Pretreatment and Extraction of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore in Acidic Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pretreatment in Acidic Condition
2.1. Pressure Oxidation
2.2. Bio-Oxidation
3. Gold Extraction in Acidic Condition
3.1. Thiourea Leaching Process
3.2. Halogen Leaching Process
3.2.1. Chlorination Leaching Process
3.2.2. Bromination Leaching Process
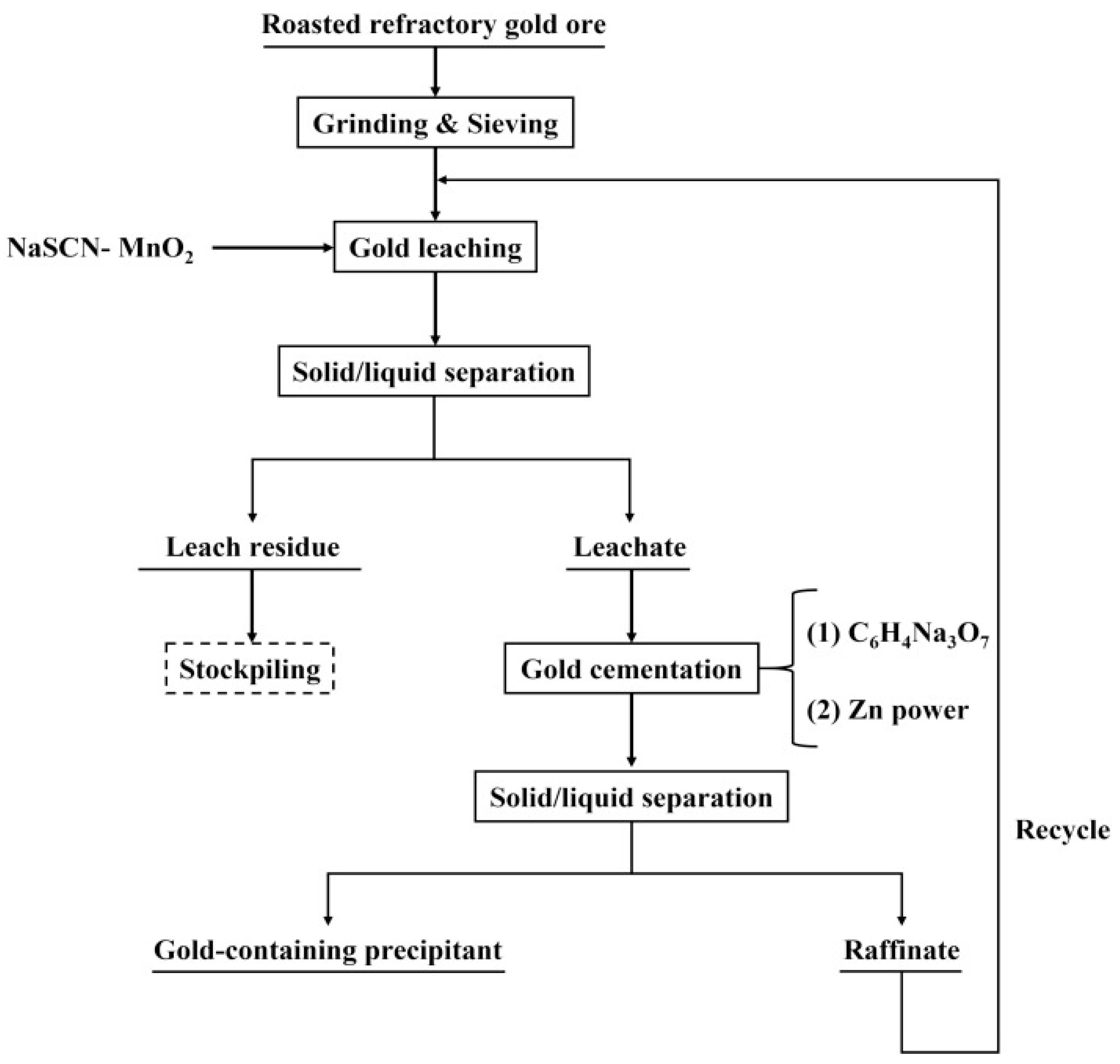
3.3. Thiocyanate Leaching Process
3.4. Research Progress on Thiocyanate Leaching
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Celep, O.; Alp, İ.; Deveci, H. Improved Gold and Silver Extraction from a Refractory Antimony Ore by Pretreatment with Alkaline Sulphide Leach. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, A.D.; Larachi, F.; Laflamme, P. The Effect of Pyrite Particle Size on the Electrochemical Dissolution of Gold during Cyanidation. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, K.L.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. The Role of Metal-Cyanide Species in Leaching Gold from a Copper Concentrate. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, A.D.; Koc, E.; Yazici, E.Y.; Deveci, H. Treatment of Copper-Rich Gold Ore by Cyanide Leaching, Ammonia Pretreatment and Ammoniacal Cyanide Leaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celep, O.; Serbest, V. Characterization of an Iron Oxy/Hydroxide (Gossan Type) Bearing Refractory Gold and Silver Ore by Diagnostic Leaching. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremolada, J.; Dzioba, R.; Bernardo-Sánchez, A.; Menéndez-Aguado, J.M. The Preg-Robbing of Gold and Silver by Clays during Cyanidation under Agitation and Heap Leaching Conditions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 94, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, C.; Mensah, S.; Ackah, K.; Amankwah, R.K. Reducing Preg-Robbing in Carbonaceous Gold Ores Using Passivative or Blanking Agents. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtiainen, R.; Lundström, M.; Liipo, J. Preg-Robbing Verification and Prevention in Gold Chloride-Bromide Leaching. Miner. Eng. 2018, 128, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.M.; Ghahreman, A.; Bell, S. A Comparative Study of Gold Refractoriness by the Application of QEMSCAN and Diagnostic Leach Process. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 169, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, F.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y.; Fu, Y.; Dreisinger, D. Eco-Friendly Leaching of Gold from a Carbonaceous Gold Concentrate in Copper-Citrate-Thiosulfate Solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, P.; Abdollahi, H.; Amini, A.; Noaparast, M.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Habashi, F. Cyanidation of Gold Ores Containing Copper, Silver, Lead, Arsenic and Antimony. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 95, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, C.A. Basic Iron Sulphate—A Potential Killer for Pressure Oxidation Processing of Refractory Gold Concentrates if Not Handled Appropriately. Miner. Metall. Process. 2010, 27, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hilson, G.; Monhemius, A.J. Alternatives to Cyanide in the Gold Mining Industry: What Prospects for the Future? J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, K.E. Gold Leaching from Refractory Ores—Literature Survey. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1987, 2, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Collins, M.; Dennett, J.; Stiksma, J.; Ji, J.; Kalanchey, R.; Berezowsky, R. Pilot Plant Pressure Oxidation of Refractory Gold-Silver Concentrate from Eldorado Gold Corporation’s Certej Project in Romania. Can. Metall. Q. 2015, 54, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, I.; Thorpe, S.J.; Papangelakis, V.G. Redox Potential Measurement during Pressure Oxidation (POX) of a Refractory Gold Ore. Can. Metall. Q. 2018, 57, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, D.R.; King, J.A.; Robinson, P.C. Pre Concentration and Pressure Oxidation of Porgera Refractory Gold Ore. Min. Metall. Explor. 1986, 3, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckard, W.J.; Sparrow, G.J.; Woodcock, J.T. Gold and Silver Extraction from Hellyer Lead-Zinc Flotation Middlings Using Pressure Oxidation and Thiourea Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 1993, 33, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ahn, J.; Lee, J. Characterization of Gold Deportment and Thiosulfate Extraction for a Copper-gold Concentrate Treated by Pressure Oxidation. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 207, 105771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ahn, J.; Lee, J. Gold Deportment and Leaching Study from a Pressure Oxidation Residue of Chalcopyrite Concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 201, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dreisinger, D. Pressure Oxidation of Ferrous Ions by Oxygen and Hematite Precipitation from Concentrated Solution of Calcium, Copper and Iron Chlorides. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 140, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudyanga, F.P.; Mahlangu, T.; Roman, R.J.; Mungoshi, J.; Mbeve, K. An Acidic Pressure Oxidation Pre-Treatment of Refractory Gold Concentrates from the KweKwe Roasting Plant, Zimbabwe. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shimei, L.; Quanjun, L.; Jiushuai, D.; Bin, L.; Yuanqin, L.; Liuchuang, Z.; Hao, L. Gold Recovery from Refractory Gold Concentrates by Pressure Oxidation Pre-Treatment and Thiosulfate Leaching. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 55, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, M.; Sadri, F.; Ghahreman, A. Effect of Mixing Acidic and Alkaline Pressure Oxidation Discharges with Different Ratios on Gold Thiosulfate Leaching Efficiency. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 205, 105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Tian, Q.; Zhong, S.; Qin, H. Extraction of Gold from Typical Carlin Gold Concentrate by Pressure Oxidation Pretreatment—Sodium Jarosite Decomposition and Polysulfide Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 208, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tributsch, H. Direct versus Indirect Bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, K.T.; Sasaki, K.; Kaneta, T.; Ofori-Sarpong, G.; Osseo-Asare, K. Bio-Modification of Carbonaceous Matter in Gold Ores: Model Experiments Using Powdered Activated Carbon and Cell-Free Spent Medium of Phanerochaete Chrysosporium. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 168, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Acuña, C.C.R.; Boxall, N.J.; Li, J.; Collinson, D.; Morris, C.; Du Plessis, C.A.; Streltsova, N.; Kaksonen, A.H. Effect of Initial Cell Concentration on Bio-Oxidation of Pyrite before Gold Cyanidation. Minerals 2021, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, S.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, T. Bio-Oxidation of a High-Sulfur and High-Arsenic Refractory Gold Concentrate Using a Two-Stage Process. Miner. Eng. 2018, 120, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, O.P.; Rajasekar, A.; Balasubramanian, R. Bio-Oxidation and Biocyanidation of Refractory Mineral Ores for Gold Extraction: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1611–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Ma, P.; Luan, Z.; Tong, L.; Jin, Z.; Sand, W. Column Bio-Oxidation of Low-Grade Refractory Gold Ore Containing High-Arsenic and High-Sulfur: Insight on Change in Microbial Community Structure and Sulfide Surface Corrosion. Miner. Eng. 2022, 175, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Wu, J.; Ahn, J.; Lee, J. Comparative Investigations on Sulfidic Gold Ore Processing: A Novel Biooxidation Process Option. Miner. Eng. 2019, 140, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Huo, Q.; Xie, J.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Guo, Y. Novel Two-Step Process to Improve Efficiency of Bio-Oxidation of Axi High-Sulfur Refractory Gold Concentrates. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 4119–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraz, S.; Hossna, D.; Rezgar, B.; Piroz, Z. Improved Recovery of a Low-Grade Refractory Gold Ore Using Flotation–Preoxidation–Cyanidation Methods. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konadu, K.T.; Mendoza, D.M.; Huddy, R.J.; Harrison, S.T.L.; Kaneta, T.; Sasaki, K. Biological Pretreatment of Carbonaceous Matter in Double Refractory Gold Ores: A Review and Some Future Considerations. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.J.; Yang, H.Y.; Jin, Z.N. Study on the Gold Recovery of Double Refractory Gold Ore Concentrate by Biological Oxidation Pretreatment. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1130, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Song, X.; Dong, J. Research Status of Carbonaceous Matter in Carbonaceous Gold Ores and Bio-Oxidation Pretreatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 3405–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravyov, M. Two-Step Processing of Refractory Gold-Containing Sulfidic Concentrate via Biooxidation at Two Temperatures. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, A.; Aguirre, P.; Gentina, J.C. Biooxidation of Iron by Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans in the Presence of D-Galactose: Understanding Its Influence on the Production of EPS and Cell Tolerance to High Concentrations of Iron. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarok, M.Z.; Winarko, R.; Chaerun, S.K.; Rizki, I.N.; Ichlas, Z.T. Improving Gold Recovery from Refractory Gold Ores through Biooxidation Using Iron-Sulfur-Oxidizing/Sulfur-Oxidizing Mixotrophic Bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 168, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Santini, J.M. Mechanisms of Bioleaching: Iron and Sulfur Oxidation by Acidophilic Microorganisms. Essays Biochem. 2023, 67, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomchenko, N.V.; Muravyov, M.I.; Kondrat’eva, T.F. Two-Stage Bacterial–Chemical Oxidation of Refractory Gold-Bearing Sulfidic Concentrates. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 101, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, A.; Van Der Weijden, R.D.; Van Weert, G.; Kondos, P.; Buisman, C.J.N. Processing of Arsenopyritic Gold Concentrates by Partial Bio-Oxidation Followed by Bioreduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6316–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, H. Succession of Acidophilic Bacterial Community During Bio-Oxidation of Refractory Gold-Containing Sulfides. Geomicrobiol. J. 2010, 27, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwah, R.K.; Yen, W.-T.; Ramsay, J.A. A Two-Stage Bacterial Pretreatment Process for Double Refractory Gold Ores. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomchenko, N.V.; Kondrat’eva, T.F.; Muravyov, M.I. A New Concept of the Biohydrometallurgical Technology for Gold Recovery from Refractory Sulfide Concentrates. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, Q.; Meng, F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Yin, H.; Jiang, T. Bio-Oxidation of a Double Refractory Gold Ore and Investigation of Preg-Robbing of Gold from Thiourea Solution. Metals 2020, 10, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boduen, A.; Zalesov, M.; Melamud, V.; Grigorieva, V.; Bulaev, A. Combined Bacterial and Pressure Oxidation for Processing High-Sulfur Refractory Gold Concentrate. Processes 2023, 11, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Tong, L.; Ma, P.; Luan, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Y. Two-Stage Chemical-Biological Oxidation Process for Low-Grade Refractory Gold Concentrate with High Arsenic and Sulfur. Miner. Eng. 2023, 191, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Wu, J.; Lee, J. Comparative Studies of Novel Biooxidation Process to Low-Grade Sulphide Gold Ores. Geosystem Eng. 2022, 25, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, L.C.; Da Silva, S.R.; Giardini, R.M.N.; De Souza, L.F.C.; Leão, V.A. Bio-Oxidation of Refractory Gold Ores Containing Stibnite and Gudmundite. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L. Sulfide Minerals Bio-Oxidation of a Low-Grade Refractory Gold Ore. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 921, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canales, C.; Acevedo, F.; Gentina, J.C. Laboratory-Scale Continuous Bio-Oxidation of a Gold Concentrate of High Pyrite and Enargite Content. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, N.; Carranza, F. Refractory Gold-Bearing Ores: A Review of Treatment Methods and Recent Advances in Biotechnological Techniques. Hydrometallurgy 1994, 34, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zi, F.; Qin, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, Y. Extraction of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore Using Bromate and Ferric Chloride Solution. Miner. Eng. 2019, 136, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Ghahreman, A. The Effect of Ore Mineralogy on the Electrochemical Gold Dissolution Behavior in Various Cyanide and Oxygen Concentrations; Effect of Sulfidic Ores Containing Heavy Metals. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 184, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidari, E.; Aghazadeh, V. Pyrite from Zarshuran Carlin-Type Gold Deposit: Characterization, Alkaline Oxidation Pretreatment, and Cyanidation. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 179, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, G.J.; Woodcock, J.T. Cyanide and Other Lixiviant Leaching Systems for Gold with Some Practical Applications. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1995, 14, 193–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, M.I.; Breuer, P.L. The Cyanide Leaching of Gold in Solutions Containing Sulfide. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, F.; Spiteller, M.; Coulston, F. The Cyanide Leaching Gold Recovery Process Is a Nonsustainable Technology with Unacceptable Impacts on Ecosystems and Humans: The Disaster in Romania. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 46, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaini, H.; Kasongo, K.; Naude, N.; Katabua, J. Enhanced Leachability of Gold and Silver in Cyanide Media: Effect of Alkaline Pre-Treatment of Jarosite Minerals. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Erust, C.; Gahan, C.S.; Ozgun, M.; Sahin, M.; Tuncuk, A. Precious Metal Recovery from Waste Printed Circuit Boards Using Cyanide and Non-Cyanide Lixiviants—A Review. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A. The Fate of Cyanide in Leach Wastes at Gold Mines: An Environmental Perspective. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, R.K.; Skinner, W.; Addai-Mensah, J. Alkaline Cyanide Leaching of Refractory Gold Flotation Concentrates and Bio-Oxidised Products: The Effect of Process Variables. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 179, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidari, E.; Aghazadeh, V. Alkaline Leaching Pretreatment and Cyanidation of Arsenical Gold Ore from the Carlin-Type Zarshuran Deposit. Can. Metall. Q. 2018, 57, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.G. Alkaline Sulfide Gold Leaching Kinetics. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kou, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H. A Review of Environmentally Friendly Gold Lixiviants: Fundamentals, Applications, and Commonalities. Miner. Eng. 2023, 197, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ritchie, I.M.; La Brooy, S.R. Electrochemical Oxidation of Gold and Thiourea in Acidic Thiourea Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, D146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanti, I.; Marliana, T.; Anugrahwati, M.; Wicaksono, W.P.; Winata, W.F. The Comparison of Gold Extraction Methods from the Rock Using Thiourea and Thiosulfate. Open Chem. 2023, 21, 20230102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miller, J.D. Reaction Kinetics of Gold Dissolution in Acid Thiourea Solution Using Ferric Sulfate as Oxidant. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örgül, S.; Atalay, Ü. Reaction Chemistry of Gold Leaching in Thiourea Solution for a Turkish Gold Ore. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 67, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Miller, J.D. A Review of Gold Leaching in Acid Thiourea Solutions. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2006, 27, 177–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örgül, S.; Atalay, Ü. Gold Extraction from Kaymaz Gold Ore by Thiourea Leaching. In Developments in Mineral Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 13, pp. C6-22–C6-28. ISBN 978-0-444-50283-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ubaldini, S.; Fornari, P.; Massidda, R.; Abbruzzese, C. An Innovative Thiourea Gold Leaching Process. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 48, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsova, O.N.; Bek, R.Y.; Zelinskii, A.G.; Vais, A.A. Anodic Behavior of Gold in Acid Thiourea Solutions: A Cyclic Voltammetry and Quartz Microgravimetry Study. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2006, 42, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Hagiwara, T.; Haseba, H.; Takahashi, T. Reduction of Thiourea Consumption in Gold Extraction by Acid Thiourea Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 2757–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T. Role of Foreign Ions in the Thiourea Leaching of Gold. Miner. Eng. 2023, 202, 108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Qiu, G.; Wang, D. A Novel Bio-Oxidation and Two-Step Thiourea Leaching Method Applied to a Refractory Gold Concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Q.; Qin, H. Stepwise Extraction of Gold and Silver from Refractory Gold Concentrate Calcine by Thiourea. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 194, 105330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olyaei, Y.; Noparast, M.; Tonkaboni, S.Z.S.; Haghi, H.; Amini, A. Response of Low-Grade Gold Ore to Cyanidation and Thiourea Leaching. Part. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hu, X.; Zi, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y. Synergistical Thiourea and Thiosulfate Leaching Gold from a Gold Concentrate Calcine with Copper-Ammonia Catalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Valdivieso, A.L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Zainiddinovich, N.Z.; Wu, C.; Song, S.; Jia, F. A Highly Efficient Clean Hydrometallurgy Process for Gold Leaching in a Fenton Oxidation Assisted Thiourea System. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T. Improved Thiourea Leaching of Gold from a Gold Ore Using Additives. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 222, 106204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.A.; Baniasadi, M.; Graves, J.E.; Greenwood, A.; Farnaud, S. Thiourea Leaching: An Update on a Sustainable Approach for Gold Recovery from E-Waste. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 8, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Molstad, E.; Mishra, B. Recovery of Gold and Silver from Secondary Sources of Electronic Waste Processing by Thiourea Leaching. JOM 2018, 70, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Michelis, I.; Olivieri, A.; Ubaldini, S.; Ferella, F.; Beolchini, F.; Vegliò, F. Roasting and Chlorine Leaching of Gold-Bearing Refractory Concentrate: Experimental and Process Analysis. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yin, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Yang, K. Investigation on the Recovery of Gold from Pretreated Cyanide Tailings Using Chlorination Leaching Process. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D. Chloride as an Alternative Lixiviant to Cyanide for Gold Ores. In Gold Ore Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 525–531. ISBN 978-0-444-63658-4. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Xu, Z. Recycling Gold and Copper from Waste Printed Circuit Boards Using Chlorination Process. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8957–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Qian, G.; Zhou, M. Kinetics of Leaching Refractory Gold Ores by Ultrasonic-Assisted Electro-Chlorination. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2012, 19, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, M.I.; Breuer, P.L.; Choo, W.L. A Kinetic Study That Compares the Leaching of Gold in the Cyanide, Thiosulfate, and Chloride Systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dönmez, B.; Ekinci, Z.; Çelik, C.; Çolak, S. Optimisation of the Chlorination of Gold in Decopperized Anode Slime in Aqueous Medium. Hydrometallurgy 1999, 52, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karppinen, A.; Seisko, S.; Nevatalo, L.; Wilson, B.P.; Yliniemi, K.; Lundström, M. Gold Recovery from Cyanidation Residue by Chloride Leaching and Carbon Adsorption—Preliminary Results from CICL Process. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 226, 106304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, K.-S.; Zhang, T.-A.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, G.-H. Research on Chlorination Leaching of Pressure-Oxidized Refractory Gold Concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 194, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Liddell, K.S.; Smith, L.A. Cyanide-Free Recovery of Metals from Polymetallic and Refractory Gold Concentrates by the KellGold Process. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddell, K.S.; Adams, M.D.; Smith, L.A.; Muller, B. Kell Hydrometallurgical Extraction of Precious and Base Metals from Flotation Concentrates—Piloting, Engineering, and Implementation Advances. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2019, 119, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Anderson, C. Hydrometallurgical Treatment of Waste Printed Circuit Boards: Bromine Leaching. Metals 2020, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesic, B.; Sergent, R.H. Reaction Mechanism of Gold Dissolution with Bromine. Metall. Trans. B 1993, 24, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Jing-Ze, D.; Peng-Zhi, X. Bromic Acid-Thiourea Synergistic Leaching of Sulfide Gold Ore. Green Process. Synth. 2024, 13, 20240079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Futuro, A.; Fiúza, A.; Vila, M.C.; Dinis, M.L. Bromine Leaching as an Alternative Method for Gold Dissolution. Miner. Eng. 2018, 118, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahtiainen, R.; Liipo, J.; Lundström, M. Simultaneous Sulfide Oxidation and Gold Dissolution by Cyanide-Free Leaching from Refractory and Double Refractory Gold Concentrates. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.; Li, W.-J.; Song, K.; Song, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.; Bai, A.-P.; Cheng, Y. Electrochemical Dissolution Behavior of Gold and Its Main Coexistent Sulfide Minerals in Acid Thiocyanate Solutions. Rare Met. 2022, 41, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholmogorov, A.G.; Kononova, O.N.; Pashkov, G.L.; Kononov, Y.S. Thiocyanate Solutions in Gold Technology. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 64, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Abdollahi, H.; Saneie, R.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Rezaei, A.; Karimi Darvanjooghi, M.H.; Brar, S.K.; Magdouli, S. A Cleaner Approach for High-Efficiency Regeneration of Base and Precious Metals from Waste Printed Circuit Boards through Stepwise Oxido-Acidic and Thiocyanate Leaching. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.J.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, R.J. A Review of Thiocyanate Hydrometallurgy for the Recovery of Gold. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 768, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizitorghabeh, A.; Mahandra, H.; Ramsay, J.; Ghahreman, A. Gold Leaching from an Oxide Ore Using Thiocyanate as a Lixiviant: Process Optimization and Kinetics. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17183–17193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Feng, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, H.; Liao, S. The Role of Glycine in the Ammonium Thiocyanate Leaching of Gold. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Moats, M.S.; Miller, J.D. Gold Dissolution in Acidic Thiourea and Thiocyanate Solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3643–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Moats, M.S.; Miller, J.D.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Xu, H. Thiourea–Thiocyanate Leaching System for Gold. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 106, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizitorghabeh, A.; Wang, J.; Ramsay, J.A.; Ghahreman, A. A Review of Thiocyanate Gold Leaching—Chemistry, Thermodynamics, Kinetics and Processing. Miner. Eng. 2021, 160, 106689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W. Gold Recovery from Roasted Refractory Gold Concentrate through Cyclic Extraction Using MnO2-Assisted Thiocyanate Leaching and Cementation with Zinc Powder. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 228, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
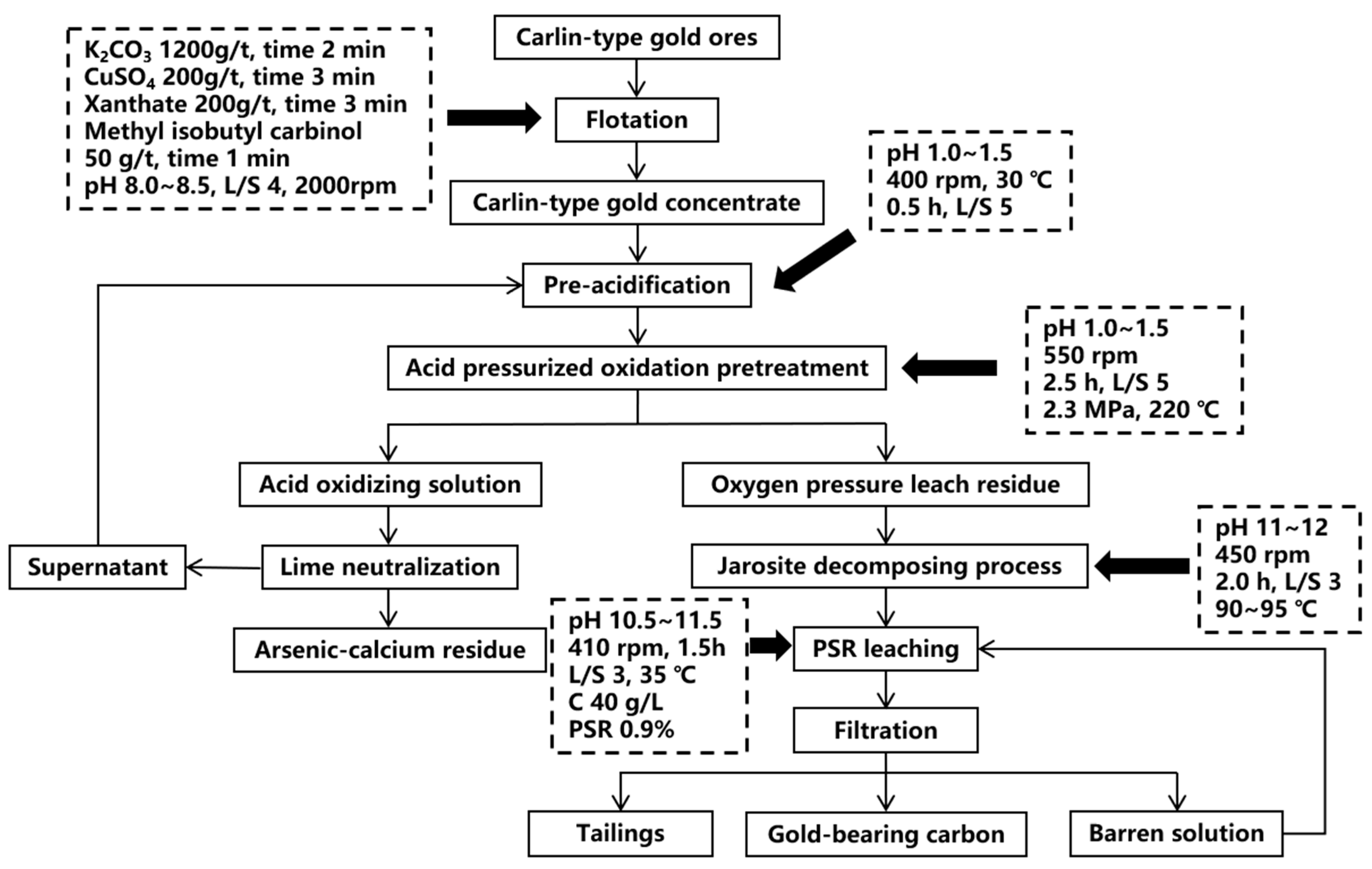

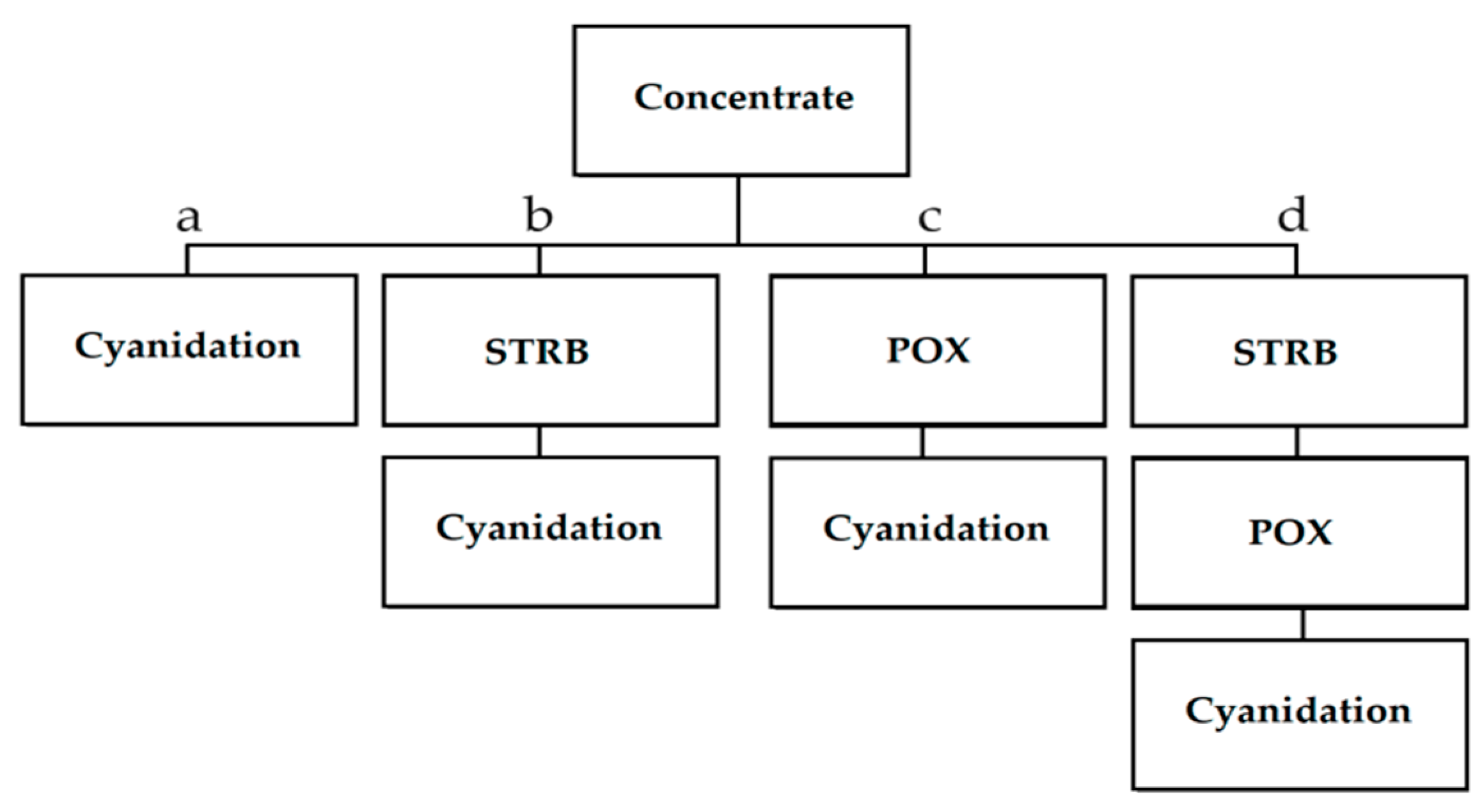
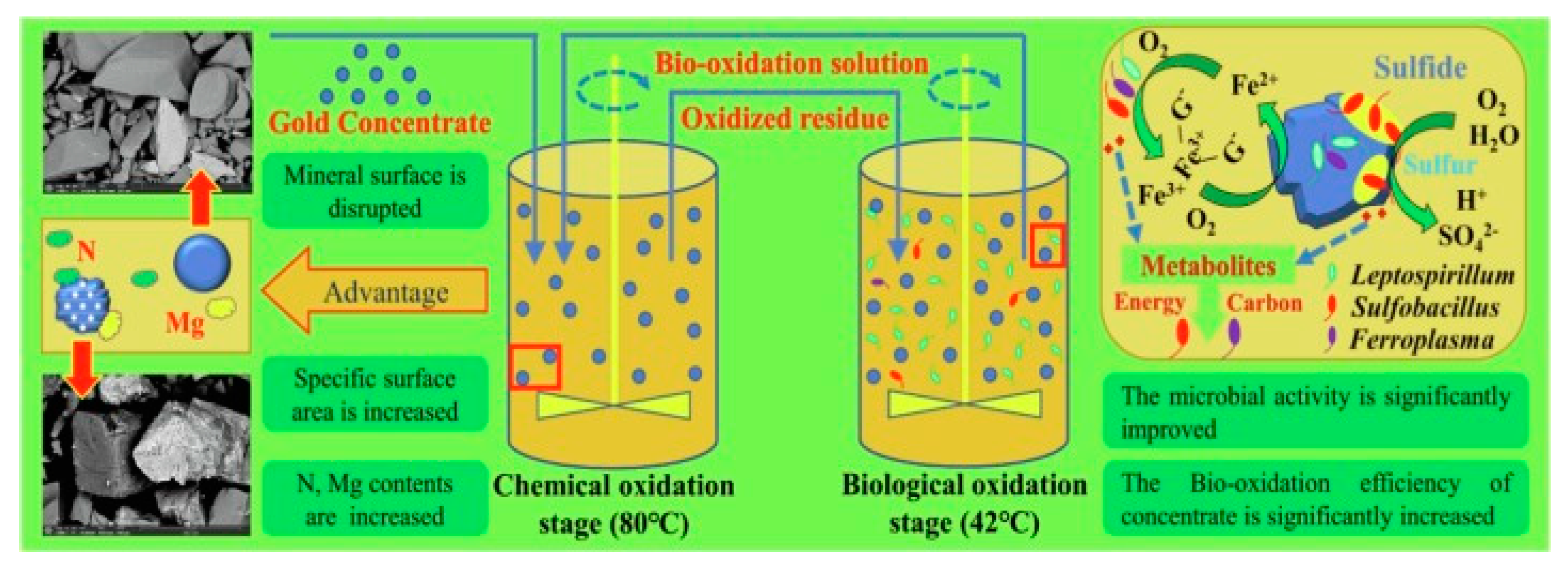


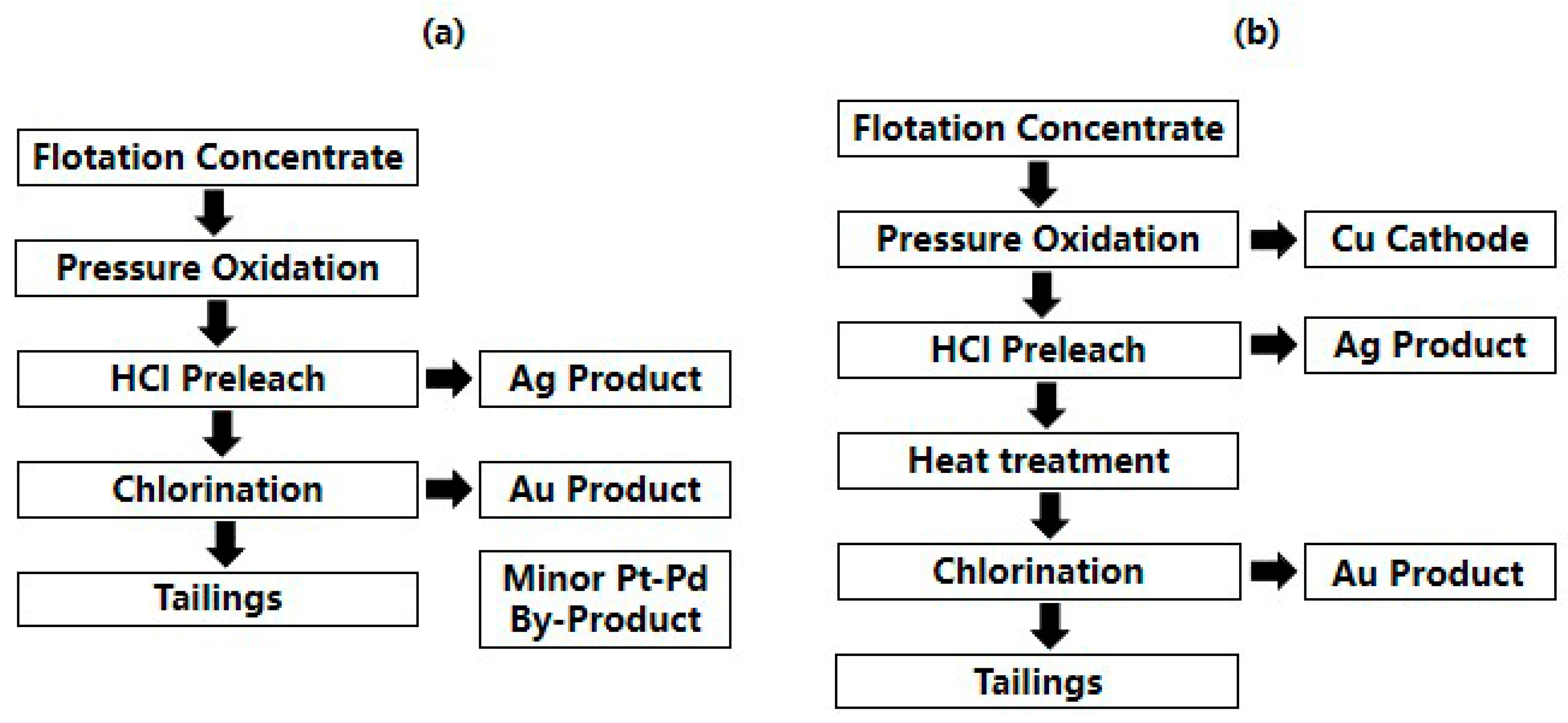
| Pretreatment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure oxidation | high sulfide oxidation degree fast kinetics wide applicability less pollution | complex process high CapEx and OpEx high corrosion resistance from equipment |
| Bio-oxidation | wide applicability less pollution low cost simple process | High construction costs demanding requirements for processing conditions. |
| Reagent Type | Concentration Range | pH Range | Basic Chemistry | Research Level | Extent of Commercialization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | High | 8–10 | Simple | Low | Pilot tests, +100 °C |
| Ammonia/cyanide | Low | 9–11 | Simple | Extensive | Applied to Cu/Au ores |
| Ammonium thiosulfate | High | 8.5–9.5 | Complex | Extensive | Semi-commercial |
| Slurry CN-electrolysis | Low | 9–11 | Simple | Historical | Limited historical |
| Sodium sulfide | High | 8–10 | Simple | Low | Geological interest only |
| Alpha-hydroxynitriles | Moderate | 7–8 | Fairly simple | Fairly popular | None |
| Malononitrile | Moderate | 8–9 | Fairly complex | Low | None |
| Alkali cyanoform | Poorly defined | ~9 | Poorly defined | Low | None |
| Calcium cyanide | Poorly defined | ~9 | Poorly defined | Low | None |
| Alkaline polysulfides | High | 8–9 | Poorly defined | Low | None |
| Hypochlorite/chloride | High chloride | 6–6.5 | Well defined | Extensive | Historical and modern |
| Bromocyanide | High | 6–7 | Poorly defined | Historical | Historical |
| Iodine | High | 3–10 | Poorly defined | Low | None |
| Bisulfate/sulfur dioxide | High | 4–5 | Fairly simple | Low | None |
| Bacteria | High | 7–10 | Fairly complex | Low, growing | None |
| Natural organic acids | High | 5–6 | Fairly complex | Low | None |
| DMSO, DMF | Poorly defined | 7 | Poorly defined | Very low | None |
| Bromine/bromide | High | 1–3 | Well defined | Low | Historical |
| Thiourea | High | 1–2 | Well defined | Fairly popular | Some concentrates |
| Thiocyanate | Low | 1–3 | Well defined | Low | None |
| Aqua regia | High | Below 1 | Well defined | Low | Analytical and refining |
| Acid ferric chloride | High | Below 1 | Well defined | Low | Electrolytic Cu slimes |
| Ethylene thiourea | High | 1–2 | Poorly defined | Very low | None |
| Haber process | Poorly defined | Proprietary | One entity | None | |
| Bio-D leachant | Poorly defined | Proprietary | One entity | None | |
| High temperature chlorination | High | 6–7 | Simple | Historical | Historical |
| Leaching Process | Reagent Dosage (g/t) | Reagent Unit Price (USD/kg) | The Cost of Reagents for Processing 1 Ton of Ore (USD/t) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thiourea leaching process | 200–300 | 13.82 | 2.76–4.14 |
| Halogen leaching process | 100–200 | 69.1 | 4.23–8.34 |
| Thiocyanate leaching process | 100–200 | 51.85 | 5.18–10.35 |
| Leaching Process | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Thiourea leaching process | High recovery rate environmentally friendly low pollution | Low acidity poor stability high reagent cost need corrosion-resistant equipment |
| Halogen leaching process | Fast leaching kinetics high recovery rate environmentally friendly low pollution low investment | High reagents consumption Highly corrosive immature technology |
| Thiocyanate leaching process | Environmentally friendly; low pollution; highly efficient and stable; good selectivity; low toxicity | High reagent consumption requires acidic conditions need corrosion-resistant equipment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Jiao, F. Pretreatment and Extraction of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore in Acidic Conditions. Minerals 2025, 15, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040340
Wang S, Wu J, Jiao F. Pretreatment and Extraction of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore in Acidic Conditions. Minerals. 2025; 15(4):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040340
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sheng, Jiajia Wu, and Fen Jiao. 2025. "Pretreatment and Extraction of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore in Acidic Conditions" Minerals 15, no. 4: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040340
APA StyleWang, S., Wu, J., & Jiao, F. (2025). Pretreatment and Extraction of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore in Acidic Conditions. Minerals, 15(4), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040340





