Attenuation of Acid Mine Drainage in a Coal Waste Deposit in Southern Brazil and the Prospect of Transitioning from Active to Passive Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
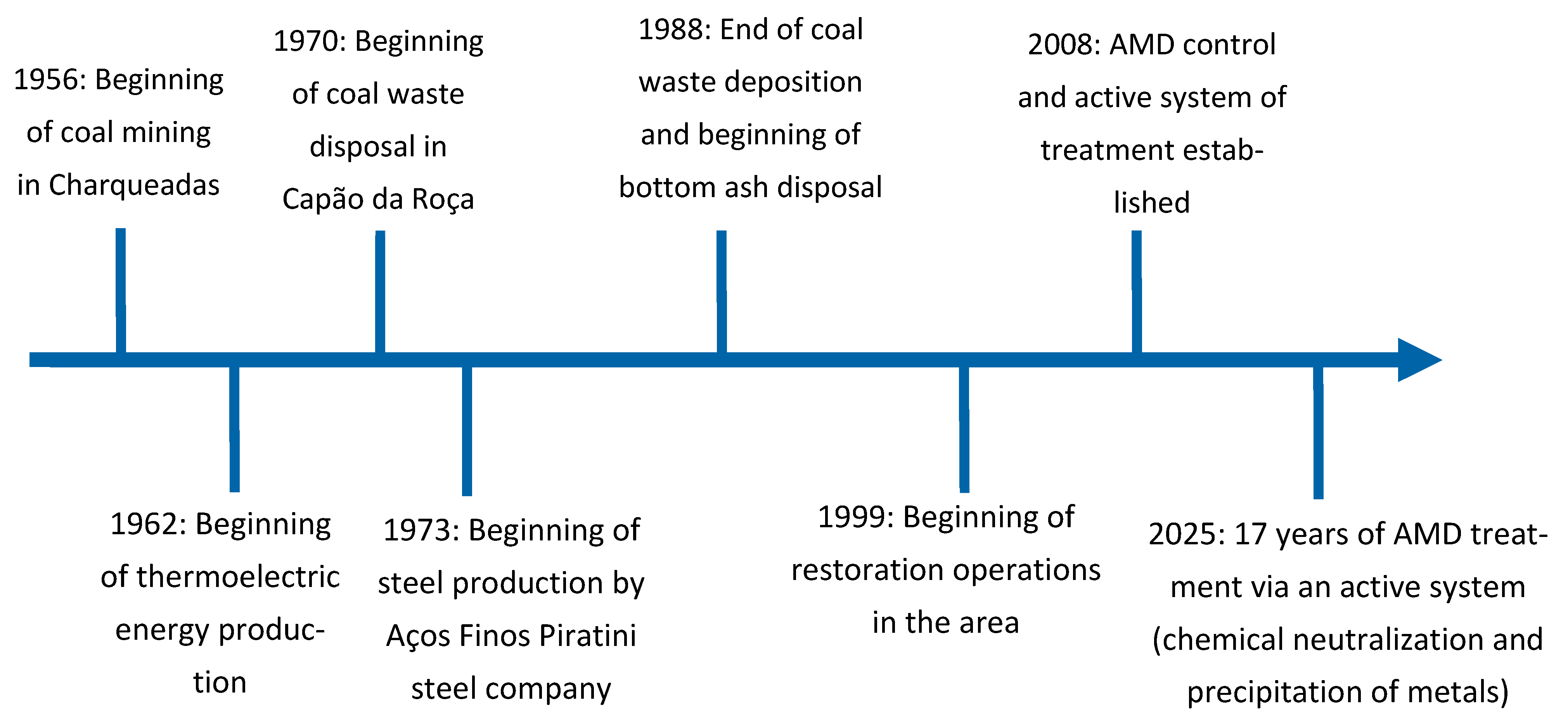
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials Characterisation
2.3. Historical Data Evaluation and Mathematical Modelling
2.4. Active Treatment
2.5. Passive Treatment Test
2.6. Chemical and Toxicological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Coal Waste Characterisation
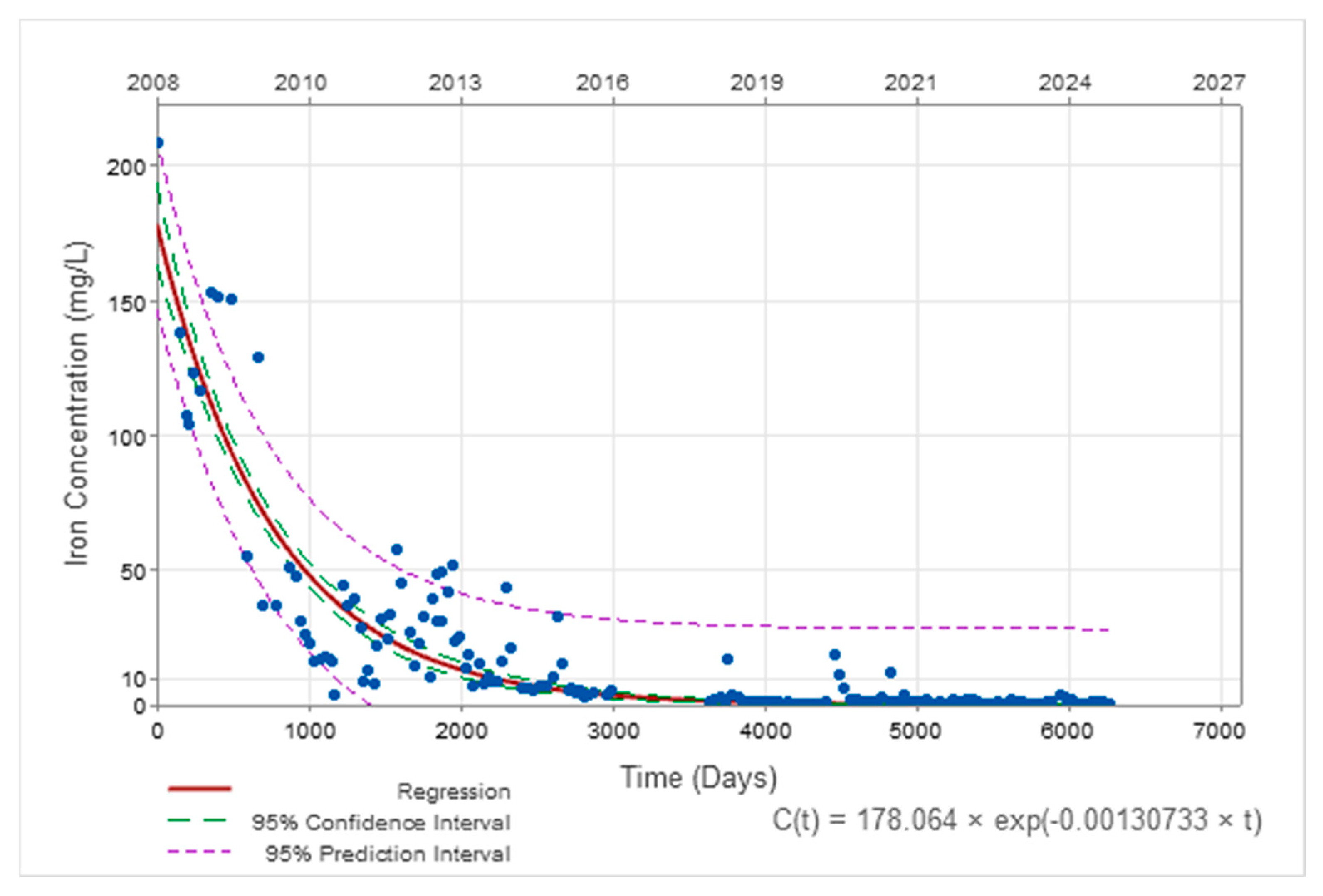
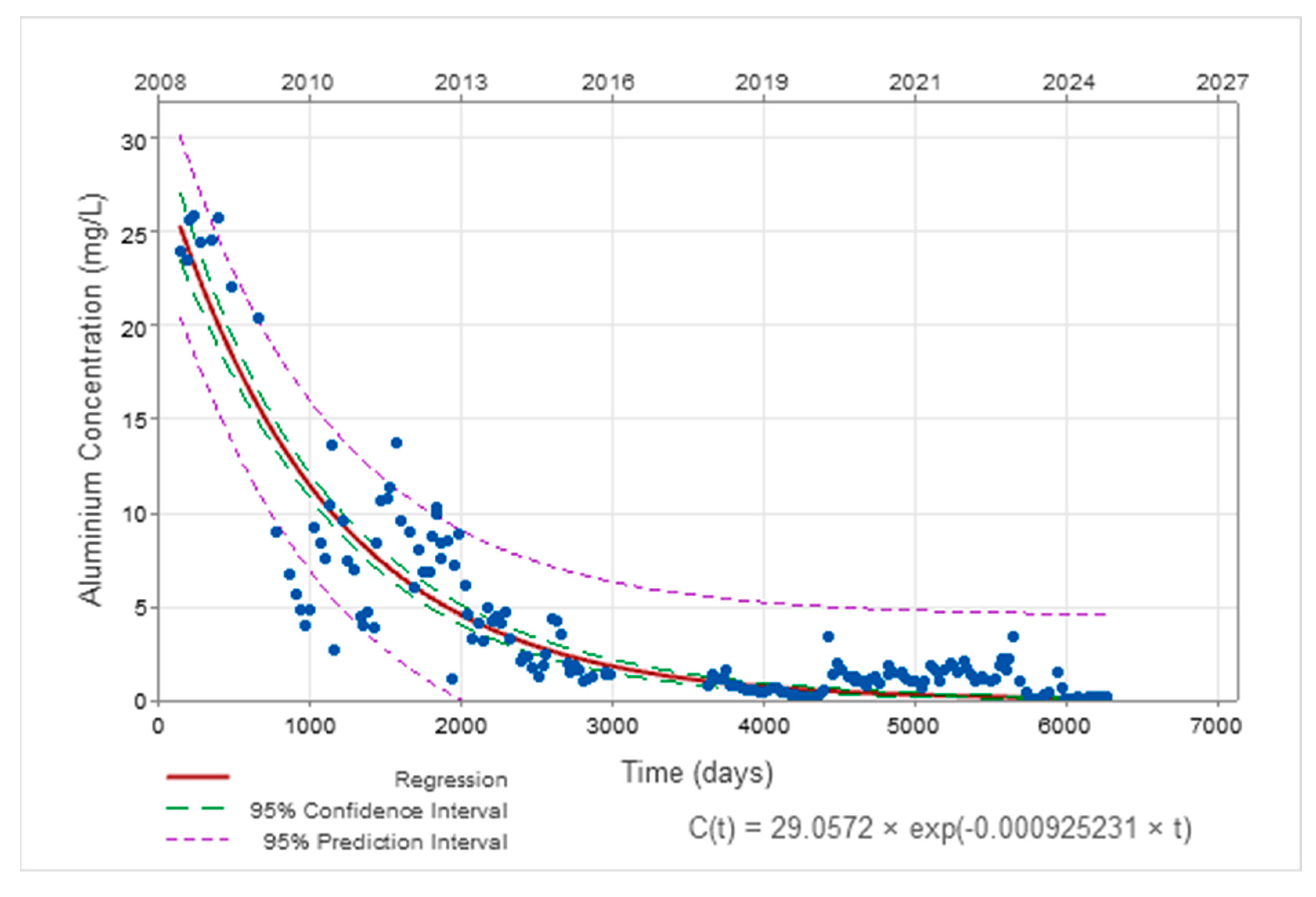
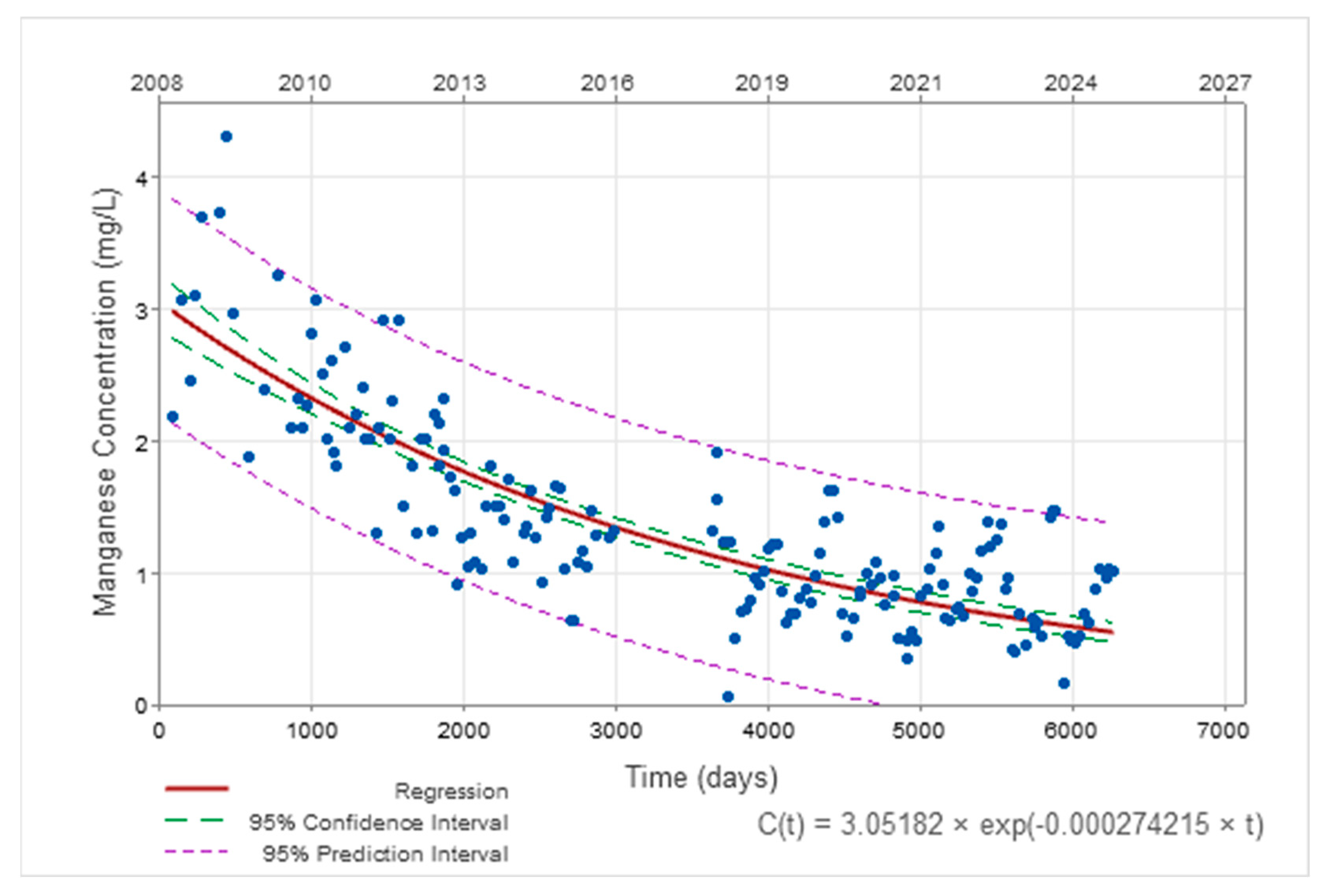
3.2. Temporal Evolution of AMD Parameters
3.3. Transition from Active to Passive Treatment
- (i)
- From 2008 to 2020 (from day 1 to day 4699): needed pH adjustment and removal of metals Fe, Al, and Mn (Table 4);
- (ii)
- From 2021 to 2023 (from day 4700 to day 5794): needed pH adjustment and removal of Mn (Table 5);
- (iii)
- From 2024 to present (from day 5798 to day 6180): needed the occasional adjustment of pH and removal of Mn (Table 6).
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kontopoulos, A. Acid mine drainage control. In Effluent Treatment in the Mining Industry; Castro, S.H., Vergara, F.S.M.A., Eds.; University of Concepción: Concepción, Chile, 1998; p. 00.57-118. ISBN 956-277-156-0. [Google Scholar]
- Skousen, J.; Rose, A.; Geidel, G.; Foreman, J.; Evans, R.; Hellier, W. Handbook of Technologies for Avoidance and Remediation of Acid Mine Drainage. Available online: https://wvwri.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/Handbook-Avoidance-Remediation-Skousen-1999.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, A.S.; Sheoran, V. Heavy metals removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: A critical review. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Rose, A.; ZIemkiewicz, P.F.; Nairn, R.; McDonald, L.M.; Kleinmann, R.L. Review of passive systems for acid mine drainage treatment. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skousen, J.G.; Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; McDonald, L.M. Acid mine drainage formation, control and treatment: Approaches and strategies. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2019, 6, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailing recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, K.; Banat, F.; Pham, Q.M.; Ho, S.-H.; Ren, N.-Q.; Show, P.L. Biological remediation of acid mine drainage: Review of past trends and current outlook. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwewa, B.; Tadie, M.; Ndlovu, S.; Simate, G.S.; Matinde, E. Recovery of rare earth elements from acid mine drainage: A review of the extraction methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Wu, Q.; He, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; He, H.; Liu, C.; Dang, Z.; Reinfelder, J.R. Reduction of acid mine drainage by passivation of pyrite surfaces: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Ajala, O.J.; Oba, S.N.; Iwuchukwu, F.U.; Ahmadi, S.; Igwegbe, C.A. A review of treatment technologies for the mitigation of the toxic environmental effects of acid mine drainage (AMD). Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.; Sheridan, C.; Holm, P. A critical review of phytoremediation for acid mine drainage-impacted environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Foteinis, S.; Renforth, P.; Ndiritu, J.; Maree, J.P.; Tekere, M.; Chatzisymeon, S. Challenges and avenues for acid mine drainage treatment, beneficiation, and valorization in circular economy: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 183, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraz, U.; Li, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Iqbal, R.; Ditta, A. Remediation technologies for acid mine drainage: Recent trends and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anekwe, H.M.S.; Isa, Y.M. Bioremediation of acid mine drainage—Review. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 65, 1047–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, T.; Liu, P.; Zhang, B.; Che, L. A review of treatment technologies for acid mine drainage and sustainability assessment. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, T. A review of acid mine drainage: Formation mechanism, treatment technology, typical engineering cases and resource utilization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 1240–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, Y.G.; Taher, T.; Khairurrijal, K.; Ramadan, B.S.; Safitri, H.; Sudibyo, S.; Yuliansyah, A.T.; Petrus, H.T.B.M. Recent advances in the adsorptive removal of heavy metals form acid mine drainage by conventional and novel materials. A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101797. [Google Scholar]
- Wibowo, Y.G.; Safitri, H.; Khairurrijal, K.; Taher, T.; Arham, L.O.; Jarwinda; Jasipto, A.; Danasla, M.A.; Fadhilah, R.; Army, E.K.; et al. Recent advances in acid mine drainage treatment through hybrid technology: Comprehensive review of scientific literature. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 21, 100945. [Google Scholar]
- Mosai, A.K.; Ndlovu, G.; Tutu, H. Improving acid mine drainage treatment by combining treatment technologies: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Che, L.; Li, M.; Liu, P.; Li, T.; Luo, Y. A review on ‘source prevention, process control, end recovery’ trinity comprehensive treatment technology for acid mine drainage. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 189, 782–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Feng, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, S. A review of passive acid mine drainage by PRB and LPB: From design, testing, to construction. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Ho, H.-J.; Iizuka, A. A critical review of current treatment methods of acid mine drainage with an assessment of associated CO2 emissions toward carbon neutrality. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 77, 108347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, P.L. The longevity of minewater pollution: A basis for decision-making. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 194/195, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younger, P.L. Predicting temporal changes in total iron concentrations in groundwaters flowing from abandoned deep mines: A first approximation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 44, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzyl, G.; Banks, D. Verification of the “first flush” phenomenon in mine water from coal mines in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, Poland. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 92, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, B.; McDonald, L.M.; Skousen, J. Acidity decay of above-drainage underground mines in West Virginia. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Merrit, P.; Power, C. Assessing the long-term evolution of mine water quality in abandoned underground mine workings using first-flush based models. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, C.R.; Cravotta, C.A.; Capo, R.C.; Hedin, B.C.; Vesper, D.J.; Stewart, B.W. Multi-decadal geochemical evolution of drainage from underground coal mines in the Apalachian Basin, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisamen, A.; Wolkersdorfer, C. Modelling the hydrogeochemical evolution of mine water in a decommissioned opencast coal mine. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 164, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.; Power, C. Evolution of acid mine drainage from a coal waste rock reclaimed with a simple soil cover. Hydrology 2019, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slesarova, A.; Kusnierova, M.; Luptakova, A.; Zeman, J. An overview of occurrence and evolution of acid mine drainage in the Slovak Republic. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference on Soils, Sediments, Water and Energy, Amherst, MA, USA, 18–21 October 2010; Volume 12, Article 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dold, B. Evolution of acid mine drainage formation in sulphidic mine tailings. Minerals 2014, 4, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, S.; Igarashi, T.; Tabelin, C.B.; Tangviroon, P.; Ii, H. Acid mine drainage sources and hydrogeochemistry at the Yatani mine, Yamagata, Japan: A geochemical and isotopic study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 225, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabelin, C.B.; Uyama, A.; Tomiyama, S.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M.; Phengsaart, T.; Silwamba, M.; Jeon, S.; Park, I.; Arima, T.; Igarashi, T. Geochemical audit of a historical tailing storage facility in Japan: Acid Mine formation, zinc migration and mitigation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-González, R.; Marcías, F.; Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.R. Temporal evolution of acid mine drainage (AMD) leachates from the abandoned tharsis mine Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedin, R.S.; Weaver, T.; Wolfe, N.; Weaver, K. Passive treatment of acidic coal mine drainage: The Anna S Mine passive treatment complex. Mine Water Environ. 2010, 29, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemkiewicz, P.F.; Brand, D.L. The Casselman River restoration project. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth West Virginia Surface Mine Drainage Task Force Symposium, Morgantown, WV, USA, 15–16 April 1996; pp. 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hedin, R.S.; Watzlaf, G.R.; Nairn, R.W. Passive treatment of acid mine drainage with limestone. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, A.; Vásquez, M.; Caparrós, A.; Ibarra, I.; García, C.; Lnares, R.; Rodríguez, R. Heavy metal removal of intermitente acid mine drainage with an open limestone channel. Miner. Eng. 2012, 26, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Weber, C.; Oliveira, C. Neutralization and uptake of pollutant cations from acid mine drainage (AMD) using limestones and zeolites in a pilot-scale passive treatment system. Miner. Eng. 2021, 170, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, L.A.; Freitas, L.V.; Villetti, P.I.C.; Tubino, R.M.C.; Schneider, I.A.H. Ladle slag of electric steelmaking as alkaline agent on controlling of acid mine drainage generation. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, E.R.; Riefler, R.G. Performance of steel slag leach beds in acid mine drainage treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Name, T.; Sheridan, C. Remediation of acid mine drainage using metallurgical slags. Miner. Eng. 2014, 64, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Osman, M.S.; Mbhele, R.N.; Rikhotso, R. Fate of pollutants post treatment of acid mine drainage with basic oxygen furnace slag: Validation of experimental results with a geochemical model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lu, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, M.; Wen, J.; Li, Z. Concurrent removal of Fe(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) cations from acid mine drainage by an industrial solid waste—Steel slag: Behaviors and mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocaan, J.; Turingan, C.O.A.; Tabelin, C.B.; Zoleta, J.B.; Arima, T.; Park, I.; Ito, M.; Orbecido, A.H. A mixed media approach using locally available neutralizing materials for the passive treatment of acid mine drainage. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemkiewicz, P.F. Acid mine drainage treatment with armored limestone in open channels. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomartino, S.; Webb, J. Estimating the longevity of limestone drains in treating acid mine drainage containing high concentrations of iron. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 2344–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.J.A.S.; Becker, E.D.; Leister, H. Evolução do Desempenho Estado Atual da Unidade de Beneficiamento de Carvão da Aços Finos Piratini. 1981. Available online: https://publicacoes.entmme.org/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Kalkreuth, W.; Holz, M.; Kern, M.; Machado, G.; Mexias, A.; Silva, M.B.; Willet, J.; Finkelman, R.; Burger, H. Petrology and chemistry of Permian coals from the Paraná Basin: 1. Santa Terezinha, Leão-Butiá and Candiota Coalfields, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 68, 79–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clima e Condições Meteorológicas Médias em Charqueadas no Ano Todo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Available online: https://pt.weatherspark.com/y/29704/Clima-caracter%C3%ADstico-em-Charqueadas-Rio-Grande-do-Sul-Brasil-durante-o-ano (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- ASTM D167; Standard Test Method for Apparent and True Specific Gravity and Porosity of Lump Coke. American Society for Testing and Material. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012; p. 3.
- EPA530-R-94-036; Technical Document. Acid Mine Drainage Prediction. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; p. 48.
- Lapakko, K. Mine Waste Drainage Quality Prediction: A Literature Review; Draft Paper; Minesota Department of Natural Resources, Division of Mineral: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rio Grande do Sul-CONSEMA-Conselho Estadual do Meio Ambiente. Resolução CONSEMA nº 355/2017. Dispõe Sobre os Critérios e Padrões de Emissão de Efluentes Líquidos para as Fontes Geradoras que Lancem seus Efluentes em Aguas Superficiais no Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Conselho Estadual do Meio Ambiente. Em vigor desde 19 July 2017, 7p. Available online: https://www.normasbrasil.com.br/norma/resolucao-485-2023-rs_444815.html (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Eaton, A.D.; Franson, M.A.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 2005. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers?ReferenceID=1870039 (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- OECD. Test N° 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. 2004. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/test-no-202-daphnia-sp-acute-immobilisation-test_9789264069947-en.html (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- EPA 821-R2-012; Technical Document. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Collischonn, W.; Brêda, J.P.L.F.; Correa, S.W.; Wongchuig, S.; Ruhoff, A.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Fan, F.M.; Machado Filho, R.C.C.; Ramalho, N. Unprecedented April-May 2024 rainfall in South Brazil sets new record. Rev. Bras. De Recur. Hídricos 2024, 29, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collischonn, W.; Fan, F.M.; Possanti, I.; Dornelles, F.; Paiva, R.; Medeiros, M.S.; Michel, G.P.; Magalhães Filho, F.J.C.; Moraes, S.R.; Marcuzzo, F.F.N.; et al. The exceptional hydrological disaster of April-May 2024 in southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. De Recur. Hídricos 2025, 30, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinchao, W.; Roger, C.; Viadero, J.; Karen, M. Recovery of iron and aluminum from acid mine drainage by selective precipitation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 22, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, P.; Meshram, P.; Jawadand, S.; Meshram, T.; Randive, K. A critical analysis of industrial slags, their hazard potential and remediation with reference to Sustainable Developments Goals (SDGs). Discov. Civ. Eng. 2025, 2, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
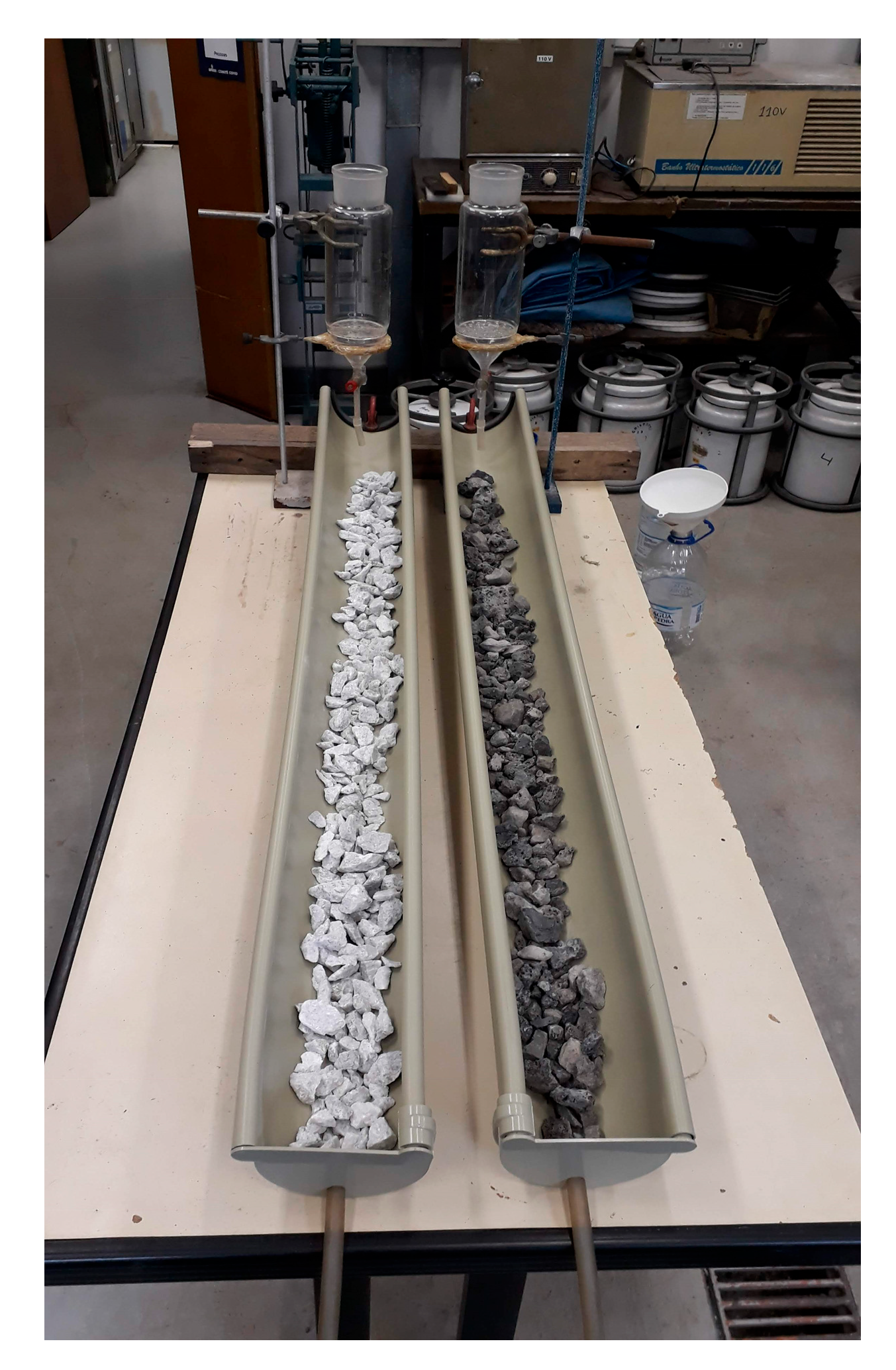




| Parameter | Limestone | Slag |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution (mm) | 9–25 | 9–25 |
| Bulk density—ρ (t m−3) | 1.45 | 1.78 |
| Void ratio—e (%) | 50 | 41 |
| Elemental analysis carried out by FRX (%) | ||
| CaO | 56.05 | 36.31 |
| SiO2 | nd | 19.92 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.07 | 18.7 |
| MgO | 1.46 | 11.59 |
| Al2O3 | nd | 6.95 |
| MnO | 0.03 | 4.94 |
| TiO2 | 0.02 | 0.83 |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | 0.34 |
| Na2O | nd | nd |
| K2O | nd | nd |
| Neutralisation potential (kg CaCO3 t−1) | 954.8 | 731.8 |
| Crystalline compounds | calcite (99.6%) | wustite (63.4%) |
| detected by XRD | quartz (0.4%) | magnetite (22.1%) |
| hematite (14.5%) |
| Material | Sample | Total Sulphur (wt.%) | AP (kg CaCO3 t−1) | NP (kg CaCO3 t−1) | NNP (kg CaCO3 t−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal waste | 1 | 0.52 | 16.2 | 1.0 | −15.2 |
| 2 | 1.79 | 56.0 | 0.0 | −56.0 | |
| 3 | 1.56 | 46.7 | 0.0 | −46.7 | |
| Average | 1.29 | 39.6 | 0.3 | −39.3 | |
| Bottom Ash | 1 | - | - | 26.8 | 26.8 |
| 2 | - | - | 21.1 | 21.1 | |
| 3 | - | - | 31.3 | 31.3 | |
| Average | - | - | 26.4 | 26.4 | |
| Covering soil | 1 | 0.12 | 3.8 | 0 | −3.8 |
| 2 | 0.13 | 4.0 | 0 | −4.0 | |
| 3 | 0.07 | 2.2 | 0 | −2.2 | |
| Average | 0.11 | 3.3 | 0 | −3.3 |
| Parameter | Exponential Regression | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | C(t) = 178.06.e−0.0013·t t in days C(t) = 178.06.e−0.48·t t in years | C0 = 7.66 k = 0.000068 (t in days) k = 0.025 (t in years) |
| Aluminium | C(t) = 29.06.e−0.00093·t t in days C(t) = 29.06.e−0.34·t t in years | C0 = 1.19 k = 0.000042 (t in days) k = 0.015 (t in years) |
| Manganese | C(t) = 3.05.e−0.00027·t t in days C(t) = 3.05.e−0.10·t t in years | C0 = 0.11 k = 0.000015 (t in days) k = 0.0055 (t in years) |
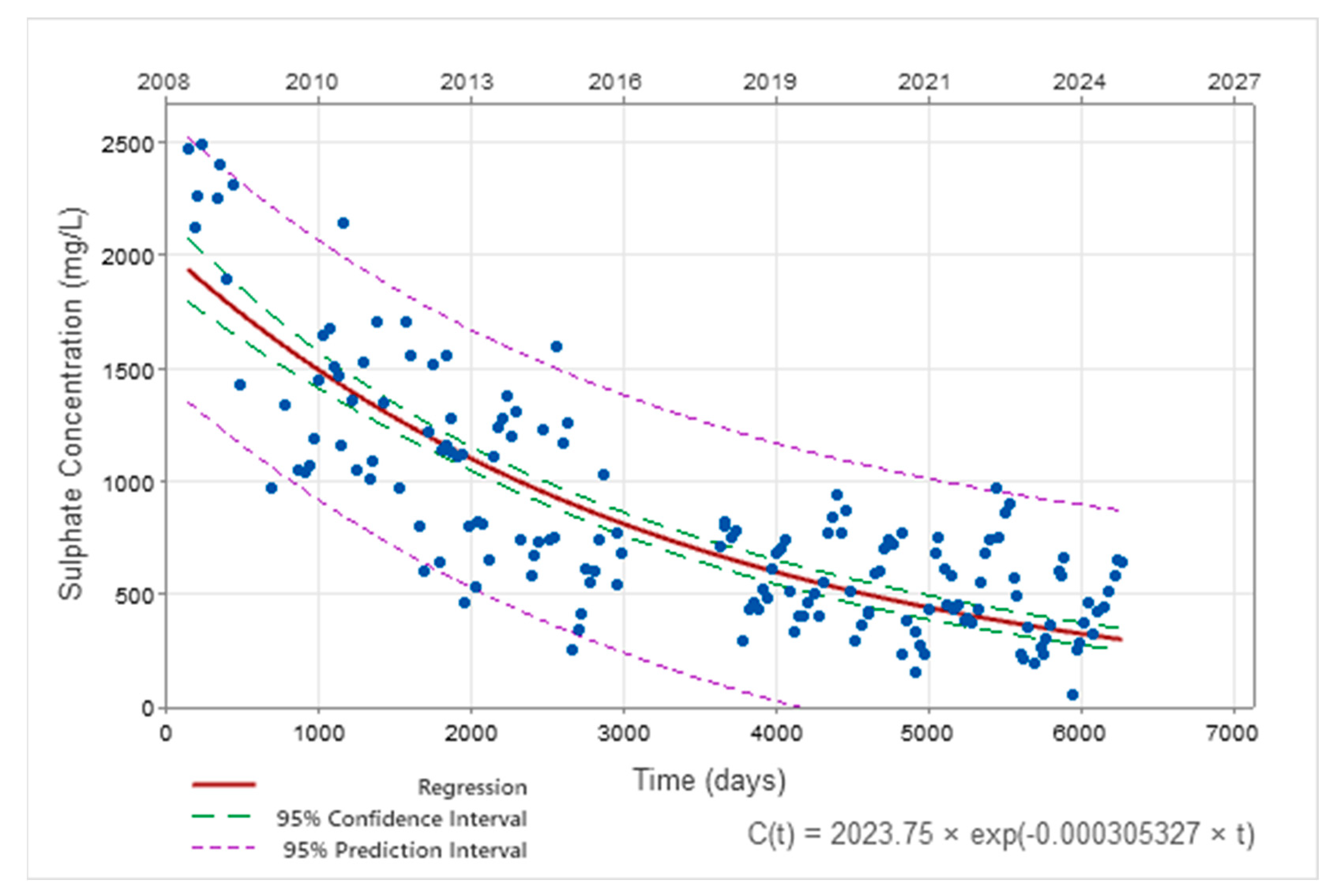
| Sulphates | C(t) = 2023.75.e−0.00031·t t in days C(t) = 2023.75.e−0.11·t t in years | C0 = 79.41 k = 0.000017 (t in days) k = 0.0064 (t in years) |
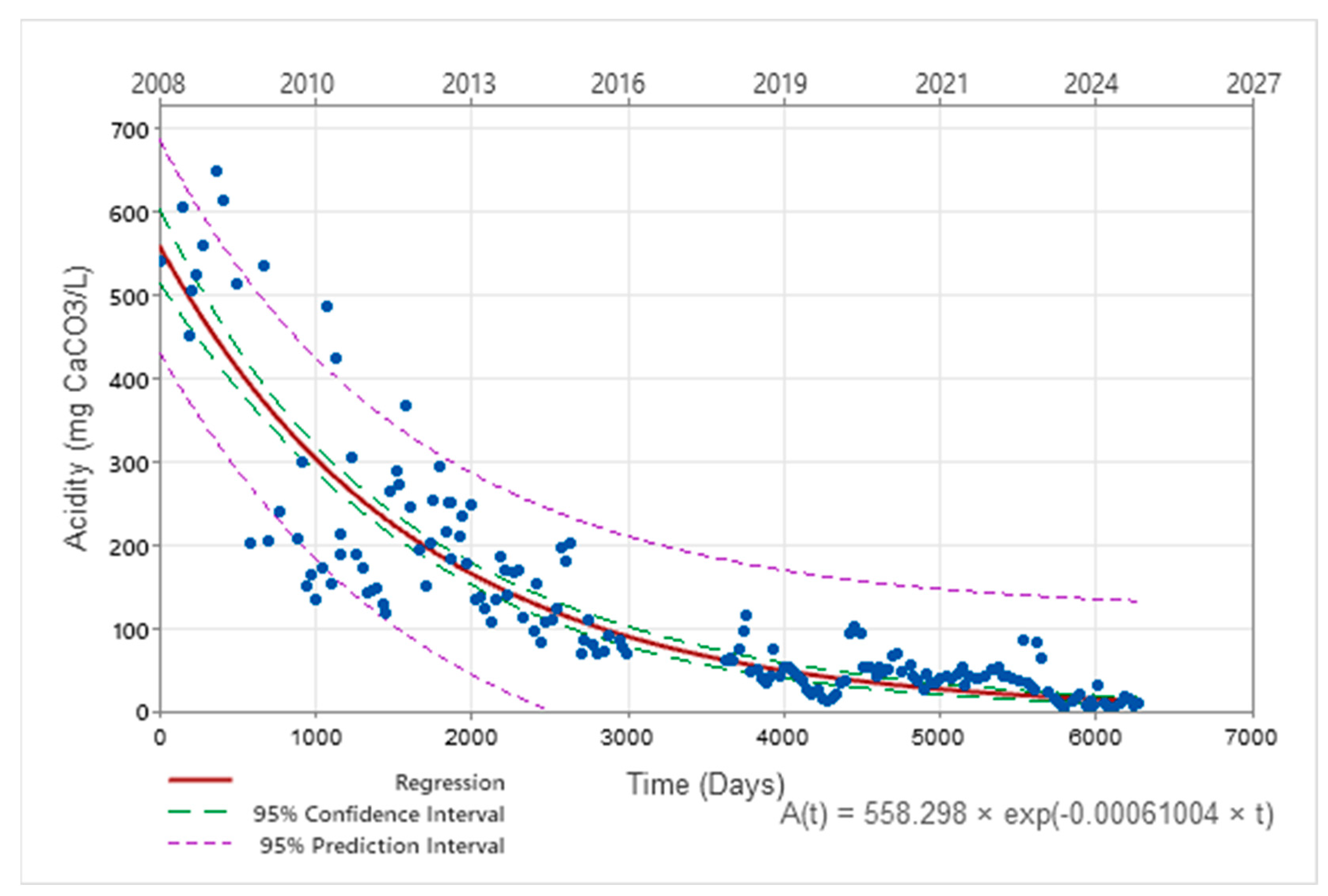
| Acidity | A(t) = 558.30.e−0.00061·t t in days A(t) = 558.30.e−0.22·t t in years | C0 = 22.45 k = 0.000031 (t in days) k = 0.011 (t in years) |
| Parameter | Raw Wastewater, n = 129 | Treated Wastewater, n = 129 | Emissions Standards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 4699 | NC | Day 1 | Day 4699 | NC | ||
| pH | 2.1 | 4.1 | 119 | 5.6 | 7.5 | 16 | 5.0–9.0 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 177.8 | 0.4 | 58 | 2.1 | 0.1 | 1 | <10.0 |
| Al (mg L−1) | 29.0 | 0.4 | 19 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 1 | <10.0 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 3.1 | 0.8 | 95 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 3 | <1.0 |
| Sulphates (mg L−1) | 2023.1 | 482.2 | - | 972.2 | 500.0 | - | - |
| Parameter | Raw Wastewater, n = 36 | Treated Wastewater, n = 36 | Emissions Standards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 4700 | Day 5794 | NC | Day 4700 | Day 5794 | NC | ||
| pH | 4.1 | 4.6 | 36 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 0 | 5.0–9.0 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | <10.0 |
| Al (mg L−1) | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | <10.0 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 0.8 | 0.6 | 9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | <1.0 |
| Sulphates (mg L−1) | 481.9 | 345.0 | - | 500.0 | 390.0 | - | - |
| Parameter | Raw Wastewater, n = 16 | Treated Wastewater, n = 16 | Emissions Standards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 5795 | Day 6525 | NC | Day 5795 | Day 6525 | NC | ||
| pH | 4.6 | 4.7 | 2 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 0 | 5.0–9.0 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | <10.0 |
| Al (mg L−1) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | <10.0 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | <1.0 |
| Sulphates (mg L−1) | 345.0 | 306.7 | - | 389.9 | 351.2 | - | - |
| Parameter | Raw AMD | After Limestone Channel | After Slag Channel | Emissions Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.4 | 7.5 | 8.2 | 5.0–9.0 |
| Fe (mg L−1) | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 15 |
| Al (mg L−1) | 2.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 10 |
| Mn (mg L−1) | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 1.0 |
| CE50-48 h (%) | 66.81 | >100 | >100 | |
| Interpretation | Toxic | Nontoxic | Nontoxic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keller, F.S.; Boff, C.; Silva, D.; Grigorieff, A.; Weber, C.C.; Weiler, J.; Schneider, I.A.H. Attenuation of Acid Mine Drainage in a Coal Waste Deposit in Southern Brazil and the Prospect of Transitioning from Active to Passive Treatment. Minerals 2025, 15, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101068
Keller FS, Boff C, Silva D, Grigorieff A, Weber CC, Weiler J, Schneider IAH. Attenuation of Acid Mine Drainage in a Coal Waste Deposit in Southern Brazil and the Prospect of Transitioning from Active to Passive Treatment. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101068
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeller, Felipe Santin, Cláudio Boff, Daniela Silva, Alexandre Grigorieff, Cristiano Corrêa Weber, Jéssica Weiler, and Ivo André Homrich Schneider. 2025. "Attenuation of Acid Mine Drainage in a Coal Waste Deposit in Southern Brazil and the Prospect of Transitioning from Active to Passive Treatment" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101068
APA StyleKeller, F. S., Boff, C., Silva, D., Grigorieff, A., Weber, C. C., Weiler, J., & Schneider, I. A. H. (2025). Attenuation of Acid Mine Drainage in a Coal Waste Deposit in Southern Brazil and the Prospect of Transitioning from Active to Passive Treatment. Minerals, 15(10), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101068







