Petrography and Geochemistry of the Middle Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous Limestones from the Mustafakemalpaşa Quarries, Bursa, Turkey: The Depositional Environmental and Diagenetic Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
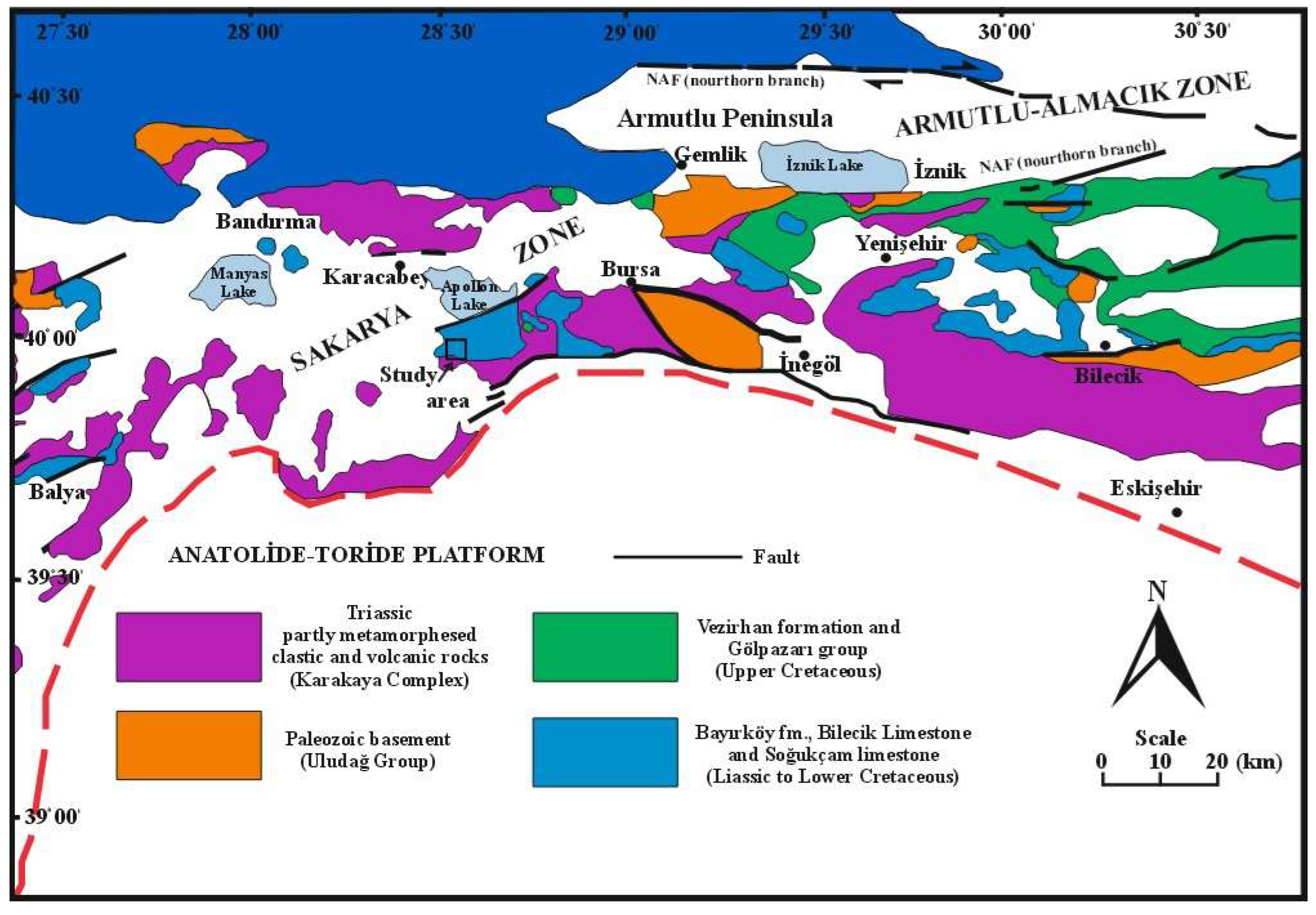
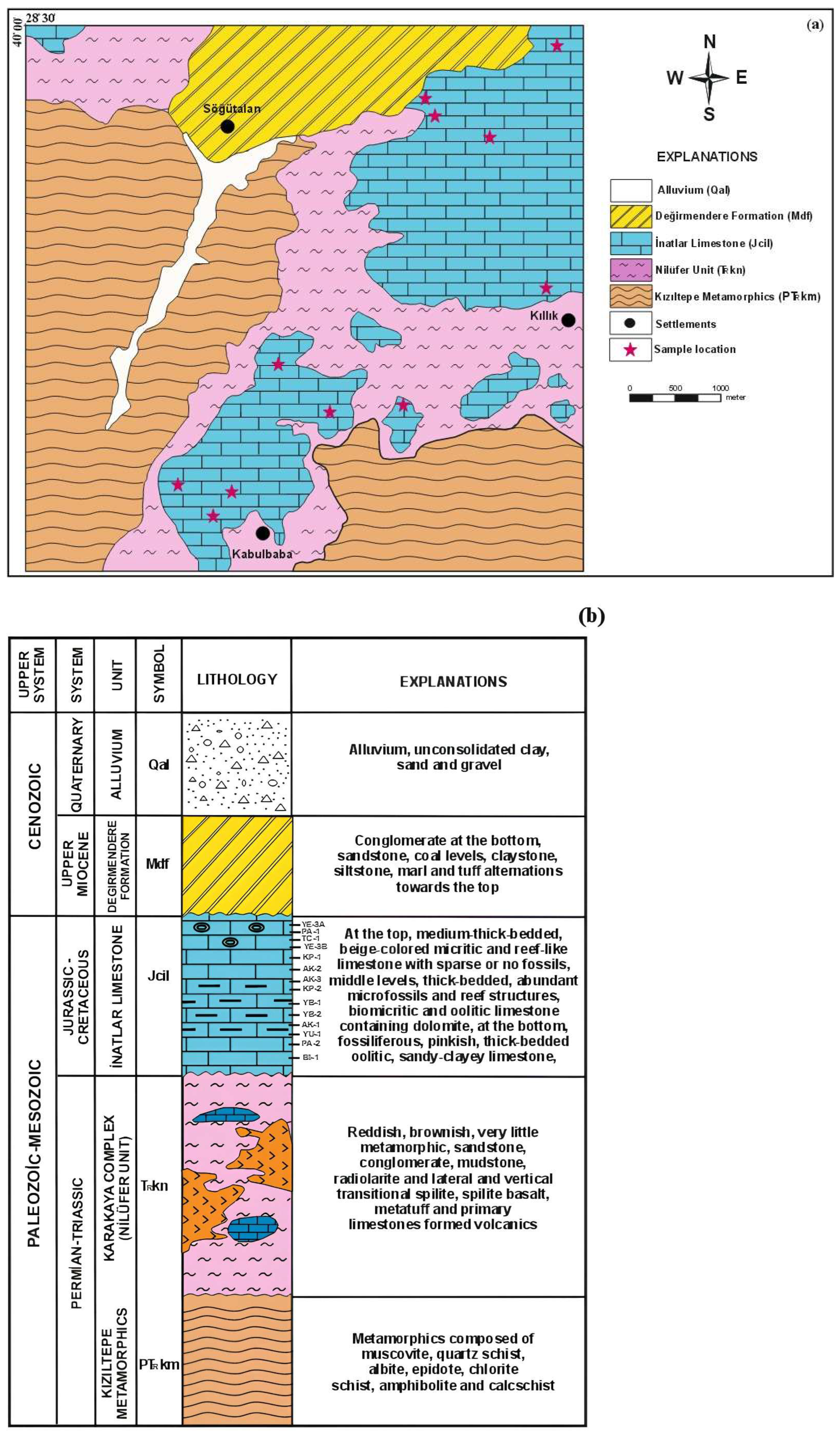
2. Geological Setting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mineralogical–Petrographic Analysis
3.2. Geochemical Analysis
3.3. Isotope Analyses
4. Results
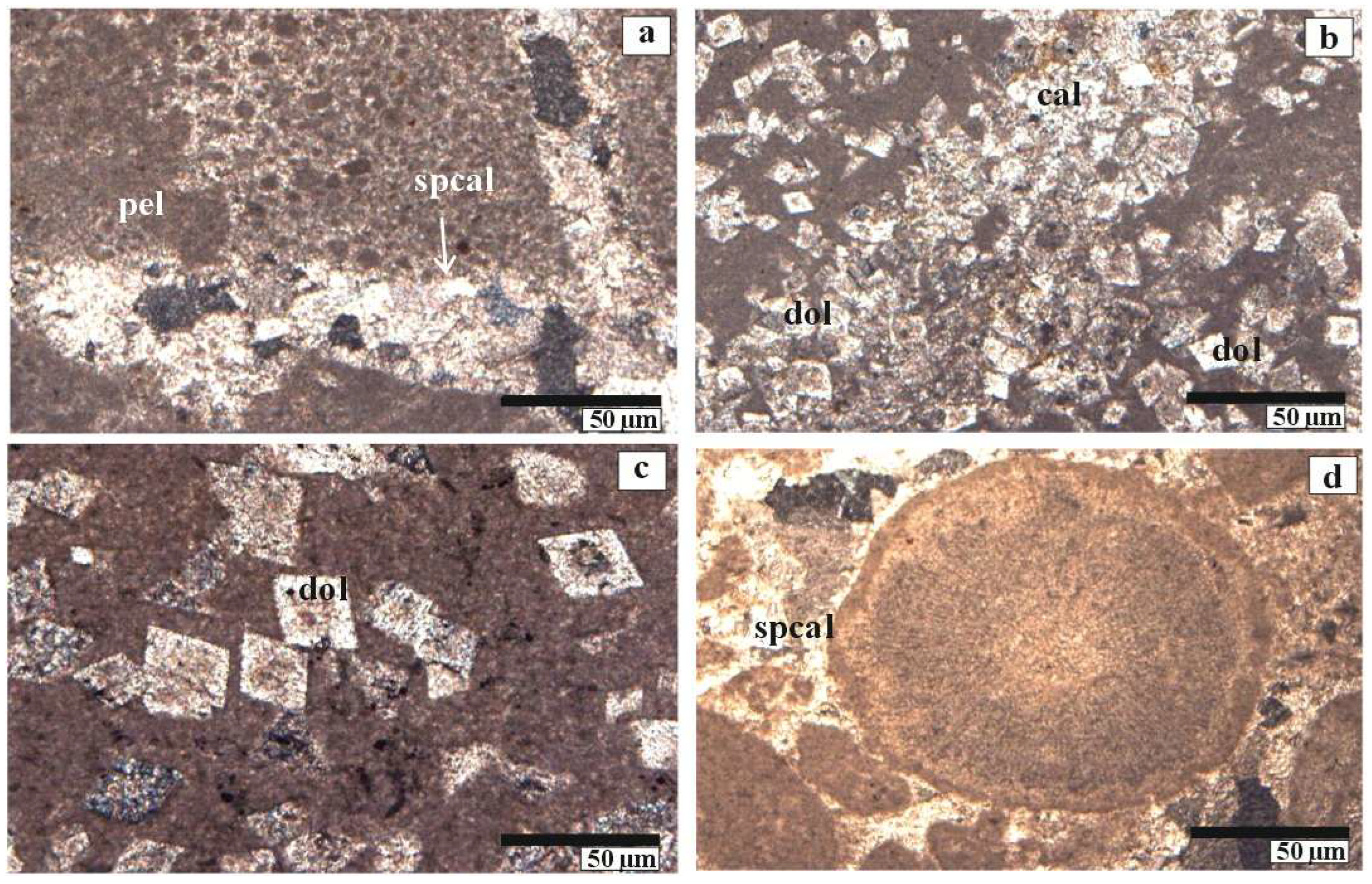
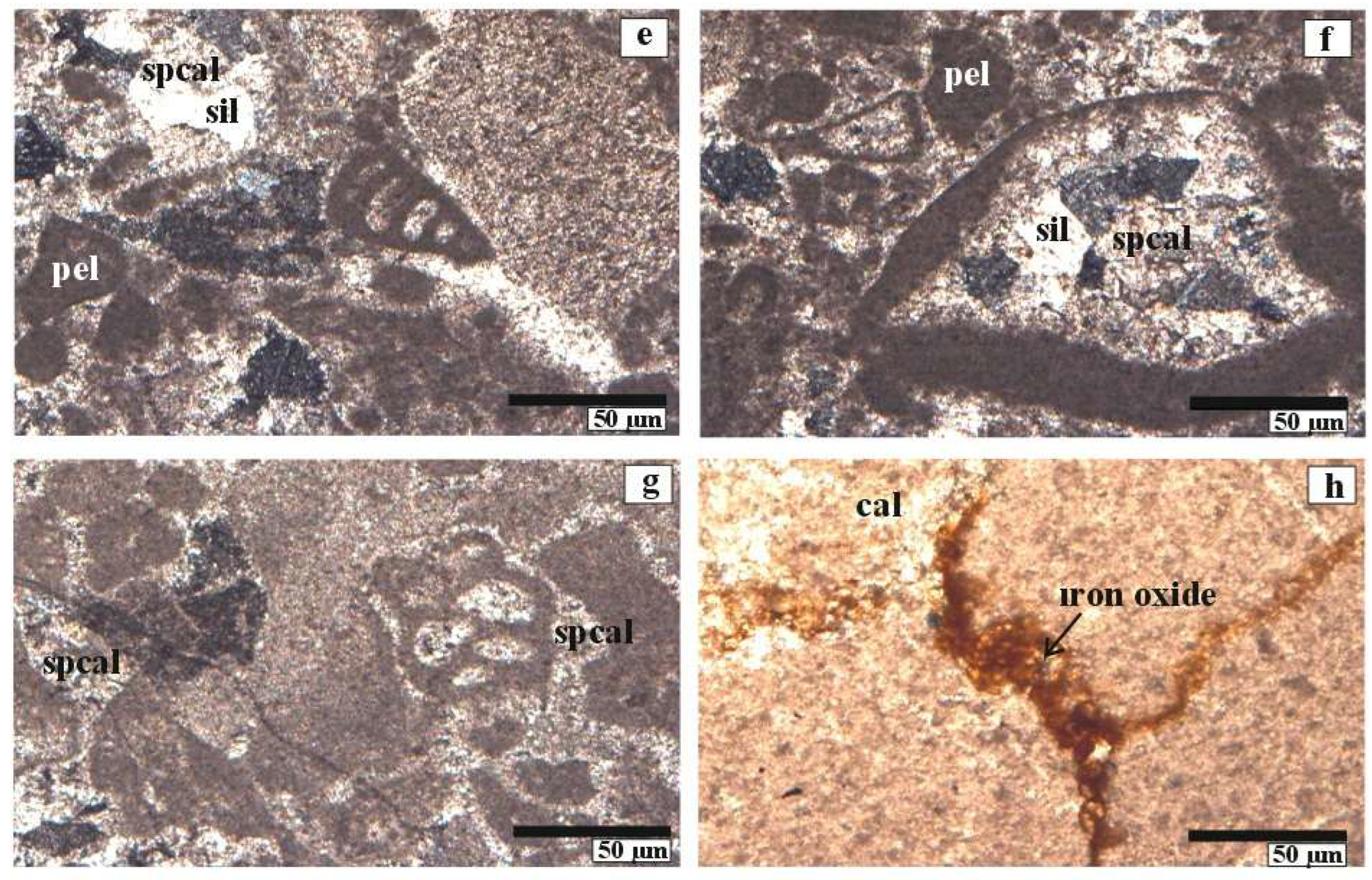
4.1. Petrographic Characteristics
4.1.1. Optical Microscopy and Diagenetic Features of Inatlar Limestone
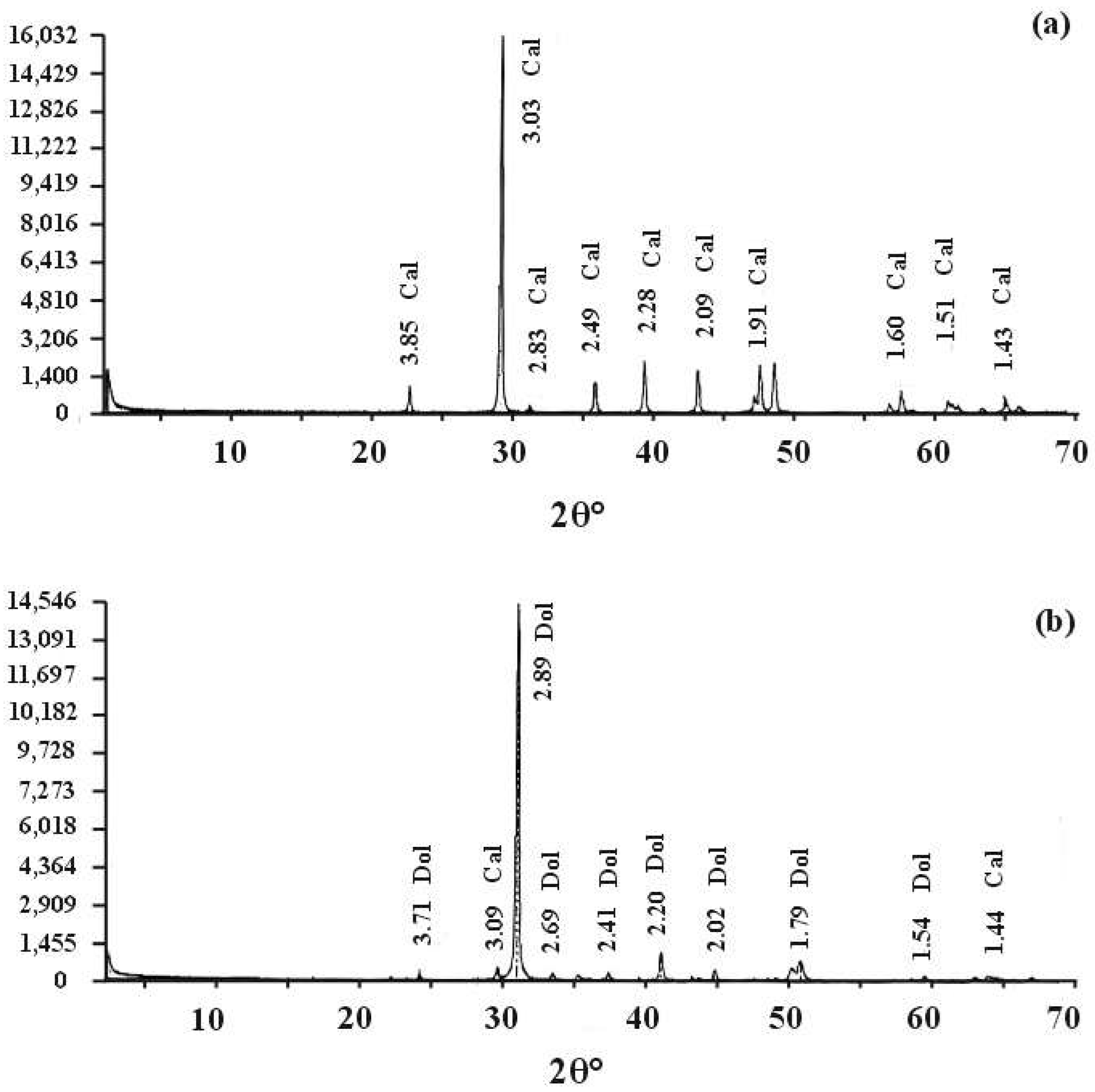
4.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
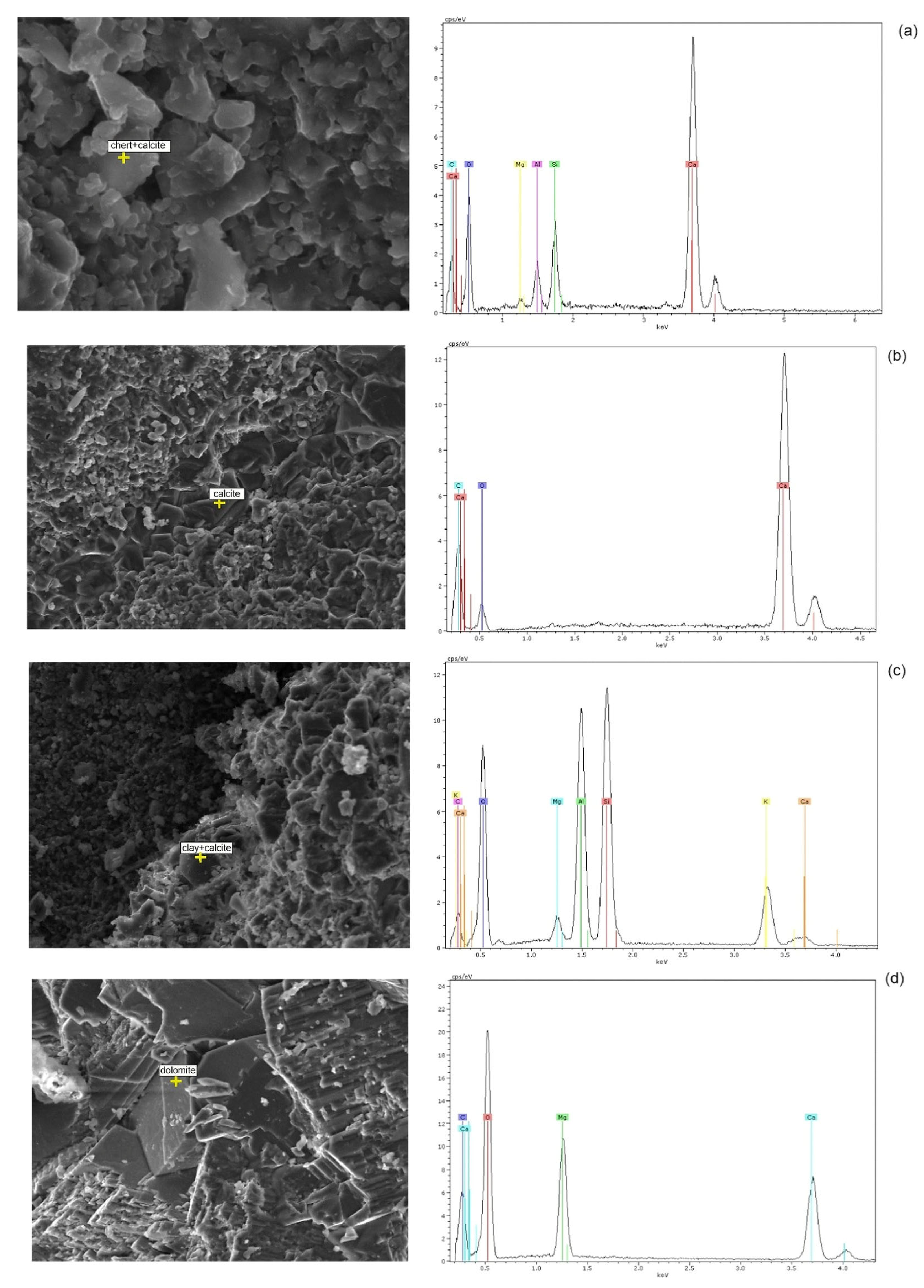
4.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Investigations
4.2. Geochemistry
4.2.1. Major–Minor Oxides’ Contents
4.2.2. Trace and Rare Earth Element Composition
4.2.3. Carbon–Oxygen Isotope Compositions
5. Discussion
5.1. Depositional Environment and Diagenetic Processes
5.2. Paleo-Environmental Implications
5.2.1. Paleo-Redox Conditions
5.2.2. Paleosalinity
6. Conclusions
- -
- Field observations show that the limestone varies from dark to light beige, locally yellowish to grayish, with medium-bedded, karstic features, fractures, fossil content, and chert nodules. This commercially significant limestone includes siliceous, micritic, fossiliferous, and dolomitic varieties, reflecting its complex mineralogical composition.
- -
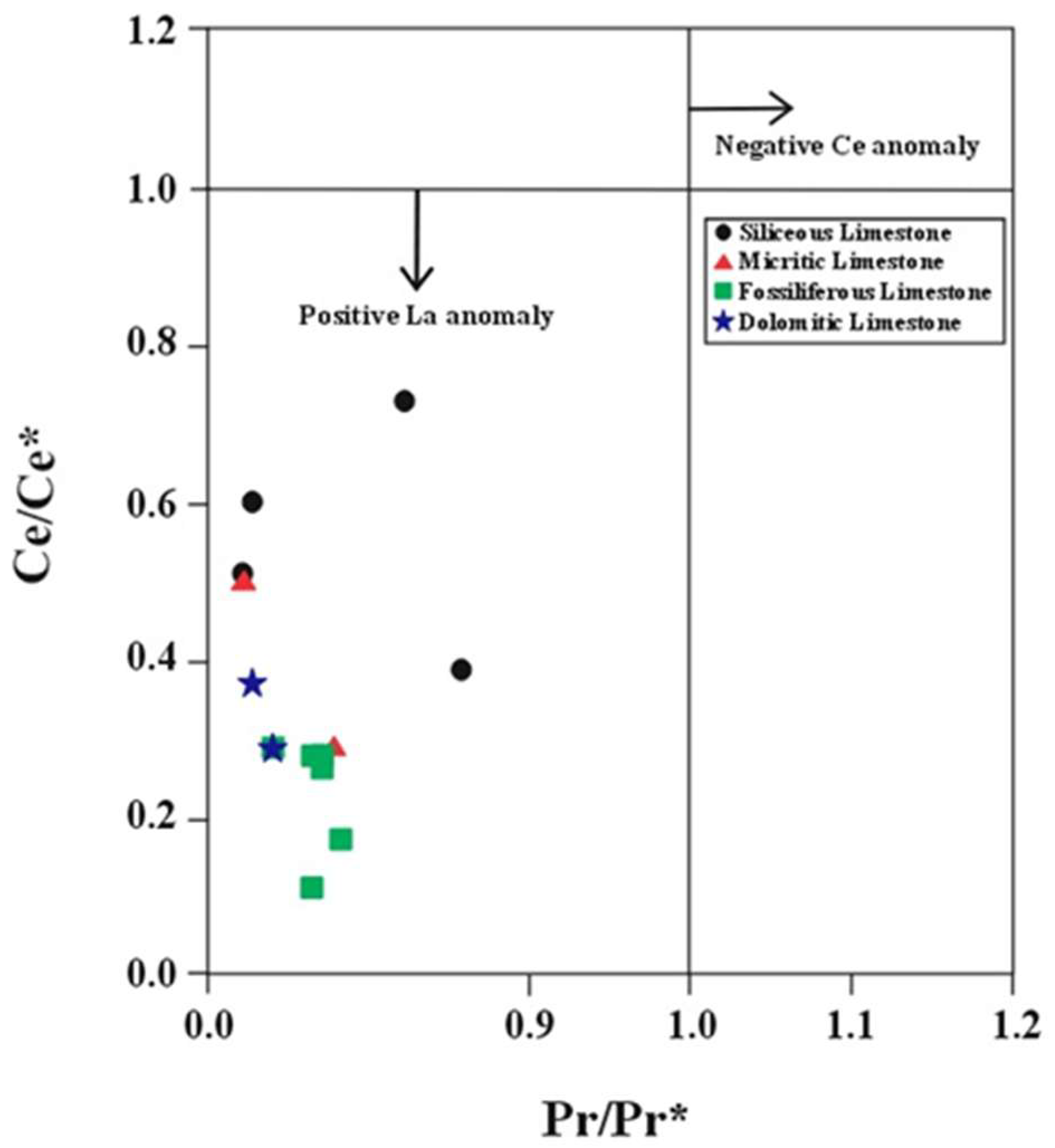
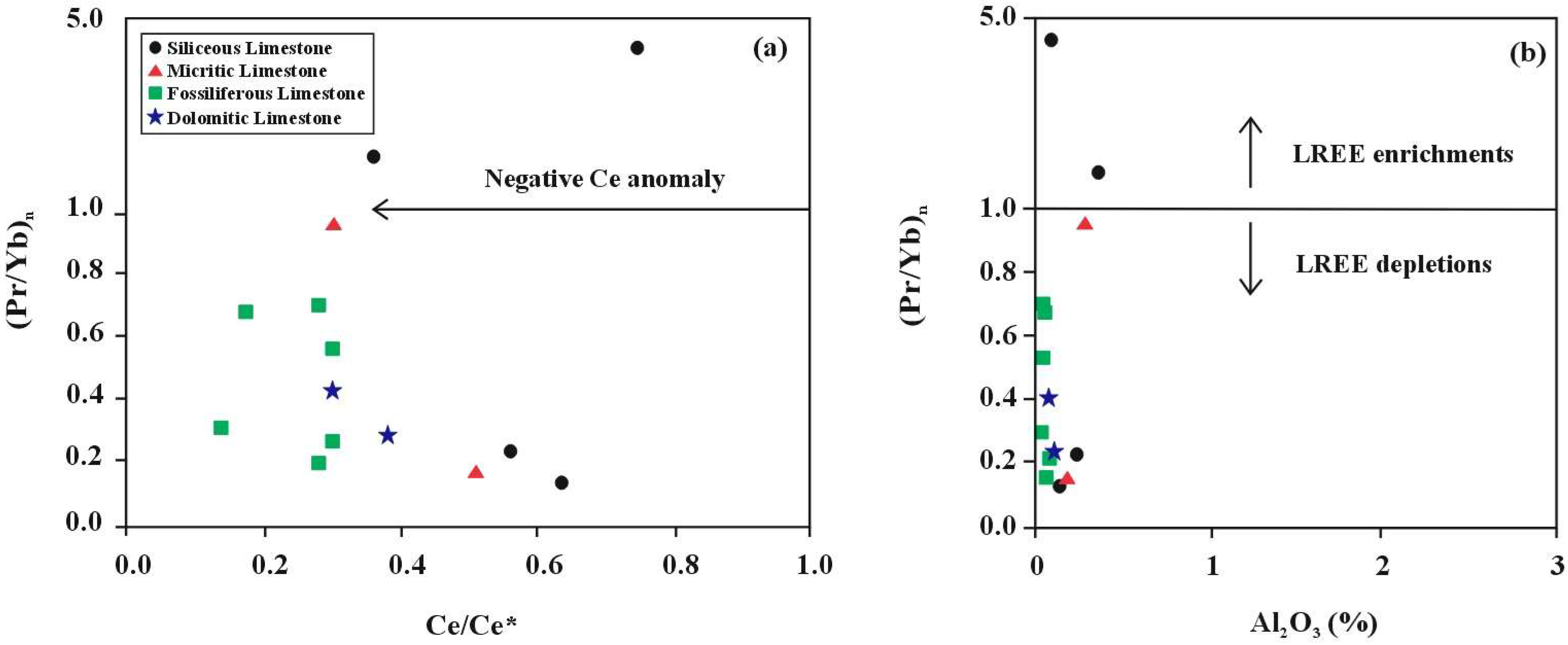
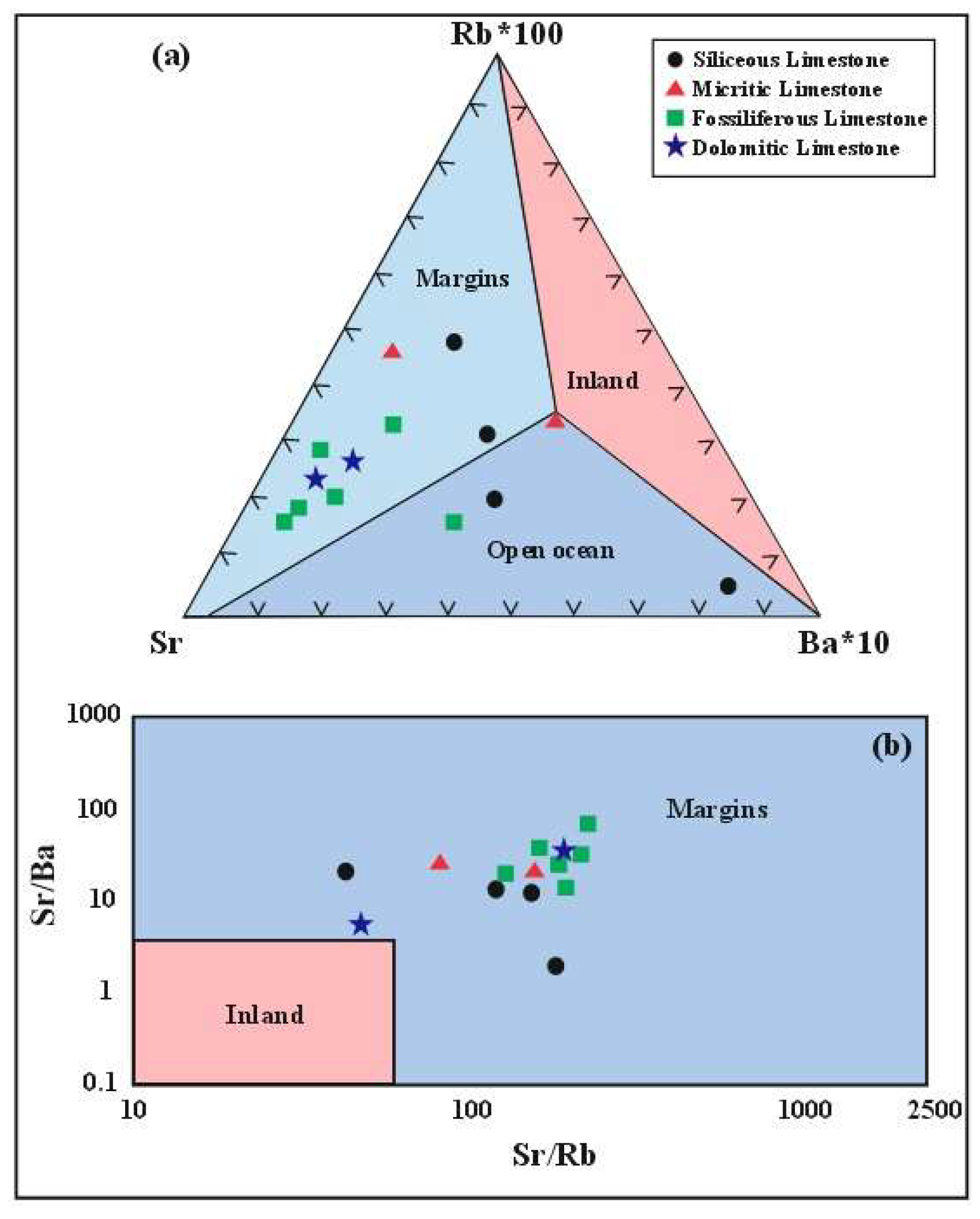
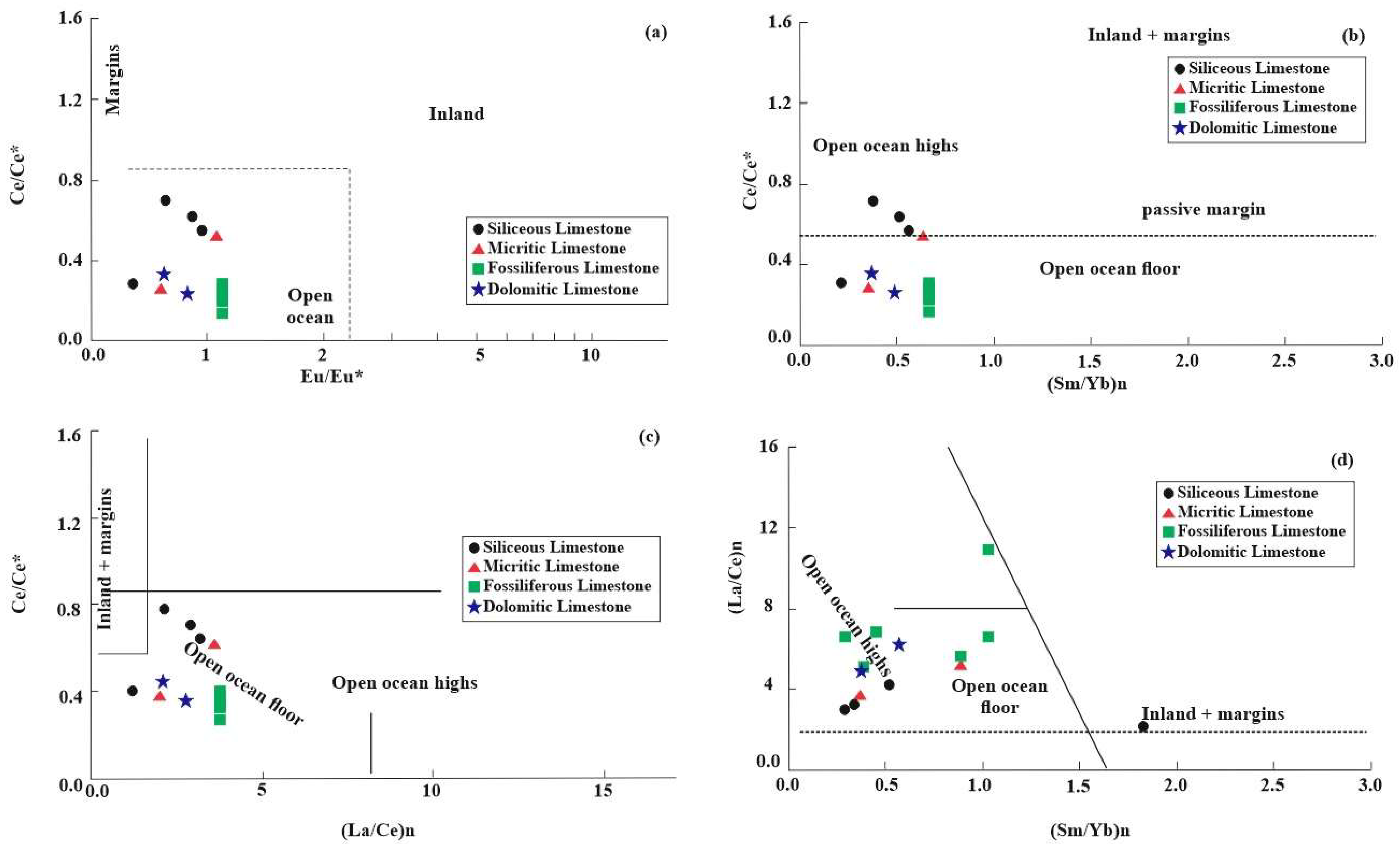
- The Rb-Sr-Ba ternary diagram and Sr/Ba and Sr/Rb ratios place the limestone environment between the continental margin and open ocean settings. Further REEs ratio analyses (Eu/Eu*, Ce/Ce*, (La/Ce)n, and (Sm/Yb)n) support an open ocean depositional environment. Negative Ce and Eu anomalies, along with positive La anomalies and LREEs depletion, indicate the influence of early diagenetic processes.
- -
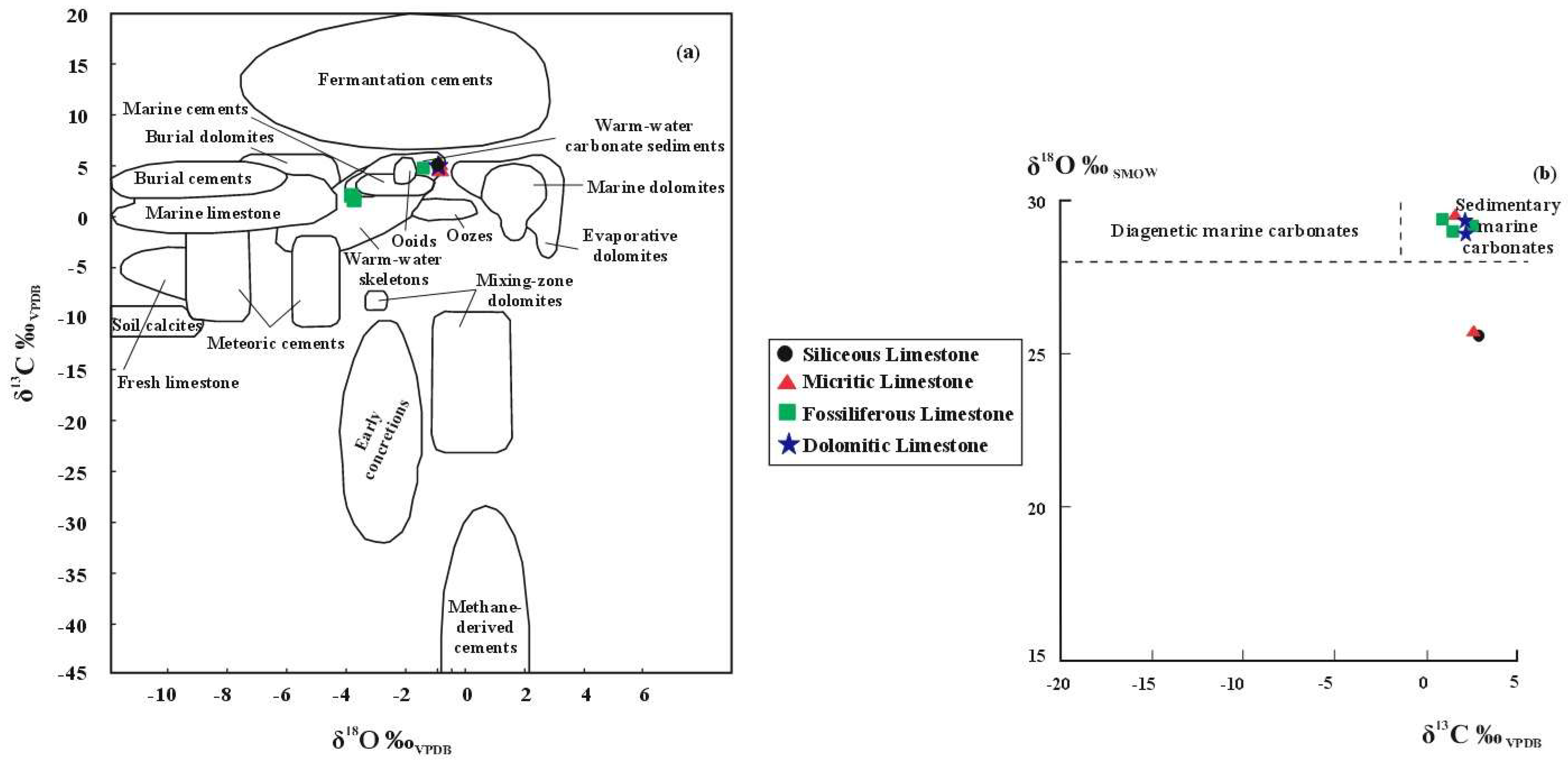
- İnatlar limestones are of marine origin according to their Z values. δ13C–δ18O isotopic values indicate that they fall within the areas of hot-water carbonate sediments and marine carbonate sediments.
- -
- The Y/Ho and Er/Nd ratios indicate that the İnatlar Limestones are affected by terrestrial material and diagenetic or detrital material.
- -
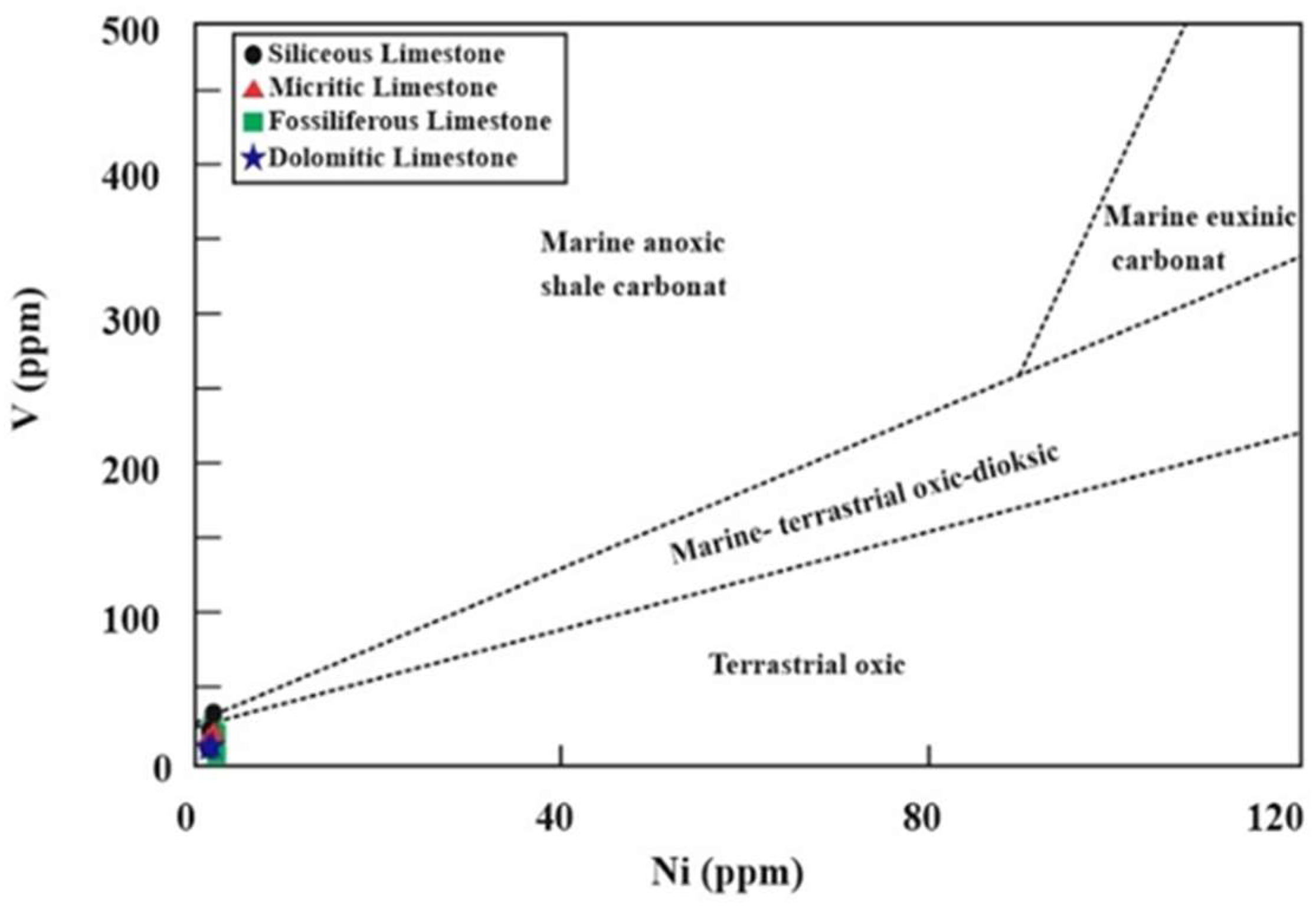
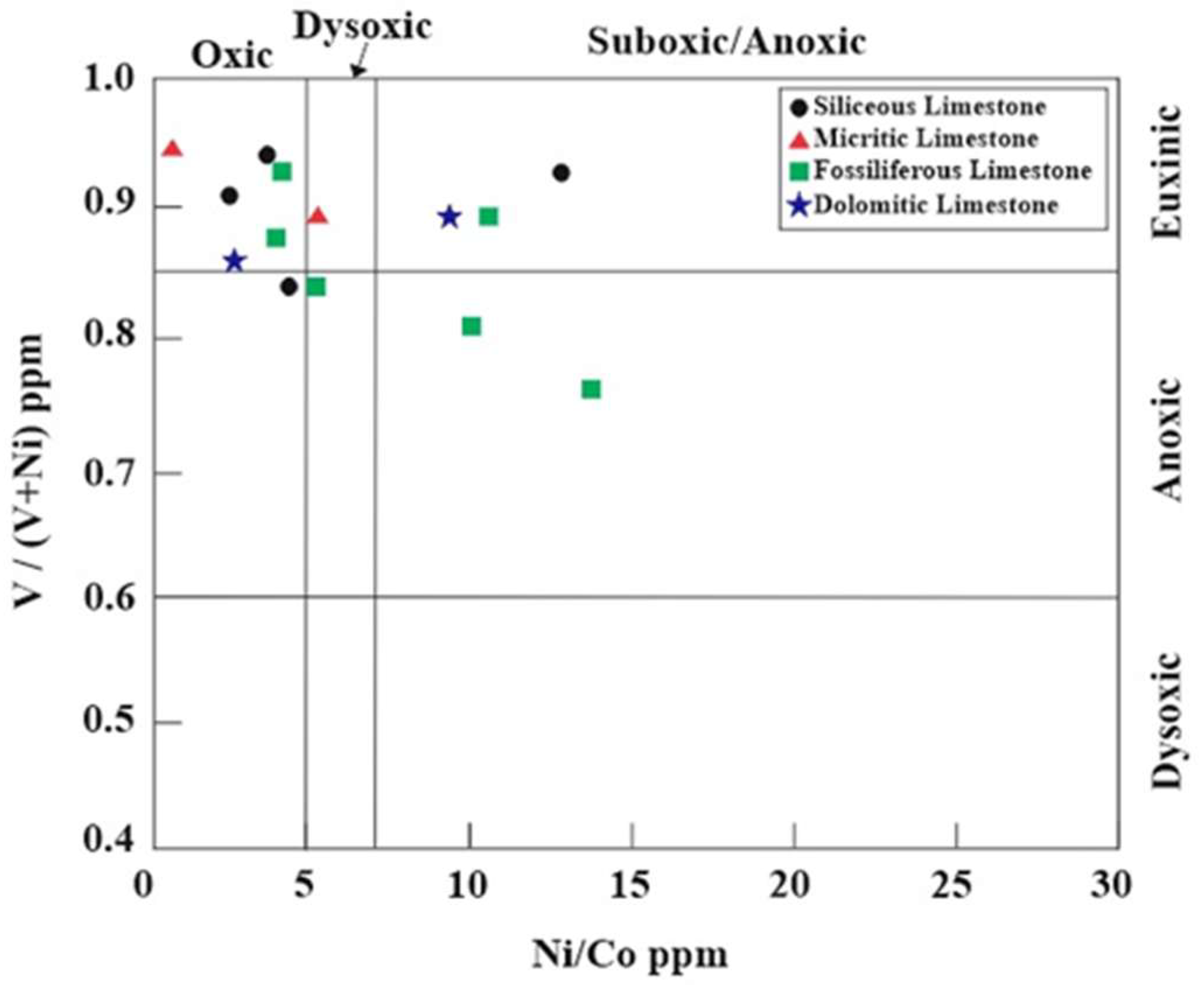
- Paleo-redox and paleosalinity conditions were evaluated through elemental anomalies and metal ratios. Variations in Ni and V concentrations suggest depositional environments ranging from terrestrial to marine–terrestrial oxic–dioxic, marine anoxic, and possible transitional conditions. V/(V + Ni) and Ni/Co ratios further reveal deposition under oxic to suboxic/anoxic and euxinic conditions, respectively, with salinity and reducing conditions exerting significant influence during limestone formation. According to V/Ni, Sr/Ba and Rb/Sr ratios, the İnatlar limestones reveal that they were in low-weathering and high-salinity paleoenvironmental conditions. These results collectively demonstrated the complex interplay of marine transgressions, redox fluctuations, and diagenesis of the Inatlar limestone.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirza, T.A.; Kalaitzidis, S.P.; Fatah, S.S.; Tsiotou, S. Petrographic and geochemical features of Gimo marble, Gole area, Kurdistan Region, Iraq: Constraints on its protolith’s origin and depositional environment. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2021, 25, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, O.; Eğin-Karaca, Y.; Kıray, D. Hacılar Ocağı kireçtaşının jeolojisi, petrografik ve jeokimyasal özellikleri (Batı Toroslar, Burdur). Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Fen Ve Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2023, 23, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeshomo, A.V.A. Geochemical assessment of limestone deposits around Omi Alayo-Akeluse Southwestern Nigeria. Earth Sci. Malays. 2024, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, M.; Elçi, H.; Akgündüz, S.; Tuğrul, A.; Dursun, G. Geological characterization of the Breccia Corallina (Marmor Sagarium) quarries in northwest Asia Minor. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2025, 34, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, R. Chapter 5 Carbonates as Hydrocarbon Source Rocks. In Developments in Petroleum Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 30, pp. 271–329. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Z.; Pang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Guo, K.; Li, P.; Li, W.; Liang, Y. Carbonate source rock with low total organic carbon content and high maturity as effective source rock in China: A review. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 176, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydam-Eker, Ç.; Arı, U.V. Geochemical characterization of late Jurassic–early Cretaceous age limestones from Gümüşhane (NE-Türkiye): Identification of the source of organic matter and paleo-environment conditions. Carbonates Evaporites 2023, 38, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, P.N.; Calagari, A.A.; Roldan, F.V.; Simmonds, V.; Siahcheshm, K. C and O stable isotopes and rare earth elements in the Devonian carbonate host rock of the Pivehzhan iron deposit, NE Iran. Geol. Acta 2018, 16, 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.; Liu, X.; Fan, T.; Duncan, I.J. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) geochemistry of reefal limestones in the Ordovician, Tarim Basin, NW China and their paleoenvironment implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, M.; Kırmacı, M.Z.; Al-Aasm, I.S. Geochemical characteristics of Upper Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous platform carbonates in Hazine Mağara, Gümüşhane (northeast Turkey): Implications for dolomitization and recrystallization. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 56, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, P.M. Modeling Hydrothermal Alteration and Dissolution in Carbonate Hosted Ore Deposits. Master’s Thesis, University of Tasmania, Lilyfield, Australia, 2022; 108p. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, P.; Santos, A.M.; Steed, G.; Silva, A.A.; Meere, P.; Corcoran, L.; Simonetti, A.; Unitt, R. The carbonate-hosted Gortdrum Cu-Ag(±Sb-Hg) deposit, SW Ireland: C-O-Sr-Nd isotopes and whole-rock geochemical signatures. J. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 248, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.; Klappa, C.F. Subaerial Exposure Environment. In Carbonate Depositional Environments; Scholle, P.A., Bebout, D.G., Moore, C.H., Eds.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1983; Volume 33, pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Choquette, P.W.; James, N.P. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists. Midyear Meeting (1985: Colorado School of Mines). In Paleokarst; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzullo, S.J. Geochemical and neomorphic alteration of dolomite: A review. Carbonates Evaporites 1992, 7, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, V.J.; Güven, N. Alunite, natroalunite and hydrated halloysite in Carlsbad Cavern and Lechuguilla Cave, New Mexico. Clays Clay Miner. 1996, 44, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuenbunchom, S.; Heward, A.P.; Makel, G. The reservoir geology of the ‘‘pre-tertiary’’ sequences of palaeokarst structures, gulf of Thailand. J. Geol. Soc. Thai 2000, 1, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dill, H.G.; Botz, R.; Luppold, F.W.; Henjes-Kunts, F. Hypogene and supergene alteration of the Late Palaeozoic Ratburi Limestone during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic (Thailand, Surat Thani Province). Implications for the concentration of mineral commodities and hydrocarbons. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2005, 94, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimmel, H.E. Trace element distribution in Neoproterozoic carbonates as palaeoenvironmental indicator. Chem. Geol. 2009, 258, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopelliti, G.; Neri, R.; Bellanca, A.; Stefano, P.; Barbieri, M. Sedimentology, petrography and geochemistry of a limestone breccia (Pietra di Billiemi) from north-west Sicily, Italy: Implications for evolution of the Tethyan basins around the Triassic/Jurassic boundary. Sedimentology 2009, 56, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fio, K.; Spangenberg, J.E.; Vlahovic, I.; Sremac, J.; Velic, I.; Mrinjek, E. Stable isotope and trace element stratigraphy across the Permian–Triassic transition: A redefinition of the boundary in the Velebit Mountain, Croatia. Chem. Geol. 2010, 278, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobia, F.H.; Aqrawi, A.M. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in carbonate rocks of the Mirga Mir Formation (Lower Triassic), Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelabu, I.O.; Opeloye, S.A.; Oluwajana, O.A. Petrography and geochemistry of Paleocene-Eocene (Ewekoro) limestone, eastern Benin basin, Nigeria: Implications on depositional environmentand post-depositional overprint. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, S.V.; Morin, G.L.F.; Bidzhova, L.; Botoucharov, N.; Геoргиев, C.B.; Гатиен, J.; Мoрин, Φ.; Биджoва, Λ.; Бoтушарoв, H. Depositional conditions for Lower–Middle Jurassic sedimentary rocks from Northern Bulgaria inferred from whole-rock elemental composition. Rev. Bulg. Geol. Soc. 2022, 83, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaji, T.A.; Oyebamiji, A.R.; Okon, O.S.; Ndukwe, V.N.; Ohaeri, O.S.; Akinpelu, R.A. Rare-earth elements geochemistry of the Palaeocene Ewekoro Formation, southwestern Nigeria: Implications for terrigenous inputs, diagenetic alteration, palaeoredox and depositional conditions. Carbonates Evaporites 2024, 39, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asjad, S.; Khan, K.F.; Quasim, M.A.; Javed, A. Geochemistry of Kuldhar Member Limestone (Callovian–Oxfordian), Jaisalmer Basin, western Rajasthan, India: Implications on depositional conditions and sources of rare earth elements. J. Sediment. Environ. 2023, 8, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, B.P.; Kanhaiya, S.; Quasim, M.A.; Patra, A.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, V.K. Geochemistry of Palaeoproterozoic Kajrahat Limestone, Vindhyan Supergroup, central India: Insights into depositional conditions and sources of rare earth elements. Carbonates Evaporites 2024, 39, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Elderfield, H. Application of the Ce anomaly as a paleoredox indicator: The ground rules. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatology 1990, 5, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.W.; Buchholtz Ten Brink, M.R.; Gerlach, D.C.; Russ, G.P.; Jones, D.L. Rare earth, majör, and trace elements in chert from the Franciscan Complex and Monterey Group, California: Assessing REE sources to fine-grained marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 1875–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.N.; Roelandts, I.; Sudhakar, M.; Plüger, W.L. Rare earth element patterns of the Central Indian Basin sediments related to their lithology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavaraju, J.; Ramasamy, S. Rare earth elements in limestones of Kallankurichchi Formation of Ariyalur Group, Tiruchirapalli Cretaceous, Tamil Nadu. J. Geol. Soc. India 1999, 54, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Verma, S.P.; Madhavaraju, J.; Lee, Y., II; Ramasamy, S. Geochemistry of Upper Miocene Kudankulam limestones, Southern India. Int. Geol. Rev. 2003, 45, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, B.; Emmanuel, L.; Houel, P.; Loreau, J.P. Geodynamic control on carbonate diagenesis: Petrographic and isotopic investigation of the Upper Jurassic formations of the Paris Basin (France). Sediment. Geol. 2007, 197, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, M. Dispersion and Two-Phase Flow in Material from Different Carbonate Pore Classes. Master’s Thesis, University of Bergen, Department of Chemistry, Bergen, Norway, 2008; 94p. [Google Scholar]
- Ozyurt, M.; Kırmacı, M.Z.; Al-Aasm, I.; Hollis, C.; Tasli, K.; Kandemir, R. REE characteristics of Lower Cretaceous limestone succession in Gümüşhane, NE Turkey: Implications for ocean paleoredox conditions and diagenetic alteration. Minerals 2020, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Shah, M.M.; Janjuhah, H.T.; Trave, A.; Antonarakou, A.; Kontakiotis, G. Multiphase Diagenetic Processes and Their Impact on Reservoir Character of the Late Triassic (Rhaetian) Kingriali Formation, Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan. Minerals 2022, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A. Geochemistry and Paleoredox Conditions of The Carbonate Reservoir Khasib Formation in East Baghdad Oilfield-Central Iraq. J. Pet. Res. Stud. 2023, 41, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Hameed, A.; Tiwari, P.; Kumar, N.; Srivastava, P. Major, trace and rare earth element geochemistry of Archaean carbonate sediments of Tanwan group rocks of the Bhilwara supergroup, India: Implications for seawater geochemistry and depositional environment. Carbonates Evaporites 2024, 39, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H. The Oceanic Chemistry of the Rare-Earth Elements. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1988, 325, 105–126. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavaraju, J.; González-León, C.M. Depositional conditions and source of rare earth elements in carbonate strata of the Aptian-Albian Mural Formation, Pitaycachi section, northeastern Sonora, Mexico. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2012, 29, 478–491. [Google Scholar]
- Geel, T. Recognition of stratigraphic sequences in carbonate platform and slope deposits: Empirical models based on microfacies analysis of Palaeogene deposits in southeastern Spain. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2000, 155, 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudagher-Fadel, M.K. Chapter 1 Biology and evolutionary history of larger benthic foraminifera. Dev. Palaeontol. Stratigr. 2008, 21, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Flügel, E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Interpretation and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; 976p. [Google Scholar]
- Yalçınkaya, S.; Avşar, Ö.P. Mustafakemalpaşa (Bursa) ve Dolayının Jeolojisi; Maden Tetkik Arama Enstitüsü: Ankara, Türkiye, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Altiner, D. Microfossil biostratigraphy (mainly foraminifers) of the Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous carbonate successions in Northwestern Anatolia (Turkey). Geol. Romana 1991, 27, 167–215. [Google Scholar]
- Cengiz, O.; Özeğdemir, E. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of marble: A case study from the Mustafa Kemalpaşa-Bursa, Northwest Turkey. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. Geoconf. SGEM Surv. Geol. Min. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 1, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Kop, A.; Özalp, S.; Elmacı, H.; Kara, M.; Duman, T.Y. Active tectonic and palaeoseismological features of the western section of Mustafakemalpaşa Fault; Bursa, NW Anatolia. Geodin. Acta 2016, 28, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özeğdemir, E. Kabulbaba (Mustafa Kemalpaşa-Bursa) Bölgesindeki Mermerlerin Jeolojik, Mineralojik ve Jeokimyasal Özellikleri. Master’s Thesis, Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Isparta, Türkiye, 2016; 86p. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, M.Y.; Özkan, Ö. Geotechnical characterization of low-porous limestones (beige–cream marble, Turkey) and evaluation of durability by salt crystallization experiments. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Nikishin, A.M. Tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Laurasia in the Black Sea region. Int. Geol. Rev. 2015, 57, 1051–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Topuz, G. Variscan orogeny in the Black Sea region. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 106, 569–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.B.; Belousova, E.A.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Romanyuk, T.V.; Rud’ko, S.V. Pre-Mesozoic Crimea as a continuation of the Dobrogea platform: Insights from detrital zircons in Upper Jurassic conglomerates, Mountainous Crimea. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 108, 2407–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgül, N. Toroslar’ın bazı temel jeoloji özellikleri. Geol. Soc. Turk. Bull. 1976, 19, 65–78, (In Turkish with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Saner, S. Paleogeography and depositional features of the Jurassic and younger sediments of the Mudurnu-Göynük basin. Türkiye Jeol. Kurumu Bülteni 1980, 23, 39–52. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Görür, N.; Şengör, A.M.C.; Akkök, R.; Yılmaz, Y. Pontidlerde Neo-Tetis’ in kuzey kolunun açılmasına ilişkin sedimantolojik veriler. Bull. Geol. Soc. Turk. 1983, 26, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, A.İ.; Siyako, M.; Bürkan, K.A. Biga Yarımadası’nın Jeolojisi ve Tektonik Evrimi. Türkiye Pet. Jeologları Derneği Derg. 1990, 2, 83–121. [Google Scholar]
- Altiner, D.; Koçyiğit, A.; Farinacci, A.; Nicosia, U.; Conti, M.A. Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous stratigraphy and paleogeographic evolution of the southern part of North Western Anatolia (Turkey). Geol. Romana 1991, 27, 13–81. [Google Scholar]
- Koçyiğit, A.; Altiner, D.; Farinacci, A.; Nicosia, U.; Conti, M.A. Late Triassic–Aptian evolution of the Sakarya divergent margin: Implications for the opening history of the Northern Neo-Tethys, in the North-Western Anatolia, Turkey. Geol. Romana 1991, 27, 81–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, I.O.; Altiner, D. Use of sedimentary structures in the recognition of sequence boundaries in the Upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian)–Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian) peritidal carbonates of the Fele (Yassıbel) area (Western Taurides, Turkey). Int. Geol. Rev. 2001, 43, 736–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dercourt, J.; Ricou, L.E.; Vrielynck, B. Atlas Tethys Palaeoenvironmental Maps; Commission Carte Ge´ologique du MondeCommission Geological Map of the World; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 259–307. [Google Scholar]
- Ketin, I. Anadolu’nun tektonik birlikleri. Maden Tetk. Aram. Derg. 1966, 66, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; Yılmaz, Y. Tethyan evolution of Turkey: A plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 181–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Tüysüz, O. Tethyan sutures of northern Turkey. Geol. Soc. Spec. Pub. Lond. 1999, 156, 475–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikishin, A.M.; Okay, A.; Tüysüz, O.; Demirer, A.; Wannier, M.; Amelin, N.; Petrov, E. The Black Sea basins structure and history: New model based on new deep penetration regional seismic data. Part 2: Tectonic history and paleogeography. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 59, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüysüz, O. Geology of the Cretaceous sedimentary basins of the Western Pontides. Geol. J. 1999, 34, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, A.I.; Altiner, D.; Sunal, G.; Aygül, M.; Akdoğan, R.; Altiner, S.; Simmons, M. Geological evolution of the Central Pontides. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2018, 464, 33–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Y. Geology of western Anatolia. In Active Tectonics of Northwestern Anatolia–The Marmara Polyproject, vdf Hochschulverlag AG an der ETH Zürich; Amazon: Seattle, WA, USA, 1997; pp. 31–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kalvoda, J.; Bábek, O. The margins of Laurussia in central and southeast Europe and southwest Asia. Gondwana Res. 2010, 17, 526–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrier, E.; Vrielynck, B.; Brouillet, J.F.; Brunet, M.F. Paleotectonic reconstruction of the Central Tethyan Realm. In Tectonono-Sedimentary-Palinspastic Maps from Late Permian to Pliocene; CCGM: Fransa, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hinsbergen, D.J.; Torsvik, T.H.; Schmid, S.M.; Maţenco, L.C.; Maffione, M.; Vissers, R.L.; Gürer, D.; Spakman, W. Orogenic architecture of the Mediterranean region and kinematic reconstruction of its tectonic evolution since the Triassic. Gondwana Res. 2020, 81, 79–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göncüoğlu, M.C.; Turhan, N.; Şentürk, K.; Özcan, A.; Uysal, Ş. A geotraverse across northwestern Turkey: Tectonic units of the Central Sakarya region and their tectonic evolution. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2000, 173, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, G.; Altherr, R.; Schwarz, W.H.; Dokuz, A.; Meyer, H.P. Variscan amphibolite-facies rocks from the Kurtoğlu metamorphic complex (Gümüşhane area, Eastern Pontides, Turkey). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuz, A. Aslab detachment and delamination model for the generation of Carboniferous high-potassium I-type magmatism in the Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey: The Köse composite pluton. Gondwana Res. 2011, 19, 926–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, M.J.; Brocard, G.Y.; Whitney, D.L.; Mulch, A. Paleoenvironmental conditions and drainage evolution of the central Anatolian lake system (Turkey) during late Miocene to Pliocene surface uplift. Geosphere 2020, 16, 490–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdoğan, R.; Okay, A.I.; Dunkl, I. Kuzeydoğu Türkiye’deki Jura kumtaşlarındaki U-Pb detrital zirkonyum yaşlarının ortaya çıkardığı Pontidler’deki Triyas-Jura yay magmatizması. Türkiye Yer Bilim. Derg. 2018, 27, 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, A.I.; Sunal, G.; Tüysüz, O.; Sherlock, S.; Keskin, M.; Kylander-Clark, A.R.C. Low-pressure–high-temperature metamorphism during extension in a Jurassic magmatic arc, Central Pontides, Turkey. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2014, 32, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, S.C. Geology of the region between Uludağ and the İznik Lake. In Guide Book for the Field Excursion Along Western Anatolia; MTA Enstitüsü: Ankara, Turkey, 1986; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, B.; Kazancı, N. Litho-and biofacies properties of upper Jurassic–lower Cretaceous carbonate succession in Nallihan–Seben (Bolu) region. Bull. Geol. Soc. Turk. 1981, 24, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bingöl, E. Batı Anadolu’nun jeotektonik evrimi. Bull. Miner. Res. Explor. 1976, 86, 14–34. [Google Scholar]
- Akyüz, H.S.; Okay, A.I. A section across a Tethyan suture in northwestern Turkey. Int. Geol. Rev. 1996, 38, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameil, N. Early diagenetic dolomitization and dedolomitization of Late Jurassic and earliest Cretaceous platform carbonates: A case study from the Jura Mountains (NW Switzerland, E France). Sediment. Geol. 2008, 212, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhloufi, Y.; Rusillon, E.; Brentini, M.; Moscariello, A.; Meyer, M.; Samankassou, E. Dolomitization of the Upper Jurassic carbonate rocks in the Geneva Basin, Switzerland and France. Swiss J. Geosci. 2018, 111, 475–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. Dev. Geochem. 1984, 2, 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1985; p. 349. [Google Scholar]
- Veizer, J.; Ala, D.; Azmy, K.; Bruckschen, P.; Buhl, D.; Bruhn, F.; Jasper, T. 87Sr/86Sr, d13C and d18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater. Chem. Geol. 1999, 161, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanca, A.; Masetti, D.; Neri, R. Rare earth elements in limestone/marlstone couplets from the Albian-Cenomanian Cismon section (venetian region, northern Italy): Assessing REE sensitivity to environmental changes. Chem. Geol. 1997, 141, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Schrader, H.; Holser, W.T. Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Miah, M.R.U.; Schmitt, R.A. Cerium: A chemical tracer for paleo-oceanic redox conditions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijf, J.; de Baar, H.J.W.; Millero, F.J. Vertical distributions and speciation of dissolved rare earth elements in the anoxic brines of Bannock Basin, eastern Mediterranean Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 3285–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Rare earth elements in the pore waters of reducing nearshore sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1987, 82, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, S.; Aldega, L.; Perri, F.; Critelli, S.; Muto, F.; Schito, A.; Tripodi, V. Detecting syn-orogenic extension and sediment provenance of the Cilento wedge top basin (southern Apennines, Italy): Mineralogy and geochemistry of fine-grained sediments and petrography of dispersed organic matter. Tectonophysics 2019, 750, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baar, H.J.W.; Brewer, P.G.; Bacon, M.P. Anomalies in rare earth distribution in seawater: Gd and Tb. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Piepgras, D.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. The pore water chemistry of rare elements Buzzard Bay sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Greaves, M.J. The rare earth elements in seawater. Nature 1982, 296, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Cappetta, P.H.; Michard, A.; Albarede, F. The assessment of REE patterns and 143Nd/144Nd ratios in fish remains. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1987, 84, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, P.; Cappetta, P.H.; Albarede, F. The REE and eNd of 40–70 Ma old fish debris from the West-African platform. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepgras, D.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. The behaviour of rare earth elements in seawater: Precise determination of variations in the North Pacific water column. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.N.Ü.; Roelandts, I.; Sudhakar, M.; Plueger, W.L.; Balaram, V. Cerium anomaly variations in ferromanganese nodules and crusts from the Indian Ocean. Mar. Geol. 1994, 120, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavaraju, J.; Lee, Y.I. Geochemistry of the Dalmiapuram Formation of the Uttatur Group (Early Cretaceous), Cauvery Basin, southeastern India: Implications on provenance and paleo-redox conditions. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2009, 26, 380–394. [Google Scholar]
- Madhavaraju, J.; González-León, C.M.; Lee, Y.I.; Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Reyes-Campero, L.M. Geochemistry of the Mural Formation (Aptian-Albian) of the Bisbee Group, Northern Sonora, Mexico. Cretac. Res. 2010, 31, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Landing, W.M.; Lewis, B.L. Ocean particle chemistry: The fractionation of rare earth elements between suspended particles and seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.A.; Klinkhammer, G.P.; McManus, J. Rare earth elements in pore waters of marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baar, H.J. On cerium anomalies in the Sargasso Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 2981–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Algeo, T.J.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Diagenetic uptake of rare earth elements by bioapatite, with an example from Lower Triassic conodonts of South China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 149, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Distribution of yttrium and rare-earth elements in the Penge and Kuruman iron-formations, Transvaal Supergroup, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 1996, 79, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Madhavaraju, J.; Armstron-Altrin, J.S.; Nagendra, R. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic limestones of the Shahabad Formation, Bhima Basin, Karnataka, southern India. Geosci. J. 2011, 15, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A.; Albarede, F.; Michard, G.; Minster, J.F.; Charlou, J.L. Rare-earth elements and uranium in high-temperature solutions from East Pacific rise hydrothermal vent field (13°N). Nature 1983, 303, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Hergt, J.; Palmer, M.R.; Edmond, J.M. Geochemistry of a hydrothermal sediment core from the OBS vent-field, 21°N East Pacific Rise. Chem. Geol. 1999, 155, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, U.; Veizer, J. Chemical diagenesis of a multicomponent carbonate system-I: Trace elements. J. Sediment. Res. 1980, 50, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Banner, J.L.; Hanson, G.N. Calculation of simultaneous isotopic and trace element variations during water-rock interaction with applications to carbonate diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 3123–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynard, B.; Lécuyer, C.; Grandjean, P. Crystal-chemical controls on rare-earth element concentrations in fossil biogenic apatites and implications for paleoenvironmental reconstructions. Chem. Geol. 1999, 155, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Pagett, R. Rare earth elements in ichthyoliths: Variations with redox conditions and depositional environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 49, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagender Nath, B.; Plüger, W.L.; Roelandts, I. Geochemical Constraints on the Hydrothermal Origin of Ferromanganese Encrustations from the Rodriguez Triple Junction, Indian Ocean; Special Publications; Geological Society: London, UK, 1997; Volume 119, pp. 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Masuzawa, T.; Koyama, M. Settling particles with positive Ce anomalies from the Japan Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1989, 16, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Amakawa, H.; Nozaki, Y. The comparative behaviors of yttrium and lanthanides in the seawater of the North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2677–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromet, L.P.; Haskin, L.A.; Korotev, R.L.; Dymek, R.F. The “North American shake composite”: Its compilation, major and trace element charachteristic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.L.; Weber, J.N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1787–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.D. Stable isotopes and limestone lithification. J. Geol. Soc. 1977, 133, 637–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.S.; Smith, A.M. Stable oxygen and carbon isotope fields for skeletal and diagenetic components in New Zealand Cenozoic non tropical carbonate sediments and limestones: A synthesis and review. N. Z. J. Geol. Geophys. 1996, 39, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, V.N.; Bych, A.F. Isotopic composition (δ13C, δ18O) and origin of manganese carbonate ores of the Usa deposit (Kuznetskii Alatau). Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2002, 37, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogdahl, O.T.; Melsom, S.; Bowen, V.T. Neutron activation analysis of lanthanide elements in sea water. Adv. Chem. 1968, 73, 308–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P.; Möller, P. Yttrium and holmium in South Pacific seawater: Vertical distribution and possible fractionation mechanisms. Chem. Erde 1995, 55, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, Y.; Zhang, J.; Amakawa, H. The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 148, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothdurft, L.D.; Webb, G.E.; Kamber, B.S. Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, Canning Basin, Western Australia: Confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baar, H.J.; German, C.R.; Elderfield, H.; Van Gaans, P. Rare earth element distributions in anoxic waters of the Cariaco Trench. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 1203–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwise, A.J. Role of nickel and vanadium in petroleum classification. Energy Fuels 1990, 4, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.E.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide: Interpreting Molecular Fossils in Petroleum and Ancient Sediments; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bechtel, A.; Gratzer, R.; Sachsenhofer, R.F. Chemical characteristics of upper cretaceous (Turonian) jet of the Gosau Group of gams/Hieflau (Styria, Austria). Int. J. Coal Geol. 2001, 46, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarraga, F.; Reategui, K.; Martínez, A.; Martínez, M.; Llamas, J.F.; Marquez, G. V/Ni ratio as a parameter in palaeoenvironmental characterisation of nonmature medium-crude oils from several Latin American basins. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2008, 61, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, S.M. Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian Mississippian black shales, Central Appalachian Basin (USA). Chem. Geol. 2004, 206, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, J.R.; Leventhal, J.S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, USA. Chem. Geol. 1992, 99, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Manning, D.A. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Cao, L.M.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, H.N.; Chu, T.Q.; Zhang, J.R. Element Geochemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 283–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.W.; Qian, K. Analysis of Sedimentary Geochemistry and Environment; Gansu Science and Technology Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.H. Discriminant effect of sedimentary environment by the Sr/Ba ratio of different existing forms. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 1996, 14, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Adegoke, A.K.; Abdullah, W.H.; Hakimi, M.H.; Yankoka, B.M.S. Geochemical characterization and organic matter enrichment of upper Cretaceous Gongila shales from Chad (Bornu) Basin, northeastern Nigeria: Bioproductivity versus anoxia conditions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Chemical Elements in the Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 397. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhuang, X.; Li, J.; Querol, X.; Font, O.; Moreno, N. Geological controls on mineralogy and geochemistry of the Late Permian coals in the Liulong Mine of the Liuzhi Coalfield, Guizhou Prov ince, Southwest China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 154–155, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, P.; Ren, D.; Lei, J. Late Permian coal-bearing carbonate succession in southern China; coal accumulation on carbonate platform. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 37, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandoka, B.M.S.; Abdullah, W.H.; Abubakar, M.B.; Hakimi, M.H.; Adegoke, A.K. Geochemistry of the Cretaceous coals from Lamja Formation, Yola Sub-basin, Northern Benue Trough, NE Nigeria: Implications for paleoenvironment, paleoclimate and tectonic setting. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.; McDaniel, D.K.; Hanson, G.N. Geochemical Approaches to Sedimentation, Provenance, and Tectonics; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Özyurt, M.; Kırmacı, M.Z. Microfacies and geochemistry of Kimmeridgian limestone strata in the Eastern Pontides (North-East Turkey): Palaeoclimate and palaeoenvironmental influence on organic matter enrichment. Depos. Rec. 2025, 11, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Siliceous Limestone | Micritic Limestone | Fossiliferous Limestone | Dolomitic Limestone | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Oxides (wt.%) | DL | YE-3A | PA-1 | TC-1 | YE-3B | KP-1 | AK-2 | AK-3 | KP-2 | YB-1 | YB-2 | AK-1 | YU-1 | PA-2 | BI-1 |
| SiO2 | 0.01 | 1.87 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.48 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
| Al2O3 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.12 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| MgO | 0.01 | 0.74 | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.98 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 1.3 | 17.56 | 15.86 |
| CaO | 0.01 | 53.68 | 54.93 | 54.71 | 54.72 | 54.79 | 54.63 | 56.31 | 55.76 | 56.03 | 55.81 | 56.18 | 55.17 | 35.97 | 37.42 |
| Na2O | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| K2O | 0.01 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.08 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| TiO2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| MnO | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002 |
| TOT/C | 0.02 | 12.13 | 12.28 | 12.33 | 12.3 | 12.19 | 12.14 | 12.3 | 12.36 | 12.37 | 12.36 | 12.3 | 12.39 | 13.1 | 12.98 |
| TOT/S | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.08 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| LOI | −5.1 | 42.8 | 43.1 | 43.2 | 43.4 | 43.1 | 43.3 | 43.4 | 43.5 | 43.5 | 43.3 | 43.4 | 42.8 | 45.7 | 45.8 |
| Total | 0.01 | 99.96 | 99.89 | 99.95 | 99.95 | 99.99 | 99.98 | 100.1 | 99.95 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 100 | 99.94 | 99.69 | 99.72 |
| Trace element (ppm) | |||||||||||||||
| Ba | 1 | 15 | 139 | 21 | 11 | 25 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 19 | 2 | 3 |
| Sr | 0.5 | 264.6 | 221.7 | 227.0 | 130.0 | 153.1 | 86.9 | 151.5 | 135.9 | 184.6 | 92.8 | 271.9 | 147.3 | 133.6 | |
| Rb | 0.1 | 3.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| U | 0.1 | 3.3 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 0.6 | <0.1 | 0.3 | <0.1 | 0.5 | <0.1 | 0.3 | 2.8 | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| V | 8 | 41 | 17 | 13 | 31 | 20 | 22 | 17 | 16 | 9 | <8 | 24 | 18 | 15 | 13 |
| Zr | 0.1 | 5.7 | 4.8 | 9 | 3.9 | 20.8 | 5.8 | 9 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 3 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 4.1 |
| Y | 0.1 | 4.1 | 3 | 2.2 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 2.6 |
| Ni | 0.1 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 2 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| Co | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 0.5 | <0.2 | 0.7 | <0.2 | <0.2 | 0.5 | 0.7 | <0.2 | 0.7 |
| V/V + Ni | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.86 | |
| Ni/Co | 12.67 | 2.43 | 4.33 | 3.17 | 0.79 | 5.40 | 11.00 | 3.29 | 14.00 | 10.00 | 4.40 | 5.14 | 9.50 | 3.14 | |
| V/Ni | 10.79 | 10.00 | 5.00 | 16.32 | 18.188 | 8.15 | 7.73 | 6.96 | 3.21 | 4.00 | 10.91 | 5.00 | 7.89 | 5.91 | |
| Sr/Ba | 17.64 | 1.59 | 10.81 | 11.82 | 6.12 | 44.75 | 86.9 | 75.75 | 45.30 | 92.30 | 90.93 | 14.31 | 73.65 | 44.53 | |
| Sr/Rb | 69.63 | 277.13 | 206.36 | 118.18 | 76.55 | 94.21 | 217.25 | 378.75 | 339.75 | 461.50 | 154.67 | 302.11 | 294.60 | 202.42 | |
| Y/Ho | 58.57 | 60.00 | 55.00 | 55.00 | 51.11 | 106.67 | 20.00 | 32.50 | 25.00 | 30.00 | 30.00 | 70.00 | 110.00 | 86.67 | |
| Rare Earth Element (ppm) | DL | Siliceous limestone | Micritic limestone | Fossiliferous limestone | Dolomitic limestone | ||||||||||
| La | 0.1 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.6 |
| Ce | 0.1 | 1.8 | 5.4 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| Pr | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Nd | 0.3 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Sm | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Eu | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Gd | 0.05 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.3 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.26 |
| Tb | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Dy | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.29 |
| Ho | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| Er | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Tm | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Yb | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.35 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.13 |
| Lu | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ce/Ce* | 0.39 | 0.73 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.38 | |
| Eu/Eu* | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.70 | 1.04 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 0.91 | 0.54 | |
| Pr/Pr* | 0.79 | 0.65 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.15 | |
| (Pr/Yb)n | 1.26 | 4.32 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.94 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.26 | |
| (La/Yb)n | 11.35 | 21.12 | 10.59 | 4.43 | 12.81 | 8.99 | 1.79 | 8.58 | 7.87 | 10.79 | 4.12 | 8.67 | 16.85 | 13.48 | |
| (La/Sm)n | 20.13 | 11.67 | 27.68 | 18.08 | 14.94 | 25.16 | 10.06 | 17.61 | 8.81 | 10.06 | 13.84 | 22.65 | 25.16 | 32.71 | |
| (Sm/Yb)n | 0.56 | 1.85 | 0.39 | 0.25 | 0.90 | 0.36 | 1.08 | 0.49 | 0.90 | 1.08 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.42 | |
| (La/Ce)n | 4.63 | 2.27 | 3.59 | 3.18 | 5.50 | 3.91 | 6.97 | 7.29 | 6.11 | 10.32 | 7.10 | 5.87 | 6.52 | 5.21 | |
| Er/Nd | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.09 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cengiz, O.; Kıray, D.; Özeğdemir, E. Petrography and Geochemistry of the Middle Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous Limestones from the Mustafakemalpaşa Quarries, Bursa, Turkey: The Depositional Environmental and Diagenetic Processes. Minerals 2025, 15, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111135
Cengiz O, Kıray D, Özeğdemir E. Petrography and Geochemistry of the Middle Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous Limestones from the Mustafakemalpaşa Quarries, Bursa, Turkey: The Depositional Environmental and Diagenetic Processes. Minerals. 2025; 15(11):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111135
Chicago/Turabian StyleCengiz, Oya, Didem Kıray, and Ertan Özeğdemir. 2025. "Petrography and Geochemistry of the Middle Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous Limestones from the Mustafakemalpaşa Quarries, Bursa, Turkey: The Depositional Environmental and Diagenetic Processes" Minerals 15, no. 11: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111135
APA StyleCengiz, O., Kıray, D., & Özeğdemir, E. (2025). Petrography and Geochemistry of the Middle Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous Limestones from the Mustafakemalpaşa Quarries, Bursa, Turkey: The Depositional Environmental and Diagenetic Processes. Minerals, 15(11), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15111135






