The Application of Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometric Multi-Element Composite Parameters in the Prediction of Uranium Prospecting Areas in Qinling Region, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
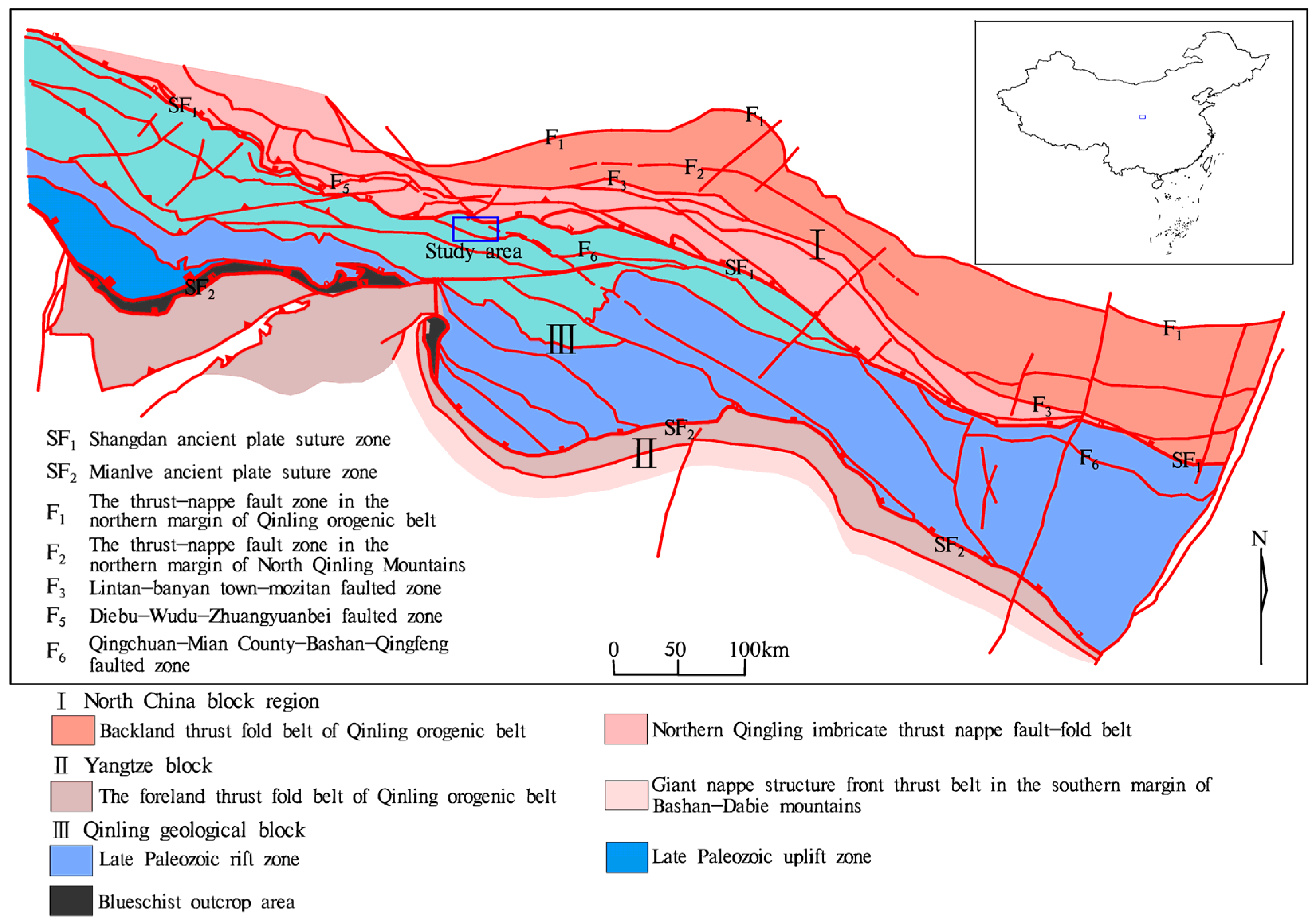
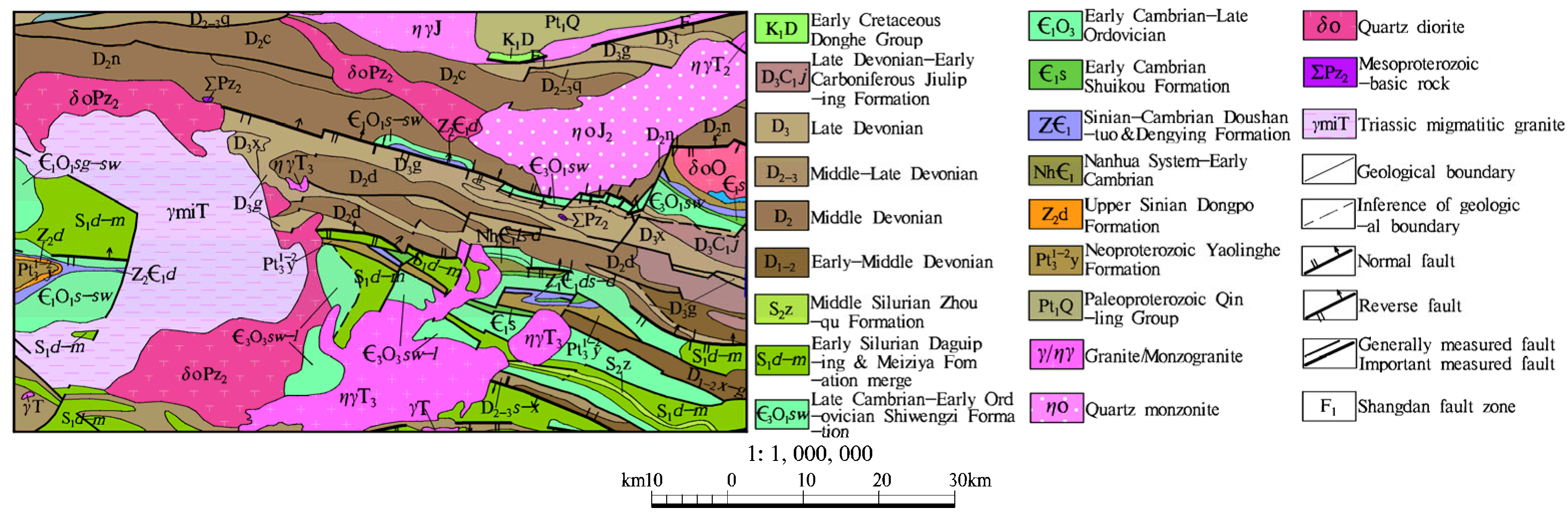
2. Geological Overview of Study Area
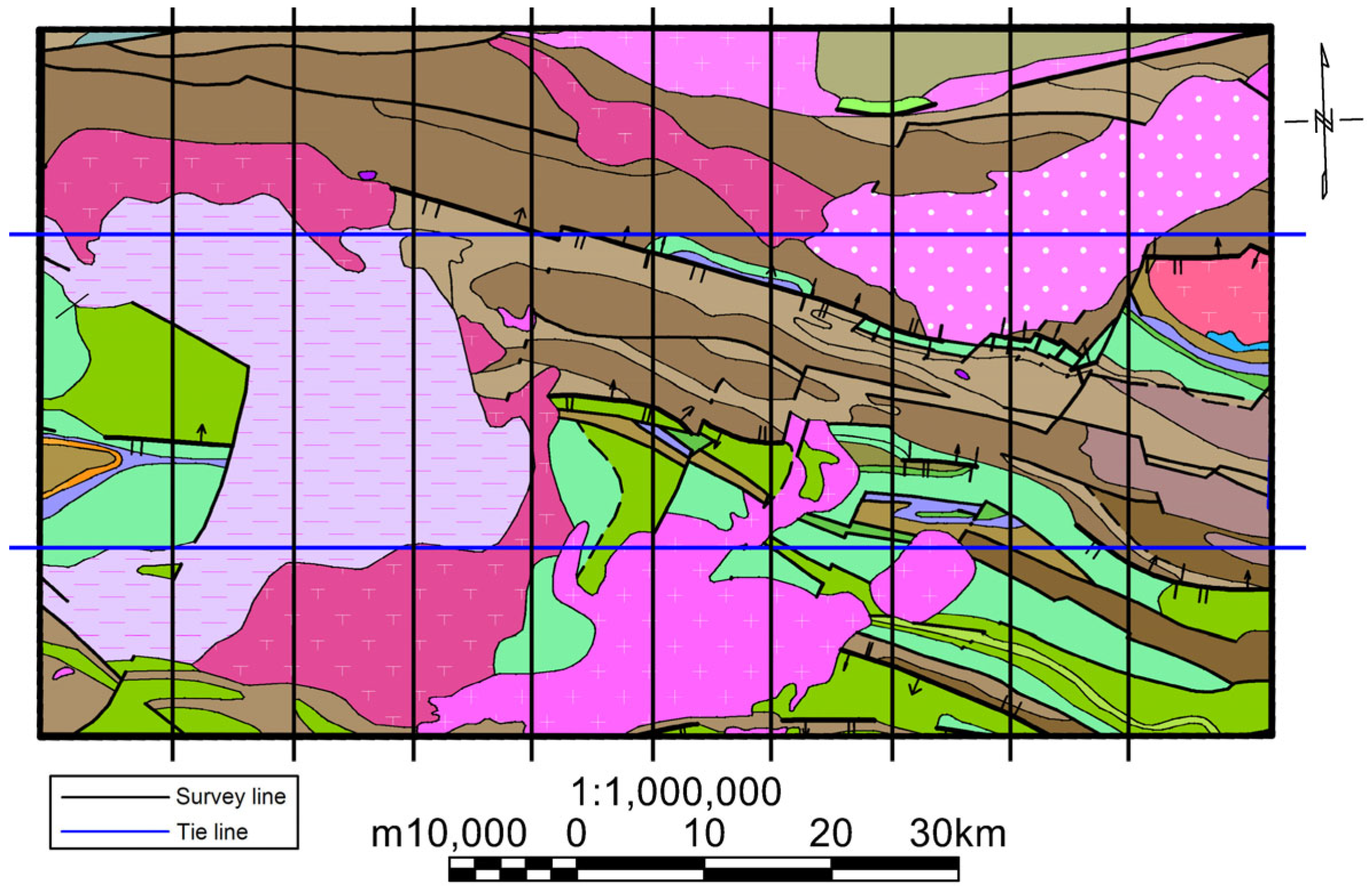
3. Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometry Measurement
4. Method for Extracting Weak Information from Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometry Data
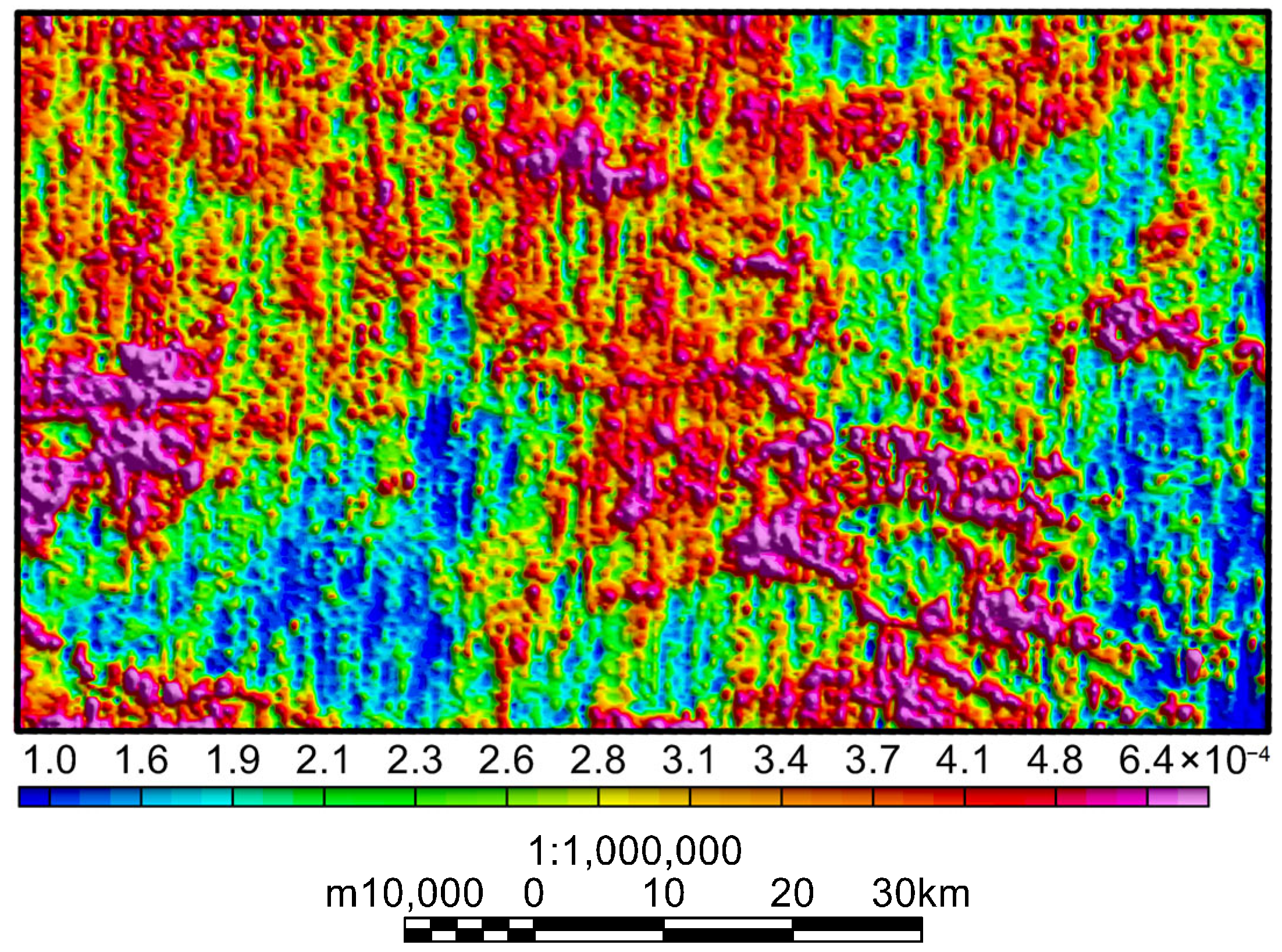
5. Analysis and Discussion of Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometry Data from the Study Area
5.1. Overall Characteristics of Aerial Gamma-Ray Spectrometry
5.2. Ratio Parameters of Airborne Radioactive Elements
5.2.1. Thorium–Potassium Ratio
5.2.2. Thorium–Uranium Ratio
5.2.3. Uranium–Potassium Ratio
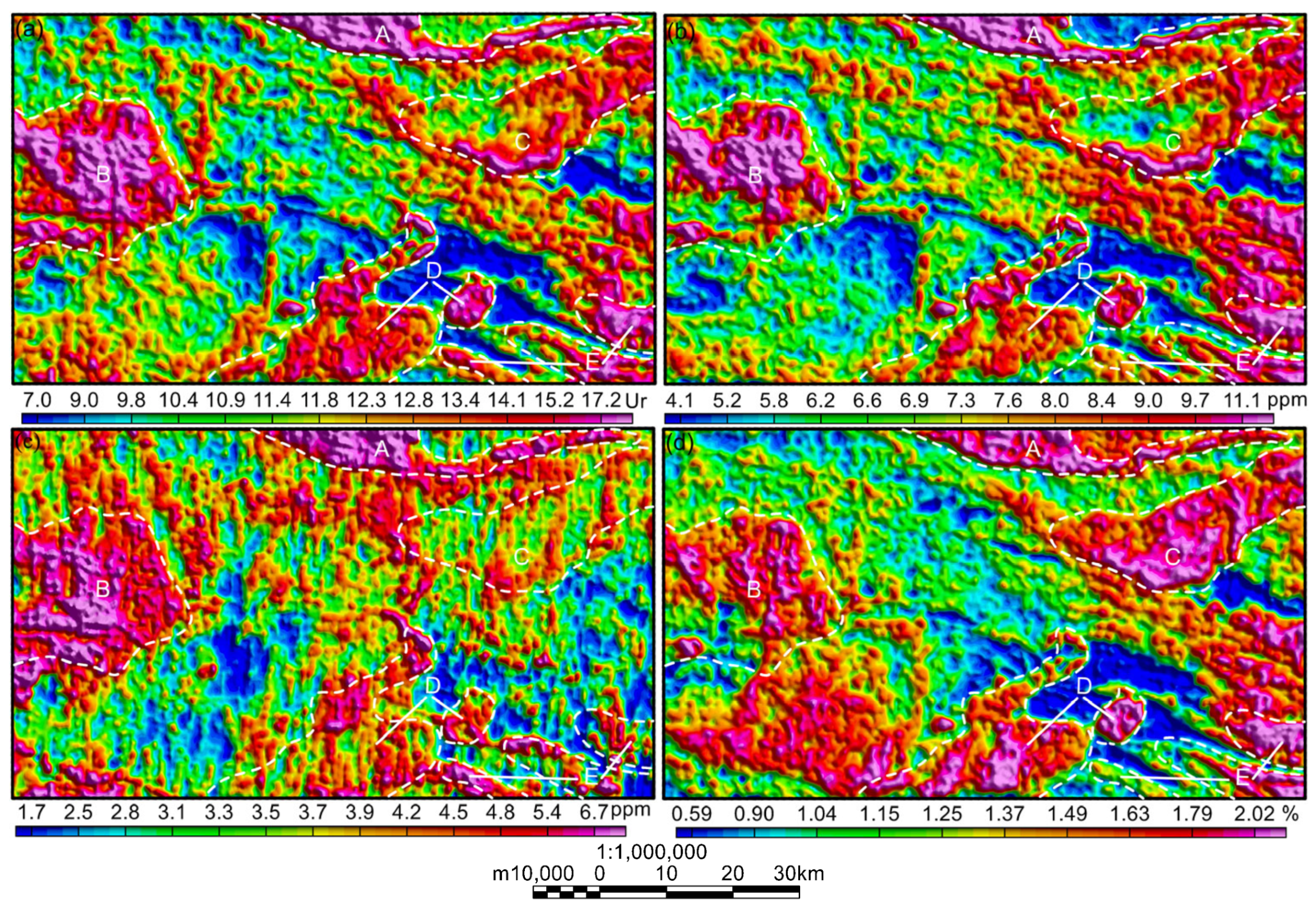
5.3. Characteristics of Multi-Element Combination Parameters in Key Areas
5.3.1. The Radioactive Parameter Characteristics in Area A
5.3.2. The Radioactive Parameter Characteristics in Area B
5.3.3. The Radioactive Parameter Characteristics in Area C
5.3.4. The Radioactive Parameter Characteristics in Area D
5.3.5. The Radioactive Parameter Characteristics in Area E
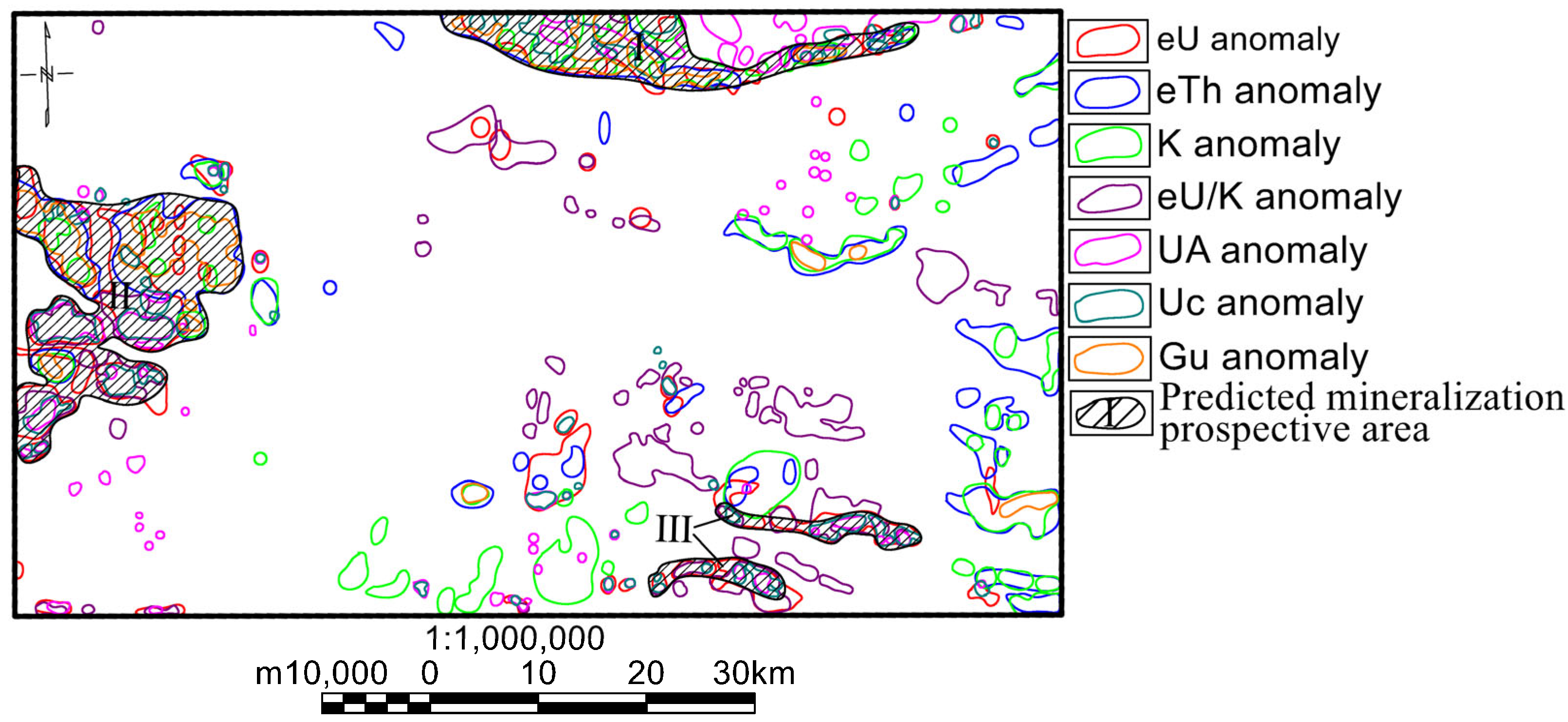
5.4. Prediction of Uranium Mineralization Prospective Area
6. Conclusions
- By utilizing the geochemical properties and geochemical activity characteristics of the radioactive elements uranium, thorium, and potassium, a mathematical model based on multi-element combination parameters was developed in addition to the traditional analysis of uranium content, thorium content, potassium content, total count, and basic ratio parameters from airborne gamma-ray spectrometry data. This model aids in elucidating the geological significance represented by these parameters and enhances the extraction of subtle information from the data. It enables the rapid assessment of uranium mineralization conditions, the prediction of prospective mineralization zones, and the analysis of uranium abundance, uranium source layers (bodies), uranium element activation and migration patterns, and uranium migration enrichment levels within the study area. This approach demonstrates practical value in evaluating uranium mineralization conditions and predicting prospective mineralization zones.
- Prospective uranium areas exhibit elevated uranium, potassium, and thorium contents, characterized by a high uranium–potassium ratio. Following the enhancement and extraction of subtle information, these areas or their vicinity display high paleo-uranium values (Gu), indicating the presence of uranium source layers (bodies). The overall activated uranium migration amount (Fu) is predominantly positive, signifying uranium influx after rock formation. The increase in potassium and uranium content is significantly greater than that of thorium content, leading to a notable rise in the uranium abundance index (UA), indicative of possible hydrothermal alteration in the area. The uranium migration enrichment factor (Uc) also exhibits high values, suggesting that uranium elements have migrated and accumulated on top of existing high-uranium source layers through geochemical processes. These high-value anomalies of elements serve as crucial indicators for predicting prospective uranium mineralization zones, with richer indicator information indicating more favorable uranium mineralization conditions.
- By combining geological data from the study area with the overall characteristics of airborne gamma-ray spectrometry total count and uranium, potassium and thorium content, in addition to the characteristics of ratio parameters between elements, a detailed analysis was conducted. Following a comprehensive explanation of the multi-element combination parameters in key areas, favorable uranium mineralization anomalies from airborne gamma-ray spectrometry data were identified. Three prospective uranium mineralization zones were predicted, characterized by superior mineralization geological conditions, rich airborne gamma-ray spectrometry anomaly information, and promising mineral exploration potential within the area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; Zhao, T.Y.; Li, S.J.; Jia, Z.Y.; Jin, J.Q.; Liang, X.J. Anomaly characteristics of airborne gamma- ray spectrometric survey and uranium prospecting direction in Huayangchuan, Qinling. Geol. China 2019, 46, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.K.; Li, Z.Y.; Cai, Y.Q.; Guo, Q.; Song, J.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, S.H. Strategic Thinking on Strengthening Three New Breakthroughs for the Uranium Exploration in China. World Nucl. Geosci. 2022, 39, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.K.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, S.H.; Cai, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.; Ye, F.W.; Li, H.Y.; Ge, X.K.; Zhang, J.L.; et al. Significant Progresses and Prospects in the Science and Technology Innovation of Uranium Geology in China Since 2000. Uranium Geol. 2024, 40, 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Q.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.F.; Li, B.H. Research on the Extraction Technology of Aero Radioactive Information for Uranium Exploration. Uranium Geol. 2024, 40, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Raghuwanshi, S.S. Airborne gamma-ray spectrometry in uranium exploration. Adv. Space Res. 1992, 12, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Nabi, H.S. Evaluation of airborne gamma-ray spectrometric data for the Missikat uranium deposit, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2001, 54, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, I.; Thomas, M.; Vogl, K. Aerial measurements on uranium ore mining, milling and processing areas in Germany. J. Environ. Radioact. 2001, 53, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfahani, J.; Al-Hent, R.; Aissa, M. Aerial gamma spectrometric survey as a tool for evaluating the uranium remobilization degree: Case study from Al-Awabed area, Northern Palmyrides, Syria. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2008, 66, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfahani, J.; Al-Hent, R.; Aissa, M. Radioactive and geological analysis of airborne gammas pectrometric data for locating favorable traps for uranium prospecting in the Syrian desert (Area-1), Syria. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, D.; Han, S.Y.; Hou, H.Q.; Zhao, D. Aero-radioactive information extraction and integration for the exploration of granite-type uranium deposits. Uranium Geol. 2009, 25, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.K.; Cai, G.Q.; Shen, Z.X.; Li, B.H. Prognoses of prospective areas for uranium metallogenesis with full-spectrum information of airborne gamma-ray survey. Prog. Rep. China Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2009, 1, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Lin, Z.Y. Application of airborne spectrometry data to the exploration of calcrete-hosted uranium deposit in Yilgarn Area Western Australia. Uranium Geol. 2015, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hafeez, T.H.A.; Youssef, M.A.S.; Waheed, H. Mohamed. Utilization of airborne gamma ray spectrometric data for geological mapping and radioactive mineral exploration of Gabel Umm Tineidba area, south eastern desert, Egypt. World J. Eng. 2015, 12, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maacha, L.; Jaffal, M.; Jarni, A.; Kchikach, A.; Mouguina, E.M.; Zouhair, M.; Ennaciri, A.; Saddiqi, O. A contribution of airborne magnetic, gamma ray spectrometric data in understanding the structure of the Central Jebilet Hercynian massif and implications for mining. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, D.; Babu, V.R.; Patra, I.; Tripathi, S.; Ramayya, M.S.; Chaturvedi, A.K. Assessment of background gamma radiation levels using airborne gamma ray spectrometer data over uranium deposits, Cuddapah Basin, India e A comparative study of dose rates estimated by AGRS and PGRS. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 167, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhadragy, A.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Eltarras, M.M.; Azzazy, A.A. Utilization of airborne gamma ray spectrometric data for radioactive mineral exploration of G.Abu Had—G.Umm Qaraf area, South Eastern Desert, Egypt. Nriag J. Astron. Geophys. 2017, 6, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.A.S.; Sabra, M.E.M.; Abdeldayem, A.L.; Masoud, A.A.; Mansour, S.A. Uranium migration and favourable sites of potential radioelement concentrations in Gabal Umm Hammad area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2017, 6, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, E.; Rasmussen, T.M. Use of airborne hyperspectral and gamma-ray spectroscopy data for mineral exploration at the Sarfartoq carbonatite complex, southern West Greenland. Geosci. J. 2018, 22, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Jiang, M.Z.; Chen, G.S.; Quan, X.D.; Chang, S.S. The brilliant achievements and technological innovation of airborne radioactivity survey in China. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 42, 645–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ismael, M.I.; El-Husseiny, A.A.; Othman, A.A. Structural and mineral exploration study at the transition zone between the North and the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt, using airborne magnetic and gamma-ray spectrometric data. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 13098–13126. [Google Scholar]
- Mamouch, Y.; Attou, A.; Miftah, A.; Ouchchen, M.; Dadi, B.; Achkouch, L.; Et-tayea, Y.; Allaoui, A.; Boualoul, M.; Randazzo, G.; et al. Mapping of Hydrothermal Alteration Zones in the Kelâat M’Gouna Region Using Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometry and Remote Sensing Data: Mining Implications (Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarshan, A. Detection of Uranium Anomalies and Alteration Zones Using Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometry at Gabal Attala and Its Surrounding Area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Earth Sci. 2022, 11, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Han, X.Z.; Lin, Z.Y.; Hu, H.; Lai, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Zhao, X. Large-Scale Aerial Gamma Spectroscopy for Exploring Sandstone-type Uranium Deposits: A Case Study of Gexi Area, Inner Mongolia. Appl. Geophys. 2023, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.C. The development of airborne radiometric survey in China. Uranium Geol. 1990, 6, 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.G.; Wu, H.N.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.P.; Bai, G.J.; Wang, J.H. Geological significance of weak information enhancement of airborne gamma energy spectral data for sandstone type uranium deposits. Geol. China 2007, 34, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, H.Q.; Han, S.Y.; Ke, D. Application study of methods and techniques for weak information extraction of sandstone-hosted uranium deposits. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, E.; Duan, M.; Lu, H.X.; Feng, B.; Cao, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.C. Application of airborne gamma energy spectral data to uranium metallogenic prognosis in Zhalantun area. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2019, 34, 601–607. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, B.H.; Zhang, J.W.; Feng, C.Y.; Shan, Y.; Cao, Q.Y. Airborne radioactivity data processing and application in the potential evaluation of uranium resource in China. Uranium Geol. 2012, 28, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Zhang, E.; Cheng, X.; Lu, H.X.; Fan, F. Application of airborne gamma energy spectral data to uranium metallogenic prognosis in Baiyintaohai area. Prog. Rep. China Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 526–533. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.W.; Zhang, B.R.; Yuan, X.C.; Xiao, Q.H. Qinling Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 117–154. [Google Scholar]
- Shanxi Institute of Geological Survey. 1:250000 Regional Geological Survey Report of Zhen’an; Shanxi Institute of Geological Survey: Xi’an, China, 2003; pp. 13–211. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.F.; Ding, X.Z.; Han, K.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, A.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.H.; Yao, D.S. The national 1:1000000 geological map spatial database. Geol. China 2017, 44 (Suppl. S1), 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, W.C.; Song, C.Z.; Ren, S.L.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. An analysis of tectonic deformation and forming environment of Shang-Dan fault zone, Qinling. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. 2012, 35, 820–827. [Google Scholar]
- State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defence (SASTIND). Specification for Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometry Survey; State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defence (SASTIND): Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, F.C.; Xin, L.; Li, Z.D. Gamma energy spectrum ratio parameters: Geologic implication and application in searching of hidden gold deposit. Geol. Resour. 2007, 16, 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J.; Zhang, W.B.; Ou, J.F.; Wang, S.T.; Xiong, S.Q.; Fan, Z.G. Explanation of Aerial Geophysical Exploration Methods and Applications; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 66–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F. The Course of Uranium Geochemistry; Atom Energy Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 1–572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Fan, Y.R.; Li, H.Y. Karst carbonate reservoir division and contrast based on natural gamma ray spectrometry logging in Tahe Oilfield. J. China Univ. Pet. 2006, 30, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.F.; Lin, C.S.; Yang, H.J.; Peng, L.; Liu, J.Y.; Xiao, T.J.; Tong, J.Y.; Wang, H.P.; Li, H.P. Application of natural gamma ray spectrometry in analysis of Late Ordovician carbonate sequence stratigraphic analysis in middle Tarim Basin. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2010, 45, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.P. Study and application on gamma energy spectrum data in Erlian basin, Inner Mongolia. Uranium Geol. Northwest China 1998, 1, 38–42. [Google Scholar]



| Method Type | Parameters | Mathematical Model | Geological Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-element | Uranium content Potassium content Thorium content | Studying the regional distribution patterns and trends of various elements and comparing differences in elemental contents to obtain valuable geological prospecting information. | |
| Single-element ratios | Uranium–thorium ratio Uranium–potassium ratio Thorium–potassium ratio | In special circumstances, elements may be relatively enriched or depleted, with U separating from Th and K through precipitation. Therefore, changes in ratios can indicate processes such as weathering, depositional environments, mineralization, and other specific geological actions. | |
| Multi- element combination parameters | Paleo-uranium content (Gu) | Using the relative stability of thorium elements, high-value zones indicate the uranium source layer (body) under the element’s state. | |
| Activated uranium migration amount (Fu) | Utilizing the difference between measured uranium and “paleo-uranium” to quantify the activation migration of uranium elements in the later stages of diagenesis. Evaluating the leaching or superimposed enrichment of uranium elements in the study area based on the average value or trend of Fu within the region to understand the differences and numerical changes between paleo-uranium and present-day measured uranium. Assessing the activation migration amount of uranium in the region. | ||
| Uranium abundance index (UA) | Also known as the F-parameter, the alteration degree of rocks in hydrothermal uranium exploration plays a significant indicative role. By normalizing uranium and thorium to potassium elements, it can highlight the low-to-medium temperature potassic alteration zones. A higher value indicates a stronger degree of rock alteration. Additionally, it is important to understand the original abundance level and superimposed enrichment status of uranium. | ||
| Uranium migration enrichment factor (Uc) | The migration and enrichment of uranium under geochemical processes in the search for prospective areas. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Lu, N.; Liao, G.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Qu, N. The Application of Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometric Multi-Element Composite Parameters in the Prediction of Uranium Prospecting Areas in Qinling Region, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050492
Xi Y, Liu J, Wu S, Lu N, Liao G, Li Y, Li F, Qu N. The Application of Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometric Multi-Element Composite Parameters in the Prediction of Uranium Prospecting Areas in Qinling Region, China. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050492
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Yongzai, Junjie Liu, Shan Wu, Ning Lu, Guixiang Liao, Yongbo Li, Fei Li, and Niannian Qu. 2025. "The Application of Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometric Multi-Element Composite Parameters in the Prediction of Uranium Prospecting Areas in Qinling Region, China" Minerals 15, no. 5: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050492
APA StyleXi, Y., Liu, J., Wu, S., Lu, N., Liao, G., Li, Y., Li, F., & Qu, N. (2025). The Application of Airborne Gamma-Ray Spectrometric Multi-Element Composite Parameters in the Prediction of Uranium Prospecting Areas in Qinling Region, China. Minerals, 15(5), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050492









