Abstract
In order to clarify the pore evolution and coupling characteristics with hydrocarbon charging in the deep-buried ultra-tight sandstone reservoirs of the second member of Xujiahe Formation (hereinafter referred to as the Xu 2 Member) on the eastern slope of the Western Sichuan Depression, this study integrates burial history and thermal history with analytical methods including core observation, cast thin section analysis, scanning electron microscopy, carbon-oxygen isotope analysis, and fluid inclusion homogenization temperature measurements. The Xu 2 Member reservoirs are predominantly composed of lithic sandstones and quartz-rich sandstones, with authigenic quartz and carbonates as the main cementing materials. The reservoir spaces are dominated by intragranular dissolution pores. The timing of reservoir densification varies among different submembers. The upper submember underwent compaction during the Middle-Late Jurassic period due to the high ductility of mudstone clasts and other compaction-resistant components. The middle-lower submembers experienced densification in the Late Jurassic period. Late Cretaceous tectonic uplift induced fracture development, which enhanced dissolution in the middle-lower submembers, increasing reservoir porosity to approximately 5%. Two distinct phases of hydrocarbon charging are identified in the Xu 2 Member. The earlier densification of the upper submember created unfavorable conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation. In contrast, the middle-lower submembers received hydrocarbon charging prior to reservoir densification, providing favorable conditions for natural gas enrichment and reservoir formation. Three sweet-spot reservoir development patterns are recognized: paleo-structural trap + (internal source rock) + source-connected fracture assemblage type, paleo-structural trap + internal source rock + late-stage fracture assemblage type, and paleo-structural trap + (internal source rock) + source-connected fracture + late-stage fracture assemblage type.
1. Introduction
With the increasing maturity of conventional oil and gas exploration, tight sandstone gas as an important unconventional natural gas resource has gradually become a research hotspot for geologists [,,]. Tight sandstone reservoirs exhibit complex diagenetic alterations and strong reservoir heterogeneity [,,], so an accurate reconstruction of their pore evolution process is crucial for assessing reservoir availability during hydrocarbon accumulation and improving exploration success rates.
Previous studies on porosity evolution in deep-burial tight sandstone reservoirs have primarily focused on hydrocarbon charging periods through fluid-inclusion homogenization temperature analysis, and on combining hydrocarbon emplacement history [,]. Lithology, provenance characteristics, diagenetic processes, and abnormal high pressures have been identified as key controlling factors in porosity evolution. By investigating water–rock interactions and diagenetic reactions during sandstone burial [,], researchers have quantified the impacts of compaction, cementation, and dissolution on pore space development and their temporal relationships [,,]. This approach has enabled reconstructing porosity evolution characteristics of sandstone reservoir [,]. Recent study advancements, including inversion methods using recent reservoir pore types and cement content to inverse porosity evolution and to establish quantitative diagenetic models, have been increasingly applied []. Some scholars have employed physical simulation experiments of diagenetic processes to reproduce porosity evolution under controlled experimental conditions [,].
The Sichuan Basin represents a significant repository of tight sandstone gas resources in China, with proven reserves and ongoing exploration activities highlighting its potential [,]. Within the western Sichuan Depression, commercial gas discoveries such as the Xinchang, Dayi, and Qiongxi gas fields in the Xujiahe Formation have demonstrated the region’s hydrocarbon-bearing capacity [,]. Notably, the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation, abbreviated as the Xu 2 Member, on the eastern slope of this depression exhibits exceptional geological characteristics, with maximum paleo-burial depths exceeding 6000 m, classifying its reservoirs as ultra-deep and ultra-tight sandstones [,]. Previous investigations in western Sichuan have primarily focused on the Xinchang and Dayi areas, and secondary porosity development [], chlorite-coated grain preservation [], and tectonic fracture networks [] constitute key factors controlling reservoir quality. However, critical knowledge gaps exist in porosity evolution mechanisms in the eastern slope’s ultra-compact systems, which fundamentally constrains effective exploration and development of deep tight-gas resources in this frontier area. The study uses a systematic investigation of the Xu 2 Member’s ultra-tight sandstone reservoirs through an integrated analytical approach combining burial/thermal history reconstruction with advanced petrographic characterization (casting thin sections, SEM, isotopic analysis, and fluid inclusion microthermometry). This research establishes a chronostratigraphic framework for reservoir evolution, quantitatively delineates diagenetic modification phases, and identifies distinct sweet-spot development patterns. These findings can provide critical insights for predicting favorable exploration targets in ultra-deep tight sandstone systems, and can advance methodological frameworks for reservoir porosity evolution studies in similar geological settings.
2. Geological Setting
The study area encompasses the Zhongjiang and Huilong structural units in the eastern slope of the western Sichuan Depression. This transitional zone is characterized by a north-northeast-oriented slope tectonic setting, and is bound by the Chuanzhong Paleo-uplift to the east and the Longquanshan thrust belt to the west []. The structural framework, characterized by high-angle reverse faults with predominant SN and NE trends, creates effective migration pathways through fault–sand coupling systems, particularly facilitating vertical hydrocarbon transport from the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation source rocks [] (Figure 1a). Stratigraphically, the Upper Triassic succession comprises, in ascending order: the Ma’antang (T3m), Xiaotangzi (T3t), and Xujiahe (T3x) formations. Within the study area, the 300–500m thick Xujiahe Formation is subdivided into four members (Xu 2 to Xu 5), with the Xu 2 Member (T3x2) being the principal reservoir unit. This member demonstrates vertical heterogeneity through three distinct submembers: lower (fluvial-dominated), middle (transitional), and upper (wave-dominated shoreface), reflecting progressive transgressive–regressive cycles (Figure 1b).
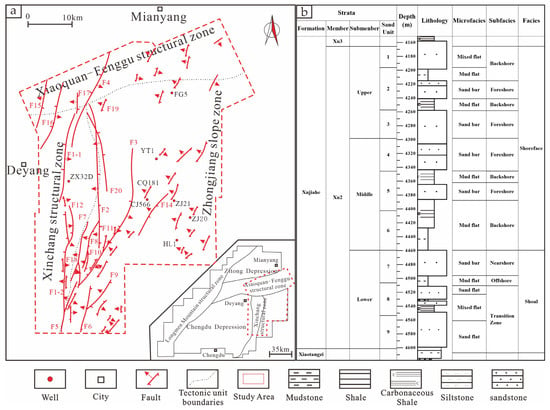
Figure 1.
The location (a) and sedimentary microfacies map (b) of the second member of the Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression.
3. Samples and Methods
Core samples were collected from three wells in the study area. A total of 210 thin sections were prepared for analysis. The experimental workflow comprised five key analyses: (1) thin-section petrography, (2) physical property characterization, (3) scanning electron microscopy (SEM), (4) carbon and oxygen isotope analysis, and (5) fluid inclusion microthermometry.
The sections were triple polished, blue epoxy resin was injected, and one-third was dyed with alizarin red. Thin-section petrography was conducted using Leica DM4500P polarized light microscope (Leica, Germany) following the standard methodology for sedimentary rock analysis []. The observations include the grain size, minerals, pore types, and porosity distribution of reservoir rocks at the millimeter to micrometer scale.
SEM analysis was performed with a Quanta250FEG (FEI, America, San Jose, CA, USA, resolution: 1.04 nm, magnification: 15 to 300,000 times, acceleration voltage: 0.2 to 30 kV, and detection current: 0.3 to 22 nA.) field emission environmental scanning electron microscope, operated in accordance with the standard methods for SEM analysis of geological samples []. The sample needs to be cut into 1 cubic centimeter. The cut surface must be a fresh rock surface. After the surface is gold-plated, it can be observed under an SEM. This technique overcomes the resolution limitations of optical microscopy and enables mineral identification through energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS).
To investigate porosity evolution mechanisms, advanced geochemical methods were applied. (1) Carbon and oxygen isotope analysis: Laser ablation sampling of targeted areas was conducted, and the sample was ground to 200 mesh, and then dried. The MAT253 gas isotope mass spectrometer (Finnigan, Germany) was used to directly measure the isotopic composition of the CO2 produced. The SMOW standard was used, with the standard sample being GBW04405 []. (2) Fluid inclusion microthermometry: The instrument used was the Linkam THMS-600 (Linkam Scientific Instruments, Redhill, UK) heating-freezing stage. The temperature measurement range was −120 °C to +500 °C. The room temperature in the laboratory was 25 °C and the humidity was 35%. Selected thin sections were heated on a calibrated microscope heating stage to determine the uniform temperature and freezing point temperature [].
4. Results
4.1. Rock Mineralogical Characteristics
There are differences in the characteristics of reservoir rock types in each submember of the Xu 2 Member of the eastern slope of the Western Sichuan Depression. The upper submember predominantly comprises lithic sandstone, with a quartz content range of 51%–73% (avg. 60%) and a lithic fragments range of 18%–45% (avg. 33.2%). The middle submember shows increased feldspar content (avg. 7.1%), characterized by feldspathic lithic sandstone to lithic quart sandstone, containing 54%–74% quartz (avg. 67.2%) and 18%–41% lithic fragments (avg. 25.6%). The lower submember is dominated by lithic quartz sandstone, displaying much more quartz content (72%–83%, avg. 80.4%) with reduced lithic components (10%–20%, avg. 14.2%) (Figure 2) [].
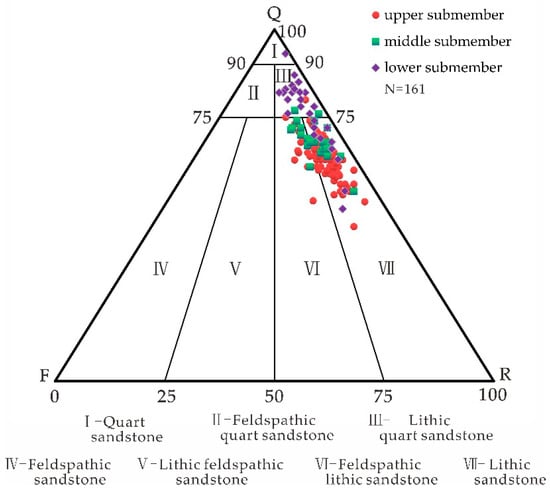
Figure 2.
Classification of reservoir rocks in the Xu 2 Member in the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression.
4.2. Pore Characteristics
The reservoir space in the Xu 2 Member of the study area is dominated by intragranular pores resulting from the dissolution of feldspars and lithic fragments (Figure 3a–c), followed by fractures, and residual primary intergranular pores are rare. Intragranular pores, predominantly tectonic fractures, are locally developed in the Xu 2 Member, predominantly cross-cutting lithic fragments under a polarized light microscope (Figure 3d–e). Enhanced feldspar dissolution can be observed in fracture-developed zones (Figure 3f).

Figure 3.
Typical photos of reservoir space in Xu 2 Member of Xujiahe Formation in eastern slope of Western Sichuan Depression. (a) Lithic fragment dissolution (red arrows), ZJ20, 4196.58 m, PPL. (b) Feldspar dissolution (red arrows), ZJ20, 4204 m, XPL. (c) Feldspar dissolution (red arrows), ZJ20, 4069.34 m, PPL. (d) Fractures (red arrows), ZJ20, 4195.76 m, PPL. (e) Fracture (red arrow) cutting mudstone fragments, CJ566, 4346.11 m, PPL. (f) Fracture (red arrow) and feldspar dissolution around fracture (yellow arrow), ZJ20, 4197.97 m, PPL.
The reservoir spaces of each submember of the Xu 2 Member have some differences. The reservoir space in the upper submember is dominated by intragranular pores, with a small amount of cracks that developed and an average areal porosity of 3.6%. In the middle submember, the reservoir space has more fractures in addition to intragranular pores, and the average areal porosity is 3.41%. The reservoir space in the lower submember is dominated by intragranular pores, with a small number of residual primary intergranular pores, and the average areal porosity is 5.5%, which is significantly higher than that in the middle and upper submembers (Table 1).

Table 1.
The reservoir space data in the Xu 2 Member of the Xujiahe Formation on the eastern slope of the Western Sichuan Depression.
4.3. Physical Properties
The physical properties of the submembers in the Xu 2 Member vary from each other. The upper submember exhibits a porosity range of 4%–6% with low permeability. The middle submember shows improved porosity and slightly enhanced permeability. The lower submember demonstrates the most favorable reservoir quality, with porosity exceeding 8% and permeability exceeding 0.1 mD. Porosity–permeability correlations vary significantly among submembers: weak correlations can be observed in the upper and middle submembers, while the lower submember displays stronger correlation trends (Figure 4).
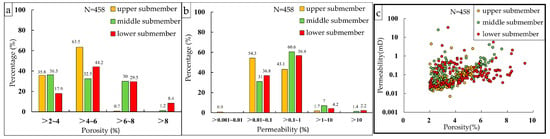
Figure 4.
The reservoir physical property distribution histograms of the Second Member of Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression ((a) porosity distribution histogram; (b) permeability distribution histogram; and (c) porosity and permeability cross plot).
4.4. Type of Diagenesis
4.4.1. Compaction Effect
The Xu 2 Member in the study area exhibits significant mechanical compaction and pressure dissolution, showing linear contact and severe deformation of the ductile components (e.g., mica) (Figure 5a). Intense compaction has eliminated primary intergranular pores, and the quartz overgrowths, occurring due to the pressure dissolution at some intervals, serve as critical contributors to reservoir densification. These combined processes have substantially reduced both pore connectivity and reservoir quality.
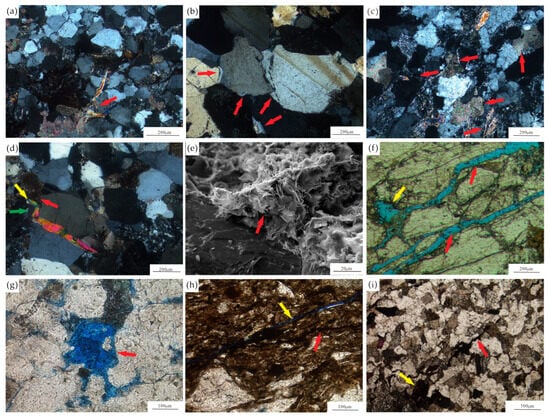

Figure 5.
Optical and SEM images showing reservoir diagenesis in Second Member of Xujiahe Formation on east slope of Western Sichuan Depression. (a) Strong mica deformation (red arrow), HL1, 4523 m, XPL. (b) Multiple phases of quartz enlargement (red arrows), HL1, 4344.7 m, XPL. (c) Carbonate (red arrows), ZJ20, 4322 m, XPL. (e) Filamentous illite (red arrow), HL1, 4340.5 m, SEM. (d) Early to late: quartz enlargement (green arrow) → carbonate (red arrow) → mica deformation (yellow arrow), CJ566, 4346.11 m, XPL. (f) Unfilled cracks (red arrows) and feldspathic holes at crack margins (yellow arrow), HL1, 4342.63 m, PPL. (g) Feldspathic alteration (red arrow), ZJ20, 4 300.14 m, PPL. (h) Two phases of cracks, one filled with asphalt (red arrow) and one unfilled (yellow arrow), ZJ20, 4294.01 m, PPL. (i) Asphalt-filled cracks (red arrow) and asphalt agglomerates (yellow arrow), ZJ20, 4 294.34 m, PPL.
4.4.2. Authigenic Mineral Precipitation
The Xu 2 Member contains authigenic quartz, carbonate minerals, and clay minerals. Authigenic quartz is extensively developed, exhibiting two primary modes of occurrence: overgrowths and pore-filling cement. Multistage quartz overgrowths are widely observed (Figure 5b), with some displaying unevenly thickened rim textures. Pore-filling quartz predominantly occupies intergranular pores, significantly reducing pore–throat connectivity. Carbonate minerals including dolomite and calcite are also highly developed in the Xu 2 Member (Figure 5c), primarily like intergranular pore filling and the replacement of detrital particles. Microscopic observations reveal that carbonate cementation occurred prior to quartz overgrowth and mica deformation (Figure 5d). Authigenic clay minerals in the Xu 2 Member are dominated by illite, and filamentous illite is commonly observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Figure 5e).
4.4.3. Dissolution
Dissolution serves as a crucial constructive diagenetic process during the formation of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Xu 2 Member, significantly enhancing the physical properties of the reservoir [,], with high-quality reservoirs predominantly developing in the zones of intense dissolution []. In the study area, two distinct types of dissolution pores are identified. One is casting pores, which are generated by intense dissolution of feldspar or lithic fragments along fractures, and often contain minor dissolution residues within the pores, with this dissolution pattern demonstrating pronounced improvements to reservoir quality (Figure 5f). Another type occurs along particle margins, creating intergranular dissolution-enlarged pores that modify pore–throat configurations (Figure 5g). Both dissolution mechanisms contribute to the development of reservoir heterogeneity, particularly through selective dissolution that preferentially modifies specific mineral components and structural features.
4.4.4. Tectonic Rupture and Hydrocarbon Injection
Tectonic fractures in the Xu 2 Member exhibit significant development characteristics, which can be seen to have different filling phases through microscopical observation. The early fractures are completely filled with bitumen while the later fractures remain unfilled (Figure 5h). The hydrocarbon injection exhibits phased evolution, where Phase 1, containing heavy hydrocarbons, has undergone metamorphosis into bitumen. The bitumen manifests in two primary modes: striped distributions along fractures (Figure 5i) and patchy occurrences within the rock framework, reflecting different migration pathways and diagenetic environments during hydrocarbon emplacement.
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Reservoir Pore Evolution Characteristics
5.1.1. Chronology of Reservoir Porosity
- (1)
- Formation period of major authigenic minerals
The initial porosity was perhaps mainly intergranular and depositional, which was reduced down the line as different diagenetic/tectonic post depositional events occurred. The key to analyzing pore evolution timing lies in accurately constraining the timing of major diagenetic events, particularly the formation stages of dominant authigenic minerals. In the Xu 2 Member of the eastern slope in the Western Sichuan Depression, quartz and carbonate minerals are the most significant authigenic minerals. Determining their formation time is critical for reconstructing porosity evolution history. This can be done based on fluid inclusion homogenization temperatures from authigenic quartz (Figure 6), which exhibits a broad range of formation temperatures in the Xu 2 Member.
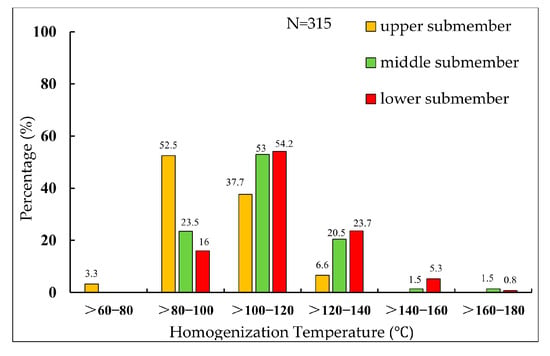
Figure 6.
The homogenization temperature distribution histogram of the homogeneous quartz oil and gas inclusions in the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression.
Combined with the thermal and burial history of the study area [], the authigenic quartz of the first phase can be interpreted to have formed during the Late Jurassic period, while the second phase occurred in the Early Cretaceous period. Petrographic observations reveal that the early quartz cement constitutes the earliest authigenic phase in the Xu 2 Member, predating carbonate cementation. The homogenization temperatures of fluid inclusions (<80 °C) suggest the quartz cement precipitated at burial depths < 2000 m. Stable isotope analyses of the authigenic carbonates show δ18OSMOW values ranging from −8.4‰ to −12.7‰ for early-stage cements and −15.2‰ for later-stage cements, and the corresponding precipitation temperatures calculated using these isotopic values are 82.8–118 °C and 144.1 °C, respectively [].
Combined with the paleotemperature gradient, it was determined that the earliest phase of carbonate cementation phases is slightly later than the early quartz cement, which is consistent with the microscopic characteristics growing outside of the caliche. The second phase occurred around the Late Jurassic period, and the burial depth was close to 5000 m at the time of the precipitation of the latest-stage dolomite.
- (2)
- Analysis of dissolution period
Determination of dissolution period was primarily based on paleothermometric data from dissolution byproducts and their distribution characteristics coupled with diagenetic features. In the Xu 2 Member, overgrowth quartz and illite cements constitute the main products of feldspar dissolution. Under the microscope, it was found that feldspar is strongly dissolved near cracks, and is basically not dissolved in areas without fracture development. The main reason is that the acidic fluid brought by a fracture leads to strong feldspar dissolution. The present reservoirs in the study area of the Xu 2 Member were formed late, and were formed by dissolution during the tectonic movement of the late Yanshan–Xishan period. In addition, another phase of dissolution in the reservoir of the Xu 2 Member occurred earlier, and the paleotemperature of the authigenic quartz occurred mainly in the Middle Jurassic period.
- (3)
- Diagenetic sequence
Based on the interconnected relationships among the diagenetic phenomena observed in the Xu 2 Member in the study area, the diagenetic sequence of reservoir sandstone has been established (Figure 7).
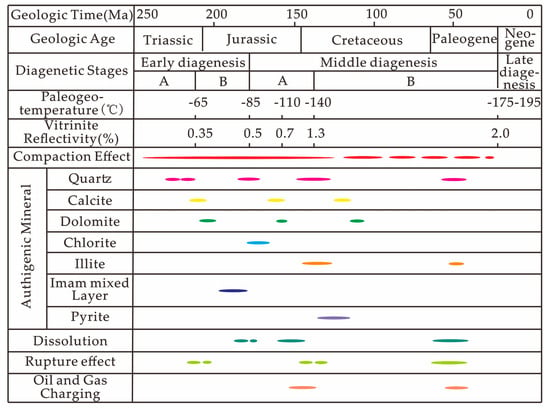
Figure 7.
The diagenetic sequence of the Second Member of Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression. Different colors merely represent different types in front of the table. Uniform color but different sizes represent the duration of diagenesis.
5.1.2. Quantitative Pore-Type Characterization of Reservoir Pore
A thin-section line counting method was utilized for statistical analyses, and authigenic minerals were classified into distinct morphological categories. For instance, authigenic quartz was categorized into overgrowth, pore-filling, and other forms. Statistical quantification of both authigenic mineral assemblages and pore types was achieved (Table 2).

Table 2.
Statistics of reservoir interstitial and pore contents in each submember of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression (N = 40).
Based on statistically derived data for authigenic quartz, illite, and dissolution reaction characteristics (e.g., feldspars), the secondary porosity magnitude can be quantified. The current reservoir secondary porosity was derived from quantitative analysis of casting thin section porosity (Table 2). Compaction-destroyed porosity at each diagenetic stage was determined through porosity evolution modeling and specific- stage proportion of secondary porosity in total pore space [,,].
5.1.3. Characterization of Reservoir Pore
Based on the above analysis results, the porosity evolution characteristics of the three submembers of the Xu 2 Member can be performed inversely.
From the beginning of deposition to the end of the Late Triassic period, the porosity of the reservoirs in the upper, middle, and lower submembers decreased from initial values of 38% to 11%, 16%, and 18%, respectively. The upper submember exhibited the most significant porosity reduction, primarily driven by its higher abundance of ductile components (e.g., clay-rich matrix and mudstone intraclasts), which enhanced compaction-induced pore destruction.
Toward the end of the Middle Jurassic period, porosity continued to decrease, with the upper submember reservoir declining to 3%. The middle and lower submembers exhibited a relatively smaller reduction, both decreasing to 9%, which may be attributed to being near the underlying source rocks. Fault-driven hydrocarbon migration may have inhibited compaction and pore destruction. This stage represents the primary phase of densification for the upper submember.
Toward the end of the Late Jurassic period, the reservoirs were predominantly affected by pressure solution due to the continued increases in burial depth and tectonic compression. Consequently, the original reservoir pore systems were nearly compromised, with their residual porosity reduced to extremely low values. This stage represents a phase of intense densification in the upper submember and moderate densification in the middle and lower submembers of the study area.
By the late Yanshan–Xishan tectonic stage, in the regions characterized by well-developed fractures and rift-related fault systems, the petrophysical properties of sandstone reservoirs were significantly enhanced, with their porosity increasing to approximately 5%.
5.2. Hydrocarbons Charge History
In the study area, significant differences in hydrocarbon charging are observed among the submembers of the Xu 2 Member. The mean homogenization temperatures of the hydrocarbon inclusions in the upper submember range from 60 °C to 140 °C, with the modal values concentrated between 80 °C and 120 °C. In contrast, the middle and lower submembers exhibit markedly higher temperatures, spanning 60 °C to 200 °C, where the predominant thermal regime occurs between 100 °C and 120 °C.
Combined with the burial and thermal histories of the study area (Figure 8) [], the main hydrocarbon charging episodes can be determined. The upper submember experienced two primary charging phases: 180–150 Ma (corresponding to the Middle-Late Jurassic period) and 25 Ma to the present (Neogene to Quaternary periods). In contrast, the middle and lower submembers were predominantly charged during 200–130 Ma (the Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous periods) and 60 Ma to present (Paleocene to Holocene periods).
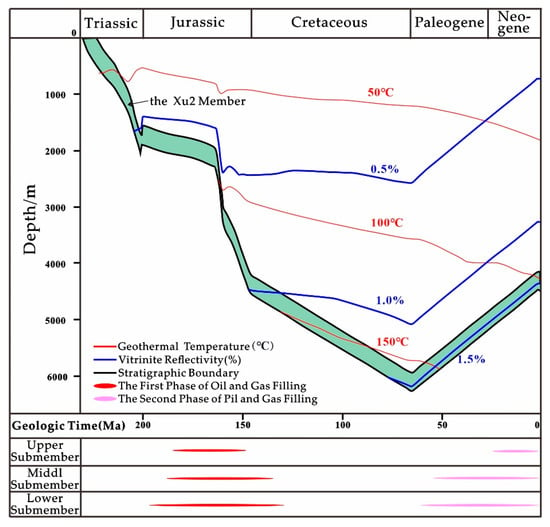
Figure 8.
The burial history–thermal history and hydrocarbon charging period of the Second Member of the Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression [].
5.3. Reservoir Evolution and Oil and Gas Filling Coupling Characteristics
The coupling of the reservoir evolution process and hydrocarbon injection period is the key factor controlling the formation and hydrocarbon enrichment of tight sandstone. Based on the reservoir porosity evolution characteristics and hydrocarbon-filling periods of each submember in the study area, the temporal–spatial coupling relationships between reservoir evolution and hydrocarbon filling can be classified into four distinct phases (Figure 9).
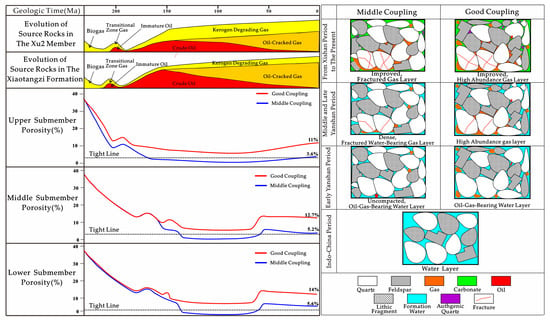
Figure 9.
Coupling characteristics of reservoir evolution and hydrocarbon charging in Xu 2 Member of Xujiahe Formation on east slope of Western Sichuan Depression.
By the end of the Indosinian Orogeny, the porosity of the upper, middle, and lower submembers approximately reached 11%, 16%, and 18%, respectively. At this stage, the source rock had not yet entered the thermal maturity window. Consequently, only trace amounts of hydrocarbons were expelled, and the reservoir fluid system was predominantly composed of formation water.
In the early Yanshan Period, the porosity of ultra-tight sandstone in the upper submember without developed faults decreased to 2.6%, essentially lacking the reservoir conditions for natural gas charging. The early water pressure rose, forming a high-pressure water layer. Hydrocarbon-source faults developed in the upper submember, and the middle/lower submembers became near-tight sandstone through dissolution. During the initial maturation phase of the lower hydrocarbon source rocks, natural gas migrated into the sandstone, displacing pore water and forming a gas-bearing water layer.
In the middle and late Yanshan period, the hydrocarbon source rocks entered the peak discharge phase. The sandstone in the upper, middle, and lower submembers of the non-faulted region became super-tight due to tectonic compression, with no oil and gas filling. During this stage, in the areas containing developed ancient traps, syngenetic faults, or mature hydrocarbon source rocks, the sandstone porosity could reach 7%–8%, allowing hydrocarbon charging to form either water-bearing gas layers or pure gas reservoirs.
From the Xishan period to present, in the areas with late-stage fracture development, sandstone experiences erosional processes and porosity enhancement. Within ultra-compacted zones, sandstone porosity increased, which significantly improved permeability. Subsequent hydrocarbon charging further transforms pre-existing water-bearing gas reservoirs or transitional gas layers into conventional gas reservoirs.
5.4. Development Mode of Sweet-Spot Reservoir
The coupling mechanism between reservoir pore evolution and hydrocarbon charging in the Xu 2 Member reveals three distinctive sweet-spot formation models along the eastern slope of the Sichuan Foreland Basin. They are type 1 (paleo-structural trap + source-connected fracture assemblage type), type 2 (paleo-structural trap + internal source rock + late-stage fracture assemblage type), and type 3 (paleo-structural trap + internal source rock + source-connected fracture + late-stage fracture assemblage type). These models demonstrate optimal spatial–temporal coupling relationships among diagenetic alteration, porosity–permeability enhancement, and hydrocarbon migration–accumulation processes.
5.4.1. Type 1
The paleo-structural trap was formed during the late Indosinian period. At that time, the hydrocarbon source rocks had not yet reached thermal maturity. Although the sandstone exhibited favorable physical properties, no hydrocarbon migration occurred. During the early Yanshan period, physical conditions met the requirements for hydrocarbon migration. The hydrocarbon source rock was in a low-maturity stage, and the paleo-trap’s geometry (e.g., anticlinal closure and cap rock integrity) provided critical confinement, directing gas migration upward toward the structural crest. A minor accumulation of hydrocarbons collected at the crest of the paleo-trap, forming a gas-bearing aqueous zone. The hydrocarbon source rock acts as a cap rock, effectively organizing the migration of oil and gas. During the middle and late Yanshan period, extensive fractures formed, originating from source-rock fractures. These fractures served as secondary migration channels, while the structural trap prevented the escape of gas and guided the airflow into the paleo-structural trap. Natural gas migrated and accumulated along these fractures within the porous and permeable paleo-closures, ultimately forming gas-bearing water layers in fractured reservoirs. From the Xishan Period to the present, the reactivated through-source fractures enhanced gas accumulation in the paleo-trap, forming a gas-dominated reservoir (gas–water contact). The ZJ20 well, representative of this gas reservoir type, exhibits a daily gas production of 5.87 × 104 m3 (Figure 10a).
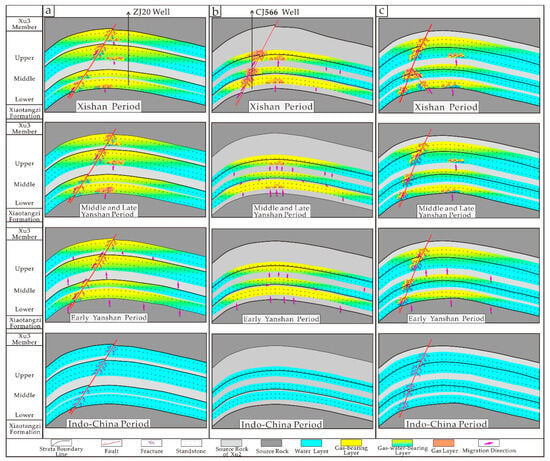
Figure 10.
Development pattern diagram of reservoirs in the Second Member of Xujiahe Formation on the east slope of the Western Sichuan Depression((a) Type 1; (b) Type 2; (c) Type3).
5.4.2. Type 2
The paleo-trap formed during the Late Indo-Chinese Orogeny, when source rocks were immature with no hydrocarbon generation. During the Early Yanshanian Movement, the Xu 2 Member paleo-trap exhibited gas-bearing water layers as the dominant reservoir type. Progressive fracturing in the Middle-Late Yanshanian facilitated hydrocarbon migration through source-connected faults, enhancing gas saturation within the fracture-modified paleo-traps and establishing fractured gas–water systems. Since the Himalayan Orogeny, structural adjustments have optimized gas accumulation in structural highs. The CJ566 well exemplifies such reservoirs, where favorable source–reservoir configurations yield a perforated interval gas flow rate of 2.33 × 104 m3/d (Figure 10b).
5.4.3. Type 3
During the late Indo-Chinese period, early through-going fractures formed in the Xu 2 Member, with numerous subsidiary fractures branching from them. At this stage, the sandstone exhibited favorable reservoir quality. However, the source rocks had not yet reached maturity, and the pore spaces were primarily occupied by formation water.
During the early Yanshan period, hydrocarbon source rocks entered a low maturity phase. Oil and gas migrated along fractures and accumulated in the elevated portions of the paleo-trap, forming gas-bearing water layers.
During the Middle-Late Yanshanian period, sandstones deficient in primary hydrocarbon charging underwent significant compaction–cementation processes. Pre-existing gas-water transitional zones experienced secondary hydrocarbon migration during this phase, with gas saturation indices demonstrating marked enhancement through multiphase fluid interactions, ultimately forming water–wet gas reservoir systems.
From the Xishan Period to the present, late-stage fracture formation and intense tectonic activity have driven the upward migration of natural gas along fractures. This process significantly enhanced gas abundance within the paleo-containment system, while displacing formation water downward to the reservoir base. Such sweet-spot reservoir development patterns represent critical future targets for unconventional gas exploration (Figure 10c).
6. Conclusions
(1) The study area is located in the Xu 2 Member of the eastern slope within the Western Sichuan Depression. The upper and middle submembers are predominantly composed of lithic sandstone, while the lower submember consists mainly of quartz-rich clastic sandstone. The reservoir spaces are dominated by intragranular pores, with well-developed fractures observed in the middle and upper submembers. The reservoir quality is superior in the middle and lower submembers, whereas the upper submember exhibits poorer physical properties. The key diagenetic processes include dissolution and fracturing, which serve as the primary constructive mechanisms for reservoir formation.
(2) The pore evolutionary processes of the submembers on the eastern slope of the Western Sichuan Depression vary significantly. Compaction and pore reduction effects are most pronounced in the upper submember. During the Middle to Late Jurassic period, the upper submember underwent densification. Feldspar dissolution enhanced porosity in the middle and lower submembers, leading to significant porosity improvement. Subsequent continuous deep burial and quartz pressure solutions exerted dual destructive effects. The sandstones in the middle and lower submembers were densified, while the upper submember experienced hyper-densification. By the end of the Cretaceous period, under the tectonic action, the fracture development area was improved by dissolution, and the porosity of the reservoir was increased to about 5%, and the permeability was improved more significantly.
(3) Natural gas charging in the Xu 2 Member of the eastern slope of the Western Sichuan Depression occurred predominantly during two critical intervals: the Jurassic-Early Cretaceous and the Paleocene to present. Distinct coupling relationships between reservoir evolution and hydrocarbon charging are observed across different stratigraphic intervals and temporal phases.
(4) There are three sweet-spot reservoir development modes in the Xu 2 Member of the eastern slope of the West Sichuan depression: paleo-structural trap + source-connected fracture assemblage type, paleo-structural trap + internal source rock + late-stage fracture assemblage type, and paleo-structural trap + (internal source rock) + source-connected fracture + late-stage fracture assemblage type.
Author Contributions
Software, Z.Q. and C.X.; Formal analysis, X.L.; Resources, Z.L. (Zheyuan Liao), Y.L. and F.L.; Writing – original draft, B.C.; Writing – review & editing, B.C., X.L. and Z.L. (Zhengxiang Lv); Funding acquisition, Y.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [Centre for Southeast Asia Economic and Culture Studies, Chengdu Normal University] grant number [DNY2401].
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Feng Li was employed by the company Southwest Oil and Gas Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Dai, J.; Dong, D.; Ni, Y.; Gong, D.; Huang, S.; Hong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Feng, Z. Distribution patterns of tight sandstone gas and shale gas. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yong, Z.; Ma, H. Tight Sandstone Reservoir Characteristics and Sand Body Distribution of the Eighth Member of Permian Shihezi Formation in the Longdong Area, Ordos Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, H.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; Fu, M.; Ling, C.; Duan, B.; Chen, Q.; Chen, G. The conditions and modelling of hydrocarbon accumulation in tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study from the Jurassic Shaximiao formation of western Sichuan Basin, China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 225, 211702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, W.; Bo, D.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hao, J. Densification Mechanism and Natural Gas Accumulation Process, Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Hechuan Area, Sichuan Basin, China. Lithosphere 2023, 2022, 4522740. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, K.; Cao, B.; Gao, J.; Qiu, G. Diagenetic history and reservoir evolution of tight sandstones in the second member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 201, 108451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Li, M.; Duan, T. Sedimentary system and sand bodies distribution of the second member of the Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang area, Western Sichuan Depression, China. Interpretation 2021, 9, T927–T944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, M.; Wen, Z.; Luo, X.; Ding, Z.; Li, B.; Xue, Y. Hydrocarbon fluid evolution and accumulation process in ultradeep reservoirs of the northern Fuman Oilfield, Tarim Basin Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1399595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Feng, W.-P.; Guan, J.; Hao, J.-C. Key Questions of the Fluid Inclusion Analysis in Petroliferous Basins and their Significances. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2018, 37, 441–450+561. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xi, K.; Song, G.; Liu, H. A recovery method for porosity evolution of clastic reservoirs with geological time: A case study from the upper submember of Ess in the Dongying depression, Jiyang Subbasin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2013, 34, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Yang, Y.; Cai, L.; Yan, L.; Li, W.; He, J. Reservoir densification process in overlying tight sandstone gas area. Nat. Gas Ind. 2019, 39 (Suppl. S1), 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ji, Y.; Yang, K. Impacts of sedimentary characteristics and diagenesis on reservoir quality of the 4th member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation in the western Sichuan basin, southwest China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 167, 106981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Sang, Q.; Li, W.; Xiong, J.; Liang, L. Pore-throat structure and fractal characteristics of tight gas sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the second member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Zhongba area, western Sichuan depression, China. Geol. J. 2024, 59, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.S.; Luo, L.; Tan, X.F.; Tan, D.P.; Sun, X.; Gao, Z.P.; Wang, J.; Cha, X.J. Genesis and pore evolution of tight sandstone reservoir: Taking Lower Shihezi Formation in the Shilijiahan block of Hangjinqi area as an example. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2021, 28, 598–603. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, G.; Jones, S.J.; Zhou, Z.; Ran, Y.; Lai, J.; Li, R.; Deng, L. Prediction of diagenetic facies using well logs—A case study from the upper Triassic Yanchang formation, Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 81, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Gao, X.; Meng, W.; Tan, X.; Shao, H.; Xiao, C. The origin and alteration of calcite cement in tight sandstones of the Jurassic Shishugou Group, Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China: Implications for fluid–rock interactions and porosity evolution. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 65, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, T. A recovery method of porosity evolution based on forward and inverse analyses: A case study of the tight sandstone of Xujiahe Formation, Northeast Sichuan Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2021, 42, 708–723. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Dou, T.; Shi, X.; Lin, M.; Yang, Q. Mechanism of Pore Structure Evolution in Tight Sandstone Subjected to ScCO2–H2O Treatment. Processes 2025, 13, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Y. Exploration potential and development direction of continental tight sandstone gas in the Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Ye, X. Study on Reservoir Characteristics, the Tightening Process and Reservoir Quality in Source-to-Sink Systems in the Xu-2 Member of the Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan Basin, Western China. Minerals 2025, 15, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.S.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Xu, Z.H. Exploration status and potential evaluation of tight gas in Sichuan Basin. Strateg. Study CAE 2012, 14, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Zhihong, Z.; Denghua, L.; Senshu, B.; Jun, J.; Xin, Z.; Zhuoya, L.; Xuan, G. Resource potentials of natural gas in Sichuan Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2017, 22, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, S. Characteristics and Control Factors of a High-Quality Deeply Buried Calcareous Sandstone Reservoir, the Fourth Member of the Upper Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2024, 14, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.S.; Yan, J.P.; Liu, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Xie, G. Diagenetic facies logging identification and application of deep tight sandstone gas reservoir: A case study of the third member of Xujiahe formation in Dayi area of western Sichuan depression. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2022, 51, 107–123. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Xu, S.L.; Liu, J.L.; Ma, L.Y.; Liu, S.B.; Fan, X.; Jin, W.J.; Li, W.P. Enrichment laws of deep tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.K.; Lin, L.B.; Yu, Y.U.; Wu, D.; Liu, L. The main controlling factors of high quality reservoir in the second member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area, Western Sichuan, China. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2022, 29, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Gao, X.Z.; Meng, W.B.; Tan, X.F.; Feng, M.S.; Shao, H.B. The formation mechanism of the relatively high-quality reservoir in tight sandstones with deep burial: A case study of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang structural belt of Western Sichuan Depression. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2017, 38, 930–944. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jin, W.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Ma, A. Characteristics of and main factors controlling the tight sandstone reservoir fractures in the 2nd member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area, Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2021, 42, 884–897+1010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cai, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, S. Characteristics of Xuer gas reservoir in Zhongjiang Huilong structure on the eastern slope of western Sichuan depression. China Pet. Chem. Ind. Stand. Qual. 2022, 42, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wu, D. Prediction of fracture dominant migrating channel of eastern slope in western Sichuan depression. China Sci. 2019, 14, 476–480+523. [Google Scholar]
- SY/T 5368-2016; Identification for Thin Section of Rocks. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- SY/T 5162-2021; Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Rock Samples. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- SY/T 5238-2019; Carbon and Oxygen Isotope Analysis Method for Organic Matter and Carbonate Rock. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- SY/T 6010-2011; Test Method for Fluid Inclusion in Sedimentary Basins by Microscopic Thermometry. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zeng, Y.; Xia, W. Sedimentary Petrology; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Feng, L.; Lü, L. Diagenetic facies and pore evolution of tight sandstone reservoir: Taking Sha 21 sub-member in the north of central Sichuan Basin as an example. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2022, 29, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Shi, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Qi, R.; Xu, Q. Characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs and their controlling factors of He-1 Member in Hangjinqi Block, Ordos Basin. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 1604–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Zhong, D.K.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, W.; Du, H.Q.; Zhou, Z.H.; Tang, Z.C. Characteristics of deep tight sandstone reservoirs and their controlling factors of physical properties: A case study of the Xu-2 member in the western Yuanba area of the northeastern Sichuan Basin, China. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2022, 40, 410–421. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Z. Study on the Accumulation Chronology and Fluid Evolution History of the Western Sichuan Depression; Exploration and Development Research Institute of Sinopec Southwest Oil and Gas Branch: Chengdu, China, 2005; pp. 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, I.; O’Neil, J.R. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. In Data of Geochemistry, 6th ed.; Professional Paper; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, M. Parameters influencing porosity in sandstones: A model for sandstone porosity prediction. AAPG Bull. 1987, 71, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, D.C.; Weyl, P.K. Influence of Texture on Porosity and Permeability of Unconsolidated Sand. AAPG Bull. 1973, 57, 349–369. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert, M.K.; Ruby, W.W. Mechanics of fluid-filled porous solid and its application to overthrust faulting: Role of fluid pressure in mechanics of overthrust faulting. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1959, 70, 115–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pang, X.; Xiong, L.; Wang, L.; Xie, M. Porosity evolution in tight gas sands of the upper triassic Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Basin, China. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2014, 31, 361–375. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).