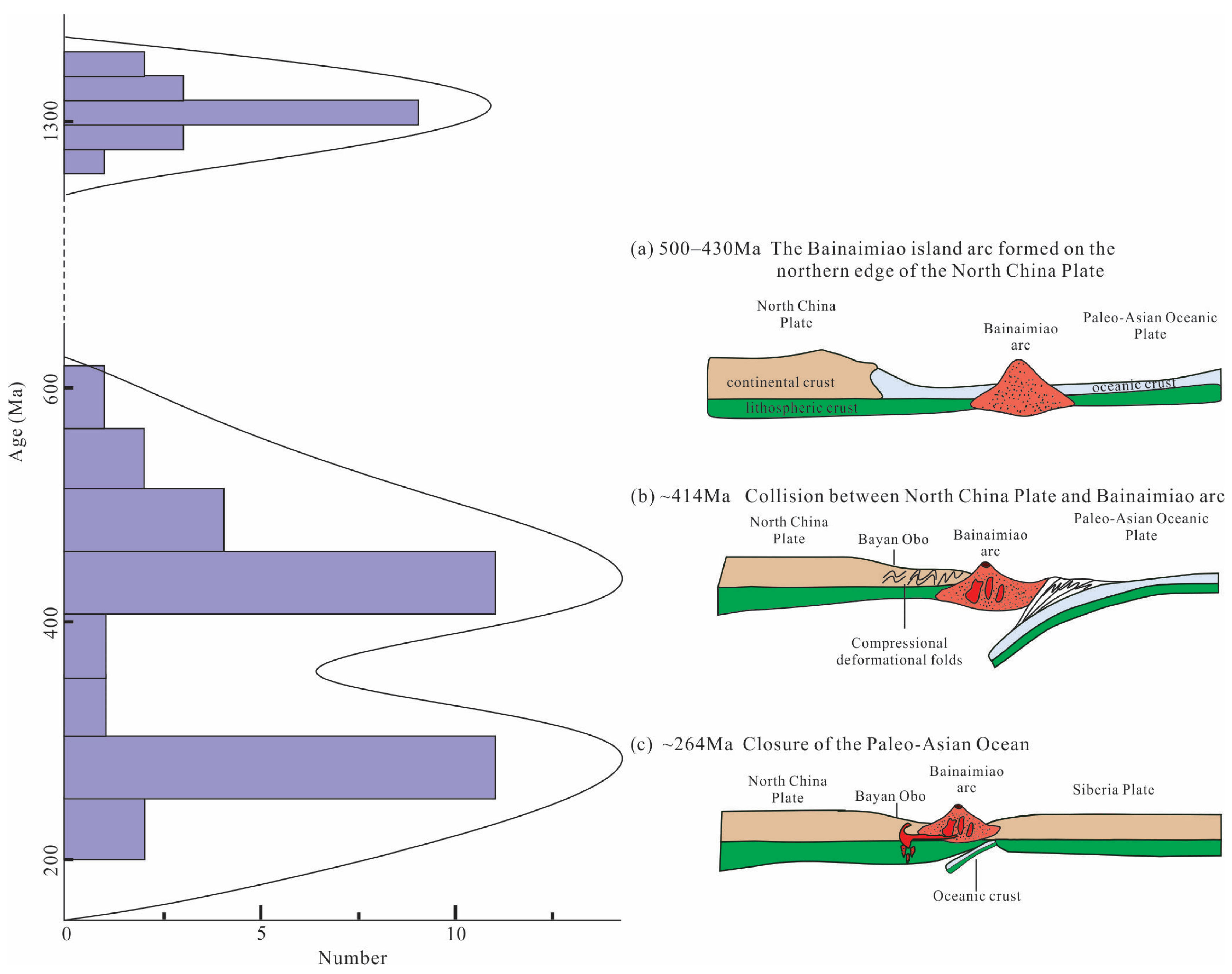
6. Discussion
6.1. The Multi-Stage Tectonic Thermal Events in Bayan Obo
6.1.1. Early Paleozoic
6.1.2. Late Paleozoic
6.2. Tectonic Significances
6.3. Implications for the Orogenic Process
6.3.1. The Age of Collisions Between the NCP and the Bainaimiao Arc
6.3.2. The Closure Age of the PAO
| No. | Location | Lithology | Methods | Interpretation | Age (Ma) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bayan Obo | niobite | U-Pb | intraplate extension | 268 ± 5 | Yu et al. (2024) [23] |
| 2 | Bayan Obo | zircon | Th-Pb | extension | 1301 ± 12 | Zhang et al. (2017) [36] |
| 3 | Bayan Obo | zircon | Th-Pb | extension | 1300 | Smith et al. (2015) [50] |
| 4 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 455.6 ± 28.2 | Campbell et al. (2014) [55] |
| 5 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | SHRIMP Th-Pb | extension | 1325 ± 60 | Campbell et al. (2014) [55] |
| 6 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Sm-Nd | extension | 1286 ± 27 Ma | Zhu et al. (2014) [59] |
| 7 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 418 ± 11 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 8 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 424 ± 5 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 9 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 429 ± 11 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 10 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 432 ± 8 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 11 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 437 ± 9 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 12 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 474 ± 4 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 13 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 475 ± 8 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 14 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 496 ± 13 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 15 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 532 ± 11 | Wang et al. (1994) [60] |
| 16 | Bayan Obo | biotite rock | Ar-Ar | subduction | 266.4 ± 3.9 | Lai et al. (2015) [64] |
| 17 | Bayan Obo | slate | CAMAECA U-Pb, zircon | subduction | 289.1 ± 1.8 | Lai et al. (2015) [64] |
| 18 | Bayan Obo | natroamphibole | Ar-Ar | subduction | 389.5 ± 3.0 | Lai et al. (2015) [64] |
| 19 | Bayan Obo | slate | CAMAECA U-Pb, zircon | subduction | 518.8 ± 7.5 | Lai et al. (2015) [64] |
| 20 | Harihana | two-mica granite | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb, zircon | mantle plume | 258 ± 2.5 | Hui et al. (2021) [88] |
| 21 | Harihana | muscovite granite | Ar-Ar | mantle plume | 268 ± 2.72 | Hui et al. (2021) [88] |
| 22 | Hexipu | granite | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb, zircon | slippage fracture | 259 | Zhang et al. (2021) [89] |
| 23 | Hexipu | granite | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb, zircon | slippage fracture | 269 ± 1.2 | Zhang et al. (2021) [89] |
| 24 | Hexipu | muscovite | Ar-Ar | slippage fracture | 425 ± 2.9 | Zhang et al. (2021) [89] |
| 25 | Fengning | quartz diorite | SHRIMP U-Pb, zircon | subduction | 279.5 ± 5.6 | Wang et al. (2007) [97] |
| 26 | Guyang | granite | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb, zircon | subduction | 282 | Zeng et al. (2008) [98] |
| 27 | Bayan Obo | monazite, fluocerite | Sm-Nd | extension | 1313 ± 41 | Zhang et al. (2001) [99] |
| 28 | Bayan Obo | rare-earth minerals from late veins | Sm-Nd | subduction | 422 ± 18 | Zhang et al. (1994) [100] |
| 29 | Bayan Obo | carbonatite | Sm-Nd, whole rock | extension | 1223 ± 65 | Zhang et al. (1994) [100] |
| 30 | Bayan Obo | natroamphibole | Ar-Ar | extension | 1288 ± 12 | Ren et al. (1994) [101] |
| 31 | Bayan Obo | monazite, fluocerite | Sm-Nd | extension | 1312.5 ± 41.2 | Ren et al. (1994) [101] |
| 32 | Bayan Obo | carbonatite dike | SHRIMP U-Pb, zircon | extension | 1374 ± 42 | Fan et al. (2006) [102] |
| 33 | Bayan Obo | carbonatite and fenitized country rocks | Sm-Nd | extension | 1308 ± 56 | Wang et al. (2018) [103] |
| 34 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Sm-Nd, whole rock | extension | 1305 ± 78 | Zhang et al. (2003) [104] |
| 35 | Bayan Obo | mica-type ore magnesium biotite | Rb-Sr | subduction | 287 ± 16 | Yao et al. (2025) [105] |
| 36 | Bayin Zhu Rihe | hornblende gabbro | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb, zircon | extension | 265 ± 2 | Luo et al. (2013) [106] |
| 37 | Bayan Obo | plagioclasite | SHRIMP U-Pb, zircon | intraplate extension | 285 ± 2 | Wang et al. (2010) [107] |
| 38 | Bayan Obo | hydrothermal alkaline amphibole | Ar-Ar | subduction | 396 ± 4 | Zhao et al. (1991) [108] |
| 39 | Bayan Obo | monazite | Th-Pb | subduction | 423 ± 3 | Zhao et al. (1991) [108] |
| 40 | Bayan Obo | yicalcite, Huanghe ore | Th-Pb | subduction | 438.2 ± 25.1 | Zhao et al. (1991) [108] |
| 41 | Bayan Obo | hydrothermal alkaline amphibole | Ar-Ar | subduction | 719 ± 2 | Zhao et al. (1991) [108] |
| 42 | Bayan Obo | hydrothermal alkaline amphibole | Ar-Ar | subduction | 720 ± 20 | Zhao et al. (1991) [108] |
| 43 | Bayan Obo | hydrothermal alkaline amphibole | Ar-Ar | subduction | 818 ± 5 | Zhao et al. (1991) [108] |
| 44 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Pb-Pb, whole rock | extension | 1283 ± 59 | Gao et al. (1995) [109] |
| 45 | Bayan Obo | monazite | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb | intraplate extension | 249 ± 13 | Wang et al. (2018) [110] |
| 46 | Bayan Obo | phlogopite | LA-ICP-MS U-Pb, zircon | subduction | 269.5 ± 3.1 | Wang et al. (2018) [110] |
| 47 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 330 | Ling et al. (2013) [111] |
| 48 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 420 | Ling et al. (2013) [111] |
| 49 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 490 | Ling et al. (2013) [111] |
| 50 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 545 | Ling et al. (2013) [111] |
| 51 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 600 | Ling et al. (2013) [111] |
| 52 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | SHRIMP Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 745 | Ling et al. (2013) [111] |
| 53 | Bayan Obo | carbonatite dike | SHRIMP U-Pb, zircon | extension | 1417 ± 19 | Fan et al. (2014) [112] |
| 54 | Bayan Obo | carbonatite dike | ID-TIMS U-Pb, zircon | extension | 1418 ± 29 | Fan et al. (2014) [112] |
| 55 | Bayan Obo | biotite | Rb-Sr | subduction | 240.2 ± 14.9 | Liang et al. (2024) [113] |
| 56 | Bayan Obo | biotite | Rb-Sr | intraplate extension | 281.8 ± 92 | Liang et al. (2024) [113] |
| 57 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Th-Pb, monazite | subduction | 455 ± 28 | Campbell et al. (2000) [114] |
| 58 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | SHRIMP Th-Pb | extension | 1314 ± 56 | Campbell et al. (2000) [114] |
| 59 | Bayan Obo | monazite | Sm-Nd, LA-ICP-MS | extension | 1320 ± 210 Ma | Yang et al. (2008) [115] |
| 60 | Bayan Obo | basement complex | Sm-Nd | extension | 1354 ± 57 Ma | Yang et al. (2010) [116] |
| 61 | Bayan Obo | pyrite | Re-Os | subduction | 439 ± 86 Ma | Liu et al. (2005a) [117] |
| 62 | Bayan Obo | biotite rock | Ar-Ar | subduction | 272.2 ± 1.9 | Qiu et al. (2009) [118] |
| 63 | Bayan Obo | dolomite | Sm-Nd, whole rock | extension | 1341 ± 59 | Yang et al. (20011b) [119] |
| 64 | Bayan Obo | carbonatite dike | Sm-Nd, whole rock | extension | 1354 ± 57 | Yang et al. (2011b) [119] |
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The widely distributed banded structure within the ore district was the product of structural transformation under the influence of north–south compression, indicating strong ductile deformation in the region.
- (2)
- The 40Ar-39Ar chronology indicates that after the formation of the Bayan Obo deposit, it was affected by two geological events in the Early Paleozoic (414.9 Ma) and Late Paleozoic (264.5 Ma), which were recorded in the banded ores of riebeckite and biotite.
- (3)
- These two geological events correspond to an arc–continent collision event in the Early Paleozoic and a Permian magmatic event, respectively, which were closely related to the evolution of the PAO on the northern side of the NCP.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, T.; Harlaux, M.; Zhai, M.G.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, X.W.; Xia, X.P.; Gao, J.; Tang, J.L.; Hu, M.X.; Gao, H.X. Syn-tectonic emplacement of Li-bearing pegmatites related to detachment faulting in the Dahongliutan pegmatite belt, Western Kunlun, NW China. Miner. Depos. 2025, 60, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, H.; Kisters, A.; Basson, I.J. Deformation, alteration and implicit 3D geomodelling of deposit-scale controls of vein-hosted copper mineralization of the Frontier Mine, Democratic Republic of Congo. Miner. Depos. 2025, 60, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.D.; Yang, Y.Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.L.; He, Y.F.; Liu, J.Z.; Huang, S.H. Poly-phase tectonic activities and mineralization processes of the Nibao gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou. Earth Sci. Front. 2025, 1–16, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosière, C.A.; Lagoeiro, L.E.; Braga, F.C.S.; Pagung, R. EBSD: Towards a better understanding of the role of deformation in the formation of schistose hypogene high-grade iron ore. J. Struct. Geol. 2025, 191, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.F. Structural basis of ore field. Geol. Prospect. 1986, 22, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chiaradia, M.; Schaltegger, U.; Spikings, R.; Wotzlaw, J.F.; Ovtcharova, M. How accurately can we date the duration of magmatic-hydrothermal events in porphyry systems?—An invited paper. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdougall, I.; Harrison, T.M. Geochronology and Thermochronology by the 40Ar/39Ar Method; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Jahn, B.; Lo, C.H.; Shu, L.; Wu, C.; Li, K.; Wang, F. Structural analysis and 40Ar/39Ar thermochronolgy of Proterozoic rocks in Sailimu area (NW China): Implication to polyphase tectonics of the North Chinese Tianshan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 42, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, J.W.; Wang, T.; Sun, Y. Deformation process of the Huachanggou ore district: Microstructure, EBSD analysis, and 40Ar-39Ar geochronology constraints. Geotecton. Et. Metallog. 2024, 48, 1167–1187, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.K.; Ke, C.H.; She, H.Q.; Wang, D.S.; Xu, C.; Wang, A.J.; Li, R.P.; Peng, Z.D.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Yang, K.F.; et al. Geology and mineralization of the Bayan Obo supergiant carbonatite-type REE-Nb-Fe deposit in Inner Mongolia, China: A review. China Geol. 2023, 6, 716–750. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.X.; Bai, G.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Ye, X.J. Geological features and genesis of the Bayan Obo REE ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Appl. Geochem. 1992, 7, 429–442. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F.; Wang, K.Y. Fluid unmixing/immiscibility as an oreforming process in the giant REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolian, China: Evidence from fluid inclusions. J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 89, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.S.; Tao, K.J.; Yang, Z.M.; Yang, X.M.; Song, R.K. Genesis of rare earths, niobium and tantalum minerals in Bayan Obo Ore deposit of China. J. Chin. Rare Earth Soc. 2001, 2, 97–102, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.R.; Xie, Y.H.; Wang, K.Y.; Tao, K.J.; Wilde, S.A. REE daughter minerals trapped in fluid inclusions in the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2004, 46, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Santosh, M.; Yan, G.; Shen, J.; Yuan, M.; Alam, M.; Li, S. Multistage ore formation in the world’s largest REE-Nb-Fe deposit of Bayan Obo, North China Craton: New insights and implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 164, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, D.H.; Li, Y.K.; Ke, C.H.; Yu, H.; Chen, Z.Y.; She, H.Q.; Wang, R.C.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.G.; et al. Detail mineralogical study and geochronological framework of Bayan Obo (China) Nb mineralization recorded by in situ U-Pb dating of columbite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 165, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.K.; Ke, C.H.; Wang, D.H.; Zhao, Y.G.; She, H.Q.; Li, R.P.; Hao, M.Z.; Wang, A.J.; Deng, Z.; Gao, Y.P.; et al. Important progress in prospecting and exploration of iron ore in deep border area of Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 202–206, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.R.; Xu, Y.; Yang, K.F.; Zhang, J.E.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, L.L.; She, H.D.; Liu, S.L.; Xu, X.W.; Huang, S.; et al. Intrusive style three-dimensional morphology of carbonatite and REE, potential resources in the Bayan Obo giant deposit, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2022, 38, 2901–2919, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, L.F.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Chen, R.; Fan, H. Audio magnetotelluric view of the giant carbonatite-hosted Bayan Obo REE deposit, Inner Mongolia, northern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 172, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Sun, W.D.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.F. Geochemical constraints on the genesis of the Bayan Obo Fe–Nb–REE deposit in Inner Mongolia, China. Geochim. Et. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.H.; Jia, H.X.; Wang, D.S.; She, H.Q.; Li, J.W.; Chen, H. Fe, Mg, Sr-Nd-Pb, C-O isotopes and geochemical constraints on the genesis of Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposit, Inner Mongolia, northern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 180, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Yang, K.F.; Spandler, C.; Fan, H.R.; Zhou, M.F.; Hao, J.L.; Yang, Y.H. The effect of fluid-aided modification on the Sm-Nd and Th-Pb geochronology of monazite and bastnasite: Implication for resolving complex isotopic age data in REE ore systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 300, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ling, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Three-stage niobium mineralization at Bayan Obo, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, J.W.; Li, L.X.; Li, Y.K.; Rasmussen, B.; Ke, C.H. Magmatic-hydrothermal history of Bayan Obo REE-rich carbonatites revealed by monazite Th-Pb geochronology of the Wu Dyke. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 2685–2696, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, X.; Fan, H. New discovery of the Early Paleozoic carbonatite in Bayan Obo (China): Insights into the giant REE accumulation. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 170, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Zhang, J.E.; Fan, H.R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wang, Q.W.; Tan, X.B. Haooin-North Jianshan thrus fault and its constraints on the extension of ore-bearing carbonatite in the Bayan Obo area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2023, 39, 2910–2926, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Shu, Y.; Wei, C.Q.; Xie, Z. Paleoplate Tectonics and regional geology at Bayan Obo in northern Inner Mongolia. Geol. J. China Univ. 2002, 1, 46–61, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lu, H.B.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, X.P.; Huang, M.; Meng, Q.W. Characteristics of ductile shear zone in the northern Bayan Obo ore deposits, North China, and its structural significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 785–792, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, T.; Jia, H.Y.; Shang, H.S. Superimposed folding and deformation mechanism in Baiyunebo area, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Miner. Resour. South China 2003, 1, 23–26, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.E.; Fan, H.; Xiao, W.; Xu, X.; Wakabayashi, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K. Configuration of carbonatite constrained in preintrusion transpositional foliation in the Bayan Obo giant rare earth element deposit, China. Econ. Geol. 2024, 119, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.H.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Y.G.; Li, Y.K.; Xu, Z.Y.; Hao, M.Z.; Li, R.P.; Zhang, L. Ore-controlling structure and deep prospecting of the Bayan Obo large-sized REE-Nb-Fe ore deposit, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Bull. China 2021, 40, 95–109, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Wer, C.W.; Xu, C.; Shi, A.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Fan, C.X.; Kuang, G.X. Rare earth mineralization in Bayan Obo super-large deposit: A review. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 29, 014–028, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Zhai, M.G.; Guo, J.H.; Peng, P.; Liu, F.; Liu, S. LA-ICP-MS U-Ph geochronology of detrital zircons from the Huade Group in the northern margin of the North China Craton and its tectonic significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 193–211, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, M.G. Tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of North China Craton. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 24–36, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.C.; Sun, M.; Wilde, S.A.; Li, S.Z. A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic supercontinent: Assembly, growth and breakup. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 67, 91–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. A precise zircon Th-Pb age of carbonatite sills from the world’s largest Bayan Obo deposit: Implications for timing and genesis of REE-Nb mineralization. Precambrian Res. 2017, 291, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Geochemistry of Bayan Obo Deposit, 1st ed; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988; p. 513. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Wu, C.Y.; Yuan, Z.X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zheng, L. Geological Characteristics and Genesis Demonstration of Bayan Obo Deposit, 1st ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Geological and Mineral Exploration and Development Bureau of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Baiyunebo 1/200,000 Geological Map, Internal report. 1996. (In Chinese)
- Tan, L.K.; Shi, T.Z. Discovery and significance of small shelly fossils in the Bayan Obo group in Shangdu, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Rev. 2000, 46, 573–583, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.Y. The giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, China: Controversy and ore genesis. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.L.; Qu, Y.W.; Yang, Z.F.; Liang, P.; Zhong, R.C.; Wang, Q.W.; Xia, J.M.; Li, B.C. Giant Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE deposit: Progresses, controversarie sand new understandings. Miner. Depos. 2019, 38, 983–1003, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q.Y. Metallogenic Geological conditions and genesis of Bayunebo lron-Niobium REE deposit. Inn. Mong. Geol. 1997, 1, 1–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, T.H.; Zhang, P.S.; Tao, K.J.; Henderson, M.J.L. Geochemical characteristics and rare earth enrichment mechanism of rare earth element-rich carbonatite dykes in Bayan Obo. Miner. Depos. 1998, 17, 527–532, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Windley, B.F.; Xiao, W.J. Ridge subduction and slab windows in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Tectonic implications for the evolution of an accretionary orogen. Gondwana Res. 2018, 61, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Hao, J.; Zhai, M.G. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics 2003, 22, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, P.; Liu, D.Y.; Kröner, A.; Windley, B.F.; Shi, Y.R.; Zhang, F.Q.; Shi, G.H.; Miao, L.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China: Implications for continental growth. Lithos 2008, 101, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Hu, M.M.; Wu, C.; Wang, G.S.; Liu, C.F.; Cai, A.R.; Jiang, T. Coupled U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis of detrital zircons from Bayan Obo Group in Inner Mongolia: Constraints on the evolution of the Bayan Obo rift belt. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 2649–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geological Survey Institute of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Regional Geological Map and Report of Bayan Obo Mining Area in Baotou City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Internal report. 2022. (In Chinese)
- Smith, M.P.; Campbell, L.S.; Kynicky, J. A review of the genesis of the world class Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposits, Inner Mongolia, China: Multistage processes and outstanding questions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Li, S.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Niu, S.W.; Sun, S.F.; Guan, A.L.; Liang, W. The Geologico-tectonical characteristics in Baiyun Obo Region. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. Tianjin Inst. Geol. Miner. Resour. 1993, 28, 1–88, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Koppers, A. ArArCALC-software for 40Ar/39Ar age calculations. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, Y.Q. Late Cenozoic episodic uplifting in southeastern part of the Tibetan plateau-evidence from Ar-Ar thermochronology. Acta Perologica Sin. 2006, 22, 867–872, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, L.G.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Selby, D.; Li, X.H. Paleozoic carbonatites controlled rare-earth-elements mineralization at Bayan Obo. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eads9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.S.; Compston, W.; Sirombe, K.N. Zircon from the east orebody of the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE deposit, China, and SHRIMP ages for carbonatite-related magmatism and REE mineralization events. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2014, 168, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Fan, H.; Pirajno, F.; Li, X. The Bayan Obo (China) giant REE accumulation conundrum elucidated by intense magmatic differentiation of carbonatite. Geology 2019, 47, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.Q.; Zhang, Z.X. The ductile shear deformation and its tectonic background in Middle-Proterozoic, central Inner Mongolia. Geoscience 2004, 18, 497–504, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Xu, C.; Smith, M.P.; Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Brenna, M.; Kynický, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, Y.; Deng, M.; Tang, H. Genesis of the world’s largest rare earth element deposit, Bayan Obo, China: Protracted mineralization evolution over ∼1 b.y. Geology 2018, 46, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.K.; Sun, J.; Pan, C.X. Sm-Nd isotopic constraints on rare-earth mineralization in the Bayan Obo ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Tatsumoto, M.; Li, X.; Premo, W.R.; Chao, E.C.T. A precise 232Th-208Pb chronology of fine-grained monazite: Age of the Bayan Obo REE-Fe-Nb ore deposit, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3155–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, E.C.T.; Back, J.M.; Minkin, J.A.; Tatsumoto, M.; Wang, J.; Conrad, J.E.; Makee, E.H.; Hou, Z.; Meng, Q.; Huang, S. The sedimentary carbonate-hosted giant Bayan Obo REE-Fe-Nb ore deposit of Inner Mongolia, China: A corner¬stone example for giant polymetallic ore deposits of hydrothermal origin. US Geol. Surv. Bull. 1997, 2143, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.S.; Gao, L.; Du, A.D.; Sun, L.Y. The Re-Os isotopic age of molybdenite from Bayan Obo REE ore deposit. Miner. Depos. 1996, 15, 188–191, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.T.; Wang, R.C.; Zhou, M.F.; Wu, F.Y. Cassiterite and Sn mineralization in the giant Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE deposit, Northern China. Am. Mineral. 2025, 110, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.D.; Yang, X.; Santosh, M.; Liu, Y.; Ling, M. New data of the Bayan Obo Fe–REE–Nb deposit, Inner Mongolia: Implications for ore genesis. Precambrian Res. 2015, 263, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, H.Y.; Jiang, S.Y.; Simonetti, A.; Xu, C.; Zhang, W. The formation of the ore-bearing dolomite marble from the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia: Insights from micron-scale geochemical data. Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F.; Wang, K.Y.; Liu, Y.S. Geochronology framework of late Paleozoic dioritic-graniticplutons in the Bayan Obo area, Inner Mongolia, and tectonic significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 2933–2938, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.C.; Zhan, Y.X.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, K.Y. The REE mineralization and remobilization history of the giant Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China: Constraint from in-situ Sm-Nd isotopes of REE minerals. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2022, 38, 2920–2932, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ling, X.X.; Wu, L.G.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Meng, W.X.; Yan, G.Y.; Li, X.Y. Lead-lead dating reveals Permian remobilization of niobium mineralization at Bayan Obo. Econ. Geol. 2024, 119, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, T.R.; Luo, H.L.; He, Y.K.; Jing, X. Geochemistry of Huheengeer complex, Bayan Obo region, Inner Mongolia and it’s tectonic lmplications. Geol. J. China Univ. 2008, 14, 29–38, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ling, M.X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, J.; Li, L.Q.; Li, C.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Sun, W. The Permian-Triassic granitoids in Bayan Obo, North China Craton: A geochemical and geochronological study. Lithos 2014, 190, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Song, C.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhou, L.L.; Zhang, Z.F.; Hu, Q.E. A comprehensive comparative study of geological characteristics as well as aeromagnetic and aeroradiometric features of the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe depoits and their implications for prospecting work. Geol. China 2016, 43, 594–606, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tian, P.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Xiao, Y.L.; Yuan, W.M.; He, Z.F. In Situ Monazite U–Pb Ages in thin sections from the giant Bayan Obo Fe–REE–Nb deposit, Inner Mongolia: Implications for formation sequences. Minerals 2022, 12, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jia, X.Q.; Wei, W.; Jin, H.L. Characteristies and geological significance of geochronologic results from the Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Technol. Bull. 2024, 43, 63–73, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Windley, B.F.; Alexeiev, D.; Xiao, W.J.; Kröner, A.; Badarch, G. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian orogenic belt. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2007, 164, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W. Geodynamic processes and metallogenesis of the Central Asian and related orogenic belts: Introduction. Gondwana Res. 2009, 16, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizenhöfer, P.R.; Zhao, G.C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M. Final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean along the Solonker Suture Zone: Constraints from geochronological and geochemical data of Permian volcanic and sedimentary rocks. Tectonics 2014, 33, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, M.M.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Allen, M.B.; Su, L. Ophiolites in the Xing’an-Inner Mongolia accretionary belt of the CAOB: Implications for two cycles of seafloor spreading and accretionary orogenic events. Tectonics 2015, 34, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, S.A. Final amalgamation of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt in NE China: Paleo-Asian Ocean closure versus Paleo-Pacific plate subduction -a review of the evidence. Tectonophysics 2015, 662, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.P.; Zhong, H.; Yang, Y.J.; Jiang, B.; Qian, C.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhao, C. Research progress on the subduction accretion complex: Reconstruction of the tectonic framework of the Great Xing’an Range. Earth Sci. Front. 2022, 29, 094–114, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Shan, H.S.; Tao, J.X.; Baoyin, W.L.J.; Hao, X.Y. The arc- basin system and tectonic significance of Early Paleozoic in Baiyun’ ebo area Inner Mongolia. Geol. Surv. Res. 2003, 3, 160–168, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.Y.; Bayin, W.L.J.; Zhang, Y.Q. Characteristics and tectonic significance of the Wude suture zone in northern Damaoql, Inner Mongolia. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 2003, 30, 30–33, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, J.X. Bainaimiao arc as an exotic terrane along the northern margin of the North China Craton: Evidences from petrography, zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the Early Devonian deposits. Tectonics 2019, 38, 2606–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, G.S.; Li, H.Y.; Yu, Y.S.; Liu, C.F.; Liu, W.C. Characteristics of Bainaimiao thrust belt along central Inner Mongolia in North China and its geological significance. Geotecton. Et. Metallog. 2018, 42, 1–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, C.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Dong, T.; Wu, H. From oblique arc-continent collision to orthogonal plate subduction in the southeastern central Asia Orogenic Belt during Paleozoic: Evidence from superimposed folds at the northern margin of the north China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 200, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zhao, Y.; Song, B.; Yang, Z.Y.; Hu, J.M.; Wu, H. Carboniferous granitic plutons from the northern margin of the North China block: Implications for a late Palaeozoic active continental margin. J. Geol. Soc. 2007, 164, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, Z.H.; Xu, Z.Y.; Peng, X.D.; Dong, X.J.; Sha, Q.; Wan, W.Q. Components of the Bainaimiao thrust and its structural features. J. Jilin Univ. 2012, 42, 309–319, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, R.; Liu, J.; Hui, J.; Niu, P.; Yun, L.; Zhao, S.; et al. Determination of an intracontinental transform system along the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt in the latest Paleozoic. Am. J. Sci. 2022, 322, 851–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, J.; Zhang, K.J.; Zhang, J.; Qu, J.F.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhao, H.; Niu, P.F. Middle-late Permian high-K adakitic granitoids in the NE Alxa block, northern China: Orogenic record following the final closure of Paleo-Asian oceanic branch? Lithos 2021, 400–401, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; Qu, J.F.; Zhang, Y.P.; Niu, P.F.; Hui, J.; Yun, L. Kinematics and geochronology of Late Paleozoic–Early Mesozoic ductile deformation in the Alxa Block, NW China: New constraints on the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithoshpere 2021, 2021, 3365581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cunningham, D.; Qu, J.F.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, R.G.; Niu, P.F.; Hui, J.; Yun, L.; Zhao, S.; et al. Poly-phase accretionary, collisional and intraplate tectonism in the Langshan region of the Alxa Block, China: Unravelling the complex structural evolution of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Res. 2022, 105, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Liang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.M. Dectile shear zone and gold deposits in Wuchuan-Guyang-Dashetai, Inner Mongolia. J. Jiling Univ. 1990, 20, 399–406, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.R.; Wei, C.J.; Chu, H. Multiple metamorphic events recorded in the metamorphic terranes in central Inner Mongolia, Northern China: Implication for the tectonic evolution of the Xing’an-Inner Mongolia Orogenic Belt. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 167, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, J.F.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.H.; Zheng, R.G.; Yun, L.; Yang, Y.Q.; et al. The nature and evolution of the Xar Moron tectonic belt in the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints from deformation and low-temperature thermochronology. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2021, 41, 190–217, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.A.; Li, S.C. Late Triassic extensional deformation and magmatism in the eastern part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraint from 40Ar/39Ar and zircon U-Pb geochronology. Acta Petrol. Sircica 2020, 36, 2447–2462, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wan, J.L. Collision-Induced Late Permian-Early Triassic transpressional deformation in the Yanshan tectonic belt, North China. J. Geol. 2014, 122, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, W.S.; Han, B.F.; He, G.Q.; Huang, B.L. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Dashigou biotite-K-felspar granites in Shangdu, Inner Mongolia, and its significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 591–596, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.C.; Zhao, F.O.; Li, H.M.; Sun, L.X.; Miao, L.C.; Ji, S.P. Zircon SHRlMP U-Ph age of the dioritic rocks from northern Hebei: The geological records of late Paleozoic magmatic arc. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 597–604, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.J.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Qi, J.H.; Dai, F.H.; Zhang, G.Y.; Pang, Y.C.; Wu, B. Foundation and geological significance of adakitic granite at Guyang of Inner Mongolia. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2008, 33, 755–763, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Tang, S.H.; Yuan, Z.X.; Bai, G.; Wang, J.H. The Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopic systems of the dolomites in the Bayan Obo ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2001, 17, 637–642, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Tang, S.H.; Wang, J.H.; Yuang, Z.X.; Bai, G. New data for ore-forming age of the Bayan Obo REE ore deposit, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1994, 1, 85–94, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.C.; Zhan, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Q. Study on heat events of ore-forming Bayan Obo deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1994, 1–2, 95–100, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Chen, F.K.; Yang, K.F.; Wang, K.Y. Instrusive age of No.1 carbonatite dyke from Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit, Inner Mongolia: With answers to comment of Dr. Le Bas. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 517–518, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Analysis on the oreforming time and genesis of the Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit: With a discussion on the mass extinction at the P-T boundary and “AMH Orogeny”. Geol. Rev. 2018, 66, 299–345, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Yuan, Z.X.; Tang, S.H. Age and Geochemistry of Bayan Obo Deposit, 1st ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Yu, Y.; Yang, B.; Li, X.H. Geochemical characteristics and in-situ Rb-Sr dating of mica in the Bayan Obo deposit: Implications for the controls on REE-Nb ore formation. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2025, 41, 1149–1169, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.L.; Wu, T.R.; Zhao, L.; He, Y.K.; Jin, X. Geochemical characteristics of Bayinzhurihe pluton and its tectonic significance, Bayan Obo, Inner Mongolia. Geol. J. China Univ. 2013, 19, 123–132, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Petrogenesis and Magma Source of Wengen a Mafic-Ultramafic Intrusion, Inner Mongolia, China. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.D.; Ren, Y.C. Muitiple lines of evidence for establishing the mineral paragenetic sequence of the Bayan Obo rare earth ore deposit of Inner Mongolia, China. Geol. Prospect. Theory 1991, 6, 1–17, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Qiao, X.F.; Liu, D.Y.; Peng, Y. Direct determination of the Pb-Pb age of carbonate rocks of the Sailinhudong Formation of Inner Mongolia. Reg. Geol. China 1995, 4, 348–352, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Fang, A.; Dong, C.; Hu, F. Fenitized wall rock geochemistry of the first carbonatite dyke at Bayan Obo, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Williams, I.S.; Teng, F.Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Ding, X.; Wei, G.J.; Xie, L.H.; Deng, W.F.; Sun, W.D. Formation of the world’s largest REE deposit through protracted fluxing of carbonatite by subduction-derived fluids. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F.; Pirajno, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.Y. Integrated U–Pb and Sm–Nd geochronology for a REE-rich carbonatite dyke at the giant Bayan Obo REE deposit, Northern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Xie, Y.; Han, J.; Xia, J.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Multi-Stage REE mineralization in the Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposit: Constraints from biotite and apatite geochemistry. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 174, 106312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.P.; Henderson, P.; Campbell, L.S. Fractionation of the REE during hydrothermal processes: Constraints from the Bayan Obo Fe-REE-Nb deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 3141–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Sun, J.F.; Xie, L.W.; Fan, H.R.; Wu, F.Y. Determination of Nd isotope in geological samples by laser in situ plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICPMS). Sci. China Press 2008, 53, 568–576. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Wang, K.Y. Intrusion sequence of carbonatite dykes and REE accumulation mechanism in Bayan Obo district. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 1523–1529, (In Chinses with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.F.; Du, A.D.; Xie, Z. Re-Os dating of pyrite from Bayan Obo super-large rare earth-niobium-iron deposit. Sci. Instrum. News 2005, 50, 172–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.Z.; Wen, H.J.; Qin, J.C. The precise dating of Haixi granite and the discovery of Yanshan granite in Bayan Obo mining area. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2011, 31, 631–632. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Santosh, M.; Hu, F.F.; Wang, K.Y. Mesoproterozoic carbonatitic magmatism in the Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia, North China: Constraints for the mechanism of super accumulation of rare earth elements. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 40, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; She, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ke, C.; Zhao, J.; Ma, S.; et al. 40Ar-39Ar Chronometry Supports Multi-Stage Tectonic Thermal Events in the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE Deposit. Minerals 2025, 15, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070683
Gao X, Wang D, Li H, Li Y, She H, Yang J, Zhang L, Ke C, Zhao J, Ma S, et al. 40Ar-39Ar Chronometry Supports Multi-Stage Tectonic Thermal Events in the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE Deposit. Minerals. 2025; 15(7):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070683
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xinke, Dongsheng Wang, Hongying Li, Yike Li, Hongquan She, Jianjun Yang, Li Zhang, Changhui Ke, Jian Zhao, Shouxian Ma, and et al. 2025. "40Ar-39Ar Chronometry Supports Multi-Stage Tectonic Thermal Events in the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE Deposit" Minerals 15, no. 7: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070683
APA StyleGao, X., Wang, D., Li, H., Li, Y., She, H., Yang, J., Zhang, L., Ke, C., Zhao, J., Ma, S., Ren, C., & Yin, F. (2025). 40Ar-39Ar Chronometry Supports Multi-Stage Tectonic Thermal Events in the Bayan Obo Fe-Nb-REE Deposit. Minerals, 15(7), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15070683