Assessment of Cobalt Recovery from Copper Tailings by Leaching with a Choline Chloride–Citric Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effects of Pretreatment and Oxidant Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tailings Origin and Characterization
2.2. Reagents and DES Preparation
2.3. Tailing Pre-Leaching Procedures
2.3.1. Froth Flotation
2.3.2. Chlorination
2.3.3. Roasting
2.4. Leaching Test
3. Results
3.1. Tailing Characterization
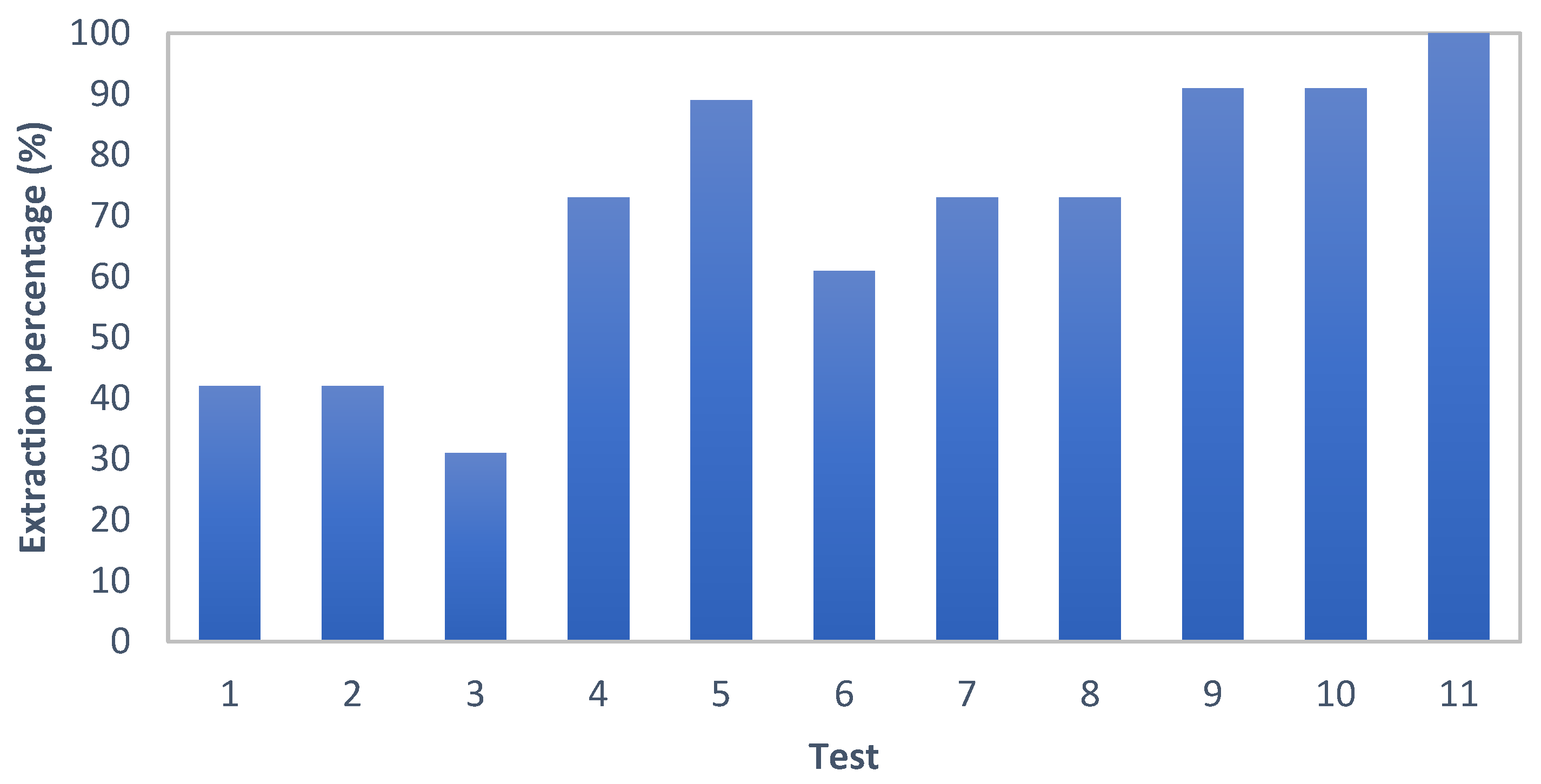
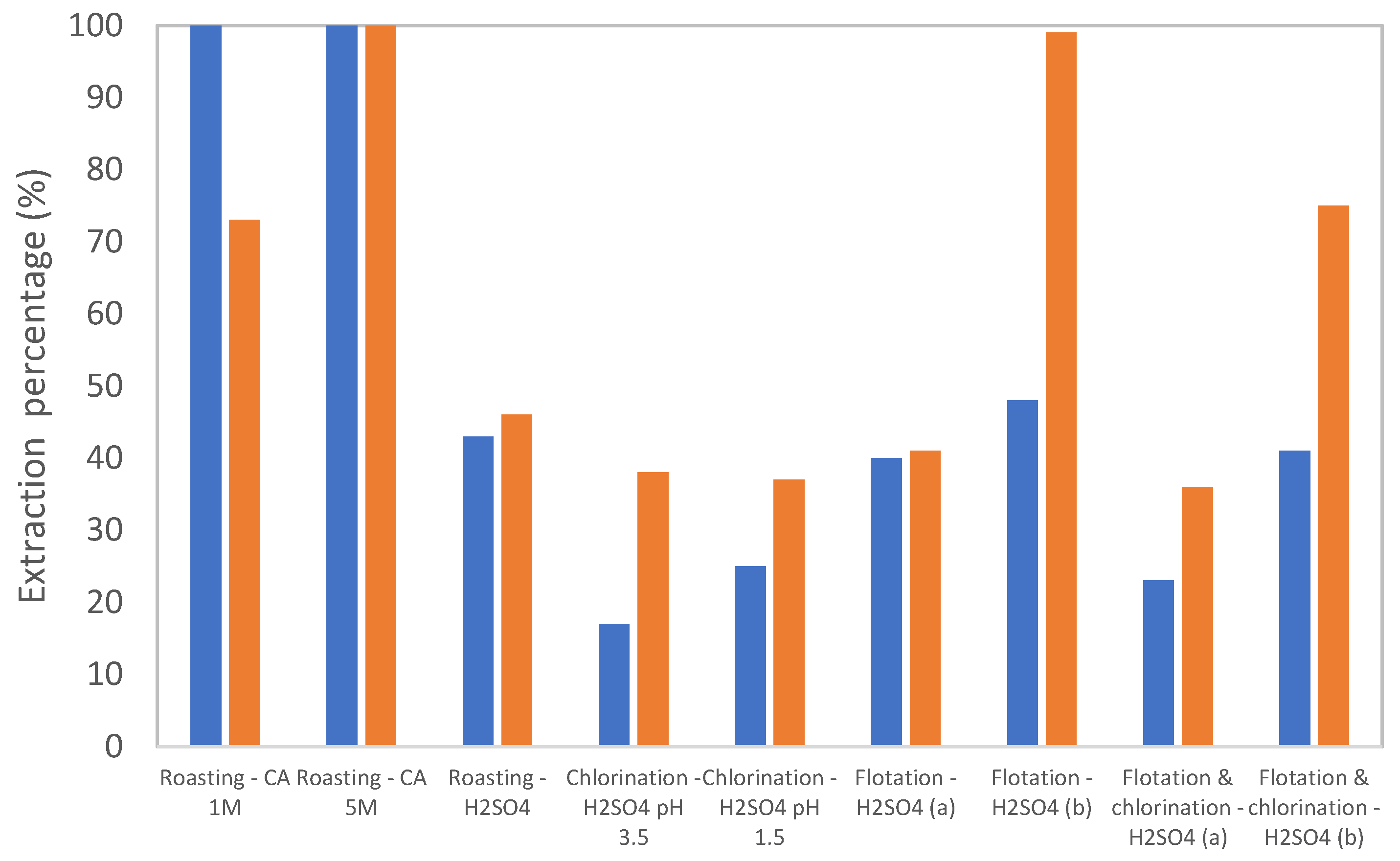
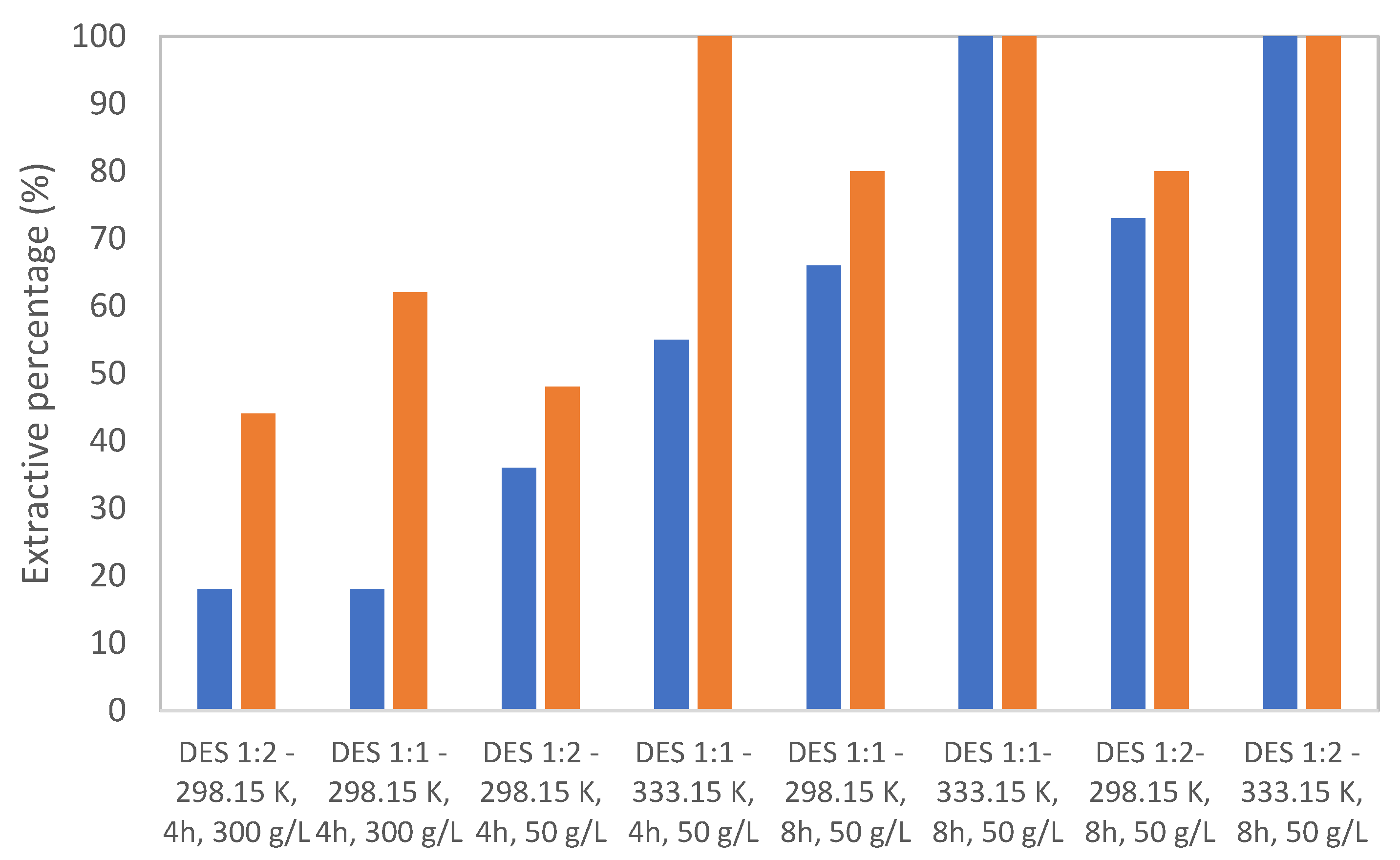
3.2. Leaching Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Leachate Chemistry and Oxidant Demand
4.2. Matrix Effects and Selectivity (Cu/Fe/S)
4.3. Particle Size: Liberation vs. Diffusion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- P. DE Nacional Depósitos De Relaves. Depósitos de Relaves para una Minería Sostenible. Available online: www.minmineria.gob.cl/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Datos Públicos Depósito de Relaves—SERNAGEOMIN. Available online: https://www.sernageomin.cl/datos-publicos-deposito-de-relaves/?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- González, J.L.; Onederra, I. Environmental Management Strategies in the Copper Mining Industry in Chile to Address Water and Energy Challenges—Review. Mining 2022, 2, 197–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, G.; Carrizo, D.; Salvi, S.; Vela, I.; Pablo, M.; Pérez, A. Tracking Cobalt, REE and Gold from a Porphyry-Type Deposit by LA-ICP-MS: A Geological Approach towards Metal-Selective Mining in Tailings. Minerals 2020, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, R.; De Miguel, E.; Cacciuttolo, C.; Atencio, E. Past, Present, and Future of Copper Mine Tailings Governance in Chile (1905–2022): A Review in One of the Leading Mining Countries in the World. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, N.; Kraslawski, A.; Cisternas, L.A. Towards mine tailings valorization: Recovery of critical materials from Chilean mine tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtnasan, E.; Kumar, A.; Wang, J.-P. Correlation between Thermodynamic Studies and Experimental Process for Roasting Cobalt-Bearing Pyrite. Metals 2024, 14, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinkaya, P.; Liipo, J.; Kolehmainen, E.; Haapalainen, M.; Leikola, M.; Lundström, M. Leaching of Trace Amounts of Metals from Flotation Tailings in Cupric Chloride Solutions. Min. Met. Explor. 2019, 36, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaine, Q.; Tijsseling, L.T.; Glass, H.J.; Törmänen, T.; Butcher, A.R. Geometallurgy of cobalt ores: A review. Min. Eng. 2021, 160, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štirbanović, Z.; Urošević, D.; Đorđević, M.; Sokolović, J.; Aksić, N.; Živadinović, N.; Milutinović, S. Application of Thionocarbamates in Copper Slag Flotation. Metals 2022, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brest, K.K.; Henock, M.M.; Guellord, N.; Kimpiab, M.; Kapiamba, K.F. Statistical investigation of flotation parameters for copper recovery from sulfide flotation tailings. Results Eng. 2021, 9, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bu, X.; Xie, G.; Chelgani, S.C. A comparative study on the influence of mono, di, and trivalent cations on the chalcopyrite and pyrite flotation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, V.; Roca, A.; Benavente, O.; Cruells, M.; Melo, E. The Effects of Sulphuric Acid and Sodium Chloride Agglomeration and Curing on Chalcopyrite Leaching. Metals 2021, 11, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, J.P.; Barrueto, Y.; Ipinza, J.; Quispe, N. Solid reaction products from NaCl+H2SO4 chemical pre-treatment of chalcopyrite. Can. Metall. Q. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Moraga, C.; Torres, D.; Saldaña, M.; Pérez, K.; Gálvez, E. Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review. Minerals 2021, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atesoglu, G.; Atilgan, İ. Effect of Roasting Temperature on the Leaching of Chalcopyrite Concentrate in Sulphuric Acid. Min. Met. Explor. 2022, 39, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, E.A.; Potgieter, H.; Mondlane, F.; Skosana, N.P.; Teimouri, S.; Nyembwe, J.K. Concurrent leaching of copper and cobalt from a copper–cobalt ore using sulfuric and organic acids. Min. Eng. 2024, 216, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karppinen, A.; Seisko, S.; Lundström, M. Atmospheric leaching of Ni, Co, Cu, and Zn from sulfide tailings using various oxidants. Min. Eng. 2024, 207, 108576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M. Understanding gangue acid consumption in copper sulfide heap leaching: Predicting the impact of carbonates, silicates and secondary precipitates. Min. Eng. 2021, 171, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokić, M.; Marković, B.; Stanković, S.; Kamberović, Ž.; Štrbac, N.; Manojlović, V.; Petronijević, N. Kinetics of Chalcopyrite Leaching by Hydrogen Peroxide in Sulfuric Acid. Metals 2019, 9, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyo, H.A.; Jia, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liang, X.; Ruan, R.; Niu, X. Effect of particle size on chalcocite dissolution kinetics in column leaching under controlled Eh and its implications. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2020, 56, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuduwe, M.J.; Shemi, A.; Ndlovu, S. Extraction of Gold from Tailings Using Ethaline Deep Eutectic Solvent. Minerals 2024, 14, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J. Utilizing Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Recycle, Recovery, Purification and Miscellaneous Uses of Rare Earth Elements. Molecules 2024, 29, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q. Highly Efficient Recovery of Cobalt-Ion Containing Waste Deep Eutectic Electrolytes: A Sustainable Solvent Extraction Approach. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202402422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.H.; Wen, J.X.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Co(II), Mn(II), and Ni(II) by solvent extraction with Cyanex 272 and D2EHPA from the sulfuric acid leaching solution of spent lithium-ion batteries. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process 2024, 60, 193742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical recovery of cobalt from lithium-ion battery cathode materials using deep-eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, İ.; Şahbudak, K.; Kartal, L.; Alkan, B. Optimization of sulfuric acid leaching of roasted chalcopyrite concentrate with Box–Wilson experimental design. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, T.; van Wyk, A.P.; Bradshaw, S.M.; Akdogan, G. Citric Acid Leaching Performance at High Solid-to-Liquid Ratios for Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling. Min. Met. Explor. 2024, 41, 3463–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Lambert, H.; Plessis, C.A.D. Lime use and functionality in sulphide mineral flotation: A review. Min. Eng. 2019, 143, 105922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, M. Effect of sulfidization on the surface property and flotation behavior of heterogenite. Min. Eng. 2023, 204, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo-Gonzalez, M.d.M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M.; Muñoz-Espinosa, M.; Rodriguez-Maroto, J.M.; Villen-Guzman, M. Extraction and selective precipitation of metal ions from LiCoO2 cathodes using citric acid. J. Power Sources 2024, 592, 233870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, E.A.; Fedai, Y.; Potgieter, J.H. Hydrometallurgical Leaching of Copper and Cobalt from a Copper–Cobalt Ore by Aqueous Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Solutions. Minerals 2025, 15, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninayan, R.; Levshakova, A.S.; Khairullina, E.M.; Vezo, O.S.; Tumkin, I.I.; Ostendorf, A.; Logunov, L.S.; Manshina, A.A.; Shishov, A.Y. Water-induced changes in choline chloride-carboxylic acid deep eutectic solvents properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 679, 132543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Ionic Liquids and Deep-Eutectic Solvents in Extractive Metallurgy: Mismatch Between Academic Research and Industrial Applicability. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarthy, J.; Nosrati, A.; Skinner, W.; Addai-Mensah, J. Acid leaching and rheological behaviour of a siliceous goethitic nickel laterite ore: Influence of particle size and temperature. Min. Eng. 2015, 77, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, J.; Salo, M.; Khoshkhoo, M.; Sundkvist, J.E.; Kinnunen, P. Bioleaching of cobalt from sulfide mining tailings; a mini-pilot study. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, O. Cobalt and Copper Recovery from the Ancient Flotation Tailings using Selective Sulfation Roast-Leaching Process. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2019, 55, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
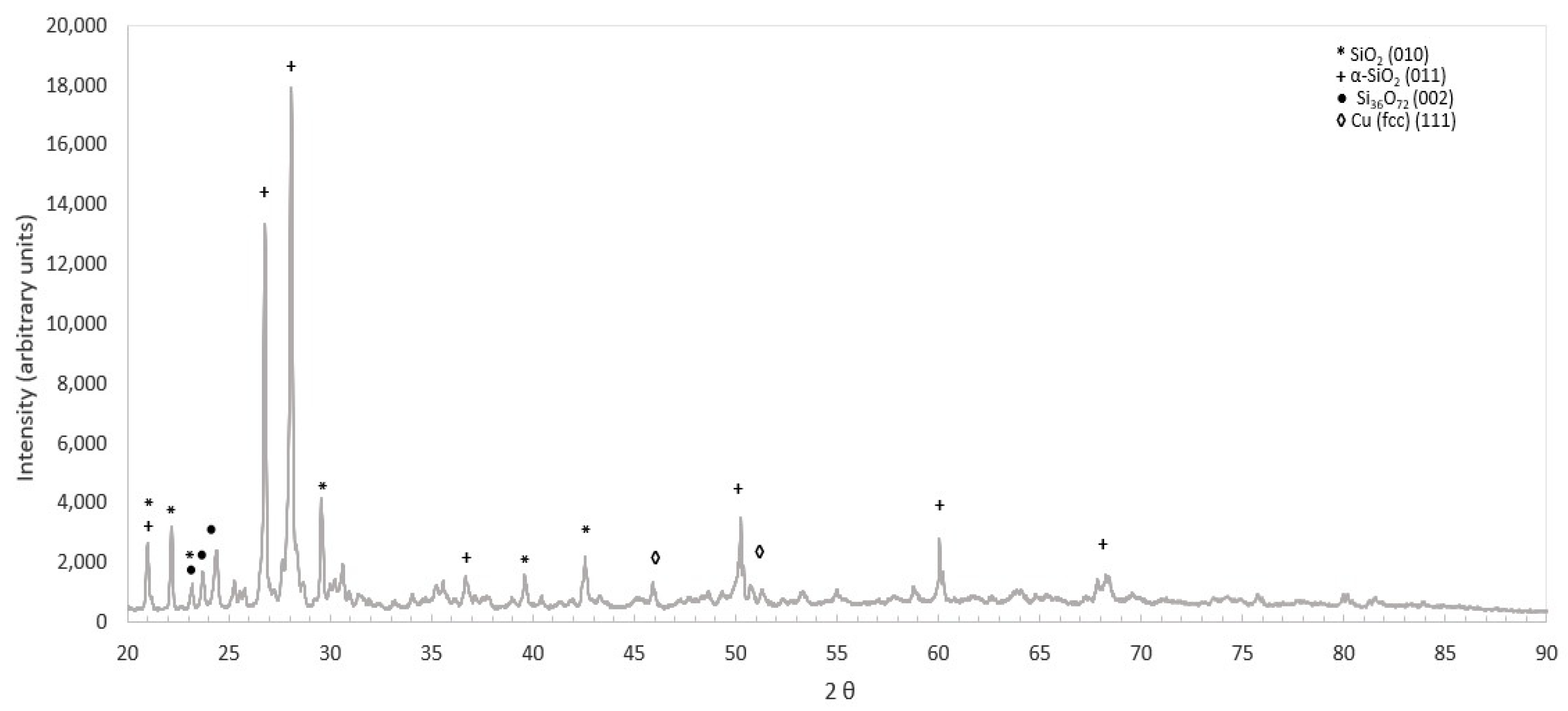
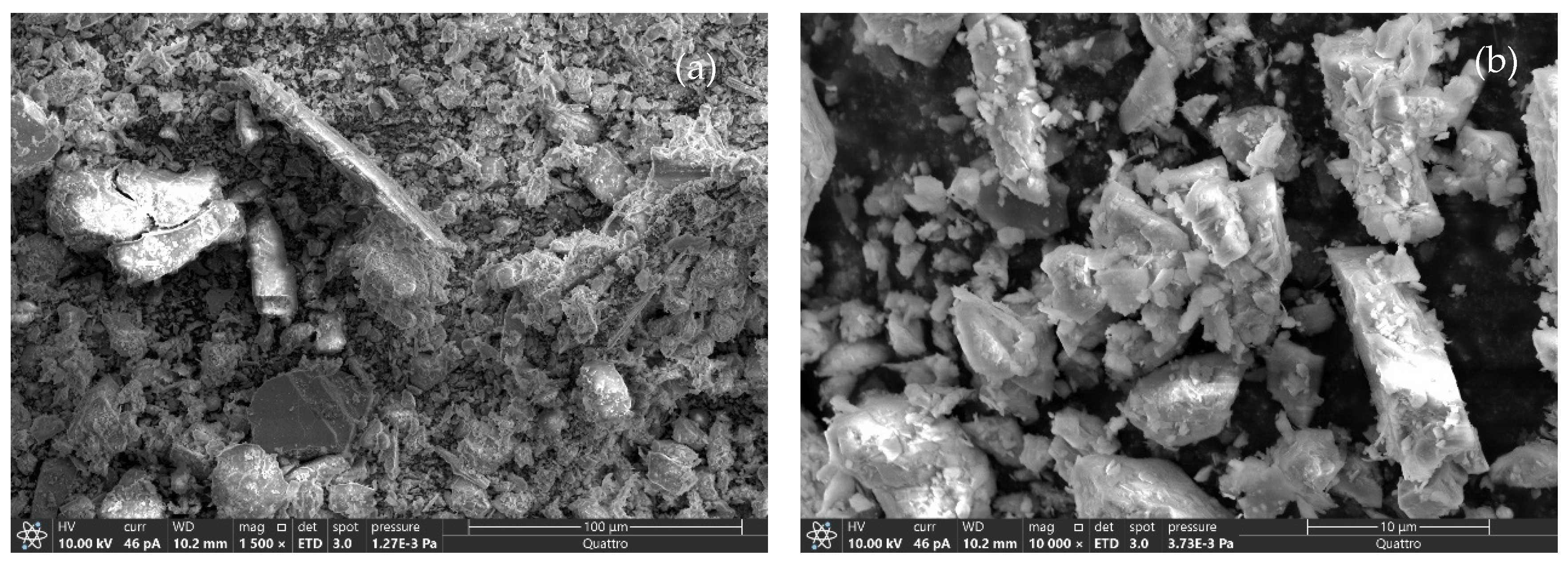
| Metals | Co (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | Al % | Ca % | Fe % | K % | Mg % | Na % | Total S % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration * | 33.3 | 3145.1 | 6.88 | 4.47 | 8.56 | 1.52 | 1.71 | 3.05 | 0.58 |
| Authors | Matrix | Route/Leaching Reagent | Key Conditions | Co Recovery | Pros and Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peeters 2020 [26] | LCO (LIB cathode) | DES ChCl:CA (2:1) + 35 wt% H2O; use of Cu/Al as in situ reducing agents. | 40 °C, S/L = 20 g L−1; 900 rpm; with Cu and Al present 1 h | ≈98% Co; Li ≈ 93% | High extraction at low T; “green” solvent; integrated separation route Viscosity/water to be controlled; need for metal reducing agents (depending on feed) |
| Mäkinen 2020 [36] | Sulfide tailings (pyrite-rich) | Bioleaching (Fe/S oxidants) in stirred tank (continuous-batch mode) | 30 °C, 100 g L−1 solids, 10 L bioreactor; adapted consortium ≈10 d | ≈87% Co (Zn 100%, Ni 67%, Cu 43%) | “Soft” reagents, low chemical consumption; scalable to sulfide tailings Slow (days), sensitivity to pH/Fe3+/jarosites; biological control required |
| Özer 2019 [37] | Old tailings (Lefke, Cyprus) | Sulfate roasting + Na2SO4 25% → leaching | 700 °C roasting; Na2SO4 promotes selective sulfation Hours (roasting) + leaching | 90.1% Co, 71.2% Cu | Improved selectivity; high Co in leachate High energy and gases; prior thermal stage; SOx/Na control in circuit. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrueto, Y.; Ibáñez, J.P.; Veliz, M.; Santana, M.; Ojeda, J.; Carlesi, C. Assessment of Cobalt Recovery from Copper Tailings by Leaching with a Choline Chloride–Citric Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effects of Pretreatment and Oxidant Use. Minerals 2025, 15, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111187
Barrueto Y, Ibáñez JP, Veliz M, Santana M, Ojeda J, Carlesi C. Assessment of Cobalt Recovery from Copper Tailings by Leaching with a Choline Chloride–Citric Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effects of Pretreatment and Oxidant Use. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111187
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrueto, Yahaira, Juan Patricio Ibáñez, Miguel Veliz, Matias Santana, José Ojeda, and Carlos Carlesi. 2025. "Assessment of Cobalt Recovery from Copper Tailings by Leaching with a Choline Chloride–Citric Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effects of Pretreatment and Oxidant Use" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111187
APA StyleBarrueto, Y., Ibáñez, J. P., Veliz, M., Santana, M., Ojeda, J., & Carlesi, C. (2025). Assessment of Cobalt Recovery from Copper Tailings by Leaching with a Choline Chloride–Citric Acid Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effects of Pretreatment and Oxidant Use. Minerals, 15(11), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111187






