Feasibility Analysis of Bacterial-Treated Coal Gangue for Soil Improvement: Growth-Promoting Effects of Alfalfa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Bacterial Culture
2.3. Bacteria Isolation and Purification
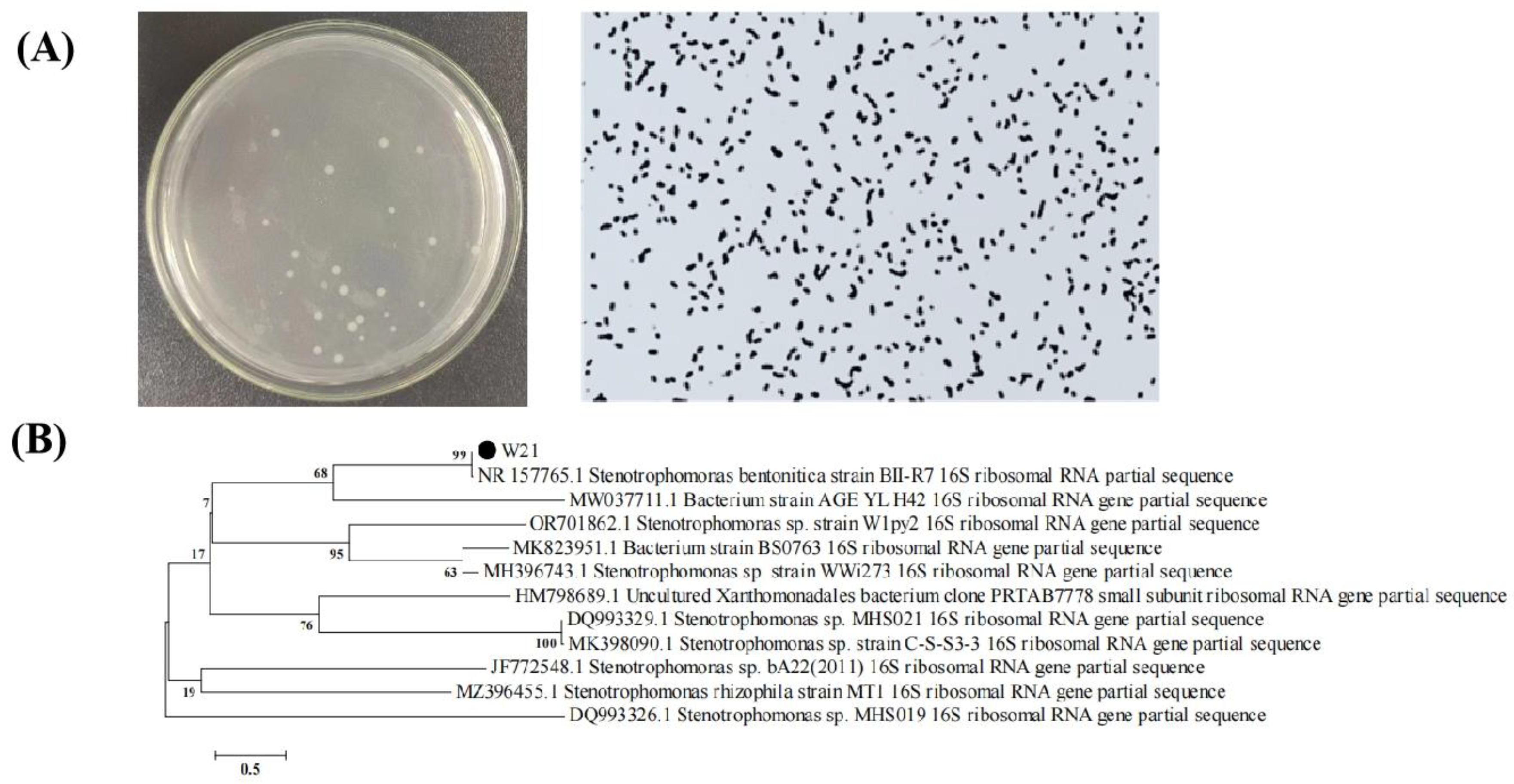
2.4. Bacteria Identification
2.5. Available P and Available K Measurements
2.6. Solubilization of Nutrient Elements from CG
2.7. Coal Gangue Analysis
2.8. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.9. Pot Experiment
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Components of Raw CG
3.2. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
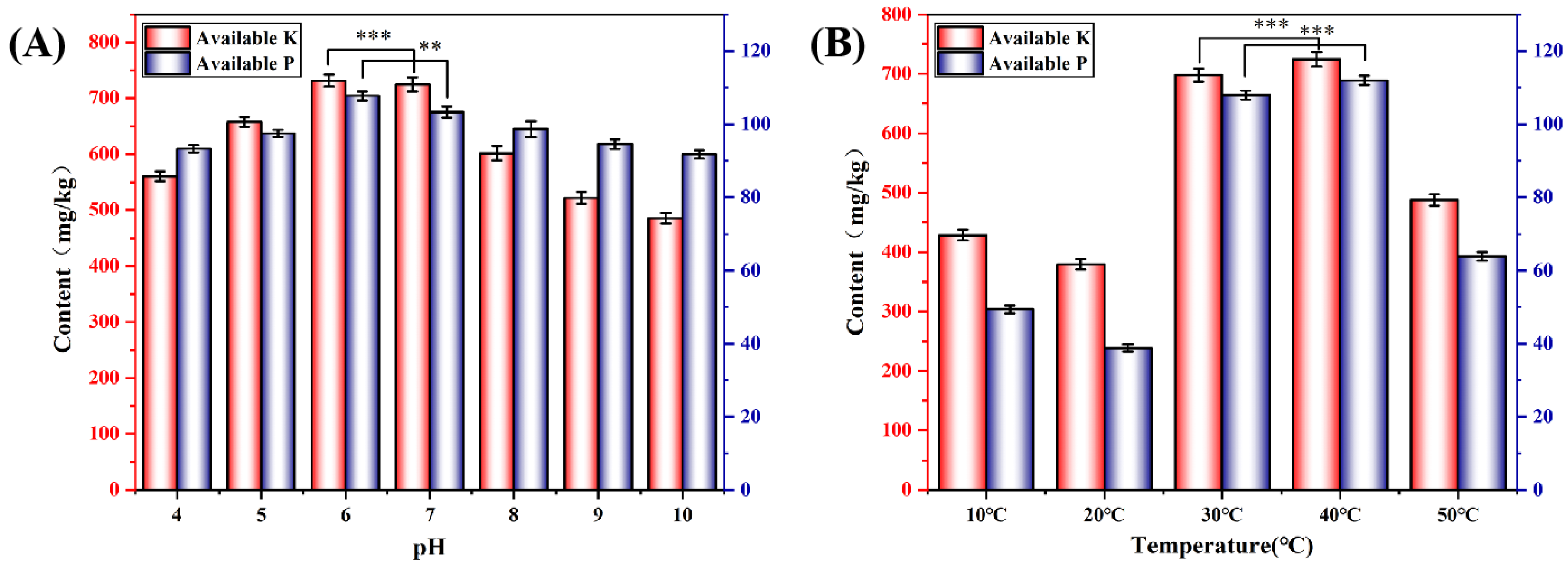
3.3. Study of Factors Affecting CG Solubilization
3.4. Optimization of Incubation Conditions on CG Solubilization
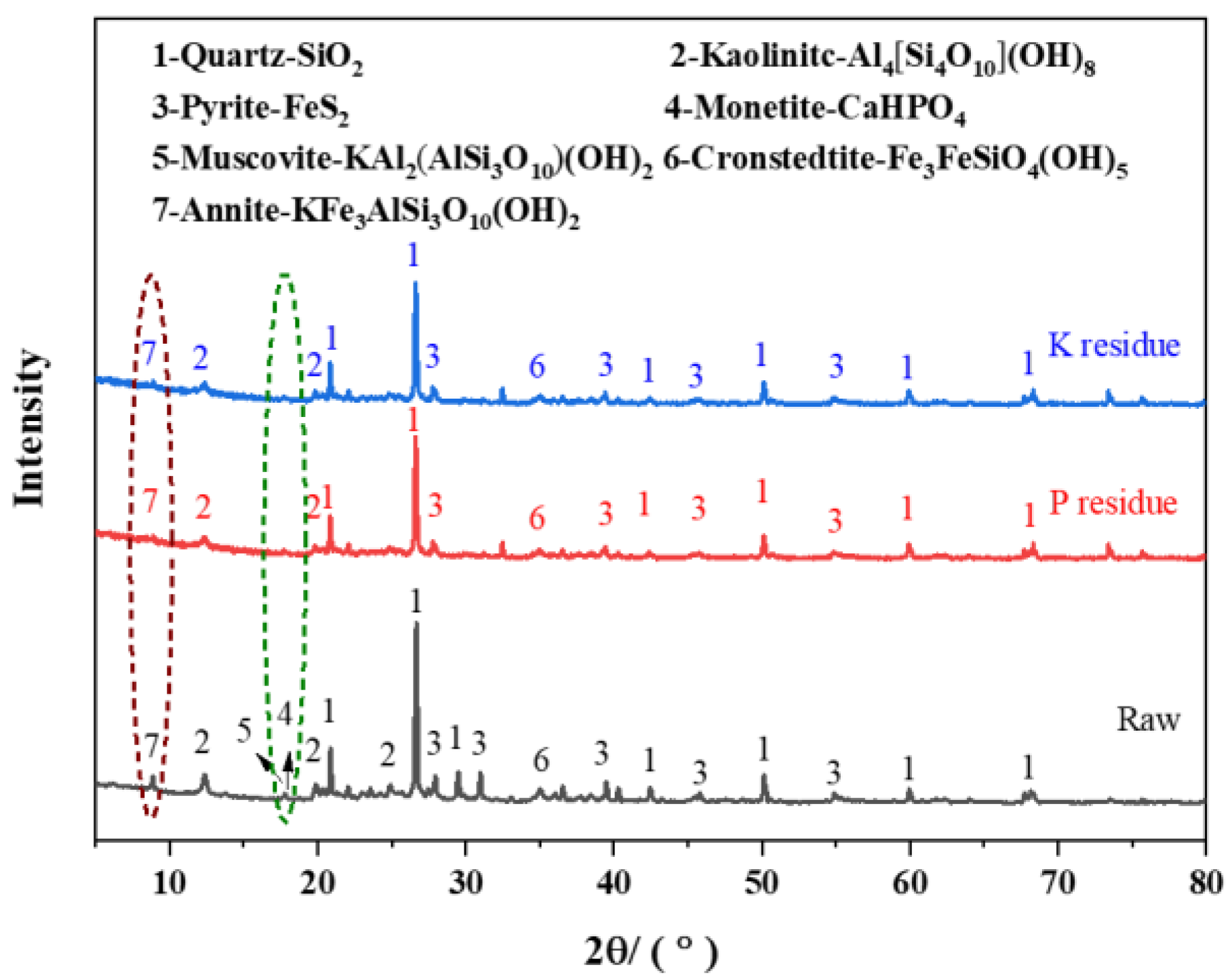
3.5. XRD and SEM Analysis of CG before and after Bacterial Treatment
3.6. The Mechanism of CG Nutrient Solubilization
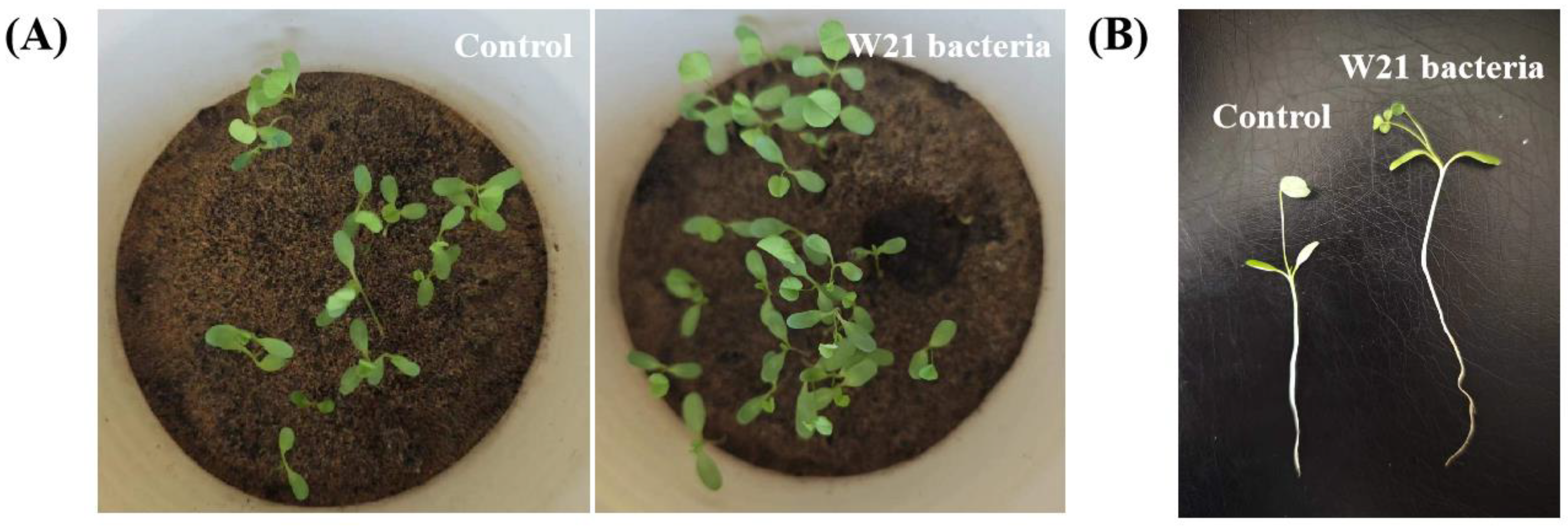
3.7. Growth-Promoting Effects of Alfalfa by Bacterial-Treated CG
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Ge, S. Uncovering the effects of external demand on China’s coal consumption: A global input–output analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J. Spatial and temporal characteristics of coal consumption and carbon emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 105770–105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, M.; Hu, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhou, T.; Nie, X. Using UAV and field measurement technology to monitor the impact of coal gangue pile temperature on vegetation ecological construction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Liao, L.; Lv, G. Environmental hazards and comprehensive utilization of solid waste coal gangue. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2024, 34, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Tian, X.; Yuan, L. Integrated green mining technology of “coal mining-gangue washing-backfilling-strata control-system monitoring”—Taking Tangshan Mine as a case study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 5798–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xin, C.; Sun, Y.; Di, J.; Liang, P. Experimental Study on the Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Basalt-Polypropylene Fibre-Reinforced Gangue Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.F.; Wang, L.A.; Huang, C. Environmental effects of coal gangue and its utilization. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2016, 38, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Zheng, L.; Jia, H.; Ma, G. The environmental pollution and control of coal gangue spontaneous combustion in mining. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 20, 3555–3562. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Song, J.; Bai, X.; Song, B.; Wang, R.; Zhou, T.; Jia, J.; Pu, H. Leaching behavior and potential environmental effects of trace elements in coal gangue of an open-cast coal mine area, Inner Mongolia, China. Minerals 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z. Environmental impact assessment of acidic coal gangue leaching solution on groundwater: A coal gangue pile in Shanxi, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yun, Y.; Li, G.; Sang, N. Heavy metals in soil from gangue stacking areas increases children health risk and causes developmental neurotoxicity in zebrafish larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Yang, F.; Ning, X.; Dong, Y.; Sang, N. Toxicity of soil leachate from coal gangue and its surrounding village of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Huanjing Kexue 2020, 41, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Han, Y. Bio-solubilization of Yunnan lignite by Penicillium ortum MJ51 and characterization of its products. Fuel 2023, 331, 125923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, G.; Hu, X. Potentially toxic elements in weathered waste-rocks of Fushun western opencast mine: Distribution, source identification, and contamination assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutao, W. Status and prospect of harmless disposal and resource comprehensive utilization of solid waste of coal gangue. Coal Geol. Explor. 2022, 50, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Xinjuan, W.; Cheng, X.; Qiuge, J.; Siyuan, S. Current situation and progress of coal gangue resource utilization. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 380–390. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shao, J.; Zheng, J.; Bai, C.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Colombo, P. Fabrication and application of porous materials made from coal gangue: A review. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2023, 20, 2099–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L. Application of coal gangue as a coarse aggregate in green concrete production: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, G.; Guo, L.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, K. Utilization of coal gangue as coarse aggregates in structural concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ling, T. Reactivity activation of waste coal gangue and its impact on the properties of cement-based materials—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, J. Study on mechanical properties of coal gangue and fly ash mixture as backfill material based on fractal characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 111936–111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Compression of aggregates of acid-leached coal gangues: Implications for coal mine backfill. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Ren, B.; He, P.; Jia, D.; Yang, J. Green synthesis of high porosity waste gangue microsphere/geopolymer composite foams via hydrogen peroxide modification. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Yang, S.; Qiao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.; Duan, C.; Liu, J. Extraction of valuable critical metals from coal gangue by roasting activation-sulfuric acid leaching. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2024, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.C.; Yang, Y.G.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Q.M. Effects of coal gangue on soil property and plant growth in mining area. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, T.; Ren, G.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shi, M.; Ding, S.; Fan, H. Reusing waste coal gangue to improve the dispersivity and mechanical properties of dispersive soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 404, 136993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Jia, H.; Pino, V.; Wu, H.; Cheng, F. A Si-K-Based Amendment Prepared by Coal Gangue and Plant Ash Could Improve the Growth of Maize Plants in Saline Soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 24, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, X.; Fang, C.; Dong, B.; Zhang, B. Sustainable and clean utilization of coal gangue: Activation and preparation of silicon fertilizer. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, X.; Fang, C.; Dong, B. Sustainable and Clean Utilization of Coal Gangue: Activation and Preparation of Citrate-Soluble Silicon Fertilizer. Res. Sq. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, X.; Hou, C.; Nie, W.; Zhang, X. Technology for producing silicon fertilizer from coal gangue. Coal Geol. Explor. 2009, 37, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Yang, S.; Deng, J.; Lei, J.; Shu, Z. Formulation of ferric/phosphorus composite coating on coal gangue as a novel fertilizer for enhancing slow–release of silicon and implication of As, Cr and Pb. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Han, H.; Yan, C. The relative role of climate change and human activities in the desertification process in Yulin region of northwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7165–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T. Exploring the dynamic coupling relationship between agricultural economy and agro-ecological environment in semi-arid areas: A case study of Yulin, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J. Screening for Calcium Phosphate Solubilizing Rhizobium leguminosarumi. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Tighe, S. Evaluation of mechanical properties and microscopic structure of coal gangue after aqueous solution treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Gong, W.; Li, W.; Bai, X.; Zhang, C. Reclamation of waste coal gangue activated by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for mine soil improvement: Solubilizing behavior of bacteria on nutrient elements. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115865. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Pandey, R.; Chauhan, N.S. Biofertilizer and biocontrol properties of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia BCM emphasize its potential application for sustainable agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1364807. [Google Scholar]
- Babalola, O.O.; Adeleke, B.S.; Ayangbenro, A.S. Draft genome sequencing of Stenotrophomonas indicatrix BOVIS40 and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia JVB5, two strains with identifiable genes involved in plant growth promotion. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e00482-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, O.O.; Agbodjato, N.A.; Ayangbenro, A.S.; Adjanohoun, A.; Baba-Moussa, L. Draft Genome Sequences of Four Strains of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Associated with Maize Rhizosphere. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e00730-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Huang, Y.; Gao, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, J. Study on the distribution characteristics and ecological risk of heavy metal elements in coal gangue taken from 25 mining areas of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 48285–48300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Zhou, G.; Yin, X.; Wang, C.; Chi, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, R. Assessment of heavy metal in coal gangue: Distribution, leaching characteristic and potential ecological risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32321–32331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.Q.; Peng, J.F.; Xu, D.J.; Tian, J.J.; Liu, T.H.; Jiang, B.B.; Zhang, F.C. Leaching characteristics and pollution risk assessment of potentially harmful elements from coal gangue exposed to weathering for different periods of time. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63200–63214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Qian, Y.; Hong, X.; Luo, Z.; Gao, X.; Liang, H. Contamination characteristics of polycyclic aromatic compounds from coal sources in typical coal mining areas in Huaibei area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Hong, X.; Qian, Y.; Liang, H. Distribution pattern of polycyclic aromatic compounds in coal gangue from coal city—East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 58674–58683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, M.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, Y.; Nie, X. 16S rDNA Sequencing-Based Insights into the Bacterial Community Structure and Function in Co-Existing Soil and Coal Gangue. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | SO3 | MgO | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt. %) | 43.82 | 15.31 | 2.95 | 3.15 | 2.09 | 1.25 | 0.96 | 0.73 |
| NO. | Retention Time (min) | Compounds | Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.405 | Oxalic acid | 2.612 |
| 2 | 5.052 | (2R,3R)-2,3-Dihydroxybernsteinsaeure | 4.012 |
| 3 | 5.397 | Formic acid | 37.155 |
| 4 | 6.573 | Malonic acid | 0.819 |
| 5 | 6.986 | DL-Malic acid | 1.516 |
| 6 | 8.045 | DL-Lactic acid | 2.363 |
| 7 | 8.476 | Acetic acid | 51.523 |
| Sample Name | Seed Germination Percentage (%) | Root Length (mm) | Plant Height (mm) | Fresh Weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy soil and CG | 70.0 ± 3.33 | 35.56 ± 3.18 | 42.5 ± 2.13 | 33.0 ± 2.69 |
| Sandy soil, CG and W21 bacteria | 81.7 ± 5.16 *** | 46.4 ± 4.22 *** | 60.3 ± 3.66 *** | 42.0 ± 3.52 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Di, Z.; Cao, W.; He, S. Feasibility Analysis of Bacterial-Treated Coal Gangue for Soil Improvement: Growth-Promoting Effects of Alfalfa. Minerals 2024, 14, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070676
Wang Y, Liu M, Di Z, Cao W, He S. Feasibility Analysis of Bacterial-Treated Coal Gangue for Soil Improvement: Growth-Promoting Effects of Alfalfa. Minerals. 2024; 14(7):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070676
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yaya, Mingwu Liu, Zhiting Di, Weilong Cao, and Shihua He. 2024. "Feasibility Analysis of Bacterial-Treated Coal Gangue for Soil Improvement: Growth-Promoting Effects of Alfalfa" Minerals 14, no. 7: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070676
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, M., Di, Z., Cao, W., & He, S. (2024). Feasibility Analysis of Bacterial-Treated Coal Gangue for Soil Improvement: Growth-Promoting Effects of Alfalfa. Minerals, 14(7), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14070676





