The Evolution of Neoproterozoic Mantle Peridotites Beneath the Arabian–Nubian Shield: Evidence from Wadi Sodmein Serpentinites, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt
Abstract
1. Introduction

2. Geologic Setting

3. Petrography

4. Materials and Methods
5. Results
5.1. Mineral Chemistry
5.1.1. Serpentine Minerals
5.1.2. Chromian-Spinels
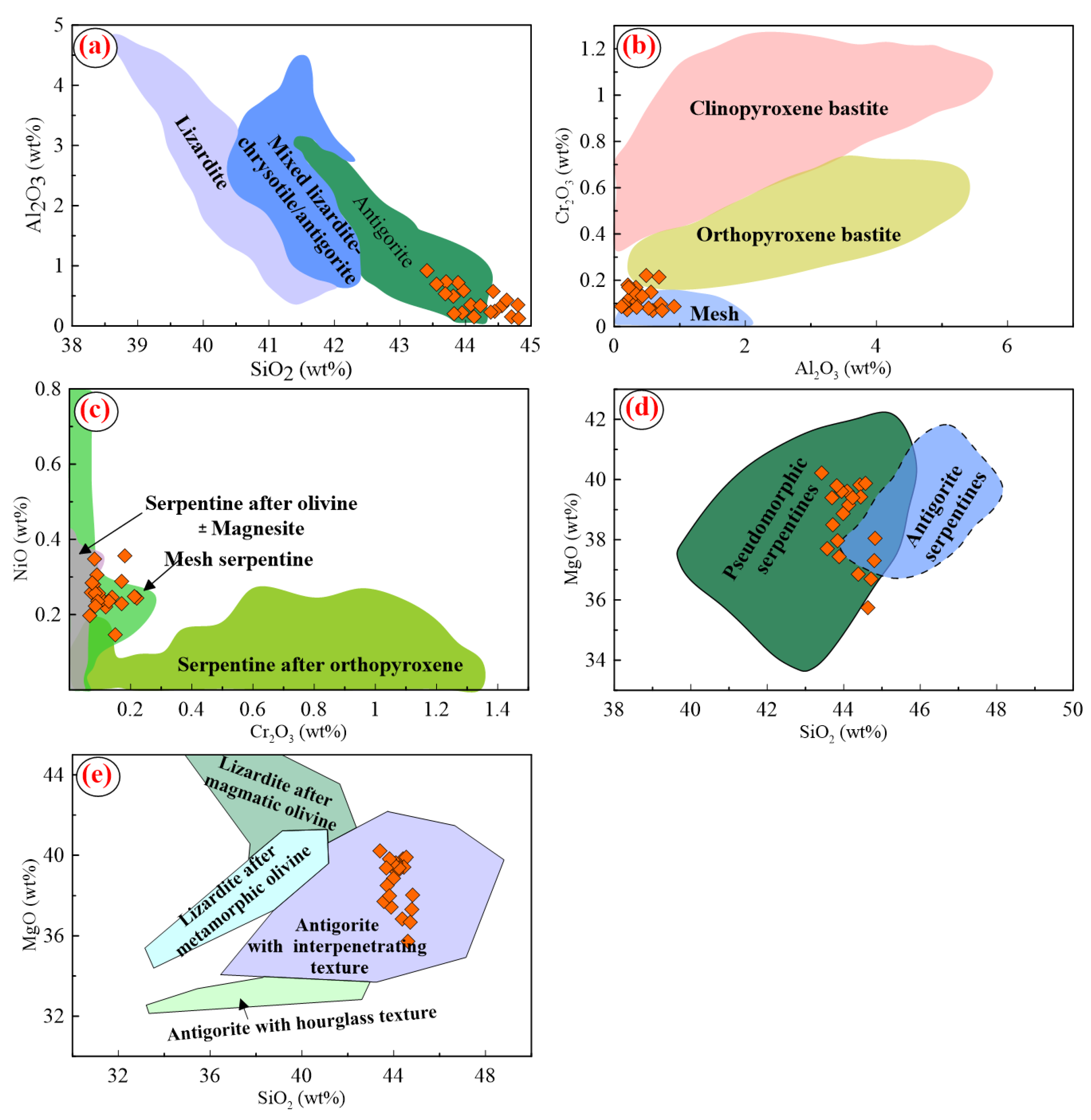
5.1.3. Chlorite
5.1.4. Magnesite

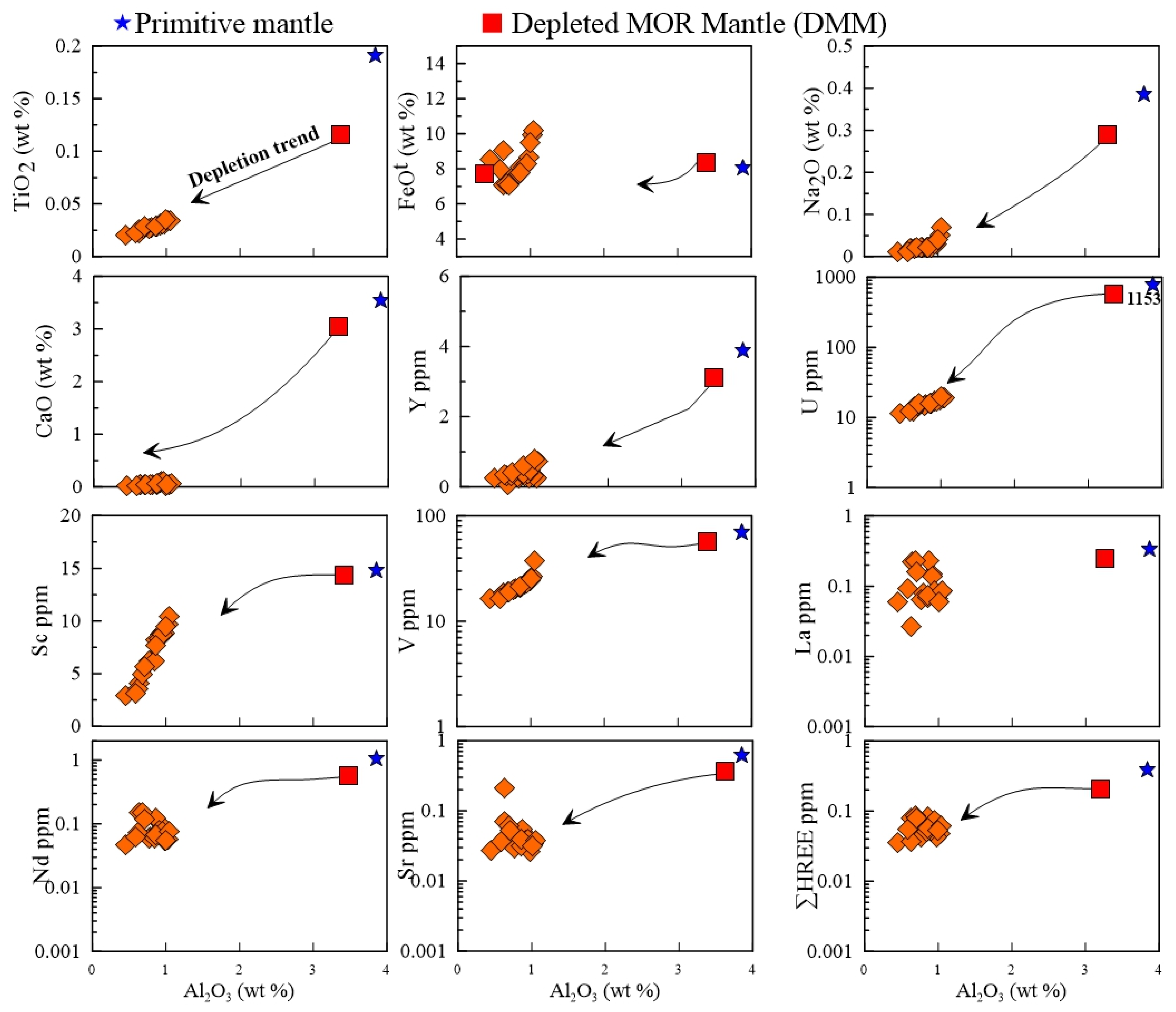
5.2. Whole-Rock Geochemistry

6. Discussion
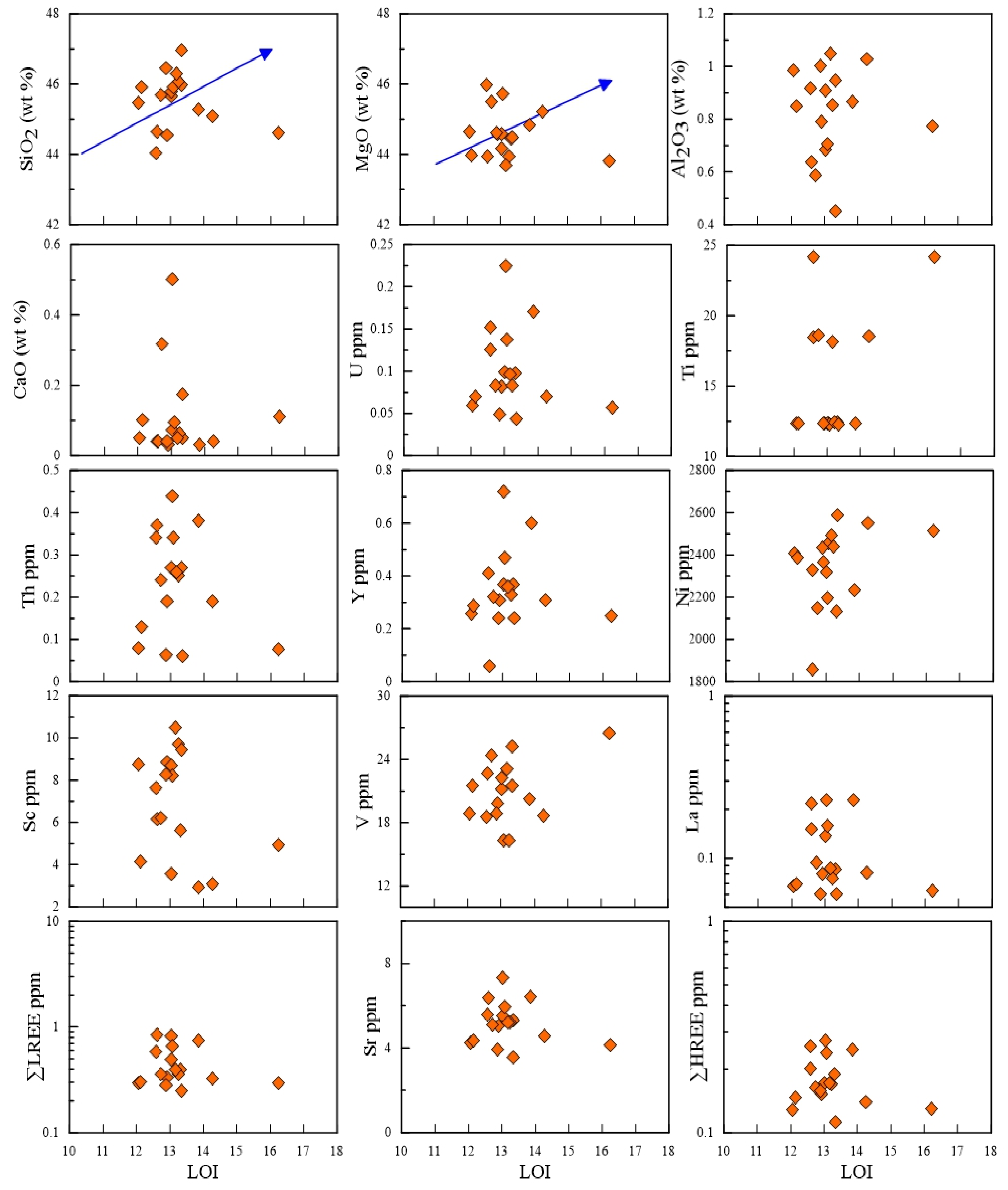
6.1. Effects of Serpentinization
6.2. Mantle Metasomatism (Melt/Rock Interaction)
6.3. Metamorphism and Incipient Carbonation of Serpentinite
6.4. Geochemical Characterization of Serpentinites
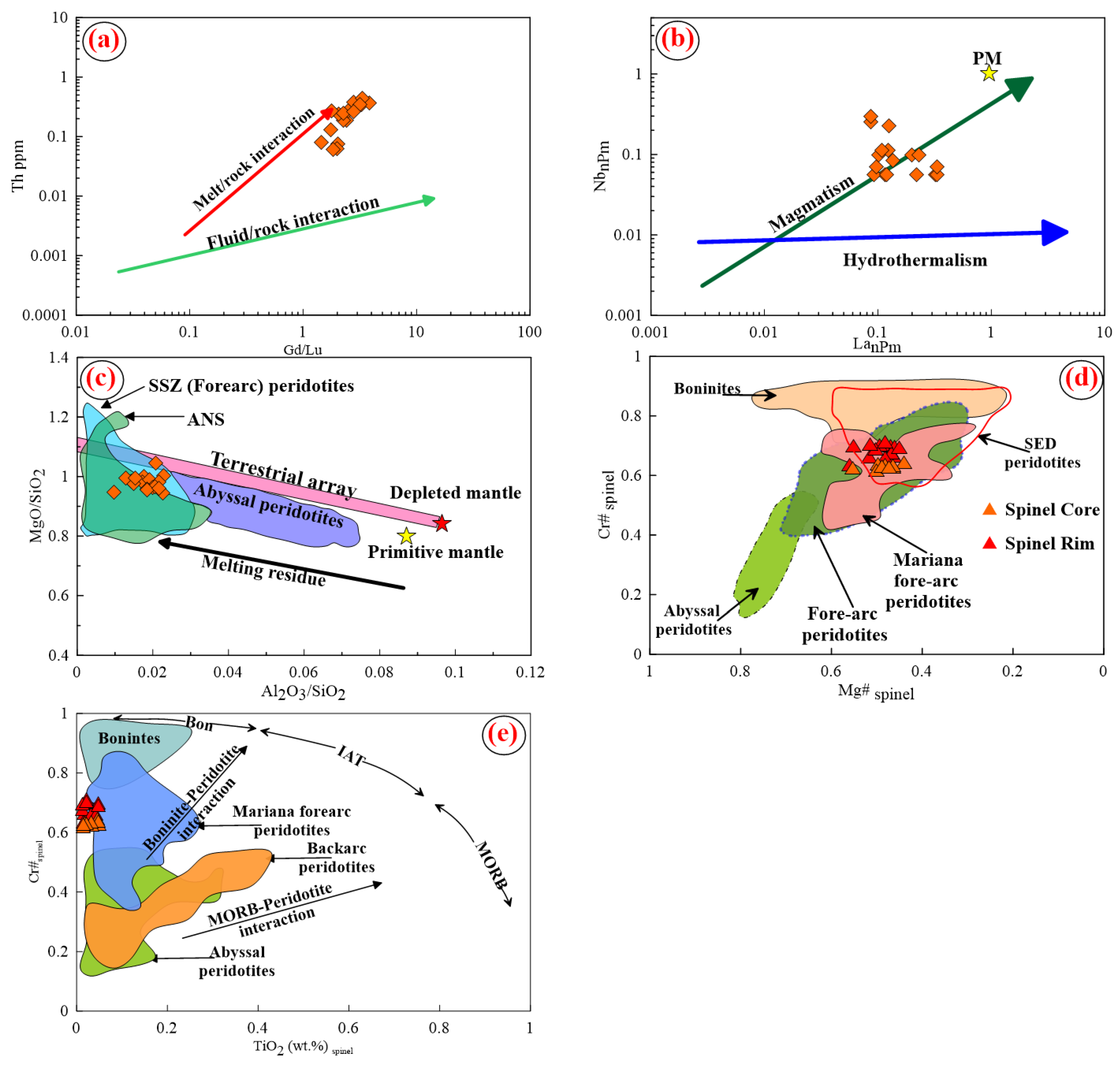
6.5. The Nature of Mantle and Melting Conditions

6.6. Tectonic Implications

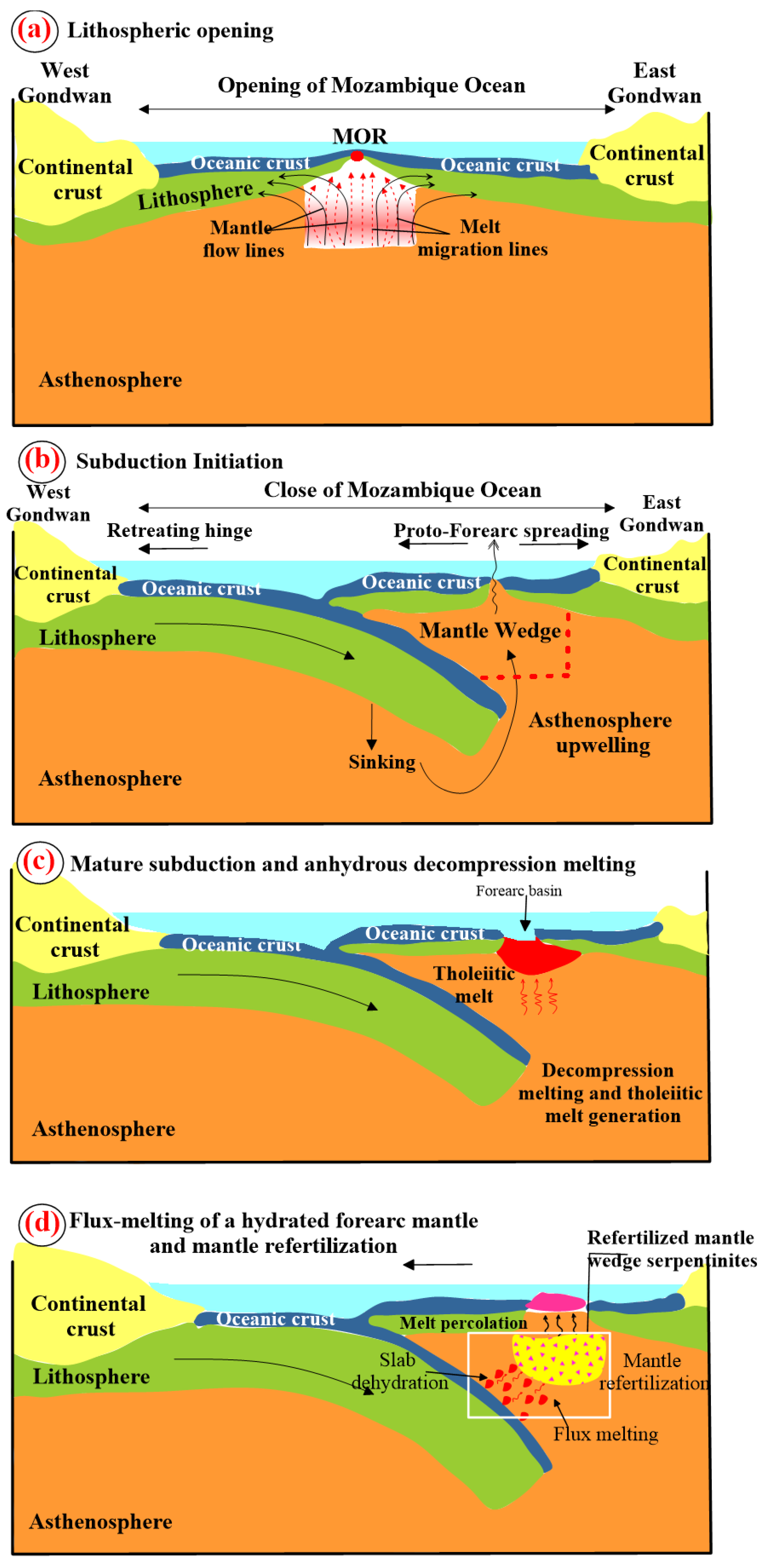
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stern, R.J. Arc-assembly and continental collision in the Neoproterozoic African orogen: Implications for the consolidation of Gondwanaland. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1994, 22, 319–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.A.; Azer, M.; Gahlan, H.; Wilde, S.; Samuel, M.; Stern, R. Age constraints on the formation and emplacement of Neoproterozoic ophiolites along the Allaqi–Heiani Suture, South Eastern Desert of Egypt. Gondwana Res. 2010, 18, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizenbauer, J.; Wallbrecher, E.; Fritz, H.; Neumayr, P.; Khudeir, A.A.; Kloetzli, U. Structural geology, single zircon ages and fluid inclusion studies of the Meatiq metamorphic core complex: Implications for Neoproterozoic tectonics in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Precamb. Res. 2001, 110, 357–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A. Supra-Subduction Zone Ophiolites: The Search for Modern Analogues; Special Papers; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2003; pp. 269–294. [Google Scholar]
- Akaad, M.; Noweir, M. Geology and Lithostratigraphy of the Arabian Desert Orogenic Belt of Egypt Between Latitudes 25 35, and 26 30′N. Evolution and Mineralization of the Arabian-Nubian Shield. Inst. App. Geol. Bull. 1980, 4, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, S.; Ghoneim, M.; Beniamin, N. Geology and origin of the Gerf serpentinites, Egypt. Egypt Mieralog. 1995, 7, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton, R.M. Review of Late Proterozoic sutures, ophiolitic mélanges and tectonics of eastern Egypt and north-east Sudan. Geol. Rundsch. 1994, 83, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, A.-A.M.; El-Shafei, S.A.; Azer, M.K. The Neoproterozoic ophiolitic ultramafic rocks in Eastern Desert of Egypt: Implications for petrogenesis and metasomatic processes. Int. Geol. Rev. 2021, 63, 208–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal El Dien, H.; Hamdy, M.; Abu El-Ela, A.S.; Abu-Alam, T.; Hassan, A.; Kil, Y.; Mizukami, T.; Soda, Y. Neoproterozoic serpentinites from the Eastern Desert of Egypt: Insights into Neoproterozoic mantle geodynamics and processes beneath the Arabian-Nubian Shield. Precamb. Res. 2016, 286, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.S. Chrome-spinels in serpentinites and talc carbonates of the El Ideid-El Sodmein District, central Eastern Desert, Egypt: Their metamorphism and petrogenetic implications. Geochemistry 2008, 68, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Furnes, H. Ophiolites and Their Origins. Elements 2014, 10, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Ahmed, Z. Proterozoic ophiolites of the Arabian Shield and their significance in Precambrian tectonics. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2003, 218, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Altunkaynak, Ş. Geochemical and temporal evolution of Cenozoic magmatism in western Turkey: Mantle response to collision, slab break-off, and lithospheric tearing in an orogenic belt. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2009, 311, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Furnes, H. Structure and geochemistry of Tethyan ophiolites and their petrogenesis in subduction rollback systems. Lithos 2009, 113, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, İ.; Ersoy, E.Y.; Karslı, O.; Dilek, Y.; Sadıklar, M.B.; Ottley, C.J.; Tiepolo, M.; Meisel, T. Coexistence of abyssal and ultra-depleted SSZ type mantle peridotites in a Neo-Tethyan Ophiolite in SW Turkey: Constraints from mineral composition, whole-rock geochemistry (major–trace–REE–PGE), and Re–Os isotope systematics. Lithos 2012, 132, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.-G.; Wang, C.-S.; Hébert, R.; Santosh, M.; Li, Y.-L.; Xu, J.-Y. Petrology and geochemistry of peridotites in the Zhongba ophiolite, Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone: Implications for the Early Cretaceous intra-oceanic subduction zone within the Neo-Tethys. Chem. Geol. 2011, 288, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, G.B.; Zanetti, A.; Müntener, O. Melt/peridotite interaction in the Southern Lanzo peridotite: Field, textural and geochemical evidence. Lithos 2007, 94, 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Shervais, J.W.; Mukasa, S.B. Supra-subduction and abyssal mantle peridotites of the Coast Range ophiolite, California. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2008, 156, 551–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, S.; Uysal, I.; Akmaz, R.M.; Kaliwoda, M.; Hochleitner, R. The effects of partial melting, melt–mantle interaction and fractionation on ophiolite generation: Constraints from the late Cretaceous Pozantı-Karsantı ophiolite, southern Turkey. Lithos 2014, 202–203, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, S.; Saikawa, Y.; Miura, M.; Parlak, O.; Arai, S. Decoding of Mantle Processes in the Mersin Ophiolite, Turkey, of End-Member Arc Type: Location of the Boninite Magma Generation. Minerals 2018, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, I.J.; Pearce, J.A. Peridotites from the Izu–Bonin–Mariana forearc (ODP Leg 125): Evidence for mantle melting and melt–mantle interaction in a supra-subduction zone setting. J. Petrol. 1998, 39, 1577–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.S.; Zaki Khedr, M.; Chiaradia, M.; Stern, R.J.; Bakhshizad, F.; Arai, S.; Ottley, C.J.; Tamura, A. Supra-subduction zone magmatism of the Neyriz ophiolite, Iran: Constraints from geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 1395–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Alam, T.; Santosh, M.; Brown, M.; Stüwe, K. Gondwana collision. Mineral. Petrol. 2013, 107, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogahed, M.M.; Abdelfadil, K.M. Constraints of Mantle and Crustal Sources Interaction during Orogenesis of Pre- and Post-Collision Granitoids from the Northern Arabian-Nubian Shield: A Case Study from Wadi El-Akhder Granitoids, Southern Sinai, Egypt. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 95, 1527–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, F.; Godard, M.; Guillot, S.; Hattori, K. Geochemistry of subduction zone serpentinites: A review. Lithos 2013, 178, 96–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, M.; Kröner, A.; Jochum, K.; Reischmann, T.; Todt, W. The Gabal Gerf complex: A Precambrian N-MORB ophiolite in the Nubian shield, NE Africa. Chem. Geol. 1995, 123, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bahariya, G.; Arai, S. Petrology and origin of Pan-African serpentinites with particular reference to chromian spinel composition, Eastern Desert, Egypt. implications for supra-subduction zone ophiolite. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on the Geology of Africa, Assiut, Egypt, 7–9 December 2003; pp. 371–388. [Google Scholar]
- Azer, M.K.; Stern, R.J. Neoproterozoic (835–720 Ma) serpentinites in the Eastern Desert, Egypt: Fragments of forearc mantle. J. Geol. 2007, 115, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H. Highly depleted harzburgite–dunite–chromitite complexes from the Neoproterozoic ophiolite, south Eastern Desert, Egypt: A possible recycled upper mantle lithosphere. Precamb. Res. 2013, 233, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Arai, S. Origin of Neoproterozoic ophiolitic peridotites in south Eastern Desert, Egypt, constrained from primary mantle mineral chemistry. Mineral. Petrol. 2013, 107, 807–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Alam, T.S.; Hamdy, M.M. Thermodynamic modelling of Sol Hamed serpentinite, South Eastern Desert of Egypt: Implication for fluid interaction in the Arabian–Nubian Shield ophiolites. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 99, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfadil, K.M.; Mansour, S.; Asran, A.; Younis, M.; Lentz, D.; Fowler, A.-R.; Fnais, M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Radwan, A. Composite Granitic Plutonism in the Southern Part of the Wadi Hodein Shear Zone, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: Implications for Neoproterozoic Dioritic and Highly Evolved Magma Mingling during Volcanic Arc Assembly. Minerals 2024, 14, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Arai, S. Petrology of a Neoproterozoic Alaskan-type complex from the Eastern Desert of Egypt: Implications for mantle heterogeneity. Lithos 2016, 263, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abart, R.; Sayyed, M.I.; Hauzenberger, C.A.; Sami, M. Petrogenesis of the Wadi El-Faliq Gabbroic Intrusion in the Central Eastern Desert of Egypt: Implications for neoproterozoic post-collisional magmatism associated with the Najd fault system. Minerals 2022, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Arai, S.; Tamura, A.; Morishita, T. Clinopyroxenes in high-P metaperidotites from Happo-O’ne, central Japan: Implications for wedge-transversal chemical change of slab-derived fluids. Lithos 2010, 119, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Parkinson, I.J. Trace element models for mantle melting: Application to volcanic arc petrogenesis. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1993, 76, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfadil, K.M.; Gharib, M.E.; Uher, P.; Putiš, M. Petrogenesis of Post-Orogenic Pan-African Rare-Element Granitic Pegmatites in the Western Arabian-Nubian Shield, Aswan Area, Southern Egypt. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 224, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, H.R.; El-Harairey, M.A. Physico-chemical conditions of Sodmein fluorite deposit, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 205, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gaby, S.; El-Nady, O.; Khudeir, A. Tectonic evolution of the basement complex in the central eastern desert of Egypt. Geol. Rundsch. 1984, 73, 1019–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.E.; Ahmed, A.A.; El Nady, O.M. Two orogenies in the Meatiq area of the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Precamb. Res. 1985, 30, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azer, M.; Khalil, A. Petrological and mineralogical studies of Pan-African serpentinites at Bir Al-Edeid area, central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2005, 43, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouméjon, S.; Cannat, M. Serpentinization of mantle-derived peridotites at mid-ocean ridges: Mesh texture development in the context of tectonic exhumation. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 2354–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, N.; Terashima, S.; Itoh, S.; Ando, A. 1994 Compilation Of Analytical Data for Minor and Trace Elements In Seventeen Gsj Geochemical Reference Samples, “Igneous Rock Series”. Geostand. Newslett. 1995, 19, 135–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proenza, J.A.; Ortega-Gutiérrez, F.; Camprubı, A.; Tritlla, J.; Elıas-Herrera, M.; Reyes-Salas, M. Paleozoic serpentinite-enclosed chromitites from Tehuitzingo (Acatlán Complex, southern Mexico): A petrological and mineralogical study. J. S. Am. Earth. Sci. 2004, 16, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surour, A.A. Chemistry of serpentine “polymorphs” in the Pan-African serpentinites from the Eastern Desert of Egypt, with an emphasis on the effect of superimposed thermal metamorphism. Mineral. Petrol. 2016, 111, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Ntaflos, T.; Sami, M. Geochemistry of Khor Um-Safi ophiolitic serpentinites, central Eastern desert, Egypt: Implications for neoproterozoic arc-basin system in the Arabian-Nubian shield. Geochemistry 2021, 81, 125690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, M.A. A microprobe study of antigorite and some serpentine pseudomorphs. Can. Mineral. 1979, 17, 711–784. [Google Scholar]
- Lafay, R.; Deschamps, F.; Schwartz, S.; Guillot, S.; Godard, M.; Debret, B.; Nicollet, C. High-pressure serpentinites, a trap-and-release system controlled by metamorphic conditions: Example from the Piedmont zone of the western Alps. Chem. Geol. 2013, 343, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodolányi, J.; Pettke, T.; Spandler, C.; Kamber, B.S.; Gméling, K. Geochemistry of ocean floor and fore-arc serpentinites: Constraints on the ultramafic input to subduction zones. J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 235–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.J. Chromite in komatiites, II. Modification during greenschist to mid-amphibolite facies metamorphism. J. Petrol. 2000, 41, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S. Chemistry of chromian spinel in volcanic rocks as a potential guide to magma chemistry. Mineral. Mag. 1992, 56, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, N.V.; Logvinova, A.M. Significance of Accessory Chrome Spinel in Identifying Serpentinite Paragenesis. Int. Geol. Rev. 2005, 47, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, P.L. Chromite; from the fiery rain of chondrules to the Kilauea Iki lava lake. Can. Mineral. 1994, 32, 729–746. [Google Scholar]
- Ohara, Y.; Stern, R.J.; Ishii, T.; Yurimoto, H.; Yamazaki, T. Peridotites from the Mariana Trough: First look at the mantle beneath an active back-arc basin. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 143, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, H.J.; Bullen, T. Chromian spinel as a petrogenetic indicator in abyssal and alpine-type peridotites and spatially associated lavas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1984, 86, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S. Characterization of spinel peridotites by olivine-spinel compositional relationships: Review and interpretation. Chem. Geol. 1994, 113, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenetsky, V.S.; Crawford, A.J.; Meffre, S. Factors controlling chemistry of magmatic spinel: An empirical study of associated olivine, Cr-spinel and melt inclusions from primitive rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 655–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Guillot, S.; Reynard, B.; Lafay, R.; Debret, B.; Nicollet, C.; Lanari, P.; Auzende, A.L. Pressure–temperature estimates of the lizardite/antigorite transition in high pressure serpentinites. Lithos 2013, 178, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R.B. Genetic implications of Zn- and Mn-rich Cr-spinels in serpentinites of the Tidding Suture Zone, eastern Himalaya, NE India. Geol. J. 2013, 48, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, F.J.; Plant, A. Electron microprobe and X-ray microbeam studies of serpentine textures. Can. Mineral. 1979, 17, 785–830. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.D. Principles of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2013; p. 702. [Google Scholar]
- Deer, W.; Howie, R.; Zussman, J. An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals, 2nd ed.; Harlow: Essex, UK; Longman Scientific & Technical: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 696. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, R.J.; Gwinn, C. Origin of late Precambrian intrusive carbonates, Eastern Desert of Egypt and Sudan: C, O and Sr isotopic evidence. Precamb. Res. 1990, 46, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.J.; Roeder, P.L. The range of spinel compositions in terrestrial mafic and ultramafic rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2279–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Robinson, P.T.; Hirokazu, M.; Richard, F. Petrological studies of peridotites from diapiric serpentinite seamounts in the Izu-Ogasawara-Mariana forearc, Leg 125. In Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Yokohama, Japan, 19 May–20 July 1992; Texas A & M University, Ocean Drilling Program: College Station, TX, USA, 1992; pp. 445–485. [Google Scholar]
- Kapsiotis, A.; Grammatikopoulos, T.A.; Tsikouras, B.; Hatzipanagiotou, K.; Zaccarini, F.; Garuti, G. Chromian Spinel Composition and Platinum-Group Element Mineralogy of Chromitites from The Milia Area, Pindos Ophiolite Complex, Greece. Can. Mineral. 2009, 47, 1037–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.K.; Baidya, T.K.; Rao, K.N.G.; Glascock, M.D. PGE and Ag mineralization in a breccia zone of the Precambrian Nuasahi ultramafic-mafic complex, Orissa, India. Can. Mineral. 2001, 39, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.Q.; Windley, B.F. Chromian spinel-silicate chemistry in ultramafic rocks of the Jijal complex, Northwest Pakistan. J. Petrol. 1990, 31, 667–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Arai, S. Peridotite-chromitite complexes in the Eastern Desert of Egypt: Insight into Neoproterozoic sub-arc mantle processes. Gondwana Res. 2017, 52, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, L.; Wirth, R. Spinel inclusions in olivine of peridotite xenoliths from TUBAF seamount (Bismarck Archipelago/Papua New Guinea): Evidence for the thermal and tectonic evolution of the oceanic lithosphere. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2000, 140, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Arai, S.; Attia, A.K. Petrological characteristics of podiform chromitites and associated peridotites of the Pan African Proterozoic ophiolite complexes of Egypt. Mineral. Depos. 2001, 36, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streckeisen, A. To each plutonic rock its proper name. Earth Sci. Rev. 1976, 12, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Azer, M. Supra-subduction affinity in the Neoproterozoic serpentinites in the Eastern Desert, Egypt: Evidence from mineral composition. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2007, 49, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatti, E.; Michael, P.J. Mantle peridotites from continental rifts to ocean basins to subduction zones. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1989, 91, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bahariya, G.A. Classification and origin of the Neoproterozoic ophiolitic mélanges in the Central Eastern Desert of Egypt. Tectonophysics 2012, 568, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, P. Oceanic islands and seamounts. In Oceanic Basalts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 174–218. [Google Scholar]
- El Bahariya, G.A. Classification of the Neoproterozoic ophiolites of the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt based on field geological characteristics and mode of occurrence. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.J.; Falloon, T.; Green, D. Classification, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of boninites. J. Boninites Relat. Rocks 1989, 1, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hey, M.H. A new review of the chlorites. Mineral. Mag. 1954, 30, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, H.R. Fluid-Gesteins-Interaktion in Metamorphen Ultramafititen der Zentralalpen; ETH Zürich: Zurich, Switzerland, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiler, H. Major and Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams to Determine Possible Protoliths of Orogenic Ultramafic Rocks; Universite’de Lausanne: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gülaçar, O.F.; Delaloye, M. Geochemistry of nickel, cobalt and copper in alpine-type ultramafic rocks. Chem. Geol. 1976, 17, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.G. Ophiolites: Ancient Oceanic Lithosphere? Minerals, Rocks and Mountains; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; Volume 12, p. 229. [Google Scholar]
- McDonough, W.F.; Sun, S.-S. The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 1995, 120, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Barker, P.; Edwards, S.; Parkinson, I.; Leat, P. Geochemistry and tectonic significance of peridotites from the South Sandwich arc–basin system, South Atlantic. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2000, 139, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, A.M.; El-Desoky, H.M.; Shalaby, B.N.A.; Awad, H.A.; Ene, A.; Heikal, M.A.; El-Awny, H.; Fahmy, W.; Taalab, S.A.; Zakaly, H.M.H. Ultramafic Rocks and Their Alteration Products from Northwestern Allaqi Province, Southeastern Desert, Egypt: Petrology, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 894582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palandri, J.L.; Reed, M.H. Geochemical models of metasomatism in ultramafic systems: Serpentinization, rodingitization, and sea floor carbonate chimney precipitation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1115–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, S.; Hattori, K. Serpentinites: Essential Roles in Geodynamics, Arc Volcanism, Sustainable Development, and the Origin of Life. Elements 2013, 9, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yuan, H.L.; Lyu, N.; Peng, Z.L. The behavior of fluid mobile elements during serpentinization and dehydration of serpentinites in subduction zones. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2020, 36, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, B.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Long, X. Mineral chemistry and geochemistry of serpentinites from the Bianmagou ophiolite in the North Qilian Belt, NW China: Implications for protoliths, melt extractions, and melt/fluid metasomatism. Geol. J. 2021, 56, 5163–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salters, V.J.; Stracke, A. Composition of the depleted mantle. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2004, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, A.-A.M.; Ali, S.; El-Shafei, S.A. Mineral chemistry and geochemistry of ophiolitic metaultramafics from Um Halham and Fawakhir, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 2337–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Sun, W.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y. Mechanism for serpentinization of mafic and ultramafic rocks and the potential of mineralization. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 4336–4348. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.-S.; McDonough, W. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, I.; Ersoy, E.Y.; Dilek, Y.; Kapsiotis, A.; Sarıfakıoğlu, E. Multiple episodes of partial melting, depletion, metasomatism and enrichment processes recorded in the heterogeneous upper mantle sequence of the Neotethyan Eldivan ophiolite, Turkey. Lithos 2016, 246–247, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xiong, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W. Subduction-zone peridotites and their records of crust-mantle interaction. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1033–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, R.K.; Hart, S.R. Major and trace element composition of the depleted MORB mantle (DMM). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 231, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.-d.; Zhang, Z.-F.; An, Y.; Liu, F. Iron Isotope Behavior During Melt-Peridotite Interaction in Supra-subduction Zone Ophiolite From Northern Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Song, S.; Su, L.; Jung, H.; Niu, Y. Highly refractory peridotites in Songshugou, Qinling orogen: Insights into partial melting and melt/fluid–rock reactions in forearc mantle. Lithos 2016, 252–253, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Santosh, M.; Ganguly, S.; Manikyamba, C.; Ray, J.; Dutta, J. Geochemical cycling during subduction initiation: Evidence from serpentinized mantle wedge peridotite in the south Andaman ophiolite suite. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 1755–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Halim, A.H.; Helmy, H.M.; Elhaddad, M.A.; El–Mahallawi, M.M.; Mogessie, A. Petrology of a Neoproterozoic mantle peridotite–chromitite association from Abu Dahr area, Eastern Desert, Egypt: Infiltration of a boninitic melt in highly depleted harzburgite. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 165, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodinier, J.-L.; Godard, M. Orogenic, ophiolitic, and abyssal peridotites. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 2, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.M. Global variations in abyssal peridotite compositions. Lithos 2016, 248–251, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulick, H.; Bach, W.; Godard, M.; De Hoog, J.C.M.; Suhr, G.; Harvey, J. Geochemistry of abyssal peridotites (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 15°20′N, ODP Leg 209): Implications for fluid/rock interaction in slow spreading environments. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodel, F.; Macouin, M.; Trindade, R.I.F.; Triantafyllou, A.; Ganne, J.; Chavagnac, V.; Berger, J.; Rospabe, M.; Destrigneville, C.; Carlut, J.; et al. Fossil black smoker yields oxygen isotopic composition of Neoproterozoic seawater. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-X.A.; Lee, C.-T.A. Geochemical investigation of serpentinized oceanic lithospheric mantle in the Feather River Ophiolite, California: Implications for the recycling rate of water by subduction. Chem. Geol. 2006, 235, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Ding, X.; Ling, M.-X.; Sun, W.-d.; Zhang, L.-P.; Hu, Y.-B.; Huang, R.-F. Origins of two types of serpentinites from the Qinling orogenic belt, central China and associated fluid/melt-rock interactions. Lithos 2018, 302–303, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.D. Interpretation of the Composition and a Classification of the Chlorites; Professional Paper 414-A; U.S. Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; pp. A1–A33. [Google Scholar]
- Padron-Navarta, J.A.; Lopez Sanchez-Vizcaino, V.; Garrido, C.J.; Gomez-Pugnaire, M.T. Metamorphic Record of High-pressure Dehydration of Antigorite Serpentinite to Chlorite Harzburgite in a Subduction Setting (Cerro del Almirez, Nevado-Filabride Complex, Southern Spain). J. Petrol. 2011, 52, 2047–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, M.D.; Garrido, C.J.; López Sánchez-Vizcaíno, V.; Marchesi, C.; Hidas, K.; Escayola, M.P.; Delgado Huertas, A. Carbonation of mantle peridotite by CO2-rich fluids: The formation of listvenites in the Advocate ophiolite complex (Newfoundland, Canada). Lithos 2018, 323, 238–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskabadi, A.; Pitcairn, I.K.; Broman, C.; Boyce, A.; Teagle, D.A.H.; Cooper, M.J.; Azer, M.K.; Stern, R.J.; Mohamed, F.H.; Majka, J. Carbonate alteration of ophiolitic rocks in the Arabian–Nubian Shield of Egypt: Sources and compositions of the carbonating fluid and implications for the formation of Au deposits. Int. Geol. Rev. 2017, 59, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, Y.; Polat, A. Suprasubduction zone ophiolites and Archean tectonics. Geology 2008, 36, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamori, H.; Nakamura, H. Isotopic heterogeneity of oceanic, arc and continental basalts and its implications for mantle dynamics. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 1131–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.-Y.; Santosh, M.; Ganguly, S.; Arun-Gokul, J.; Dhanil Dev, S.G.; Tsunogae, T.; Shaji, E.; Dong, Y.; Manikyamba, C. Melt-fluid infiltration in Archean suprasubduction zone mantle wedge: Evidence from geochemistry, zircon U–Pb geochronology and Lu–Hf isotopes from Wynad, southern India. Precamb. Res. 2016, 281, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.; Hoinkes, G.; Mogessie, A. Petrogenetic and geotectonic significance of Neoproterozoic suprasubduction mantle as revealed by the Wizer ophiolite complex, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 100, 1433–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Dilek, Y.; Shallo, M.; Tamura, A.; Arai, S. Insight into the uppermost mantle section of a maturing arc: The Eastern Mirdita ophiolite, Albania. Lithos 2011, 124, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoutz, E.; Palme, H.; Baddenhausen, H.; Blum, K.; Cendales, M.; Dreibus, G.; Spettel, B.; Lorenz, V.; Wänke, H. The abundances of major, minor and trace elements in the earth’s mantle as derived from primitive ultramafic nodules. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Proceedings, Houston, TX, USA, 19–23 March 1979; pp. 2031–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, S.R.; Zindler, A. In search of a bulk-Earth composition. Chem. Geol. 1986, 57, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, Y.; Ishii, T. Peridotites from the southern Mariana forearc: Heterogeneous fluid supply in mantle wedge. Isl. Arc 1998, 7, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogahed, M.M. Genesis and Tectonic Implications of the Kabr El-Bonaya Ultramafic Rocks, Sinai Peninsula, Egypt: Constraints from Mineralogical and Geochemical Characteristics. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 95, 393–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogahed, M.M. Petrogenesis of Zeiatit gabbroic rocks in the Southern Eastern Desert of Egypt: Discrimination of arc-related Neoproterozoic gabbros. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 150, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezard, R.; Hébert, R.; Wang, C.; Dostal, J.; Dai, J.; Zhong, H. Petrology and geochemistry of the Xiugugabu ophiolitic massif, western Yarlung Zangbo suture zone, Tibet. Lithos 2011, 125, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldanmaz, E.; Schmidt, M.; Gourgaud, A.; Meisel, T. Mid-ocean ridge and supra-subduction geochemical signatures in spinel–peridotites from the Neotethyan ophiolites in SW Turkey: Implications for upper mantle melting processes. Lithos 2009, 113, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umino, S.; Kanayama, K.; Kitamura, K.; Tamura, A.; Ishizuka, O.; Senda, R.; Arai, S. Did boninite originate from the heterogeneous mantle with recycled ancient slab? Isl. Arc 2017, 27, e12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppa, M.; Koller, F.; Putiš, M. Petrology and geochemistry of a peridotite body in Central- Carpathian Paleogene sediments (Sedlice, eastern Slovakia). Geol. Carpath. 2014, 65, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Z.; Wu, F.-Y.; Chu, Z.-Y.; Ji, W.-Q.; Yu, L.-J.; Li, J.-L. Preservation of ancient Os isotope signatures in the Yungbwa ophiolite (southwestern Tibet) after subduction modification. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 53, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebrand, E.; Snow, J.E.; Dick, H.J.B.; Hofmann, A.W. Coupled major and trace elements as indicators of the extent of melting in mid-ocean-ridge peridotites. Nature 2001, 410, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellini, M.; Rumori, C.; Viti, C. Hydrothermally reset magmatic spinels in retrograde serpentinites: Formation of “ferritchromit” rims and chlorite aureoles. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2005, 149, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Yang, J.; Robinson, P.T.; Liu, F.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Wu, W. Tectonic Evolution of the Western Yarlung Zangbo Ophiolitic Belt, Tibet: Implications from the Petrology, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry of the Peridotites. J. Geol. 2016, 124, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodinier, J.; Dupuy, C.; Dostal, J. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Eastern Pyrenean peridotites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 2893–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusky, T.M.; Wang, L.; Dilek, Y.; Robinson, P.; Peng, S.; Huang, X. Application of the modern ophiolite concept with special reference to Precambrian ophiolites. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caran, Ş.; Çoban, H.; Flower, M.F.J.; Ottley, C.J.; Yılmaz, K. Podiform chromitites and mantle peridotites of the Antalya ophiolite, Isparta Angle (SW Turkey): Implications for partial melting and melt–rock interaction in oceanic and subduction-related settings. Lithos 2010, 114, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, M.; Picard, C.; Guillot, S.; Chauvel, C.; Cluzel, D.; Meffre, S. Multiple melting stages and refertilization as indicators for ridge to subduction formation: The New Caledonia ophiolite. Lithos 2010, 115, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985; p. 312. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-H.; Zhou, M.-F. Geochemistry of the ~430-Ma Jingbulake mafic–ultramafic intrusion in Western Xinjiang, NW China: Implications for subduction related magmatism in the South Tianshan orogenic belt. Lithos 2009, 113, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldanmaz, E.; Koprubasi, N. Platinum-Group-Element Systematics of Peridotites from Ophiolite Complexes of Northwest Anatolia, Turkey: Implications for Mantle Metasomatism by Melt Percolation in a Supra-subduction Zone Environment. Int. Geol. Rev. 2006, 48, 420–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizimis, M.; Salters, V.J.; Bonatti, E. Trace and REE content of clinopyroxenes from supra-subduction zone peridotites. Implications for melting and enrichment processes in island arcs. Chem. Geol. 2000, 165, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, C.; Garrido, C.J.; Proenza, J.A.; Hidas, K.; Varas-Reus, M.I.; Butjosa, L.; Lewis, J.F. Geochemical record of subduction initiation in the sub-arc mantle: Insights from the Loma Caribe peridotite (Dominican Republic). Lithos 2016, 252, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Wasserburg, G.J. The neodymium isotopic compositions and rare earth patterns in highly depleted ultramafic rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4537–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, R.; Ries, A.; Graham, R.; Fitches, W. Late Precambrian ophiolitic melange in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Nature 1980, 285, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El Ela, F. Supra-subduction zone ophiolite of Qift-Quseir Road, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Bull. Fac. Sci. Assiut Univ. 1990, 19, 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Azer, M.K. Petrological studies of Neoproterozoic serpentinized ultramafics of the Nubian Shield: Spinel compositions as evidence of the tectonic evolution of Egyptian ophiolites. Acta Geol. Pol. 2014, 64, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rahman, Y.A.; Polat, A.; Dilek, Y.; Fryer, B.; El-Sharkawy, M.; Sakran, S. Geochemistry and tectonic evolution of the Neoproterozoic Wadi Ghadir ophiolite, Eastern Desert, Egypt. Lithos 2009, 113, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, E.; El Mahalawi, M.; Hoinkes, G.; Aal, A.A. Continental back-arc basin origin of some ophiolites from the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Mineral. Petrol. 2004, 82, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlan, H.A.; Azer, M.K.; Khalil, A.E. The Neoproterozoic Abu Dahr ophiolite, South Eastern Desert, Egypt: Petrological characteristics and tectonomagmatic evolution. Mineral. Petrol. 2015, 109, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, A.-A.M.; Ahmed, Z. Possible origin of the ophiolites of Eastern Desert, Egypt, from geochemical perspectives. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2010, 35, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelfadil, K.M.; Asimow, P.D.; Azer, M.K.; Gahlan, H.A. Genesis and Petrology of Late Neoproterozoic Pegmatites and Aplites Associated with the Taba Metamorphic Complex in Southern Sinai, Egypt. Geol. Acta 2016, 14, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azer, M.K. Evolution and economic significance of listwaenites associated with Neoproterozoic ophiolites in south Eastern Desert, Egypt. Geol. Acta 2013, 11, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; van der Laan, S.R.; Arculus, R.J.; Murton, B.J.; Ishii, T.; Peate, D.W.; Parkinson, I.J. Boninite and harzburgite from Leg 125 (Bonin-Mariana forearc): A case study of magma genesis during the initial stages of subduction. In Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Yokohama, Japan, 19 May–20 July 1992; Texas A & M University, Ocean Drilling Program: College Station, TX, USA, 1992; pp. 623–659. [Google Scholar]
- Defant, M.J.; Drummond, M.S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 1990, 347, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Lippard, S.; Roberts, S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1984, 16, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, R.L.; Frey, F.A. Geochemical characteristics of boninite series volcanics: Implications for their source. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 2099–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palme, H.; O’Neill, H.S.C. 3.1—Cosmochemical Estimates of Mantle Composition. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Takazawa, E.; Hauzenberger, C.; Tamura, A.; Arai, S.; Stern, R.J.; Morishita, T.; El-Awady, A. Petrogenesis of arc-related serpentinized peridotites (Egypt): Insights into Neoproterozoic mantle evolution beneath the Arabian-Nubian Shield. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 226, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelfadil, K.M.; Asran, A.M.; Rehman, H.U.; Sami, M.; Ahmed, A.; Sanislav, I.V.; Fnais, M.S.; Mogahed, M.M. The Evolution of Neoproterozoic Mantle Peridotites Beneath the Arabian–Nubian Shield: Evidence from Wadi Sodmein Serpentinites, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Minerals 2024, 14, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14111157
Abdelfadil KM, Asran AM, Rehman HU, Sami M, Ahmed A, Sanislav IV, Fnais MS, Mogahed MM. The Evolution of Neoproterozoic Mantle Peridotites Beneath the Arabian–Nubian Shield: Evidence from Wadi Sodmein Serpentinites, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Minerals. 2024; 14(11):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14111157
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelfadil, Khaled M., Asran M. Asran, Hafiz U. Rehman, Mabrouk Sami, Alaa Ahmed, Ioan V. Sanislav, Mohammed S. Fnais, and Moustafa M. Mogahed. 2024. "The Evolution of Neoproterozoic Mantle Peridotites Beneath the Arabian–Nubian Shield: Evidence from Wadi Sodmein Serpentinites, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt" Minerals 14, no. 11: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14111157
APA StyleAbdelfadil, K. M., Asran, A. M., Rehman, H. U., Sami, M., Ahmed, A., Sanislav, I. V., Fnais, M. S., & Mogahed, M. M. (2024). The Evolution of Neoproterozoic Mantle Peridotites Beneath the Arabian–Nubian Shield: Evidence from Wadi Sodmein Serpentinites, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Minerals, 14(11), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14111157