Surface Physicochemical Property Differences Between Gold-Bearing and Gold-Free Pyrite for Efficient and Clean Processing of Refractory Pyritic Gold Ores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material and Reagents
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2.4. Calculation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
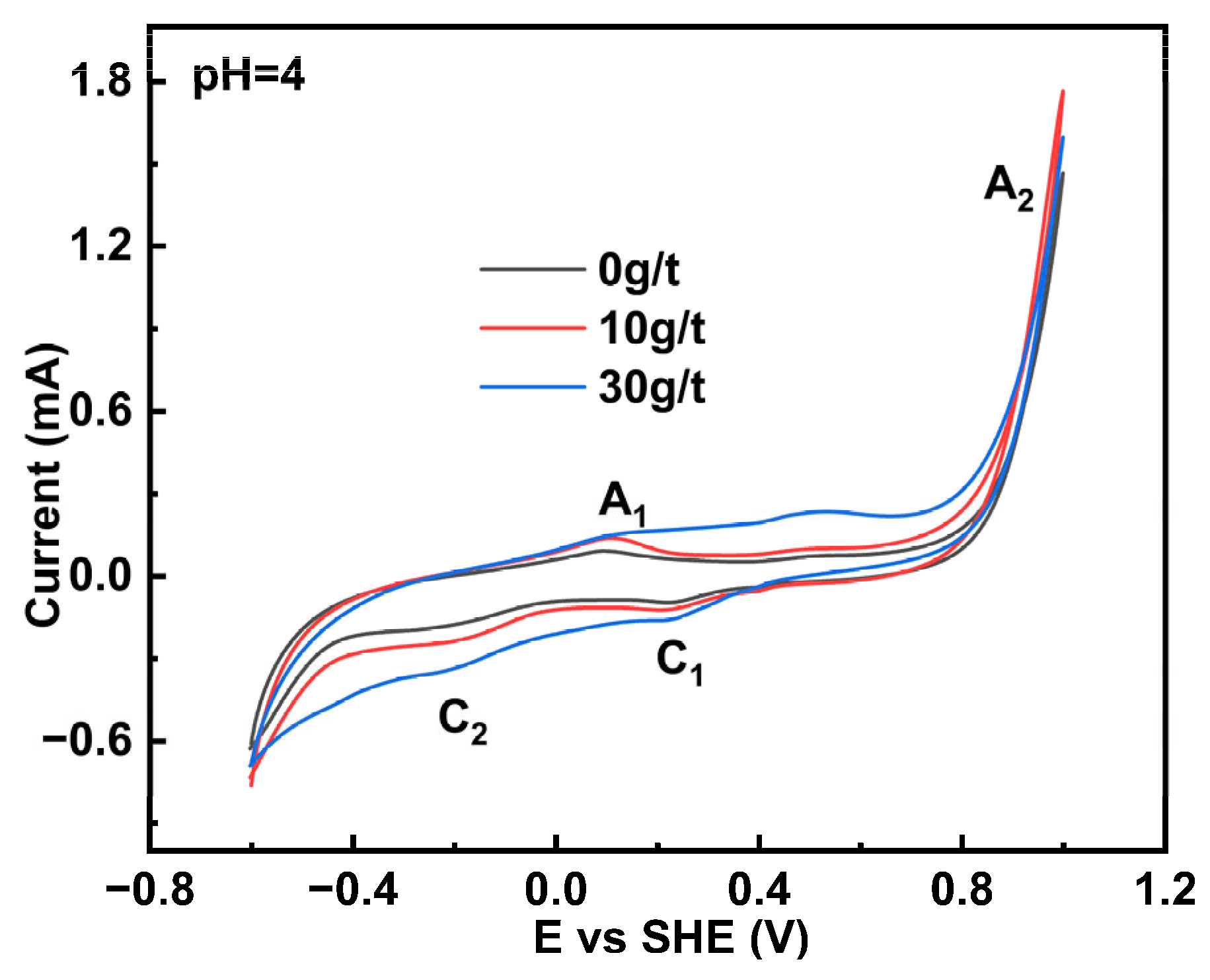
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry Measurement
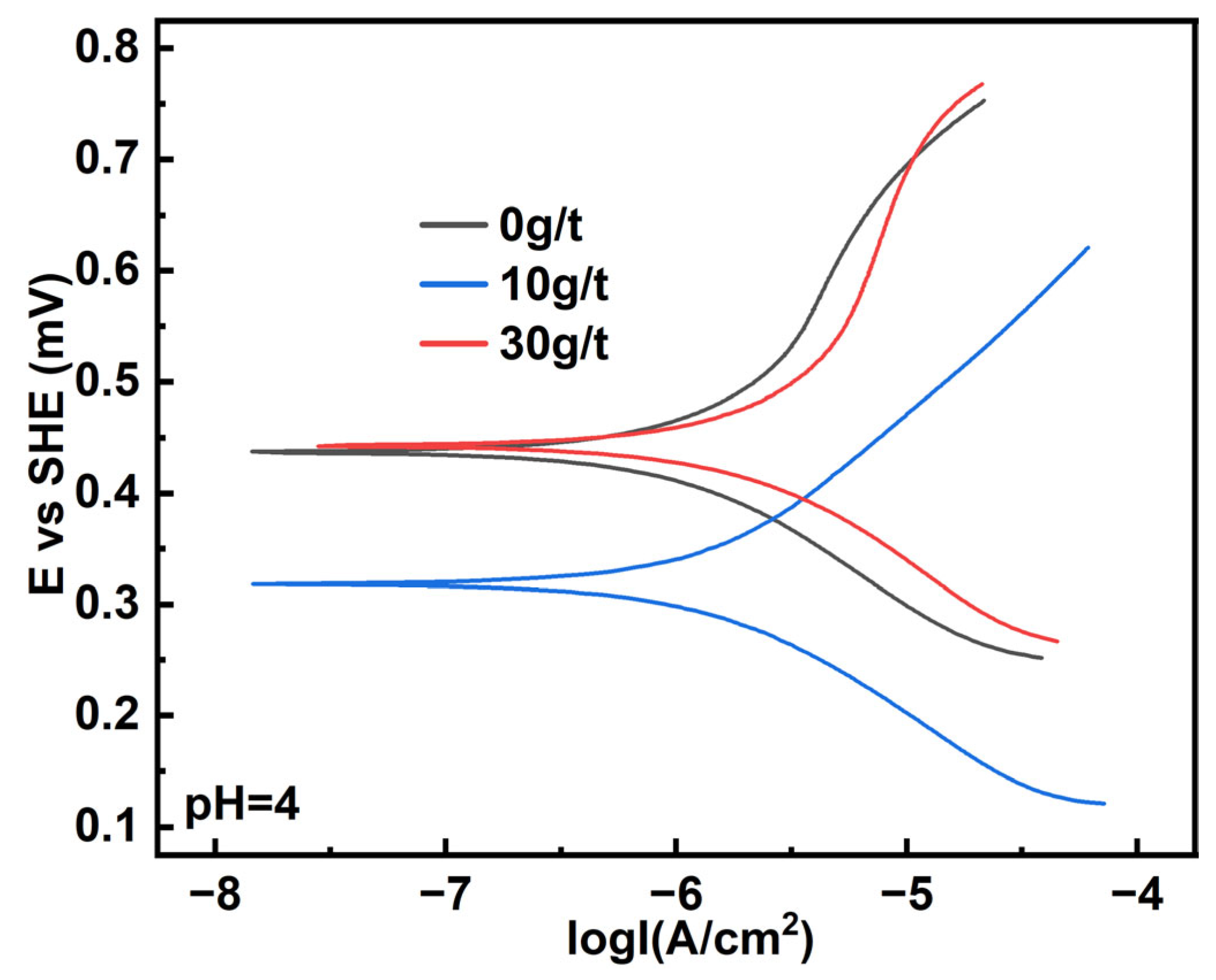
3.2. Polarization Curve Measurement
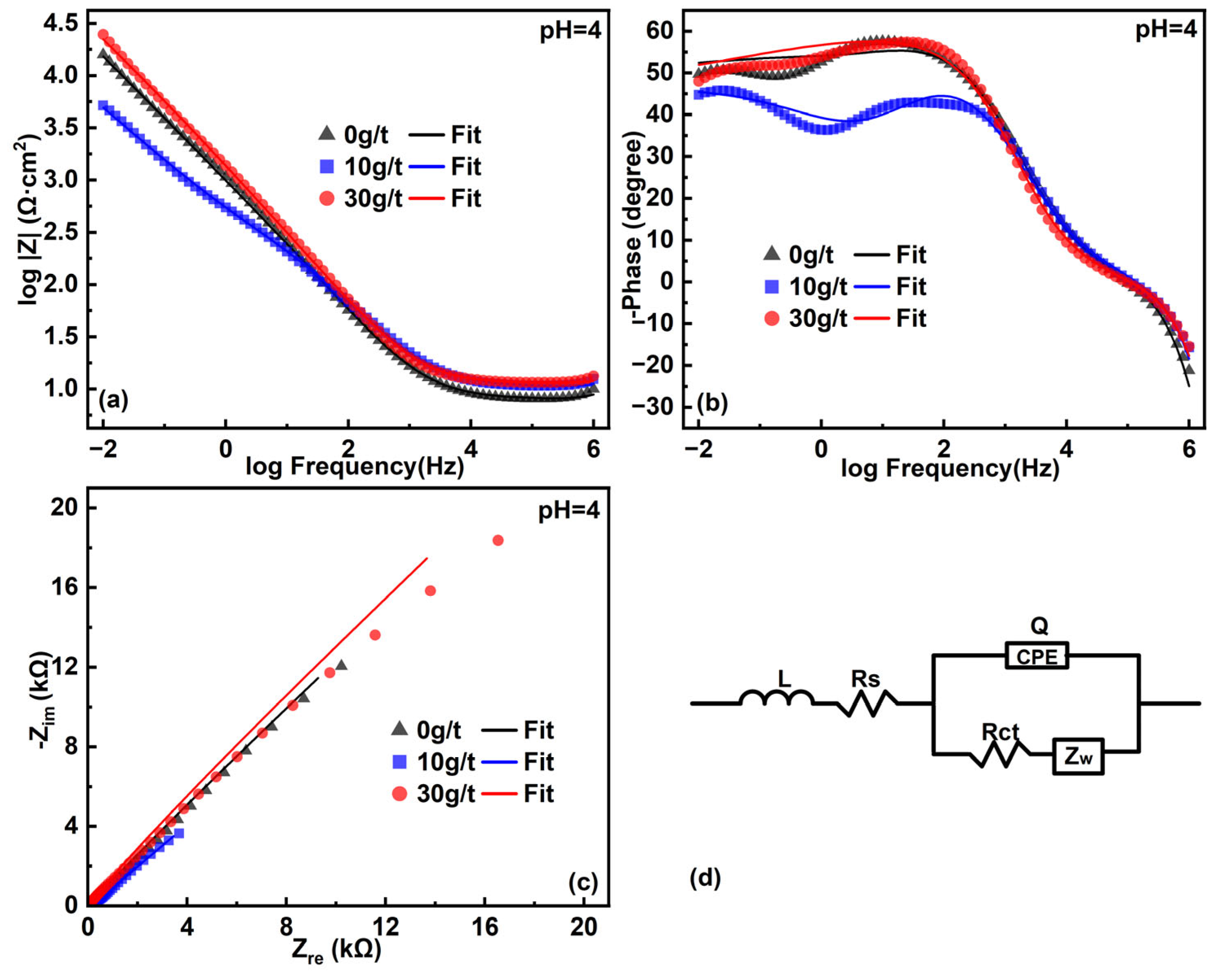
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
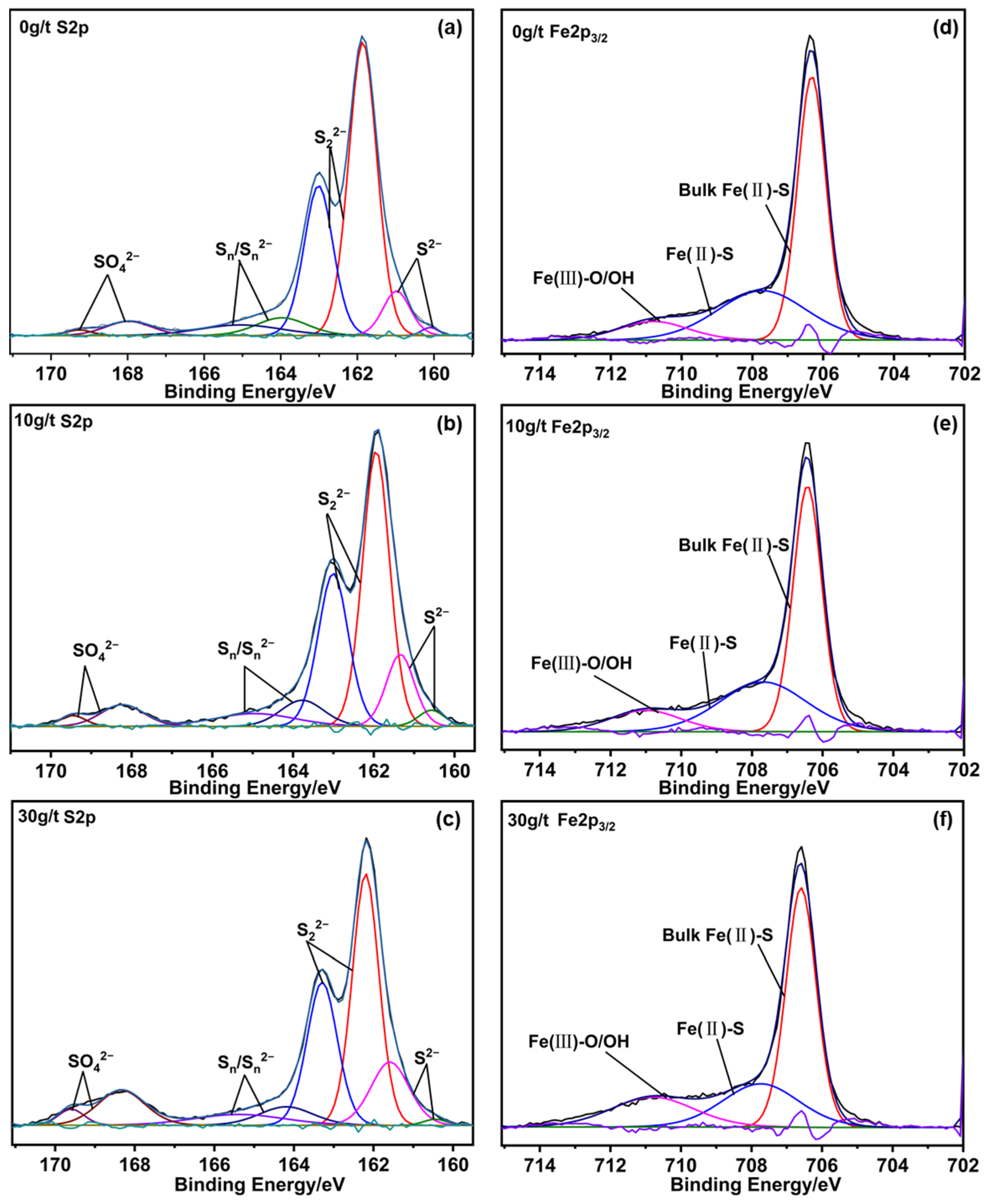
3.4. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analysis
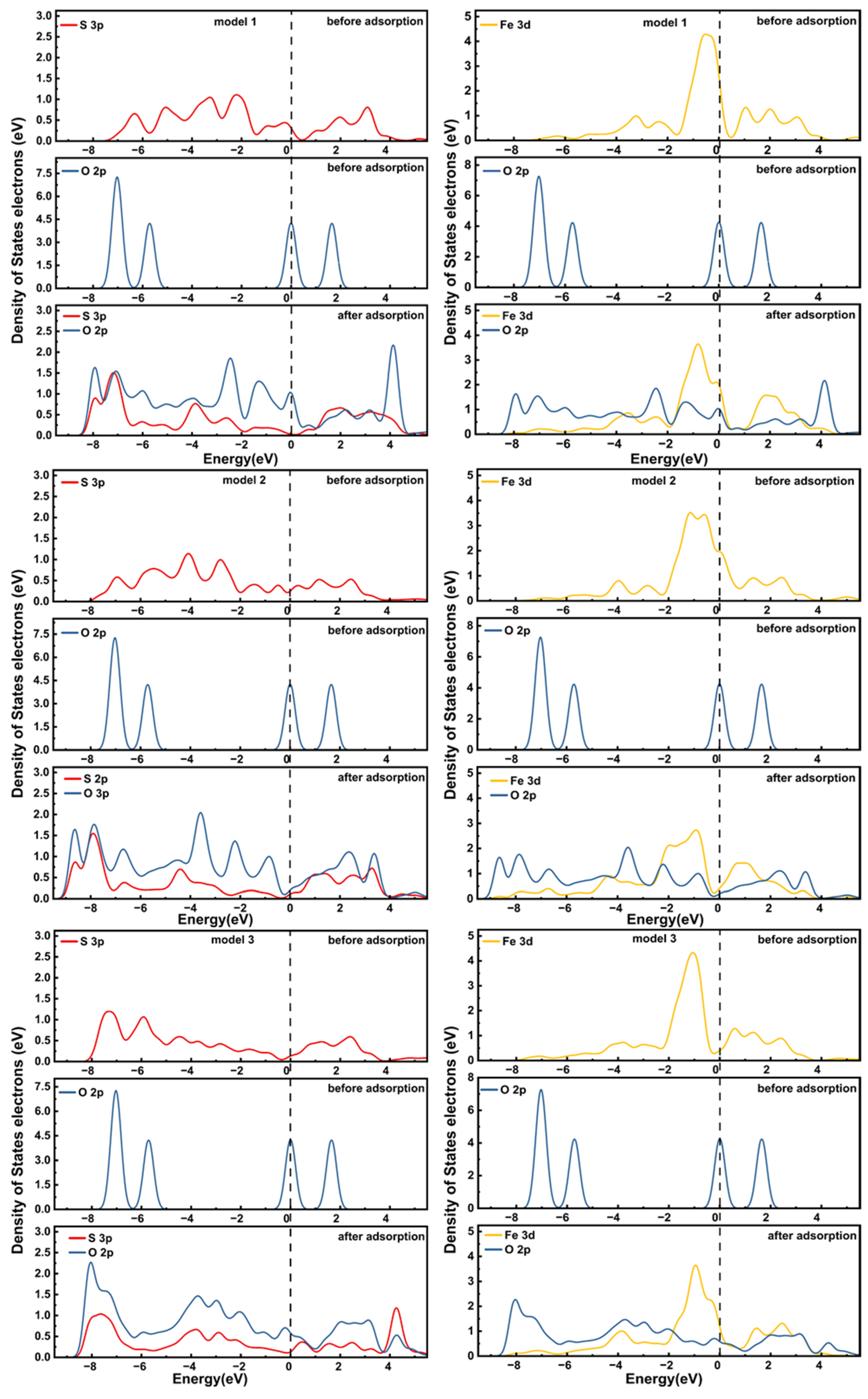
3.5. DOS Analysis of Different Pyrite Surfaces Before and After Oxygen Adsorption
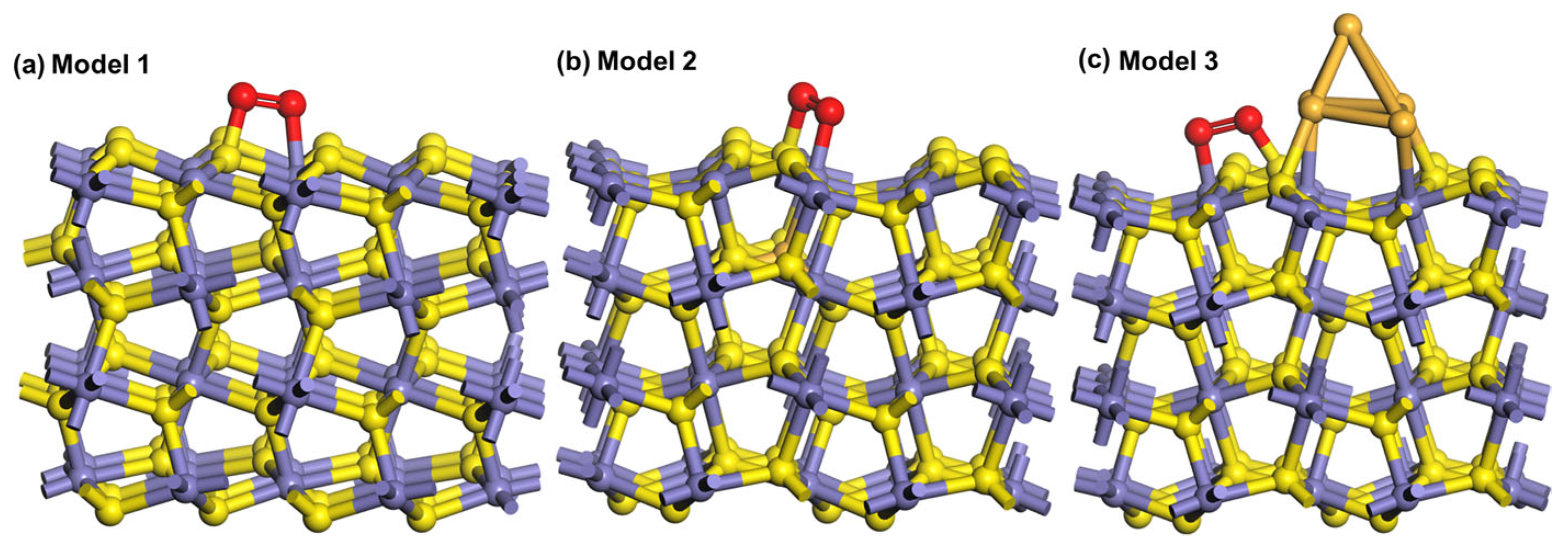
3.6. Adsorption Energy and Structure of Oxygen on Different Pyrite Surfaces
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- All electrochemical analyses indicated that the occurrence of gold enhanced the electrochemical reactivity of pyrite, with reactivity positively correlated with gold content.
- (2)
- XPS results confirmed the findings of the electrochemical tests, demonstrating that under identical oxidation conditions, high-gold pyrite had the most oxidation products on its surface, followed by low-gold pyrite, and gold-free pyrite had the least.
- (3)
- DFT simulations revealed that the presence of gold lowered the adsorption energy of oxygen on the pyrite surface while also promoting the interaction between oxygen atoms and sulfur and iron atoms on the pyrite surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, R.; Tong, L.; Chen, Q. Mineralogical characteristics and recovery process optimization analysis of a refractory gold ore with gold particles mainly encapsulated in pyrite and Arsenopyrite. Geochemistry 2023, 83, 125941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.S.; Walton, R.H.; Wells, J.A. Processing of refractory gold ores. Miner. Eng. 1991, 4, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afenya, P.M. Treatment of carbonaceous refractory gold ores. Miner. Eng. 1991, 4, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Lai, S.; Liang, G.; Wang, X.; Tan, B. Identification of elements hindering gold leaching from gold-bearing dust and selection of gold extraction process. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Mines, K.C.G.; Kalgoorlie, W. Ultra fine grinding-a practical alternative to oxidative treatment of refractory gold ores. In Proceedings of the Eighth Mill Operators Conference, Townsville, QLD, Australia, 22–23 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Wu, F.-D.; Chen, A.; Shi, L.-J.; Zeng, W.-M.; Gu, G.-H.; Qin, W.-Q.; Qiu, G.-Z. Effect of mixed moderately thermophilic adaptation on leachability and mechanism of high arsenic gold concentrate in an airlift bioreactor. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Guo, X.; Tian, Q.; Yu, D.; Zhang, L. Recovery of gold from sulfide refractory gold ore: Oxidation roasting pretreatment and gold extraction. Miner. Eng. 2021, 164, 106822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dabrowski, B.; Miller, J.D.; Acar, S.; Dietrich, M.; LeVier, K.; Wan, R. The influence of pyrite pre-oxidation on gold recovery by cyanidation. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Dixon, D.G. Pressure oxidation of pyrite in sulfuric acid media: A kinetic study. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylina, I.; Trevani, L.; Mojumdar, S.; Tremaine, P.; Papangelakis, V.G. Measurement of reaction enthalpy during pressure oxidation of sulphide minerals. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 96, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylina, I.V.; Mojumdar, S.C.; Papangelakis, V.G. Effect of storage time on the pressure oxidation enthalpy of pyrite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 108, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papangelakis, V.G.; Demopoulos, G.P. On the attainment of stable autothermal operation in continuous pressure leaching reactors. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 29, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.G. Examining the economics of some pressure oxidation process options. Hydrometallurgy 1992, 29, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, Y.; Plackowski, C.; Peng, Y. The surface properties of pyrite coupled with gold in the presence of oxygen. Miner. Eng. 2017, 111, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boduen, A.; Zalesov, M.; Melamud, V.; Grigorieva, V.; Bulaev, A. Combined Bacterial and Pressure Oxidation for Processing High-Sulfur Refractory Gold Concentrate. Processes 2023, 11, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Lin, S.; Zhai, J.; Kang, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, R. A new combined collector for flotation separation of ilmenite from titanaugite in acidic pulp. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, H.; Li, W. Optimize flotation process of Mo–Bi sulfide ore for cleaner production. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Zhai, Q.; Dong, W.; Xie, Z.; Sun, W.; Hu, W. Prospects of pulp aeration for the cleaner production of pyrrhotite-rich type copper sulfide ore: Mechanism and application. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chai, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Meng, X. The effect of calcium hypochlorite on the adsorption of diethyldithiocarbamate (DDTC) on the surface of molybdenite and bismuthinite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 676, 132270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; He, J.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W. Depression behavior and mechanism of pyrogallol on bismuthinite flotation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C. First principles study of the occurrence of gold in pyrite. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 88, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, Y.; Plackowski, C.; Peng, Y. The effect of gold coupling on the surface properties of pyrite in the presence of ferric ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; He, B.; Luo, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zou, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z. Effects of Au doping on the adsorption of xanthate on pyrite surface in presence of H2O: A DFT study. Miner. Eng. 2024, 210, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.; Lindan, P.J.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1990, 41, 7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.I.; Zaanen, J.; Andersen, O.K. Band theory and Mott insulators: Hubbard U instead of Stoner I. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 44, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pack, J.D.; Monkhorst, H. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations—A reply. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 16, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, D.; Larachi, F. DFT simulations of pyrite galvanic interactions with bulk, solid-solution and nanoparticle Au occurrences–Insights into gold cyanidation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 149, 106239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ke, B.; Lan, L.; Li, Y. DFT and experimental studies of oxygen adsorption on galena surface bearing Ag, Mn, Bi and Cu impurities. Miner. Eng. 2015, 71, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Moslemi, H.; Gharabaghi, M. A review on electrochemical behavior of pyrite in the froth flotation process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbalnia, M.; Dixon, D.G. In situ electrochemical characterization of natural pyrite as a galvanic catalyst using single-particle microelectrode technique in ferric sulfate solutions. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2013, 17, 235–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Peng, Y.; Parker, G. Electrochemical and spectroscopic studies of pyrite–cyanide interactions in relation to the depression of pyrite flotation. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Ao, S.; Ning, S.; Liu, R.; Qin, W. A comprehensive electrochemical analysis revealing the surface oxidation behavior difference between pyrite and arsenopyrite. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2024, 969, 118552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, I.C.; Woods, R. An investigation of surface oxidation of pyrite and pyrrhotite by linear potential sweep voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1981, 118, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, B.F.; Bonilla, S.H.; Zinola, C.F.; Rabóczkay, T. A study of the main oxidation products of natural pyrite by voltammetric and photoelectrochemical responses. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W. Mechanism and Applications of Potential-Controlled Flotation in Lime Adjust High Alkali Pulp. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R.; White, H.S. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Influence of differential stress on the galvanic interaction of pyrite–chalcopyrite. Ionic 2013, 19, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejtemaei, M.; Nguyen, A.V. Characterisation of sphalerite and pyrite surfaces activated by copper sulphate. Miner. Eng. 2017, 100, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinder, J.W.; Major, G.H.; Baer, D.R.; Terry, J.; Whitten, J.E.; Čechal, J.; Crossman, J.D.; Lizarbe, A.J.; Jafari, S.; Easton, C.D.; et al. Avoiding common errors in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy data collection and analysis, and properly reporting instrument parameters. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 19, 100534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, Y. Surface properties of fractured and polished pyrite in relation to flotation. Miner. Eng. 2017, 101, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Khoso, S.A.; Lu, H.; Sun, W.; Ni, Z.; Lyu, F. Combined inhibitory effect of calcium hypochlorite and dextrin on flotation behavior of pyrite and galena sulphides. Miner. Eng. 2020, 150, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Han, Y. Surface properties and flotation inhibition mechanism of air oxidation on pyrite and arsenopyrite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-H.; Eric Forssberg, K.S. Mechanisms of pyrite flotation with xanthates. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1991, 33, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.P.; Gerson, A.R. The mechanisms of pyrite oxidation and leaching: A fundamental perspective. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2010, 65, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Nagayama, M. X-ray photoelectron spectra of hexavalent iron. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1980, 18, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.; Gómez, V.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Revés, M.; Echeverría, J.; Cremades, E.; Barragán, F.; Alvarez, S. Covalent radii revisited. Dalton Trans. 2008, 21, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanty, T.K.; Ghosh, S.K. Simple density functional approach to polarizability, hardness, and covalent radius of atomic systems. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 9197–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
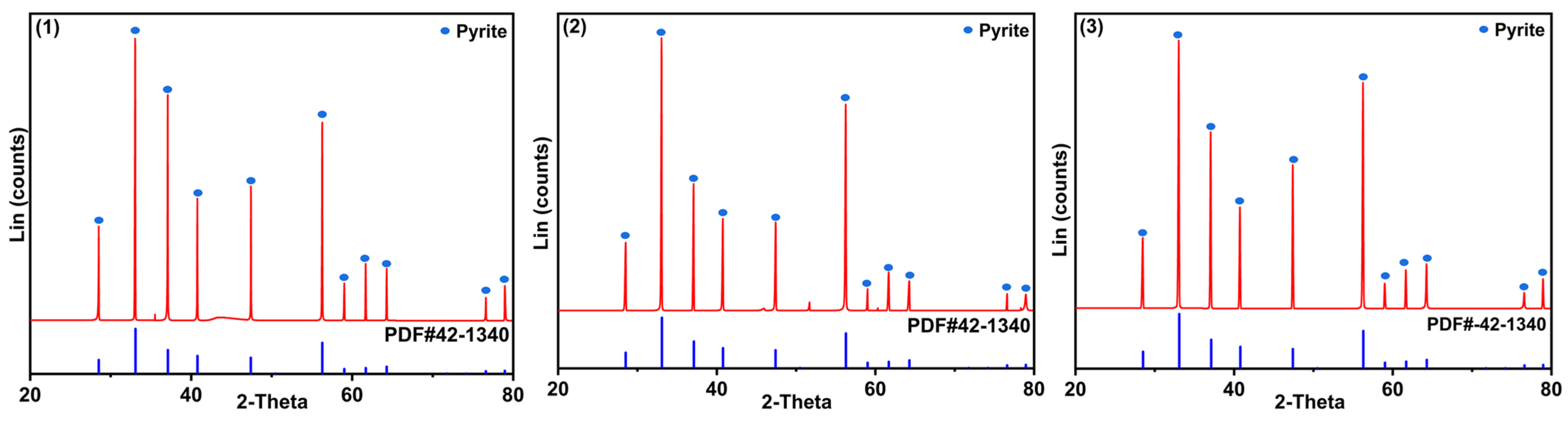
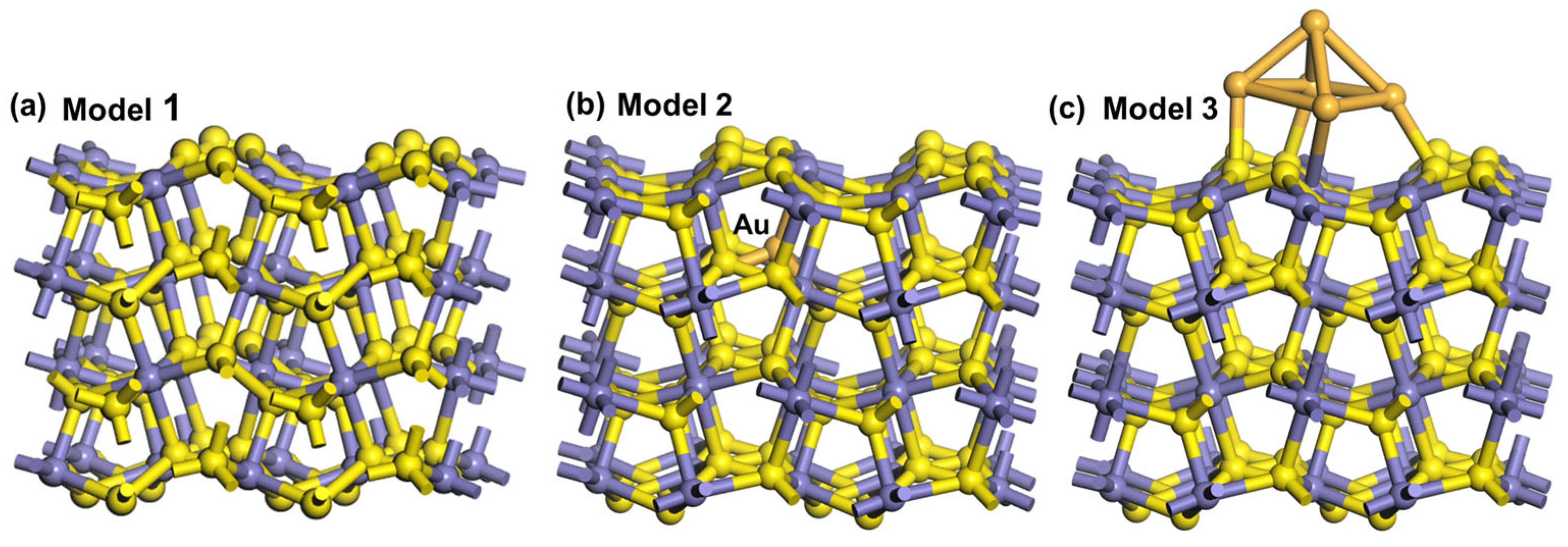
| Sample | Elements | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au(g/t) | Fe | S | Pb | Zn | O | Si | Al | Others | |
| 1 | 0 | 45.84 | 53.40 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| 2 | 7.58 | 44.87 | 50.62 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 1.97 | 1.33 | 0.22 | 0.66 |
| 3 | 29.69 | 43.97 | 49.21 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 3.11 | 2.14 | 0.34 | 0.83 |
| Sample | Ecorr/V | Icorr/μA | ba/V | bc/V | Rp/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 g/t | 0.44 | 1.00 | 0.181 | 0.138 | 33,976.06 |
| 10 g/t | 0.32 | 1.36 | 0.176 | 0.133 | 24,222.11 |
| 30 g/t | 0.44 | 1.93 | 0.231 | 0.143 | 19,823.60 |
| pH | Mineral | L (10−7 H) | Rs (Ω/cm2) | Rct (kΩ/cm2) | Q (10−5 Ssn/cm2) | n | W (103 Ω−1S0.5cm2) | χ (10−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0 g/t | 6.14 | 8.00 | 1.01 | 21.67 | 0.69 | 7.13 | 1.86 |
| 10 g/t | 5.83 | 10.51 | 0.52 | 21.15 | 0.66 | 1.14 | 1.69 | |
| 30 g/t | 5.81 | 11.58 | 0.15 | 9.26 | 0.77 | 6.78 | 1.72 |
| Species | 0 g/t | 10 g/t | 30 g/t | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.E. | at. % | B.E. | at. % | B.E. | at. % | |
| S2−2p1/2 | 161.56 | 7.49 | 161.63 | 6.75 | 162.16 | 5.92 |
| S2−2p3/2 | 160.92 | 3.86 | 161.13 | 10.46 | 161.45 | 11.64 |
| S22−2p1/2 | 163.02 | 23.38 | 163.03 | 25.39 | 163.30 | 26.24 |
| S22−2p3/2 | 161.89 | 47.03 | 161.98 | 38.43 | 162.18 | 34.57 |
| Sn/Sn2−2p1/2 | 165.26 | 4.39 | 165.19 | 4.58 | 166.07 | 3.17 |
| Sn/Sn2−2p3/2 | 163.75 | 9.03 | 163.81 | 7.55 | 164.48 | 6.83 |
| SO42−2p1/2 | 169.31 | 0.82 | 169.46 | 1.56 | 169.60 | 2.39 |
| SO42−2p3/2 | 168.01 | 4.02 | 168.23 | 5.28 | 168.35 | 9.24 |
| Species | 0 g/t | 10 g/t | 30 g/t | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.E. | at. % | B.E. | at. % | B.E. | at. % | |
| Bulk Fe(II)-S | 706.32 | 56.76 | 706.43 | 55.84 | 706.59 | 55.41 |
| Fe(II)-S | 707.72 | 33.39 | 707.68 | 32.34 | 707.74 | 25.46 |
| Fe(III)-O/OH | 710.80 | 9.86 | 711.01 | 11.81 | 710.80 | 19.14 |
| Adsorption Model | Bond | Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | S-O | 0.22 |
| Fe-O | 0.29 | |
| 2 | S-O | 0.23 |
| Fe-O | 0.38 | |
| 3 | S-O | 0.29 |
| Fe-O | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, X.; Liu, R.; Dong, W.; Sun, W.; Lin, S. Surface Physicochemical Property Differences Between Gold-Bearing and Gold-Free Pyrite for Efficient and Clean Processing of Refractory Pyritic Gold Ores. Minerals 2025, 15, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060577
Chai X, Liu R, Dong W, Sun W, Lin S. Surface Physicochemical Property Differences Between Gold-Bearing and Gold-Free Pyrite for Efficient and Clean Processing of Refractory Pyritic Gold Ores. Minerals. 2025; 15(6):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060577
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Xujian, Runqing Liu, Wenchao Dong, Wei Sun, and Shangyong Lin. 2025. "Surface Physicochemical Property Differences Between Gold-Bearing and Gold-Free Pyrite for Efficient and Clean Processing of Refractory Pyritic Gold Ores" Minerals 15, no. 6: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060577
APA StyleChai, X., Liu, R., Dong, W., Sun, W., & Lin, S. (2025). Surface Physicochemical Property Differences Between Gold-Bearing and Gold-Free Pyrite for Efficient and Clean Processing of Refractory Pyritic Gold Ores. Minerals, 15(6), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15060577







