Leveraging Biomineralization in Repurposed Stirred Reactors for Mn/Zn Removal from Mine Water: Insights from a Laboratory-Scale Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioactive Mn-Sludge
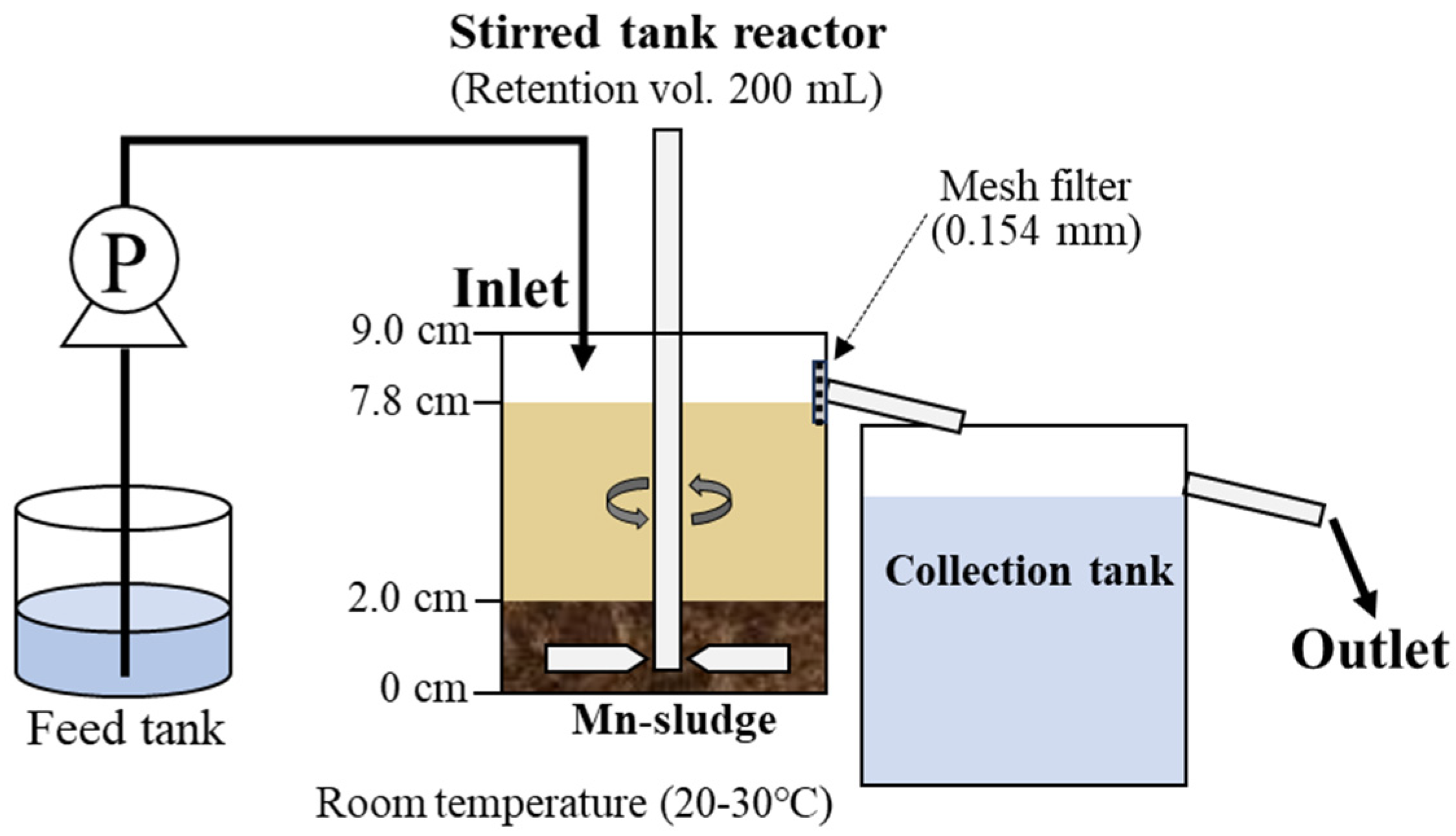
2.2. Mn/Zn Removal by Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor
2.2.1. Baseline Mn Oxidation Test (Mn-System)
2.2.2. Enhanced Mn Oxidation with Zn Co-Treatment (Mn/Zn-System)
2.3. Liquid Analyses
2.4. Solid Analyses
2.4.1. XANES Analysis
2.4.2. ATP Analysis
2.4.3. Microbial Community Structure Analysis
2.4.4. Stability and Composition of the Resulting Mn Precipitates
3. Results and Discussion
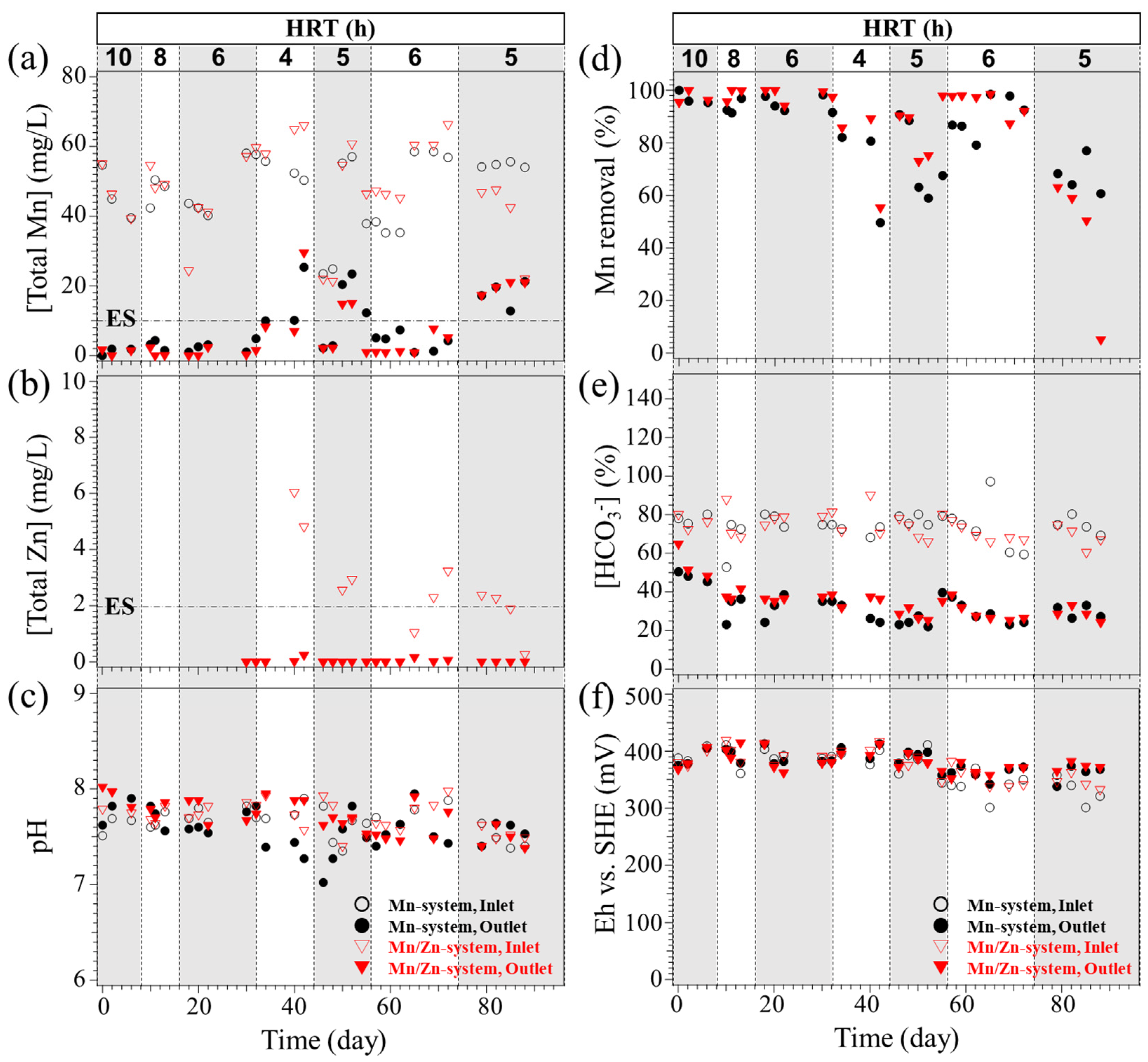
3.1. Liquid Analysis and System Performance
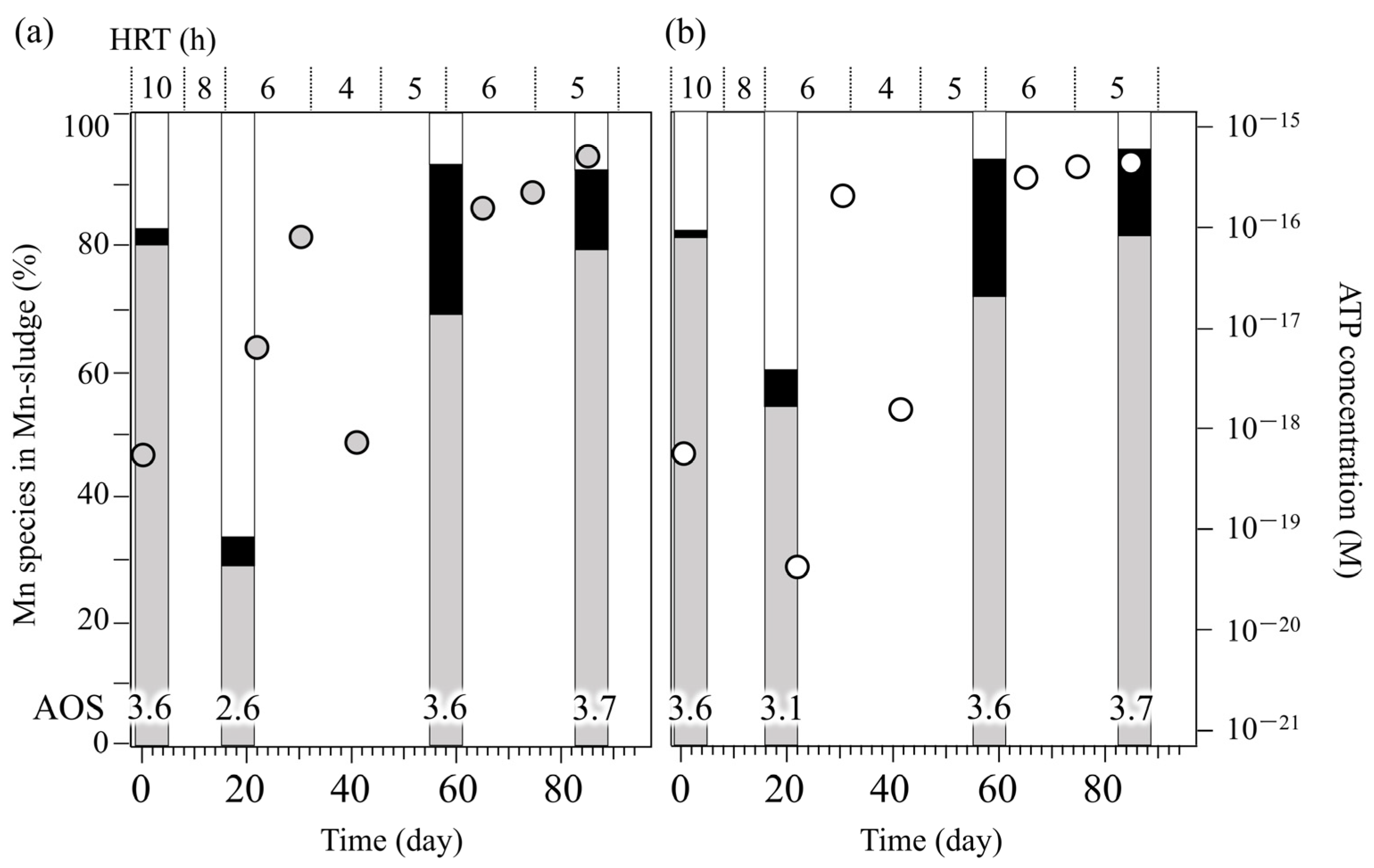
3.2. Mineralogical and Biochemical Dynamics of Mn Oxidation in Two Stirred Tank Reactors
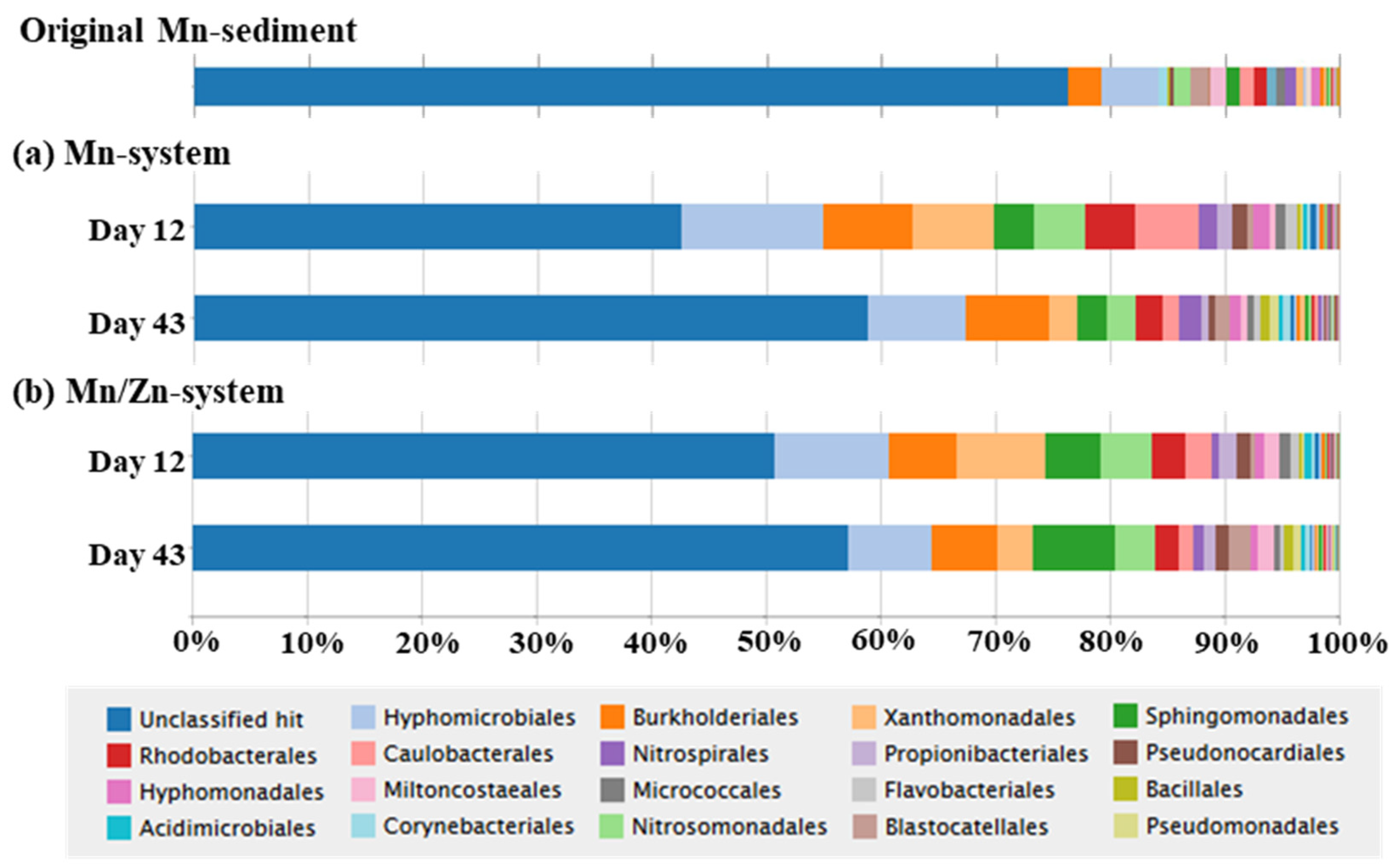
3.3. Microbial Community Composition and Dynamics in Mn- and Mn/Zn-Systems
3.3.1. Microbial Community Composition in the Mn-System
3.3.2. Microbial Community Composition in the Mn/Zn-System
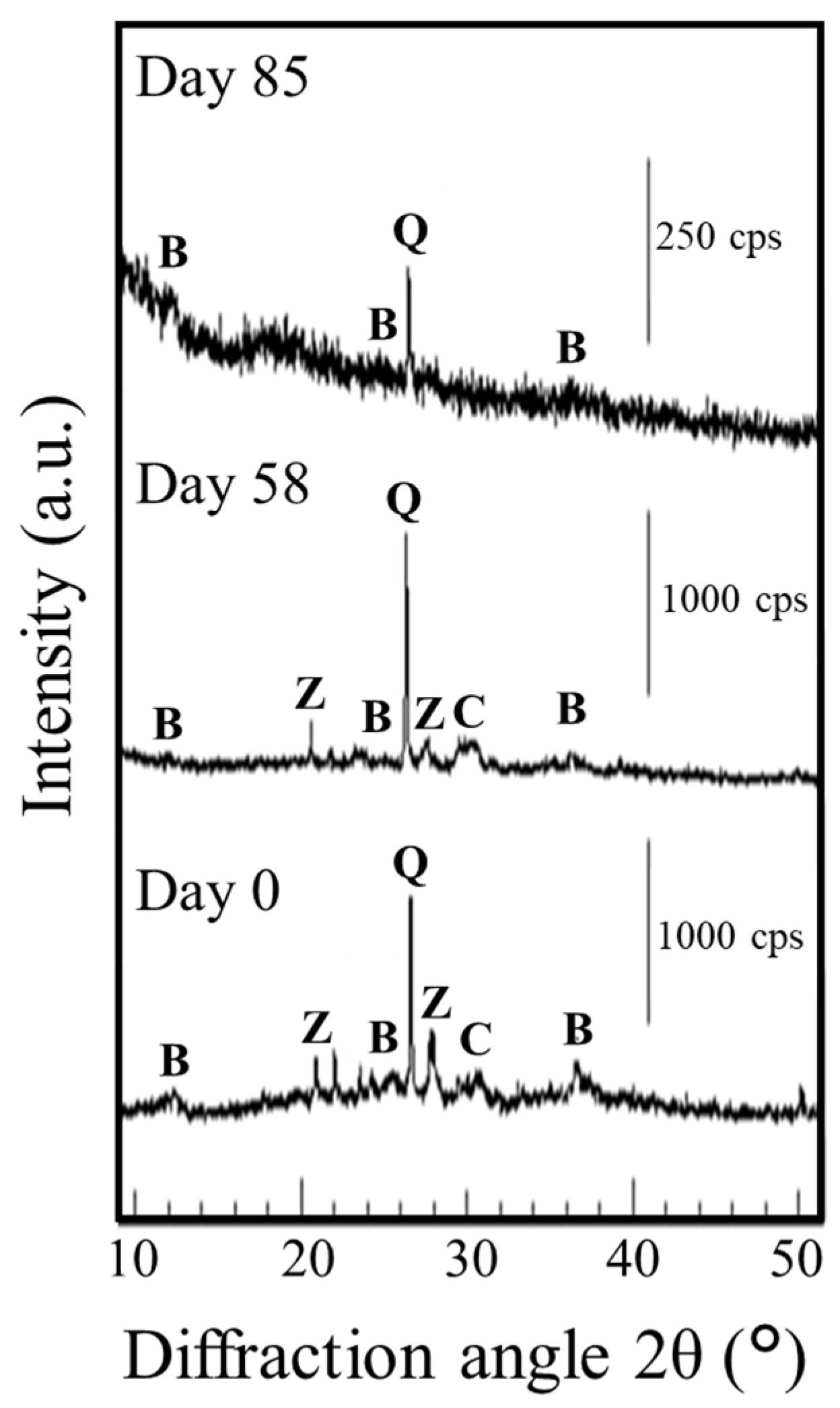
3.4. Composition and Stability of the Resulting Mn Minerals
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luan, F.; Burgos, W.D. Effects of solid-phase organic carbon and hydraulic residence time on manganese (II) removal in a passive coal mine drainage treatment system. Mine Water Environ. 2019, 38, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/water/impure/haisui.html (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ma, H.; Hursthouse, A.S. Removal of Manganese(II) from Acid Mine Wastewater: A Review of the Challenges and Opportunities with Special Emphasis on Mn-Oxidizing Bacteria and Microalgae. Water 2019, 11, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neculita, C.M.; Rosa, E. A Review of the Implications and Challenges of Manganese Removal from Mine Drainage. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.M.; Perilli, T.A.G.; Ladeira, A.C.Q. Oxidative Precipitation of Manganese from Acid Mine Drainage by Potassium Permanganate. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 287257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hao, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, B. Powdered activated carbon enhanced Manganese(II) removal by chlorine oxidation. Water Res. 2019, 156, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculita, C.-M.; Zagury, G.J.; Bussière, B. Passive Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage in Bioreactors Using Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria: Critical Review and Research Needs. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkele, K.; Mpenyana-Monyatsi, L.; Masindi, V. Challenges, advances and sustainabilities on the removal and recovery manganese from wastewater: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liang, J.; Chen, C.; Qu, J. Treatment of groundwater containing Mn(II), Fe(II), As(III) and Sb(III) by bioaugmented quartz-sand filters. Water Res. 2016, 106, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya-Obando, J.A.; Rietveld, L.C.; Quesada-González, A.; Caballero-Chavarría, A.; Pacini, V.; Romero-Esquivel, L.G. Start-up of bench-scale biofilters for manganese removal under tropical conditions: A comparative study using virgin pumice, silica sand, and anthracite filter media. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R.; Clement, B.G.; Dick, G.J.; Murray, K.J.; Parker, D.; Verity, R.; Webb, S.M. Biogenic manganese oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2004, 32, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.F.; Ghiorse, W.C. Oxidation state of Mn in the Mn oxide produced by Leptothrix discophora SS-1. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2073–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D.; Lind, C.J. Nonequilibrium models for predicting forms of precipitated manganese oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.W.; Dillard, J.G.; Giovanoli, R.; Moers, H.; Stumm, W. Oxidation of Mn(II): Initial mineralogy, oxidation state and ageing. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonfueng, T.; Axe, L.; Xu, Y.; Tyson, T.A. The impact of Mn oxide coatings on Zn distribution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakamura, R. Mechanisms of pH-dependent activity for water oxidation to molecular oxygen by MnO2 electrocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohu, T.; Akob, D.M.; Abratis, M.; Lazar, C.S.; Küsel, K. Biological low-pH Mn(II) oxidation in a manganese deposit influenced by metal-rich groundwater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3009–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariner, R.; Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. Characterisation of an attenuation system for the remediation of Mn(II) contaminated waters. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 94, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, H. Depth Distribution of Microbial Diversity in Lakes. In Freshwater Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 225–262. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, C.A.; Co, E.M.; Tebo, B.M. Enzymatic manganese(II) oxidation by a marine α-proteobacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4024–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Xing, D. Characterization of manganese oxidation by Brevibacillus at different ecological conditions. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, A.; Casalini, L.C.; Pacini, V.A.; Sanguinetti, G.; Ottado, J.; Gottig, N. Environmental bacteria involved in manganese (II) oxidation and removal from groundwater. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okibe, N.; Maki, M.; Sasaki, K.; Hirajima, T. Mn(II)-oxidizing activity of Pseudomonas sp. strain MM1 is involved in the formation of massive Mn sediments around Sambe Hot Springs in Japan. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 2027–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitjanukit, S.; Takamatsu, K.; Okibe, N. Natural attenuation of Mn(II) in metal refinery wastewater: Microbial community structure analysis and isolation of a new Mn(II)-oxidizing bacterium Pseudomonas sp. SK3. Water 2019, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Nengzi, L.; Bao, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, J. Distribution and genetic diversity of microbial populations in the pilot-scale biofilter for simultaneous removal of ammonia, iron and manganese from real groundwater. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.a.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J. Operational parameters required for the start-up process of a biofilter to remove Fe, Mn, and NH3-N from low-temperature groundwater. Desal. Water Treat 2016, 57, 3588–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, K.B.; Johnson, D.B. Biological manganese removal from acid mine drainage in constructed wetlands and prototype bioreactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourre, B.L.; Neculita, C.M.; Coudert, L.; Rosa, E. Manganese removal processes and geochemical behavior in residues from passive treatment of mine drainage. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.L.; Baker, A.; Manning, D.A.C. Passive treatment of Mn-rich mine water: Using fluorescence to observe microbiological activity. Geomicrobiol. J. 2005, 22, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santelli, C.M.; Pfister, D.H.; Lazarus, D.; Sun, L.; Burgos, W.D.; Hansel, C.M. Promotion of Mn(II) oxidation and remediation of coal mine drainage in passive treatment systems by diverse fungal and bacterial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4871–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginter, M.O.; Grobicki, A.M. Manganese removal mechanisms in a stirred UASB reactor. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Luo, Z.; Yan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, S.; Yang, Y.; Yao, L.; Luo, L. Manganese removal from acid mine drainage by a consortium of Mn-oxidizing bacteria in continuous stirred tank bioreactor: Long-term treatment and reactive mixture characterization. ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okibe, N.; Nonaka, K.; Kondo, T.; Shimada, K.; Liu, P. Microbiological passive treatment of Mn/Zn-containing mine water. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 219, 106084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurogi, F. Development of Semi-Passive Bioprocess for Treatment of Neutral Mn/Zn Containing Mine Wastewater. Bachelor’s Thesis, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zahoransky, T.; Wegorzewski, A.V.; Huong, W.; Mikutta, C. X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of Mn reference compounds for Mn speciation in terrestrial surface environments. Am. Mineral. 2023, 108, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Okibe, N. Factors to enable crystallization of environmentally stable bioscorodite from dilute As(III)-contaminated waters. Minerals 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, S.; Fuchida, S.; Tokoro, C. Coprecipitation mechanisms of Zn by birnessite formation and its mineralogy under neutral pH conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 121, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sánchez, A.; Álvarez-Ayuso, E. Sorption of Zn, Cd and Cr on calcite: Application to purification of industrial wastewaters. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgung, S.; Lee, G. Rhodochrosite oxidation by dissolved oxygen and the formation of Mn oxide product: The impact of goethite as a foreign solid substrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14436–14444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetta, M.G.; Benaiges-Fernández, R.; Cama, J.; Queralt, I.; Soler, J.M. Microbiology of an abandoned Pb–Zn mine: Impact on environmental metal contamination. Environ. Adv. 2022, 10, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofré, I.; Matus, F.; Mendoza, D.; Nájera, F.; Merino, C. Manganese-Oxidizing Antarctic Bacteria (Mn-Oxb) Release Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) as Secondary Mn(II) Oxidation Mechanisms to Avoid Toxicity. Biology 2021, 10, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Su, J.; Wen, Q.; Huang, T.; Chang, Q.; Ali, A. Characterization and mechanism of Mn(II)-based mixotrophic denitrifying bacterium (Cupriavidus sp. HY129) in remediation of nitrate (NO3−-N) and manganese (Mn(II)) contaminated groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, S.K.; Bräuer, S.L. Microbial diversity and manganese cycling: A review of Mn-oxidizing microbial cave communities. In Microbial Life of Cave Systems; Engel, A.S., Ed.; De Gruyter: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 137–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sly, L.I.; Arunpairojana, V.; Hodgkinson, M.C. Pedomicrobium manganicum from drinking-water distribution systems with manganese-related “dirty water” problems. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 11, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, D.; Ghiorse, W.C. Isolation, Cultural Maintenance, and Taxonomy of a Sheath-Forming Strain of Leptothrix discophora and Characterization of Manganese-Oxidizing Activity Associated with the Sheath. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Ma, Q.; Bai, Y.; Qu, J. Manganese oxides in Phragmites rhizosphere accelerate ammonia oxidation in constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Bai, Y.; Men, Y.; Qu, J. Microbe–microbe interactions trigger Mn(II)-oxidizing gene expression. ISME J. 2017, 11, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalman, B.; Peng, J.; Kinet, R.; Bernard, C.; Hullebusch, E.D.V.; Lens, P.N.L. Manganese oxidation by modified reaction centers in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13286–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardino, J.; Bijlani, S.; Singh, N.K.; Wood, J.M.; Barker, R.; Gilroy, S.; Wang, C.C.C.; Venkateswaran, K. Genomic characterization of potential plant growth-promoting features of Sphingomonas strains isolated from the international space station. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 10, e01994-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, L.; Chograni, H.; Ben Rejeb, F.; Ben Romdhane, M.; Masmoudi, A.S.; Cherif, A. Efficient in vitro regeneration of the endangered species Artemisia arborescens L. through direct organogenesis and impact on secondary metabolites production. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2022, 63, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.L.; Boddum, J.K.; Tjell, J.C.; Christensen, T.H. The solubility of rhodochrosite (MnCO3) and siderite (FeCO3) in anaerobic aquatic environments. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 17, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Sexstone, A.; Ziemkiewicz, P. Review of Passive Systems for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2000, 19, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genus | Relative Abundance of Potential Mn-Oxidizing Microorganisms (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Mn-System | Mn/Zn-System | |||
| Day 12 | Day 43 | Day 12 | Day 43 | ||
| Hyphomicrobium | 2.08 | 8.16 | 4.74 | 5.28 | 3.66 |
| Nitrospira | 0.88 | 1.56 | 1.92 | 0.61 | 0.95 |
| Sphingomonas | - | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 1.97 |
| Sphingopyxis | 0.67 | 1.31 | 0.727 | 1.27 | 1.00 |
| Rhodococcus | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.24 |
| Pseudonocardia | 0.36 | 1.31 | 0.58 | 1.19 | 1.14 |
| Pedomicrobium | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.17 |
| Pseudomonas | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.78 | 0.19 | 0.22 |
| Variovorax | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.07 |
| Mycobacterium | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.13 |
| Streptomyces | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.10 |
| Rhodobacter | 0.11 | 1.83 | 0.77 | 1.14 | 0.47 |
| Caulobacter | 0.11 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.14 |
| Terrimonas | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| Afipia | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.227 | 0.17 | 0.19 |
| Paracoccus | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Cupriavidus | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Shinella | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.055 | 0.02 | 0.08 |
| Microbacterium | 0.02 | 0.004 | - | - | 0.01 |
| Corynebacterium | 0.02 | 0.004 | - | - | 0.004 |
| Propionibacterium | 0.02 | 0.004 | - | - | 0.004 |
| Achromobacter | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | 0.04 |
| Chromobacterium | 0.02 | - | - | - | - |
| Brevibacillus | - | - | 0.004 | - | - |
| Methylobacterium | - | - | - | 0.07 | 0.01 |
| Bosea | - | - | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Bacillus | - | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Erythrobacter | - | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Aurantimonas | - | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| Rhizobium | - | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.16 |
| Aeromonas | - | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
| Arthrobacter | - | 0.02 | - | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Lapillicoccus | - | - | - | 0.004 | - |
| Leifsonia | - | - | 0.03 | 0.004 | - |
| Terrabacter | - | - | 0.07 | - | 0.05 |
| Cellulomonas | - | - | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.004 |
| Nocardia | - | 0.02 | 0.09 | - | 0.03 |
| Geodermatoiphilus | - | - | - | - | 0.004 |
| Cytophaga | - | 0.004 | - | - | - |
| Flavobacterium | - | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.18 |
| Sphingobacterium | - | 0.004 | 0.01 | - | - |
| Lysinibacillus | - | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Staphylococcus | - | - | - | 0.004 | - |
| Agrobacterium | - | 0.01 | - | 0.01 | - |
| Sulfitobacter | - | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.09 |
| Duganella | - | 0.02 | - | - | - |
| Total | 6.1 | 16.6 | 12.8 | 11.5 | 11.4 |
| TCLP Test | Composition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn Leached | Zn Leached | Mn | Zn | |||
| Mn-system Mn/Zn-system Control: MnO2 | mg/L | % | mg/L | % | mg/g | mg/g |
| 1.72 | 14.7 | BDL | <0.01 | 234.5 | BDL | |
| 1.34 | 11.1 | BDL | <0.01 | 241.4 | 0.94 | |
| BDL | <0.01 | - | - | 537.0 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurogi, F.; Liu, P.; Okibe, N. Leveraging Biomineralization in Repurposed Stirred Reactors for Mn/Zn Removal from Mine Water: Insights from a Laboratory-Scale Study. Minerals 2025, 15, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030211
Kurogi F, Liu P, Okibe N. Leveraging Biomineralization in Repurposed Stirred Reactors for Mn/Zn Removal from Mine Water: Insights from a Laboratory-Scale Study. Minerals. 2025; 15(3):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030211
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurogi, Fumiya, Peiyu Liu, and Naoko Okibe. 2025. "Leveraging Biomineralization in Repurposed Stirred Reactors for Mn/Zn Removal from Mine Water: Insights from a Laboratory-Scale Study" Minerals 15, no. 3: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030211
APA StyleKurogi, F., Liu, P., & Okibe, N. (2025). Leveraging Biomineralization in Repurposed Stirred Reactors for Mn/Zn Removal from Mine Water: Insights from a Laboratory-Scale Study. Minerals, 15(3), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030211






