Beneficiation of Fine-Grained Bayan Obo Niobium Ore Using a Slime Vibrating Table
Abstract
1. Introduction
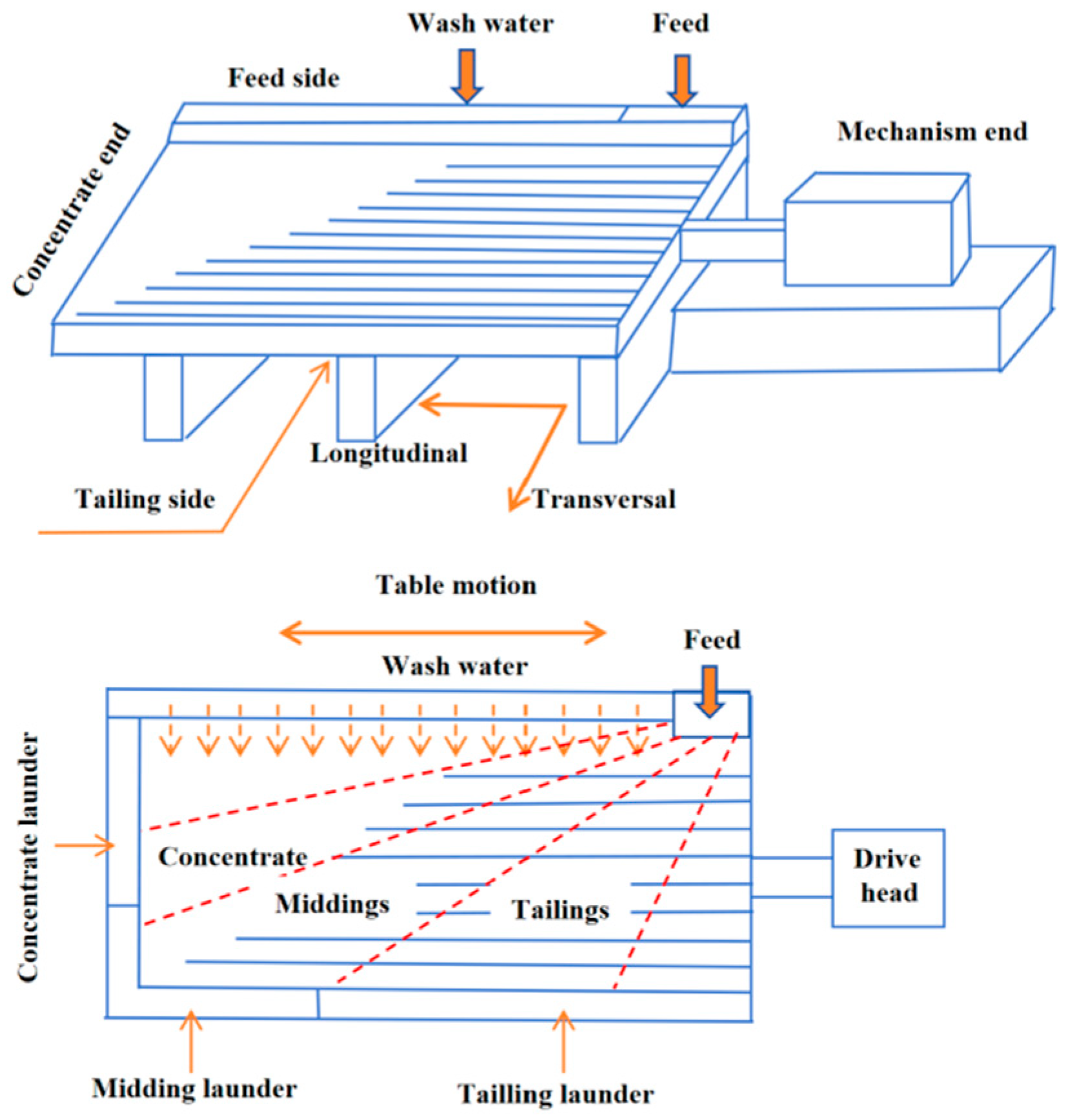
2. Equipment Descriptions
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Properties of the Tested Sample
3.2. Methodology of the Tests
3.3. Evaluation on Separation Efficiency
4. Results and Discussions
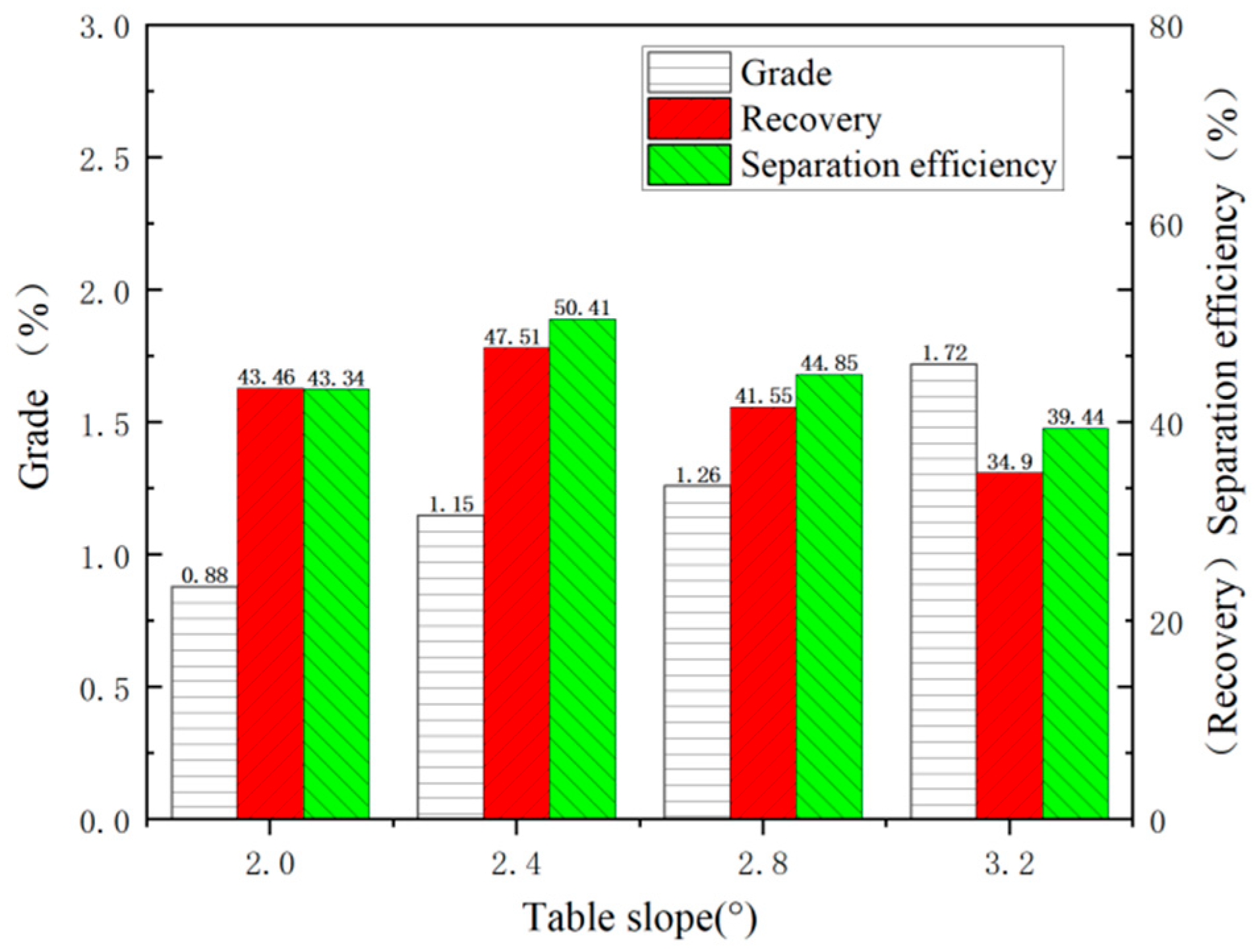
4.1. Effect of Table Slope
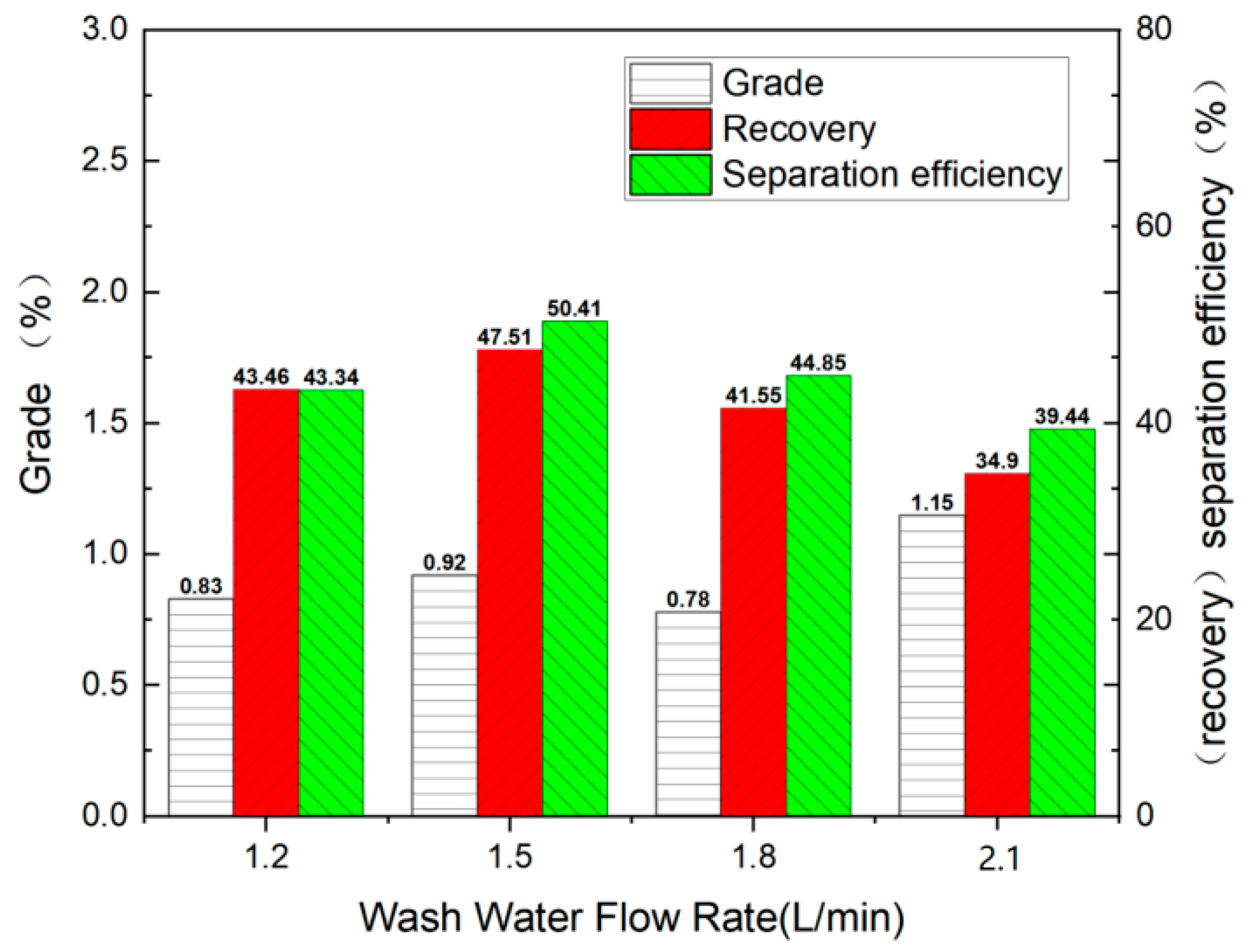
4.2. Effect of Wash-Water Flow Rate
4.3. Effect of Vibrating Voltage
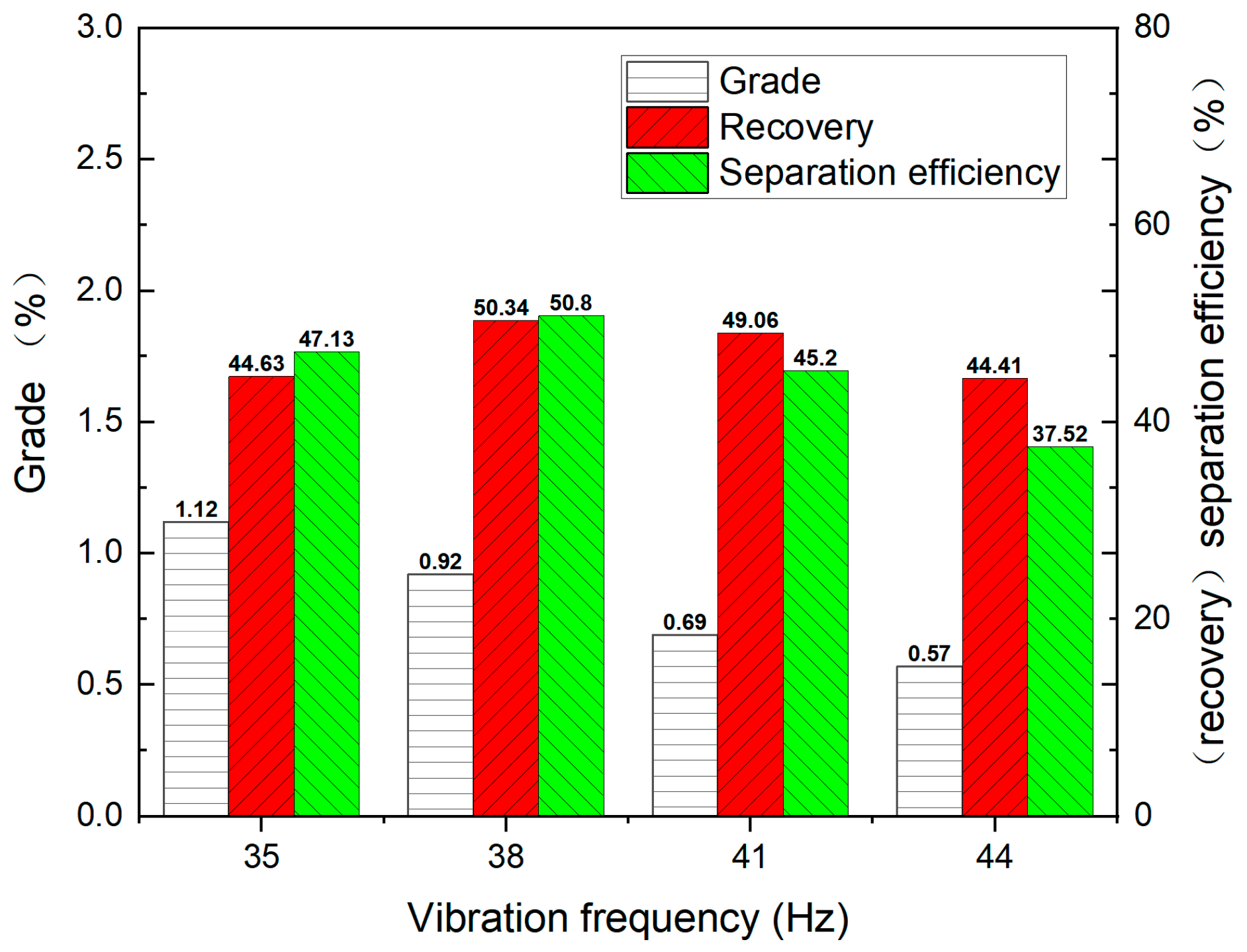
4.4. Effect of Vibrating Frequency
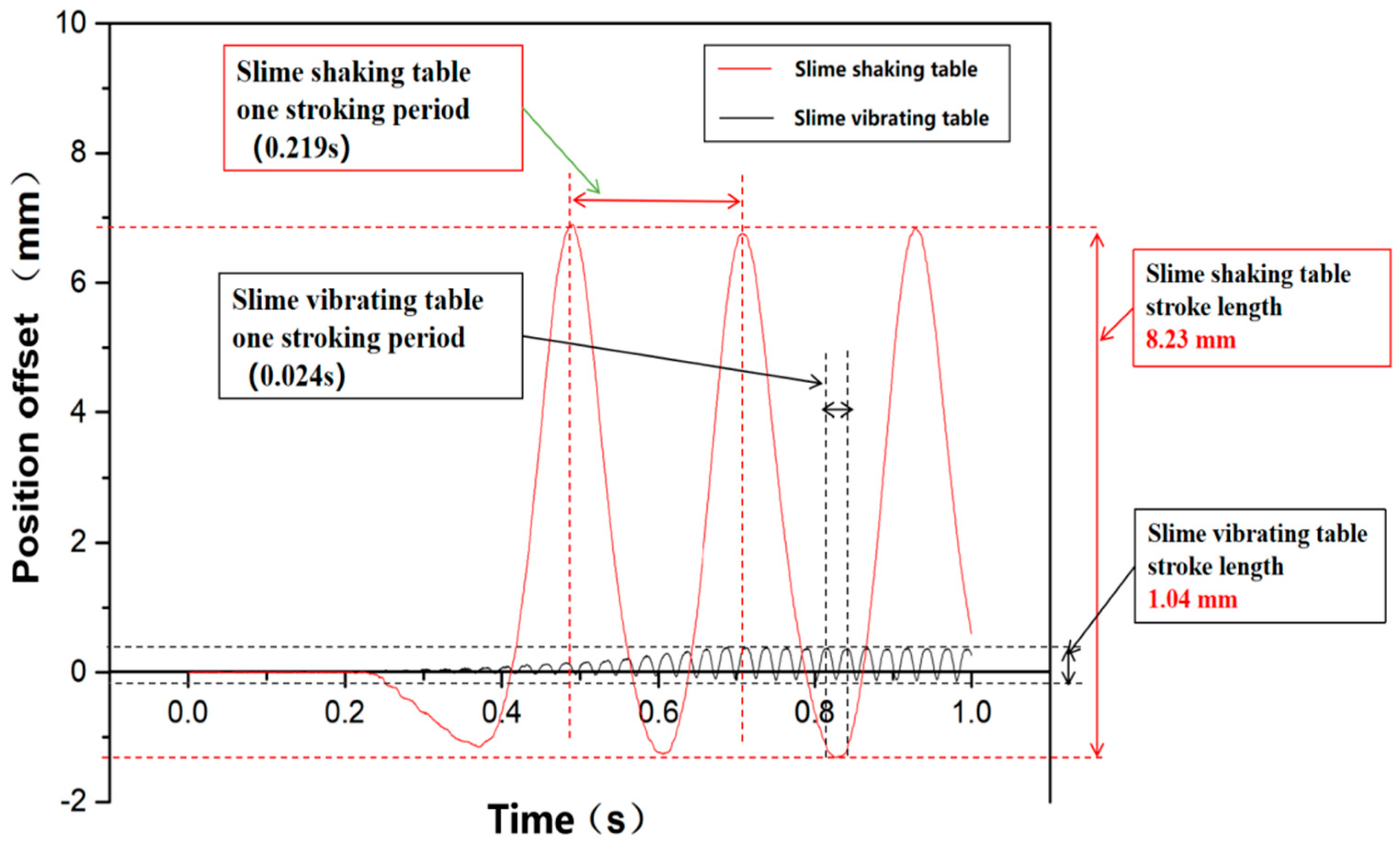
4.5. Comparison Between SST and SVT
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The SVT was developed from the Slime Shaking Table (SST), with its drive head replaced from an eccentric mechanism to electromagnetic mechanism, and the driving mode changing from shaking to vibrating.
- (2)
- The effect of key parameters, including table slope, wash-water flow rate, vibration voltage, and vibration frequency, was tested. The optimized operating condition was table slope at 2.4°, wash-water flow rate at 1.5 L/min, vibration voltage at 190 V, and vibration frequency at 38 Hz.
- (3)
- Under the optimized operating condition, SVT produced a primary concentrate assaying 1.31% Nb2O5 with a recovery of 52.64%, which was 0.22% and 26.59% higher than that of SST, respectively. Size-by-size analysis indicated that the enhanced separation performance of SVT was mainly attributed to its superior recovery of Nb2O5 in the −38 μm fraction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graham, S.J.; Gallagher, E.; Baxter, G.J.; Azakli, Y.; Weeks, J.; Gelmetti, M.; D’Souza, N.; Boettcher, C.; Roebuck, B.; Tsakiropoulos, P.; et al. Powder production, FAST processing and properties of a Nb-silicide based alloy for high temperature aerospace applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 3217–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Lee, Y.; Tran, D.T.; Choi, W.S.; Kang, W.N.; Yun, J.; Kim, J.; Song, J.; Han, Y.; Park, T.; et al. Effect of C additives with 0.5 % in weight on structural, optical and superconducting properties of Ta–Nb–Hf–Zr–Ti high entropy alloy films. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1008, 176863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, M.; Lopez-Cazalilla, A.; Sarakinos, K.; Rosaz, G.J.; Carlos, C.P.A.; Leith, S.; Calatroni, S.; Himmerlich, M.; Djurabekova, F. Growth of Nb films on Cu for superconducting radio frequency cavities by direct current and high power impulse magnetron sputtering: A molecular dynamics and experimental study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, S.; Song, X.; Yin, G.; Lou, S.; Tan, L. Highly oxidized state dopant induced Nb-O bond distortion of TiNb2O7 for extremely fast-charging batteries. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, H.; Niu, L. A DFT prediction of two-dimensional MB3 (M = V, Nb, and Ta) monolayers as excellent anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 28525–28532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Luo, D.; Wang, Z.L.; Ren, K. Enhanced hydrogen evolution rate using piezoelectric K1/2Na1/2NbO3 nanosheets by Controlling annealing temperature. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 37678–37687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liu, M.; Long, M.; Shan, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, F. Enhanced piezoelectric and energy harvesting performance of monophase NaNbO3-based ceramics doped with BaAlO2.5. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 520, 166047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, H.; Jiang, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, R.; Nie, X.; Tu, N.; Huang, X. Enhanced piezoelectricity in 0.4CaBi2Nb2O9-0.6Na0.5Bi2.5Nb2O9 through Ce/Mo co-doping. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2025, 199, 109841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Valery, Z.; Vereschaka, A.; Keshin, A.; Huo, Y.; Milovich, F.; Sotova, C.; Seleznev, A. Influence of niobium and hafnium doping on the wear and corrosion resistance of coatings based on ZrN. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 6386–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylali, B.; Gulten, G.; Efeoglu, I.; Totik, Y.; Kelly, P.; Kulczyk-Malecka, J. Influence of Nb and Ta on the corrosion and mechanical properties of CrYN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Sippel, J.F.; CM D’Oliveira, A.S. Oxidation of Nb-Ti-W and Nb-Ti-Mo alloys processed by plasma transferred arc in the temperature range 500–700°C. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 133, 107382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Song, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, K. Development of novel superelastic metastable Ti-Mo-Nb-Sn biomedical alloys with low modulus: Compositional design and microstructure-mechanical property relationships. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1036, 181838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Tao, L.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Huang, G.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Liao, K.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. A new strategy for designing Nb-based H2-selective alloys based on physical-chemical parameter matching rules. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 2782–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Ran, M.; Lu, X.; Jiang, C.; Chen, W. The effects of multielement basicity on niobium-bearing phase reconstruction in low grade niobium rougher concentrate. Miner. Eng. 2024, 217, 108951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Occurrence of niobium in biotite-type Fe-REE-Nb ore in the Bayan Obo deposit. Solid Earth Sci. 2023, 8, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yuan, R.; Lan, X.; Xu, H.; Guo, Z. Fundamental Research on Selective Pre-enrichment of Low-Grade Niobium Concentrate from Bayan Obo Mine Via Super Gravity. JOM 2024, 76, 7034–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzeh, N.S.; Popoola, P.A. Physical beneficiation of heavy minerals—Part 2, A state of the art literature review on magnetic and electrostatic concentration techniques. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzeh, N.S.; Popoola, P.; Okanigbe, D.; Adeosun, S.; Adeleke, A. Physical beneficiation of heavy minerals—Part 1, A state of the art literature review on gravity concentration techniques. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negeri, T. Flotation-Calcination-Magnetic Separation Hybrid Process for Concentration of Rare Earth Minerals Contained in a Carbonatite Ore. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2021, 09, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, S. Review on the Beneficiation of Li, Be, Ta, Nb-Bearing Polymetallic Pegmatite Ores in China. Minerals 2023, 13, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lu, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J. Mineralogical characterization and comprehensive utilization of micro-fine tantalum–niobium ores from Songzi. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Zou, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, K.; Wang, C. Experimental Study on Comprehensive Recovery of Associated Elements in Pegmatite Lithium Polymetallic Ore in Xinjiang. Met. Mine 2021, 11, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Altun, N.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, J. Gravity-based pre-concentration strategies for complex rare earth ore containing niobium and zirconium. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2024, 60, 183609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, C.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Rudinsky, S.; Langlois, R.; Williams, H.; Chu, P.; Awais, M.; Gauvin, R.; Rowson, N.A.; Waters, K.E. A mineralogical investigation into the pre-concentration of the Nechalacho deposit by gravity separation. Miner. Eng. 2018, 121, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaka-Wood, G.B.; Quast, K.; Zanin, M.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Skinner, W. A study of the feasibility of upgrading rare earth elements minerals from iron-oxide-silicate rich tailings using Knelson concentrator and Wilfley shaking table. Powder Technol. 2019, 344, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Cheng, H.; Wei, M.; Zhao, D.; Wu, D.; Liu, C. Mineralogical characteristic and beneficiation evaluation of a Ta-Nb-Li-Rb deposit. Minerals 2022, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihu, L.; Min, W.; Dongyin, W.; Changmiao, L.; Dengkui, Z. A new technology for processing niobite ore found in Jiangxi province. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.A.; Napier-Munn, T. (Eds.) 10—Gravity Concentration. In Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Analysis and Calculation of the Stroke-Frequency Combination in Shaking Tables. Nonferrous Met. (Miner. Process. Sect.) 1979, 5, 13–17. [Google Scholar]



| Mineral | Niobite | Aeschynite | Pyrochlore | Biotite | Pyroxene | Calcite |
| % | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 55.39 | 17.38 | 10.72 |
| Mineral | Dolomite-Ankerite | Amphibole | Siderite | Feldspar | Pyrite | Others |
| % | 6.41 | 2.10 | 1.81 | 1.12 | 1.04 | 1.75 |
| Size, μm | Wt., % | Nb2O5, % | Distribution of Nb2O5, % | Negative Cum Wt., % | Negative Cum. Distribution of Nb2O5, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +75 | 31.22 | 0.08 | 12.12 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| +38 | 33.83 | 0.11 | 18.06 | 68.78 | 87.88 |
| +20 | 23.00 | 0.18 | 19.93 | 34.95 | 69.82 |
| +10 | 8.72 | 0.60 | 25.40 | 11.95 | 49.89 |
| −10 | 3.23 | 1.56 | 24.49 | 3.23 | 24.49 |
| Particle size | 68.78% passing 75 μm |
| Slurry density | 10% (by Wt.) |
| Slurry flow rate | 0.25 L/min |
| Table slope | 2.0°, 2.4°, 2.8°, 3.2° |
| Wash-water flowrate | 1.2 L/min, 1.5 L/min, 1.8 L/min, 2.1 L/min, |
| Vibration voltage | 170 V, 180 V, 190 V, 200 V |
| Vibration frequency | 35 Hz, 38 Hz, 41 Hz, 44 Hz |
| Equipment | Product | Yield (%) | Nb2O5 Grade (%) | Nb2O5 Recovery (%) | Separation Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | Concentrate | 4.55 | 1.09 | 26.05 | 27.5 |
| Tailing | 95.65 | 0.15 | 73.95 | ||
| Raw Ore | 100 | 0.19 | 100 | ||
| SVT | Concentrate | 7.82 | 1.31 | 52.64 | 56.96 |
| Tailing | 92.18 | 0.1 | 47.36 | ||
| Raw Ore | 100 | 0.19 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Chen, W. Beneficiation of Fine-Grained Bayan Obo Niobium Ore Using a Slime Vibrating Table. Minerals 2025, 15, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101056
Li S, Chen W. Beneficiation of Fine-Grained Bayan Obo Niobium Ore Using a Slime Vibrating Table. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101056
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Si, and Wen Chen. 2025. "Beneficiation of Fine-Grained Bayan Obo Niobium Ore Using a Slime Vibrating Table" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101056
APA StyleLi, S., & Chen, W. (2025). Beneficiation of Fine-Grained Bayan Obo Niobium Ore Using a Slime Vibrating Table. Minerals, 15(10), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101056










