Geochemical Survey of Stream Sediments and Stream Water for Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposits (IAREDs): A Pilot Study in Jiaping IARED, Guangxi, South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
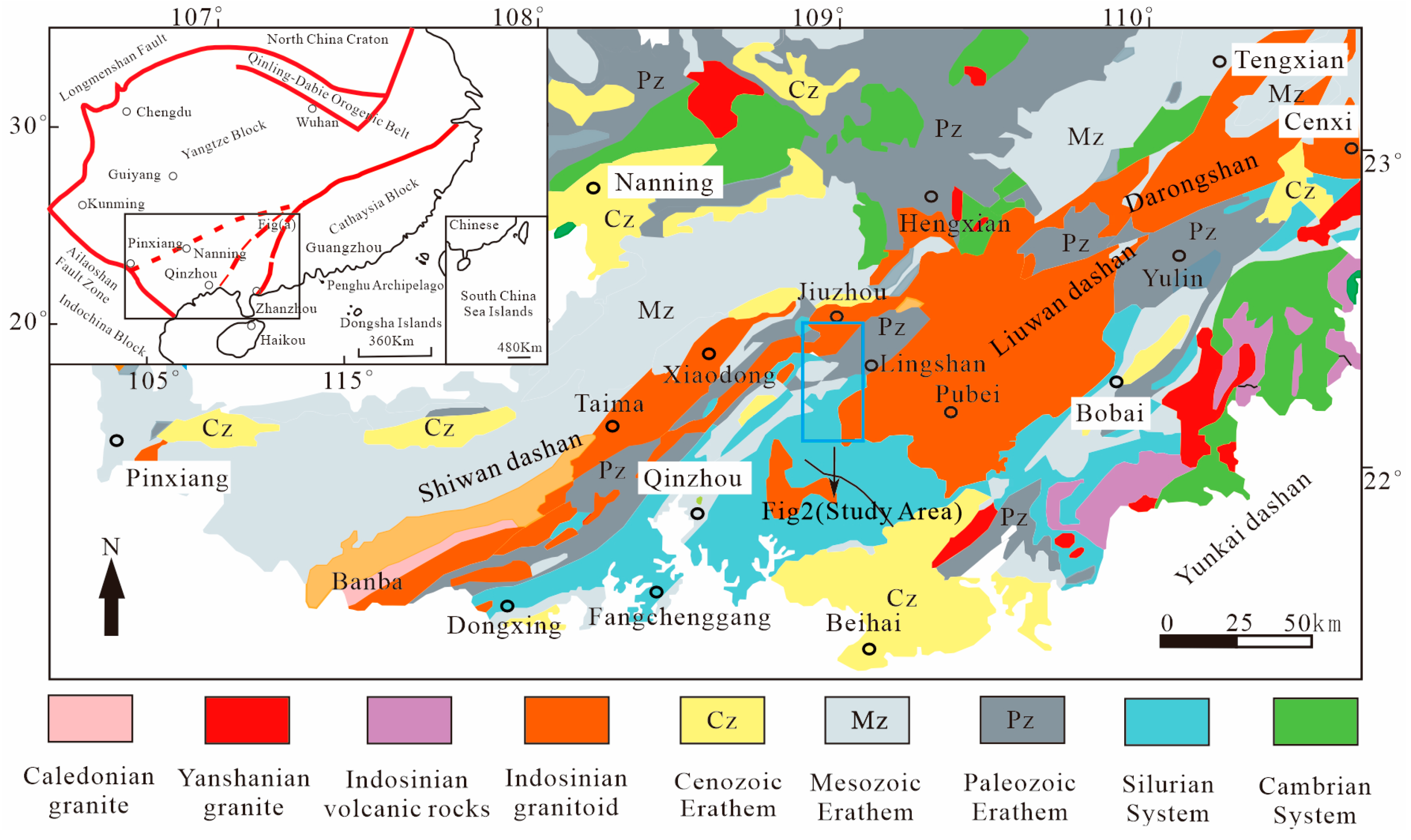
2. Regional Geological Background
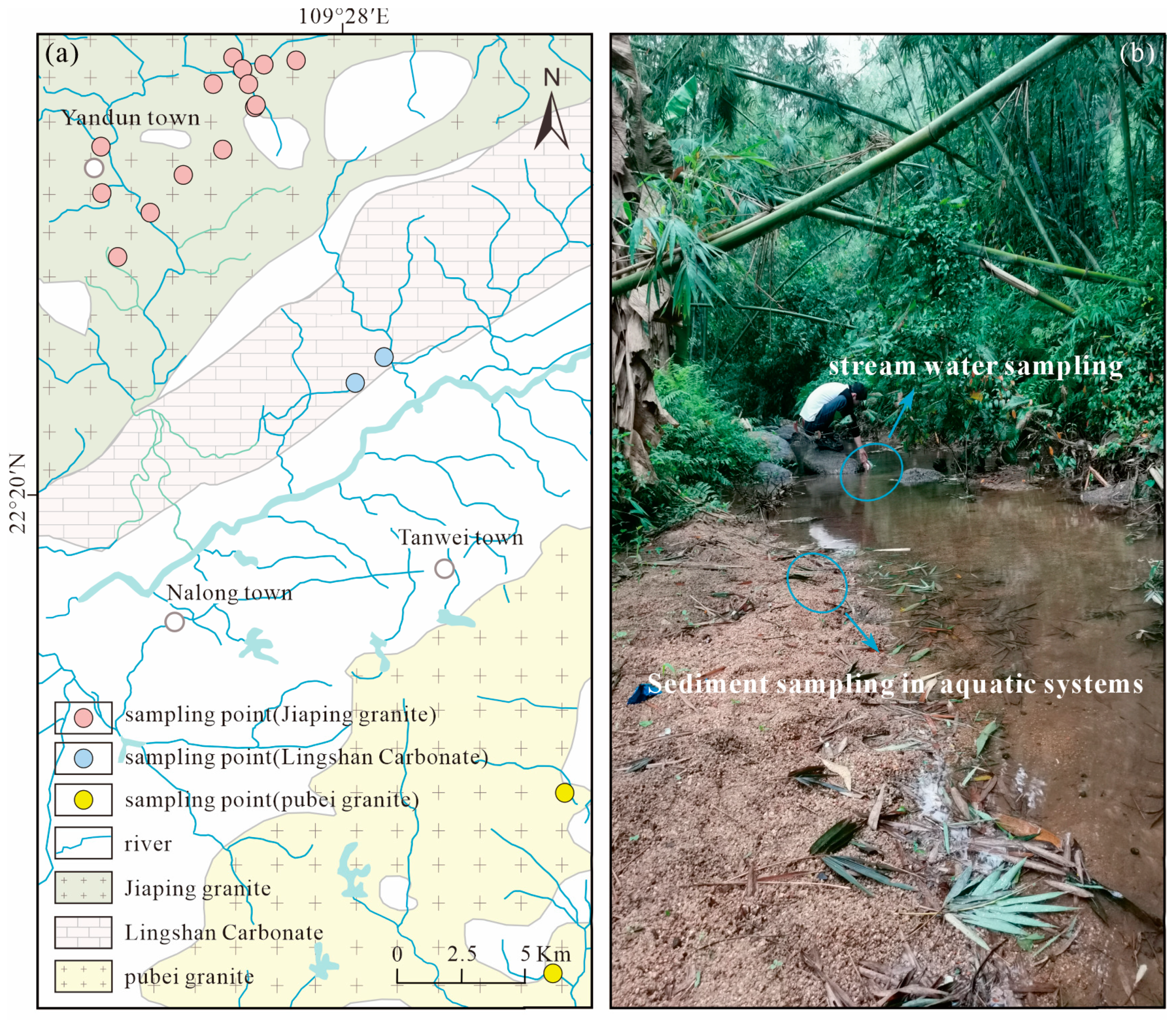
3. Sample Collection and Analysis
3.1. Sample Collection
- (1)
- Collection of sediment and water samples
- (2)
- Weathered crust soil and bedrock sampling in Jiaping IARED
3.2. Sample Pretreatment
- (1)
- Stream Water
- (2)
- Stream Sediments
- (3)
- Weathered Crust Soils
- (4)
- Bedrocks
3.3. Chemical Analysis
- (1)
- Chemical analysis of REEs
- (2)
- Analysis of major elements for stream sediments
- (3)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
4. Results
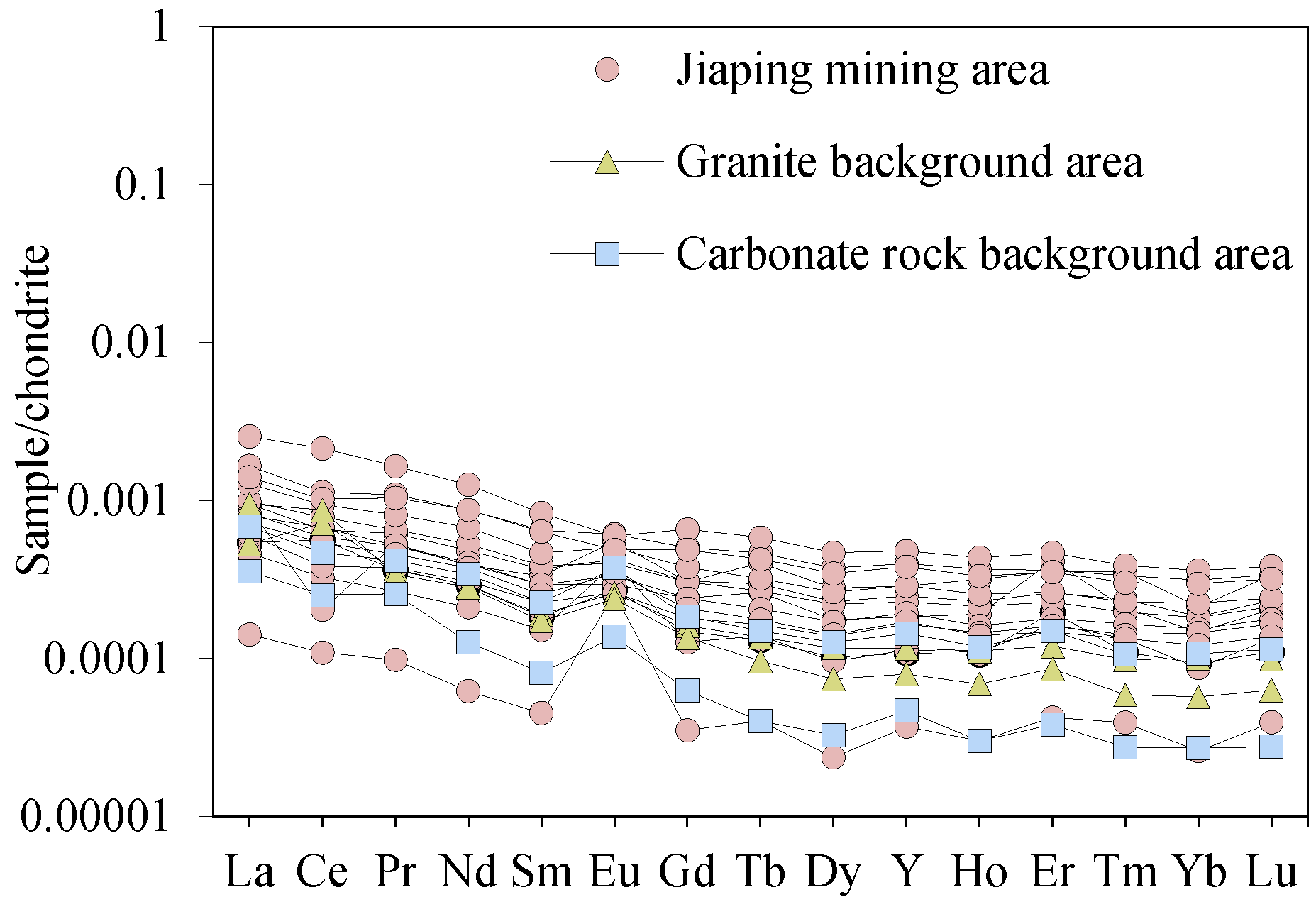
4.1. REE Characteristics of Stream Sediments
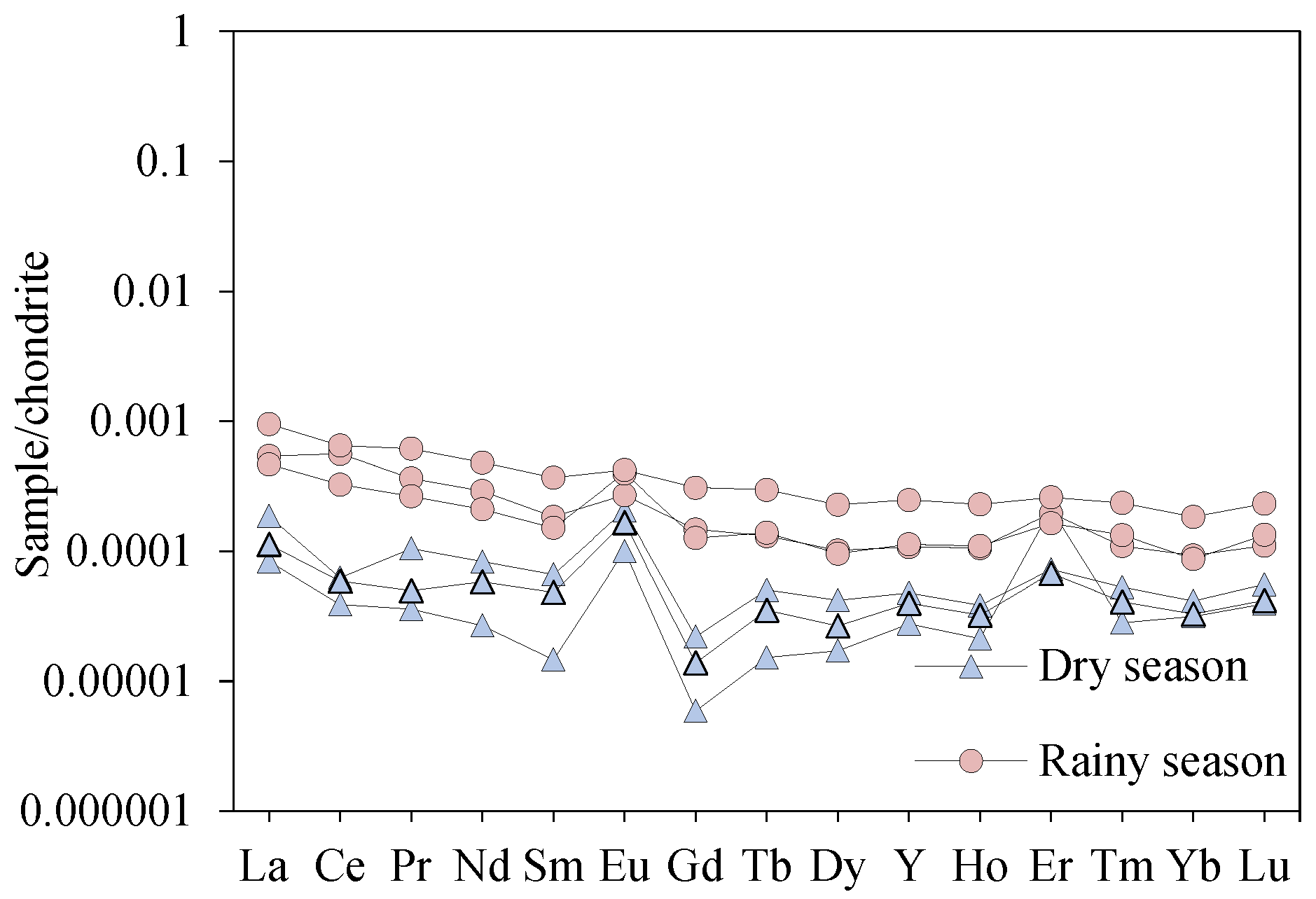
4.2. Geochemical Characteristics of Dissolved REE in Stream Water
4.3. REE Characteristics of Crust Soils and Bedrocks in Jiaping IARED Area
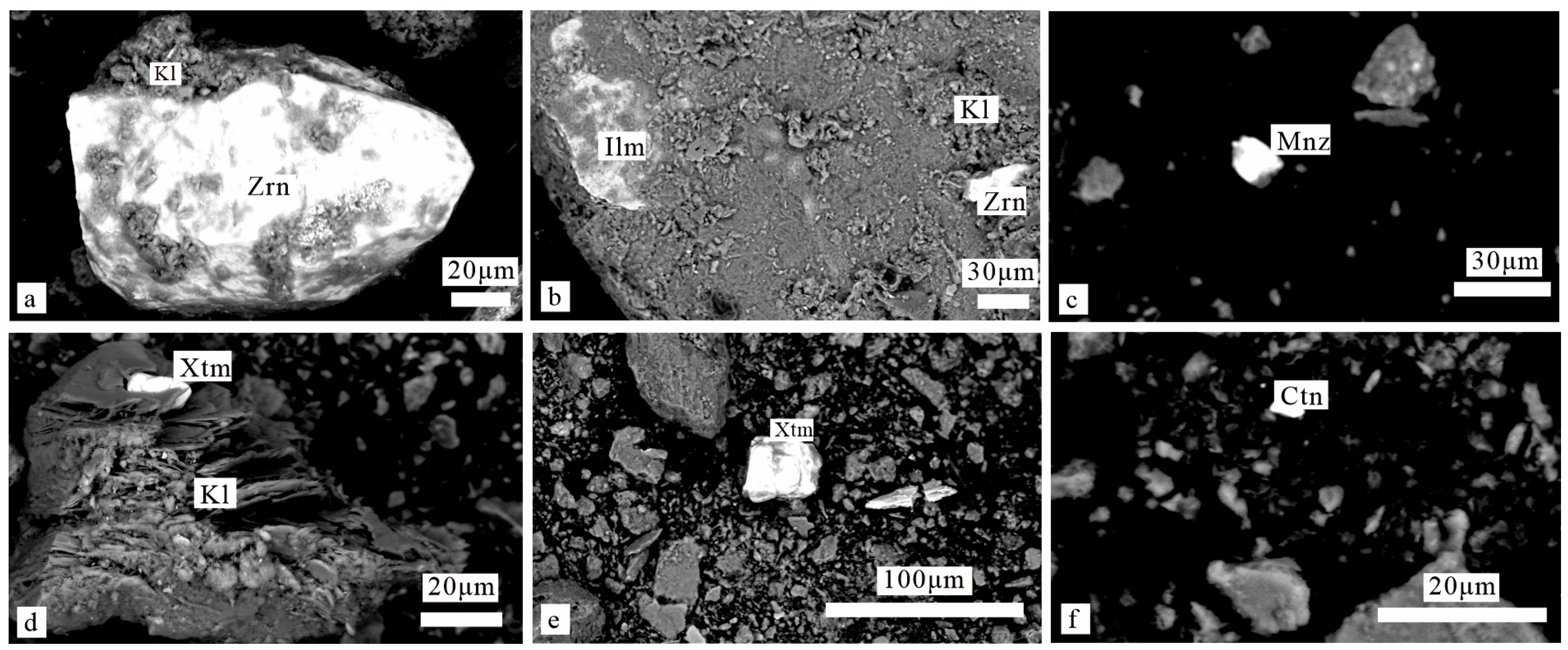
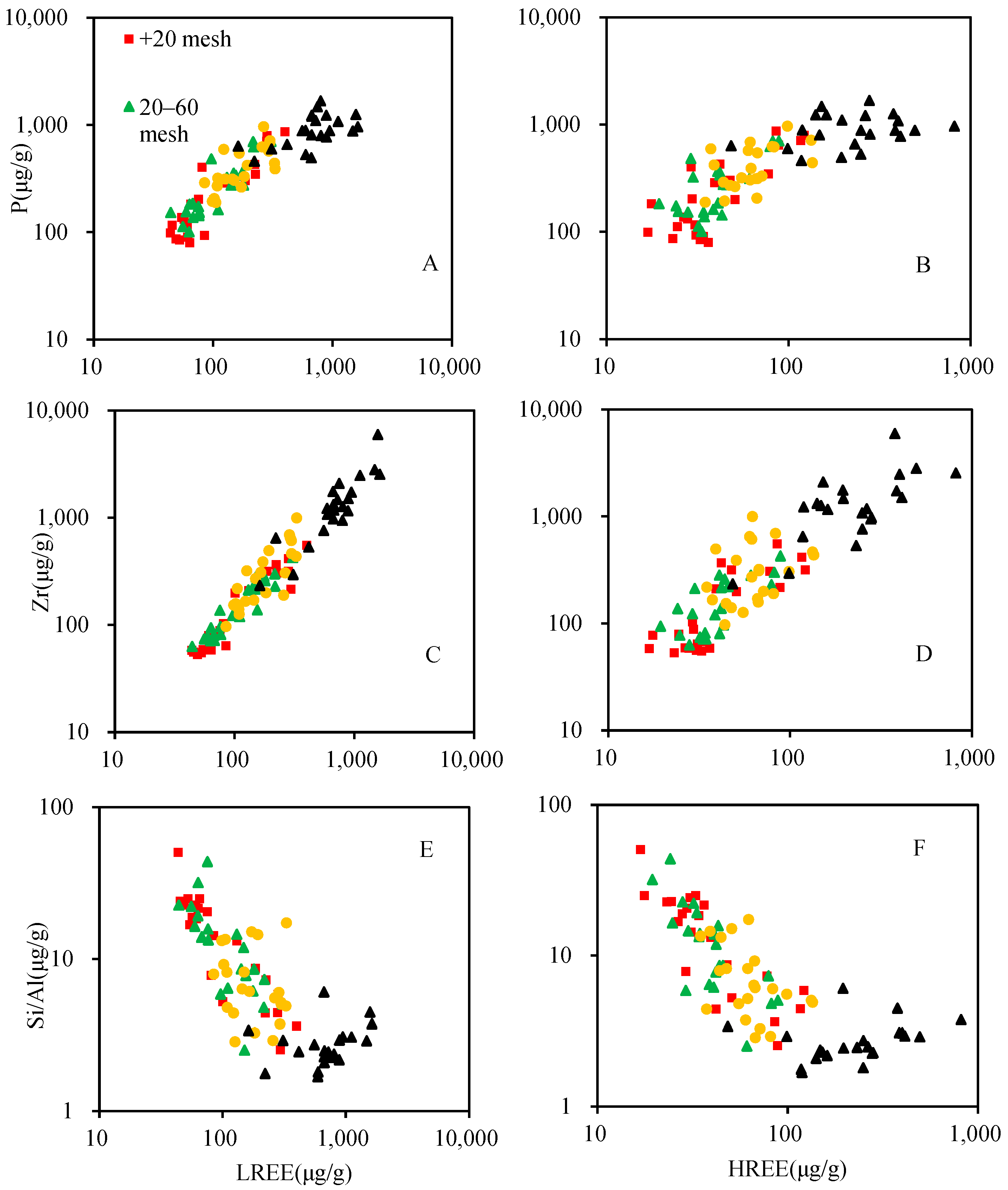
4.4. Mineralogical Characteristics of -150-Mesh Stream Sediments in Jiaping Area
5. Discussion
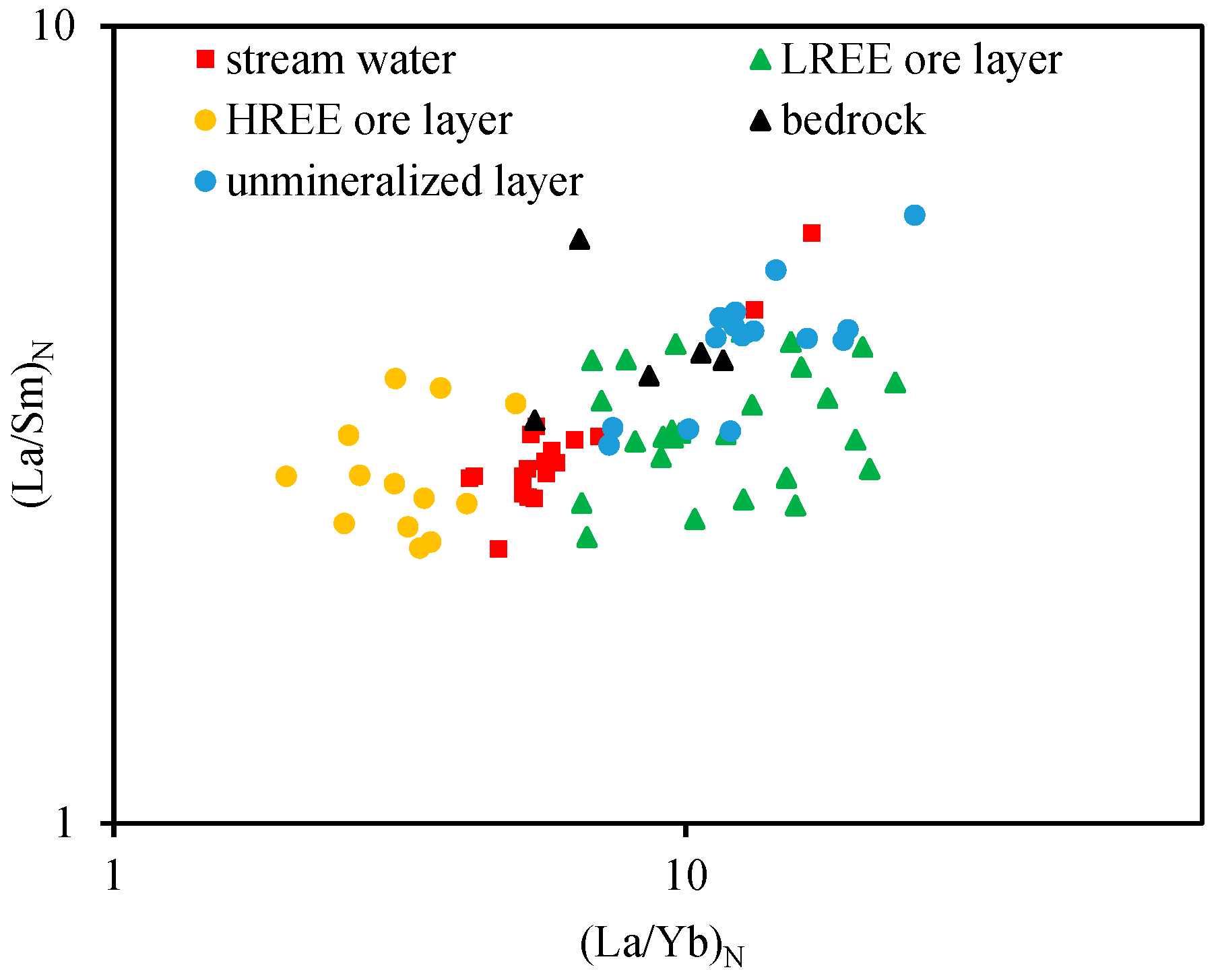
5.1. Geochemical Characteristics of Dissolved REE in Stream Water and Their Indicative Significance for IAREDs
5.1.1. Dissolved REE Variation in Stream Water in Dry and Rainy Season
5.1.2. Indicative Significance of Dissolved REE in Stream Water for IAREDs
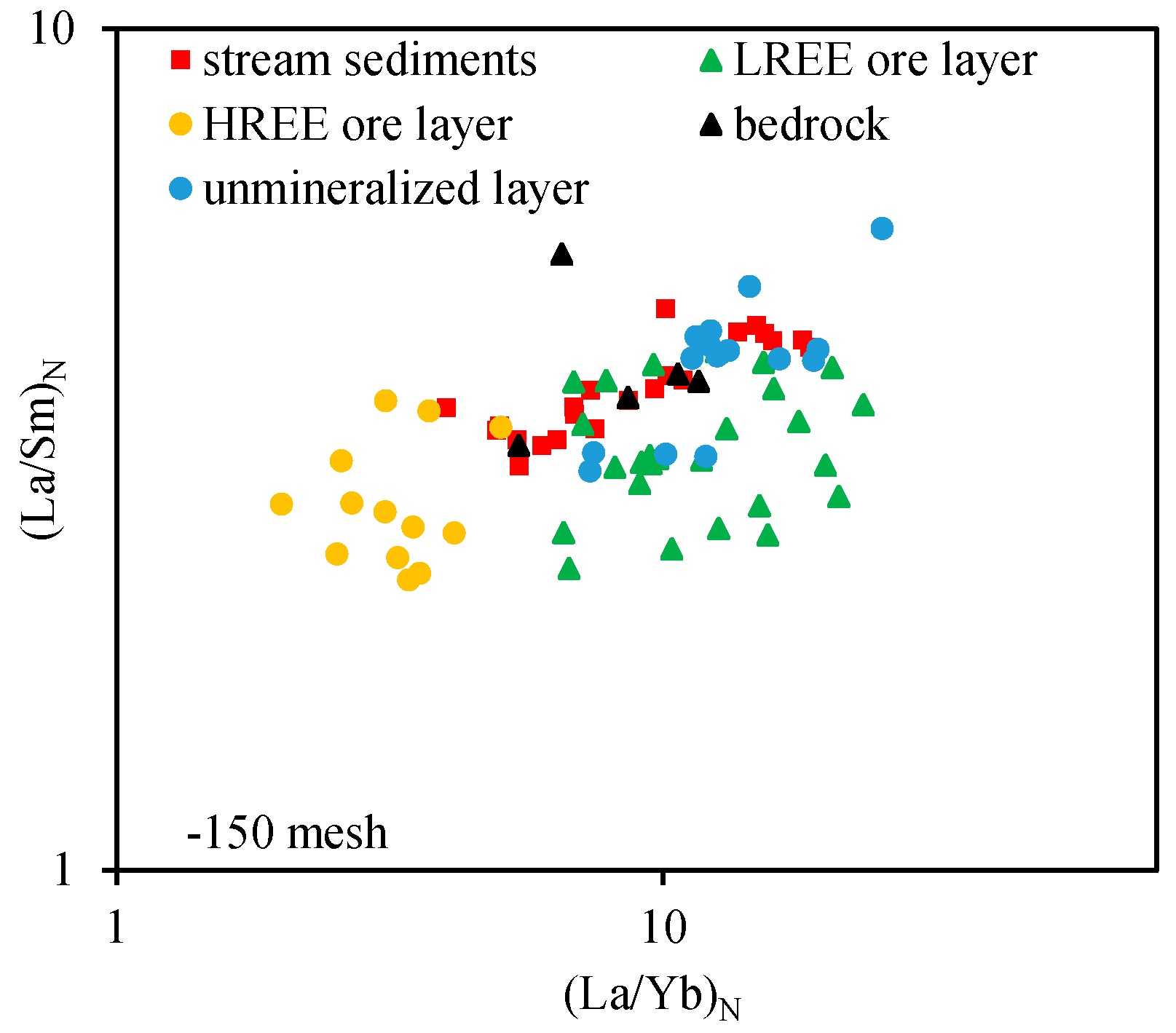
5.2. Geochemical Signatures of Stream Sediments and Their Indicative Significance for IAREDs
5.2.1. Distribution Characteristics of REE in Stream Sediments of Different Grain Sizes in the Mining Area and the Background Area
5.2.2. The REE Enrichment Mechanism of Fine-Grained (-150-Mesh) Stream Sediments
5.2.3. Indicative Significance of Stream Sediment Survey for IAREDs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.H. Applications and Prospects of Rare Earth Magnetic Materials. Nonferrous Met. Eng. 2002, 01, 60–61, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Chang, M.H.; Pecht, M. Rare-earth elements in lighting and optical applications and their recycling. Jom 2013, 65, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhmouradian, A.; Wall, F. Rare earth elements: Minerals, mines, magnets (and more). Elements 2012, 8, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.W.; Li, H.W.; Wang, C.F.; Wang, G.Z.; Xue, X.X.; Zhang, G.C. Development Status and Research Progress in Rare Earth Industry in China. China. J. Rare Met. 2007, 03, 279–288, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Malavekar, D.B.; Magdum, V.V.; Khot, S.D.; Kim, J.H.; Lokhande, C.D. Doping of rare earth elements: Towards enhancing the electrochemical performance of pseudocapacitive materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Fan, H.R.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Butcher, A.R.; Yann, L.; Yang, K.F.; Li, X.C. Global rare earth elements projects: New developments and supply chains. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 157, 105428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.W.; Song, S.W.; Liu, M.; Meng, J.Y. REE deposits: Basic characteristics and global metallogeny. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3675–3697, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.F.; Williams-jones, E.A. The genesis of regolith-hosted heavy rare earth element deposits: Insights from the world-class Zudong deposit in Jiangxi Province, South China. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 541–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Dai, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.K.; Huang, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; et al. A review of the achievements in the survey and study of Ion-absorption type REE deposits in China. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 2017, 38, 317–325, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, H.P.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.R.; Ma, L.Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Yang, W.B. Remobilization and transferring of rare earth elements in the formation of regolith-hosted REE deposits. J. Geomech. 2024, 30, 707–722, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.F. Research Progress on the Enrichment and Differentiation Mechanism of Rare Earth Elements During Granite Weathering. Acta Geologica Sichuan 2024, 44, 3–6, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chi, R.A.; Tian, J. Review of Weathered Crust Rare Earth Ore. J. Rare Earths 2007, 06, 641–650, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Padrones, J.T.; Imai, A.; Takahashi, R. Geochemical behavior of rare earth elements in weathered granitic rocks in northern Palawan, Philippines. Resour. Geol. 2017, 67, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, R.; Becker, M.; Brugger, J.; Etschmann, B.; Burcher-jones, C.; Howard, D.; Kooyman, P.J.; Petersen, J. Characterisation of a rare earth element-and zirconium-bearing ion-adsorption clay deposit in Madagascar. Chem. Geol. 2019, 522, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, A.M.; Smith, M.P.; Finch, A.A.; Estrade, G.; Villanova-de-benavent, C.; Nason, P.; Marquis, E.; Horsburgh, N.J.; Goodenough, K.M.; Xu, C. Adsorption of rare earth elements in regolith-hosted clay deposits. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, I.V.; Botelho, N.F. REE residence, behaviour and recovery from a weathering profile related to the Serra Dourada Granite, Goiás/Tocantins States, Brazil. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 143, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaga, C.R.L.; Samaniego, J.O.; Tanciongco, A.M.; Quierrez, R.N.M.; Montano, M.O.; Gervasio, J.H.C.; Reyes, R.C.G.; Peralta, M.J.V. The rare earth element (REE) potential of the Philippines. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 242, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Meng, M.M.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, N.; Huang, F.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.F. Review of Remote Sensing Technology Application in Rare-Earth Mining. J. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 524–534, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.L.; Liang, J.S.; Wu, B.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, X.Y. Application of Gannan Drill in Rare Earth Ore Prospecting. Explor. Eng. (Rock Soil Drill. Tunneling) 2016, 43, 44–47, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; He, K.; Luo, C.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X. Review on the development and utilization of ionic rare earth ore. Minerals 2022, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.J. New strategy for exploration of ore resources. J. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 06, 402–410, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.J.; Cheng, H.X. Sixty years of exploration geochemistry in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.R. Analysis of geochemical characteristics and prospecting direction of stream sediment survey. World Nonferrous Met. 2018, 05, 101–102, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, G.Y.; Yu, B.; Li, D.L. The 20THC century’s 10 new achievements in the metallurgical geology field. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2006, S1, 125–130, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, L.X.; Ma, S.M.; Tan, S.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhou, W.W. Application of the multi-attribute anomaly model for prospecting potential at depth: A case study of the Haiyu Au deposit in the Jiaodong Gold Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 207, 106359. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, I.B. Geochemical Exploration for Gold and the Association of As-Cu-Pb-Sn-Zn-Li in the Upper Proterozoic Granitoids of the Wadi Rumman Area, Southwest Jordan. Int. J. Geosci. 2015, 6, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.A.; Tian, J.; Luo, X.P.; Xu, Z.G.; He, Z.Y. The basic research on the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores. Nonferrous Met. Sci. Eng. 2012, 3, 1–13, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.X.; Lu, H.T.; Zhang, B.M.; Cheng, Z.Z.; Fu, W.; Lao, C.L.; Xu, C. Delineating preliminary prospective areas of IAREDs with stream sediments geochemical mapping in South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 243, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, B.M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.S.; Han, Z.X.; LAOLO, S.; SOUKSAN, P.; Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.; et al. National-Scale Geochemical Baseline of 69 Elements in Laos Stream Sediments. Minerals 2022, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Hu, Z.G.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, B.T.; Li, C.X.; Hua, B.; Zhang, Z.W.; Cao, Q.T.; Zhao, L.; et al. Application of stream sediment survey for prospecting the ion adsorption type REE deposit in the Lincang area, Yunnan Province. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2021, 41, 171–180, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.P.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, H.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Dong, G.F.; Luo, Y.P. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the qulong copper ore district in tibet and their indication significance to copper mineralization. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 06, 509–512, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.P. A review and some considerations of water geochemical survey. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 01, 13–18, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, R.W. The prospect for geochemical exploration--predictable advances and new approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 1984, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.F.; Li, X.X.; Wang, Z.Z.; Li, X.C.; Liu, J.C. The genesis of regolith-hosted rare earth element and scandium deposits: Current understanding and outlook to future prospecting. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 3809–3824, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, D.X.; Wang, D.H.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.L.; Tian, Z.X.; Deng, M.C. Distribution and impact factor of dissolved rare earth elements insurface waters in the suburb of typical ion-adsorption rare earth orefield. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 172–181, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Lin, X.J.; Liang, X.L.; Yamaguchi, A.; Zhu, J.X.; Takahashi, Y.; Zhu, R.L. Distribution of rare earth elements (REEs) in supergene environment around a typical ion adsorption--type REE deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 660, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.L.; Hao, Z.D.; Zhang, P.X. The soyrces of ore-forming materials and controlling factors of main weathering deposits in guangxi. Guangxi Geol. 1996, Z1. 129–130+101–128. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, P.; Li, P.Q.; Lu, Q.P.; Zhou, H.; Yi, Z.B.; Xu, C. Mineralization diversity of ion-adsorption type REE deposit in southern China and the critical influence of parent rocks. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3901–3925, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Dong, C.F.; Xu, C.; Wang, R.H.; Lu, Q.P.; Zhou, H.; Han, Z.X.; Yi, Z.B.; Lv, Y.Z.; Huang, G.Q.; et al. Research on Prospecting Direction of Ion-Adsorption Type Heavy Rare Earth Element Resources in Guangxi and Progresses in Scientific Demonstration Exploration. J. Earth Sci. 2024, 49, 1931–1945, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.B.; Fu, J.M.; Liu, Y.H. The Discovery and Significance of A-type Charnokite in Southeast Guangxi Province, China. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2004, 10, 832–834, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q.K. Forming time of darongshan-shiwandashan granite batholith in guangxi. Guangxi Geol. 1991, 04, 59–68, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.H.; Xin, Y.J.; Sun, H.S.; Yu, Y.Q. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Dating and Geochemical Analysis of the Darongshan–Shiwandashan Granitoids in Southwestern South China and Their Geological Implications. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 2018, 39, 179–194, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.H.; Feng, J.C.; He, L.Y. The S-type granite suite in darongshan, guangxi province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 1987, 03. 23–34+100. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.M.; Li, C.W.; Qing, X.F.; Li, H.X. Crustal Evolution of the Shiwandashan in Guangxi: Insights from Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Hf Isotopic Records of Granulite Enclaves in Indosinian Granites. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1489–1500, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Guo, F.; Fan, W.M.; Li, C.W.; Qin, X.F.; Li, H.X. Origin of the granulite enclaves in Indo-Sinian peraluminous granites, South China and its implication for crustal anatexis. Lithos 2012, 150, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.J.; Li, X.H.; Huang, H.Q.; Deng, X.G. Metasedimentary melting in the formation of charnockite: Petrological and zircon U-Pb-Hf-O isotope evidence from the Darongshan S-type granitic complex in southern China. Lithos 2015, 239, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.H.; Zhou, M.F.; Williams-jones, A.E. Controls on the dynamics of rare earth elements during subtropical hillslope processes and formation of regolith-hosted deposits. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 1097–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.; Cullers, R.L. The distribution of rare-earth elements in deeply buried Gulf Coast sediments. Chem. Geol. 1979, 24, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, X.Z.; Ming, Q.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, L.Y.; Cheng, X.S.; Ma, L.C. Conceptual Models for Correlation between Detrital Particles Contents and Pore Distribution of Shale: Taking the Silurian Longmaxi Formation in northwestern Guizhou as an example. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2018, 36, 969–980, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.X.; Nie, H.K.; Liu, G.X.; Zhang, G.R.; Du, W.; Wang, R.Y. Quartz Type and Its Control on Shale Gas Enrichment and Production:A Case Study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Sichuan Basin and Its Surrounding Areas, China. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 3692–3704, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.B.; Wang, X.D.; Shu, J.S. Heterogeneity of geochemical compositions of the changjiang river sediments and provenance indication. Quat. Sci. 2013, 33, 645–655, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.Y.; Azimi, G. Impact of particle size and associated minerals on rare earth desorption and incorporation mechanisms in a South American ion-adsorption clay. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, Y.; Kamitani, M. Rare earth minerals and resources in the world. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 408, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Jung, H.S.; Sikchoi, M.; Li, C.X. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bea, F. Residence of REE, Y, Th and U in granites and crustal protoliths; implications for the chemistry of crustal melts. J. Petrol. 1996, 37, 521–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M.; Sanematsu, K.; Watanabe, Y. REE mineralogy and resources. Handb. Phys. Chem. Rare Earths 2016, 49, 129–291. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.F.; He, H.P.; Liang, X.L.; Bao, Z.W.; Tan, W.; Ma, L.Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Huang, J.; Wang, H. Characteristics and genesis of ion adsorption type REE deposits in the weathering crusts of metamorphic rocks in Ningdu, Ganzhou, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 135, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munksgaard, N.C.; Lim, K.; Parry, D.L. Rare earth elements as provenance indicators in North Australian estuarine and coastal marine sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Lim, D.; Jeong, D.; Xu, Z.; Li, T. Discrimination of sediment provenance in the Yellow Sea: Secondary grain-size effect and REE proxy. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 123, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Tao, C.H.; Su, X.; Lv, S.H.; Zhou, J.P.; Deng, X.M.; Yu, C.H.; Song, B. Characteristics of rare earth elements in the surface sediments of Southwest Indian Ridge: Implication of grain size for the identification of hydrothermal activity. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2022, 42, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.L.; Sun, J.M.; Yang, S.L.; Liu, T.S. Geochemistry of the Pliocene red clay formation in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for its origin, source provenance and paleoclimate change. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrat, M.; Weiss, D.J.; Strekopytov, S.; Dong, S.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Najorka, J.; Sun, Y.B.; Gupta, S.; Tada, R.; Sinhagupta, R.; et al. Improved provenance tracing of Asian dust sources using rare earth elements and selected trace elements for palaeomonsoon studies on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 6374–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, K.; Sanematsu, K.; Kon, Y.; Takagi, T.; Murakami, T. REE redistributions during granite weathering: Implications for Ce anomaly as a proxy for paleoredox states. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 2020, 105, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicconi, M.R.; Losq, C.L.; Henderson, G.S.; Neuville, D.R. The redox behavior of rare earth elements. Magma Redox Geochem. 2021, 381–398. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during weathering of a granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durn, G.; Perković, I.; Stummeyer, J.; Ottner, F.; Mileusnić, M. Differences in the behaviour of trace and rare-earth elements in oxidizing and reducing soil environments: Case study of Terra Rossa soils and Cretaceous palaeosols from the Istrian peninsula, Croatia. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.F.; Han, Z.X.; Lu, H.T.; Zhao, R.W.; Cai, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, B.M. Concentration, speciation, and fractionation of rare earth elements in alluvial soils in contiguous karst landform, southwestern China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 256, 107360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Shi, X.F.; Kao, S.J.; Liu, Y.G.; Lyu, H.H.; Zou, J.J.; Liu, S.F.; Qiao, S.Q. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Type | Statistical Value (μg/g) | LREE | HREE | L/H | REE | δEu | δCe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +20-mesh stream sediments | Jiaping IARED (15) | Median | 64.28 | 31.83 | 2.36 | 97.45 | 0.29 | 1.04 |
| Average value | 108.30 | 43.18 | 2.51 | 151.48 | 0.29 | 1.08 | ||
| Maximum value | 281.15 | 121.59 | 5.29 | 402.74 | 0.41 | 1.29 | ||
| Minimum value | 43.80 | 16.81 | 1.48 | 60.61 | 0.17 | 0.98 | ||
| Granite background area (2) | Average value | 291.37 | 66.49 | 4.27 | 357.85 | 0.26 | 1.14 | |
| Carbonate rock background area (2) | Average value | 187.04 | 58.62 | 3.05 | 245.66 | 0.59 | 0.99 | |
| 20–60-mesh stream sediments | Jiaping IARED (15) | Median | 76.40 | 36.56 | 2.56 | 114.97 | 0.31 | 1.07 |
| Average value | 107.77 | 40.72 | 2.65 | 148.49 | 0.31 | 1.09 | ||
| Maximum value | 217.96 | 81.81 | 4.36 | 297.92 | 0.39 | 1.34 | ||
| Minimum value | 44.12 | 19.41 | 1.58 | 72.10 | 0.22 | 0.98 | ||
| Granite background area (2) | Average value | 242.52 | 66.11 | 3.78 | 308.63 | 0.28 | 1.19 | |
| Carbonate rock background area (2) | Average value | 125.48 | 35.45 | 3.51 | 160.93 | 0.55 | 1.03 | |
| 60–150-mesh stream sediments | Jiaping IARED (15) | Median | 157.55 | 61.61 | 2.50 | 217.26 | 0.30 | 1.01 |
| Average value | 178.60 | 60.16 | 3.00 | 238.75 | 0.30 | 1.06 | ||
| Maximum value | 330.17 | 98.68 | 5.31 | 392.36 | 0.45 | 1.38 | ||
| Minimum value | 84.73 | 34.82 | 1.53 | 128.59 | 0.12 | 0.93 | ||
| Granite background area (2) | Average value | 313.19 | 134.11 | 2.33 | 447.30 | 0.25 | 1.14 | |
| Carbonate rock background area (2) | Average value | 189.68 | 59.34 | 3.22 | 249.01 | 0.57 | 0.99 | |
| -150-mesh stream sediments | Jiaping IARED (15) | Median | 696.73 | 256.72 | 2.67 | 926.87 | 0.16 | 1.04 |
| Average value | 829.53 | 297.51 | 3.02 | 1127.03 | 0.16 | 1.06 | ||
| Maximum value | 1627.56 | 814.94 | 4.98 | 2442.50 | 0.31 | 1.26 | ||
| Minimum value | 220.97 | 117.44 | 1.80 | 338.41 | 0.06 | 0.93 | ||
| Granite background area (2) | Average value | 841.77 | 154.51 | 5.45 | 996.28 | 0.19 | 1.08 | |
| Carbonate rock background area (2) | Average value | 235.46 | 73.56 | 3.24 | 309.02 | 0.49 | 0.98 | |
| Sample Type | Statistical Value (ng/mL) | LREE | HREE | L/H | REE | δEu | δCe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream water | Jiaping IARED (15) | Median | 0.88 | 0.54 | 1.78 | 1.38 | 1.25 | 0.90 |
| Average value | 1.05 | 0.59 | 1.78 | 1.64 | 1.72 | 0.88 | ||
| Maximum value | 2.81 | 1.21 | 2.37 | 4.03 | 6.33 | 1.24 | ||
| Minimum value | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.90 | 0.25 | 0.80 | 0.28 | ||
| Granite background area (2) | Average value | 0.87 | 0.25 | 3.64 | 1.13 | 1.51 | 1.47 | |
| Carbonate rock background area (2) | Average value | 0.53 | 0.23 | 2.54 | 0.76 | 1.87 | 0.83 | |
| Sample Type | Statistical Value (μg/g) | LREE | HREE | L/H | REE | δEu | δCe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LREE ore layer (26) | Median | 737.80 | 272.27 | 2.67 | 1010.4 | 0.64 | 0.19 |
| Average value | 814.08 | 332.07 | 3.06 | 1146.2 | 0.65 | 0.23 | |
| Maximum value | 1331.6 | 814.63 | 7.61 | 2146.2 | 0.96 | 0.85 | |
| Minimum value | 449.96 | 97.91 | 1.08 | 704.19 | 0.46 | 0.10 | |
| HREE ore layer (13) | Median | 460.02 | 742.47 | 0.69 | 1311.5 | 0.71 | 0.36 |
| Average value | 544.60 | 820.44 | 0.68 | 1365.0 | 0.70 | 0.36 | |
| Maximum value | 1031.5 | 1324.2 | 0.93 | 2325.8 | 0.85 | 0.60 | |
| Minimum value | 306.15 | 474.93 | 0.42 | 800.5 | 0.56 | 0.18 | |
| Unmineralized layer (15) | Median | 269.81 | 34.61 | 6.58 | 310.53 | 0.35 | 1.47 |
| Average value | 272.17 | 50.16 | 6.58 | 322.34 | 0.39 | 1.69 | |
| Maximum value | 467.74 | 117.46 | 10.17 | 557.42 | 0.60 | 3.32 | |
| Minimum value | 144.43 | 23.45 | 2.59 | 171.94 | 0.23 | 0.85 | |
| Bedrock (5) | Median | 215.94 | 59.32 | 2.98 | 275.25 | 0.58 | 0.95 |
| Average value | 189.19 | 68.25 | 2.94 | 257.44 | 0.59 | 0.88 | |
| Maximum value | 230.95 | 101.86 | 3.89 | 293.96 | 0.72 | 0.99 | |
| Minimum value | 124.16 | 46.96 | 1.52 | 171.12 | 0.52 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Han, Z.; Dong, C.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y. Geochemical Survey of Stream Sediments and Stream Water for Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposits (IAREDs): A Pilot Study in Jiaping IARED, Guangxi, South China. Minerals 2025, 15, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060642
Liu J, Han Z, Dong C, Wei X, Chen Y. Geochemical Survey of Stream Sediments and Stream Water for Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposits (IAREDs): A Pilot Study in Jiaping IARED, Guangxi, South China. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060642
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Junhong, Zhixuan Han, Chunfang Dong, Xiaocheng Wei, and Yingnan Chen. 2025. "Geochemical Survey of Stream Sediments and Stream Water for Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposits (IAREDs): A Pilot Study in Jiaping IARED, Guangxi, South China" Minerals 15, no. 6: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060642
APA StyleLiu, J., Han, Z., Dong, C., Wei, X., & Chen, Y. (2025). Geochemical Survey of Stream Sediments and Stream Water for Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposits (IAREDs): A Pilot Study in Jiaping IARED, Guangxi, South China. Minerals, 15(6), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060642







