The Efficiency of Fibrous Mg Clays for the Removal of Ciprofloxacine and Lidocaine from Water—The Role of Associated Clay Minerals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Mineralogical and Physicochemical Characterization of Raw Mg Clays
2.2.2. Batch Adsorption Studies
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Raw Mg Clays
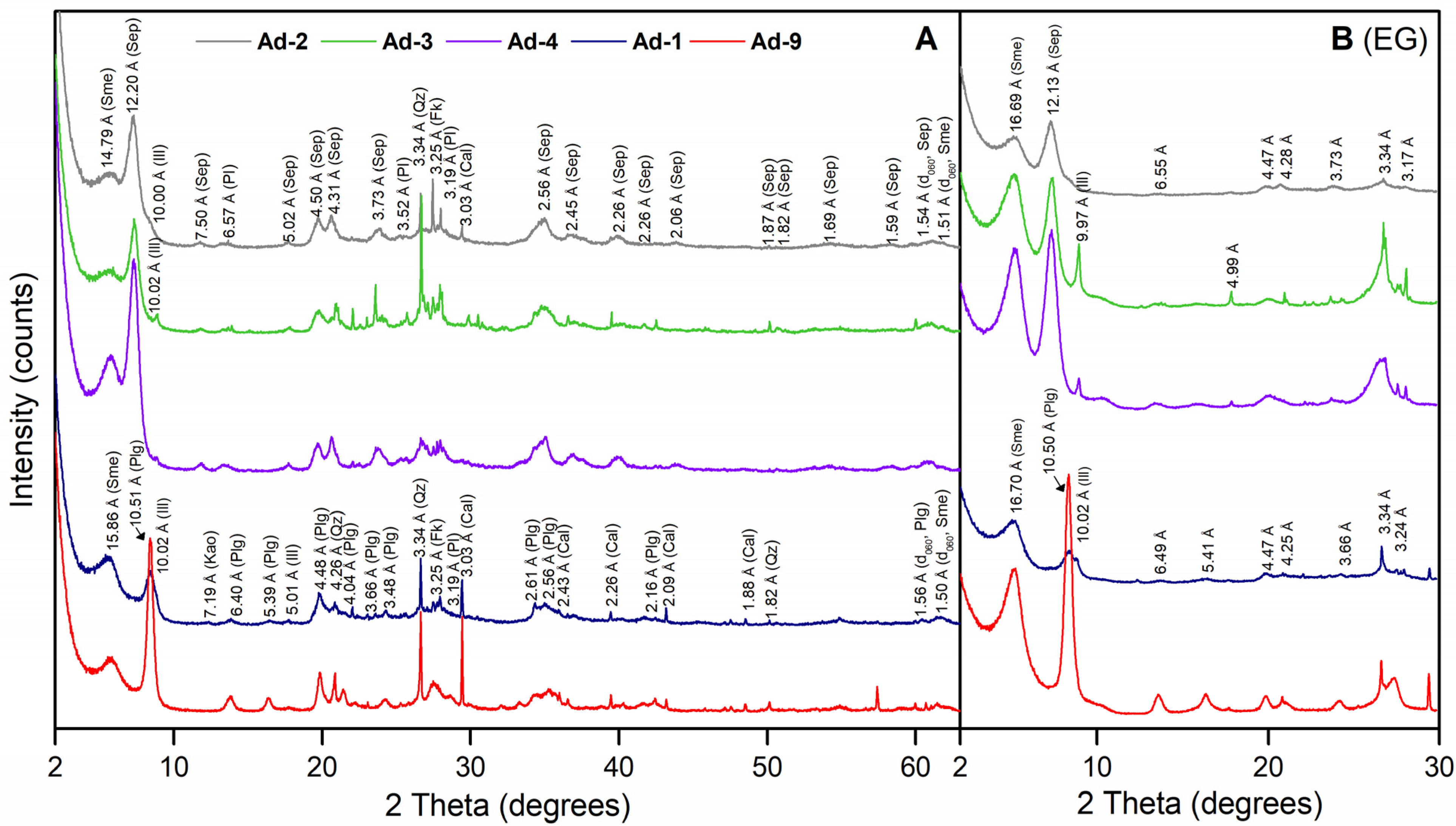
3.1.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.1.2. Chemical Analysis
3.1.3. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.1.4. Thermal Analysis
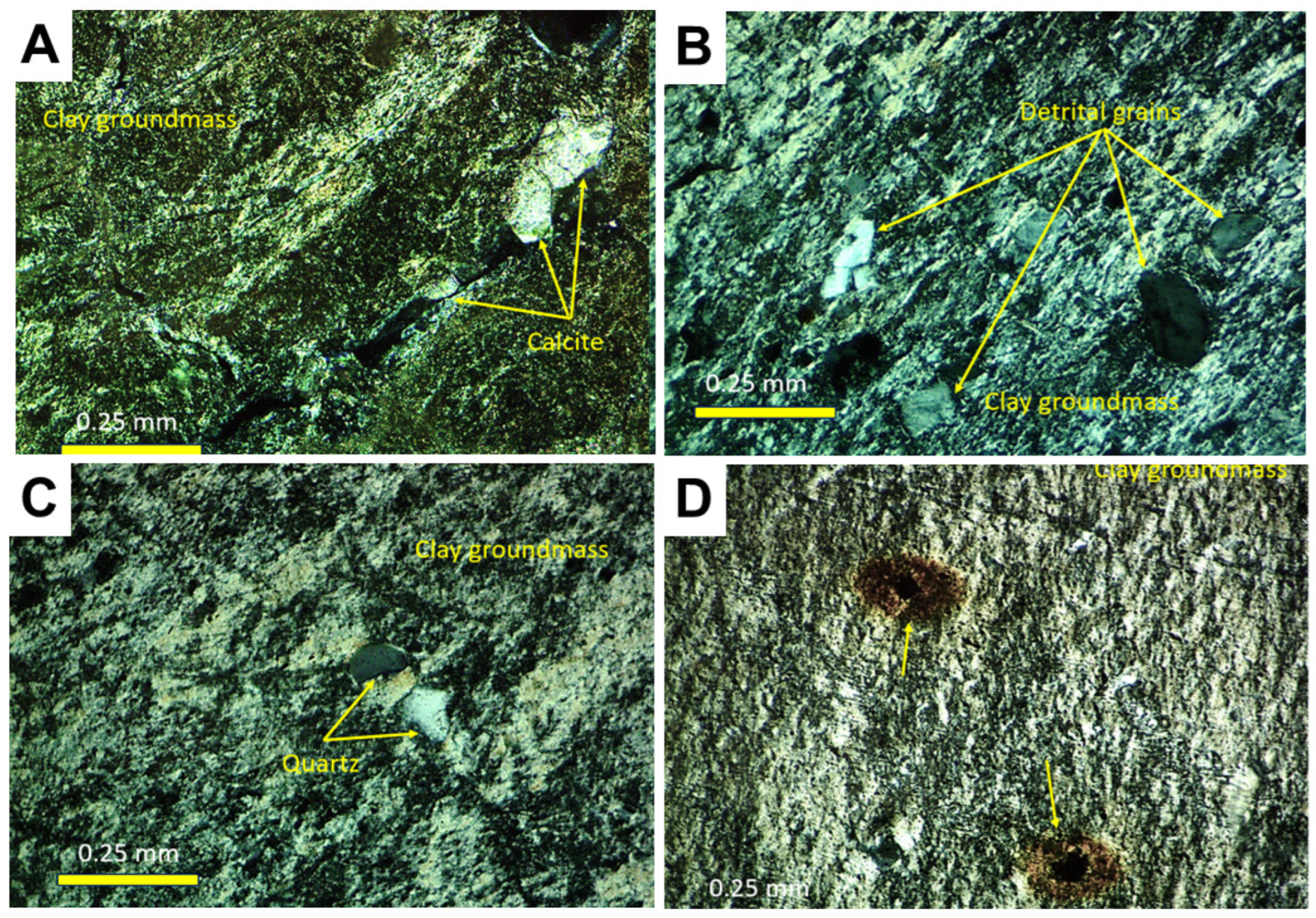
3.1.5. Petrography
3.1.6. SEM-TEM
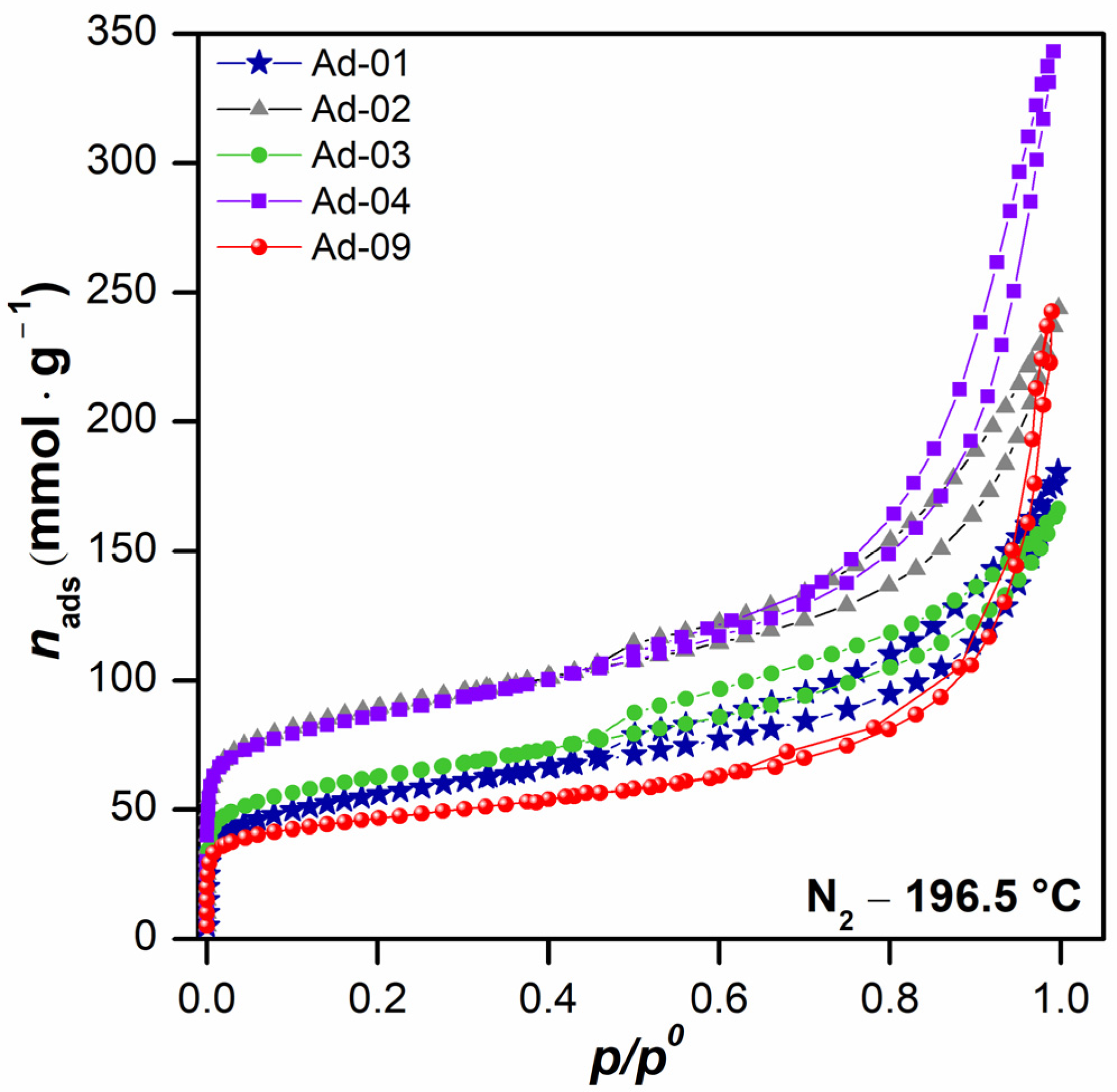
3.1.7. Physicochemical and Textural Properties
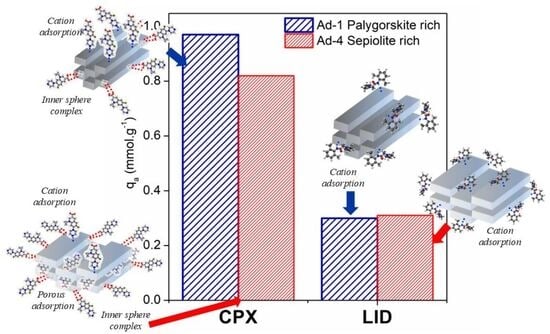
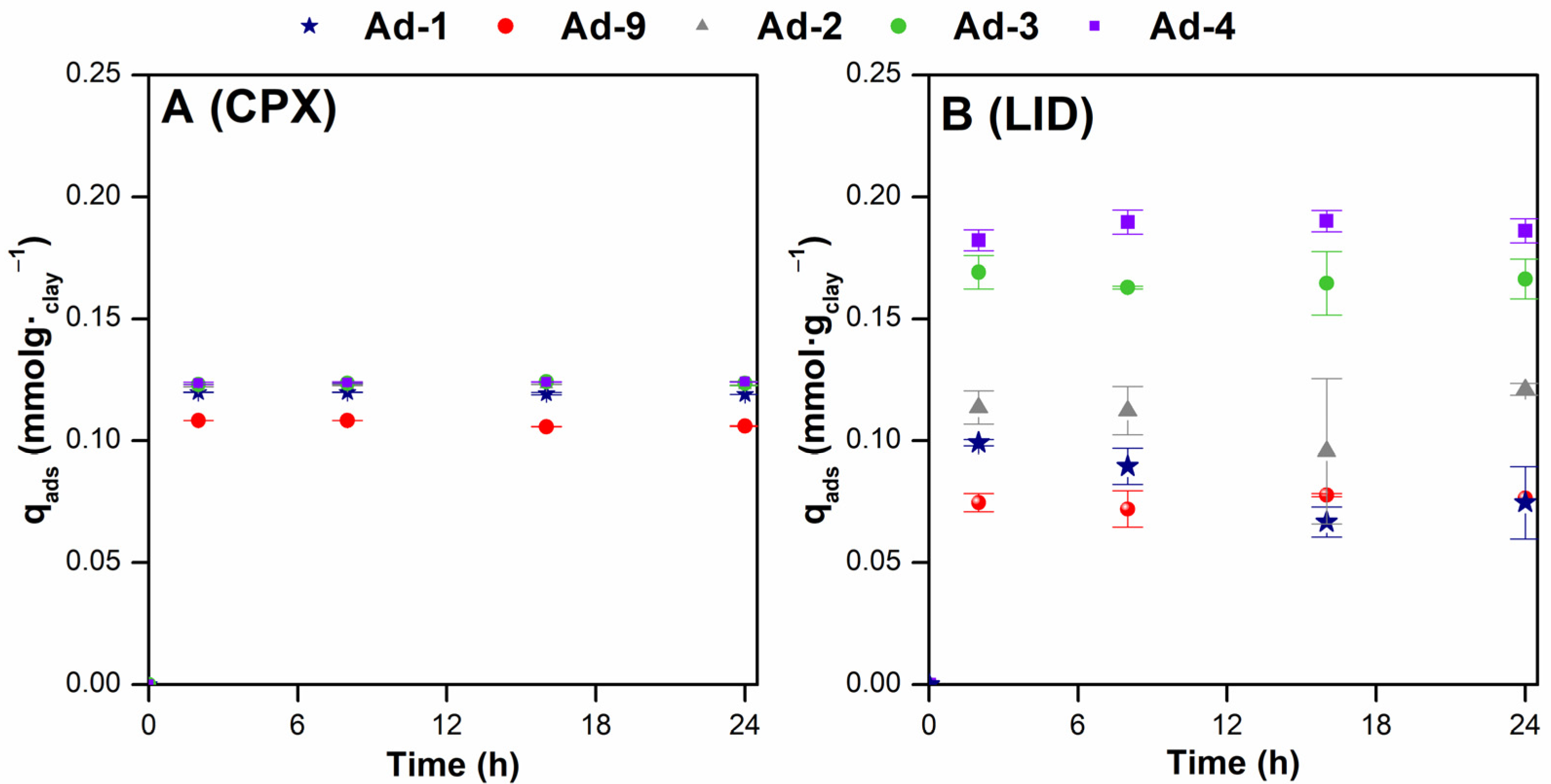
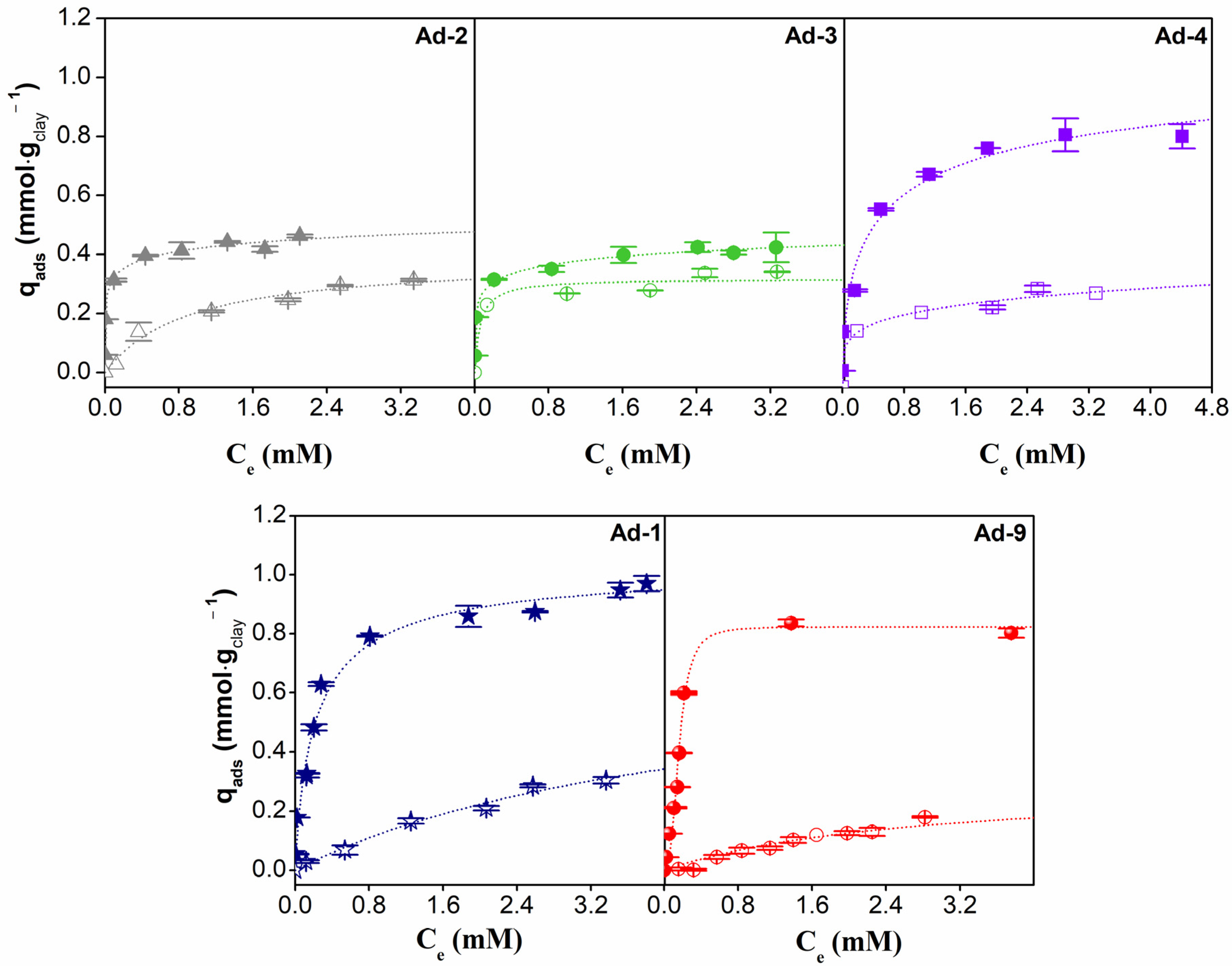
3.2. Adsorption Studies
4. Discussion
4.1. Assemblage 1 (Sepiolite + Trioctahedral Smectite)
4.2. Assemblage 2 (Palygorskite + Dioctahedral Smectite)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Undabeytia, T.; Madrid, F.; Vázquez, J.; Pérez-Martínez, J.I. Grafted sepiolites for the removal of pharmaceuticals in water treatment. Clays Clay Miner. 2019, 67, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caban, M.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Kumirska, J. Current issues in pharmaceutical residues in drinking water. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2016, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, S.M.; Mohd Rashid, M.Z.; Mohd Nasir, F.A.; Sze Yee, W.; Aris, A.Z. Occurrence and potential human health risk of pharmaceutical residues in drinking water from Putrajaya (Malaysia). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Concha-Graña, E.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. Emerging pollutants in sewage, surface and drinking water in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 2012, 86, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meffe, R.; de Bustamante, I. Emerging organic contaminants in surface water and groundwater: A first overview of the situation in Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rúa-Gómez, P.C.; Püttmann, W. Degradation of lidocaine, tramadol, venlafaxine and the metabolites O-desmethyltramadol and O-desmethylvenlafaxine in surface waters. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nie, Q.; Huang, B.; Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; He, Q. Removal of ciprofloxacin as an emerging pollutant: A novel application for bauxite residue reuse. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 120049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Harsha, N.V.M.S.; Singh, S.P.; Shriwastav, A. Simultaneous removal of ciprofloxacin and disinfection from wastewater by combined photocatalytic reactor (PCR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Zafariyan, M.; Siddiqui, S. Investigation of adsortive properties of surfactant modified sepiolite for removal of ciprofloxacin. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2020, 10, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jara-Cobos, L.; Peñafiel, M.E.; Montero, C.; Menendez, M.; Pinos-Vélez, V. Ciprofloxacin removal using pillared clays. Water 2023, 15, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.R.; Brooks, B.W. Global Aquatic Hazard Assessment of Ciprofloxacin: Exceedances of Antibiotic Resistance Development and Ecotoxicological Thresholds. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 159, 59–77. [Google Scholar]
- Berhane, T.M.; Levy, J.; Krekeler, P.S.; Danielson, N.D. Adsorption of bisphenol A and ciprofloxacin by palygorskite-montmorillonite: Effect of granule size, solution chemistry and temperature. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132–133, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulen, B.; Demircivi, P. Adsorption properties of flouroquinolone type antibiotic ciprofloxacin into 2:1 dioctahedral clay structure: Box-Behnken experimental design. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1206, 127659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Jalil, M.E.; Musso, T.; Rodriguez-Ameijide, V.; Sanchez, M.; Maggio, A.; Baschini, M.T.; Pettinari, G.; Villa, L.; Pozo, M.; Pérez-Abad, A. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin and lidocaine by non-fibrous raw Mg-clays: The role of composition and texture. Minerals 2024, 14, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, O.; Peralta-Hernandez, J.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Bandala, E.R. Treatment Technologies for Emerging Contaminants in water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, A.; Ibrahim, Y.S.; Yaro, N.A.; Olanrewaju, O.A.; Alhassan, B.; Iyayosa, D.A.; Lawal, K. Emerging contaminants removal from wastewater using organo-modified bentonite clay. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 2023, 25, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Sánchez, P.; Hrichi, A.; Garrido-Zoido, J.M.; Alvarez-Torrellas, S.; Larriba, M.; Gil, M.V.; Ben Amor, H.; García, J. Natural clays as adsorbents for the efficient removal of antibiotic ciprofloxacin from wastewaters: Experimental and theoretical studies using DFT method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 134, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krekeler, M.P.S.; Guggenheim, S. Defects in microstructure in palygorskite-sepiolite minerals: A transmission electron microscopy (TEM) study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 39, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W. Structure of layer silicates. In Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-Ray Identification; Brindley, G.W., Brown, G., Eds.; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1980; pp. 1–123. [Google Scholar]
- Galán, E. Industrial applications of sepiolite from Vallecas-Vicalvaro, Spain: A review. In Proceedings of the International Clay Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 28 July–2 August 1985; Schultz, L.C., Van Olphen, H., Mumpton, F.A., Eds.; Bloomington, IN, USA, 1987; pp. 400–404. Available online: https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/clays/books/edited-volume/2670/chapter-abstract/145119976/Industrial-Applications-of-Sepiolite-from-Vallacas?redirectedFrom=fulltext (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Molecular access to intracrystalline tunnels of sepiolite. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, E.; Pozo, M. Palygorskite and sepiolite deposits in continental environments. Description, genetic patterns and sedimentary settings. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 125–173. [Google Scholar]
- Song, N.; Hursthouse, A.; McLellan, I.; Wang, Z. Treatment of environmental contamination using sepiolite: Current approaches and future potential. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2679–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, A.; Santarén, J.; Esteban-Cubillo, A.; Aparicio, P. Current industrial applications of palygorskite and sepiolite. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Viseras, C.; Lopez-Galindo, A. Pharmaceutical applications of some spanish clays (sepiolite, palygorskite, bentonite): Some preformulation studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I.; Pozo, M. Clay and non-clay minerals in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries Part II. Active ingredients. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, T.M.; Levy, J.; Krekeler, M.P.S.; Danielson, N.D.; Stalcup, A. Sorption-desorption of carbamazepine by palygorskite-montmorillonite (PM) filter medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-H.; Li, Z.; Yu, T.-L.; Munkhbayer, S.; Kuo, T.-H.; Hung, Y.-C.; Jean, J.-S.; Lin, K.-H. Sorptive removal of tetracycline from water by palygorskite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fitzgerald, N.M.; Jiang, W.T.; Lv, G. Palygorskite for the uptake and removal of pharmaceuticals for wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 101, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.L.; Chang, P.H.; Gao, Z.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, T.H.; Jean, J.-S.; et al. Amitriptyline removal using palygorskite clay. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.U.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Araujo, M.E.B.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A.; Lira, H.L. Adsorption of sodium diclofenac in functionalized palygoskite clays. Materials 2022, 15, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelomov, L.; Gertsen, M.; Mandzhieva, S.; Sychev, V.; Dudnikova, T.; Khaidanov, I.; Perelomova, I.; Minkina, T.; Atroshchenko, Y. Adsorption of antibiotics by natural clay minerals. Minerals 2025, 15, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wang, A. Adsorption of dyes onto palygorskite and its composites: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1274–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.C.; Araújo, M.E.B.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Cartaxo, J.M.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A. Adsorption behavior of acid-treated Brazilian palygorskite for cationic and anionic dyes removal from the water. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, D.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Adsorption properties and mechanisms of palygorskite for removal of various ionic dyes from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 151, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.; Martínez-Hernández, V.; Meffe, R.; Lillo, J.; de Bustamante, I. Clinoptilolite and palygorskite as sorbents of neutral emerging organic contaminants in treated wastewater: Sorption-desorption studies. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.V.; Silva, F.A.N.G.; Pontes, F.V.M.; Barbato, C.N.; Teixeira, V.G.; de Assis, T.C.; Brandão, V.S.; Bertolino, L.C. Adsorption of glyphosate by palygorskite. Mater. Res. 2023, 26, e20220335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Afsin, B. Investigation of a basic dye adsorption from aqueous solution onto raw and pre-treated sepiolite surfaces. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 73, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Y.; Doǧan, M.; Alkan, M. Adsorption of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by sepiolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 96, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.C.R.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Adsorption modelling of textile dyes by sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küncek, I.; Şener, S. Adsorption of methylene blue onto sonicated sepiolite from aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Yuzer, H.; Sabah, E.; Celik, M. Adsorption of cobalt from aqueous solutions onto sepiolite. Water Res. 2003, 37, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocaoba, S. Adsorption of Cd(II), Cr(III) and Mn(II) on natural sepiolite. Desalination 2009, 244, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Avilés, A.; Sellaoui, L.; Badawi, M.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Bedia, J.; Belver, C. Simultaneous adsorption of acetaminophen, diclofenac and tetracycline by organo-sepiolite: Experiments and statistical physics modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, X. Adsorption properties and mechanism of sepiolite modified by anionic and cationic surfactants on oxytetracycline from aqueous solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, N.; Bulut, E.; Sabah, E. Mechanistic insight into amoxicillin removal by natural sepiolite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 8897–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.G. Quantitative Interpretation of Mineralogical Composition from X-Ray and Chemical Data for the Pierre Shale. Geological Survey Professional Paper 391-C; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Marei, H.W. Quantitative analysis of clay minerals and their admixtures. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1966, 12, 96–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, L.P.; Kahr, G. Determination of the cation exchange capacity (cec) of clay minerals using the complexes of copper(ii) ion with triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 38–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Barrera, D.; Blanco, A.A.; Jalil, M.E.R.; Sapag, K. Importance of the αs-plot Method in the Characterization of Nanoporous Materials. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.A.; Roca Jalil, M.E.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Sapag, K.; Baschini, M.T. Fe- and SiFe-pillared clays from a mineralogical waste as adsorbents of ciprofloxacin from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 220, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Toschi, F.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Silica pillared montmorillonites as possible adsorbents of antibiotics from water media. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C., Jr. X-Ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals; Mineralogical Society: Oxford, MS, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.D.; Fraser, A.R. Infrared methods. In Clay Mineralogy: Spectroscopic and Chemical Determinative Methods; Wilson, M.J., Ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994; pp. 11–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sabah, E.; Ouki, S. Sepiolite and sepiolite-bound humic acid interactions in alkaline media and the mechanism of the formation of sepiolite-humic acid complexes. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 162, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J.; Gates, W.P.; Petit, S. IR Spectra of clay minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 8, pp. 107–149. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Anbalagan, G. Spectroscopic characterization of natural calcite minerals. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2007, 68, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabak, A.; Eren, E.; Afsin, B.; Caglar, B. Determination of adsorptive properties of a Turkish Sepiolite for removal of Reactive Blue 15 anionic dye from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, J.L.; Galán, E. Determination of impurity in sepiolite by thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. 1994, 42, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.; Sarikaya, Y. Some physicochemical properties of a clay containing smectite and palygorskite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 44, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; Pozo, M.; Cecilia, J.A.; Benítez-Guerrero, M.; Pozo, E.; Martín Rubí, J.A. Microwave assisted acid treatment of sepiolite: The role of composition and ‘crystallinity’. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 102, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, M.; García-Romero, E. Variability of the surface properties of sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67–68, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Huang, H.; Xu, W.; Qin, F.; Liu, S. Adsorption properties and mechanism of purified palygorskite on methylene blue. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A General Treatment and Classification of the Solute Adsorption Isotherm. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Ferraz, E.; Santarén, J.; Rasteiro, M.G.; Gamelas, J.A.F. Improving colloidal stability of sepiolite suspensions: Effect of the mechanical disperser and chemical dispersant. Minerals 2020, 10, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkur, H.; Can, M.F.; Sabah, E. Rheological behavior of sepiolite suspensions homogenized by ultra-turrax high-speed homogenizer. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2022, 58, 153415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, E. Properties and applications of palygorskite-sepiolite clays. Clay Miner. 1996, 31, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hong, H.; Liao, L.; Ackley, C.J.; Schulz, L.A.; MacDonald, R.A.; Mihelich, A.L.; Emard, S.M. A mechanistic study of ciprofloxacin removal by kaolinite. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Influence of pH and antibiotic solubility on the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous media using montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pan, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, F.; Xu, L.; Xu, G.; Peng, X. Removal of ciprofloxacin with aluminum-pillared kaolin sodium alginate beads (CA-Al-KABs): Kinetics, isotherms, and BBD model. Water 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Oba, S.N.; Aniagor, C.O.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Ighalo, J.O. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water: A comprehensive review. Korean Soc. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Langmuir Model |
|
| Freundlich Model |
|
| Sips Model |
|
| Sample | Bulk Mineralogy (%) | Clay Fraction (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phy | Qz | Pl | Fd K | Cal | Plg | Sep | Sme | Ill | Kao | |
| Ad-1 | 90 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 66 | - | 27 | 7 | Tr |
| Ad-2 | 93 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | 86 | 14 | - | - |
| Ad-3 | 85 | 8 | 3 | 4 | - | - | 70 | 23 | 7 | - |
| Ad-4 | 99 | <1 | <1 | <1 | - | - | 78 | 21 | 1 | - |
| Ad-9 | 87 | 6 | - | - | 7 | 83 | - | 17 | - | - |
| Major Elements (%) | Ad-1 | Ad-2 | Ad-3 | Ad-4 | Ad-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 51.63 | 51.74 | 52.98 | 51.05 | 54.15 |
| Al2O3 | 13.72 | 6.22 | 7.09 | 3.65 | 8.54 |
| Fe2O3 | 4.54 | 1.83 | 2.13 | 0.85 | 4.16 |
| MgO | 7.20 | 16.10 | 15.53 | 21.83 | 8.58 |
| CaO | 2.91 | 3.85 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 4.27 |
| Na2O | 0.37 | 0.14 | 0.81 | 0.37 | 0.10 |
| K2O | 1.73 | 0.56 | 2.43 | 0.87 | 0.52 |
| TiO2 | 0.43 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.44 |
| P2O5 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.58 |
| LOI | 16.95 | 18.94 | 16.93 | 20.28 | 18.49 |
| Ad-2 | Ad-3 | Ad-4 | Ad-1 | Ad-9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEC (cmol+·kg−1) | 48 | 37 | 37.5 | 53 | 32 |
| SBET (m2·g−1) | 325 | 227 | 316 | 201 | 170 |
| VT (cm3·g−1) | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.35 |
| Vμp (cm3·g−1) | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Vmp (cm3·g−1) | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.23 | 0.32 |
| Ad-2 | Ad-3 | Ad-4 | Ad-1 | Ad-9 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPX | LID | CPX | LID | CPX | LID | CPX | LID | CPX | LID | ||
| Langmuir | qm (mmol·g−1) | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.88 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.73 | 0.90 | 0.30 |
| k (L·mmol−1) | 250.9 | 1.11 | 83.4 | 17.06 | 3.78 | 6.83 | 4.79 | 0.22 | 5.14 | 0.36 | |
| R2 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.92 | |
| Freundlich | kf (L·g−1) | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.62 | 0.25 | 0.70 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 0.07 |
| n | 6.07 | 2.09 | 7.54 | 7.71 | 4.10 | 5.12 | 3.57 | 1.37 | 3.64 | 0.99 | |
| R2 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.80 | 0.95 | |
| Sips | qm (mmol·g−1) | 0.77 | 0.42 | 0.71 | 0.4 | 1.16 | 0.50 | 1.03 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.30 |
| b (L·mmol−1)1/n | 4.52 | 1.10 | 4.14 | 2.78 | 1.90 | 2.70 | 1.18 | 1.00 | 0.36 | 0.74 | |
| n | 2.43 | 0.89 | 1.56 | 11.4 | 1.71 | 1.02 | 4.22 | 0.22 | 6.23 | 0.39 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.94 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musso, T.B.; Roca-Jalil, M.E.; Rodriguez-Ameijide, V.; Sanchez, M.; Maggio, A.; Baschini, M.T.; Pettinari, G.; Villa, L.; Pérez-Abad, A.; Pozo, M. The Efficiency of Fibrous Mg Clays for the Removal of Ciprofloxacine and Lidocaine from Water—The Role of Associated Clay Minerals. Minerals 2025, 15, 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101083
Musso TB, Roca-Jalil ME, Rodriguez-Ameijide V, Sanchez M, Maggio A, Baschini MT, Pettinari G, Villa L, Pérez-Abad A, Pozo M. The Efficiency of Fibrous Mg Clays for the Removal of Ciprofloxacine and Lidocaine from Water—The Role of Associated Clay Minerals. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101083
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusso, Telma Belén, Maria Eugenia Roca-Jalil, Vanina Rodriguez-Ameijide, Micaela Sanchez, Andrea Maggio, Miria Teresita Baschini, Gisela Pettinari, Luis Villa, Alejandro Pérez-Abad, and Manuel Pozo. 2025. "The Efficiency of Fibrous Mg Clays for the Removal of Ciprofloxacine and Lidocaine from Water—The Role of Associated Clay Minerals" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101083
APA StyleMusso, T. B., Roca-Jalil, M. E., Rodriguez-Ameijide, V., Sanchez, M., Maggio, A., Baschini, M. T., Pettinari, G., Villa, L., Pérez-Abad, A., & Pozo, M. (2025). The Efficiency of Fibrous Mg Clays for the Removal of Ciprofloxacine and Lidocaine from Water—The Role of Associated Clay Minerals. Minerals, 15(10), 1083. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101083