The Cavitation Characteristics of Micro–Nanobubbles and Their Effects on the Flotation Recovery of Fine-Grained Ilmenite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
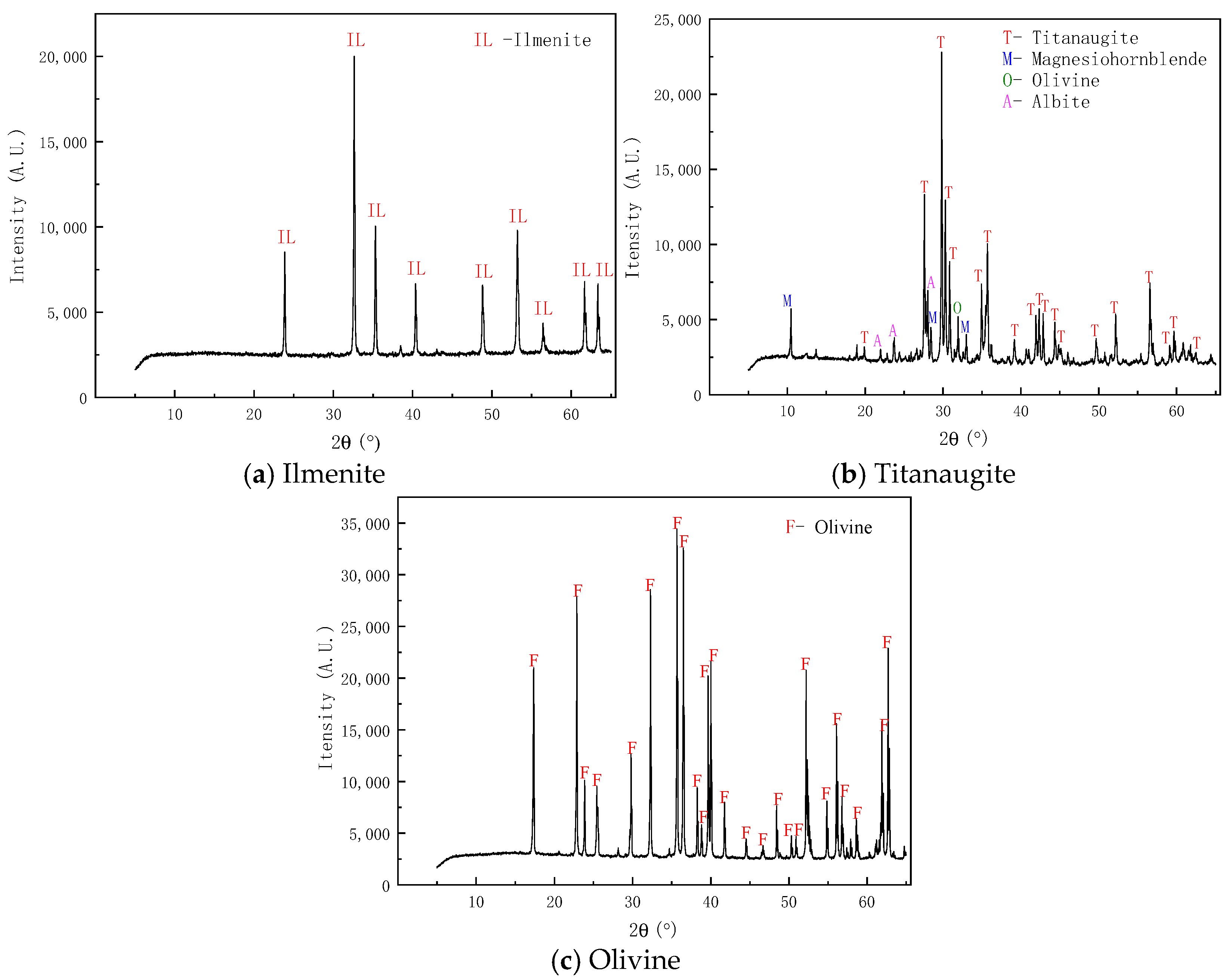
2.2. XRD Detection
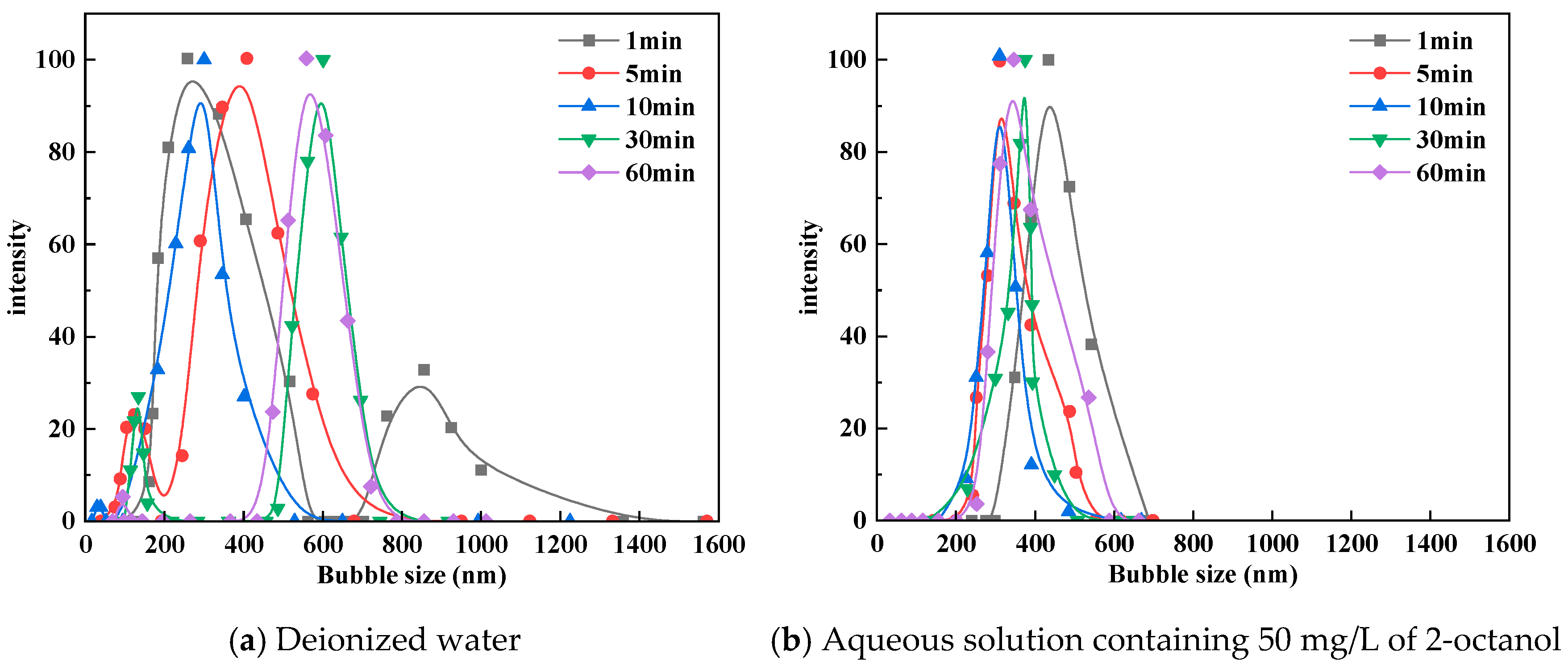
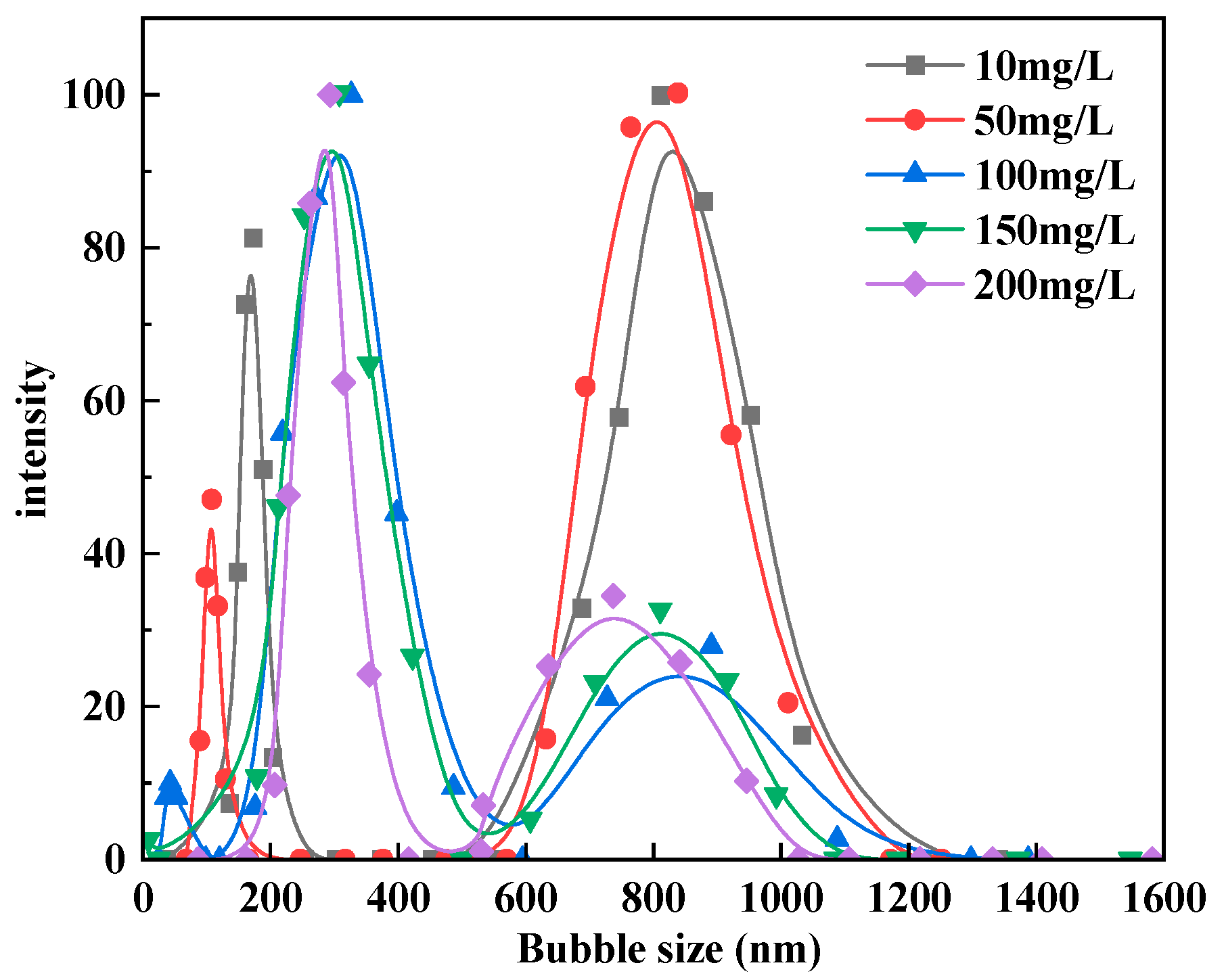
2.3. Bubble Cavitation Property Tests
2.4. Micro-Flotation Tests
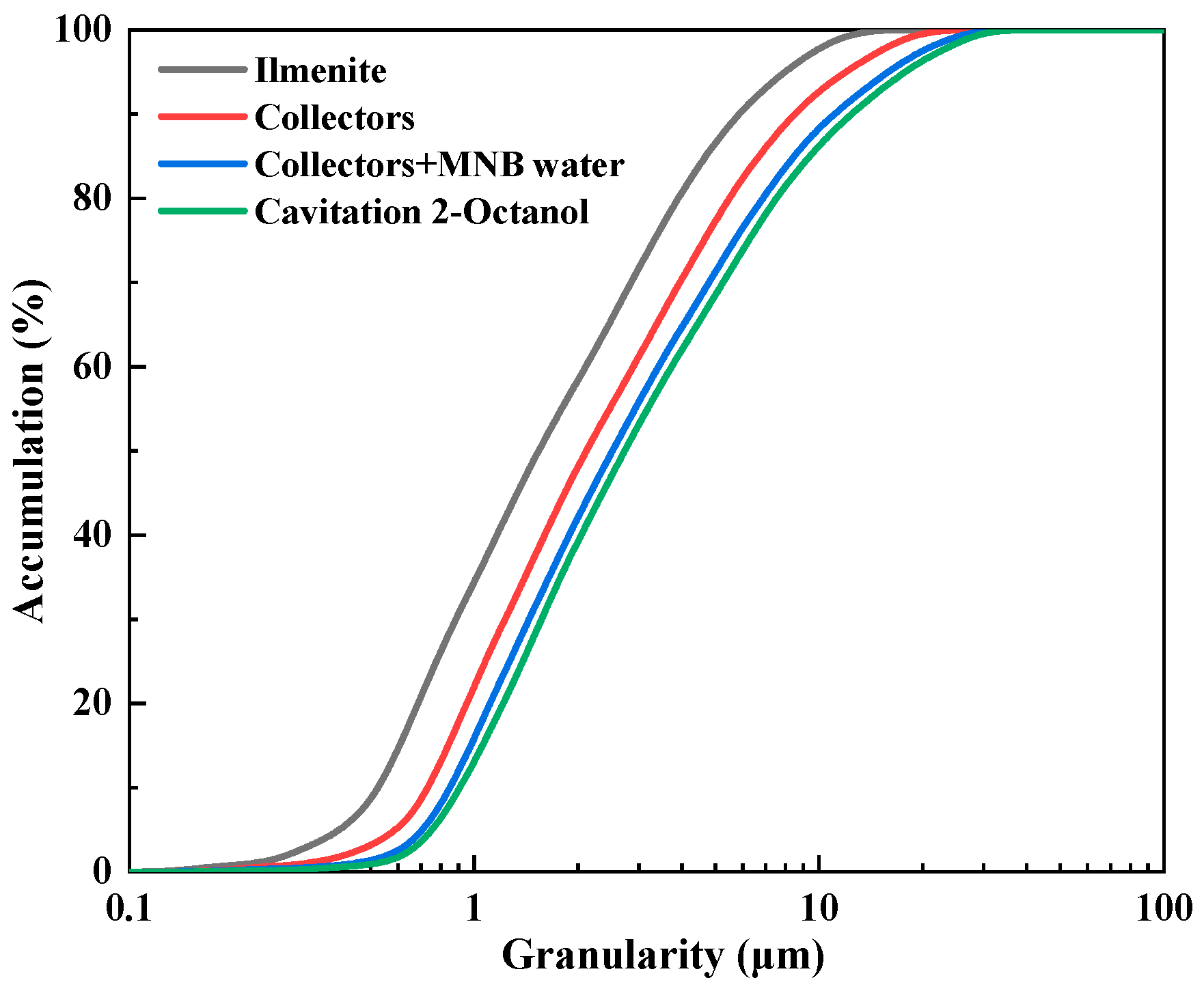
2.5. Particle Size Testing
2.6. Zeta Potential Analysis
2.7. Adsorption Capacity Test
2.8. Contact Angle Measurement
2.9. Precision Bubble Monitoring System Observation Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
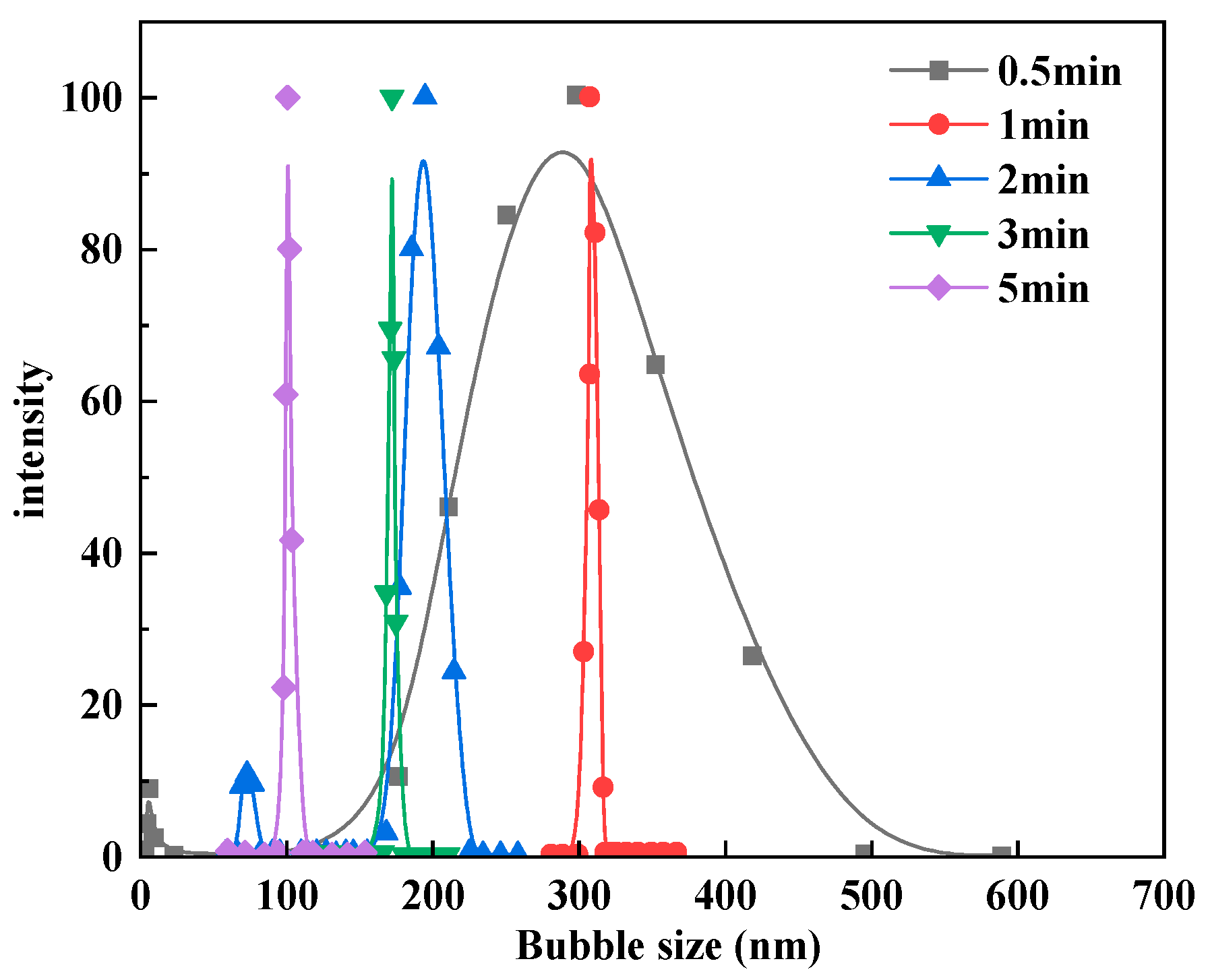
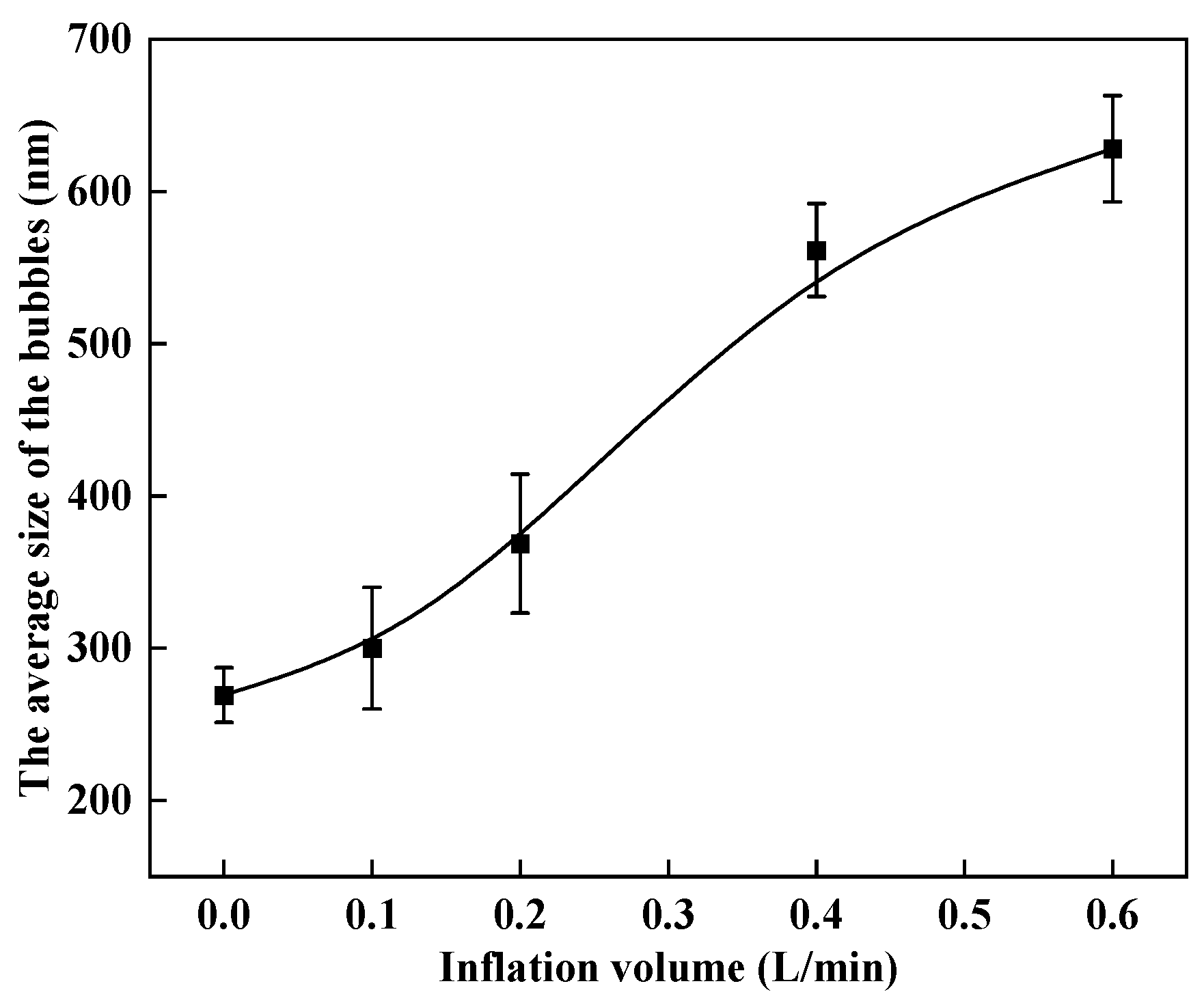
3.1. Bubble Cavitation Property Test Results
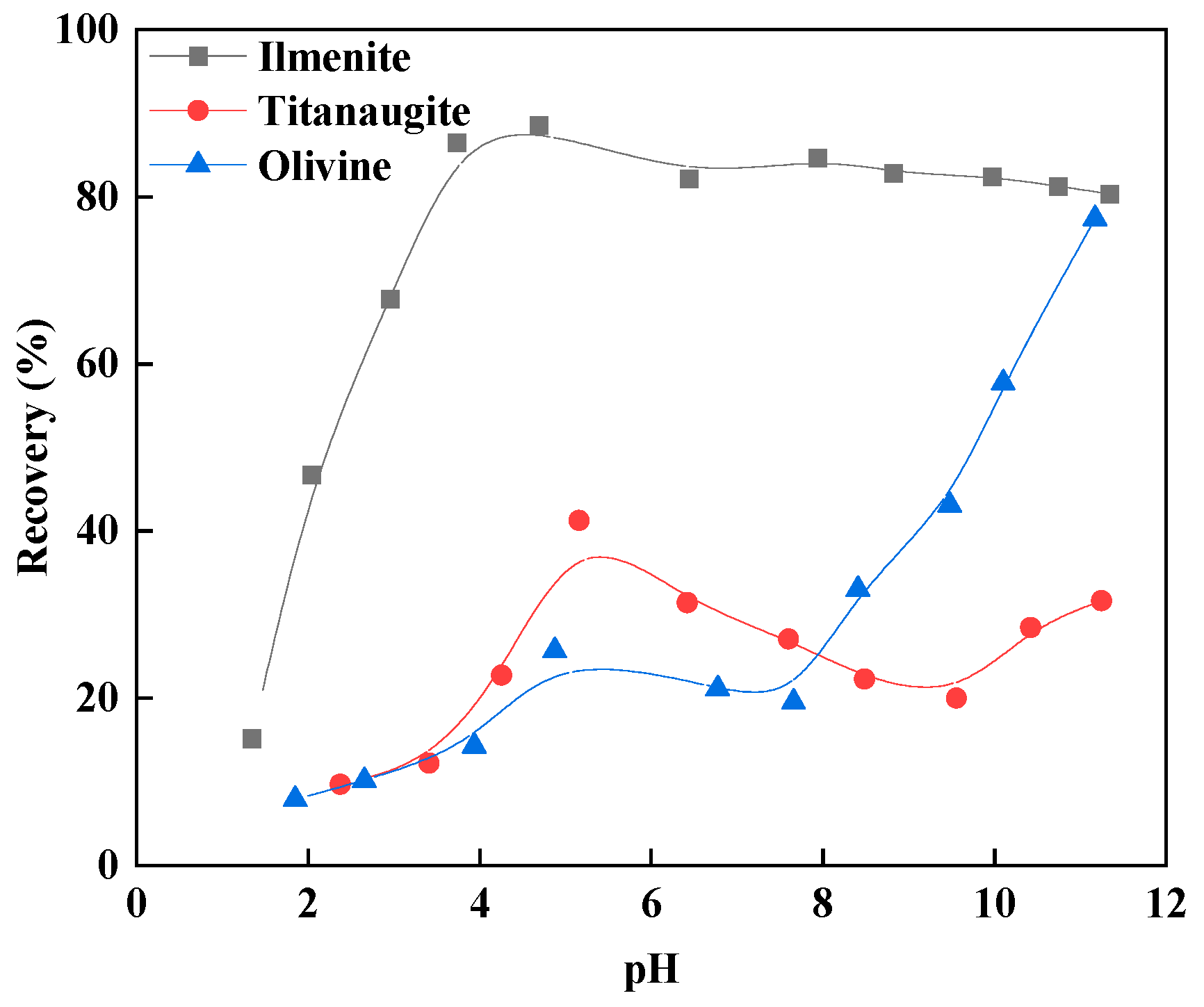
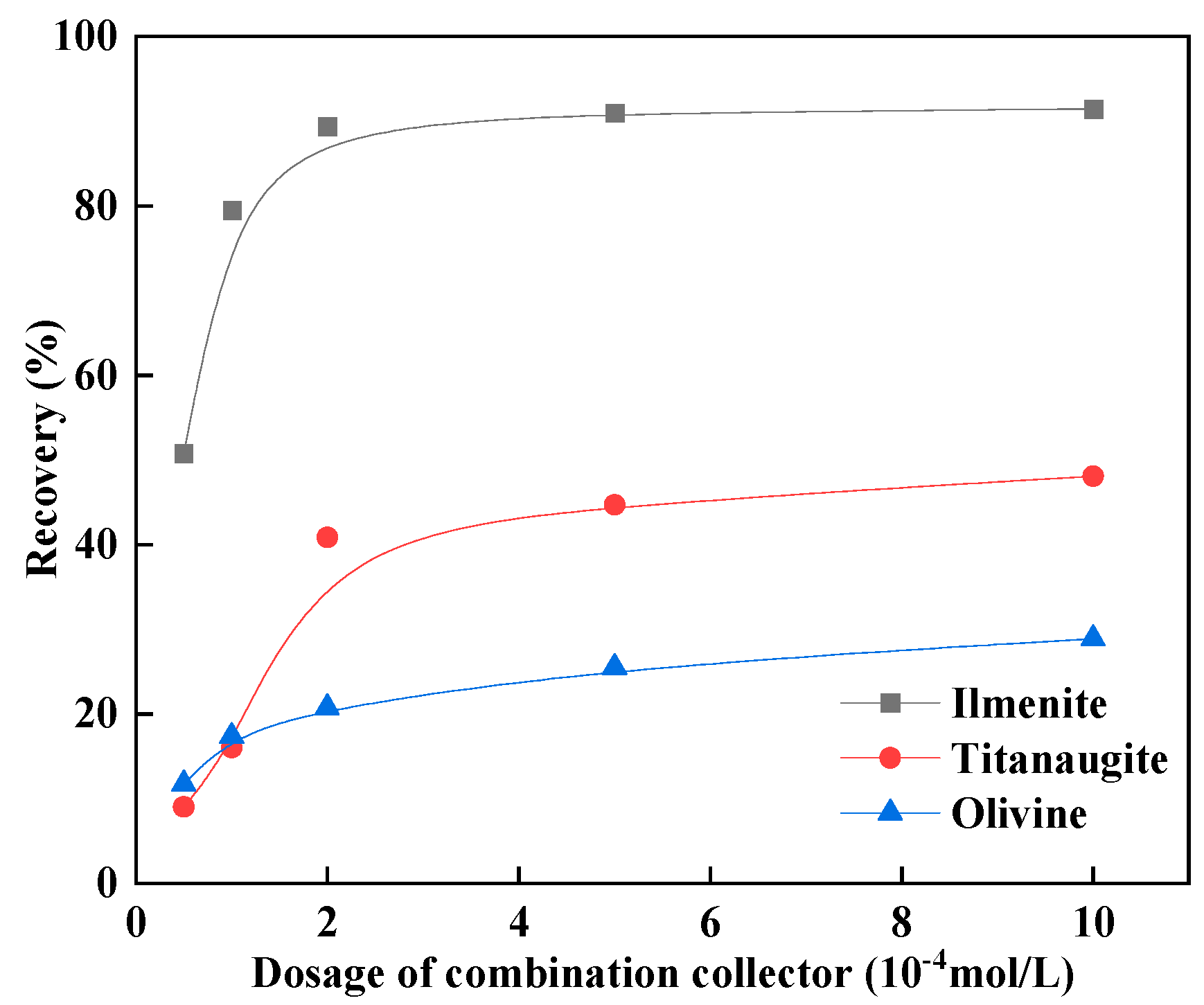
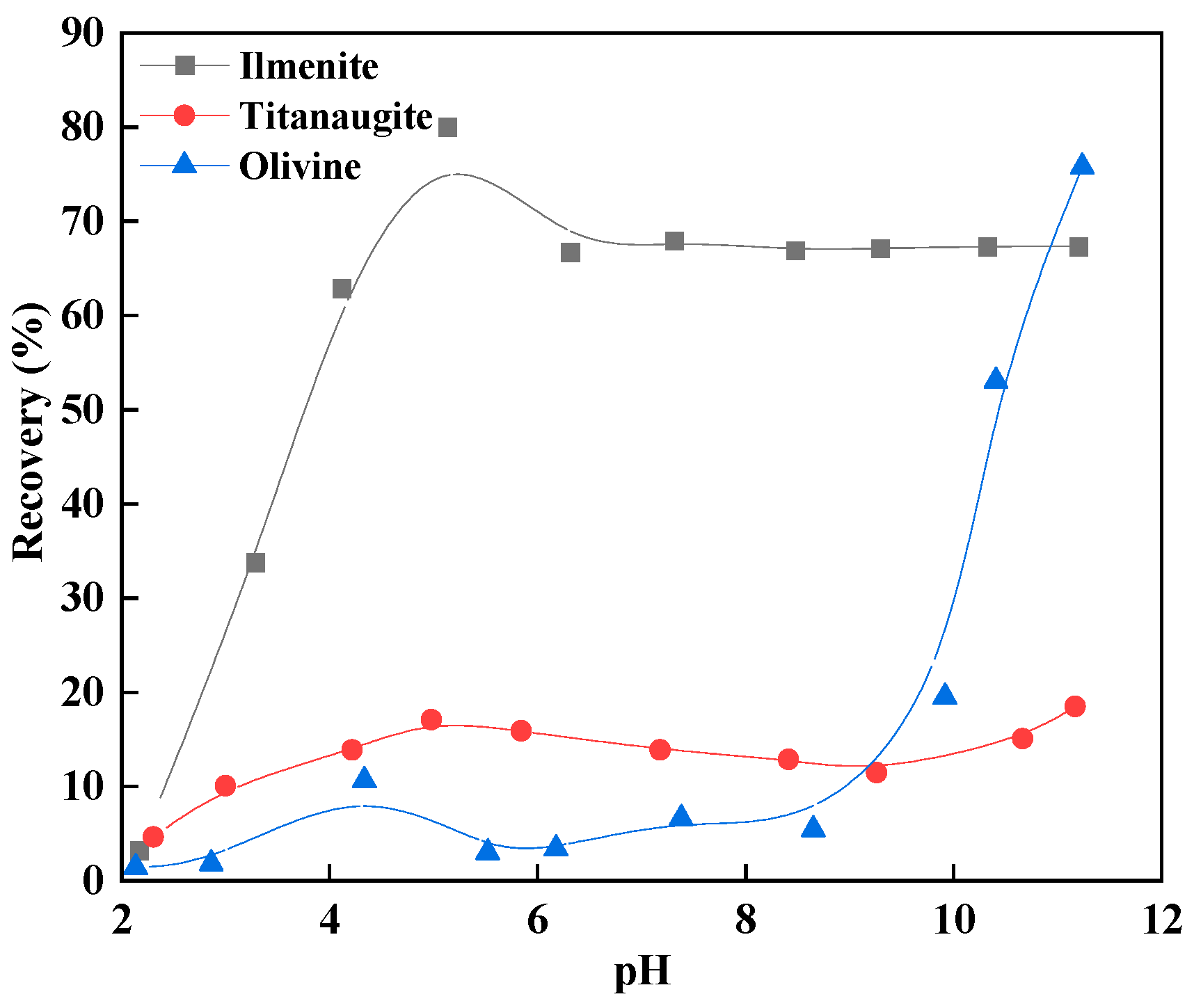
3.2. Micro-Flotation Test Results
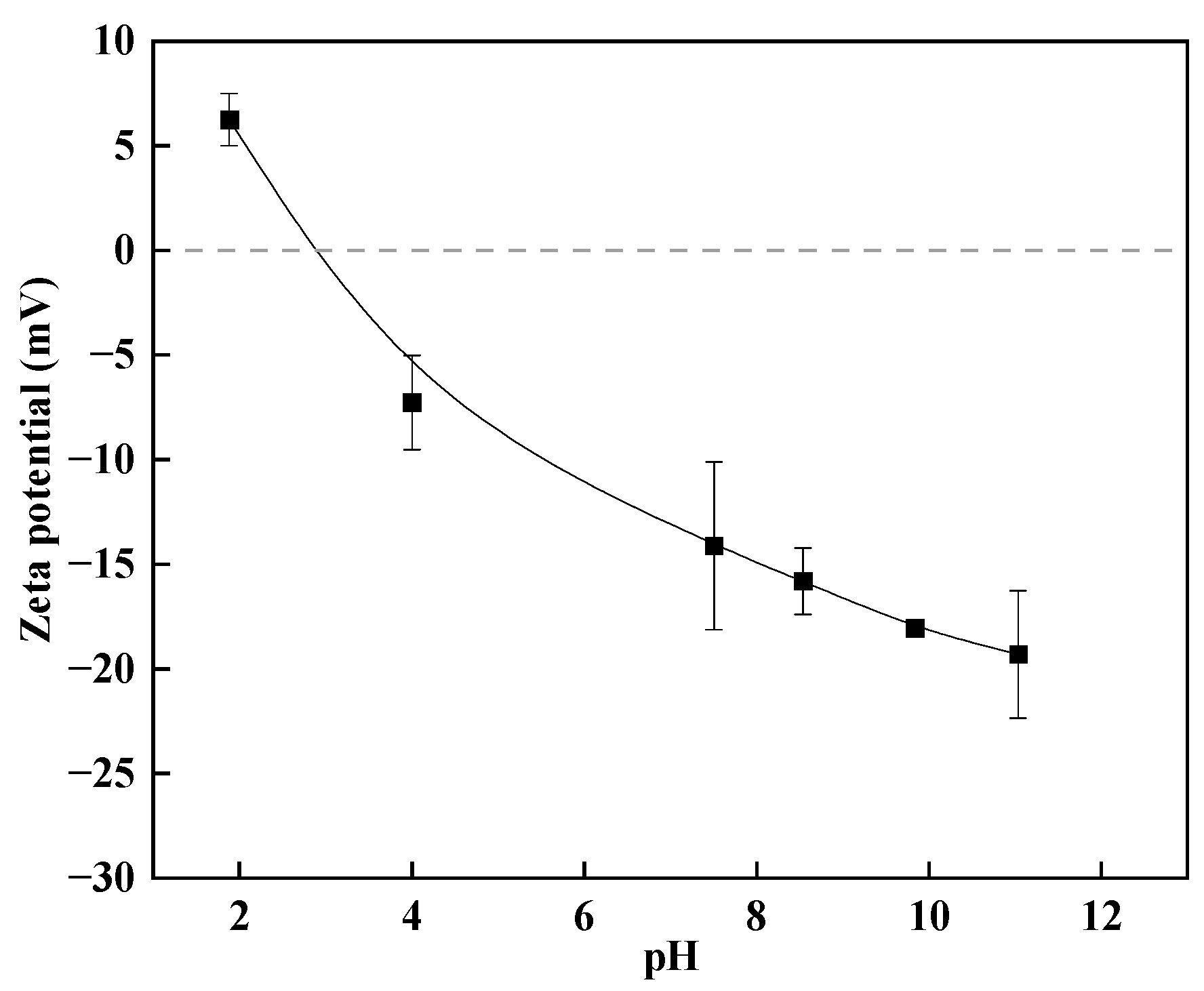
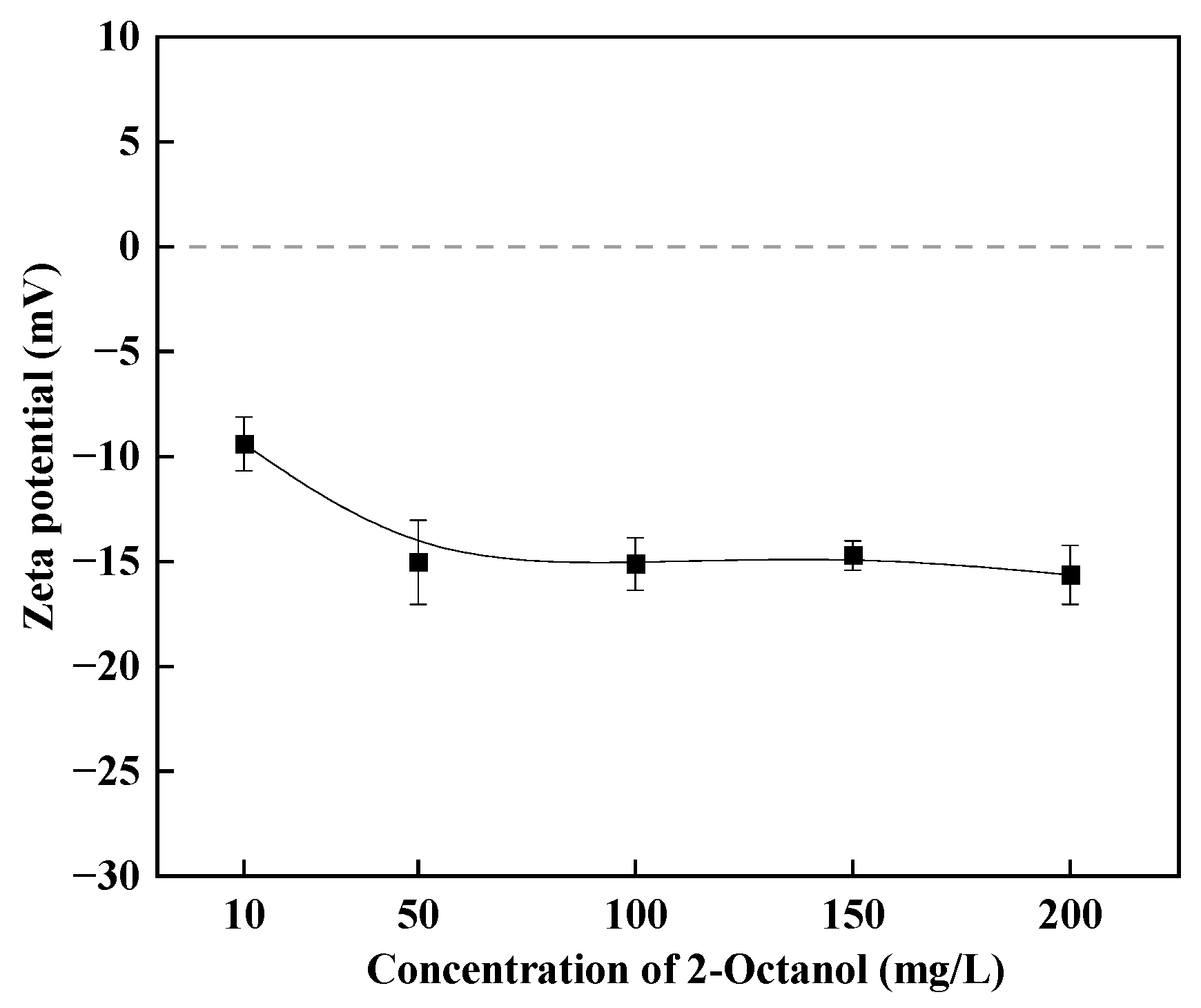
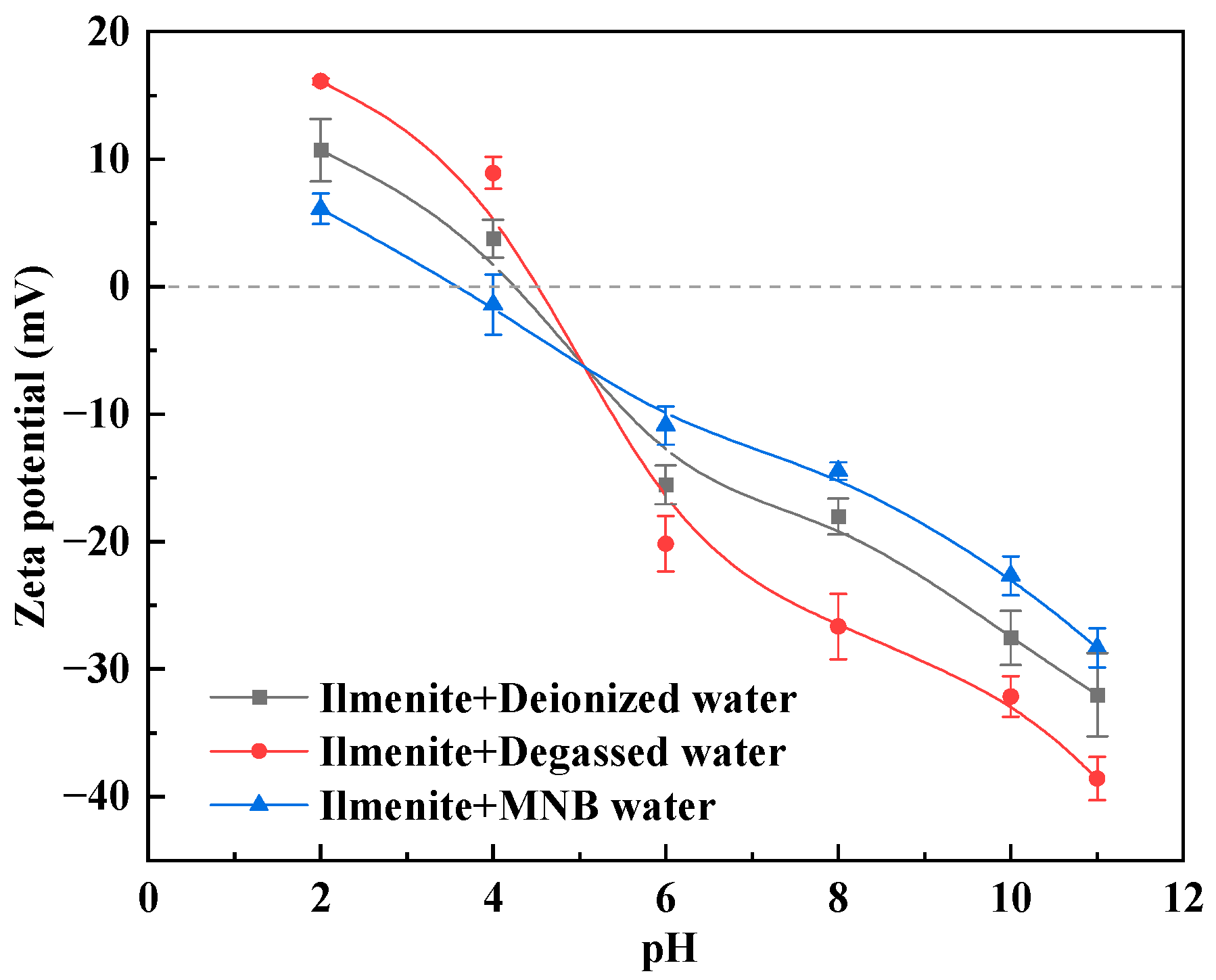
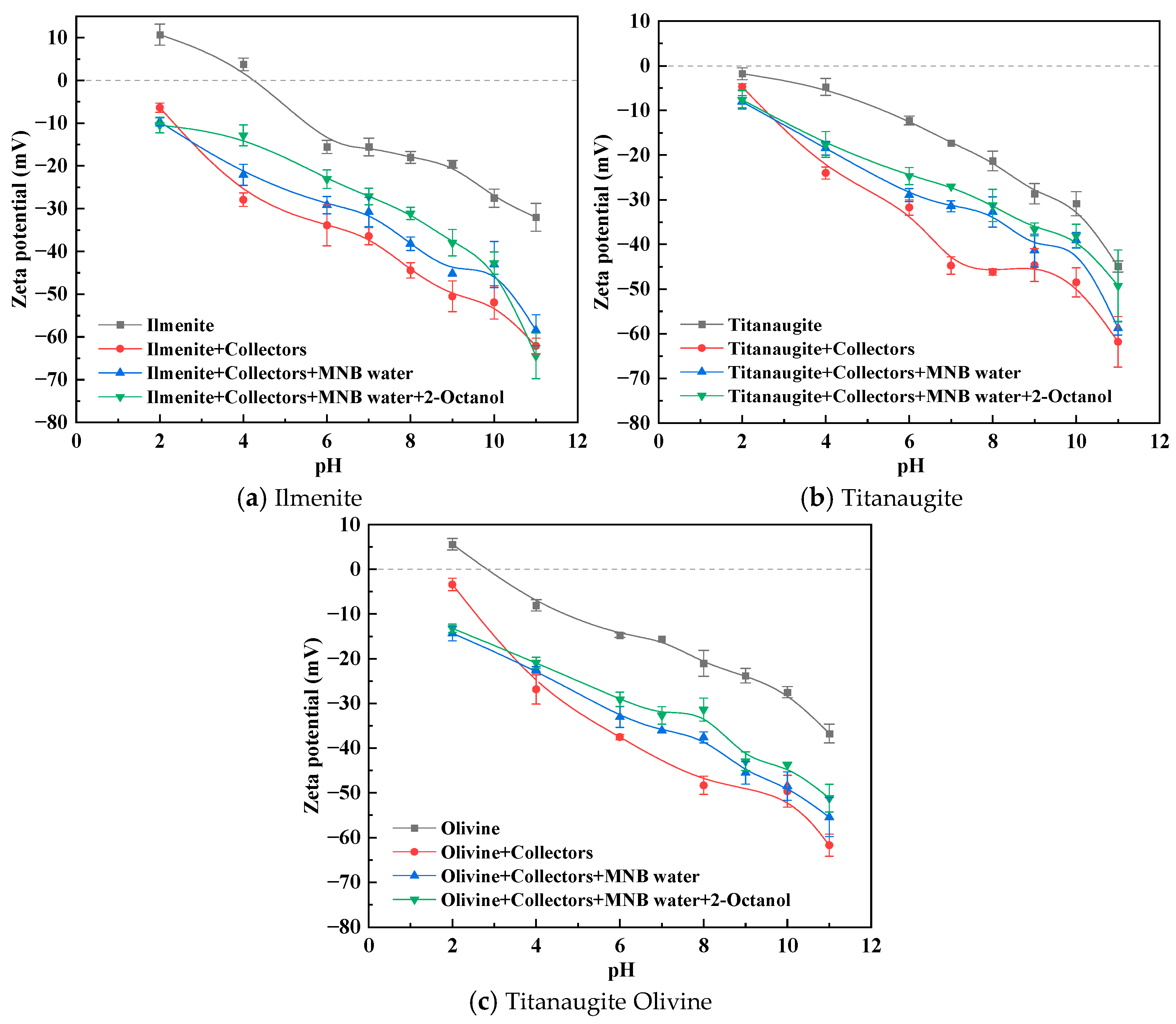
3.3. Zeta Potential Analysis
3.4. Adsorption Capacity Detection
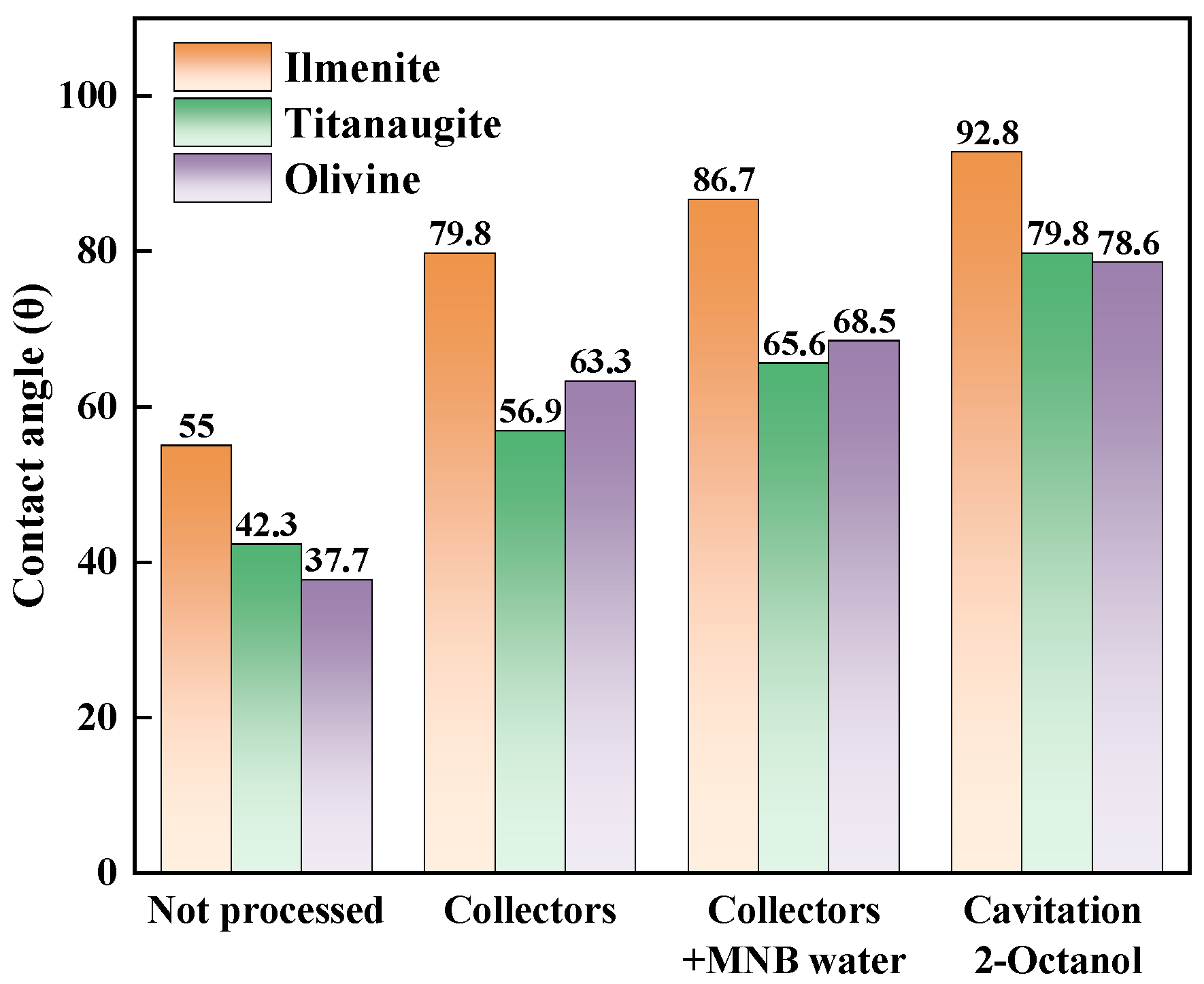
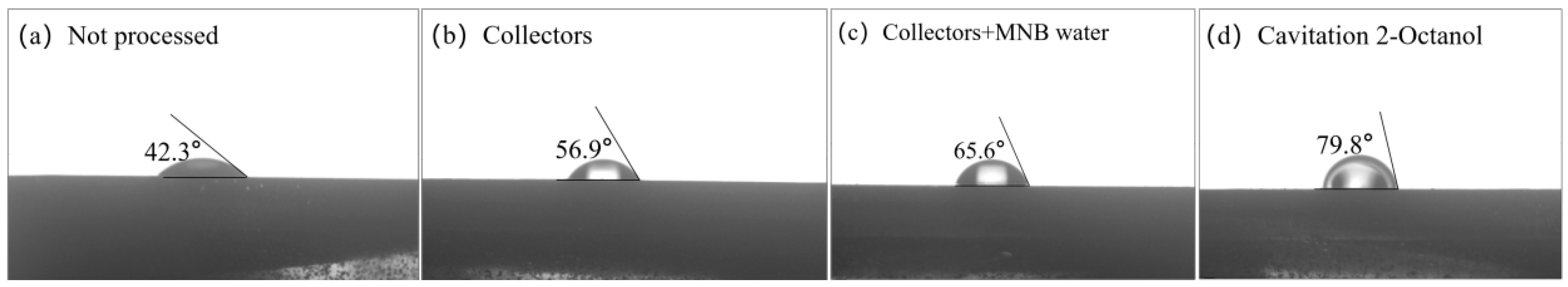
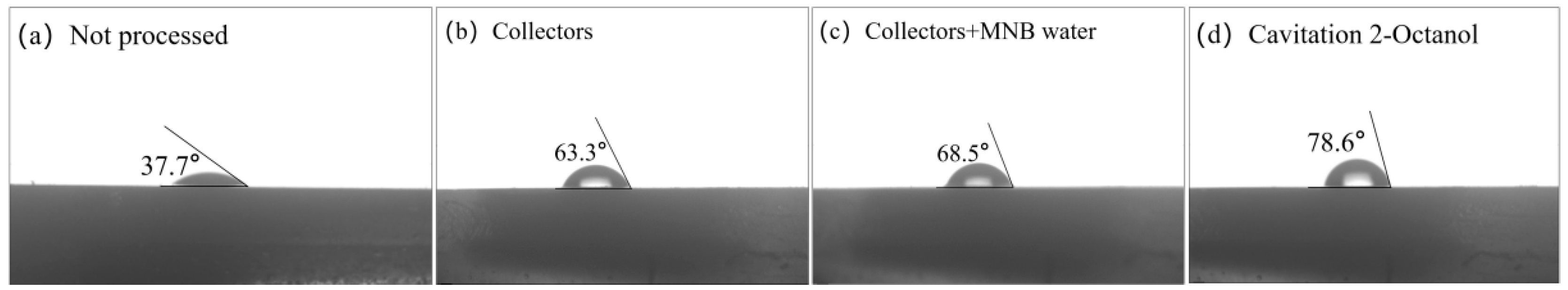
3.5. Contact Angle Measurement
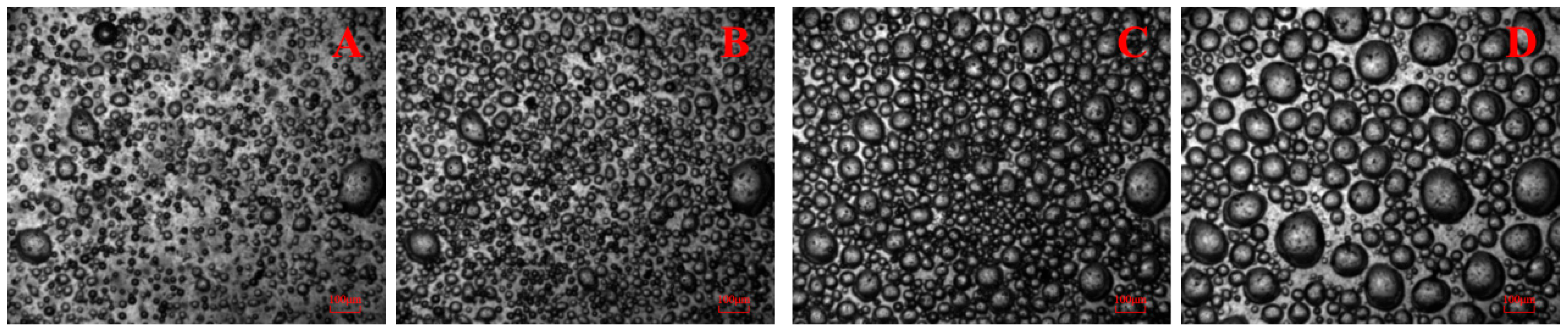
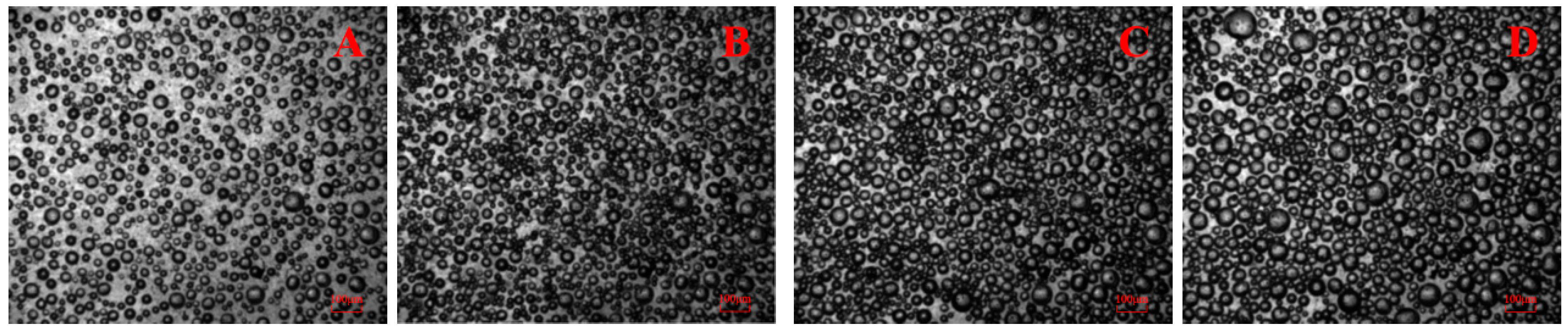
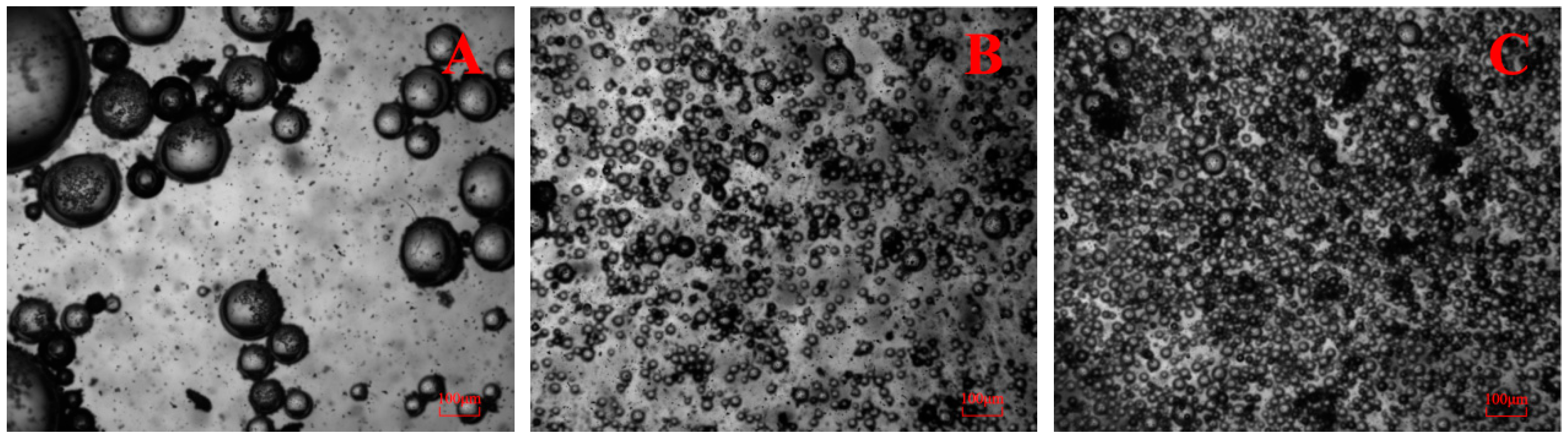
3.6. Microbubble Monitoring System Observations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, W.; Chen, W.; Wan, S. A review of mineral processing of ilmenite by flotation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 157, 106558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qu, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, W. Recent technology developments in beneficiation and enrichment of ilmenite: A review. Miner. Eng. 2024, 219, 109084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Meng, Q.; Han, C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, P. Impact of acid surface pretreatment on the aggregation and flotation behavior of micro-fine ilmenite and its functional mechanism. Adv. Powder Technol. 2025, 36, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhang, G.-F.; Feng, Q.-M.; Yan, D.-C.; Wang, W.-Q. Effect of surface dissolution on flotation separation of fine ilmenite from titanaugite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Du, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yu, L. Influence of sodium silicate on the selective dispersion and flotation separation of ilmenite against fine titanaugite in hydrophobic systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 680, 161348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Wen, S.; Feng, Q.; Bai, S. Co-adsorption mechanism of NaOL/OHA mixed collectors and its contribution to surface hydrophobicity of micro-fine ilmenite: An experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 411, 125689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Particle-bubble collision models-A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfruns, J.F.; Kitchener, J.A. Rate of capture of small particles in flotation. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sect. C Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 1977, 86, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fornasiero, D.; Filippov, L. Innovations in the flotation of fineand coarse particles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 879, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, T.V.; Forssberg, K.S.E. Fine particles processing: Shear-flocculation and carrier flotation-a review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1990, 30, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamohan, R. The problem of recovering very fine particles in mineral processing: A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1990, 28, 247–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjaguin, B.V.; Dukhin, S.S. Theory of flotation of small and medium-size particles. Bull.—Inst. Min. Metall. 1961, 651, 21–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.V.; George, P.; Jameson, G.J. Demonstration of a minimum in the recovery of nanoparticles by flotation: Theory and experiment. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 2494–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Han, C.; Li, L.; Lu, J.; Liu, T. Impact of acid surface pretreatment on the hydrophobic agglomeration of micro-fine ilmenite and titanaugite in flotation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 218, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, K.L. Physical chemistry of flotation XⅠ. Kinetics of the flotation process. J. Phys. Colloid Chem. 1948, 52, 394–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobby, G.S.; Finch, J.A. Particle size dependence in flotation derived from a fundamental model of the capture process. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1987, 21, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheludko, A.; Toshev, B.V.; Bojadjiev, D.T. Attachment of particles to a liquid surface (capillary theory of fotation). J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1976, 72, 2815–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Q.; Wang, H.; Jiang, F.; Tan, W.; Chen, J.; Zhong, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z. Enhancing flotation separation of fine copper oxide from silica by microbubble assisted hydrophobic aggregation. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.; Azevedo, A.; Rodrigues, R.; Olivares, G.R. Amine-coated nanobubbles-assisted flotation of fine and coarse quartz. Miner. Eng. 2024, 218, 108983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulyov, N.N.; Sadovskiy, D.Y.; Rulyova, N.A.; Filippov, L.O. Column flotation of fine glass beads enhanced by their prior heteroaggregation with microbubbles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 617, 126398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Darban, A.K.; Mahmoud, A.; Fan, M. Nano-microbubble flotation of fine and ultrafine chalcopyrite particles. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin, A.M.; Schuhmann, R., Jr.; Schlechten, A.W. Flotation kinetics II. The effect of size on the behaviour of galena particles. J. Phys. Chem. 1942, 46, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Y. Nanobubble-enhanced flotation of ultrafine molybdenite and the associated mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 118312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Miller, J.D. Bubble/particle contact time in the analysis of coal fotation. Coal Prep. 1988, 5, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Xie, G.; Peng, Y. Interaction of fine, medium, and coarse particles in coal fines flotation. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liang, L.; Tan, J.; Sha, J.; Xie, G. Effect of flotation reagent adsorption by different ultra-fine coal particles on coal flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 142, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Tao, D.; Tao, Y. Effects of nanobubbles incolumn flotation of Chinese sub-bituminous coal. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2022, 42, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, K.; Huang, L.; Bao, S.; Liu, C.; Yang, S. Interaction mechanism of interfacial nano-micro bubbles with collectors and its effects on the fine apatite flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 682, 161736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabcová, Z.; Karapantsios, T.; Kostoglou, M.; Basařová, P.; Matis, K. Bubble–particle collision interaction in flotation systems. Colloids Surf A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 473, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryagin, B.V.; Dukhin, S.S.; Rulev, N.N. Kinetic Theory of the flotation of small particles. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1982, 51, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsave, P.K.; Kostoglou, M.; Karapantsios, T.D.; Lazaridis, N.K. A hybrid device for enhancing flotation of fine particlesby combining micro-bubbles with conventional bubbles. Minerals 2021, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.H.; Luttrell, G.H. The effect of bubble size on fine particle flotation. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1989, 5, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinjenab, Z.T.; Azimi, E.; Shadman, M.; Hosseini, M.R. Maximization of ultrafine poly-mineral ore sequential flotation recovery through synergistic effect of conventional and nano-size bubble combination. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 401, 124698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.M.; Ata, S.; Jameson, G.J. The effect of flotation variables on the recovery of different particle size fractions in the froth and the pulp. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2012, 106–109, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Particle-bubble attachment in mineral fotation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 217, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, K.E.; Hadler, K.; Cilliers, J.J. The flotation of fine particles using charged microbubbles. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.; Ratclif, G.A. Removal of fine particles from water by dispersed air flotation. Effects of bubble size and particle size on collection efficiency. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1973, 51, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H. On the optimization of hydrodynamics in fine particle flotation. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.H. The role of hydrodynamic and surface forces in bubble-particle interaction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000, 58, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yi, J.; Chen, W.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Z. Effect of frothers on the interaction between air bubbles and coal particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 715, 136612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Deng, J.; Chen, B.; Yan, W.; Xiong, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J. Flotation behaviors of ilmenite, titanaugite, and forsterite using sodium oleate as the collector. Miner. Eng. 2015, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoswell, D.R.E.; Duan, J.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Colloid stability and the influence of dissolved gas. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 2986–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, J.; Fornasiero, D.; Mishchuk, N. The hydrophobic force in flotation-a critique. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 192, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Li, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, N. Effect of the adding order of sulfuric acid on the flotation behaviors of ilmenite and titanaugite and its functional mechanism. Miner. Eng. 2023, 199, 108116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Wu, Z.; Huang, H.; Ran, J.; Ma, G.; Shao, H.; Tao, D. An investigation of nanobubble treatment on fine particle flotation and associated mechanisms. Green Smart Min. Eng. 2025, 2, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
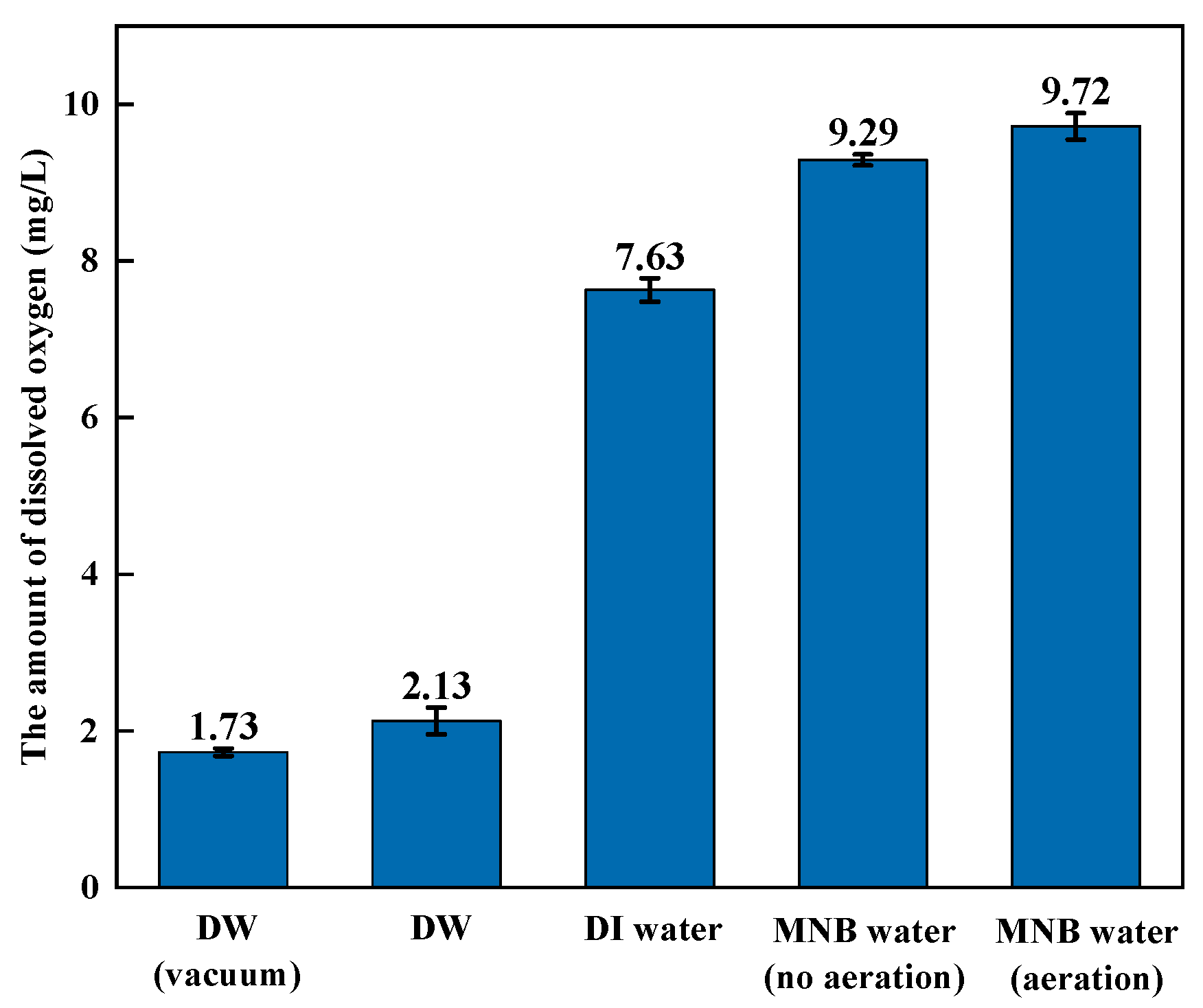








| Flotation Conditions | Product | Yield (%) | TiO2 Grade (%) | TiO2 Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deionized water | Concentrate | 34.05 | 31.07 | 61.53 |
| Tailing | 65.95 | 10.03 | 38.47 | |
| Feed | 100.00 | 17.19 | 100.00 | |
| Micro–nanobubble water | Concentrate | 36.74 | 32.52 | 68.59 |
| Tailing | 63.26 | 8.65 | 31.41 | |
| Feed | 100.00 | 17.42 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, W.; Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, W. The Cavitation Characteristics of Micro–Nanobubbles and Their Effects on the Flotation Recovery of Fine-Grained Ilmenite. Minerals 2025, 15, 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060628
Yan W, Zhang B, Yang Y, Deng J, Li W. The Cavitation Characteristics of Micro–Nanobubbles and Their Effects on the Flotation Recovery of Fine-Grained Ilmenite. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):628. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060628
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Weiping, Boyuan Zhang, Yaohui Yang, Jian Deng, and Weisi Li. 2025. "The Cavitation Characteristics of Micro–Nanobubbles and Their Effects on the Flotation Recovery of Fine-Grained Ilmenite" Minerals 15, no. 6: 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060628
APA StyleYan, W., Zhang, B., Yang, Y., Deng, J., & Li, W. (2025). The Cavitation Characteristics of Micro–Nanobubbles and Their Effects on the Flotation Recovery of Fine-Grained Ilmenite. Minerals, 15(6), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060628





