Geodynamic Evolution of Flat-Slab Subduction of South Tianshan Ocean: Constraints from Devonian Dioritic Porphyrites and Granitoids in the Kumishi Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
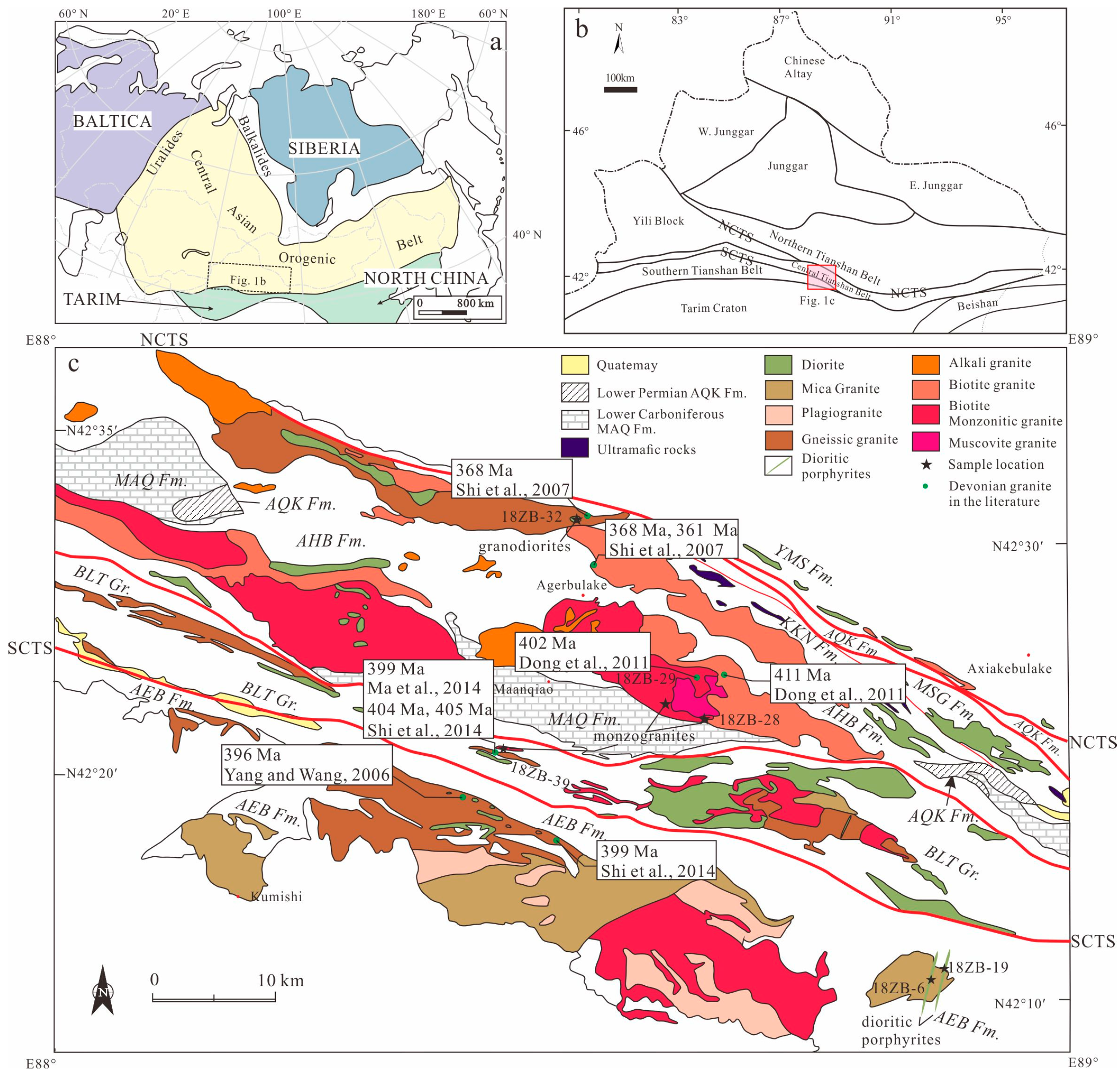
2. Geological Setting
3. Sampling and Petrography
4. Analytical Methods
4.1. Zircon U–Pb and Lu–Hf Isotopes
4.2. Geochemical Analyses of Whole Rocks
5. Results
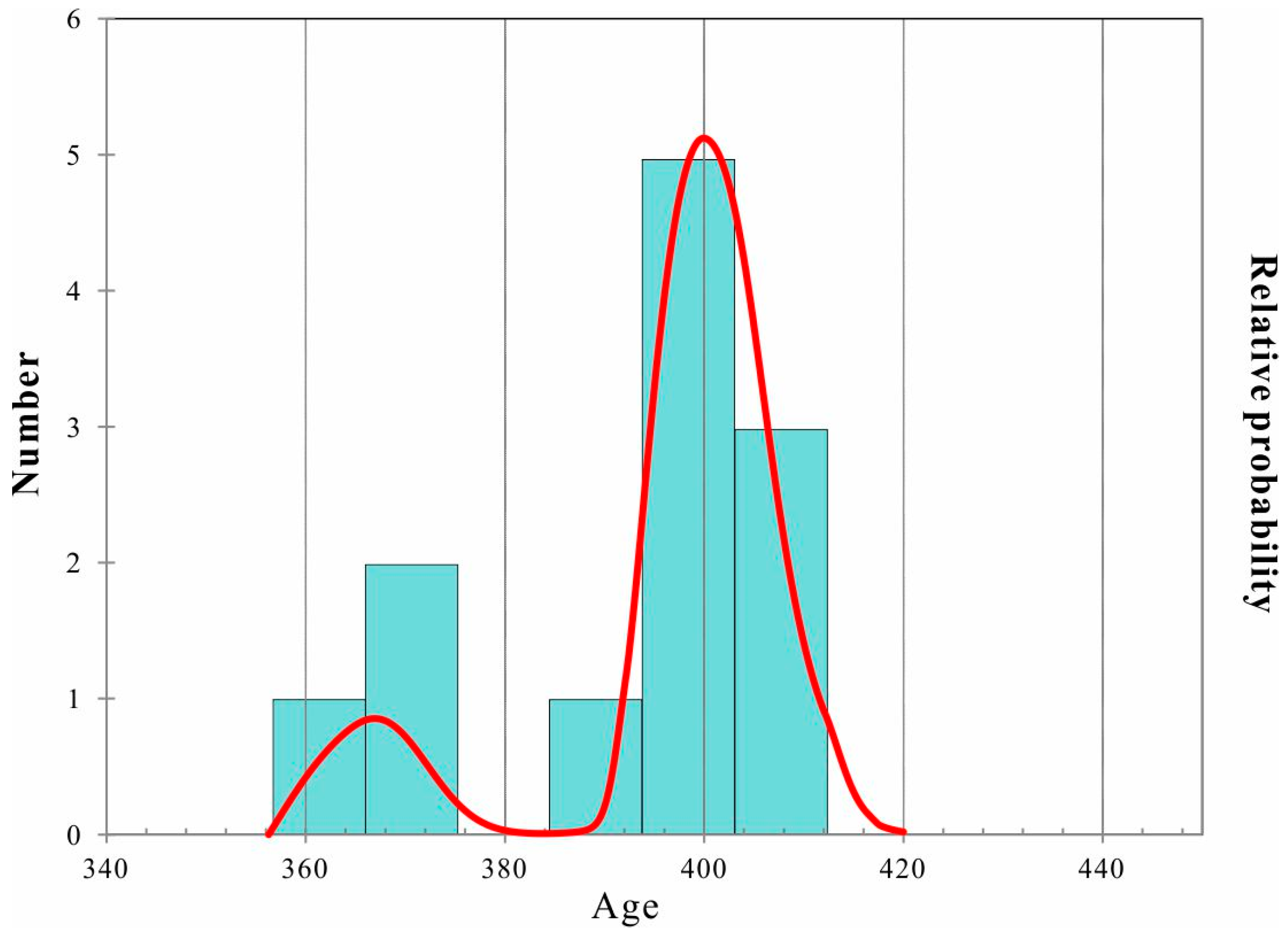
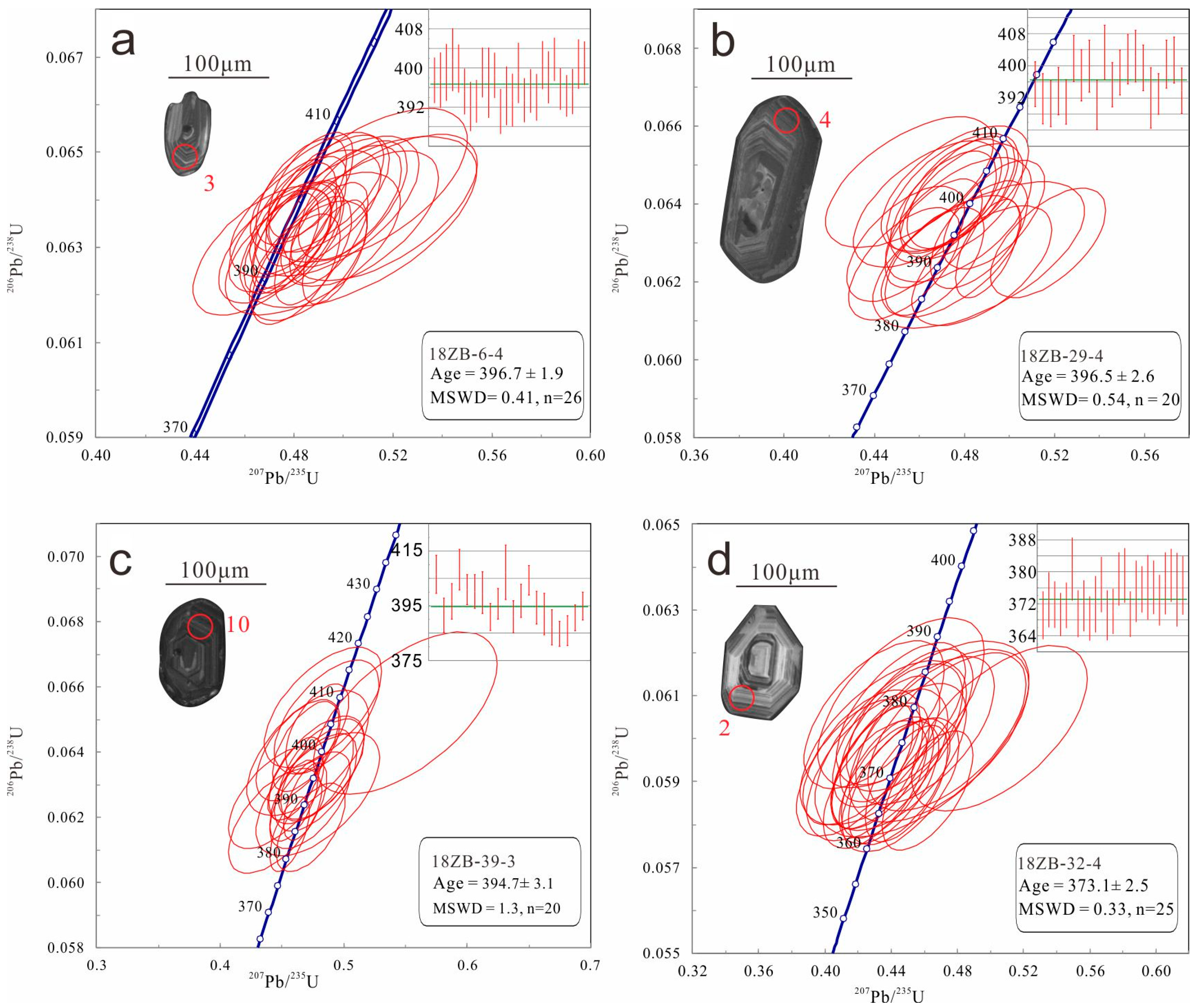
5.1. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Hf Isotopic Analyses of Zircon
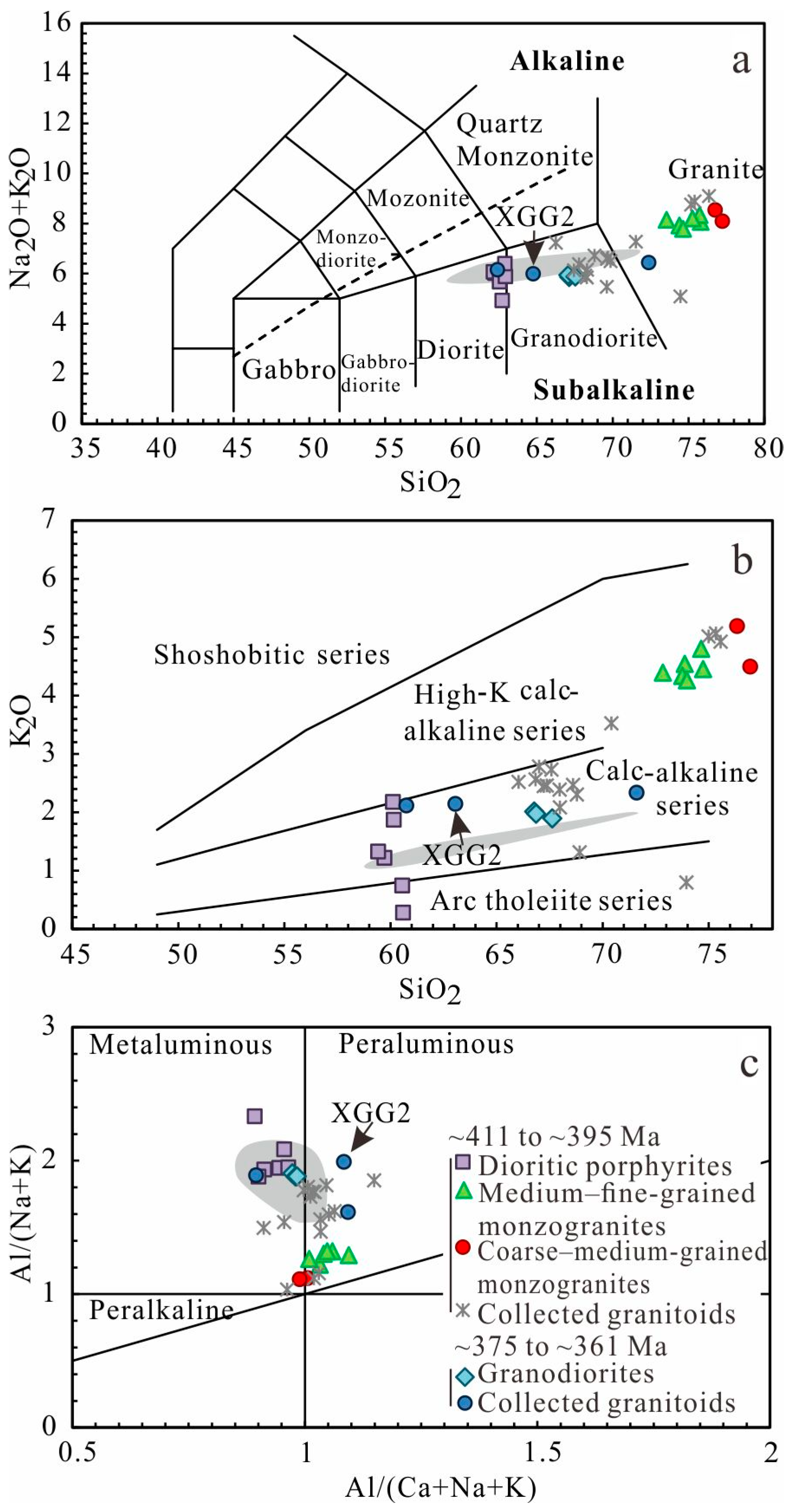
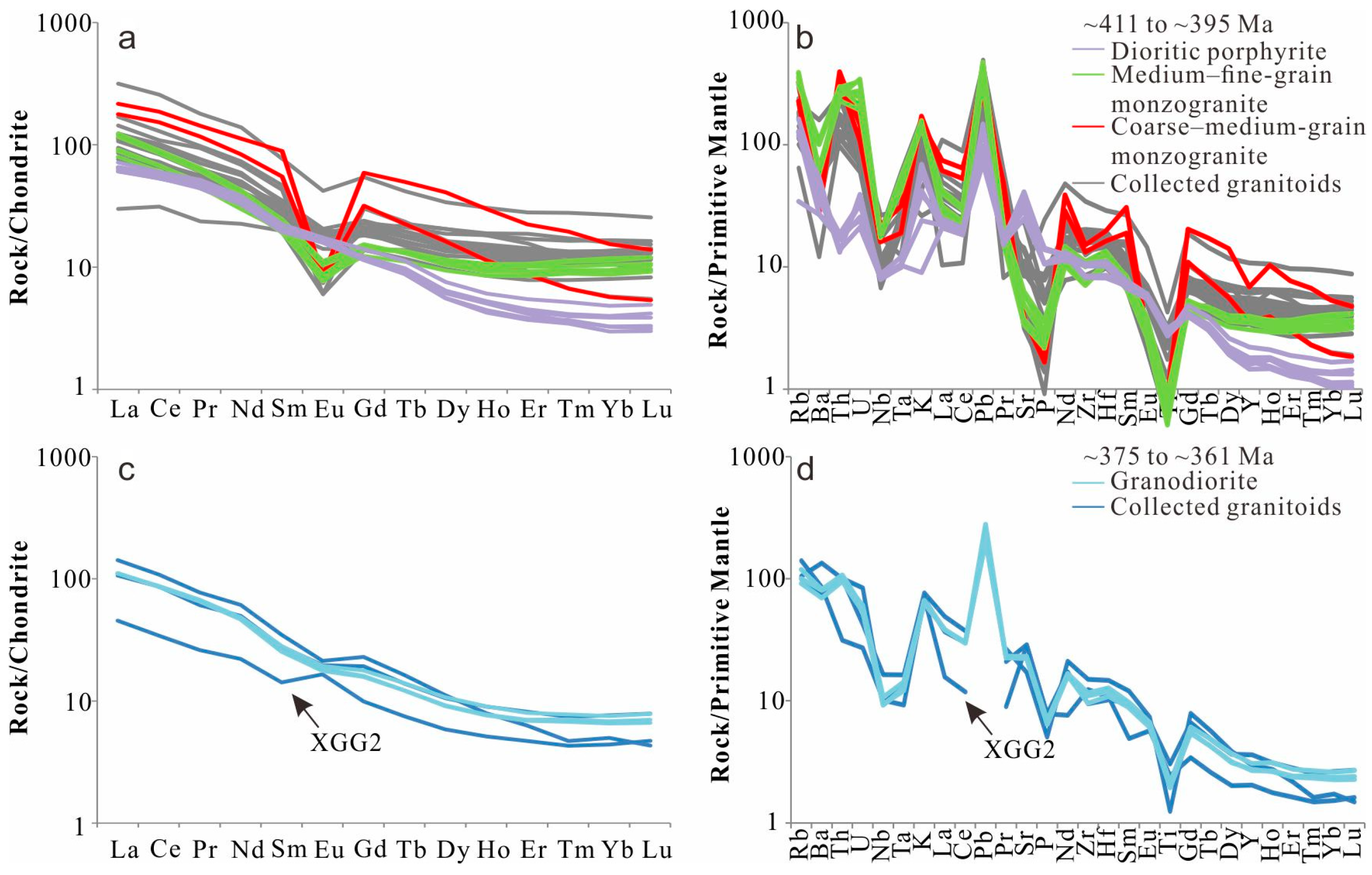
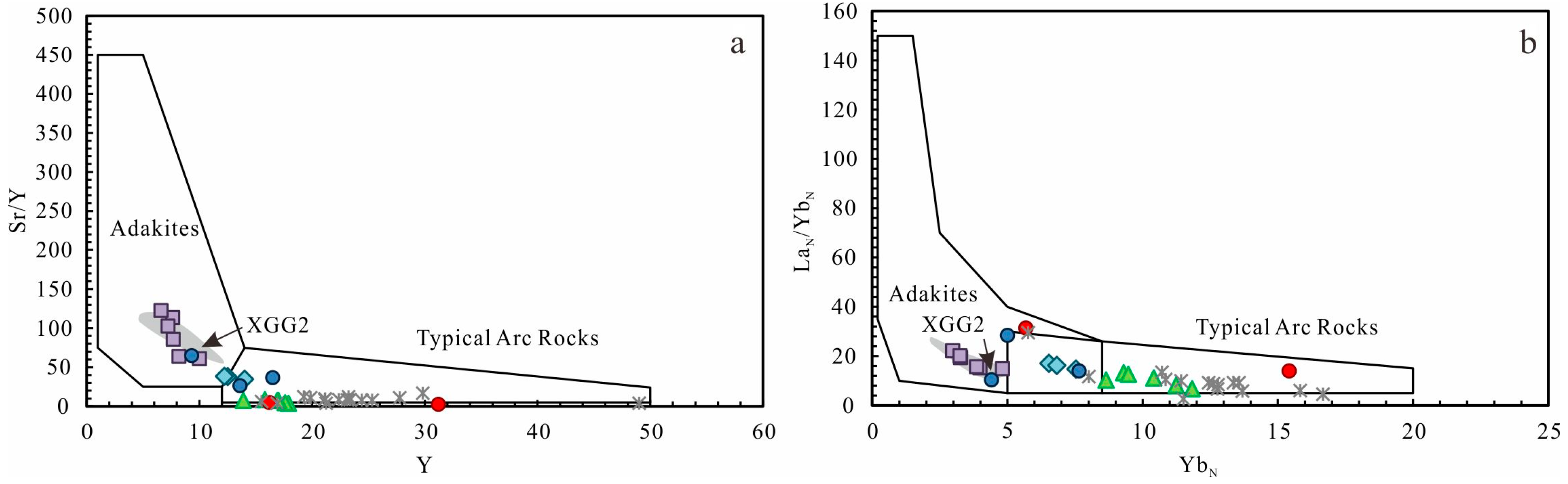
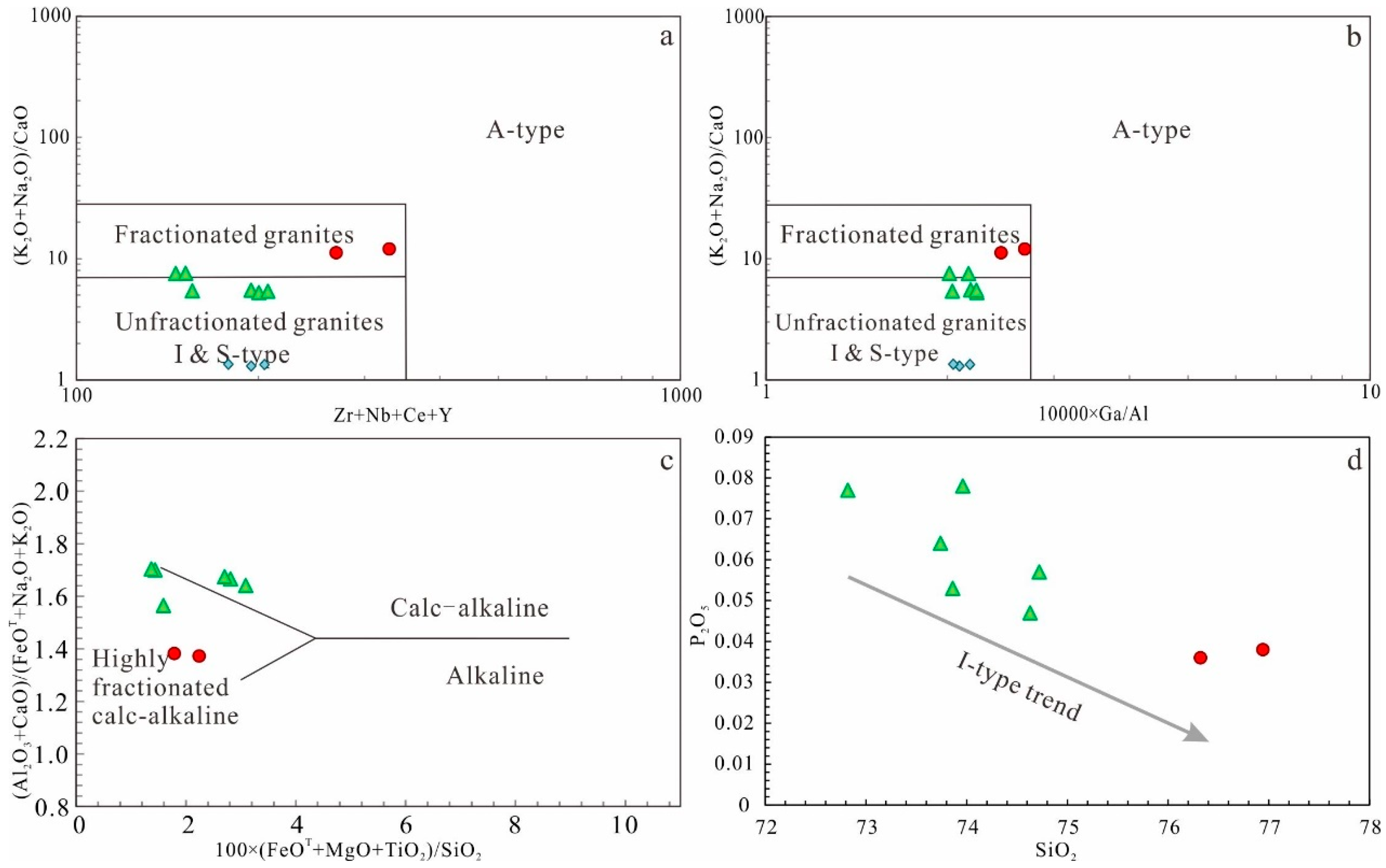
5.2. Geochemical Characteristics
6. Discussion
6.1. Geochemical Affinities
6.1.1. Early Devonian
6.1.2. Late Devonian
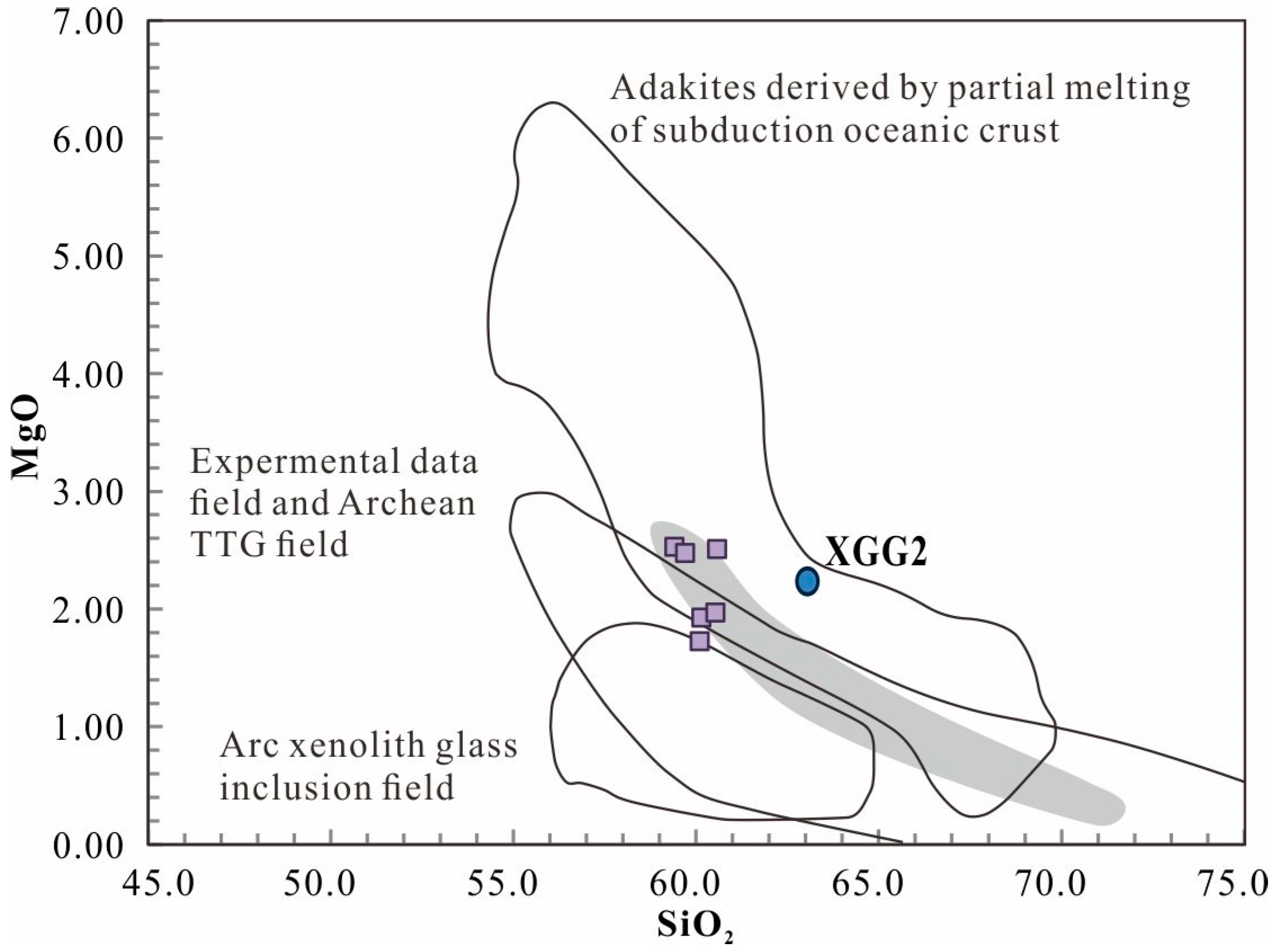
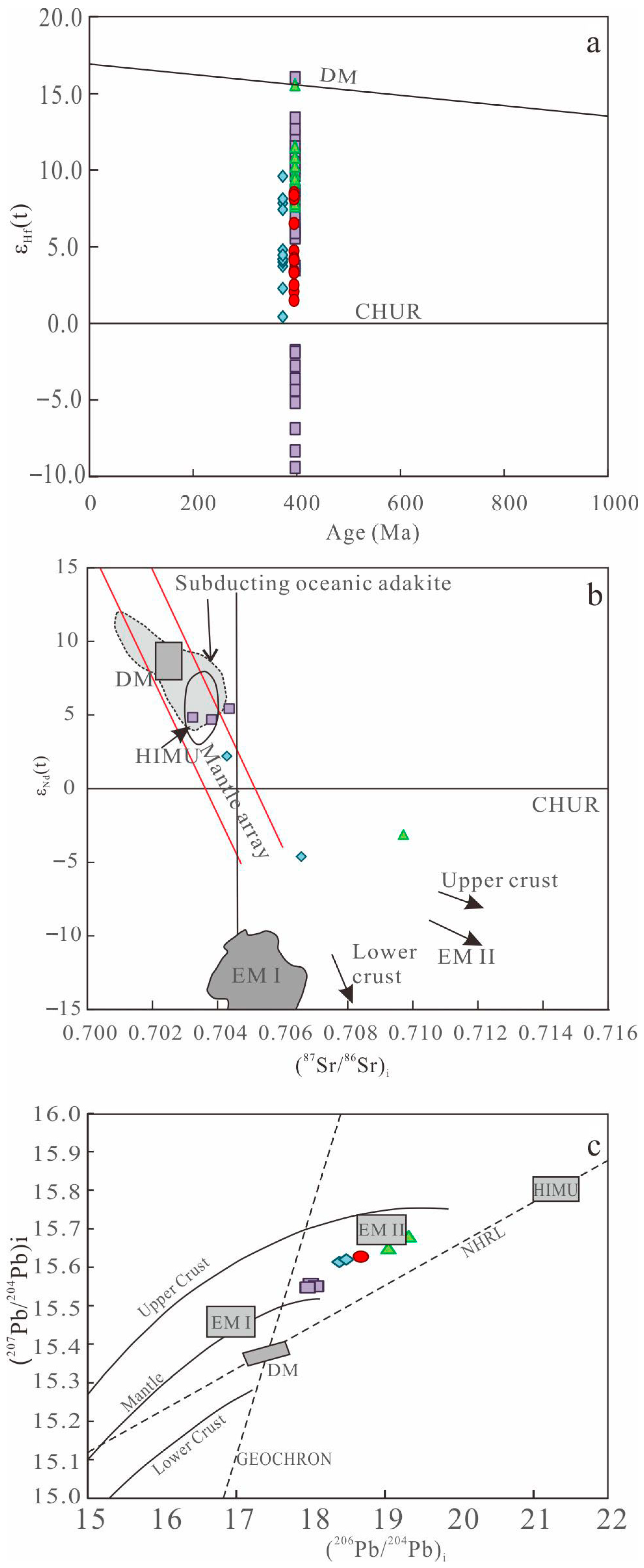
6.2. Magma Genesis
6.2.1. Early Devonian
6.2.2. Late Devonian
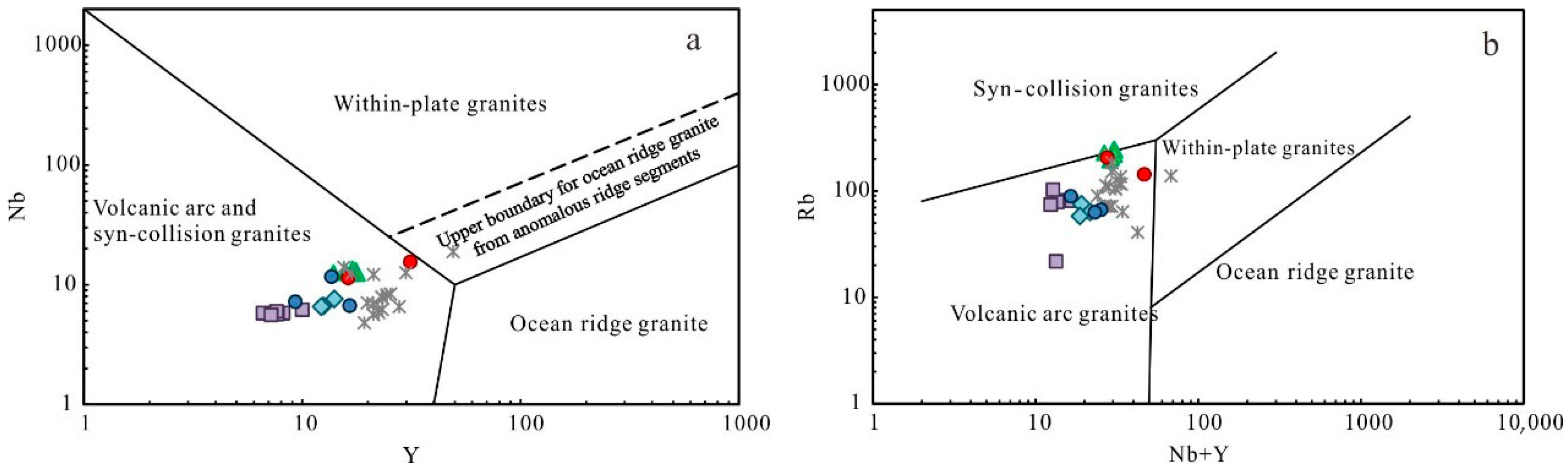
6.3. Implications for Tectonic Setting
6.3.1. Early Devonian
6.3.2. Late Devonian
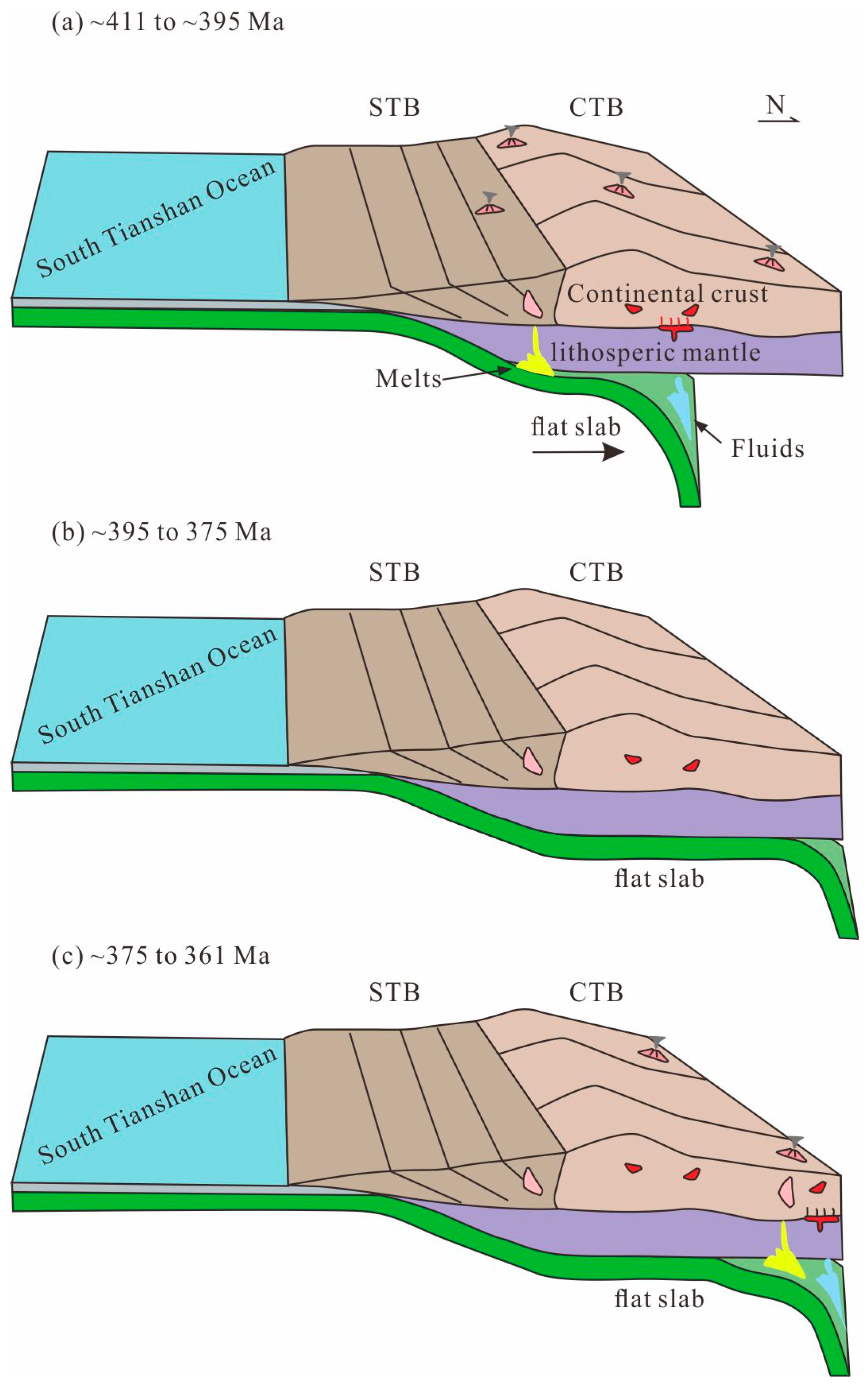
6.4. Implication for Continental Growth and Geodynamic Evolution
7. Conclusions
- The zircon U-Pb dating results indicate that the emplacement age of dioritic porphyrites is 392.1 ± 2.4 Ma, while the formation ages of medium–fine-grained monzogranites, coarse–medium-grained monzogranites, and granodiorites are 396.5 ± 2.6 Ma, 394.7 ± 3.1 Ma, and 373.1 ± 2.5 Ma, respectively.
- Geochemically, dioritic porphyrites exhibit adakitic attributes, characterized by high Na2O/K2O ratios, high Sr contents, significant depletion of HREE, and enrichment of LILE. In contrast, monzogranites and granodiorites show typical features of I-type granites, belonging to the calc-alkaline series, with LREE and LILE enrichment and HREE and HFSE depletion.
- Regarding magma genesis, dioritic porphyrites are derived from the partial melting of subducted oceanic crust in an arc setting, with minor incorporation of ancient crustal material. For monzogranites and granodiorites, their magma sources are a mixed magma source of the crust and mantle-wedge components above the subduction zone, indicating a significant crust-mantle magma mixing process, which is also supported by the presence of mafic microgranular enclaves and whole-rock Pb isotopic compositions.
- Tectonically, Devonian magmatism in this area is closely associated with the northward subduction of the South Tianshan Ocean beneath the CTB. During this subduction process, two stages of oceanic slab melting occurred, both producing adakitic magmas. Notably, the studies area of Devonian magmatism completely records the spatiotemporal evolution of the subduction of the South Tianshan Ocean slab, ranging from the initial shallowing of the subduction angle to flat-slab subduction and, finally, to the slab rollback stage.
- These magmatic activities, including slab-melted adakites and granitic intrusions, along with the southward accretion of the Southern Tianshan accretionary complex belt, played crucial roles in continental crust growth during the Paleozoic.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutscher, M.-A.; Maury, R.; Eissen, J.-P.; Bourdon, E. Can Slab Melting Be Caused by Flat Subduction? Geology 2000, 28, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijevic, S.K.; Wagner, L.S.; Kumar, A.; Beck, S.L.; Long, M.D.; Zandt, G.; Tavera, H.; Condori, C. The Role of Ridges in the Formation and Longevity of Flat Slabs. Nature 2015, 524, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, A.R.; Kerr, A.C.; McDonald, I.; Mitchell, S.F.; Pearce, J.A.; Millar, I.L.; Barfod, D.; Mark, D.F. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Rhyodacite Lavas in Eastern Jamaica: A New Adakite Subgroup Analogous to Early Archaean Continental Crust? Chem. Geol. 2010, 276, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.; Smithies, R.H.; Rapp, R.; Moyen, J.-F.; Champion, D. An Overview of Adakite, Tonalite–Trondhjemite–Granodiorite (TTG), and Sanukitoid: Relationships and Some Implications for Crustal Evolution. Lithos 2005, 79, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithies, R.H.; Champion, D.C.; Cassidy, K.F. Formation of Earth’s Early Archaean Continental Crust. Precambrian Res. 2003, 127, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beate, B.; Monzier, M.; Spikings, R.; Cotten, J.; Silva, J.; Bourdon, E.; Eissen, J.-P. Mio–Pliocene Adakite Generation Related to Flat Subduction in Southern Ecuador: The Quimsacocha Volcanic Center. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 192, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gurnis, M.; Seton, M.; Saleeby, J.; Müller, R.D.; Jackson, J.M. The Role of Oceanic Plateau Subduction in the Laramide Orogeny. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Meng, Q.; Wan, C.; Zhu, D.; Ge, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Dong, Y. Geodynamic Evolution of Flat-Slab Subduction of Paleo-Pacific Plate: Constraints from Jurassic Adakitic Lavas in the Hailar Basin, NE China. Tectonics 2019, 38, 4301–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Li, Z.-X.; Li, W.-X.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wei, G.; Qi, C. U–Pb Zircon, Geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf Isotopic Constraints on Age and Origin of Jurassic I- and A-Type Granites from Central Guangdong, SE China: A Major Igneous Event in Response to Foundering of a Subducted Flat-Slab? Lithos 2007, 96, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Xu, Y.-G.; Wilde, S.A.; Walker, R.J. Destruction of the North China Craton in the Mesozoic. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 47, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvet, J.; Shu, L.; Laurent-Charvet, S.; Wang, B.; Faure, M.; Cluzel, D.; Chen, Y.; De Jong, K. Palaeozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Tianshan Belt, NW China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvet, J.; Shu, L.; Laurent-Charvet, S. Paleozoic Structural and Geodynamic Evolution of Eastern Tianshan (NW China): Welding of the Tarim and Junggar Plates. Episodes 2007, 30, 162–186. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.-F.; He, G.-Q.; Wang, X.-C.; Guo, Z.-J. Late Carboniferous Collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan–Yili Terranes in the Western Segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and Implications for the Northern Xinjiang, Western China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y. Permian Geodynamic Setting of Northeast China and Adjacent Regions: Closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and Subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 26, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; Natal’in, B.A.; Burtman, V.S. Evolution of the Altaid Tectonic Collage and Palaeozoic Crustal Growth in Eurasia. Nature 1993, 364, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Han, C.; Yuan, C.; Sun, M.; Lin, S.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, S. Middle Cambrian to Permian Subduction-Related Accretionary Orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of Central Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2008, 32, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Hao, J.; Zhai, M. Accretion Leading to Collision and the Permian Solonker Suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Tectonics 2003, 22, 2002TC001484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.G. Continental Growth of Northwest China. Tectonics 1989, 8, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.-M. The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and Growth of the Continental Crust in the Phanerozoic. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spéc. Publ. 2004, 226, 73–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.-M.; Wu, F.; Chen, B. Massive Granitoid Generation in Central Asia: Nd Isotope Evidence and Implication for Continental Growth in the Phanerozoic. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2000, 23, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelty, T.K.; Yin, A.; Dash, B.; Gehrels, G.E.; Ribeiro, A.E. Detrital-Zircon Geochronology of Paleozoic Sedimentary Rocks in the Hangay–Hentey Basin, North-Central Mongolia: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Mongol–Okhotsk Ocean in Central Asia. Tectonophysics 2008, 451, 290–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, A.; Windley, B.; Badarch, G.; Tomurtogoo, O.; Hegner, E.; Jahn, B.; Gruschka, S.; Khain, E.V.; Demoux, A.; Wingate, M.; et al. Accretionary Growth and Crustformation in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and Comparison with the Arabian-Nubian Shield. Mem. Geol. Soc. Am. 2007, 200, 181–209. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.; Charvet, J.; Lu, H.; Laurent, S.C. Paleozoic Accretion-Collision Events and Kinematics of Ductile Deformation in the Eastern Part of the Southern-Central Tianshan Belt, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2002, 76, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shu, L.; Faure, M.; Jahn, B.; Cluzel, D.; Charvet, J.; Chung, S.; Meffre, S. Paleozoic Tectonics of the Southern Chinese Tianshan: Insights from Structural, Chronological and Geochemical Studies of the Heiyingshan Ophiolitic Mélange (NW China). Tectonophysics 2011, 497, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, S.; Shu, L.; Faure, M.; Cluzel, D.; Charvet, J.; Laurent-Charvet, S. Primary Carboniferous and Permian Paleomagnetic Results from the Yili Block (NW China) and Their Implications on the Geodynamic Evolution of Chinese Tianshan Belt. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 263, 288–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windley, B.F.; Alexeiev, D.; Xiao, W.; Kröner, A.; Badarch, G. Tectonic Models for Accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J. Geol. Soc. 2007, 164, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Huang, B.C.; Han, C.M.; Yuan, C.; Chen, H.L.; Sun, M.; Sun, S.; Li, J.L. End-Permian to Mid-Triassic Termination of the Accretionary Processes of the Southern Altaids: Implications for the Geodynamic Evolution, Phanerozoic Continental Growth, and Metallogeny of Central Asia. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 98, 1189–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Qin, K.; Sun, S.; Li, J. Paleozoic Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the Continental Growth of Central Asia. Am. J. Sci. 2004, 304, 370–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubchuk, A. Architecture and Mineral Deposit Settings of the Altaid Orogenic Collage: A Revised Model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2004, 23, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonenshain, L.P.; Kuzmin, M.I.; Natapov, L.M.; Page, B.M. Geology of the USSR: A Plate-Tectonic Synthesis; Geodynamics Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 21, pp. 1–242. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.B.; Windley, B.F.; Zang, C. Paleozoic Collisional Tectonics and Magmatism of the Chinese Tien Shan, Central Asia. Tectonophysics 1992, 220, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windley, B.F.; Allen, M.B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wang, G.R. Paleozoic Accretion and Cenozoic Redeformation of the Chinese Tien Shan Range, Central Asia. Geology 1990, 18, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, M.; Xiao, X.; Tang, Y.; He, G. Paleozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Tianshan Orogen, Northwestern China. Tectonophysics 1998, 287, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Y. The Collision between the Yili and Tarim Blocks of the Southwestern Altaids: Geochemical and Age Constraints of a Leucogranite Dike Crosscutting the HP–LT Metamorphic Belt in the Chinese Tianshan Orogen. Tectonophysics 2011, 499, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Faure, M.; Shu, L.; de Jong, K.; Charvet, J.; Cluzel, D.; Jahn, B.; Chen, Y.; Ruffet, G. Structural and Geochronological Study of High-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks in the Kekesu Section (Northwestern China): Implications for the Late Paleozoic Tectonics of the Southern Tianshan. J. Geol. 2010, 118, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Neubauer, F.; Liu, X.; Hauzenberger, C.; Zhou, D.; Li, W. Syn- and Post-Collisional Granitoids in the Central Tianshan Orogen: Geochemistry, Geochronology and Implications for Tectonic Evolution. Gondwana Res. 2011, 20, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shu, L.; Meert, J.G.; Li, J. The Paleozoic Evolution of Central Tianshan: Geochemical and Geochronological Evidence. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jian, P.; Kröner, A.; Jahn, B.-M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Ma, H. Zircon Ages and Hf Isotopic Compositions of Plutonic Rocks from the Central Tianshan (Xinjiang, Northwest China) and Their Significance for Early to Mid-Palaeozoic Crustal Evolution. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 1413–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Jian, P.; Zhang, F.; Miao, L. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Dating of the Gangou Granitoids, Central Tianshan Mountains, Northwest China and Tectonic Significances. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, Z.; Xia, Z.; Xia, L.; Li, X.; Wang, L. TIMS U-Pb Isotopic Dating and Geochemical Characteristics of Paleozoic Granitic Rocks from the Middle-Western Section of Tianshan. Northwestern Geol. 2006, 39, 50–75. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wang, X. Geochronology, Petrochemistry and Tectonic Implications of Early Devonian Plutons in Kumux Area, Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Mineral. 2006, 25, 401–411. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Yin, J.; Sun, M.; Wang, T.; Yuan, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, H.; Seltmann, R.; Thomson, S.N.; Chen, Y. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Geochemical and Isotopic Compositions of Paleozoic Magmatic Rocks in the Western Tianshan, NW China: A Magmatic Response of the Advancing and Retreating Subduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 232, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Badarch, G.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Qin, K.; Wang, Z. Palaeozoic Accretionary and Convergent Tectonics of the Southern Altaids: Implications for the Growth of Central Asia. J. Geol. Soc. 2004, 161, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Windley, B.F.; Yuan, C.; Sun, M.; Han, C.M.; Lin, S.F.; Chen, H.L.; Yan, Q.R.; Liu, D.Y.; Qin, K.Z.; et al. Paleozoic Multiple Subduction-Accretion Processes of the Southern Altaids. Am. J. Sci. 2009, 309, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.Q.; Wang, L.S.; Wang, L.X. Paleozoic era ophiolite of southwest part in western Junggar, Xinjiang, China. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. Bull. Xi’an Inst. Geol. Miner. Resour. 1987, 17, 3–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, D.; Luo, J.; Zhang, C.; Xia, L.; Xu, X.; Li, X. Geology and Geochemistry of the Bingdaban Ophiolitic Mélange in the Boundary Fault Zone on the Northern Central Tianshan Belt, and Its Tectonic Implications. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; Zhou, D.W.; Zhang, G.W.; Zhao, X.; Luo, J.H.; Xu, J.G. Geology and Geochemistry of the Gangou Ophiolitic Melange at the Northern Margin of the Middle Tianshan Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ma, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Xia, B. SHRIMP Dating and Nd-Sr Isotopic Tracing of Kangguertage Ophiolite in Eastern Tianshan, Xinjiang. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2008, 24, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Sun, M.; Eizenhöfer, P.R.; Han, Y.; Hou, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B. Tectonic Evolution from Subduction to Arc-Continent Collision of the Junggar Ocean: Constraints from U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopes of Detrital Zircons from the North Tianshan Belt, NW China. GSA Bull. 2016, 128, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Long, X.; Wang, X.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Yuan, C.; Xiao, W. Precambrian Evolution of the Chinese Central Tianshan Block: Constraints on Its Tectonic Affinity to the Tarim Craton and Responses to Supercontinental Cycles. Precambrian Res. 2017, 295, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Gao, J.; Klemd, R.; Beier, C.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, T. Geochemical and Geochronological Studies of Granitoid Rocks from the Western Tianshan Orogen: Implications for Continental Growth in the Southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithos 2011, 126, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Sun, L.H.; Fan, W.M. Zircon SHRIMP U–Pb Dating of the Granitic Gneisses from Bingdaban and Laerdundaban (Tianshan Orogen) and Their Geological Significances. Geochimica 2009, 38, 424–431. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Eizenhöfer, P.R.; Sun, M.; Han, Y.; Hou, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B.; et al. Tectonic Transition from Late Carboniferous Subduction to Early Permian Post-Collisional Extension in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Insights from Geochronology and Geochemistry of Mafic-Intermediate Intrusions. Lithos 2016, 256–257, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, G.; Sun, M.; Eizenhöfer, P.R.; Hou, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Xu, B. Late Paleozoic Subduction and Collision Processes during the Amalgamation of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt along the South Tianshan Suture Zone. Lithos 2016, 246–247, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopelko, D.; Biske, G.; Seltmann, R.; Eklund, O.; Belyatsky, B. Hercynian Post-Collisional A-Type Granites of the Kokshaal Range, Southern Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan. Lithos 2007, 97, 140–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopelko, D.; Seltmann, R.; Biske, G.; Lepekhina, E.; Sergeev, S. Possible Source Dichotomy of Contemporaneous Post-Collisional Barren I-Type versus Tin-Bearing A-Type Granites, Lying on Opposite Sides of the South Tien Shan Suture. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 35, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kusky, T.; Zhang, D.; Hou, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Chuanwulu Complex in the South Tianshan, Western Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for Petrogenesis and Phanerozoic Continental Growth. Lithos 2012, 140–141, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, A.; Alexeiev, D.V.; Rojas-Agramonte, Y.; Hegner, E.; Wong, J.; Xia, X.; Belousova, E.; Mikolaichuk, A.V.; Seltmann, R.; Liu, D. Mesoproterozoic (Grenville-Age) Terranes in the Kyrgyz North Tianshan: Zircon Ages and Nd–Hf Isotopic Constraints on the Origin and Evolution of Basement Blocks in the Southern Central Asian Orogen. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 272–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Ge, W.; Santosh, M.; Dong, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhou, H.; Xing, D. Generation of Nb-Enriched Mafic Rocks and Associated Adakitic Rocks from the Southeastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence of Crust-Mantle Interaction. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, P.; Xiao, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Hu, R. Neoproterozoic I-Type Granites in the Central Tianshan Block (NW China): Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Tectonic Implications. J. Arid. Land 2022, 14, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xiao, W.; Mao, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, R. Episodic Paleozoic Adakitic Magmatism in the Eastern Tianshan, Southern Altaids: Implications for Petrogenesis and Geodynamics. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2022, 96, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.L.; Powell, W.J.; Pearson, N.J.; O’Reilly, S.Y. ICP-MS. In Laser Ablation ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences: Current Practices and Outstanding Issues; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Nepean, ON, Canada, 2008; Volume 40, pp. 308–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, K.R. Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; Volume 4, p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, E.; Liu, F.-L.; Liu, P.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Yang, H.; Wang, F.; Shi, J.-R.; Cai, J. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of Paleoproterozoic Meta-Mafic Rocks from Central Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China: Evidence from Zircon U–Pb Dating and in Situ Lu–Hf Isotopes, and Whole-Rock Geochemistry. Precambrian Res. 2014, 247, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.J. Laser Ablation-MC-ICP-MS Technique for Hf Isotope Microanalysis of Zircon and Its Geological Applications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 23, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Zheng, J.; Griffin, W.L.; Zhang, M.; Tang, H.; Su, Y.; Ping, X. Triassic “Adakitic” Rocks in an Extensional Setting (North China): Melts from the Cratonic Lower Crust. Lithos 2012, 149, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Rudnick, R.L.; Xu, W.-L.; Yuan, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Walker, R.J.; Puchtel, I.S.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.-R.; et al. Recycling Deep Cratonic Lithosphere and Generation of Intraplate Magmatism in the North China Craton. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 270, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, M.; Asan, K. PetroGram: An Excel-Based Petrology Program for Modeling of Magmatic Processes. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, T.N.; Baragar, W.R.A. A Guide to the Chemical Classification of the Common Volcanic Rocks. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1971, 8, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calanchi, N.; Peccerillo, A.; Tranne, C.A.; Lucchini, F.; Rossi, P.L.; Kempton, P.; Barbieri, M.; Wu, T.W. Petrology and Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks from the Island of Panarea: Implications for Mantle Evolution beneath the Aeolian Island Arc (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2002, 115, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniar, P.D.; Piccoli, P.M. Tectonic Discrimination of Granitoids. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1989, 101, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Chemical Composition of the Archaean Crust. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1986, 24, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of Some Modern Arc Magmas by Melting of Young Subducted Lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Yu, M.; Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhu, J.; Lü, X. Skarn-Mineralized Porphyry Adakites in the Harlik Arc at Kalatage, E. Tianshan (NW China): Slab Melting in the Devonian-Early Carboniferous in the Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 153, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M.S.; Defant, M.J.; Kepezhinskas, P.K. Petrogenesis of Slab-Derived Trondhjemite–Tonalite–Dacite/Adakite Magmas. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1996, 87, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H. Adakitic Magmas: Modern Analogues of Archaean Granitoids. Lithos 1999, 46, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. Two Contrasting Granite Types. Pac. Geol. 1974, 8, 173–174. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, J. S-Type Granitic Magmas—Petrogenetic Issues, Models and Evidence. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2003, 61, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, P.J. Post-Collisional Alkaline Granites. J. Geol. 1989, 97, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. I-and S-Type Granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1992, 83, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. Two Contrasting Granite Types: 25 Years Later. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2001, 48, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P. High Sr/Y Arc Magmas and Porphyry Cu ± Mo ± Au Deposits: Just Add Water. Econ. Geol. 2011, 106, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, M.P.; Petford, N. Generation of Sodium-Rich Magmas from Newly Underplated Basaltic Crust. Nature 1993, 362, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.M.; Mpodozis, C. Central Andean Ore Deposits Linked to Evolving Shallow Subduction Systems and Thickening Crust. GSA Today 2001, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Xu, J.F.; Kepezhinskas, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, L. Adakite: Some Variations on a Theme. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2002, 18, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.; Tindle, A.G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defant, M.J.; Jackson, T.E.; Drummond, M.S.; De Boer, J.Z.; Bellon, H.; Feigenson, M.D.; Maury, R.C.; Stewart, R.H. The Geochemistry of Young Volcanism throughout Western Panama and Southeastern Costa Rica: An Over-view. JGS 1992, 149, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Q.; Li, X.H.; Li, W.X.; Li, Z.X. Formation of High 18O Fayalite-Bearing A-Type Granite by High-Temperature Melting of Granulitic Metasedimentary Rocks, Southern China. Geology 2011, 39, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Parada, M.A.; Palacios, C.; Dietrich, A.; Schultz, F.; Lehmann, B. Adakite-like Signature of Late Mio-cene Intrusions at the Los Pelambres Giant Porphyry Copper Deposit in the Andes of Central Chile: Metallogenic Implications. Miner. Depos. 2003, 38, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, A.I.S.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Foster, G.L.; Paterson, B.A.; Woodhead, J.D.; Hergt, J.M.; Gray, C.M.; Whitehouse, M.J. Magmatic and Crustal Differentiation History of Granitic Rocks from Hf-O Isotopes in Zircon. Science 2007, 315, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuduxun, N.; Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, P.; Sang, M.; Li, L.; Liu, X. Terminal Suturing Between the Tarim Craton and the Yili-Central Tianshan Arc: Insights From Mélange-Ocean Plate Stratigraphy, Detrital Zir-con Ages, and Provenance of the South Tianshan Accretionary Complex. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2021TC006705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, S.; Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Mao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Ordovician to Early Permian Accretionary Tec-tonics of Eastern Tianshan: Insights from Kawabulak Ophiolitic Mélange, Granitoid, and Granitic Gneiss. Geol. J. 2018, 55, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.T.; Thorkelson, D.J. Cocos-Nazca Slab Window beneath Central America. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 146, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajona, F.G.; Maury, R.C.; Bellon, H.; Cotten, J.; Defant, M.J.; Pubellier, M. Initiation of Subduction and the Generation of Slab Melts in Western and Eastern Mindanao, Philippines. Geology 1993, 21, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, T.; Lu, P.; Wang, H.; Chen, J. Early Cambrian Xiate Gabbro in Western Tianshan: Magmatic Records of Initial Subduction of the South Tianshan Ocean. Northwestern Geol. 2024, 57, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhai, Y.; Kapp, P.; de Jong, K.; Zhong, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Gong, H.; Geng, H. Accretionary Tectonics of Back-Arc Oceanic Basins in the South Tianshan: Insights from Structural, Geochronological, and Geochemical Studies of the Wuwamen Ophiolite Mélange. GSA Bull. 2017, 130, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P.; Kerrich, R. Special Paper: Adakite-Like Rocks: Their Diverse Origins and Questionable Role in Metallogenesis. Econ. Geol. 2007, 102, 537–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Weng, K.; Cao, K.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y. Petrogenesis of Carboniferous-Permian Granitoids in the Kumishi Area of Tianshan, China: Insights into the Geodynamic Evolution Triggered by Subduction and Closure of the South Tianshan Ocean. Minerals 2024, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Vogt, K.; Gerya, T. Generation of New Continental Crust by Sublithospheric Silicic-Magma Relam-ination in Arcs: A Test of Taylor’s Andesite Model. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, D.-C.; Mo, X. Continental Collision Zones Are Primary Sites for Net Continental Crust Growth—A Testable Hypothesis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 127, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Watson, E.B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8–32 Kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling. J. Petrol. 1995, 36, 891–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, X.; Xiang, H.; He, Z.; Liou, J.G. Metagabbros of the Gangdese Arc Root, South Tibet: Implica-tions for the Growth of Continental Crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 143, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Lithology | Rb (ppm) | Sr (ppm) | 87Rb/86Sr | (87Sr/86Sr) ± 2σ | T (Ma) | (87Sr/86Sr)i | Sm (ppm) | Nd (ppm) | 147Sm/144Nd | 143Nd/144Nd | (143Nd/144Nd)i | εNd(t) | TDM (Ga) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18ZB-6-3 | Dioritic porphyrites | 21.8 | 658 | 0.095933 | 0.704899 ± 13 | 397 | 0.704357 | 2.96 | 15.2 | 0.118523 | 0.512713 | 0.512405 | 5.4 | 0.70 |
| 18ZB-19-1 | 79.0 | 866 | 0.264148 | 0.704727 ± 14 | 397 | 0.703235 | 3.05 | 16.7 | 0.111157 | 0.512664 | 0.512375 | 4.8 | 0.72 | |
| 18ZB-19-2 | 74.4 | 808 | 0.266624 | 0.705322 ± 12 | 397 | 0.703816 | 3.13 | 17.2 | 0.110757 | 0.512655 | 0.512367 | 4.7 | 0.73 | |
| 18ZB-28-1 | Medium–fine-grained monzogranites | 229 | 104 | 6.375878 | 0.745714 ± 22 | 397 | 0.709715 | 2.91 | 15.2 | 0.116521 | 0.512270 | 0.511967 | −3.1 | 1.38 |
| 18ZB-29-1 | 221 | 129 | 4.960671 | 0.708602 ± 16 | 397 | 0.680593 | 3.68 | 18.6 | 0.120417 | 0.512420 | 0.512107 | −0.4 | 1.19 | |
| 18ZB-39-1 | Coarse–medium-grained monzogranites | 144 | 80.5 | 5.179698 | 0.707740 ± 18 | 395 | 0.678628 | 13.6 | 52.4 | 0.157965 | 0.512266 | 0.511858 | −5.3 | 2.41 |
| 18ZB-32-2 | Granodiorites | 63.7 | 486 | 0.379526 | 0.708592 ± 18 | 373 | 0.706576 | 4.30 | 22.6 | 0.115801 | 0.512204 | 0.511921 | −4.6 | 1.47 |
| 18ZB-32-3 | 58.1 | 468 | 0.359475 | 0.706195 ± 13 | 373 | 0.704285 | 3.91 | 21.8 | 0.109163 | 0.512537 | 0.512270 | 2.2 | 0.89 |
| Samples | Lithology | U | Th | Pb | 206Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | t(Ma) | (206Pb/204Pb)i | (207Pb/204Pb)i | (208Pb/204Pb)i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18ZB-6-3 | Dioritic porphyrites | 0.536 | 1.41 | 10.5 | 18.233 | 15.569 | 38.204 | 397 | 18.003 | 15.556 | 38.014 |
| 18ZB-19-1 | 0.504 | 1.54 | 9.48 | 18.314 | 15.564 | 38.163 | 397 | 18.075 | 15.551 | 37.933 | |
| 18ZB-19-2 | 0.442 | 1.17 | 5.00 | 18.359 | 15.569 | 38.230 | 397 | 17.961 | 15.547 | 37.899 | |
| 18ZB-28-1 | Medium–fine-grained monzogranites | 4.03 | 19.5 | 23.2 | 20.102 | 15.723 | 38.828 | 397 | 19.321 | 15.680 | 37.639 |
| 18ZB-29-1 | 6.92 | 25.0 | 32.8 | 19.995 | 15.701 | 38.845 | 397 | 19.046 | 15.649 | 37.766 | |
| 18ZB-39-1 | Coarse–medium-grained monzogranites | 3.07 | 33.6 | 18.6 | 19.415 | 15.668 | 40.750 | 395 | 18.676 | 15.628 | 38.206 |
| 18ZB-32-2 | Granodiorites | 1.28 | 8.21 | 14.3 | 18.769 | 15.634 | 38.773 | 373 | 18.391 | 15.614 | 38.009 |
| 18ZB-32-3 | 1.13 | 8.06 | 14.7 | 18.807 | 15.638 | 38.828 | 373 | 18.482 | 15.620 | 38.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, W.; Weng, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, B.; Gao, Y. Geodynamic Evolution of Flat-Slab Subduction of South Tianshan Ocean: Constraints from Devonian Dioritic Porphyrites and Granitoids in the Kumishi Area. Minerals 2025, 15, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101019
Kang W, Weng K, Zhang X, Zhao X, Chen B, Gao Y. Geodynamic Evolution of Flat-Slab Subduction of South Tianshan Ocean: Constraints from Devonian Dioritic Porphyrites and Granitoids in the Kumishi Area. Minerals. 2025; 15(10):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Wenbin, Kai Weng, Xue Zhang, Xiaojian Zhao, Bo Chen, and Yongwei Gao. 2025. "Geodynamic Evolution of Flat-Slab Subduction of South Tianshan Ocean: Constraints from Devonian Dioritic Porphyrites and Granitoids in the Kumishi Area" Minerals 15, no. 10: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101019
APA StyleKang, W., Weng, K., Zhang, X., Zhao, X., Chen, B., & Gao, Y. (2025). Geodynamic Evolution of Flat-Slab Subduction of South Tianshan Ocean: Constraints from Devonian Dioritic Porphyrites and Granitoids in the Kumishi Area. Minerals, 15(10), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15101019







