Study on the Occurrence States and Enrichment Mechanisms of the Dispersed Elements Ga, Ge, and In in the Chipu Pb-Zn Deposit, Sichuan Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
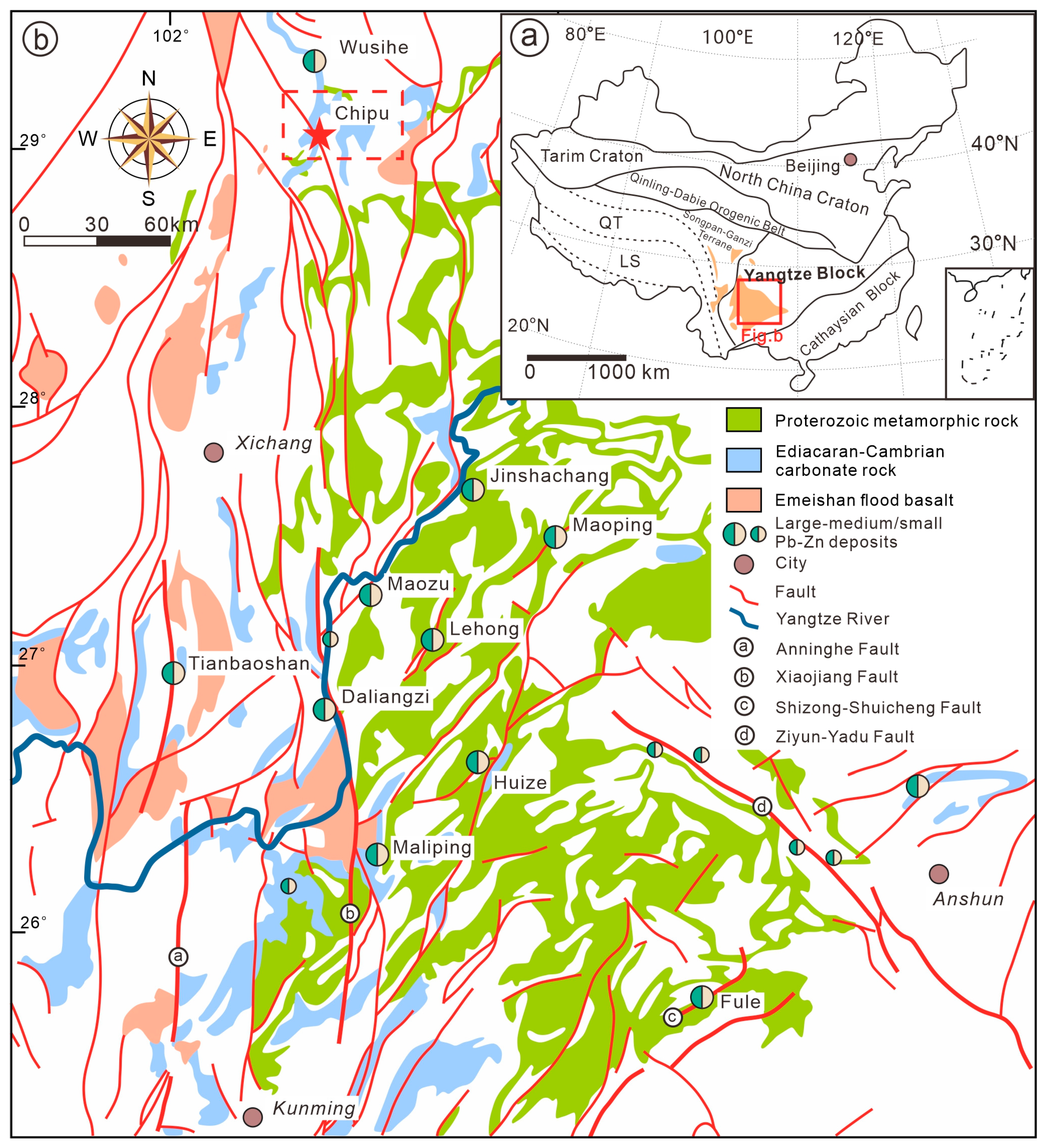
2. Regional Geology
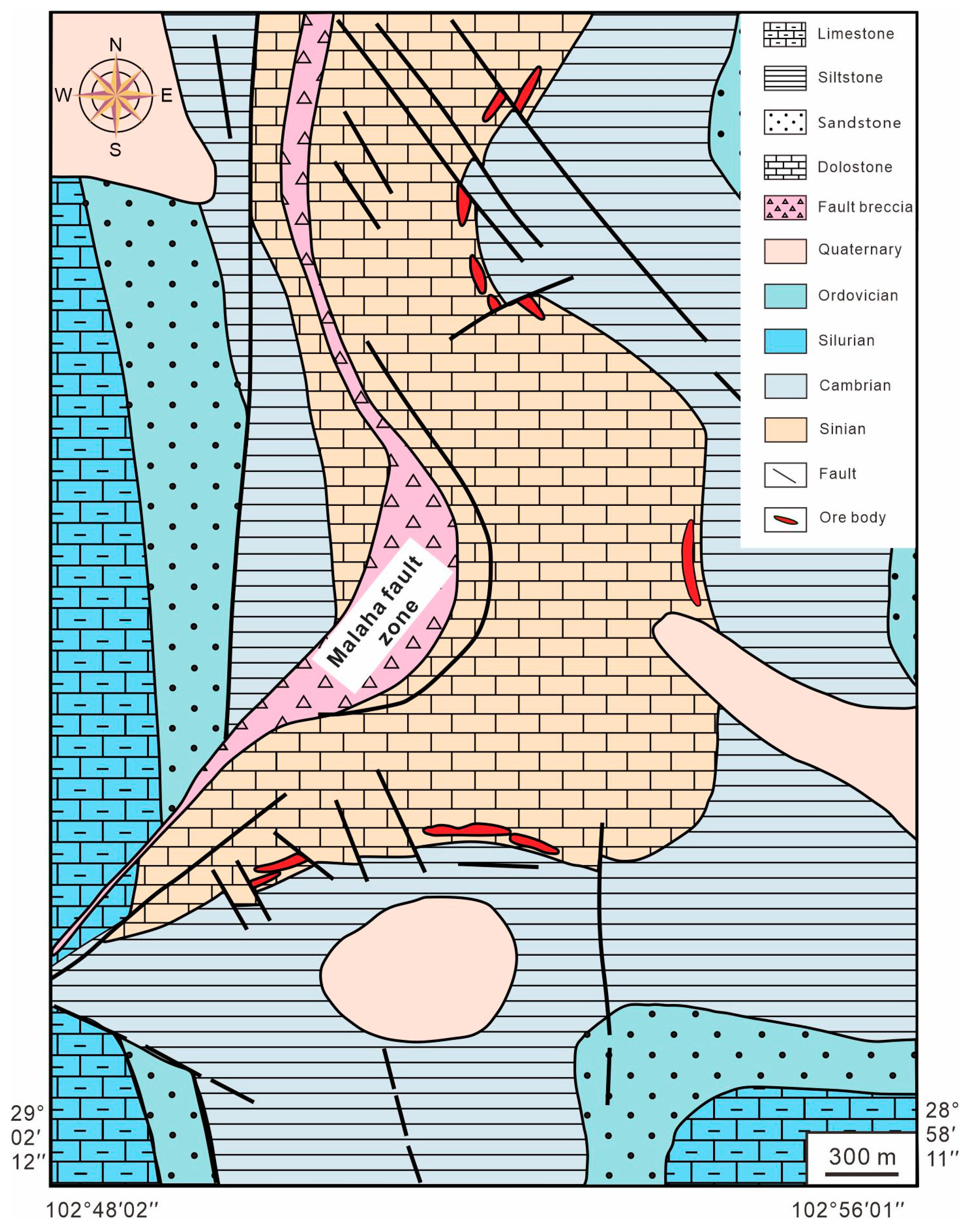
3. Deposit Geology
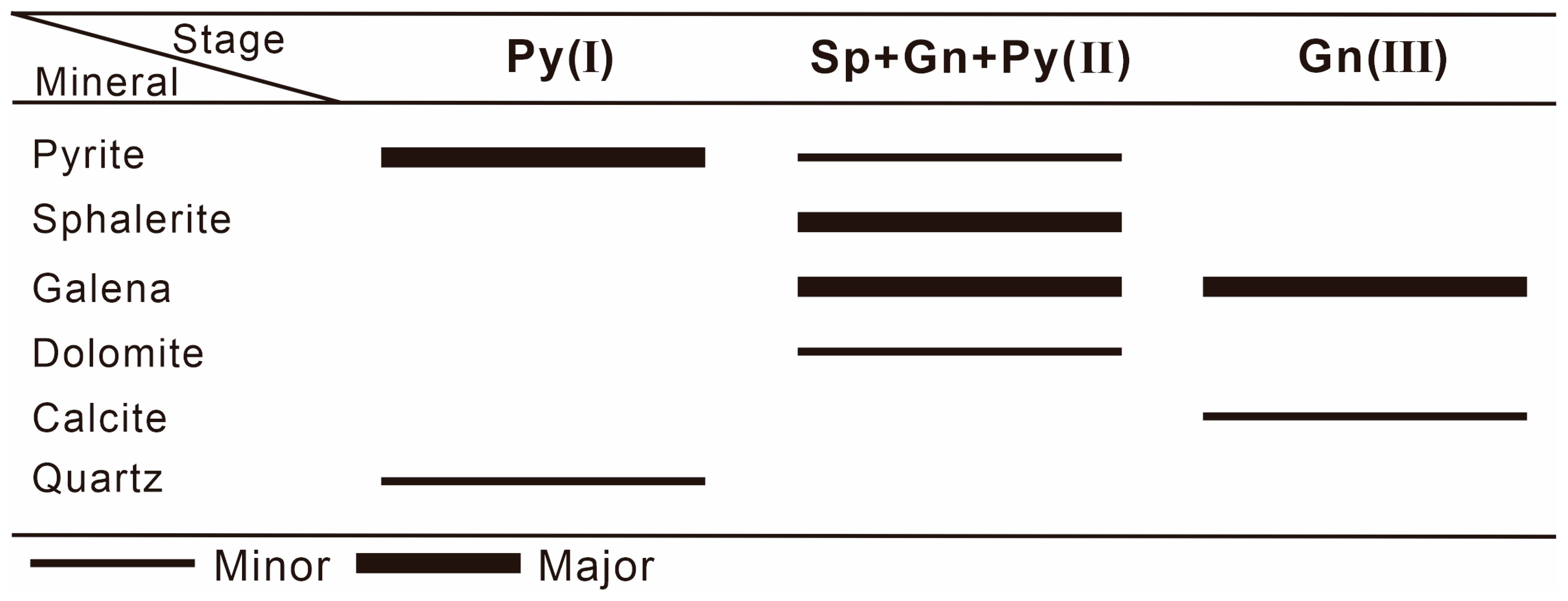
4. Characteristics and Sequences of Mineralization
5. Sampling and Analytical Methods
5.1. Sample Description
5.2. (LA)-ICP-MS Sulfides Trace Element Analysis
5.3. In Situ Sulfur Isotope Analysis
6. Results
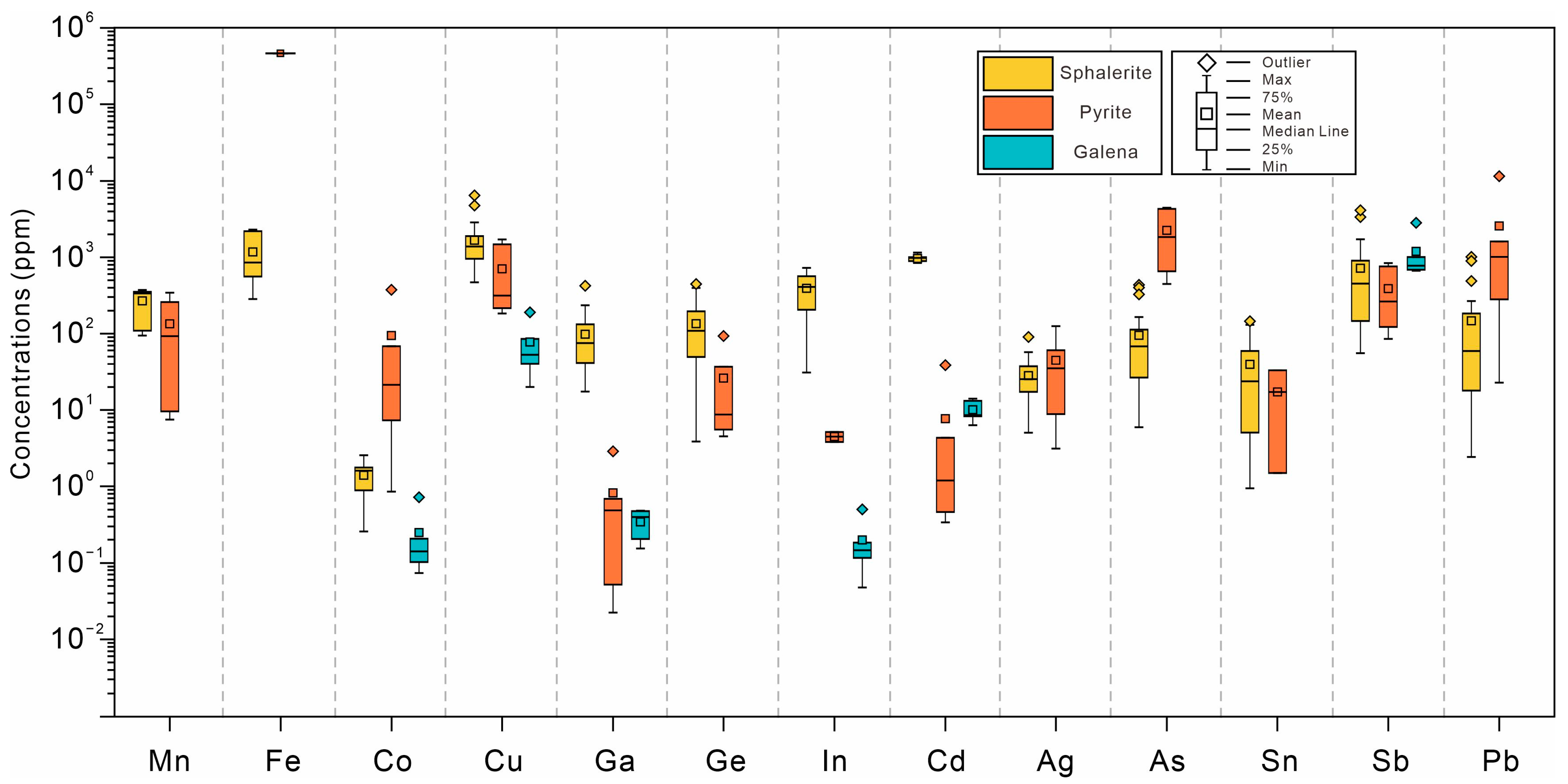
6.1. Trace Element Compositions of Sulfides
6.2. Sulfur Isotopic Compositions
7. Discussion
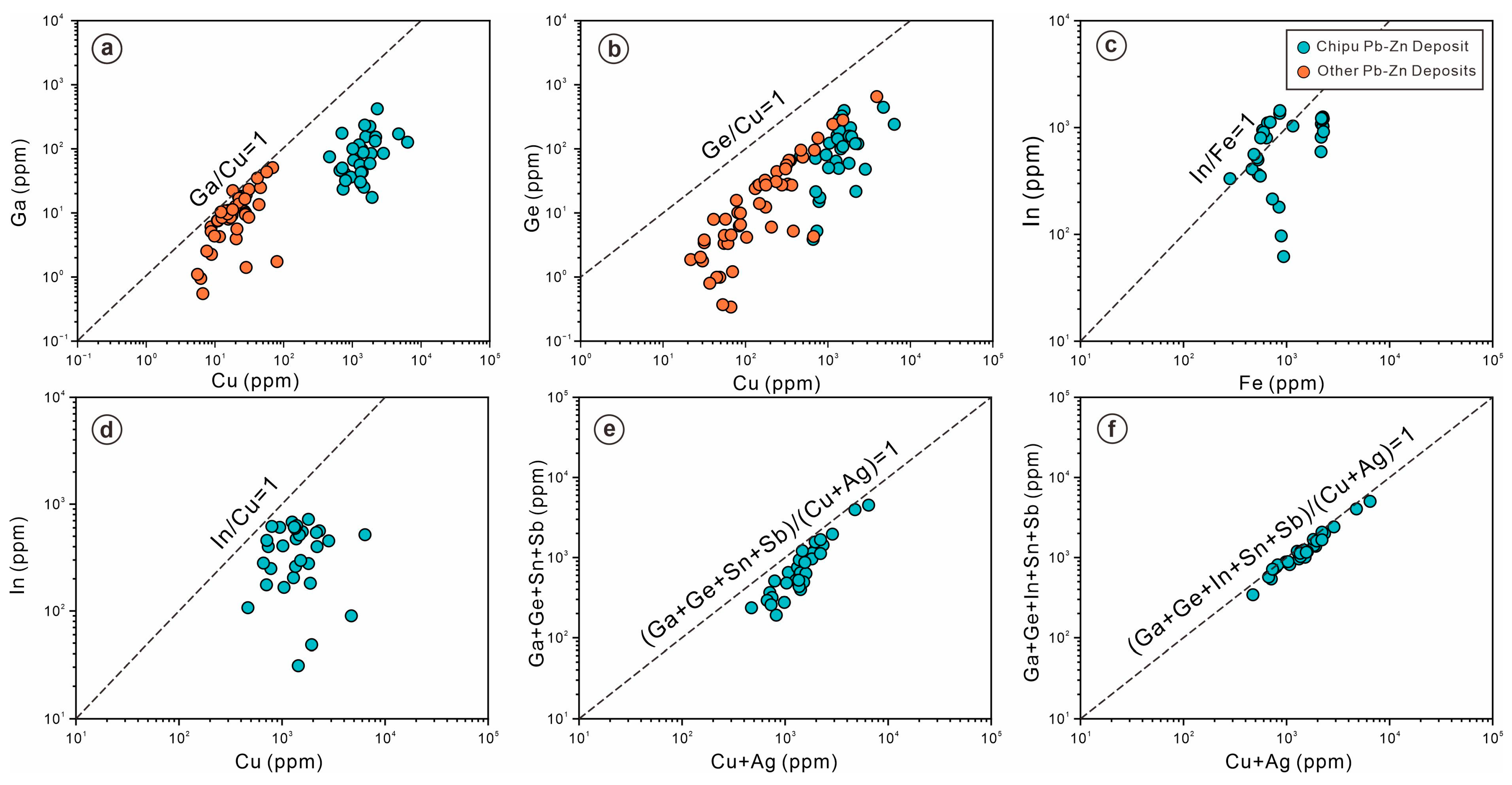
7.1. Distributions and Substitutions of Trace Elements in Sphalerite
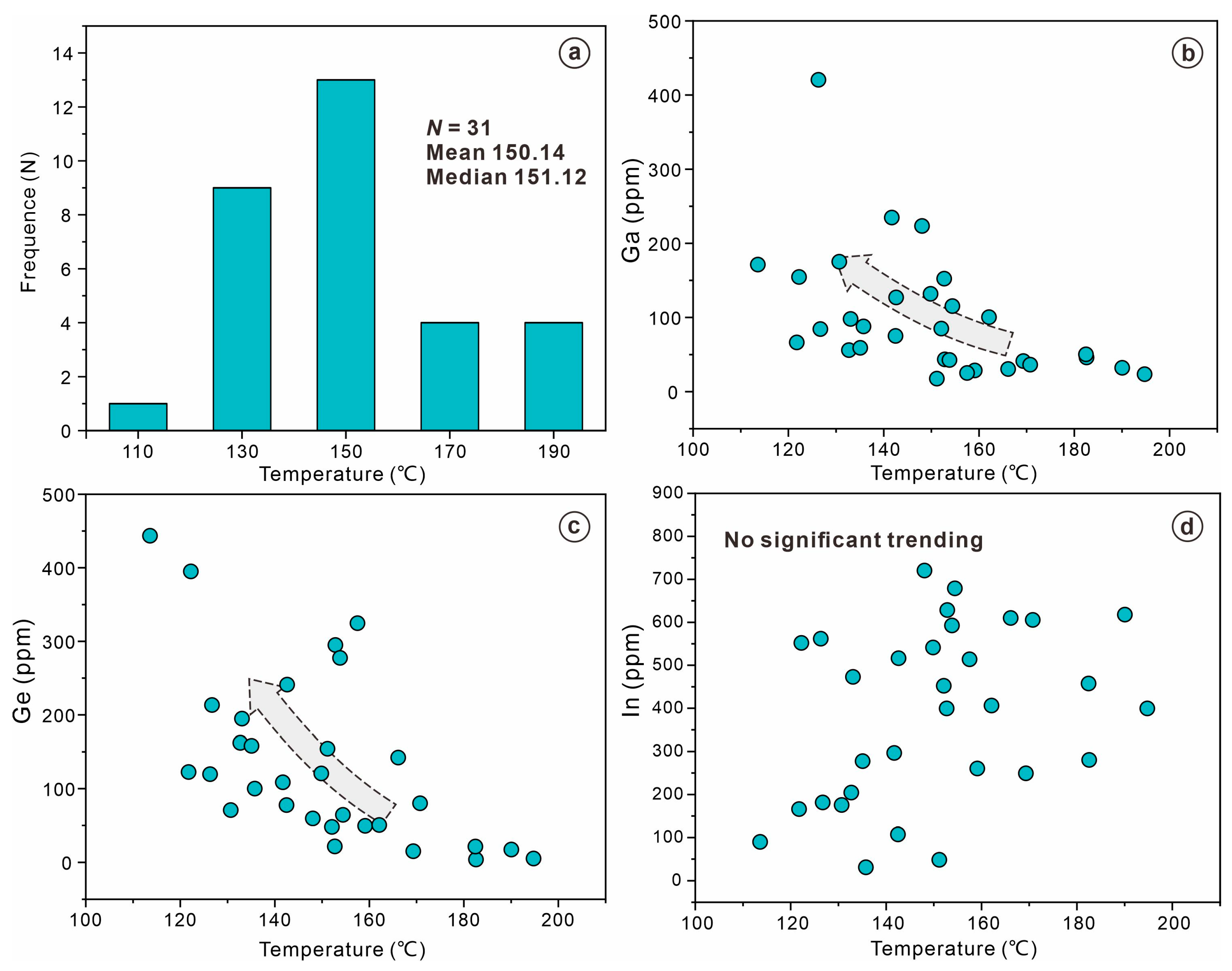
7.2. Precipitation Temperature of Sphalerite
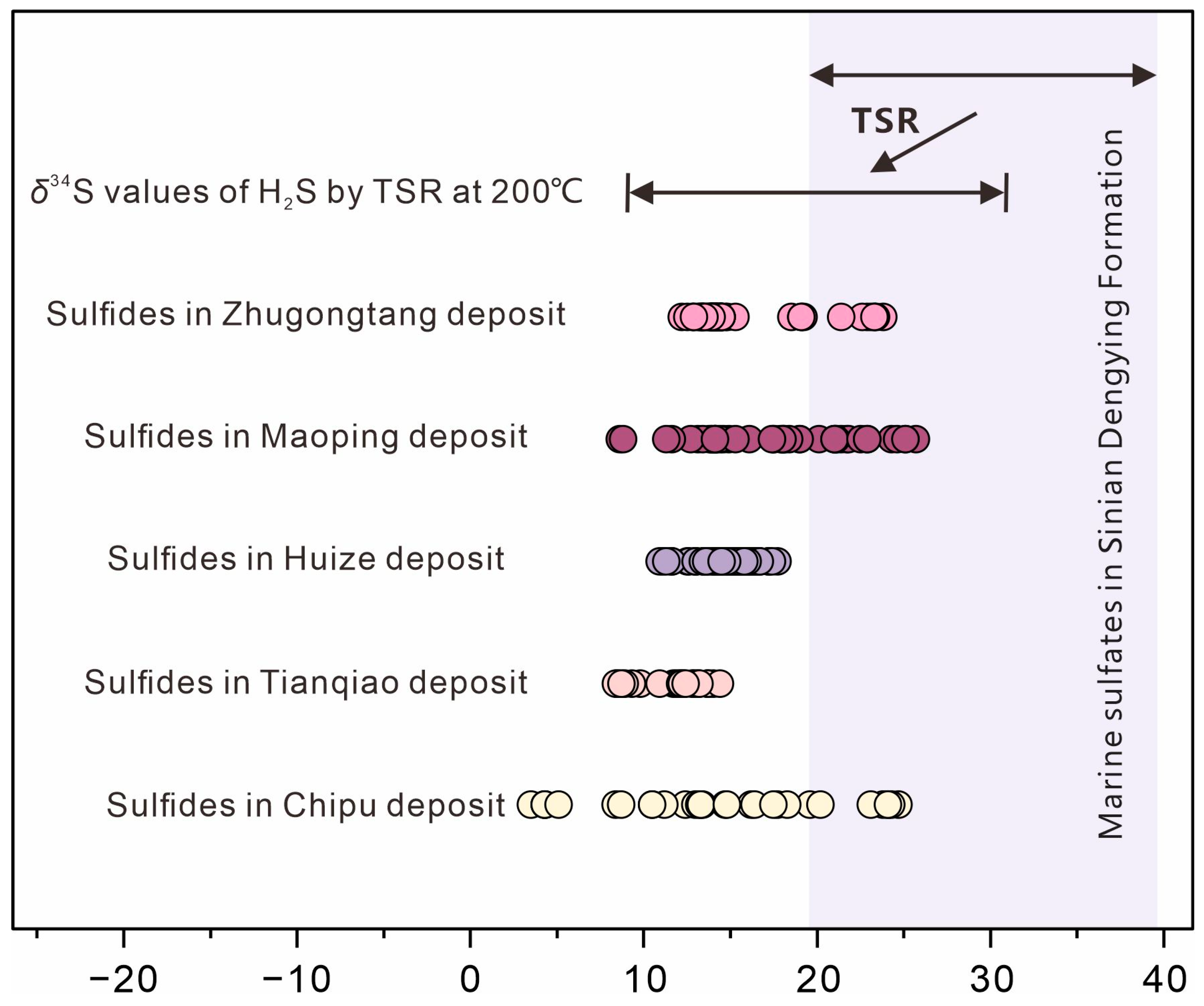
7.3. Sources of Sulfur
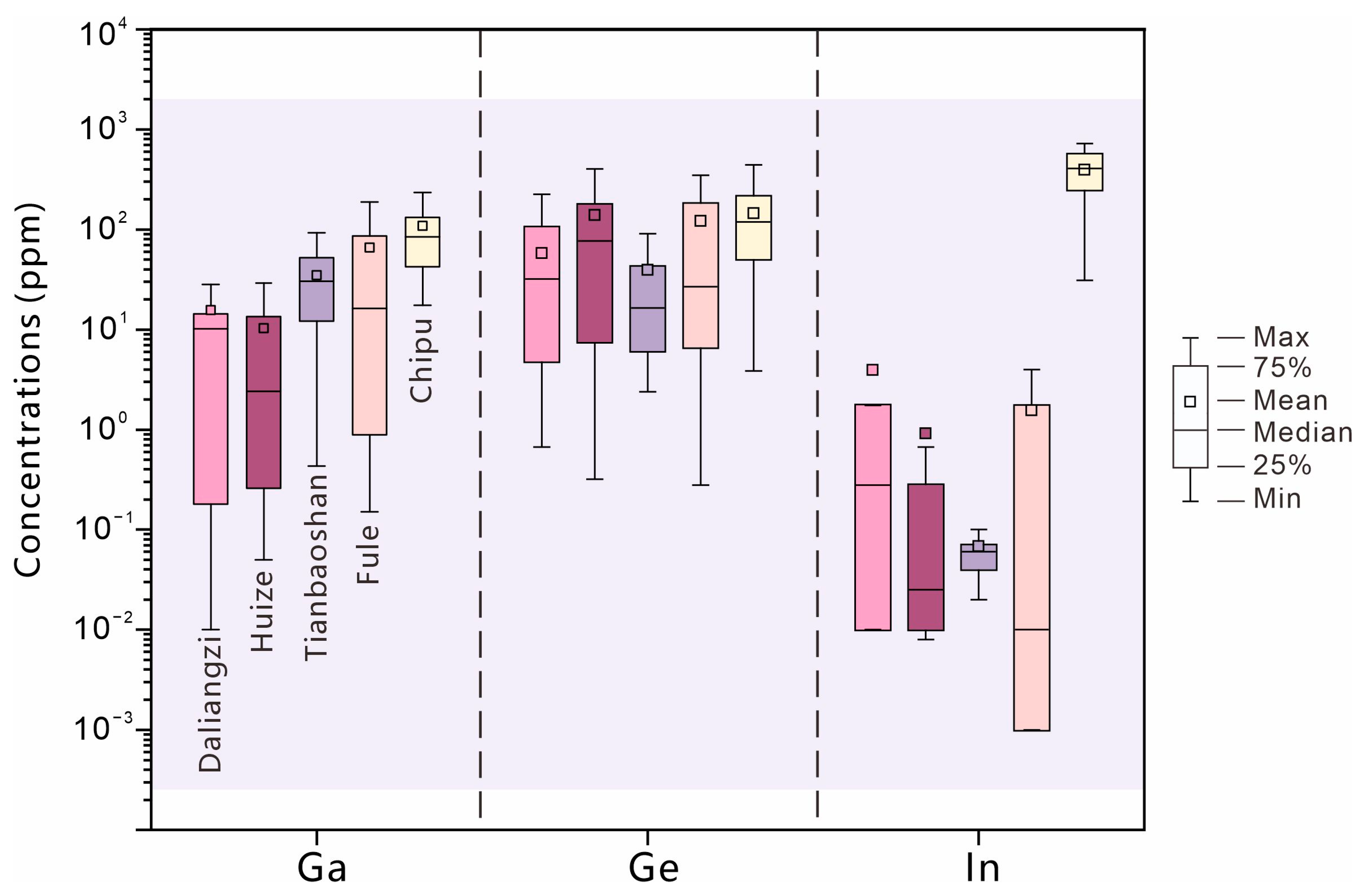
7.4. The Extraordinary Indium Enrichment in Sphalerite and Exploration Potential
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- Within the Chipu Pb-Zn deposit, sphalerite is mainly enriched in Mn, Cu, Ga, Ge, In, Cd, and Sn. Pyrite is mainly enriched in As. Galena is relatively enriched in Sb, Tl, and V. The dispersed Ga, Ge, and In are primarily enriched in sphalerite, and the substitution mechanisms include Ga3+ + Cu+ ↔ 2Zn2+, Ge4+ + 2Cu+ ↔ 3Zn2+, and 2In3+ + Fe2+ ↔ 4Zn2+.
- (2)
- Geological features, geochemical studies, and sphalerite geothermometry results reveal that the mineralization processes in the Chipu deposit occurred within a range of medium to low temperatures (114–195 °C).
- (3)
- In situ sulfur isotopes from sphalerite, pyrite, and galena in the Chipu Pb-Zn deposit exhibit δ34S values ranging from +3.48 to +24.74‰, suggesting that marine sulfate present in the ore-bearing strata of the Dengying Formation is the predominant source of sulfur for the Chipu deposit.
- (4)
- The abnormal accumulation of In in sphalerite from the Chipu deposit may be related to the circulation of basinal brine promoted by the magmatic activity associated with the Emeishan mantle plume, and the basinal brine extracted significant amounts of In from the intermediate-felsic igneous rocks in the metamorphic basement.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, M.; Wu, F.; Hu, R.; Jiang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Qi, T.; Qin, K.; Wen, H. Critical metal mineral resources: Current research status and scientific issus. Bull. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2019, 33, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Zhu, C.; Du, S.; Fan, Y.; Luo, C. Gallium (Ga), germanium (Ge), thallium (Tl) and cadmium (Cd) resources in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 3688–3699. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, L. Germanium geochemistry and mineralogy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 2409–2422. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, G.C.; Gao, Z.M. Ore-forming mechanism of the dispersed elements. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2003, 18, 358–361. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, J.D.; Culkin, F.; Riley, J.P. The abundances of gallium and germanium in terrestial materials. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1959, 16, 151–180. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, D.L.; Bradley, D.; Lewchuk, M.T.; Symons, D.T.; de Marsily, G.; Brannon, J. Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits through geological time: Implications from recent age-dating research. Miner. Depos. 2001, 36, 711–740. [Google Scholar]
- Höll, R.; Kling, M.; Schroll, E. Metallogenesis of germanium—A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 30, 145–180. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Williams, T. The mineralogy and mineral chemistry of indium in sulphide deposits and implications for mineral processing. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 226–228. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y. Pull-apart vein system of the Toyoha deposit, the most productive Ag-Pb-Zn vein-type deposit in Japan. Min. Geol. 1990, 40, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, E. Common features and genesis of tin-poly-metallic veins. Resour. Geol. Spec. Issue 1995, 18, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, G.; Gao, Z.; Hu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, B. The Geochemistry and Deposit-Forming Mechanism of Disperse Elements; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 1–424. [Google Scholar]
- Saini-Eidukat, B.; Melcher, F.; Lodziak, J. Zinc-germanium ores of the Tres Marias mine, Chihuahua, Mexico. Miner. Depos. 2009, 44, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlstrom, F.; Arribas, A.; Dirks, P.; Corral, I.; Chang, Z. Mineralogical Distribution of Germanium, Gallium and Indium at the Mt Carlton High-Sulfidation Epithermal Deposit, NE Australia, and Comparison with Similar Deposits Worldwide. Minerals 2017, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Chen, W.; Xu, D.; Zhou, M. Reviews and new metallogenic models of mineral deposits in South China: An introduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Fu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Fu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Bi, X.; Xiao, J. The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain: Reviews and a new geodynamic model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 137, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Hu, R.; Tang, Y.; Ye, L.; Qi, H.; Fan, H. Types of dispersed elements bearing ore-deposits and their enrichment regularity in Southwest China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 1210–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, T.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.; Danyushevskiy, L. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China: A LA-ICPMS study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 39, 188–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ye, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wei, C.; Danyushevsky, L. Distribution and existing forms of trace elements from Maliping Pb-Zn deposit in northeastern Yunnan, China: A LA-ICPMS study. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 3477–3492. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, J.; Ulrich, T. Mineralization processes at the Daliangzi Zn-Pb deposit, Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou metallogenic province, SW China: Insights from sphalerite geochemistry and zoning textures. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 161, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, R.; Li, X. LA-ICP-MS analyses of trace elements in zoned sphalerite: A study from the Maoping carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn(-Ge) deposit, southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 15, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z. Preliminary study on geological characteristics of Ganluo Chipu lead-zinc deposit. Acta Geol. Sichuan 1991, 3, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Xu, X. Physical-Chemical conditions of ore-formation for Chipu Pb-Zn deposit. Acta Geol. Sichuan 1997, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Long, X.; Wen, C.; Liu, W. Study on the source of ore-forming material of the Chipu lead-zinc ore deposit, Sichuan. J. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 15, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, J.; Mao, J.; Yu, H.; Li, H. Research on the Biomarker from Chipu Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan. Acta Sediment. Sin. 2010, 28, 832–848. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Mao, J.; Ouyang, H.; Sun, J. The genetic relationship between hydrocarbon systems and Mississippi Valley-type Zn-Pb deposits along the SW margin of Sichuan Basin, China. Int. Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 941–957. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Mao, J.; Zhang, W.; Wei, C. The Relationship between Oil-gas Organic Matter and MVT Mineralization: A Case Study of the Chipu Lead-zinc Deposit, Sichuan. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 425–436. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, K.; Zhou, J.; Ju, Y. A shift from BSR to TSR caused the formation of the Chipu Pb-Zn deposit, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 144, 104845. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Rui, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Lou, D. The Main Successive Strategic Bases of Resources for Pb-Zn Deposits in China. Geol. China 2013, 40, 248–272. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, D.L.; Song, Y. Chapter 9: Sediment-hosted zinc-lead and copper deposits in China. In Mineral Deposits of China; The Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. The Genetic Model of Mississippi Vally-Type Deposits in the Boundary Area of Sichuan, Yunnan and Guizhou Provinces, China. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, B.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, P.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Mineralization Model of Rich Ge-Ag-Bearing Zn-Pb Polymetallic Deposit Concentrated District in Northeastern Yunnan, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 280–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Zeng, Q. C, O Isotope and Ree Geochemistry of the Hydrothermal Calcites from the Tianqiao Pb-Zn Ore Deposit in NW Guizhou Province, China. Geotech. Metall. 2012, 36, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Mineralization systems of a mantle plume: A case study from the Emeishan igneous province, southwest China. Earth Sci. Front. 2005, 12, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Huyskens, M.H.; Yin, Q.; Cawood, P.A.; Hou, M.; Yang, J.; Xiong, F.; Du, Y.; Yang, C. Eruptive tempo of Emeishan large igneous province, southwestern China and northern Vietnam: Relations to biotic crises and paleoclimate changes around the Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary. Geology. 2022, 50, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lin, W. Research on the Metallogenic Regulation of Lead-Zinc-Silver Deposits in Northeastern of Yunnan; Yunnan University Publishing House: Kunming, China, 1999; pp. 1–419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M. Constraints of C-O-S-Pb isotope compositions and Rb-Sr isotopic age on the origin of the Tianqiao carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 53, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, S.; Gong, Y.; Yao, S.; Li, X. Enrichment mechanism of the dispersed elements in the Huize lead-zinc deposit, Yunnan province-disccussion on reasons for Cd enrichment in sphalerite with light color. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2016, 31, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Mao, J.; Chen, F.; Li, H. Rb-Sr dating of single sphalerites from the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan, and its geological significances. Geol. Rev. 2008, 54, 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Mao, J.; Yu, J.; Li, H. Study on fluid inclusion and the metallogenetic mechanism of Chipu Pb-Zn deposit in Sichuan, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2541–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, S.A.; Ridley, W.I.; Koenig, A.E. Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Li, X.; Kontonikas-Charos, A.; Gilbert, S.; Lv, Y. Indium distribution in sphalerite from sulfide–oxide–silicate skarn assemblages: A case study of the Dulong Zn–Sn–In deposit, Southwest China. Miner. Depos. 2022, 56, 307–324. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Chen, K.; Bao, Z.; Liang, P.; Sun, T.; Yuan, H. Preparation of standards for in situ sulfur isotope measurement in sulfides using femtosecond laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zong, C.; Yuan, H.; Chen, K.; Dai, M. Development of pressed sulfide powder tablets for in situ sulfur and lead isotope measurement using LA-MC-ICP-MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 421, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Bao, Z.; Chen, K.; Zong, C.; Li, X.; Qiu, J. Simultaneous measurement of sulfur and lead isotopes in sulfides using nanosecond laser ablation coupled with two multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometers. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 154, 386–396. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Pring, A.; Skinner, W.; Shimizu, M.; Danyushevsky, L.; Saini-Eidukat, B.; Melcher, F. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4761–4791. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wei, C.; Ye, L.; Huang, Z.; Danyushevsky, L.; Wang, H. LA-ICP-MS sphalerite and galena trace element chemistry and mineralization-style fingerprinting for carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposits: Perspective from early Devonian Huodehong deposit in Yunnan, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 136, 104253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fard, M.; Hou, Z. Major and trace elements and sulfur isotopes in two stages of sphalerite from the world-class Angouran Zn-Pb deposit, Iran: Implications for mineralization conditions and type. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 184–200. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Ye, L.; Wei, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H. Trace Elements in Sphalerite from the Dadongla Zn-Pb Deposit, Western Hunan-Eastern Guizhou Zn-Pb Metallogenic Belt, South China. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 94, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar]
- Johan, Z. Indium and germanium in the structure of sphalerite: An example of coupled substitution with Copper. Mineral. Petrol. 1988, 39, 211–229. [Google Scholar]
- Belissont, R.; Boiron, M.C.; Luais, B.; Cathelineau, M. LA-ICP-MS analyses of minor and trace elements and bulk Ge isotopes in zoned Ge-rich sphalerites from the Noailhac-Saint-Salvy deposit (France): Insights into incorporation mechanisms and ore deposition processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 126, 518–540. [Google Scholar]
- Belissont, R.; Munoz, M.; Boiron, M.C.; Luais, B.; Mathon, O. Distribution and oxidation state of Ge, Cu and Fe in sphalerite by μ-XRF and K-edge μ-XANES: Insights into Ge incorporation, partitioning and isotopic fractionation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 177, 298–314. [Google Scholar]
- George, L.L.; Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L. Partitioning of trace elements in co-crystallized sphalerite-galena-chalcopyrite hydrothermal ores. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 77, 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Ye, L.; Hu, Y.; Danyushevskiy, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z. Distribution and occurrence of Ge and related trace elements in sphalerite from the Lehong carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit, northeastern Yunnan, China: Insights from SEM and LA-ICP-MS studies. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Ye, L.; Hu, Y.; Wei, C.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Danyushevsky, L. Trace elements in sulfides from the Maozu Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province, China: Implications for trace-element incorporation mechanisms and ore genesis. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 1734–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, J.; Cugerone, A.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, L. Germanium-rich nanoparticles in Cu-poor sphalerite: A new mechanism for Ge enrichment. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2023, 136, 2891–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Huang, Z.; Ye, L.; Hu, Y.; Santosh, M.; Wu, T.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; He, Z.; Xiang, Z.; et al. Genesis of carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposits in the Late Indosinian thrust and fold systems: An example of the newly discovered giant Zhugongtang deposit, South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 220, 104914. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, S.; Lv, C.; Dai, Z. Genesis of the sediment-hosted Haerdaban Zn-Pb deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China: Constraints from textural, compositional and sulfur isotope variations of sulfides. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104527. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, H.V.; Thompson, R.M. Sphalerites from western Canada. Econ. Geol. 1945, 40, 309–335. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, P. Correlation of homogenization temperatures of accessory minerals from sphalerite-bearing deposits and Ga/Ge model temperatures. Chem. Geol. 1987, 61, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Frenzel, M.; Hirsch, T.; Gutzmer, J. Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type-A meta-analysis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 76, 52–78. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, M.; Haase, K.M.; Schwarz-Schampera, U.; Klemd, R.; Petersen, S.; Bach, W. Effects of temperature, sulfur, and oxygen fugacity on the composition of sphalerite from submarine hydrothermal vents. Geology 2014, 42, 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chung, S.; Jahn, B.M.; Wu, G. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian–Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China. Lithos 2001, 58, 145–168. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Putirka, K.; Hu, R.; Li, C. The magma plumbing system of the Emeishan large igneous province and its role in basaltic magma differentiation in a continental setting. Am. Mineral. 2015, 100, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Tao, Y.; Qi, L.; Ripley, E.M. Controls on PGE fractionation in the Emeishan picrites and basalts: Constraints from integrated lithophile–siderophile elements and Sr–Nd isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 90, 12–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, R.R. Sulfur isotope geochemistry of sulfide minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 61, 633–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z. Sulfur isotopic compositions of the Huize super-large Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province, China: Implications for the source of sulfur in the ore-forming fluids. J. Geochem. Explor. 2006, 89, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, T.; Huang, Z.; Ye, L.; Deng, P.; Xiang, Z. Genesis of the Maoping carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, northeastern Yunnan Province, China: Evidences from geology and C-O-S-Pb isotopes. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, England, 1993; 384p. [Google Scholar]
- Krouse, H.R. Sulfur isotope composition of H2S evolved during non-isothermal pyrolysis of sulfur contiaining materials response. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1988, 14, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machel, H.G.; Krouse, H.R.; Sassen, R. Products and distinguishing criteria of bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction. Appl. Geochem. 1995, 10, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuki, N.I.; Taylor, B.E.; Spooner, E.T.C. Sulfur isotope evidence for thermochemical reduction of dissolved sulfate in Mississippi Valley-type zinc-lead mineralization, Bongara area, northern Peru. Econ. Geol. 2008, 103, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Ellis, G.S.; Chou, I.; Burruss, R.C. Experimental investigation on thermochemical sulfate reduction in the presence of 1-pentanethiol at 200 and 250°C: Implications for in situ TSR processes occurring in some MVT deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.B.; Isaksen, M.F.; Jannasch, H.W. Bacterial sulfate reduction above 100 C in deep-sea hydrothermal vent sediments. Science 1992, 258, 1756–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, L.; Huo, W. The sulfur and carbon isotopic records in carbonates of the Dengying Formation in the Yangtze Platform, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 20, 717–724. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Ni, P.; Wang, G.; Dai, B.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. In-situ sulfur isotope characteristics of sulfides from Tianbanshan lead-zinc deposit, Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou metallogenic Province. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M.E.; Burisch, M.; Ostendorf, J.; Krause, J.; Frenzel, M.; Seifert, T.; Gutzmer, J. Trace element geochemistry of sphalerite in contrasting hydrothermal fluid systems of the Freiberg district, Germany: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analysis, near-infrared light microthermometry of sphalerite-hosted fluid inclusions, and sulfur isotope geochemistry. Miner. Depos. 2019, 54, 237–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Luo, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Source of Ore-forming Materials for the Carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn Deposits in Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Adjacent area, SW China: Constraints of Galena In-situ Pb Isotopes. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2023, 45, 266–278. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Luo, T. Origin of hydrothermal deposits related to the Emeishan magmatism. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Duan, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Mao, J.; Xiong, S.; Jiang, S. Linking carbonate-hosted ZnPb deposit to deep mantle activity: Evidence from in situ UPb geochronology of calcite from the world-class Huayuan ZnPb ore field in South China. Chem. Geol. 2023, 643, 121823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Han, R.; Chen, J. Several Problems Involved in Genetic Studies on Huize Superlarge Pb-Zn Deposit, Yunnan Province. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2004, 24, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F. The Metallogenetic Mechanism of the Huize Lead-Zinc Ore Deposit and the Occurrence of Germanium, Yunnan Province, China. M.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Yin, M. Dating of the Giant Huize Zn-Pb Ore Field of Yunnan Province, Southwest China: Constraints from the Sm-Nd System in Hydrothermal Calcite. Resour. Geol. 2006, 57, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C. Rb-Sr Isotopic Age of Sphalerite from the Paoma Lead-zinc Deposit in Sichuan Province and its Implications. Geol. China 2010, 37, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Rui, Z.; Chen, Z.; Luo, D. Brief introduction on metallogeny of Pb-Zn deposits in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 2252–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tian, G.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, W.; Zen, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C. Metallogenic age and mineral-forming sources of Lehong lead-zinc deposit in Yunnan Province: Rb-Sr and S isotope constraints. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2014, 34, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.; Muchez, P. Zinc, sulfur and lead isotopic variations in carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn sulfide deposits, southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 58, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bai, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Yan, Z.; Lv, Z. Geology, isotope geochemistry and geochronology of the Jinshachang carbonate-hosted Pb–Zn deposit, southwest China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 98, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Gao, J.; Nian, H.; Jia, F. Rb-Sr Isotopic Compositions of Sphalerite and Its Geological Implication for Maozu Pb-Zn Deposite, Northeast Yunnan Province, China. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2015, 35, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Jin, C.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Mineralization Age of the Maoping Pb-Zn Deposit in the Northeastern Yunnan Province: Evidence from Rb-Sr Isotopic Dating of Sphalerites. Geol. J. China Univ. 2016, 22, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Localization Rules of Large Pb-Zn Deposits in the Southwestern Margin of the Upper-Middle Yangtze Block. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Jin, S.; Gan, J.; Qi, S. Sphalerite Rb-Sr isotopic dating of the Dongyan Pb-Zn deposit in Southeastern Sichuan fold belt and its constraint on the timing of tectonic deformation. Geol. China 2020, 47, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Shi, W.; Lv, C.; Qin, C. Rb-Sr dating of Nayongzhi lead-zinc deposit in Guizhou Province and its geological significance. Miner. Res. Geol. 2020, 34, 918–922. [Google Scholar]

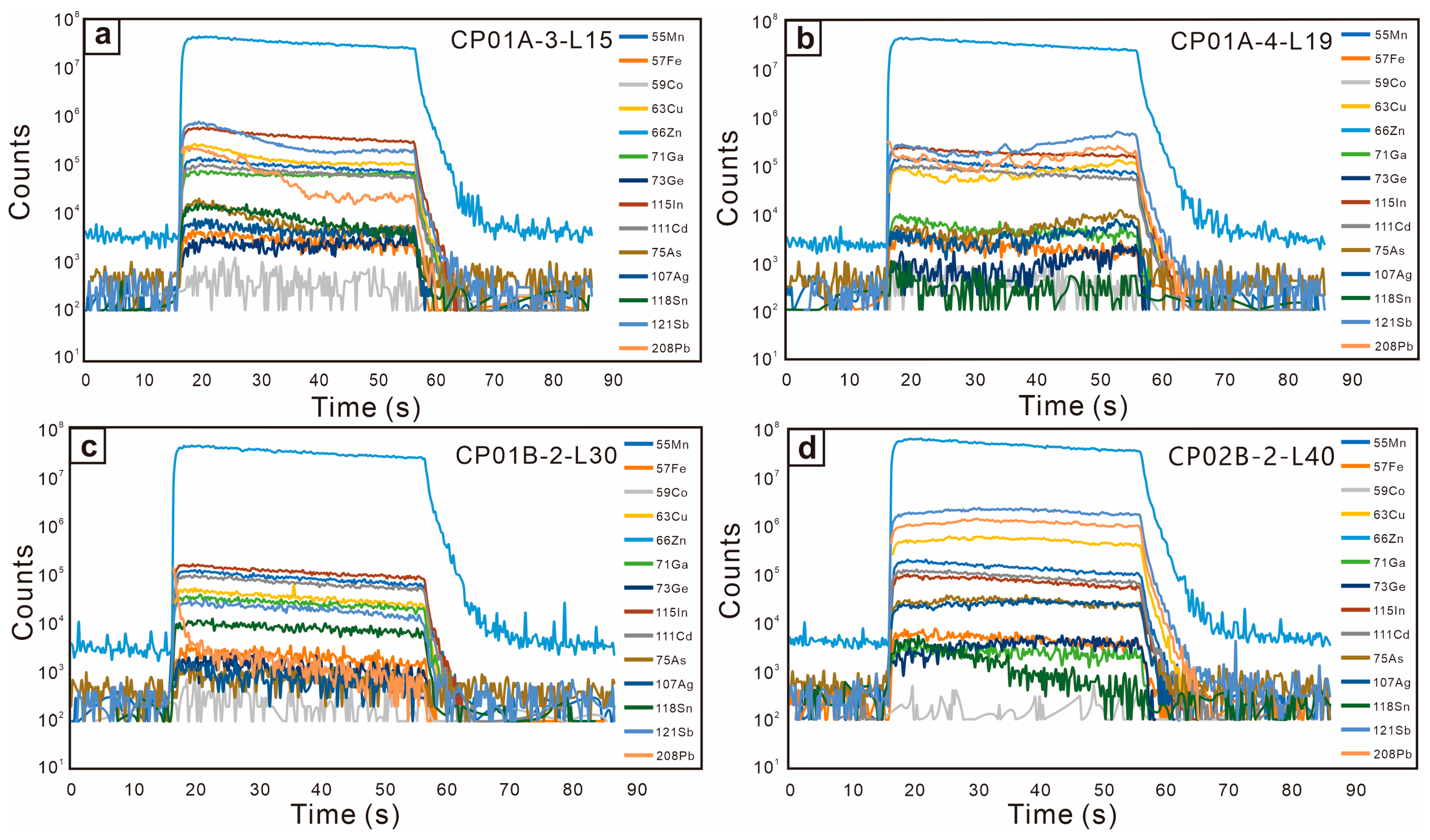
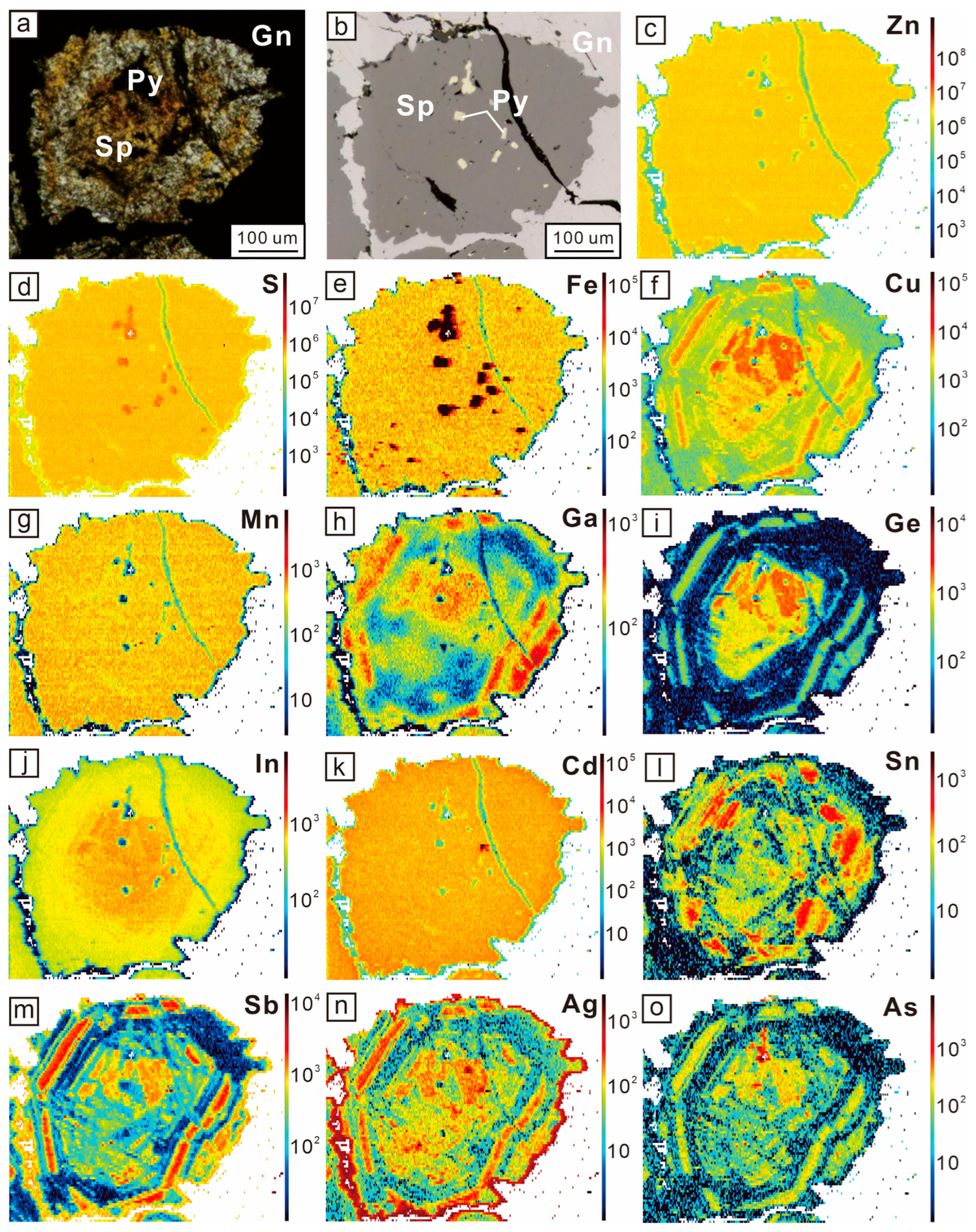
| Sphalerite | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Ga | Ge | As | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Pb |
| CP-01A-2 | 319 | 282 | 0.26 | 1045 | 66 | 123 | 434 | 30 | 1006 | 166 | 7.64 | 454 | 38 |
| 357 | 531 | 0.94 | 1881 | 84 | 213 | 111 | 37 | 992 | 182 | 8.79 | 895 | 76 | |
| 352 | 463 | 0.80 | 1292 | 56 | 162 | 68 | 27 | 1034 | 205 | 5.70 | 531 | 45 | |
| CP-01A-3 | 344 | 490 | - | 1809 | 59 | 158 | 116 | 38 | 998 | 277 | 5.09 | 915 | 101 |
| 335 | 587 | - | 1375 | 98 | 195 | 56 | 31 | 984 | 472 | 18 | 333 | 28 | |
| 336 | 653 | 0.28 | 1573 | 155 | 395 | 22 | 19 | 959 | 552 | 24 | 59 | 38 | |
| 342 | 859 | 1.88 | 1255 | 115 | 64 | 36 | 14 | 972 | 679 | 130 | 209 | 15 | |
| 348 | 862 | 2.56 | 1804 | 223 | 60 | 89 | 18 | 984 | 720 | 90 | 588 | 75 | |
| 348 | 695 | 2.30 | 2309 | 420 | 120 | 119 | 28 | 999 | 562 | 42 | 848 | 82 | |
| CP-01A-4 | 372 | 528 | 2.30 | 779 | 41 | 15 | 50 | 14 | 1001 | 249 | 4.79 | 449 | 122 |
| 367 | 517 | 2.50 | 1352 | 29 | 50 | 109 | 21 | 967 | 260 | 0.95 | 855 | 220 | |
| CP-01B-2 | 344 | 937 | 1.68 | 1438 | 88 | 100 | 113 | 31 | 899 | 31 | 1.45 | 1022 | 183 |
| 334 | 888 | 1.61 | 1940 | 17 | 154 | 137 | 21 | 886 | 48 | 1.53 | 1388 | 224 | |
| 323 | 847 | 1.83 | 4711 | 171 | 444 | 399 | 57 | 861 | 90 | 1.77 | 3337 | 1005 | |
| 326 | 730 | 1.20 | 467 | 75 | 78 | 8.51 | 5.07 | 894 | 107 | 14 | 69 | 14 | |
| 319 | 557 | 1.24 | 706 | 175 | 71 | 5.99 | 5.53 | 929 | 176 | 51 | 68 | 2.43 | |
| CP-02B-1 | 351 | 640 | 0.89 | 735 | 23 | 5.21 | 17 | 12 | 975 | 400 | 94 | 194 | 192 |
| 349 | 598 | 0.59 | 2841 | 85 | 48 | 165 | 43 | 985 | 452 | 121 | 1703 | 485 | |
| 370 | 1154 | 0.71 | 6381 | 127 | 241 | 326 | 90 | 993 | 516 | 45 | 4087 | 889 | |
| 351 | 561 | 0.36 | 2186 | 152 | 22 | 84 | 19 | 1020 | 400 | 9.54 | 1486 | 265 | |
| 355 | 483 | 0.59 | 661 | 46 | 3.87 | 18 | 8.77 | 1145 | 280 | 83 | 158 | 84 | |
| CP-03 | 96 | 2272 | 1.69 | 950 | 36 | 80 | 27 | 34 | 868 | 606 | 13 | 146 | 141 |
| 94 | 2251 | 1.73 | 1392 | 43 | 295 | 22 | 19 | 835 | 628 | 4.12 | 55 | 22 | |
| 97 | 2200 | 1.63 | 798 | 32 | 17 | 28 | 23 | 879 | 618 | 24 | 117 | 12 | |
| 105 | 2179 | 1.69 | 2154 | 132 | 121 | 109 | 52 | 935 | 541 | 109 | 759 | 43 | |
| 109 | 2169 | 1.50 | 1019 | 100 | 51 | 27 | 15 | 995 | 406 | 146 | 184 | 8.45 | |
| 98 | 2261 | 1.47 | 1475 | 25 | 325 | 44 | 37 | 851 | 514 | 3.75 | 141 | 18 | |
| 100 | 2219 | 1.77 | 1343 | 43 | 278 | 27 | 25 | 869 | 593 | 30 | 85 | 15 | |
| 104 | 2186 | 1.67 | 1313 | 30 | 142 | 83 | 44 | 873 | 610 | 47 | 301 | 59 | |
| 109 | 2284 | 2.03 | 713 | 50 | 21 | 24 | 17 | 977 | 458 | 38 | 147 | 16 | |
| 118 | 2160 | 0.95 | 1516 | 235 | 109 | 70 | 41 | 1079 | 297 | 59 | 466 | 28 | |
| Pyrite | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Ga | Ge | As | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Pb |
| CP-01A-2 | - | 460000 | 21 | 344 | 0.49 | 93 | 909 | 3.15 | 4.35 | 5.16 | 33 | 85 | 23 |
| CP-01A-3 | 174 | 460000 | - | 215 | 0.02 | 5.55 | 4269 | 8.88 | 0.47 | - | - | 190 | 280 |
| CP-01B-2 | 7.51 | 460000 | 68 | 1702 | 2.88 | 37 | 653 | 61 | 39 | 3.83 | 1.51 | 755 | 11383 |
| CP-02A | 342 | 460000 | 7.36 | 183 | - | 4.53 | 4409 | 40 | 1.81 | - | - | 335 | 1598 |
| CP-02B | 12 | 460000 | 373 | 281 | 0.05 | 5.85 | 2743 | 31 | 0.59 | - | - | 122 | 1177 |
| CP-03 | - | 460000 | 0.86 | 1468 | 0.69 | 12 | 446 | 125 | 0.34 | - | - | 833 | 828 |
| Galena | Cu | Co | Ga | Cd | In | Tl | Re | Sb | Bi | Rb | V | Pb | W |
| CP-01A | 189 | 0.10 | 0.49 | 8.59 | 0.12 | 7.99 | - | 1001 | 5.11 | 0.30 | 71 | / | 0.13 |
| CP-01B | 20 | 0.72 | 0.21 | 14 | 0.50 | 7.84 | - | 771 | 4.99 | 0.10 | 5.73 | / | 0.06 |
| CP-02A | 85 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 6.34 | 0.15 | 7.97 | - | 2800 | 5.28 | 0.12 | 26 | / | 0.11 |
| CP-02B | 53 | 0.14 | 0.40 | 8.28 | 0.19 | 7.27 | - | 661 | 4.82 | 0.13 | 58 | / | 0.05 |
| CP-03 | 40 | 0.07 | 0.48 | 13 | 0.05 | 9.42 | - | 683 | 5.35 | 0.10 | 70 | / | 0.05 |
| Sample No. | Measured Mineral | δ34SV-CDT (‰) | 2SE |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP-01A-2 | sphalerite | +24.13 | 0.18 |
| CP-01A-2 | sphalerite | +23.83 | 0.19 |
| CP-01A-3 | sphalerite | +24.74 | 0.18 |
| CP-02A-1 | sphalerite | +24.31 | 0.18 |
| CP-02A-1 | sphalerite | +23.06 | 0.21 |
| CP-01B-2 | sphalerite | +19.64 | 0.20 |
| CP-02B-3 | sphalerite | +17.72 | 0.21 |
| CP-01-1 | sphalerite | +16.20 | 0.19 |
| CP-01-5 | sphalerite | +17.50 | 0.24 |
| CP-02-3 | sphalerite | +20.15 | 0.20 |
| CP-03-1 | sphalerite | +24.11 | 0.18 |
| CP-03-1 | sphalerite | +18.30 | 0.19 |
| CP-01A-3 | sphalerite | +12.37 | 0.21 |
| CP-01B-2 | sphalerite | +14.70 | 0.21 |
| CP-02B-2 | sphalerite | +8.40 | 0.20 |
| CP-02B-2 | sphalerite | +10.51 | 0.19 |
| CP-02B-3 | sphalerite | +14.84 | 0.19 |
| CP-01-1 | sphalerite | +13.02 | 0.20 |
| CP-02-2 | sphalerite | +11.23 | 0.18 |
| CP-02-3 | sphalerite | +8.66 | 0.85 |
| CP-01A-1 | galena | +13.40 | 0.40 |
| CP-01B-1 | galena | +13.36 | 0.27 |
| CP-02B-1 | galena | +13.23 | 0.23 |
| CP-02-1 | galena | +13.31 | 0.24 |
| CP-03-1 | galena | +16.37 | 0.24 |
| CP-02B-1 | pyrite | +10.47 | 0.23 |
| CP-01-5 | pyrite | +3.48 | 0.25 |
| CP-02-3 | pyrite | +4.26 | 0.24 |
| CP-02-3 | pyrite | +5.09 | 0.23 |
| Sample | PC1* | T1/°C | T2/°C | T3/°C | T4/°C | Tmax/°C | Tmin/°C | Tmean/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-01A-2 | 1.6 | 120 | 143 | 100 | 123 | 143 | 100 | 122 |
| 1.5 | 126 | 148 | 106 | 128 | 148 | 106 | 127 | |
| 1.4 | 133 | 153 | 113 | 133 | 153 | 113 | 133 | |
| CP-01A-3 | 1.3 | 135 | 155 | 115 | 135 | 155 | 115 | 135 |
| 1.4 | 133 | 153 | 113 | 133 | 153 | 113 | 133 | |
| 1.6 | 121 | 144 | 101 | 124 | 144 | 101 | 122 | |
| 1.0 | 157 | 172 | 137 | 152 | 172 | 137 | 154 | |
| 1.1 | 150 | 166 | 130 | 146 | 166 | 130 | 148 | |
| 1.5 | 125 | 147 | 105 | 127 | 147 | 105 | 126 | |
| CP-01A-4 | 0.7 | 174 | 184 | 154 | 164 | 184 | 154 | 169 |
| 0.9 | 163 | 176 | 143 | 156 | 176 | 143 | 159 | |
| CP-01B-2 | 1.3 | 136 | 155 | 116 | 135 | 155 | 116 | 136 |
| 1.0 | 154 | 169 | 134 | 149 | 169 | 134 | 151 | |
| 1.7 | 111 | 136 | 91 | 116 | 136 | 91 | 114 | |
| 1.2 | 144 | 161 | 124 | 141 | 161 | 124 | 142 | |
| 1.4 | 130 | 151 | 110 | 131 | 151 | 110 | 131 | |
| CP-02B-1 | 0.2 | 203 | 207 | 183 | 187 | 207 | 183 | 195 |
| 1.0 | 155 | 170 | 135 | 150 | 170 | 135 | 152 | |
| 1.2 | 144 | 161 | 124 | 141 | 161 | 124 | 143 | |
| 1.0 | 155 | 170 | 135 | 150 | 170 | 135 | 153 | |
| 0.5 | 189 | 196 | 169 | 176 | 196 | 169 | 183 | |
| CP-03 | 0.7 | 176 | 186 | 156 | 166 | 186 | 156 | 171 |
| 1.0 | 155 | 170 | 135 | 150 | 170 | 135 | 153 | |
| 0.3 | 198 | 202 | 178 | 182 | 202 | 178 | 190 | |
| 1.1 | 152 | 168 | 132 | 148 | 168 | 132 | 150 | |
| 0.8 | 166 | 178 | 146 | 158 | 178 | 146 | 162 | |
| 0.9 | 161 | 174 | 141 | 154 | 174 | 141 | 158 | |
| 1.0 | 157 | 171 | 137 | 151 | 171 | 137 | 154 | |
| 0.8 | 170 | 182 | 150 | 162 | 182 | 150 | 166 | |
| 0.5 | 189 | 196 | 169 | 176 | 196 | 169 | 182 | |
| 1.2 | 143 | 161 | 123 | 141 | 161 | 123 | 142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, T.; Peng, H.; Qin, E.; Wang, Z.; Mao, X. Study on the Occurrence States and Enrichment Mechanisms of the Dispersed Elements Ga, Ge, and In in the Chipu Pb-Zn Deposit, Sichuan Province, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040341
Tan T, Peng H, Qin E, Wang Z, Mao X. Study on the Occurrence States and Enrichment Mechanisms of the Dispersed Elements Ga, Ge, and In in the Chipu Pb-Zn Deposit, Sichuan Province, China. Minerals. 2025; 15(4):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040341
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Tian, Huijuan Peng, En Qin, Ziyue Wang, and Xingxing Mao. 2025. "Study on the Occurrence States and Enrichment Mechanisms of the Dispersed Elements Ga, Ge, and In in the Chipu Pb-Zn Deposit, Sichuan Province, China" Minerals 15, no. 4: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040341
APA StyleTan, T., Peng, H., Qin, E., Wang, Z., & Mao, X. (2025). Study on the Occurrence States and Enrichment Mechanisms of the Dispersed Elements Ga, Ge, and In in the Chipu Pb-Zn Deposit, Sichuan Province, China. Minerals, 15(4), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15040341