Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals (PTMs) Pollution, Ecological Risks, and Source Apportionment in Urban Soils from University Campuses: Insights from Multivariate and Positive Matrix Factorisation Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Techniques
2.3. Assessment of PTM Pollution
2.4. Health Risk Assessment (HRA)
2.5. Positive Matrix Factorisation (PMF)
2.6. Spatial Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
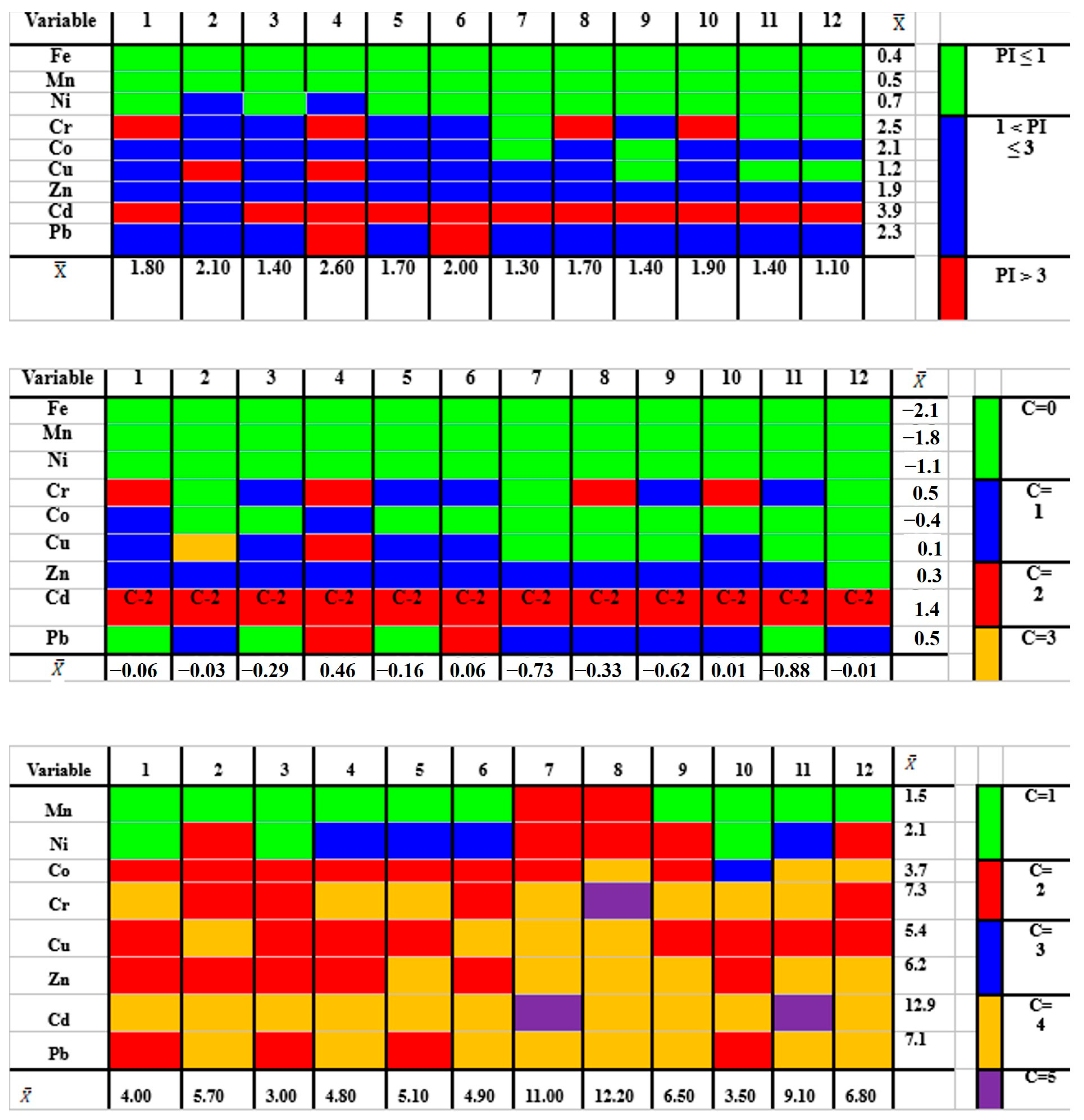
3.1. PTM Concentration and Pollution Assessment
3.2. PTM Spatial Distribution
3.3. PTM Ecological Risks
3.4. Health Risks from PTMs
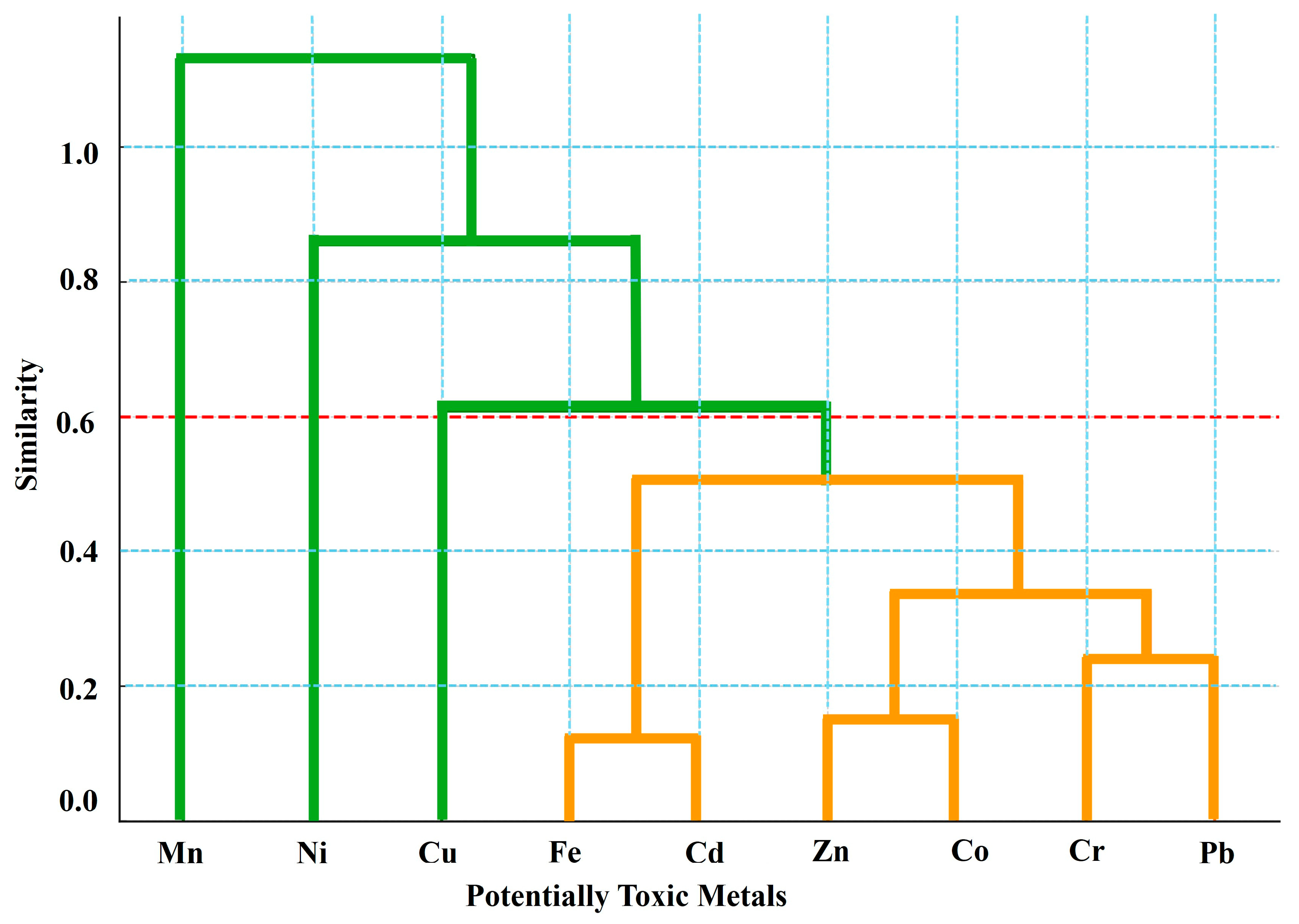
3.5. PTM Source Apportionment
3.6. Comparison with Previous Similar Works
3.7. Implications
3.8. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, N.K.; Chauhan, R. Heavy Metal Toxicity and Sustainable Interventions for Their Decontamination. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyazuddin, R.; Nisha, N.; Ejaz, B.; Khan, M.I.R.; Kumar, M.; Ramteke, P.W.; Gupta, R. A Comprehensive Review on the Heavy Metal Toxicity and Sequestration in Plants. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Schutte, B.J.; Ulery, A.; Deyholos, M.K.; Sanogo, S.; Lehnhoff, E.A.; Beck, L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Soil: Environmental Pollutants Affecting Crop Health. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of Heavy Metal Contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Feng, D.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Z.; Fan, Q.; Liu, K. Study on the Risk of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in Typical Developed Cities in Eastern China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, L.R.; Jennings, V.; Cloutier, S.A. Public Parks and Wellbeing in Urban Areas of the United States. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesli, T.X.; Hammer, T.; Knaus, F. Improving Quality of Life for Residents of Biosphere Reserves and Nature Parks: Management Recommendations from Switzerland. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2022, 18, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiak-Zielińska, M.; Borowiak, K.; Budka, A.; Kanclerz, J.; Janicka, E.; Kaczor, A.; Żyromski, A.; Biniak-Pieróg, M.; Podawca, K.; Mleczek, M. How Polluted Are Cities in Central Europe?-Heavy Metal Contamination in Taraxacum Officinale and Soils Collected from Different Land Use Areas of Three Representative Cities. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Ptak, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Krasniqi, V. Ecological and Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals Contained in Sediments of Polish Dam Reservoirs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 20, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, L.; Díaz-Barrientos, E.; Madrid, F. Distribution of Heavy Metal Contents of Urban Soils in Parks of Seville. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandari, A.; Abbasnejad, B. Environmental Pollution Status and Health Risk Assessment of Selective Heavy Metal (Oid) s in Iran’s Agricultural Soils: A Review. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 256, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Liu, X. Spatial Distribution and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Soil from a Typical County-Level City of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Yan, C.-A.; Tang, G.-Y.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Ma, L.Q.; Gu, R.-H.; Xiang, P. Heavy Metal (Loid) s in Agriculture Soils, Rice, and Wheat across China: Status Assessment and Spatiotemporal Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, L.; Lv, S. Geochemical Characteristics and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Crops from a Coal Mining Area in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmadani, A.A.; Syaifudin, Y.W.; Setiawan, B.; Panduman, Y.Y.F.; Funabiki, N. Enhancing Campus Environment: Real-Time Air Quality Monitoring Through IoT and Web Technologies. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2024, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Contents of Heavy Metals in Urban Parks and University Campuses. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 108, p. 042060. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, A. UNRAVEL THE COMPLEXITIES OF URBAN SOIL CONTAMINATION: REGULATED AND EMERGING METALS CONTAMINANTS IN A POST-INDUSTRIAL CITY. 2024. Available online: https://iris.unito.it/handle/2 (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Li, F. Heavy Metal in Urban Soil: Health Risk Assessment and Management. In Heavy Metals; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Rezapour, S.; Siavash Moghaddam, S.; Nouri, A.; Khosravi Aqdam, K. Urbanization Influences the Distribution, Enrichment, and Ecological Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Croplands. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.; Fang, G.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. A Review of Heavy Metal Pollution Levels and Health Risk Assessment of Urban Soils in Chinese Cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.F.; Brabander, D.J.; Erdil, R.M. Sources, Sinks, and Exposure Pathways of Lead in Urban Garden Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ouyang, T.; Guo, Y.; Peng, S.; He, C.; Zhu, Z. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Its Ecological Risk for City Parks, Vicinity of a Landfill, and an Industrial Area within Guangzhou, South China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brtnický, M.; Pecina, V.; Hladký, J.; Radziemska, M.; Koudelková, Z.; Klimánek, M.; Richtera, L.; Adamcová, D.; Elbl, J.; Galiová, M.V. Assessment of Phytotoxicity, Environmental and Health Risks of Historical Urban Park Soils. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal (Loid) s in Park Soils of the Largest Megacity in China by Using Monte Carlo Simulation Coupled with Positive Matrix Factorization Model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.B.; Giráldez, M.I.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C. Assessing the Environmental Availability of Heavy Metals in Geogenically Contaminated Soils of the Sierra de Aracena Natural Park (SW Spain). Is There a Health Risk? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 560, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penteado, J.O.; de Lima Brum, R.; Ramires, P.F.; Garcia, E.M.; Dos Santos, M.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Health Risk Assessment in Urban Parks Soils Contaminated by Metals, Rio Grande City (Brazil) Case Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, M.; Cao, J.; Gui, C.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Health Risk Assessment and Bioaccessibilities of Heavy Metals for Children in Soil and Dust from Urban Parks and Schools of Jiaozuo, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.O.; Albedair, L.A.; Alotaibi, N.M.; Elobeid, M.M.; Al-Swadi, H.A.; Alasmary, Z.; Ahmad, M. Pollution Indexing and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy-Metals-Laden Indoor and Outdoor Dust in Elementary School Environments in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgül, A. Assessing Heavy Metal Contamination and Health Risks in Playground Dust near Cement Factory: Exposure Levels in Children. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Gu, Q. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in PM2. 5 Samples and Effects of Heavy Metals on Hypertension among Schoolchildren in Tianjin. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 8451–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, X. Evaluating Heavy Metals Contamination in Campus Dust in Wuhan, the University Cluster in Central China: Distribution and Potential Human Health Risk Analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, A.S.; Aljumialy, A.M.; Saod, W.M.; Al-Heety, E.A. Pollution Level and Sources of Heavy Metals in Indoor Dust from College of Science, University of Anbar Campus, Iraq. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2024; Volume 1300, p. 012019. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Wu, Y.; Xuan, B. Spatial Distribution and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Campus Dust: A Case Study of the University Town of Huaxi. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, R.; Guo, X.; Cheng, C.-W.; Delorme, A.; Duruisseau-Kuntz, R.; Zhao, R. Investigation of Indoor Air Quality in University Residences Using Low-Cost Sensors. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2023, 3, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, D.D.; Habil, M. PM2.5 Exposure Estimates for College Students and Health Risk Assessment. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2024, 17, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, L. Environmental and Occupational Medicine. In Goodman and Fuller’s Pathology: Implications for the Physical Therapist; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Thongyuan, S.; Khantamoon, T.; Aendo, P.; Binot, A.; Tulayakul, P. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment, Carcinogenic and Non-Carcinogenic Effects of Heavy Metals Contamination in the Soil from Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Central, Thailand. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals for Eco-Environment and Human Health in a Rapidly Urbanization Area of the Upper Yangtze Basin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabberi, S.; Tashakor, M.; Sharifi Soltani, N.; Hursthouse, A.S. Potentially Toxic Elements in Urban Soils: Source Apportionment and Contamination Assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, A.; Ashraf, M.; Sundari, R.S.; Qamar, H.; Wajid, M.; Hasan, M. Vulnerability Assessment of Urban Expansion and Modelling Green Spaces to Build Heat Waves Risk Resiliency in Karachi. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 46, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfadil, K.M.; Mansour, S.; Asran, A.M.; Younis, M.H.; Lentz, D.R.; Fowler, A.-R.; Fnais, M.S.; Abdelrahman, K.; Radwan, A. Composite Granitic Plutonism in the Southern Part of the Wadi Hodein Shear Zone, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: Implications for Neoproterozoic Dioritic and Highly Evolved Magma Mingling during Volcanic Arc Assembly. Minerals 2024, 14, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfadil, K.M.; Asran, A.M.; Rehman, H.U.; Sami, M.; Ahmed, A.; Sanislav, I.V.; Fnais, M.S.; Mogahed, M.M. The Evolution of Neoproterozoic Mantle Peridotites Beneath the Arabian–Nubian Shield: Evidence from Wadi Sodmein Serpentinites, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Minerals 2024, 14, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, R.; Tarvainen, T. Geochemical Mapping and Databases in Finland. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 55, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, T. The Geochemical Correlation between Coarse and Fine Fractions of till in Southern Finland. J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 54, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The Composition of the Continental Crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Rushmer, T. Evolution and Differentiation of the Continental Crust; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 0521782376. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Geochemical Evolution of the Continental Crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likuku, A.S.; Mmolawa, K.B.; Gaboutloeloe, G.K. Assessment of Heavy Metal Enrichment and Degree of Contamination around the Copper-Nickel Mine in the Selebi Phikwe Region, Eastern Botswana. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2013, 1, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L. Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Sezgin, N.; Nadeem, I.; El Afandi, G. Environmental Pollution Assessment of Trace Metals in Road Dust of Istanbul in Turkey. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 6, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S. Sources and Characteristics of Lead Pollution in the Urban Environment of Guangzhou. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 385, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Soil Screening Guidance: Technical Background Document |Superfund| US EPA; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Fan, X.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Zuo, L.; Fan, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, H.; Qin, Q. Risk and Sources of Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Dust from University Campuses: A Case Study of Xi’an, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, B. Risk-Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume 1. Human Health Evaluation Manual. Part A. Interim Report (Final); Environmental Protection Agency Office of Solid Waste: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- EPA, U. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites. Peer Rev. Draft. OSWER 2001, 9355, 4–24. [Google Scholar]
- Miletić, A.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Exposure Factors in Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Sediment. Metals 2023, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and Risk Assessment of Street Dust in Luanda, Angola: A Tropical Urban Environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Luo, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.; Yang, G.; Wan, H.; Wu, L. Levels and Health Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in Urban Soils in Dongguan, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 148, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Health Evaluation Manual; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 1003. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-11/documents/defaultExposureParams.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- Public Health Assessment Guidance Manual. Appendix G: Calculating Exposure Doses. 2005. Available online: http://medbox.iiab.me/modules/en-cdc/www.atsdr.cdc.gov/hac/phamanual/appg.html (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Recommended Use of BW3/4 as the Default Method in Derivation of the Oral Reference Dose; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Ke, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Russell, A.G.; Edgerton, E.S.; Zheng, M. Comparison of PM2.5 Source Apportionment Using Positive Matrix Factorization and Molecular Marker-Based Chemical Mass Balance. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Pollution Assessment and Source Apportionment of Trace Metals in Urban Topsoil of Xi’an City in Northwest China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X. Contamination Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Topsoil from an Area in Xi’an City, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.-B.; Lee, T.-J.; Lee, E.-S.; Kim, D.-S. Enhancing Source Identification of Hourly PM2. 5 Data in Seoul Based on a Dataset Segmentation Scheme by Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1042–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Hopke, P.K. Comparison between Sample-Species Specific Uncertainties and Estimated Uncertainties for the Source Apportionment of the Speciation Trends Network Data. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reff, A.; Eberly, S.I.; Bhave, P. V Receptor Modeling of Ambient Particulate Matter Data Using Positive Matrix Factorization: Review of Existing Methods. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ali, L.; Alshamsi, D.; Aldahan, A.; El-Askary, H.; Ahmed, A. AI-Powered Water Quality Index Prediction: Unveiling Machine Learning Precision in Hyper-Arid Regions. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzombak, D.A.; Morel, F.M.M. Development of a Data Base for Modelling Adsorption of Inorganics on Iron and Aluminum Oxides. Environ. Prog. 1987, 6, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzombak, D.A.; Morel, F.M.M. Adsorption of Inorganic Pollutants in Aquatic Systems. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1987, 113, 430–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M.; Tsadilas, C.D.; Rinklebe, J. A Review of the Distribution Coefficients of Trace Elements in Soils: Influence of Sorption System, Element Characteristics, and Soil Colloidal Properties. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2013, 201, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; El-Galil, A.A.; Kotb, M.M. Total and Available Fe, Mn, Zn, and Cu in Some Soils of Sohag Governorate and Their Association with Some Soil Properties. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2001, 32, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, E.M.; El-Aziz, S.H.A.; Ghallab, A.; Negim, S.E.A. Studies on Some Soils of the College of Agriculture Farm at Sohag, South Valley University. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 34, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Alloway, B.J. The Origins of Heavy Metals in Soils; Blackie & Son Ltd.: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Shi, D.; Lu, X. Concentration and Source of Trace Metals in Street Dust from an Industrial City in Semi-Arid Area of China. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 21, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Saravi, H.N.; Younesipour, H.; Firouzkandian, S.; Golrooye, M.R. Study of Resistant and Non-Resistant Fractions of Copper, Cadmium, Lead and Mercury Based on the Sequential Extraction Method in the Surface Sediments of the Southern Caspian Sea. Sciences 2008, 35, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, M.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hussain, Z.; Shen, C. Geochemical Mapping, Risk Assessment, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Road Dust Using Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-H.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J. Characterizing Pollution and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Soils Using Geochemical Baseline and PMF Approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Anwar, S.; Fang, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, B.; Liu, D. Source Apportionment of Agricultural Soil Heavy Metals Based on PMF Model and Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Environ. Forensics 2024, 25, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L. Pollution Characteristics, Spatial Distributions, and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Cultivated Soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, C.; Sun, Y.; Lu, X.; Fan, Y. Ecological Health Evaluation of Rivers Based on Phytoplankton Biological Integrity Index and Water Quality Index on the Impact of Anthropogenic Pollution: A Case of Ashi River Basin. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 942205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R. Effect of Different Industrial Activities on Soil Heavy Metal Pollution, Ecological Risk, and Health Risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, R.; Chen, Z.; Diao, J.; Huang, Z.; Kan, Z.; Wang, T. Heavy Metals in Soils from Intense Industrial Areas in South China: Spatial Distribution, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 820536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; De Paola, D.; Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Chromium Pollution in European Water, Sources, Health Risk, and Remediation Strategies: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, N.; Parsa, M.; Lentz, D.R.; Sobhanverdi, J. Identification of Heavy Metal Pollution Sources and Its Associated Risk Assessment in an Industrial Town Using the K-Means Clustering Technique. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 135, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Pollution Characteristics, Sources, and Health Risk Assessment of Human Exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb Pollution in Urban Street Dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Norman, M.; Burman, L. Road Traffic Emission Factors for Heavy Metals. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4681–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, L.Y.; Lei, K.; Huang, L.; Kang, D. Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Heavy Metals in Street Dust of Baoji, NW China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastmanesh, F.; Mousavi, M.; Zarasvandi, A.; Edraki, M. Investigation of Elemental Enrichment and Ecological Risk Assessment of Surface Soils in Two Industrial Port Cities, Southwest Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytreberg, E.; Lagerström, M.; Holmqvist, A.; Eklund, B.; Elwing, H.; Dahlström, M.; Dahl, P.; Dahlström, M. A Novel XRF Method to Measure Environmental Release of Copper and Zinc from Antifouling Paints. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, A.; Hui, Z.; Rad, S.; Xiao, H.; Siddique, J.; Huang, L.L.; Ullah, H.; Rashid, A.; Taha, M.R.; Zada, N. A Comprehensive Review on Pollution Status and Associated Health Risk Assessment of Human Exposure to Selected Heavy Metals in Road Dust across Different Cities of the World. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Ning, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Q.; Bi, X. Inputs and Sources of Pb and Other Metals in Urban Area in the Post Leaded Gasoline Era. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Tainosho, Y. Characterization of Heavy Metal Particles Embedded in Tire Dust. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Lu, X. Accumulation Degree and Source Apportionment of Trace Metals in Smaller than 63 Μm Road Dust from the Areas with Different Land Uses: A Case Study of Xi’an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo-González, J.M.; Torres-Mora, M.A.; Keesstra, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R. Heavy Metal Accumulation Related to Population Density in Road Dust Samples Taken from Urban Sites under Different Land Uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondu, R.; Cloutier, V.; Rosa, E.; Roy, M. An Exploratory Data Analysis Approach for Assessing the Sources and Distribution of Naturally Occurring Contaminants (F, Ba, Mn, As) in Groundwater from Southern Quebec (Canada). Appl. Geochem. 2020, 114, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierczak, J.; Pietranik, A.; Pędziwiatr, A. Ultramafic Geoecosystems as a Natural Source of Ni, Cr, and Co to the Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani-Gerdefaramarzi, S.; Ghasemi, M.; Ghanbarian, B. Geogenic and Anthropogenic Sources Identification and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Urban Soil of Yazd, Central Iran. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, G.; Tulun, Ş.; Çelebi, H. Mapping of Heavy Metal Pollution Density and Source Distribution of Campus Soil Using Geographical Information System. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suciu, N.A.; De Vivo, R.; Rizzati, N.; Capri, E. Cd Content in Phosphate Fertilizer: Which Potential Risk for the Environment and Human Health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 30, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, J.; Intekhab, A.; Dhak, D. Effect of Uncontrolled Fertilization and Heavy Metal Toxicity Associated with Arsenic (As), Lead (Pb) and Cadmium (Cd), and Possible Remediation. Toxicology 2022, 477, 153274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeeck, M.; Salaets, P.; Smolders, E. Trace Element Concentrations in Mineral Phosphate Fertilizers Used in Europe: A Balanced Survey. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaralar, O.; Isinkaralar, K.; Nguyen, T.N.T. Spatial Distribution, Pollution Level and Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Street Dust at Neighbourhood Scale. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2024, 68, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Jin, Y.; Peng, T.; Zhao, B.; Hou, D. Heavy Metal Pollution in Mongolian-Manchurian Grassland Soil and Effect of Long-Range Dust Transport by Wind. Environ. Int. 2023, 177, 108019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.-Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.-Y.; Bao, Y.-B.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Zheng, Q.-X.; Xiang, P. Road Dust Exposure and Human Corneal Damage in a Plateau High Geological Background Provincial Capital City: Spatial Distribution, Sources, Bioaccessibility, and Cytotoxicity of Dust Heavy Metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawa, U. Heavy Metals Concentration in Food Crops Irrigated with Pesticides and Their Associated Human Health Risks in Paki, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2191889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, K.; Lei, M. Human Health Risk Apportionment from Potential Sources of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils and Associated Uncertainty Analysis. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, M.; Darvishiyan, M.; Momeni, M.; Eslami, H.; Fallahzadeh, R.A.; Zarei, A. Ecological Risk Assessment of Trace Elements (TEs) Pollution and Human Health Risk Exposure in Agricultural Soils Used for Saffron Cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljumialy, A.M.; Al-Rawi, A.S.; Saod, W.M.; Al-Heety, E.A. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Interior Dust from College Campus. Anal. Sci. 2024, 40, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, R.; Deng, M.; Hu, D.; Peng, L. Seasonal Variations, Source Apportionment, and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in PM2. 5 in the Typical Industrial City of Changzhi, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Z.; Qureshi, B.A.; Mumtaz, M.; Qureshi, S. Heavy Metal Content in Urban Soils as an Indicator of Anthropogenic and Natural Influences on Landscape of Karachi—A Multivariate Spatio-Temporal Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 42, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot, N.; Wojciechowska, E.; Rezania, S.; Walkusz-Miotk, J.; Pazdro, K. The Effects of Urban Vehicle Traffic on Heavy Metal Contamination in Road Sweeping Waste and Bottom Sediments of Retention Tanks. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, X.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils in a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Muhammad, S.; Umar, M.; Azhar, M.U.; Ahmed, A.; Ahmad, A.; Ullah, R. Spatial Distribution of Physicochemical Parameters and Drinking and Irrigation Water Quality Indices in the Jhelum River. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsal, M.H.; Ignatavičius, G.; Valiulis, A.; Prokopciuk, N.; Valskienė, R.; Valskys, V. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Dust in Vilnius Schools: Source Identification, Pollution Levels, and Potential Health Risks for Children. Toxics 2024, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, E.; Iribarren, I.; Chacon, E.; Ordonez, A.; Charlesworth, S. Risk-Based Evaluation of the Exposure of Children to Trace Elements in Playgrounds in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere 2007, 66, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Song, X.; Shu, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, J.; Li, R.; Fan, Z. Determination of Soil Environmental Criteria for High-Risk Trace Metals in Urban Park Soils Using Improved CLEA Model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Iniesta, M.J.; Marín-Sanleandro, P.; Canca Pedraza, M.d.C.; Díaz-Pereira, E.; Sánchez-Navarro, A. Geoenvironmental and Health Indices to Assess the Hazardousness of Heavy Metals in Urban Dust in Schoolyards in Murcia, Spain. Toxics 2024, 12, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.; Praveena, S.M.; Abidin, E.Z.; Cheema, M.S. Heavy Metal Quantification of Classroom Dust in School Environment and Its Impacts on Children Health from Rawang (Malaysia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34623–34635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohain, M.; Deka, P. Trace Metals in Indoor Dust from a University Campus in Northeast India: Implication for Health Risk. Env. Monit Assess 2020, 192, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eneji, I.S.; Adams, I.U.; Julius, K.A. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Indoor Settled Harmattan Dust from the University of Agriculture Makurdi, Nigeria. Open J. Air Pollut. 2015, 4, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, L.T.; Rasmussen, P.E.; Chénier, M.; Levesque, C. Wipe Sampling Methodologies to Assess Exposures to Lead and Cadmium in Urban Canadian Homes. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy, Amherst, MA, USA, 18–21 October 2010; Volume 15, p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Moghtaderi, T.; Aminiyan, M.M.; Alamdar, R.; Moghtaderi, M. Index-Based Evaluation of Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk of Potentially Toxic Metals in Schools Dust of Shiraz Megacity, SW Iran. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 410–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Element | RfDing (mg/kg/day) | RfDinh (mg/kg/day) | RfDdermal (mg/kg/day) | SF (mg/kg/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 7.0 | - | - | |
| Mn | 0.046 | 0.00001 | 0.00184 | |
| Ni | 0.020 | 0.02060 | 0.00054 | 0.840 |
| Cr | 0.003 | 0.00003 | 0.00006 | 42.00 |
| Cu | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.012 | |
| Zn | 0.300 | 0.300 | 0.060 | |
| Cd | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| Pb | 0.0035 | 0.003 | 0.00053 | |
| Co | 0.020 | 0.00001 | 0.01600 | 9.800 |
| Variable | Mean | Md. | StDev | CV% | Min. | Max. | [45] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical properties | pH | 8.1 | 8 | 0.3 | 4 | 7.6 | 8.6 | |
| OC% | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 71 | 0.2 | 3.9 | ||
| CaCO3% | 5.2 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 68 | 0.5 | 11.5 | ||
| Total Heavy Metal Content | Fe% | 1.61 | 1.75 | 0.58 | 33 | 0.58 | 2.64 | 4.09 |
| Mn ppm | 441 | 486 | 1.89 | 39 | 115 | 759 | 904 | |
| Ni ppm | 14 | 13 | 5 | 39 | 7 | 24 | 19 | |
| Cr ppm | 86 | 82 | 43 | 52 | 24 | 150 | 35 | |
| Co ppm | 15 | 14 | 4 | 28 | 7 | 24 | 12 | |
| Cu ppm | 29 | 24 | 23 | 96 | 6 | 93 | 14 | |
| Zn ppm | 97 | 100 | 170 | 170 | 69 | 125 | 52 | |
| Cd ppm | 0.4 | 0.38 | 0.63 | 168 | 0.32 | 0.52 | 0.102 | |
| Pb ppm | 39 | 38 | 21 | 55 | 17 | 98 | 17 |
| PTMs | HQing | HQinh | Hqdermal | HI | RT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male Students | Fe | 2.43 × 10−7 | - | - | 2.43 × 10−7 | - |
| Mn | 9.37 × 10−3 | 2.03 × 101 | 1.33 × 102 | 1.54 × 102 | - | |
| Cu | 7.38 × 10−4 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 5.99 × 10−1 | 5.99 × 10−1 | - | |
| Zn | 3.16 × 10−4 | 4.54 × 10−8 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 3.21 × 10−1 | - | |
| Pb | 1.05 × 10−2 | 1.40 × 10−6 | 1.03 × 101 | 1.03 × 101 | - | |
| Co—Non-Cancer | 7.60 × 10−4 | 3.66 × 10−4 | 1.28 × 10−1 | 1.29 × 10−1 | - | |
| Co—Cancer | 1.26 × 10−2 | 6.08 × 10−3 | 1.28 × 10−1 | - | 2.48 × 10−3 | |
| Ni—Non-Cancer | 6.58 × 10−4 | 7.98 × 10−1 | 9.87 × 100 | 1.07 × 101 | - | |
| Ni—Cancer | 1.19 × 10−2 | - | 1.07 × 101 | 1.07 × 101 | 1.99 × 10−4 | |
| Cr—Non-Cancer | 2.96 × 10−2 | 4.26 × 10−4 | 4.50 × 102 | 4.50 × 102 | - | |
| Cr—Cancer | 4.93 × 10−1 | 7.12 × 10−3 | 4.50 × 102 | - | 6.21 × 10−2 | |
| Cd—Non-Cancer | 3.96 × 10−3 | 5.54 × 10−8 | - | 3.96 × 10−3 | - | |
| Cd—Cancer | 6.60 × 10−2 | - | - | - | 0 | |
| Female Students | HQing | HQinh | Hqdermal | Hi | RT | |
| Fe | 2.49 × 10−7 | - | - | 2.49 × 10−7 | - | |
| Mn | 9.51 × 10−3 | 2.03 × 101 | 1.33 × 102 | 1.54 × 102 | - | |
| Cu | 7.60 × 10−4 | 8.15 × 10−8 | 5.99 × 10−1 | 5.99 × 10−1 | - | |
| Zn | 3.26 × 10−4 | 3.62 × 10−8 | 3.21 × 10−1 | 3.21 × 10−1 | - | |
| Pb | 1.08 × 10−2 | 1.12 × 10−6 | 1.03 × 101 | 1.03 × 101 | - | |
| Co—Non-Cancer | 7.82 × 10−4 | 2.94 × 10−4 | 1.28 × 10−1 | 1.29 × 10−1 | - | |
| Co—Cancer | 1.22 × 10−2 | 4.59 × 10−3 | - | - | 2.39 × 10−3 | |
| Ni—Non-Cancer | 6.77 × 10−4 | 7.98 × 10−1 | 9.87 × 100 | 1.07 × 101 | - | |
| Ni—Cancer | 1.14 × 10−2 | - | 2.31 × 10−⁵ | 1.14 × 10−2 | 1.92 × 10−4 | |
| Cr—Non-Cancer | 3.04 × 10−2 | 3.43 × 10−4 | 4.50 × 102 | 4.50 × 102 | - | |
| Cr—Cancer | 4.75 × 10−1 | 5.35 × 10−3 | 2.55 × 10−3 | - | 5.98 × 10−2 | |
| Cd—Non-Cancer | 4.08 × 10−3 | 4.38 × 10−8 | - | 4.08 × 10−3 | - | |
| Cd—Cancer | 6.36 × 10−2 | - | - | - | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, M.; Alshamsi, D.; Ahmad, T.; Ahmed, A.; Abdelfadil, K.M. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals (PTMs) Pollution, Ecological Risks, and Source Apportionment in Urban Soils from University Campuses: Insights from Multivariate and Positive Matrix Factorisation Analyses. Minerals 2025, 15, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050482
Ali M, Alshamsi D, Ahmad T, Ahmed A, Abdelfadil KM. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals (PTMs) Pollution, Ecological Risks, and Source Apportionment in Urban Soils from University Campuses: Insights from Multivariate and Positive Matrix Factorisation Analyses. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050482
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Mohamed, Dalal Alshamsi, Tofeeq Ahmad, Alaa Ahmed, and Khaled M. Abdelfadil. 2025. "Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals (PTMs) Pollution, Ecological Risks, and Source Apportionment in Urban Soils from University Campuses: Insights from Multivariate and Positive Matrix Factorisation Analyses" Minerals 15, no. 5: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050482
APA StyleAli, M., Alshamsi, D., Ahmad, T., Ahmed, A., & Abdelfadil, K. M. (2025). Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals (PTMs) Pollution, Ecological Risks, and Source Apportionment in Urban Soils from University Campuses: Insights from Multivariate and Positive Matrix Factorisation Analyses. Minerals, 15(5), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050482








