The Formation Process and Mechanism of Total Activated Potassium During the Preparation of Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer from Molybdenum Tailings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
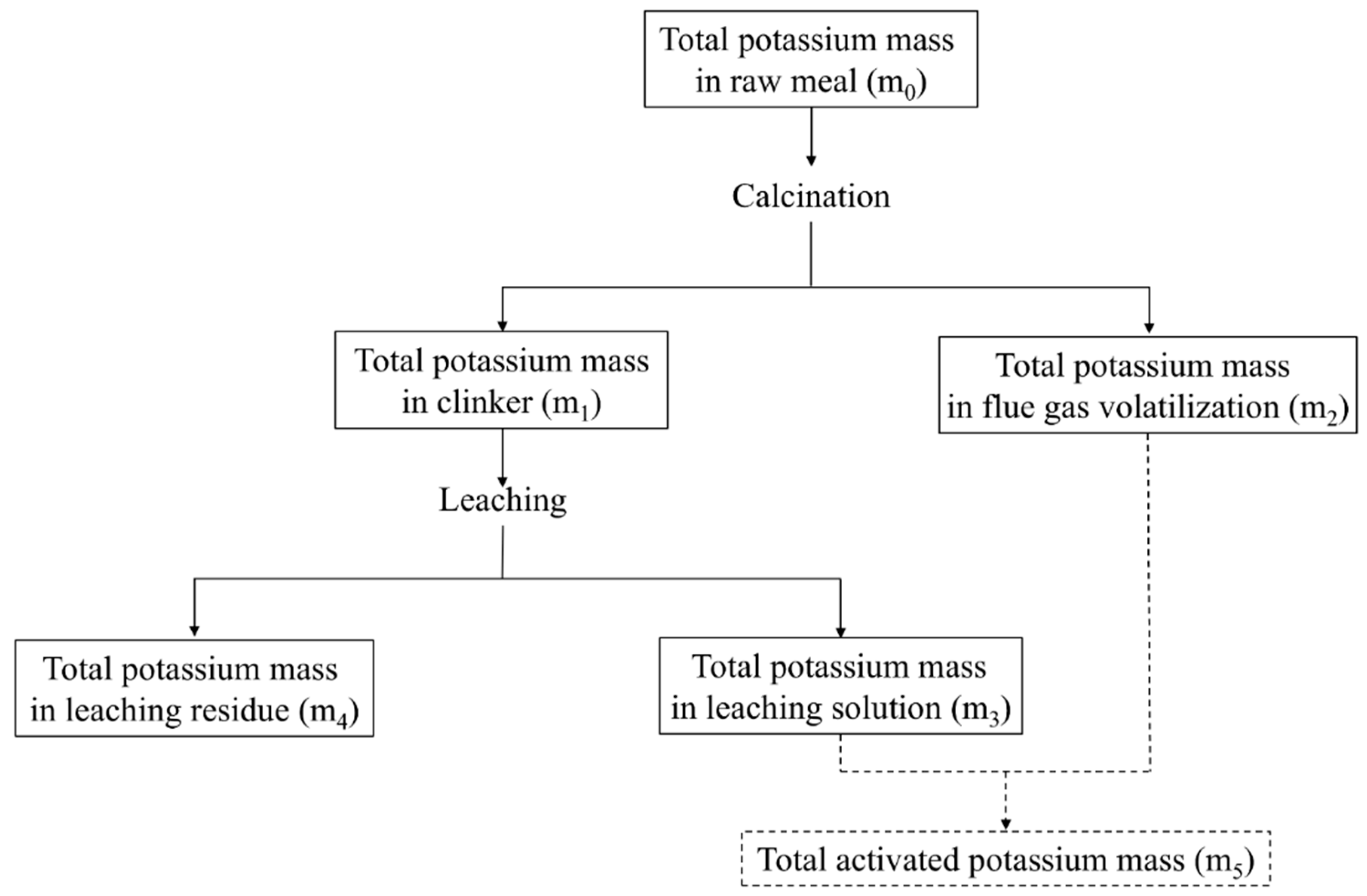
2.2. Experimental Procedures and Corresponding Calculation Formulas
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Research on the Content Regulation of Total Activated Potassium
3.1.1. The Influence of Calcination Temperature and Calcination Time
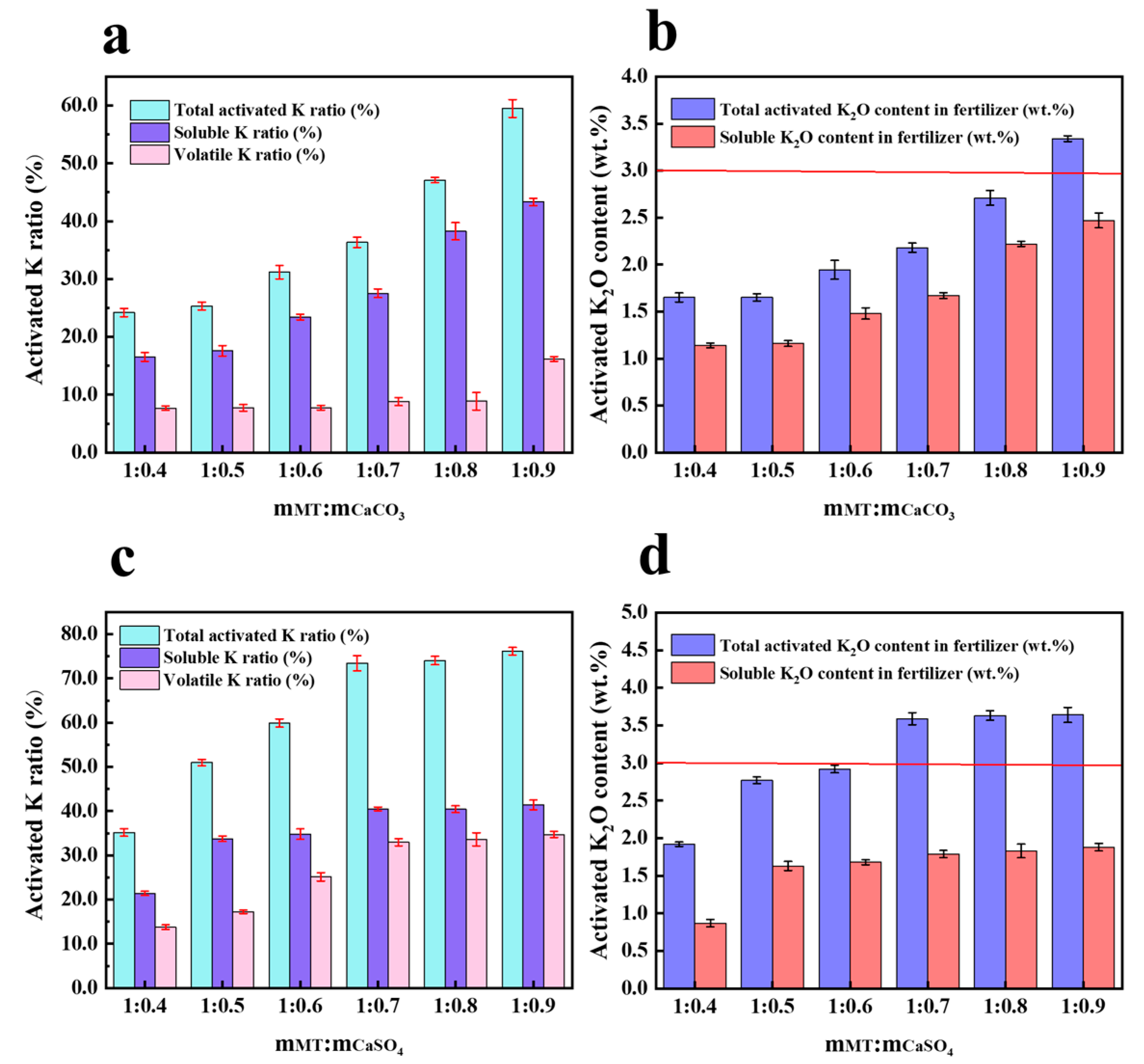
3.1.2. The Influence of Additives Ratio
3.1.3. Determination of the Process Conditions for Preparing Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer
3.2. The Formation Process and Mechanism of Soluble Potassium in the Fertilizer
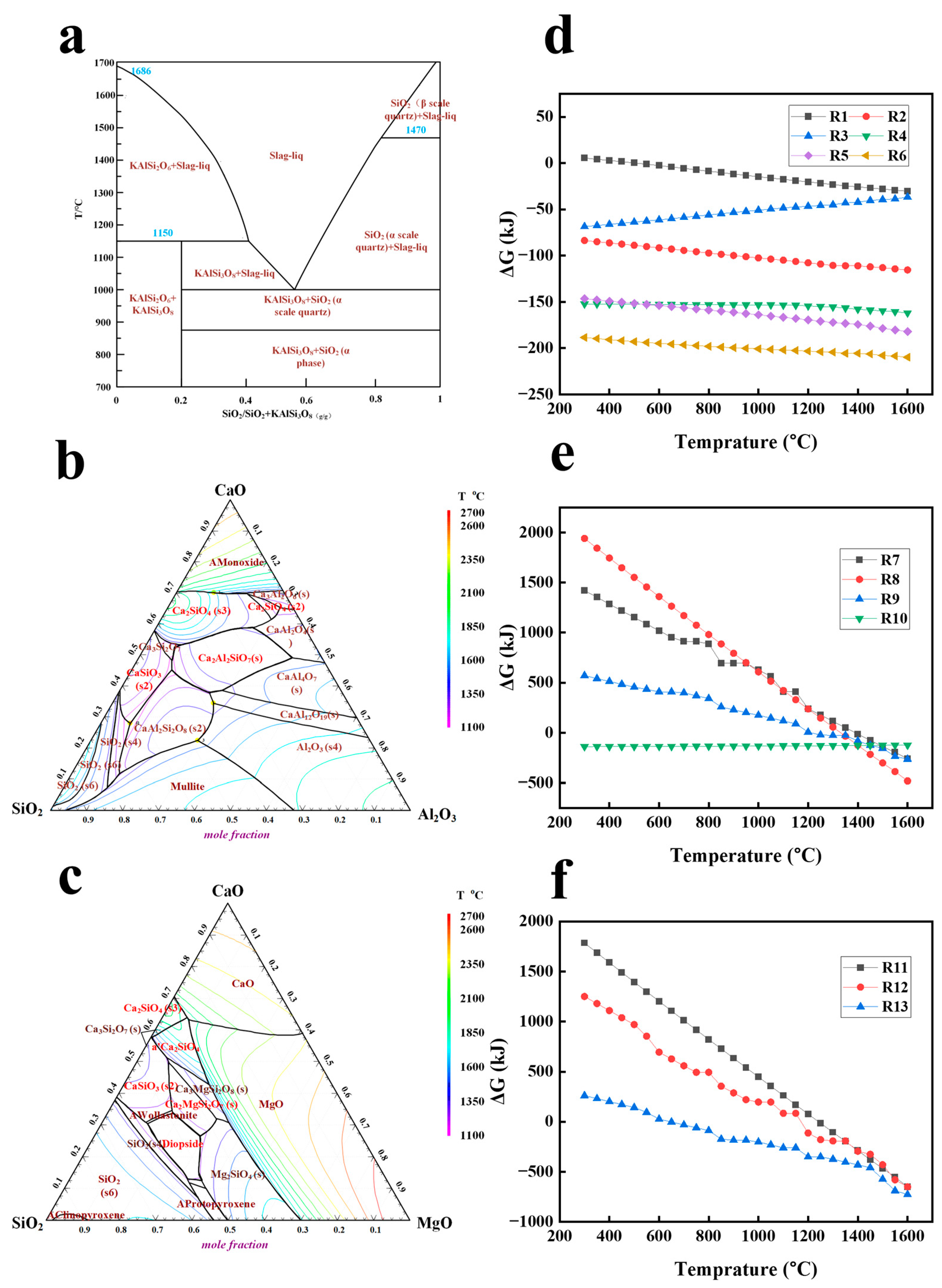
3.2.1. Thermodynamics of the Reactions Between MTs and Additives
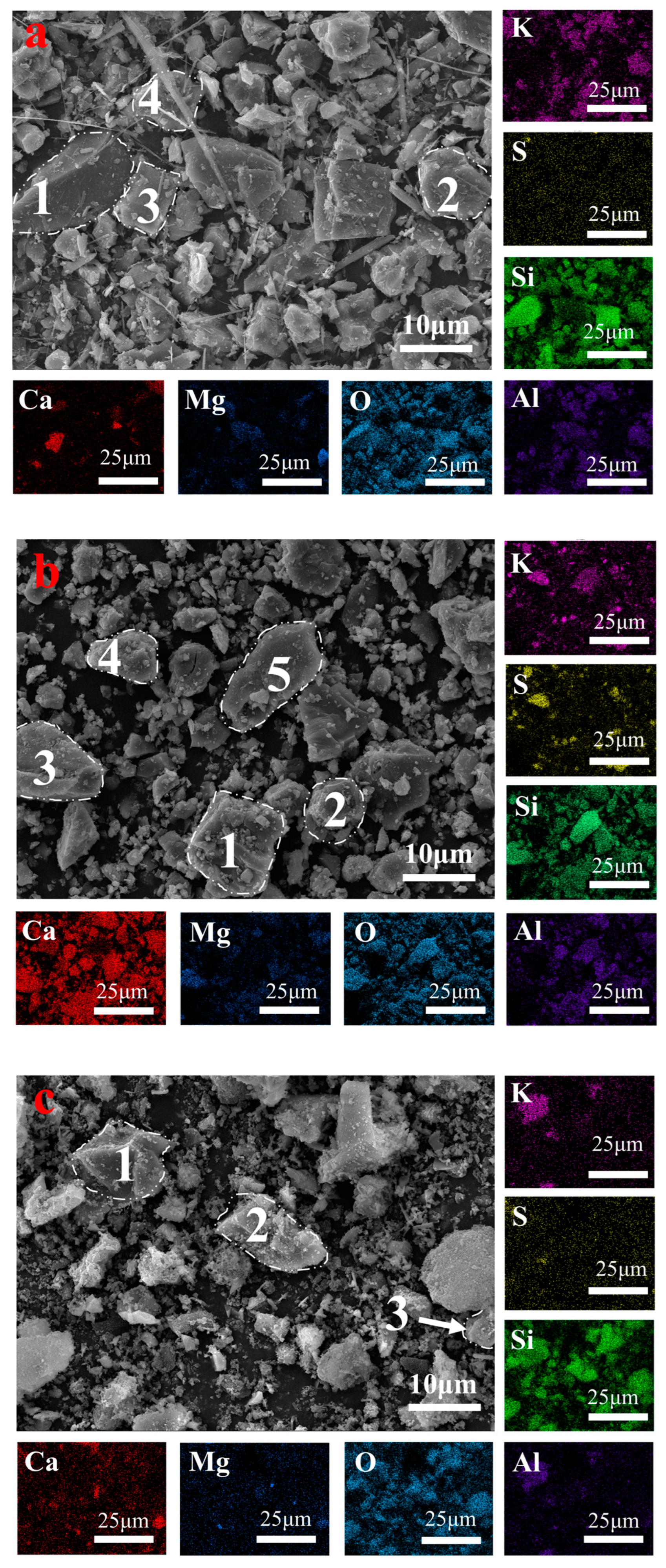
3.2.2. The Mechanism of Mineral Phase Reconstruction During the Calcination Process
3.3. The Formation Mechanism and Process of Volatile Potassium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| K–feldspar | potassium feldspar |
| MTs | molybdenum tailings |
| Si–Ca–K–Mg fertilizer | silicon–calcium–potassium–magnesium fertilizer |
References
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B. Preparation of egg–structured ceramsites from molybdenum tailings with improved properties. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; He, L.; Sun, F.; Zhao, Z. Research on removal of iron and copper from low–grade molybdenum calcine in strong acid system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 135, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wang, N. On the current situation and resource situation of molybdenum mining development and utilization in China. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2024, 42, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Luo, Z. Flotation technology of refractory low–grade molybdenum ore. Min. Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, A.; Dong, B. Research on the mechanical properties and microstructure of fly ash–based geopolymers modified by molybdenum tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 385, 131530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, T.; Xiang, A.; Liu, K.; Zhang, G. Molybdenum tailings calcination for phase composition of Si–Ca–K–Mg fertilizers: Modification of phase transformation and its effects on plant growth. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dang, F.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J. Influence of molybdenum tailings replacing river sand on mechanical properties and concrete microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Dong, R. A comprehensive study on the impact of direct electric curing on the performance of molybdenum tailings in cementitious materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xiong, X.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, D.; Pan, A.; Zhou, W. Characterization and utilization potential of typical molybdenum tailings in Shaanxi Province, China. Miner. Environ. 2024, 46, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Huang, W.; Mao, W.; Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Miao, X.; Hou, L. Preparing autoclaved aerated concrete using molybdenum tailings. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cui, X.; Kang, S.; Ding, Y. Sustainable applications for utilizing molybdenum tailings in concrete. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 266, 122020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdengeçti, M.T.; Baştürkcü, H.; Burat, F.; Kangal, M.O. The Correlation of Roasting Conditions in Selective Potassium Extraction from K–Feldspar Ore. Minerals 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; An, X.; Yang, G.; Sun, Y. Study on synergistic leaching of potassium and phosphorus from potassium feldspar and solid waste phosphogypsum via coupling reactions. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 65, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Decomposition of K–feldspar by potassium hydroxide solution in the hydrothermal system. Miner. Eng. 2022, 178, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. The supply and demand status and resource guarantee degree of potash in China. Miner. Explor. 2023, 14, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Meng, J.; Ge, W.; Li, W. Microwave–assisted extraction of potassium from K–feldspar in the presence of NaOH and CaO at low temperature. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, X. Kinetics of roasting potash feldspar in presence of sodium carbonate. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantray, J.; Anand, A.; Dash, B.; Ghosh, M.K.; Behera, A.K. Production of Potassium Chloride from K–Feldspar Through Roast–Leach–Solvent Extraction Route. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciceri, D.; Allanore, A. Nutrient release from K–feldspar ore altered in hydrothermal conditions. Chem. Pap. 2020, 742, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, H.; Gao, Y. Hydrothermal processing on potassic syenite powder: Zeolite synthesis and potassium release kinetics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. The leaching kinetics of K–feldspar in sulfuric acid with the aid of ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachani, P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Jain, D.; Patidar, S.K.; Soundarya, R.; Tirkey, S.R.; Mishra, S. Bioprospecting of Halotolerant Bacterial Isolates for Potassium Recovery from K–Feldspar. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.K.; Dash, N.; Samal, A.K.; Misra, P.K. Competency of chlorination roasting coupled water leaching process for potash recovery from K–feldspar: Mechanism and kinetics aspects. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 3612, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Li, P. Study on the integrated roasting process of kalsilite ore–CaCl2·2H2O system. Miner. Eng. 2021, 172, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Liang, B. Decomposition behavior of CaSO4 during potassium extraction from a potash feldspar–CaSO4 binary system by calcination. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, Y. Evolution of mineral phases and microstructure of high efficiency Si–Ca–K–Mg fertilizer prepared by water–insoluble K–feldspar. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 2020, 94, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, P.; Guo, Z. Recovery of Potassium from K–Feldspar by Thermal Decomposition with Flue Gas Desulfurization Gypsum and CaCO3: Analysis of Mechanism and Kinetics. Energy Fuels. 2017, 31, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, L. Manufacture of potassium sulfate by use microcline from Ya’an prefecture. Phosphate Compd. Fertil. 2000, 15, 7–10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Ju, P.; Chao, Q.; Zhao, S.; Xue, J. Research on the Thermal Decomposition Process of K–Feldspar–CaSO4–CaO System. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 734–737, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 36207-2018; Calcium Magnesium Potassium Silicate Fertilizer. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- NYT 2273-2012; Soil Amendment–Determination of Phosphorus and Potassium Content. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- NYT 2273-2012; Soil Amendment–Determination of Calcium, Magnesium and Silicon Content. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Haseli, P.; Majewski, P.; Christo, F.; Keane, P.; Jafarian, M.; Bruno, F. A review paper on the extraction of potassium from non–soluble resources with the use of acid and alkaline solution and molten salts. Miner. Eng. 2023, 204, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanmu, H.; Zhao, Z. Study of the mineral textural changes of Kalium–rich alkali trachyte in roasting process. Geol. Shaanxi 2000, 18, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, W.; Song, J.; Yue, H.; Tang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Xie, H. An efficient milling–assisted technology for K–feldspar processing, industrial waste treatment and CO2 mineralization. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Ma, H. Thermodynamic analysis and experiments of thermal decomposition for potassium feldspar at intermediate temperatures. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 32, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Kuang, F.; Liu, C. Study on extraction of potassium from K–feldspar by roasting–leaching of mixed salts. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2024, 56, 53–57+86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veit, U.; Rüssel, C.; Houet, Y.; Laurent, D. Viscosity and Liquidus Temperature of Ternary Glasses Close to the Eutectic Composition in the CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 System. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2016, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.; Decterov, S.A.; Pelton, A.D. Critical thermodynamic evaluation and optimization of the CaO–MgO–SiO2 system. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
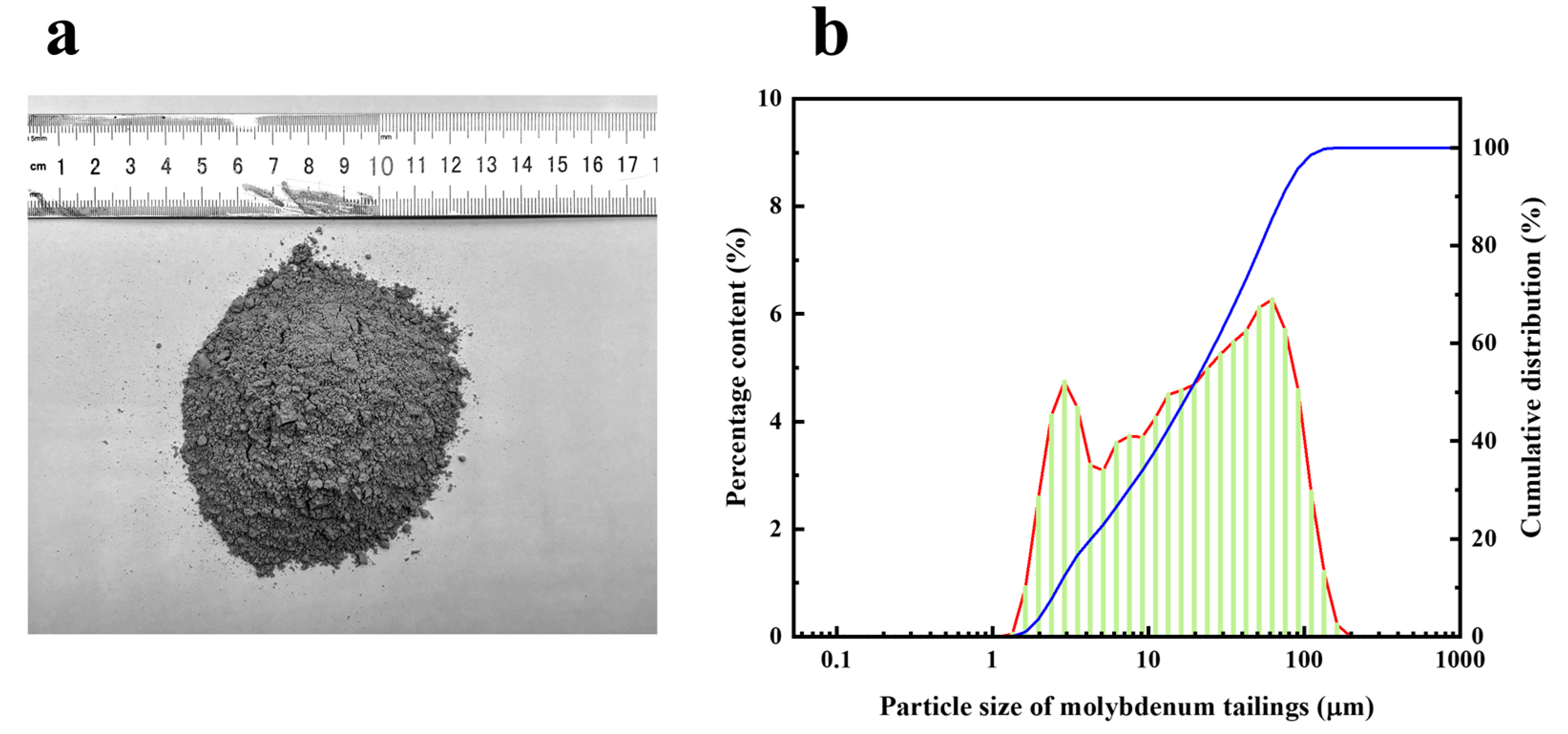
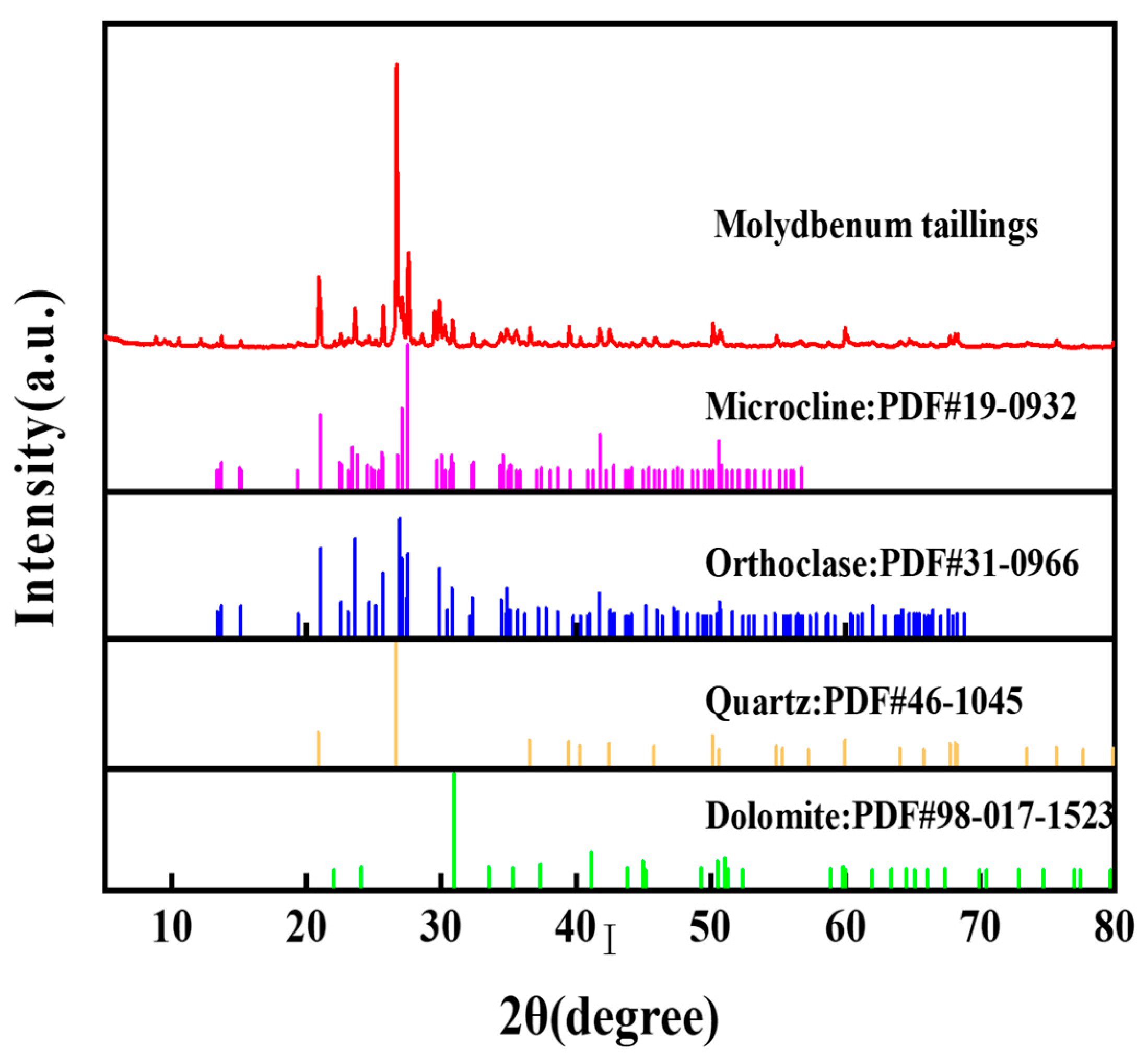





| Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | PbO | P2O5 |
| 0.758 | 6.17 | 10.547 | 58.997 | 7.983 | 8.214 | 0.247 | 4.575 | 0.005 | 0.083 |
| SO3 | Cl | MnO | CuO | ZnO | Rb2O | SrO | Y2O3 | CeO2 | MoO3 |
| 0.386 | 0.042 | 0.191 | 0.008 | 0.059 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.091 | 0.006 |
| Name | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|
| Total potassium mass balance | m0 = m1 + m2 |
| Clinker potassium mass balance | m1 = m3 + m4 |
| Total activated potassium mass balance | m5 = m2 + m3 |
| Clinker potassium ratio (wt.%) | W1 = m1/m0 × 100 |
| Volatile potassium ratio (wt.%) | W2 = m2/m0 × 100 |
| Soluble potassium ratio (wt.%) | W3 = m3/m0 × 100 |
| Insoluble potassium ratio (wt.%) | W4 = m4/m0 × 100 |
| Total activated potassium ratio (wt.%) | W5 = m5/m0 × 100 |
| Schemes | Purpose | Mass Ratio of Mixture | Addition Ratio of MTs, wt.% | Total Activated Potassium Ratio, % | Soluble K2O Content, wt.% | Total Activated K2O Content, wt.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maximizing the addition ratio of MTs | MTs:CaCO3:CaSO4 =1:0.5:0.1 | 62.50 | 52.52 | 2.21 | 3.05 |
| 2 | The highest ratio of total activated potassium | MTs:CaCO3:CaSO4 =1:0.7:0.6 | 43.48 | 92.36 | 2.76 | 4.33 |
| 3 | The highest content of soluble K2O in clinker | MTs:CaCO3:CaSO4 =1:0.7:0.2 | 52.63 | 84.89 | 3.55 | 4.21 |
| 4 | The highest content of total activated K2O in fertilizer | MTs:CaCO3:CaSO4 =1:0.7:0.4 | 47.62 | 88.1 | 2.91 | 4.50 |
| Element | MTs | Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer | Leaching Residue of Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 48.91 | 44.93 | 54.07 |
| Mg | 3.46 | 2.44 | 2.13 |
| Al | 5.66 | 3.13 | 1.43 |
| Si | 31.35 | 14.87 | 34.80 |
| S | 0.40 | 3.98 | 0.96 |
| K | 6.47 | 4.77 | 0.79 |
| Ca | 3.76 | 25.88 | 5.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Li, Y.; Xiang, A.; Li, X.; Liu, K. The Formation Process and Mechanism of Total Activated Potassium During the Preparation of Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer from Molybdenum Tailings. Minerals 2025, 15, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050450
Hu T, Li Y, Xiang A, Li X, Liu K. The Formation Process and Mechanism of Total Activated Potassium During the Preparation of Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer from Molybdenum Tailings. Minerals. 2025; 15(5):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050450
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Tuanliu, Yifan Li, Aihua Xiang, Xinglan Li, and Kun Liu. 2025. "The Formation Process and Mechanism of Total Activated Potassium During the Preparation of Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer from Molybdenum Tailings" Minerals 15, no. 5: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050450
APA StyleHu, T., Li, Y., Xiang, A., Li, X., & Liu, K. (2025). The Formation Process and Mechanism of Total Activated Potassium During the Preparation of Si–Ca–K–Mg Fertilizer from Molybdenum Tailings. Minerals, 15(5), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15050450







