The Impact of pH on the Pore and Structural Characteristics of Acid-Modified Bentonites in Oxalate Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Material Characterization
3.1.1. Chemical Analysis of Raw Materials
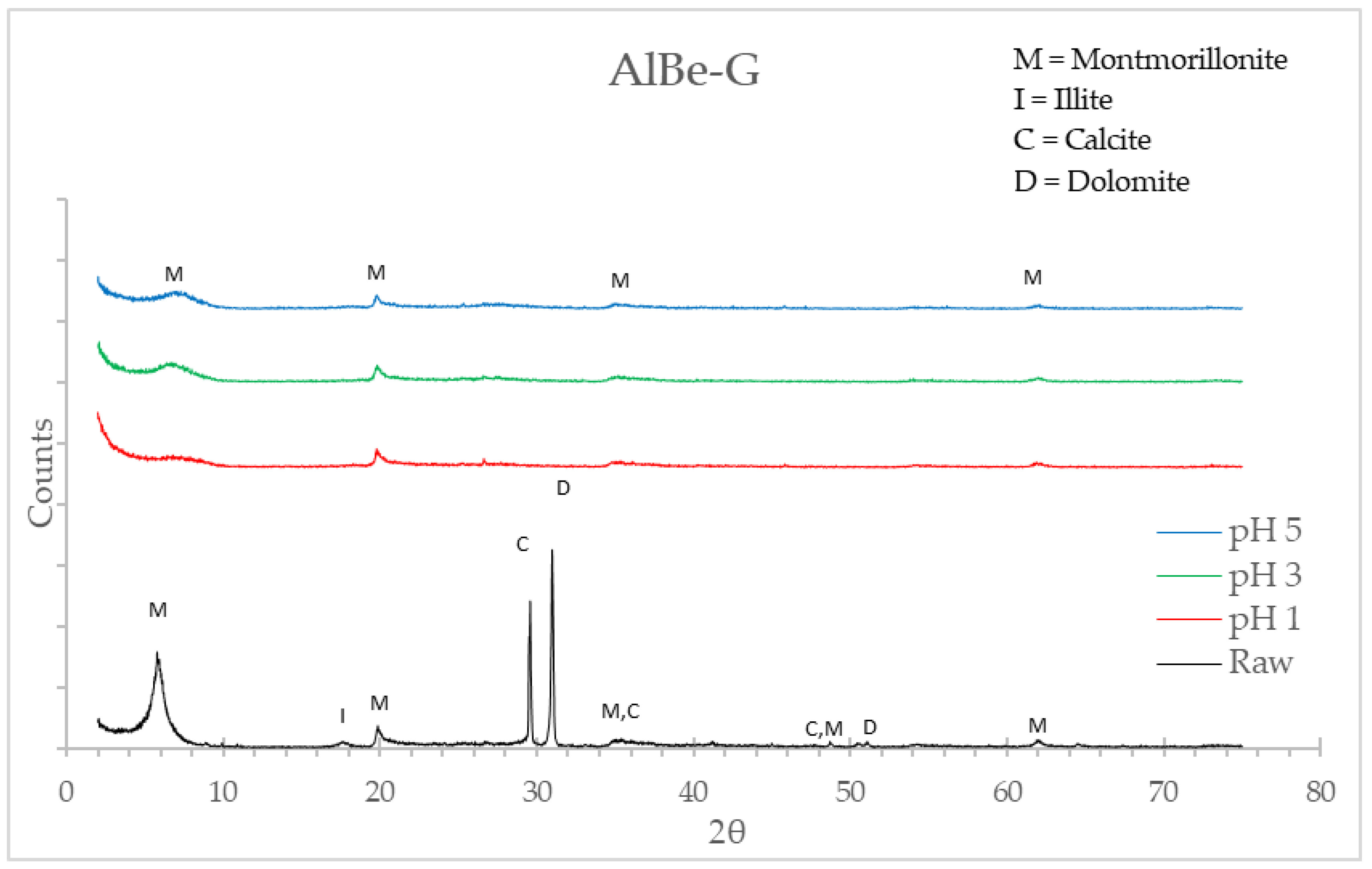
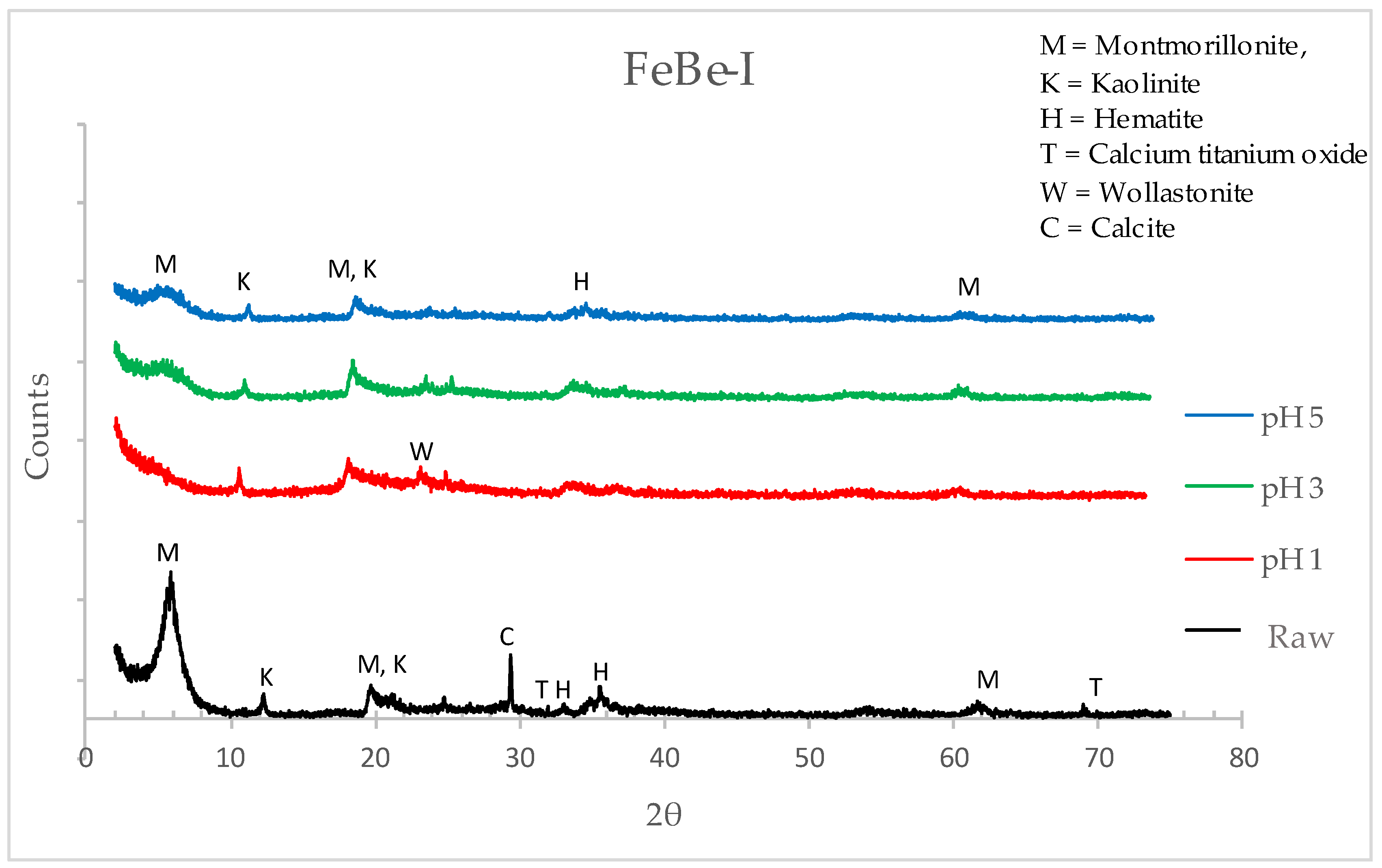
3.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
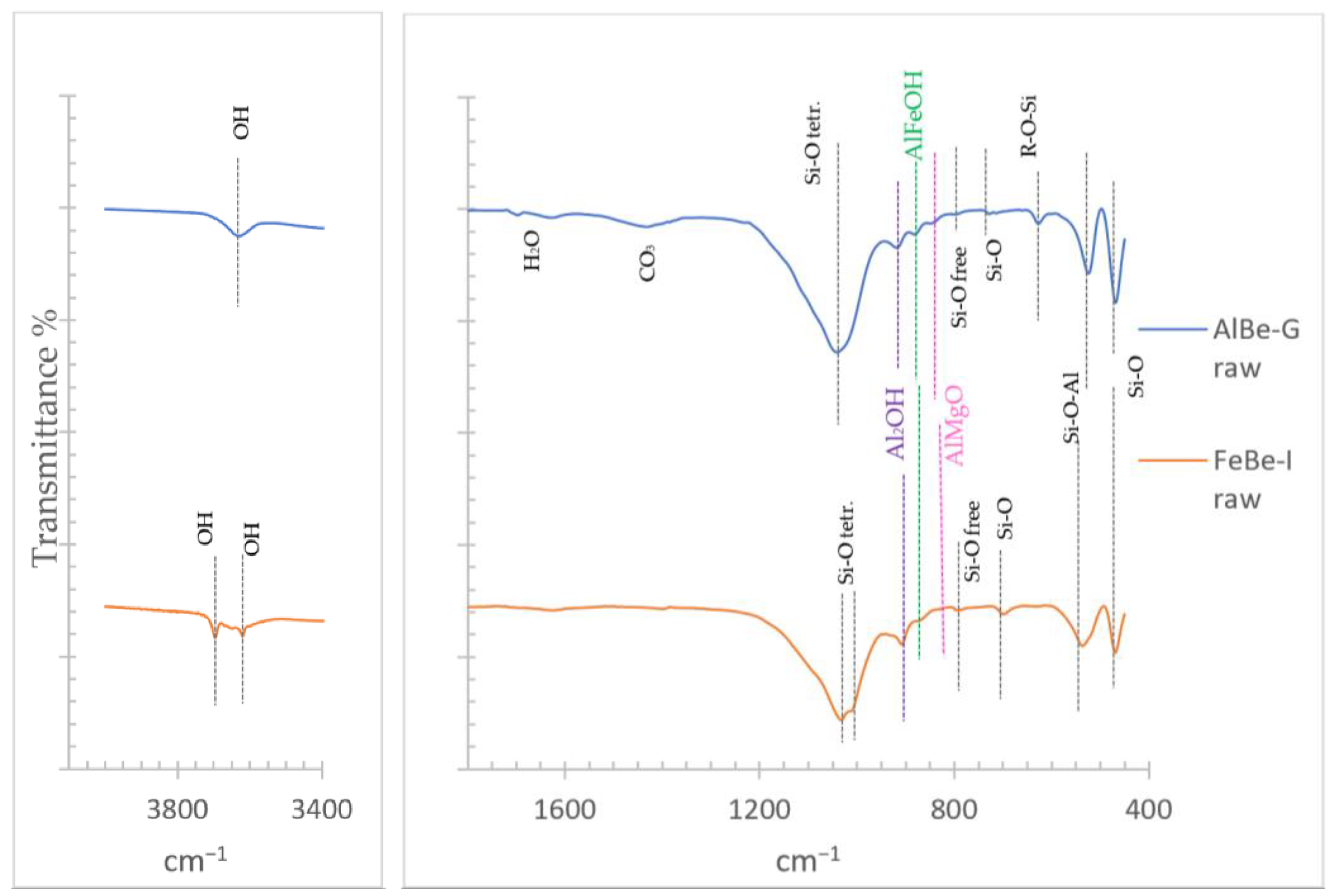
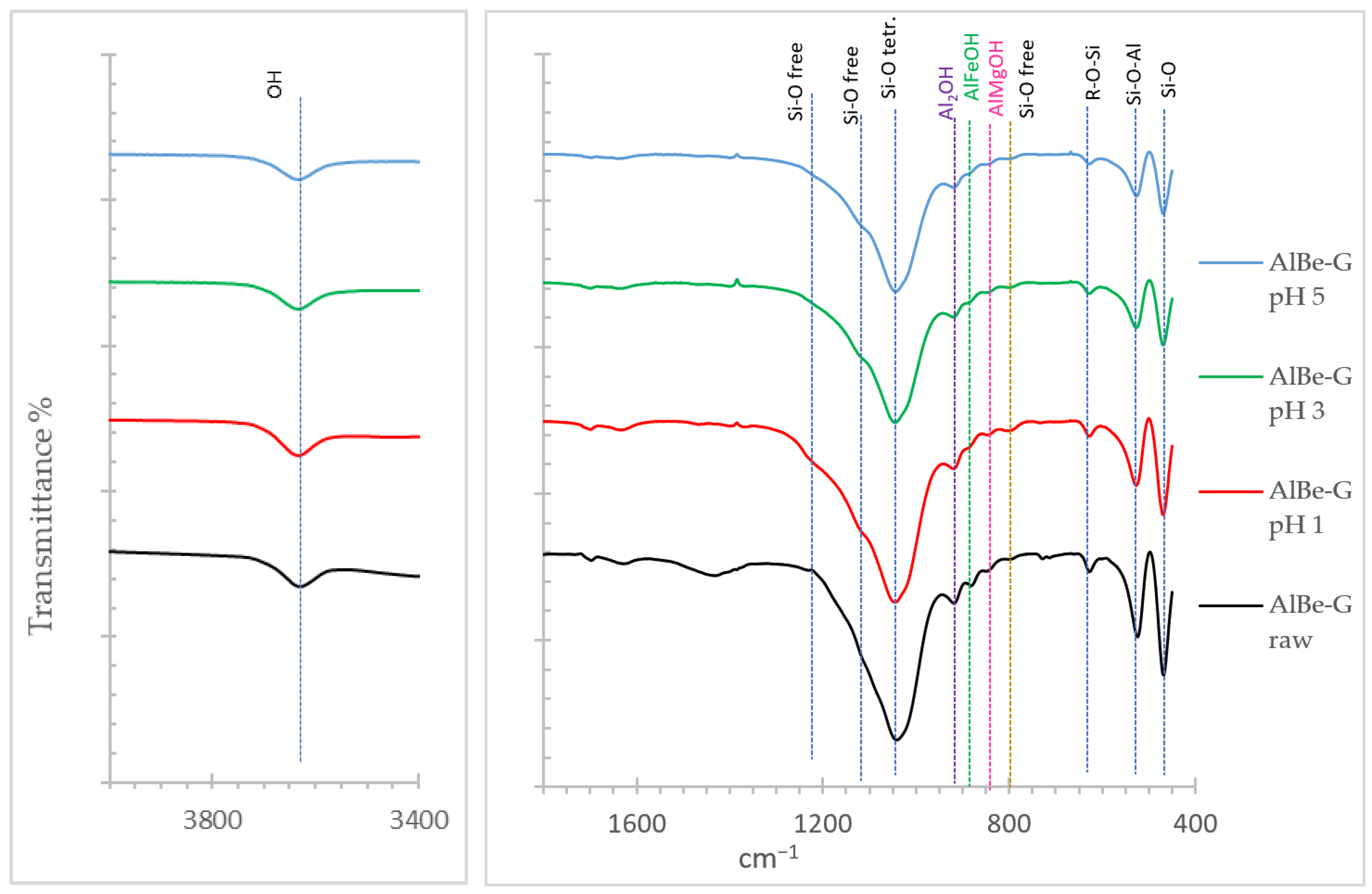
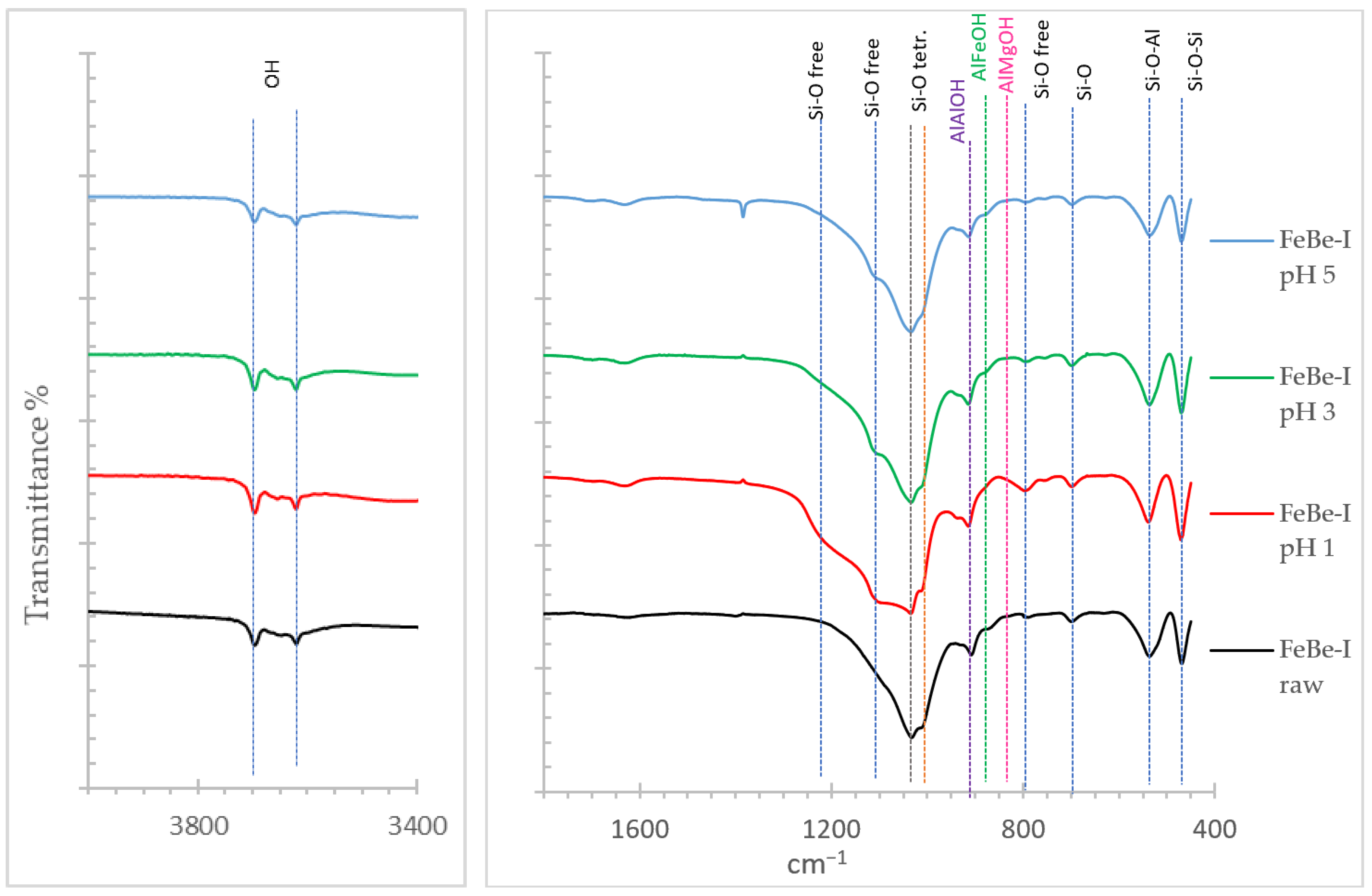
3.1.3. Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
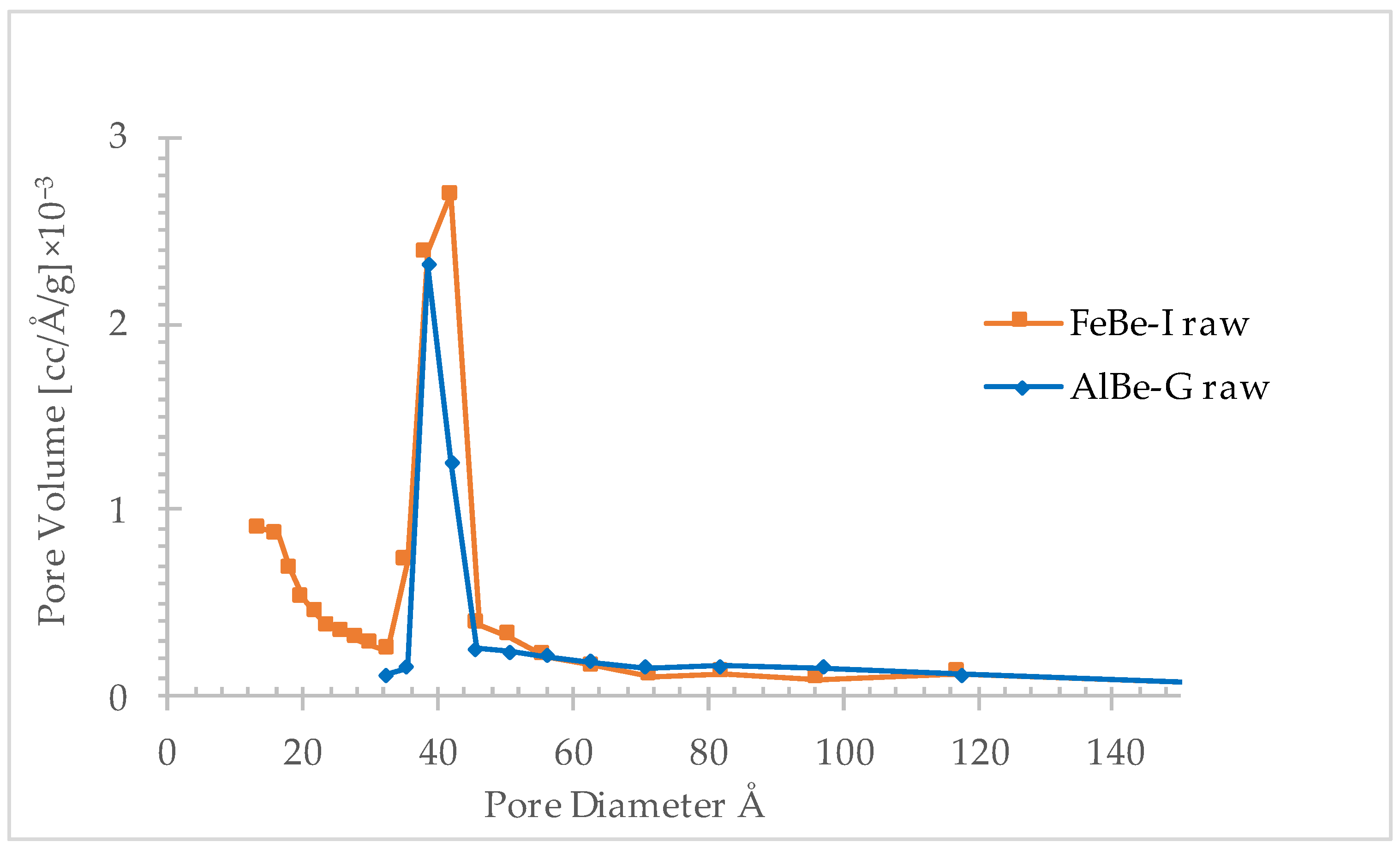
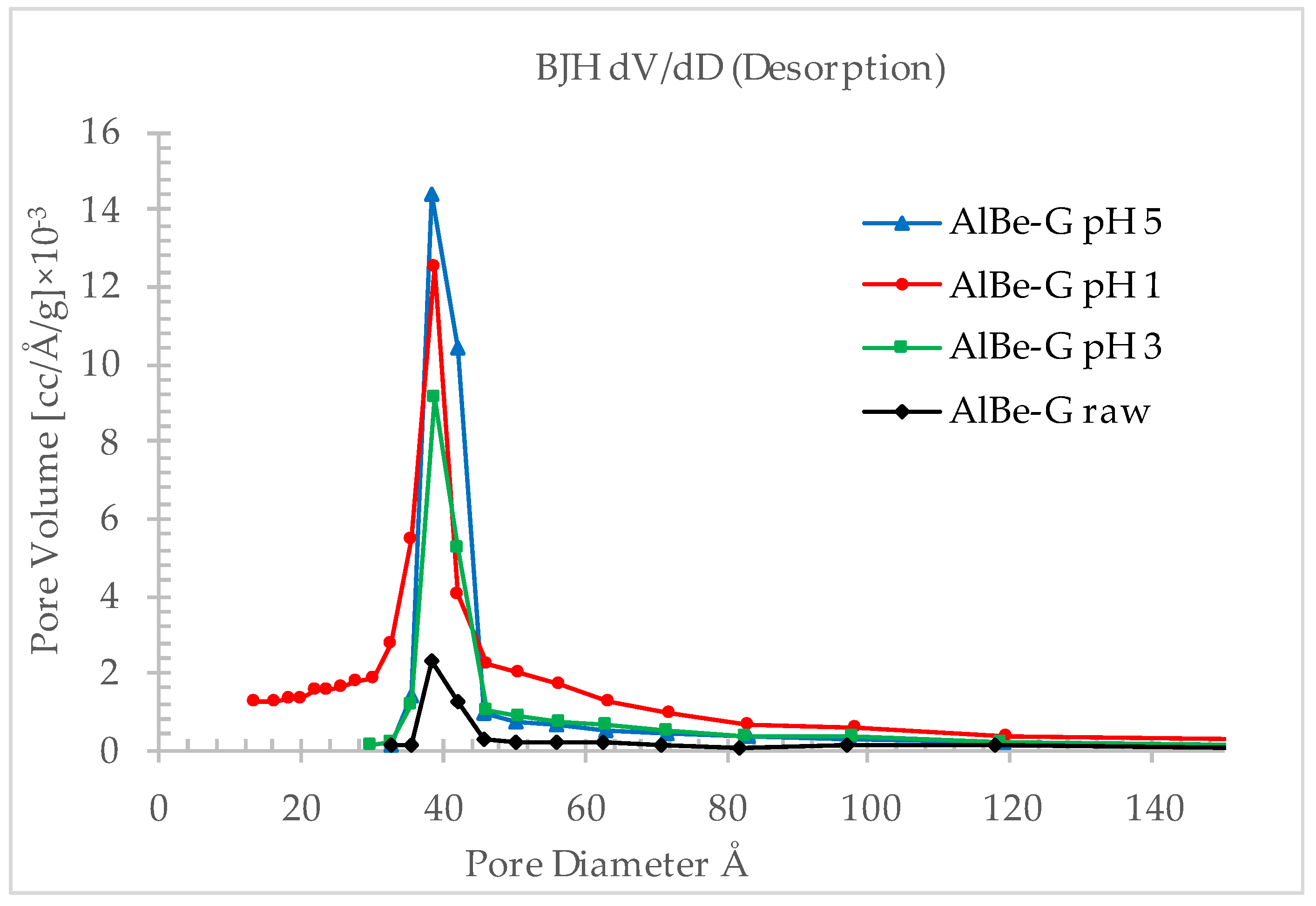
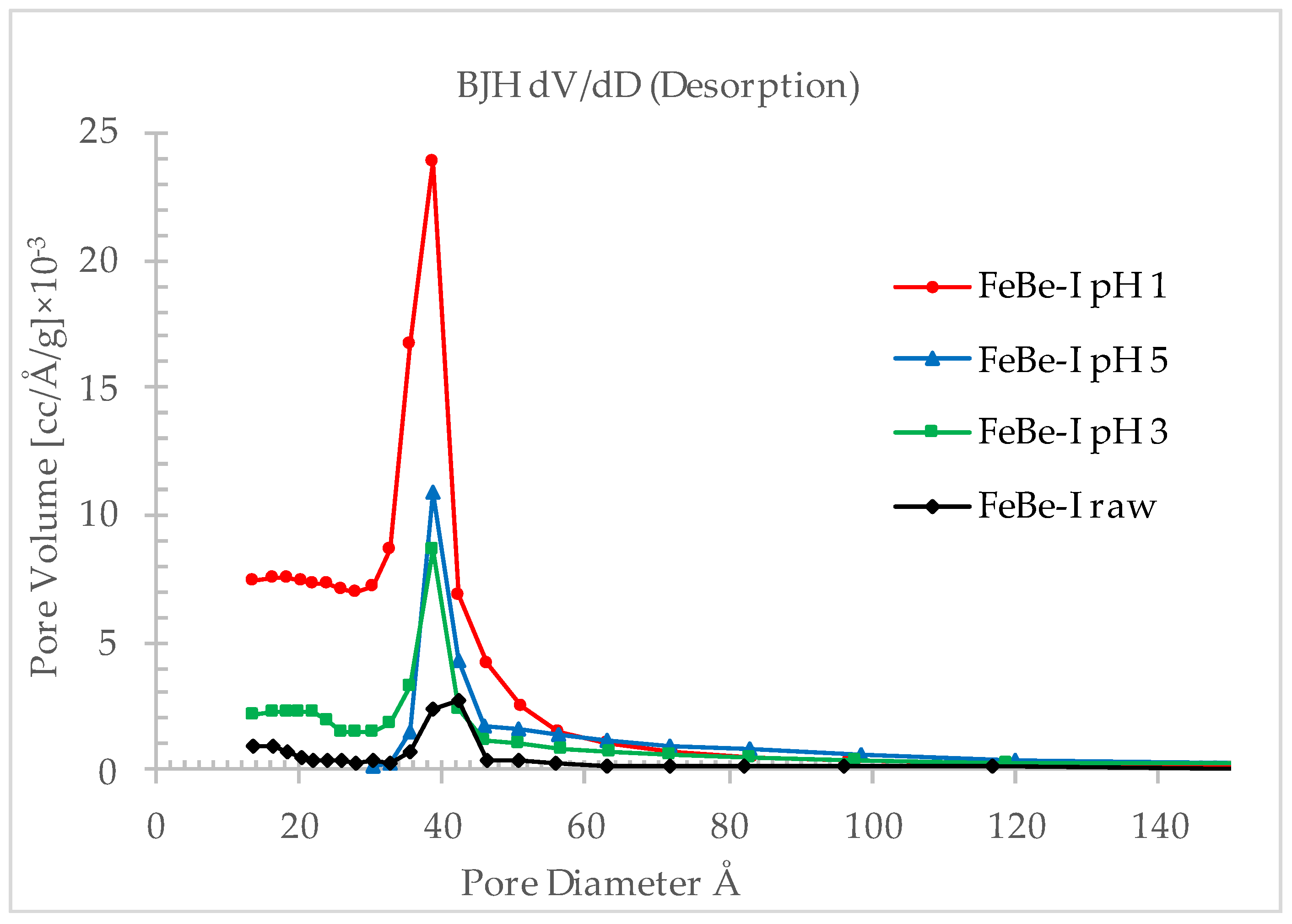
3.1.4. Pore Analysis
3.2. Experimental Results
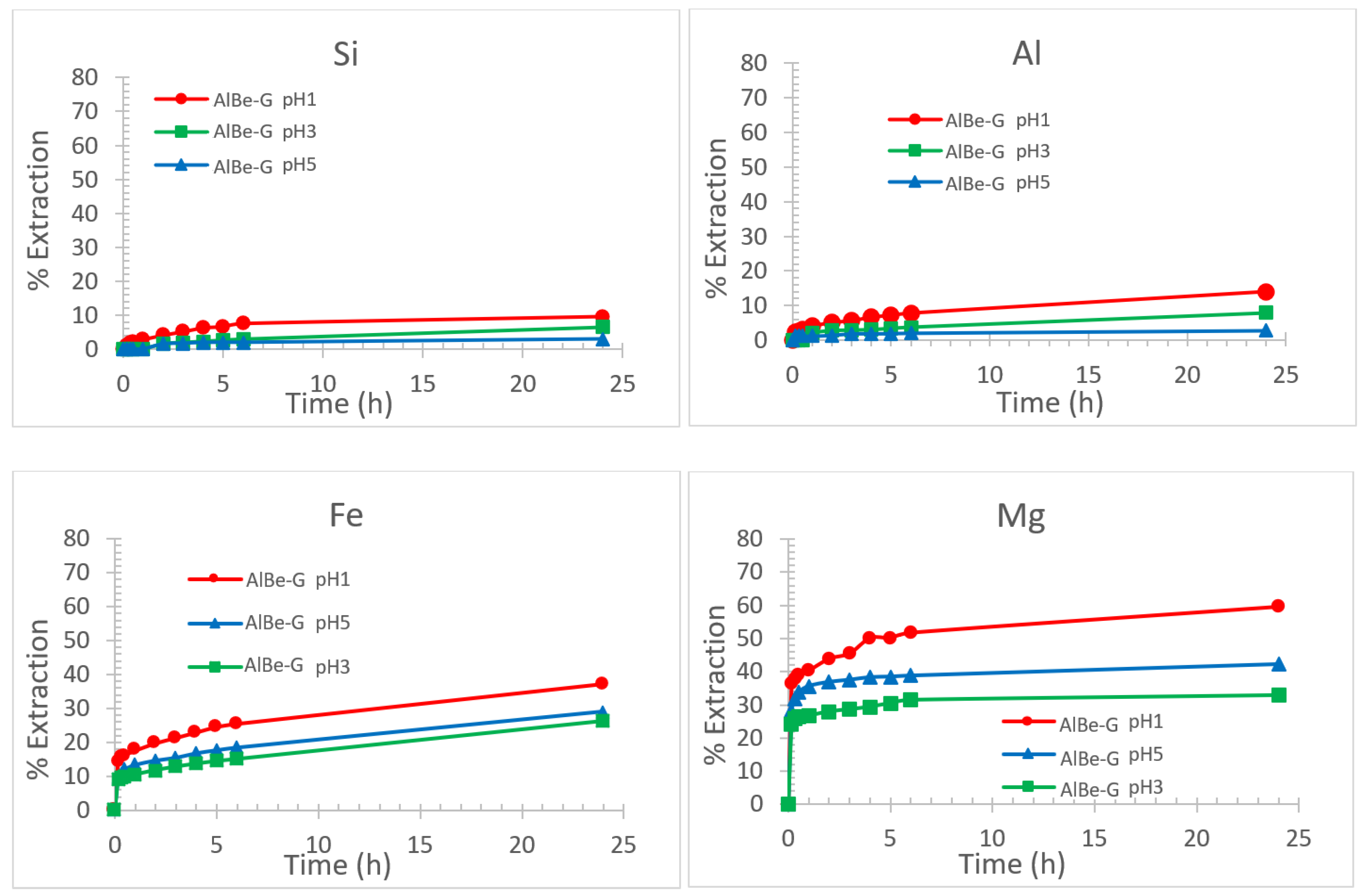
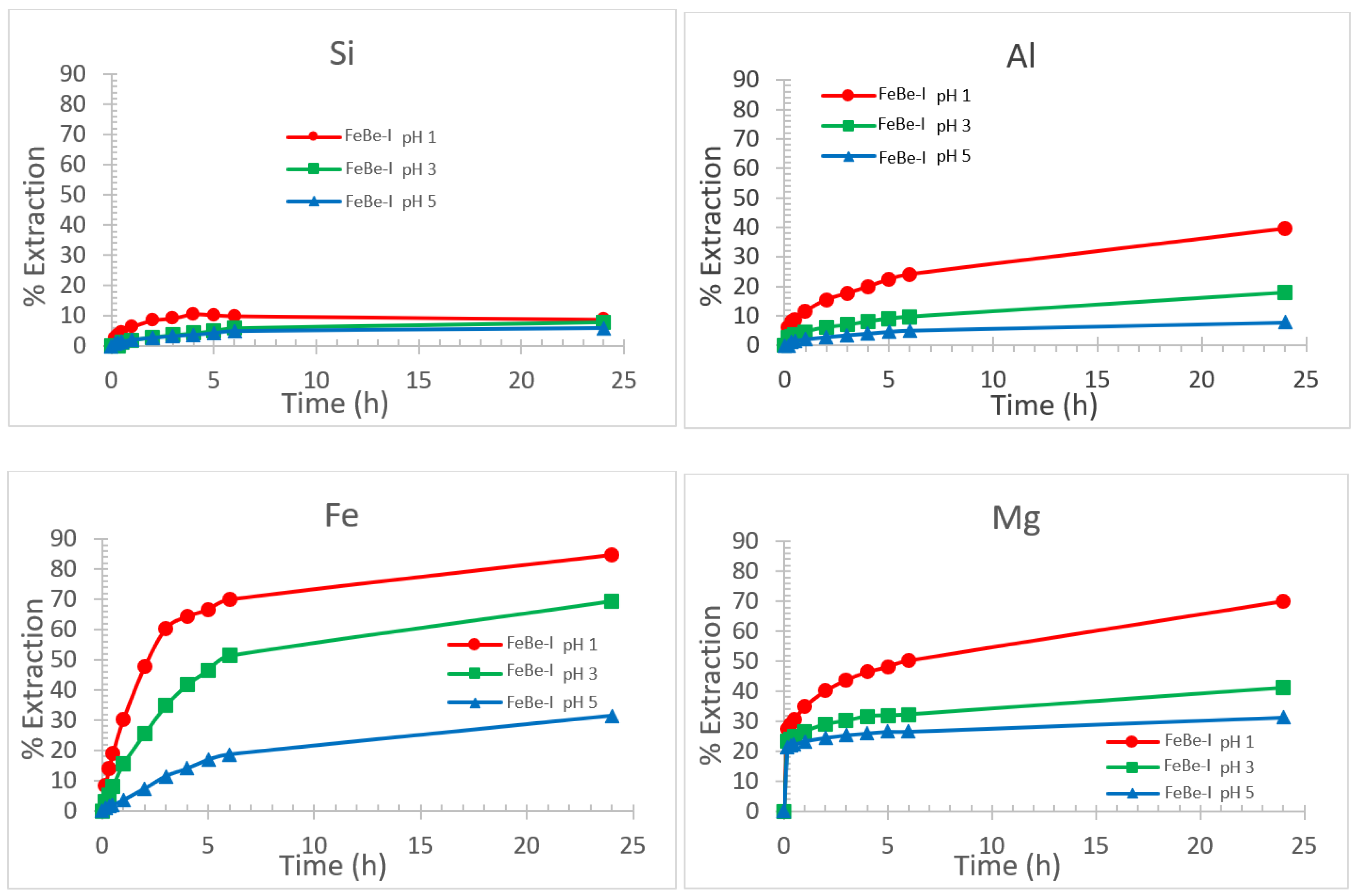
3.2.1. Effect of pH on Smectite Dissolution Rate
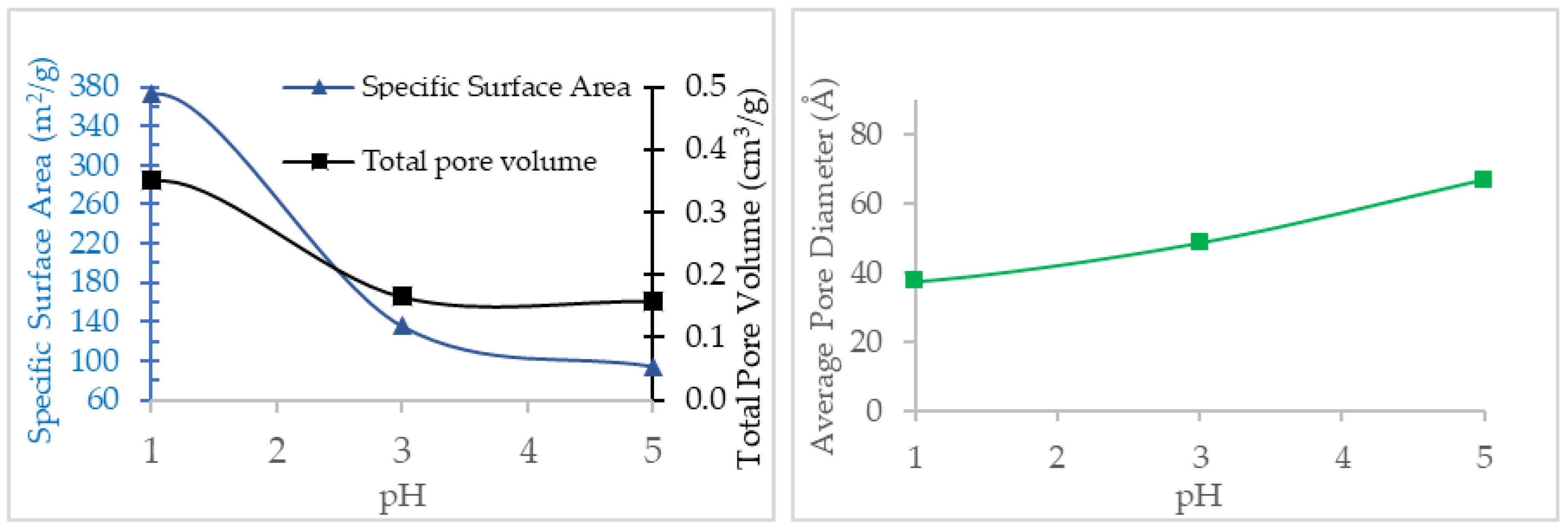
3.2.2. Effect of pH on Specific Surface Area and Porosity
3.2.3. Structural Modification of the Samples During Acid Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| XRF | X-Ray Fluorescence |
| PSD | Pore Size Distribution |
References
- Harben, P.W. The Industrial Minerals Handybook, a Guide to Markets, Specifications and Prices, 4th ed.; Metal Bulletin Books: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kogel, J.E.; Trivedi, N.C.; Barker, J.M.; Krukowsky, S.T. Industrial Minerals and Rocks, 7th ed.; Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Inc.: Englewood, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ober, J.A. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2018; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018.
- Caglar, B.; Afsin, B.; Koksal, E.; Tabak, A.; Eren, E. Characterization of Unye bentonite after treatment with sulfuric acid. Química Nova 2013, 35, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyan, H.; Önal, M.; Sarikaya, Y. The effect of sulphuric acid activation on the crystallinity, surface area, porosity, surface acidity, and bleaching power of a bentonite. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.; Almeida, C.; Belén, M.; Guerrero, V. Acid activation of bentonite clay for recycled automotive oil purification. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 191, 03002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, S.R.; Man, M.S. Industrial Applications of Acid-Treated Clays as Catalysts. React. Funct. Polym. 1997, 32, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tope, B.I.; Adedapo, O.A.; David, B.O.; Odunayo, T.O.; Babatunde, O.I.; Alabi, A.S. Pristine and activated bentonite for toxic metal removal from wastewater. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 784–797. [Google Scholar]
- Espantaleón, A.G.; Nieto, J.A.; Fernández, M.; Marsal, A. Use of activated clays in the removal of dyes and surfactants from tannery waste waters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 24, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/ (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Christidis, G.E.; Scott, P.W.; Dunham, A.C. Acid activation and bleaching capacity of bentonites from the islands of Milos and Chios, Aegean, Greece. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxiarchou, M.; Douni, I. The effect of oxalic acid activation on the bleaching properties of a bentonite from Milos Island, Greece. Clay Miner. 2014, 49, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorica, P.T.; Vesna, P.L.; Biljana, M.B.; Jelena, R.R.; Petre, M. Comparison of structural, textural and thermal characteristics of pure and acid treated bentonites from Aleksinac and Petrovac (Serbia). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 82, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Önal, M.; Sarikaya, Y.; AlemdaroǧluI, T.; Bozdoǧan, I. The Effect of Acid Activation on Some Physicochemical Properties of a Bentonite. Turk. J. Chem. 2002, 26, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, Z.; Dugić, P.; Aleksić, V.; Begić, S.; Sadadinović, J.; Mićić, V.; Kljajić, N. Composition, Structure And Textural Characteristics Of Domestic Acid Activated Bentonite. Contemp. Mater. 2014, 5, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y. Dissolution of kaolinite induced by citric, oxalic, and malic acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 290, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama, J.; Ganor, J. The effects of organic acids on the dissolution of silicate minerals: A case study of oxalate catalysis of kaolinite dissolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganor, J.; Lasaga, A.C. The Effects of Oxalic Acid on Kaolinite Dissolution Rate. Mineral. Mag. 1994, 58, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, P.-K.F.; Mills, G.L. Kinetics and mechanisms of kaolinite dissolution: Effects of organic ligands. Chem. Geol. 1991, 90, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, A. Effect of oxalic acid-leaching levels on structure, color and physico-chemical features of palygorskite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsuri, A.; Irawan, S. A study of iron removal from Sabah montmorillonite by extracting with organic acid. In Proceedings of the Regional Conference for Young Chemists, Penang, Malaysia, 13–14 April 2004; USM: Penang, Malaysia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Naqvi, S.H.J.; Kazmi, M.A.; Ashraf, Z. Surface activation of fuller’s earth (bentonite clay) using organic acids. Sci. Int. 2015, 27, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, M.K. Effects of oxalic and citric acids on three clay minerals after incubation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 99, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.E.; Garcia-Palma, S.; Rozalen, M.; Johnston, C.T.; Huertas, F.J. Kinetics of montmorillonite dissolution. An experimental study of the effect of oxalate. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.E.; Emiroglu, C.; García, D.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I.; Huertas, F.J. Modeling the Adsorption of Oxalate onto Montmorillonite. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11825–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, F.; Estoppey, A.; House, G.L.; Lohberger, A.; Bindschedler, S.; Chain, P.S.G.; Junier, P. Chapter Two—Oxalic acid, a molecule at the crossroads of bacterial-fungal interactions. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 106, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, J.; Comerford, N.; Johnston, C. Influence of Soil Organic Matter Removal and pH on Oxalate Sorption onto a Spodic Horizon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiri, D.; Douni, I.; Taxiarchou, M. Structural and Surface Modification of Oxalic-Acid-Activated Bentonites in Various Acid Concentrations for Bleaching Earth Synthesis—A Comparative Study. Minerals 2022, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Chudasama, C.D.; Jasra, R.V. Determination of structural modification in acid activated montmorillonite clay by FT-IR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2006, 64, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejova, J.; Bujdak, J.; Janek, M.; Komadel, P. Comparative FT-IR study of structural modifications during acid treatment of diocthedral smectites and hectorite. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 1998, 54, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Jadambaa, T.; Burmaa, G.; Erdenechimeg, S.; Amarsanaa, J.; MacKenzie, K.J.D. Characterisation of acid activated montmorillonite clay from Tuulant (Mongolia). Ceram. Int. 2004, 30, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, A.; Afsin, B.; Caglar, B.; Koksal, E. Characterization and pillaring of a Turkish bentonite (Resadiye). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxiarchou, M.; Panias, D.; Douni, I.; Paspaliaris, I.; Kontopoulos, A. Dissolution of hematite in acidic oxalate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 44, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.B.; Yoon, T.H.; Slowey, A.J.; Brown, G.E., Jr. Adsorption of organic matter at mineral/water interfaces: 3. Implications of surface dissolution for adsorption of oxalate. Langmuir 2004, 20, 11480–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, W.P.; Anderson, J.S.; Raven, M.D.; Churchman, G.J. Mineralogy of a bentonite from Miles, Queensland, Australia and characterisation of its acid activation products. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 20, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panias, D.; Taxiarchou, M.; Paspaliaris, I.; Kontopoulos, A. Mechanisms of dissolution of iron oxides in aqueous oxalic acid solutions. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 42, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, A.J.A.; Tunega, D.; Haberhauer, G.; Gerzabek, M.; Lischka, H. A density functional theoretical study on solvated Al3+–oxalate complexes: Structures and thermodynamic properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2845–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiri, D.; Douni, I.; Taxiarchou, M. A Comparative Study Between Surface and Physicochemical Properties of Materials Produced by Oxalic and Sulphuric Acid Activation on Different Smectite Samples. In Sustainable Industrial Processing Summit SIPS2019 Volume 6: Parameswaran Intl. Symp./Sustainable Mining and Smelting; Kongoli, F., Baiden, G., Dzombak, D., Guo, L., Liu, L., Poulton, M., Somasundaran, P., Eds.; Flogen Star Outreach: Montreal, QC, Canada; pp. 54–71.
- Tarasova, I.I.; Dudeney, A.W.L.; Pilurzu, S. Glass sand processing by oxalic acid leaching and photocatalytic effluent treatment. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Oxides (wt. %) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | L.O.I. | Total | |
| AlBe-G | 48.28 | 17.25 | 3.68 | 5.28 | 9.01 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.71 | 15.10 | 100.00 |
| FeBe-I | 46.96 | 17.66 | 19.32 | 2.80 | 1.75 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 1.39 | 9.05 | 100.00 |
| AlBe-G | FeBe-I | |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 28.11 | 63.21 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 65.98 | 40.20 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.046 | 0.064 |
| AlBe-G Raw | AlBe-G pH 1 | AlBe-G pH 3 | AlBe-G pH 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 28.1 | 149.0 | 50.7 | 92.5 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 66.0 | 56.3 | 82.3 | 57.2 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.13 |
| FeBe-I Raw | FeBe-I pH 1 | FeBe-I pH 3 | FeBe-I pH 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 63.2 | 372.3 | 135.8 | 94.7 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 40.2 | 37.6 | 48.7 | 67.0 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taxiarchou, M.; Tsakiri, D.; Douni, I. The Impact of pH on the Pore and Structural Characteristics of Acid-Modified Bentonites in Oxalate Solutions. Minerals 2025, 15, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030257
Taxiarchou M, Tsakiri D, Douni I. The Impact of pH on the Pore and Structural Characteristics of Acid-Modified Bentonites in Oxalate Solutions. Minerals. 2025; 15(3):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030257
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaxiarchou, Maria, Danai Tsakiri, and Iliana Douni. 2025. "The Impact of pH on the Pore and Structural Characteristics of Acid-Modified Bentonites in Oxalate Solutions" Minerals 15, no. 3: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030257
APA StyleTaxiarchou, M., Tsakiri, D., & Douni, I. (2025). The Impact of pH on the Pore and Structural Characteristics of Acid-Modified Bentonites in Oxalate Solutions. Minerals, 15(3), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030257







