Analysis of the Shear Strength of Iron Oxide-Kaolinite Cementing Materials in Granite Red Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Data Calculation
2.2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
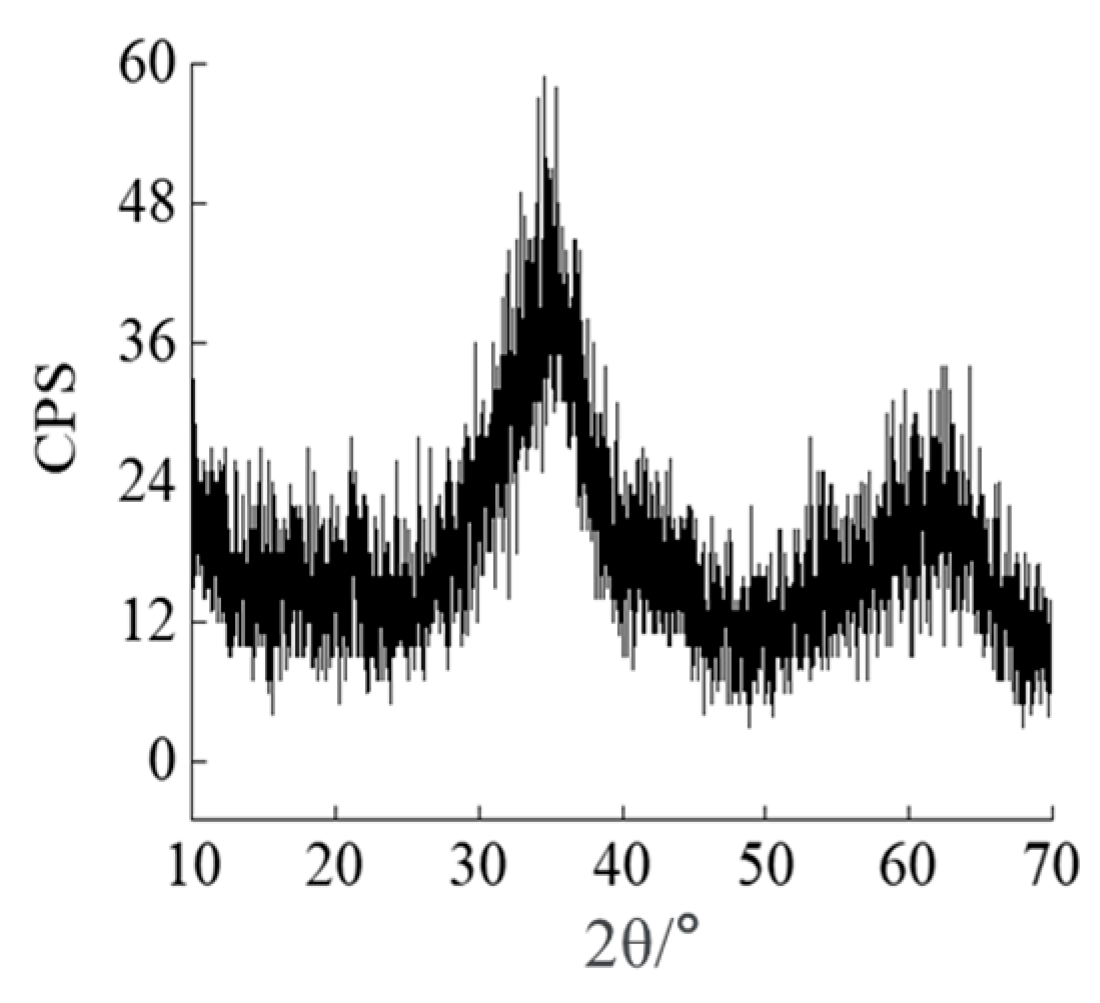
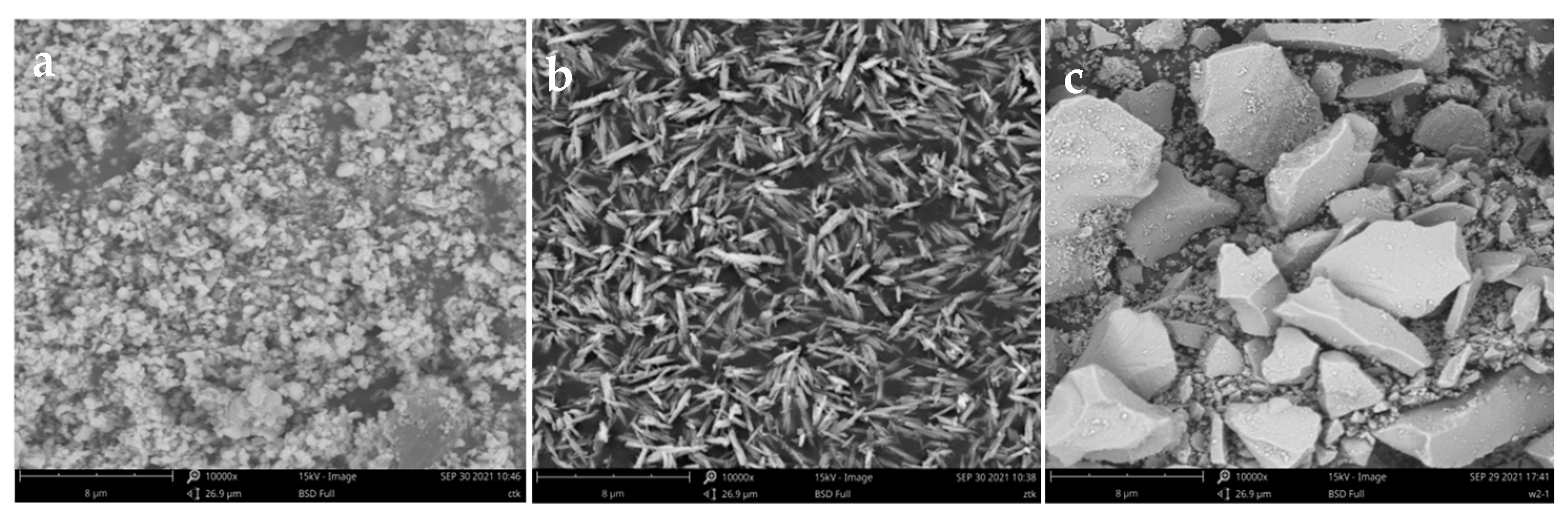
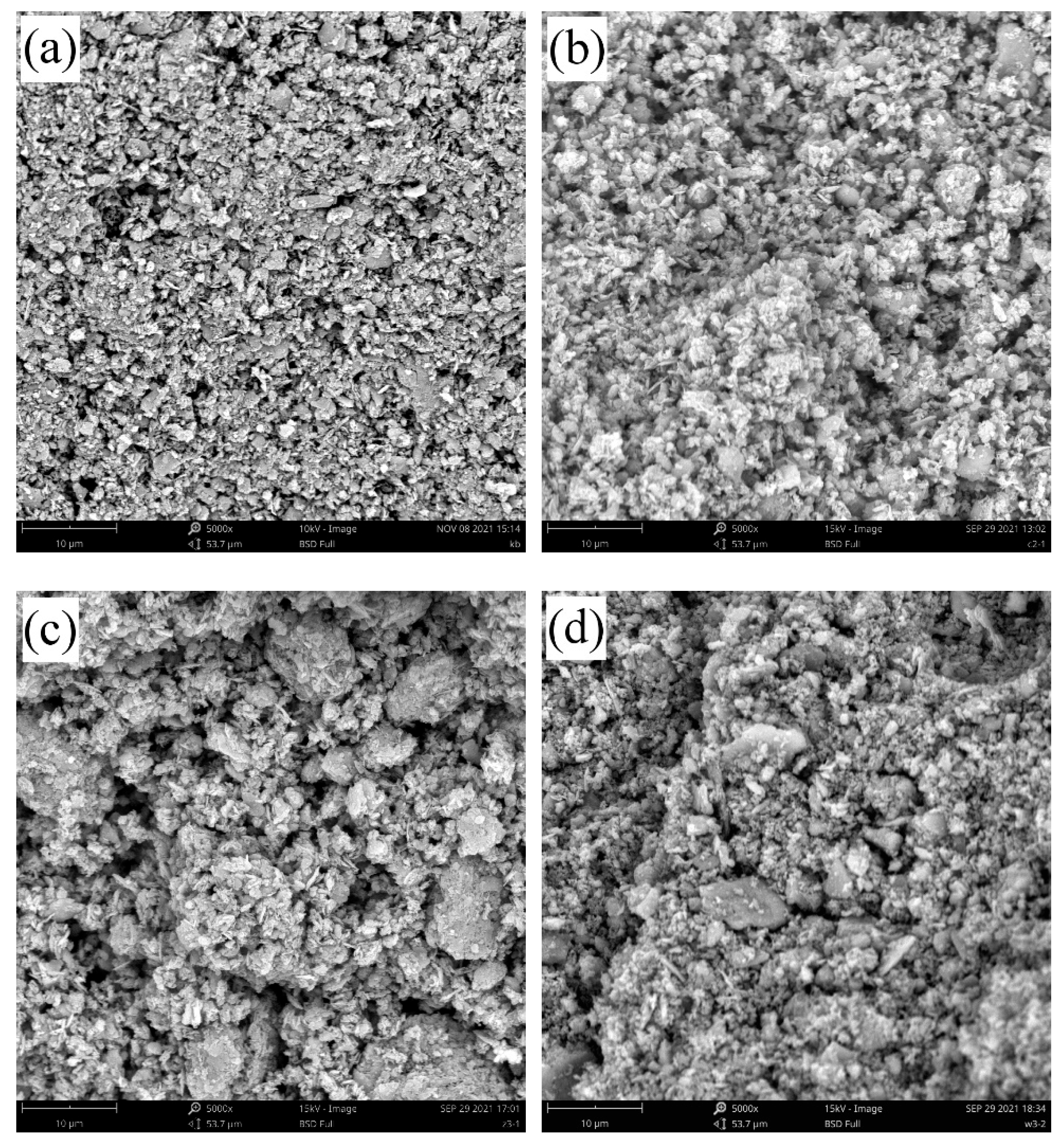
3.1. Changes in the Soil Microstructure After the Addition of Different Forms of Iron Oxide
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Microstructural Parameters of Ferric Oxide–Kaolin Complex
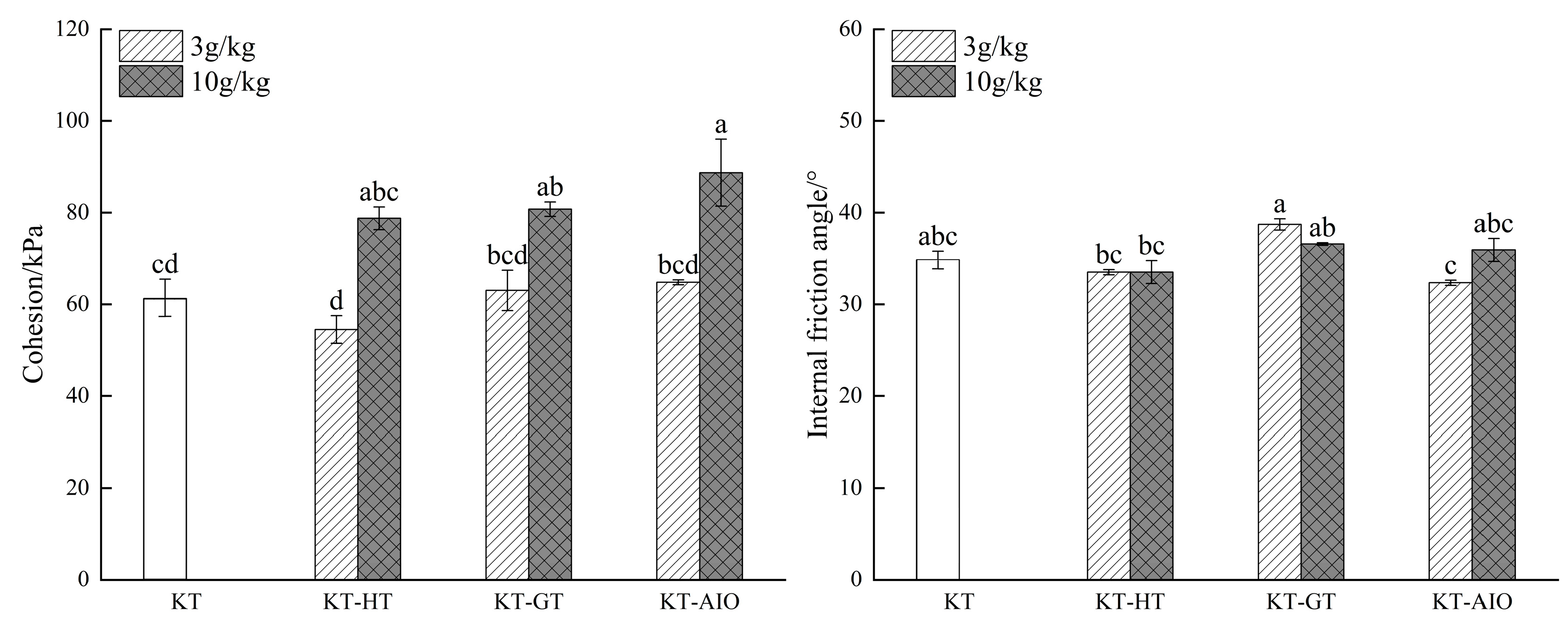
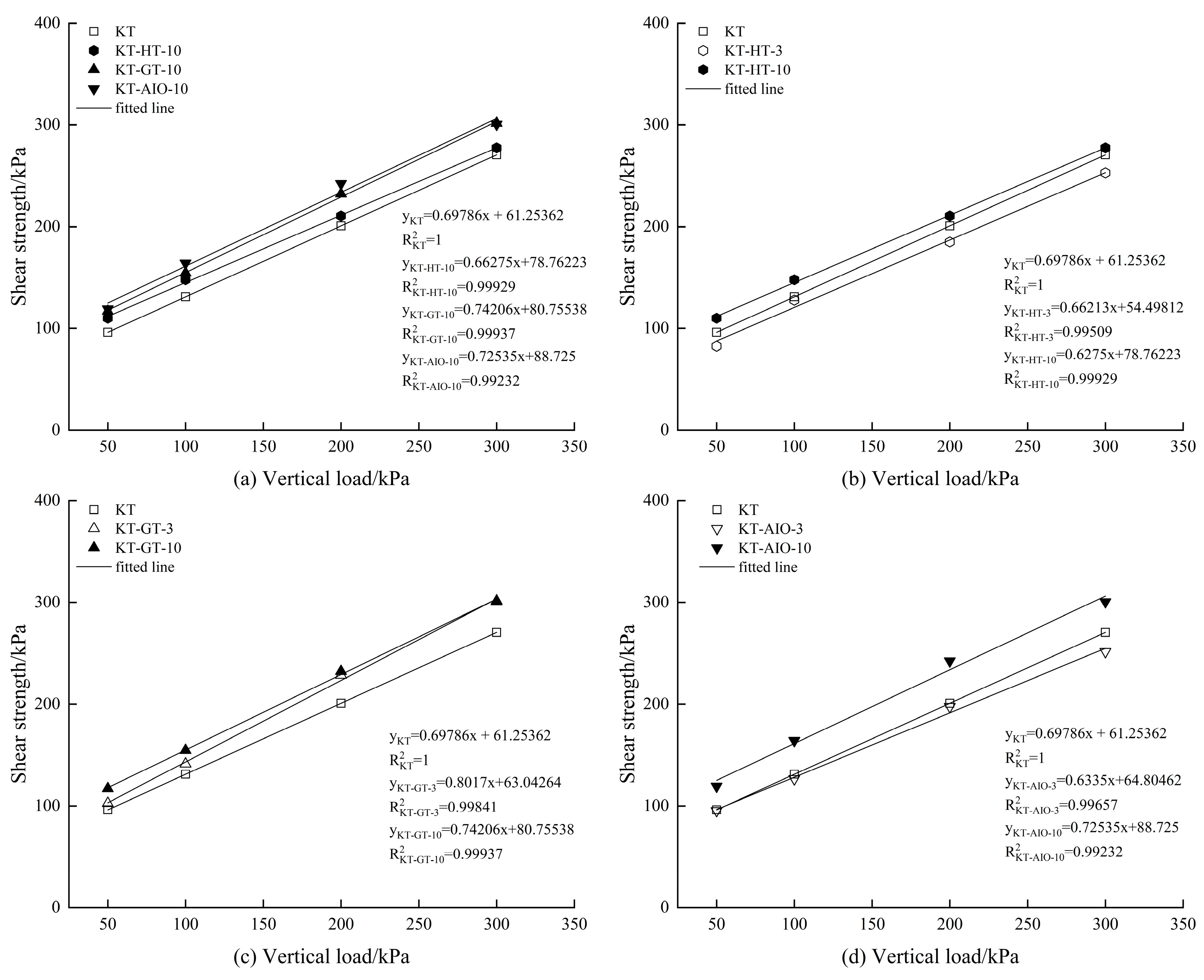
3.3. Changes in Cohesion, Internal Friction Angle, and Soil Shear Strength After the Addition of Different Forms of Iron Oxide
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Soil Microscopic Parameters and Shear Strength Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Forms of Iron Oxide on the Soil Microstructure
4.2. Effects of Different Forms of Iron Oxide on the Cohesion, Internal Friction Angle, and Shear Strength of Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.X.; Wei, Y.J.; Zhou, X.Q.; Chen, F.; Tian, Z.C.; Cai, C.F. Geospatial variation of granitic soil erodibility along a hydrothermal gradient in the gully region. Catena 2024, 245, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.L.; Deng, Y.S.; Duan, X.Q.; Cai, C.F.; Ding, S.W. Variations in weathering characteristics of soil profiles and response of the Atterberg limits in the granite hilly area of South China. Catena 2022, 215, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Zhang, X.W.; Kong, L.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, C. Drying-wetting impacts on granite residual soil: A multi-scale study from macroscopic to microscopic investigations. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.W.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.Y.; Cai, S.T. Quantitative characterization of drying-induced cracks and permeability of granite residual soil using micron-sized X-ray computed tomography. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 163213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.P.; Cui, Y.W.; Ouyang, G.Q.; Lyu, Z.T. An experimental study on influence of grain-size composition on collapsing erosion of granite residual soil. Catena 2023, 223, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Kong, L.W.; Zhang, B.X.; Liu, Z.J.; Shu, R.J.; Li, T.G. Determination of damage evolution characteristics in granite residual soil shear bands by micro-CT-based advanced digital volume correlation. Eng. Geol. 2024, 333, 107505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.J.; Wu, X.L.; Xia, J.W.; Cai, C.F. Relationship between granitic soil particle-size distribution and shrinkage properties based on multifractal method. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Cheng, Q.; Gong, X.P.; Shi, B.; Inyang, H.I. Investigation on microstructure evolution of clayey soils: A review focusing on wetting/drying process. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.Y.; Lin, J.S.; Zhao, D.F.; Jiang, F.S.; Wang, M.-K.; Ge, H.L.; Huang, Y.H. Effects of fractal dimension and water content on the shear strength of red soil in the hilly granitic region of southern China. Geomorphology 2020, 351, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Zhou, M.; Lin, J.S.; Jiang, F.S.; Huang, B.F.; Xu, T.T.; Wang, M.K.; Ge, H.L.; Huang, Y.H. Comparison of soil physicochemical properties and mineralogical compositions between noncollapsible soils and collapsed gullies. Geoderma 2018, 317, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Owusu, S.T.; Zhou, C.; Chiu, A.C.F. Effects of sesquioxide content on stress-dependent water retention behaviour of weathered soils. Eng. Geol. 2020, 266, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.W.; Kong, L.W.; Li, X.M.; Wang, G. Effect of cementation on the small-strain stiffness of granite residual soil. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefaciuk, G.; Czachor, H. Impact of organic matter, iron oxides, alumina, silica and drying on mechanical and water stability of artificial soil aggregates. Assessment of new method to study water stability. Geoderma 2014, 221, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Kong, L.W.; Yin, S.; Chen, C. Engineering geology of basaltic residual soil in Leiqiong, southern China. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duiker, S.W.; Rhoton, F.E.; Torrent, J.; Smeck, N.E.; Lal, R. Iron (Hydr)Oxide Crystallinity Effects on Soil Aggregation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, N.H.M.; de Nóbrega, M.T.; Vilar, O.M. Influence of the microstructure in the collapse of a residual clayey tropical soil. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2008, 68, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Liu, X.Y.; Kong, L.W.; Chen, C. Role of free iron oxides in the physicochemical and mechanical properties of natural clay. Eng. Geol. 2022, 303, 106665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.P.; Germaine, J.T.; Whittle, A.J. Effects of Fe-Oxides Cementation on the Deformation Characteristics of a Highly Weathered Old Alluvium in San Juan, Puerto Rico. Soils Found. 2003, 43, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Kong, L.W.; Cui, X.L.; Yin, S. Occurrence characteristics of free iron oxides in soil microstructure: Evidence from XRD, SEM and EDS. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 75, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Zhang, W.B.; Kong, L.W.; Fan, H.H.; Guo, A.G.; Xu, G.F. Effect of soaking time of dithionite–citrate–bicarbonate solution on strength and deformation characteristics of lateritic soil. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 3039–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Cattle, S.R.; Ortega, A.; Fouad, Y. In situ measurements of soil colour, mineral composition and clay content by vis–NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2009, 150, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhao, S.C.; Liu, P. Effects of drying-wetting cycles and free iron oxides on the mechanical behaviors of a partially decomposed granite residual soils. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Chadwick, O.A.; Rancourt, D.G.; Chorover, J. Iron-oxide crystallinity increases during soil redox oscillations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 1710–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.Y.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.H.; Tan, W.F.; Koopal, L.K. Formation and Transformation of Iron Oxide–Kaolinite Associations in the Presence of Iron(II). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Azhah, H.; Momtaz, H.R.; Ghaemian, N. Changes in forms and distribution pattern of soil iron oxides due to long-term cropping in the Northwest of Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 7275–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Shi, B.; Cai, Y.; Tang, C.S. 3D visualization and porosity computation of clay soil SEM image by GIS. Rock and Soil Mech. 2008, 29, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Kong, L.W.; Guo, A.G.; Tuo, Y.F. Evolution of microscopic pore of structured clay in compression process based on SEM and MIP test. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2012, 31, 406–412, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nachtegaal, M.; Sparks, D.L. Effect of iron oxide coatings on zinc sorption mechanisms at the clay-mineral/water interface. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbillon, A.J.; Mestdagh, M.M.; Vielvoye, L.; Derouane, E.G. Iron in kaolinite with special reference to kaolinite from tropical soils. Clay Min. 1976, 11, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.Y.; Tan, W.F.; Zhao, W.; Yu, Y.T.; Liu, F.; Koopal, L.K. Microstructure, Interaction Mechanisms, and Stability of Binary Systems Containing Goethite and Kaolinite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Axe, L. Ni and Zn Sorption to Amorphous versus Crystalline Iron Oxides: Macroscopic Studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 244, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gou, L.Y.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Z.M.; Chen, R.P. Role of iron oxide content on mechanical properties of granite residual soil in full suction range. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 3199–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.L.; Lin, Z.S.; Yong, Y.Y.; Zheng, C.L.; Zhu, A.B.; He, C.; Pan, H. Kaolinite loaded amorphous zero-valent iron enhanced removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 675, 132001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.F.; Qiu, M.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, J.L.; Jiang, F.S.; Wang, M.K.; Ge, H.L.; Huang, Y.H. Correlation between shear strength and soil physicochemical properties of different weathering profiles of the non-eroded and collapsing gully soils in southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3832–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, Z.M.; Shi, M.L.; Lin, J.S.; Jiang, F.S.; Ge, H.L.; Huang, Y.H. A quantitative study on the characteristics of desiccation cracks and their effect on the shear failure characteristics of granite red soil. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 83, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.; Nie, Z.H.; Aziz, M.; Fang, C.F.; Ghani, M.U.; Ijaz, Z.; Noshin, S.; Salman, M. Geotechnical properties of problematic expansive subgrade stabilized with guar gum biopolymer. Clean Techn. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 1699–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Contact Area/μm2 | Fractal Dimension | Apparent Porosity | Roundness | Abundance | Particle Long Axis/μm | Particle Short Axis/μm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KT | 296.10 ± 18.39 a | 1.22 ± 0.00 a | 0.50 ± 0.01 a | 5.86 ± 0.24 a | 0.61 ± 0.01 a | 2.27 ± 0.02 a | 1.38 ± 0.00 a |
| KT-HT-10 | 122.59 ± 16.81 b | 1.20 ± 0.00 b | 0.52 ± 0.01 a | 5.22 ± 0.21 a | 0.62 ± 0.01 a | 2.59 ± 0.09 a | 1.60 ± 0.08 a |
| KT-GT-10 | 306.41 ± 18.77 a | 1.21 ± 0.00 ab | 0.51 ± 0.01 a | 5.37 ± 0.12 a | 0.62 ± 0.00 a | 2.46 ± 0.02 a | 1.52 ± 0.02 a |
| KT-AIO-10 | 307.32 ± 32.62 a | 1.21 ± 0.00 ab | 0.51 ± 0.01 a | 5.82 ± 0.46 a | 0.60 ± 0.02 a | 2.33 ± 0.26 a | 1.39 ± 0.19 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Cen, N.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, J.; Jiang, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the Shear Strength of Iron Oxide-Kaolinite Cementing Materials in Granite Red Soil. Minerals 2025, 15, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010016
Yan H, Cen N, Zheng Q, Lin J, Jiang F, Huang Y, Zhang Y. Analysis of the Shear Strength of Iron Oxide-Kaolinite Cementing Materials in Granite Red Soil. Minerals. 2025; 15(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hualing, Nanbo Cen, Qinmin Zheng, Jinshi Lin, Fangshi Jiang, Yanhe Huang, and Yue Zhang. 2025. "Analysis of the Shear Strength of Iron Oxide-Kaolinite Cementing Materials in Granite Red Soil" Minerals 15, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010016
APA StyleYan, H., Cen, N., Zheng, Q., Lin, J., Jiang, F., Huang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Analysis of the Shear Strength of Iron Oxide-Kaolinite Cementing Materials in Granite Red Soil. Minerals, 15(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010016






