Material Characterization of Mayapán’s Effigy Censers’ Sherds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Archaeological Materials
2.2. Hyperspectral Imaging
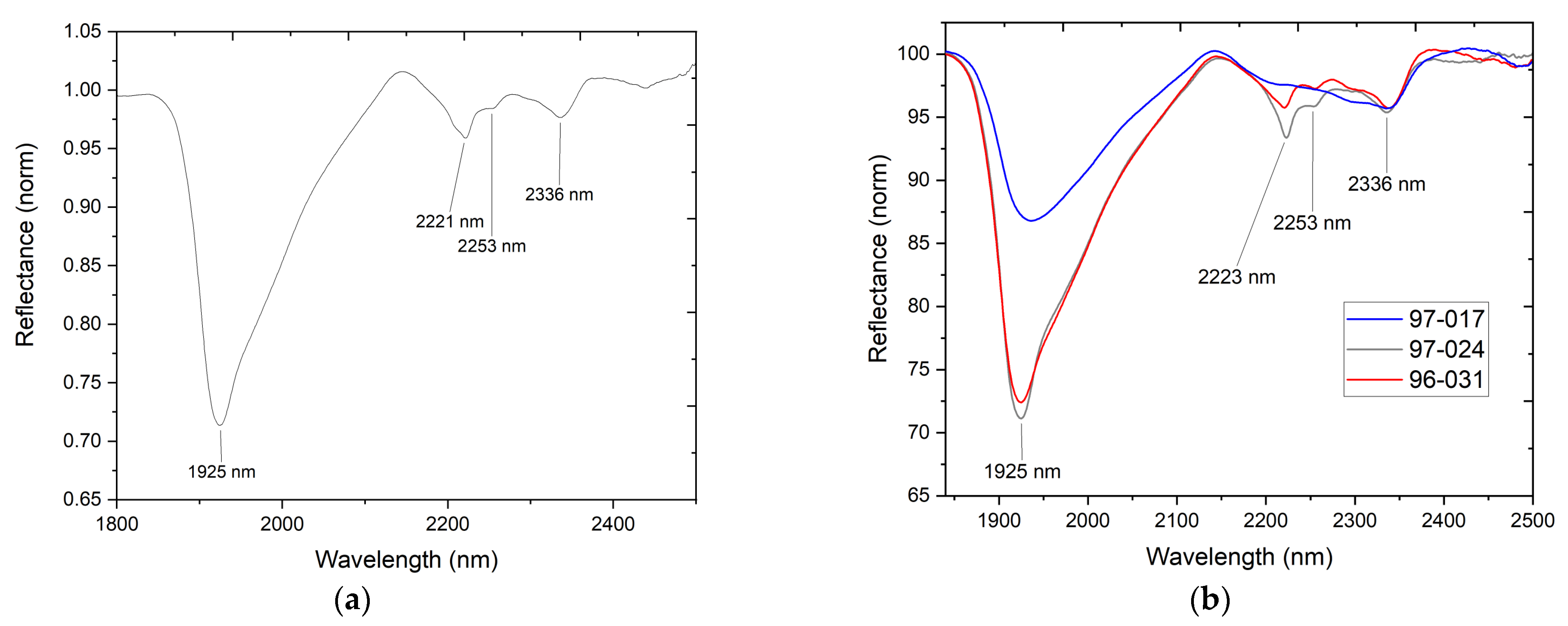
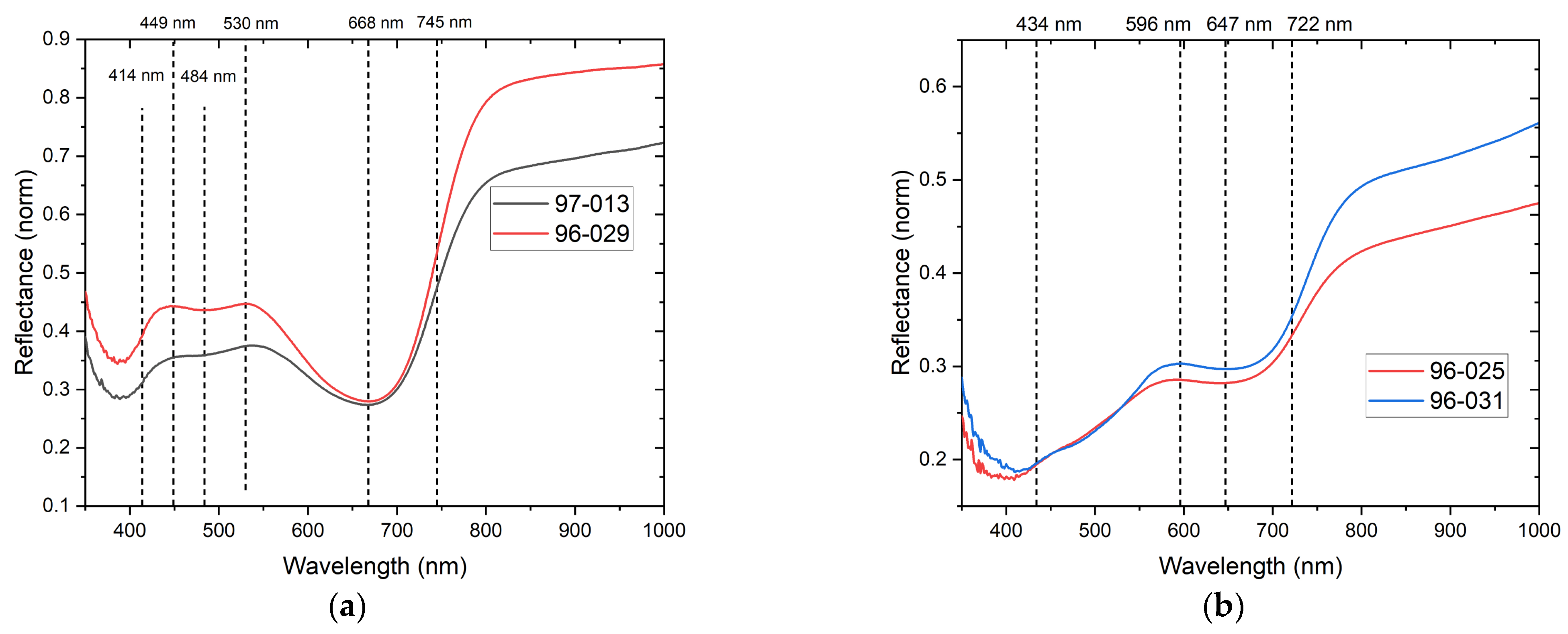
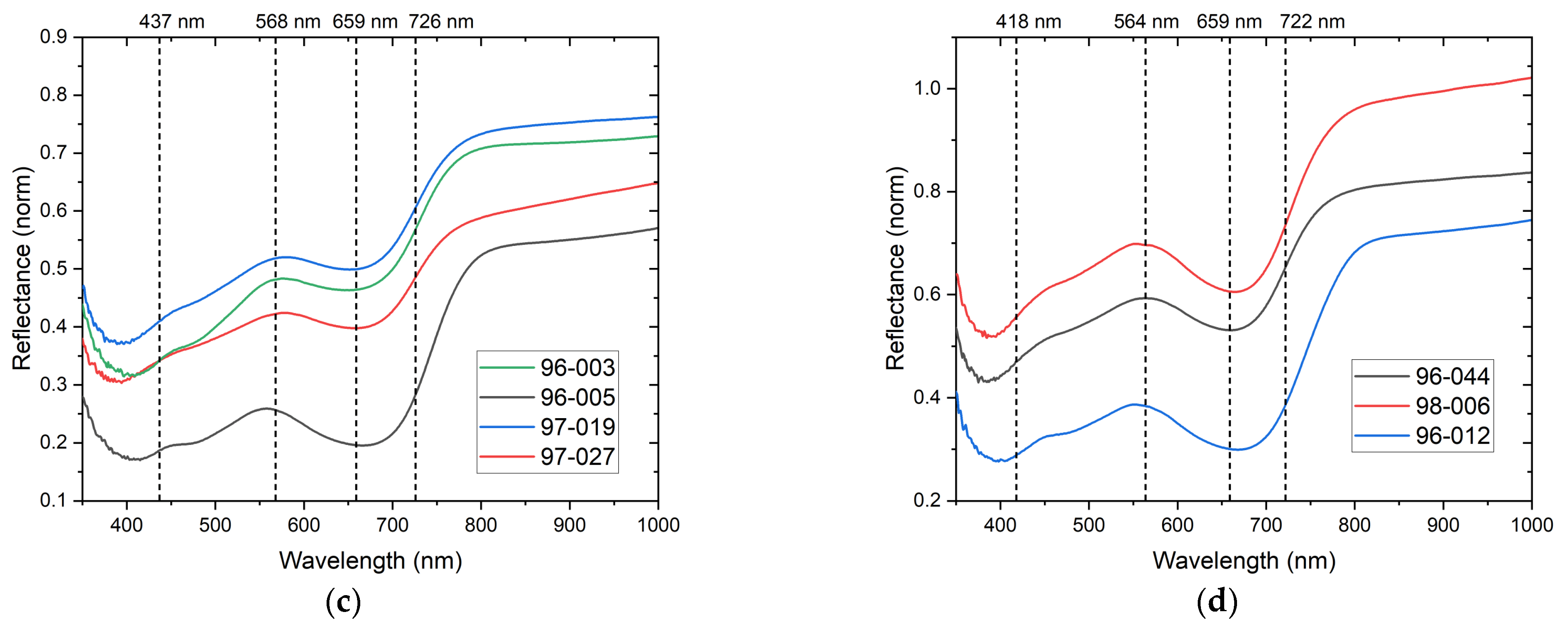
2.3. Fiber Optic Reflectance Spectroscopy (FORS)
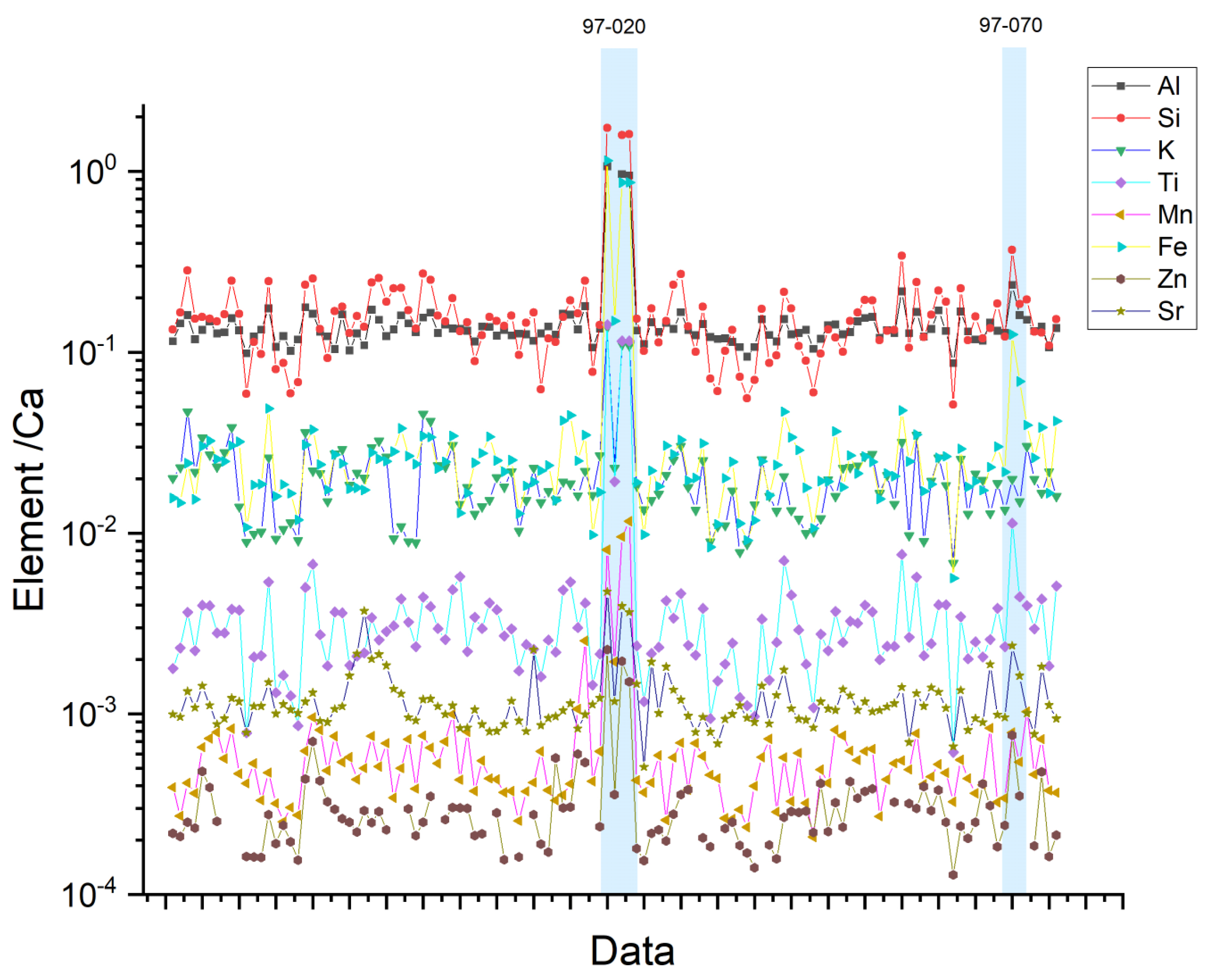
2.4. X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (XRF)
2.5. Microscopic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
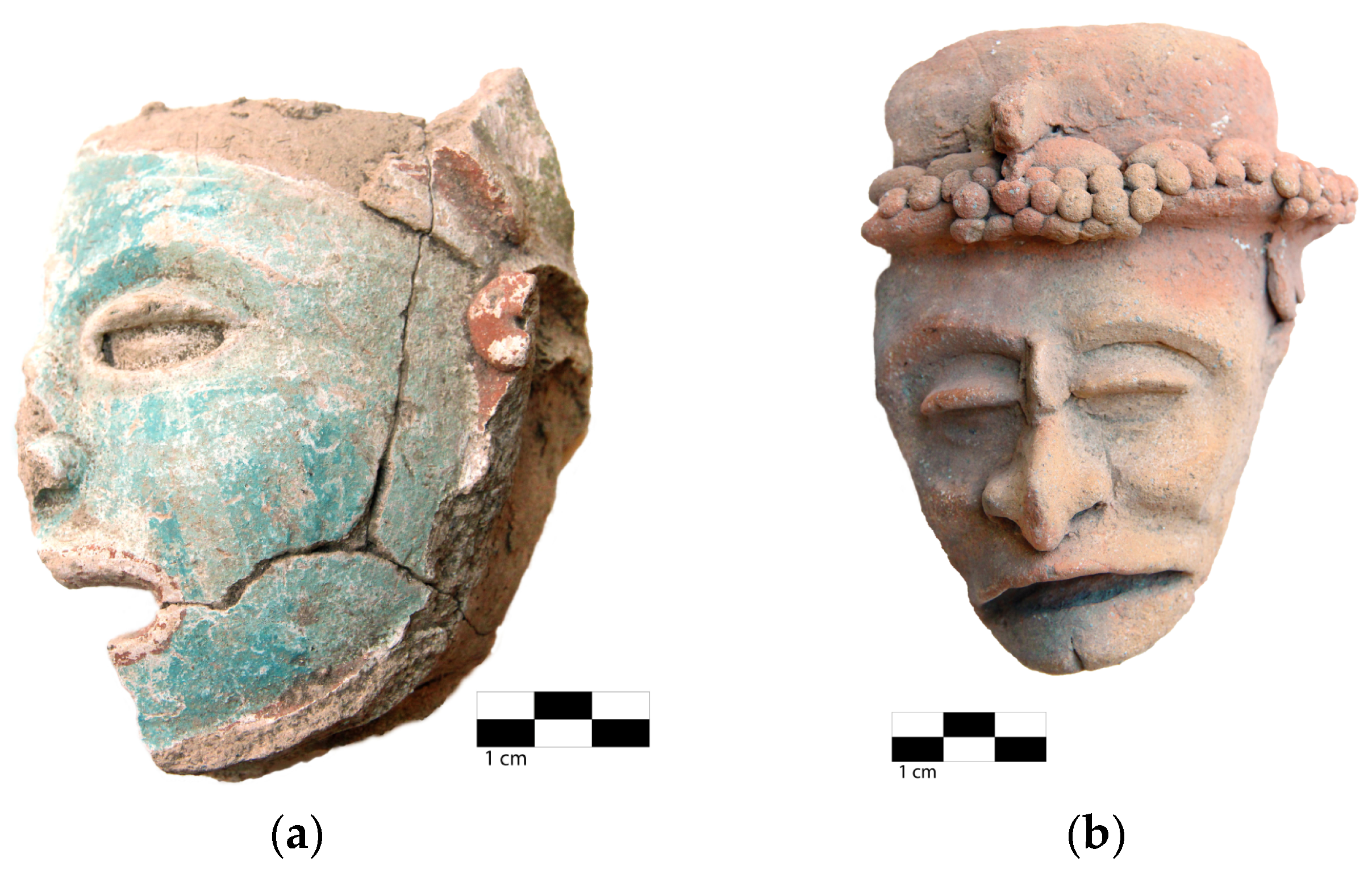
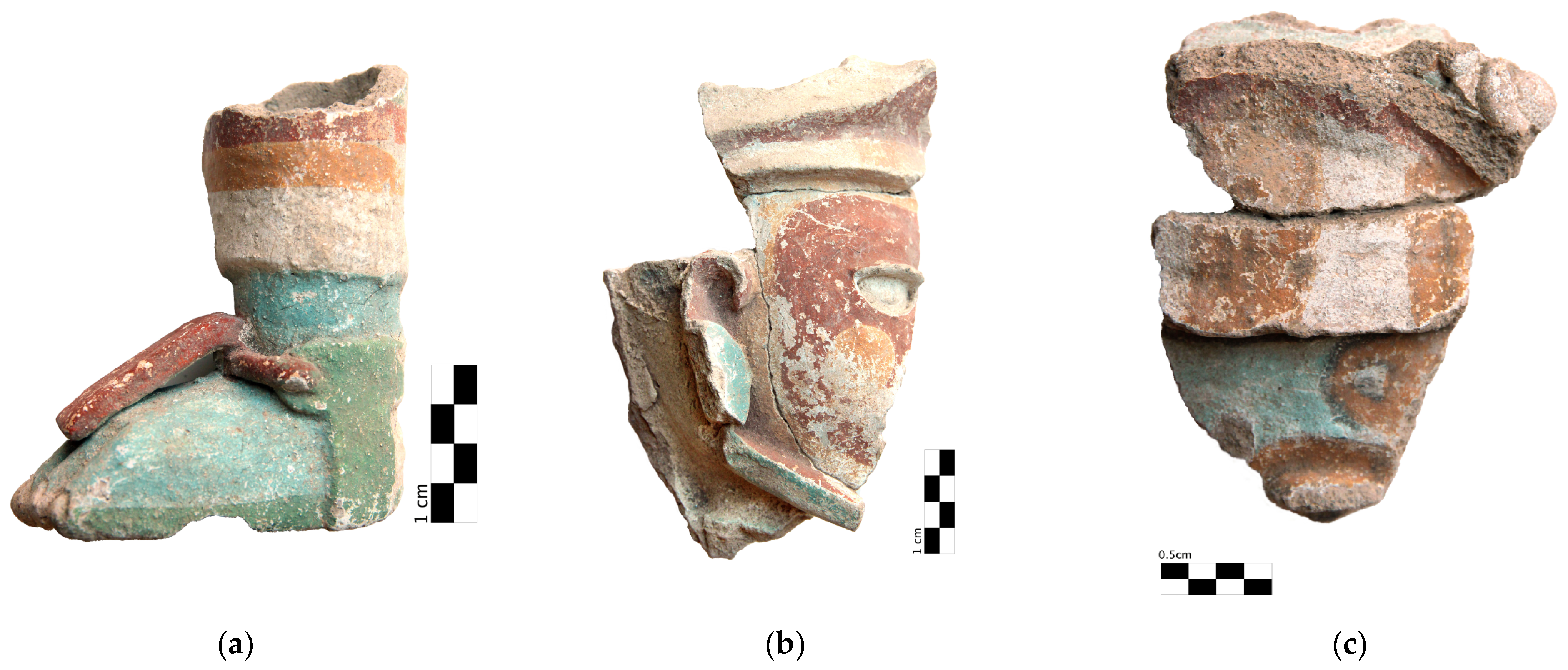
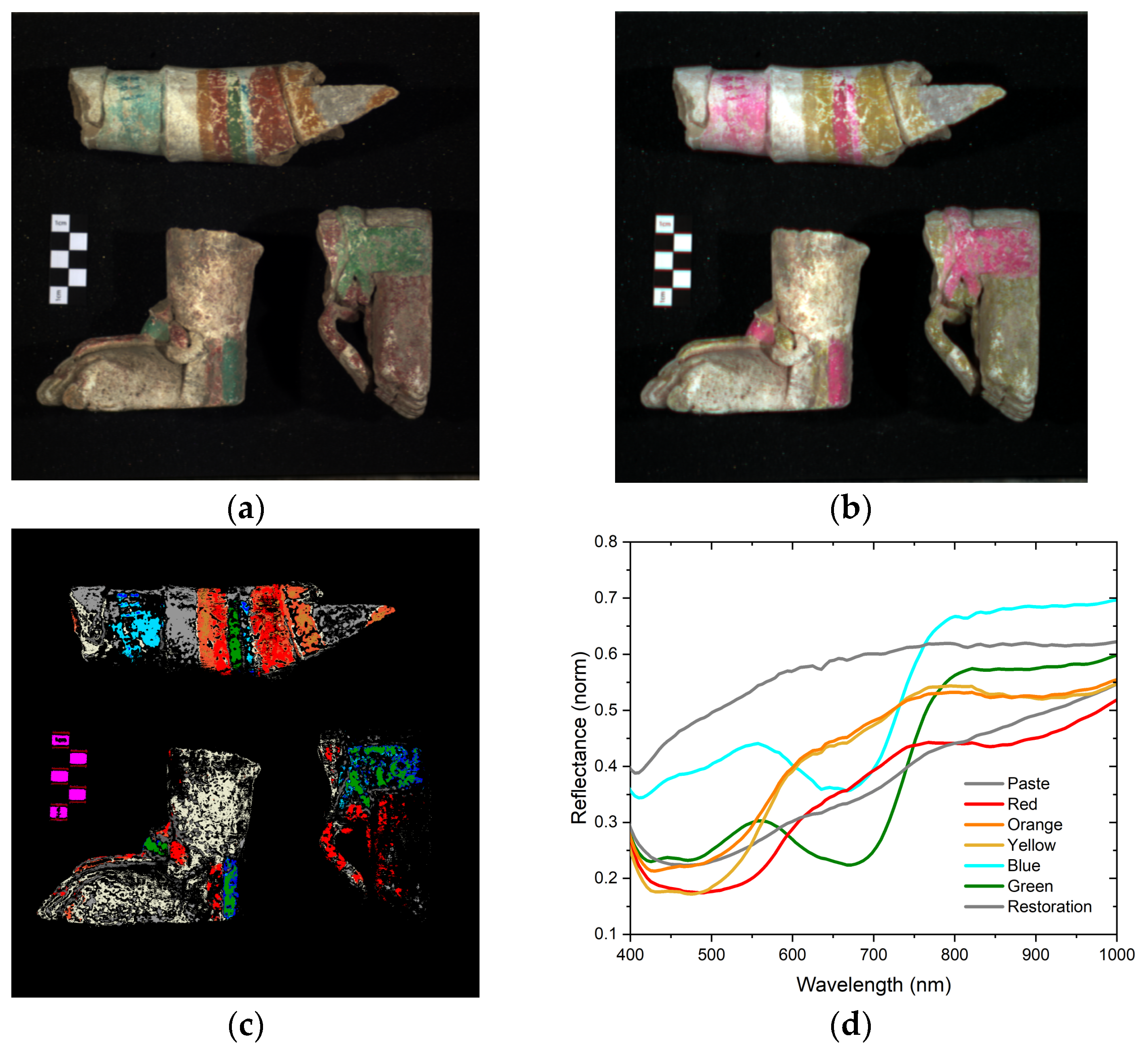
3.1. Global Properties of Objects
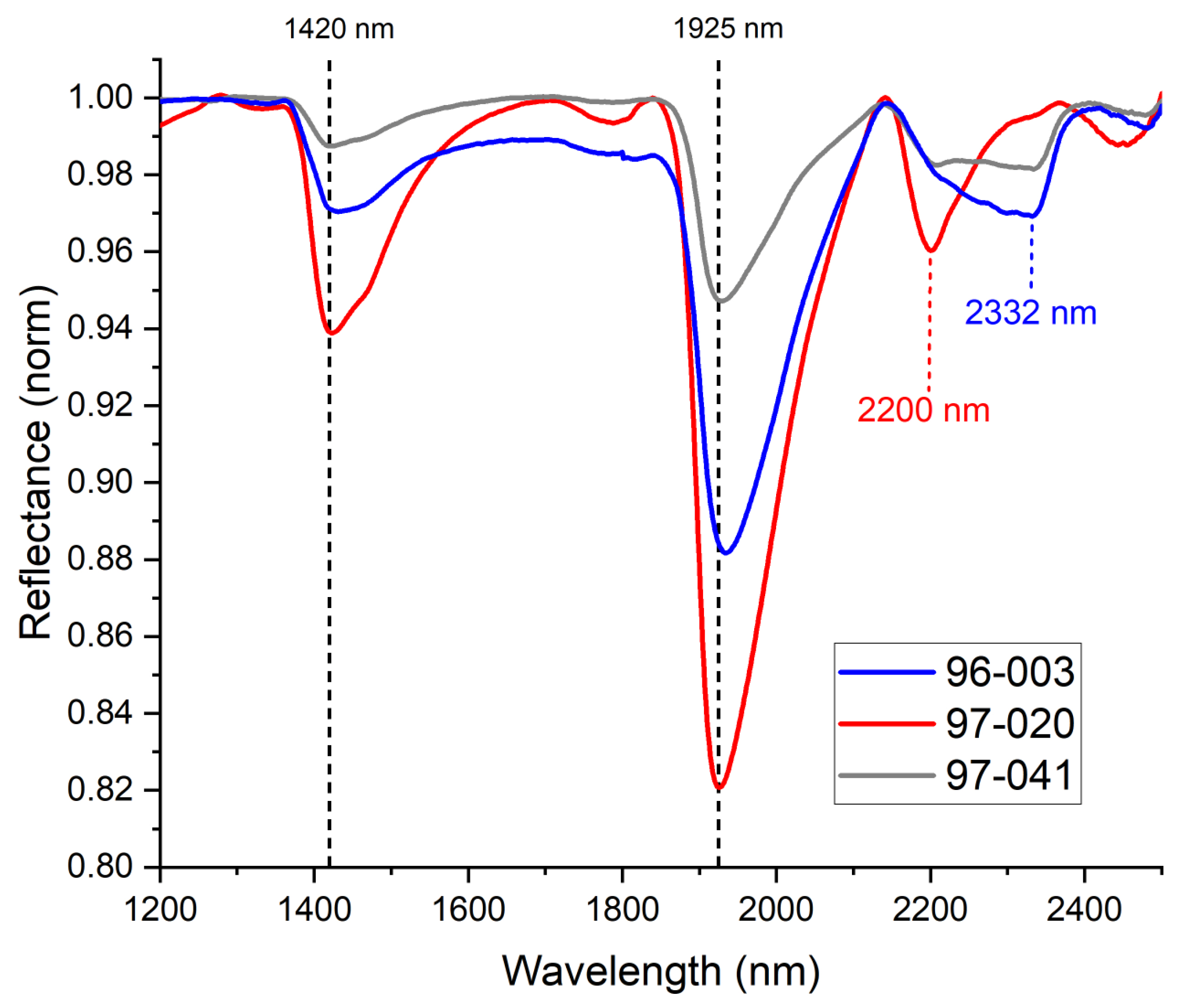
3.2. Pastes
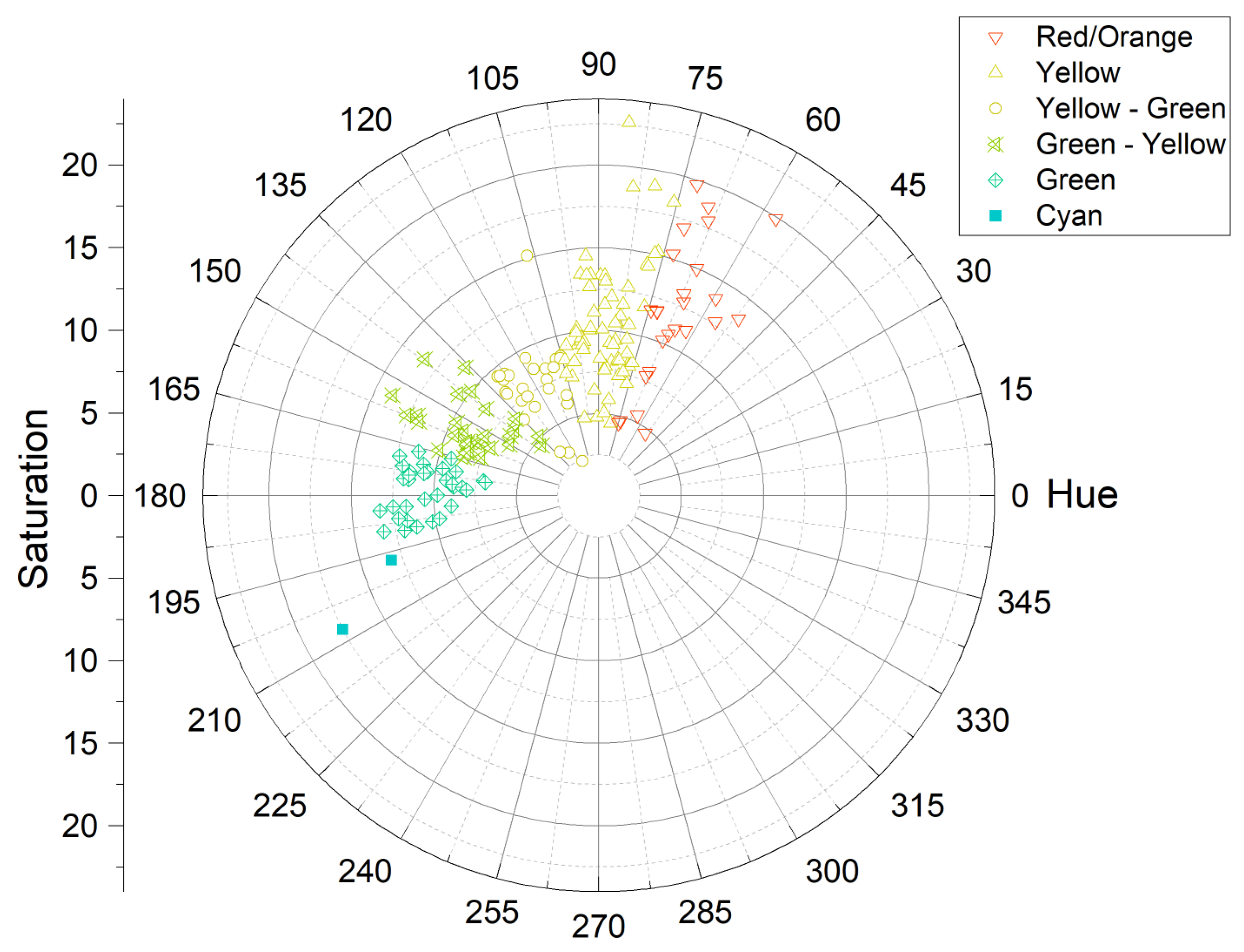
3.3. Pigments
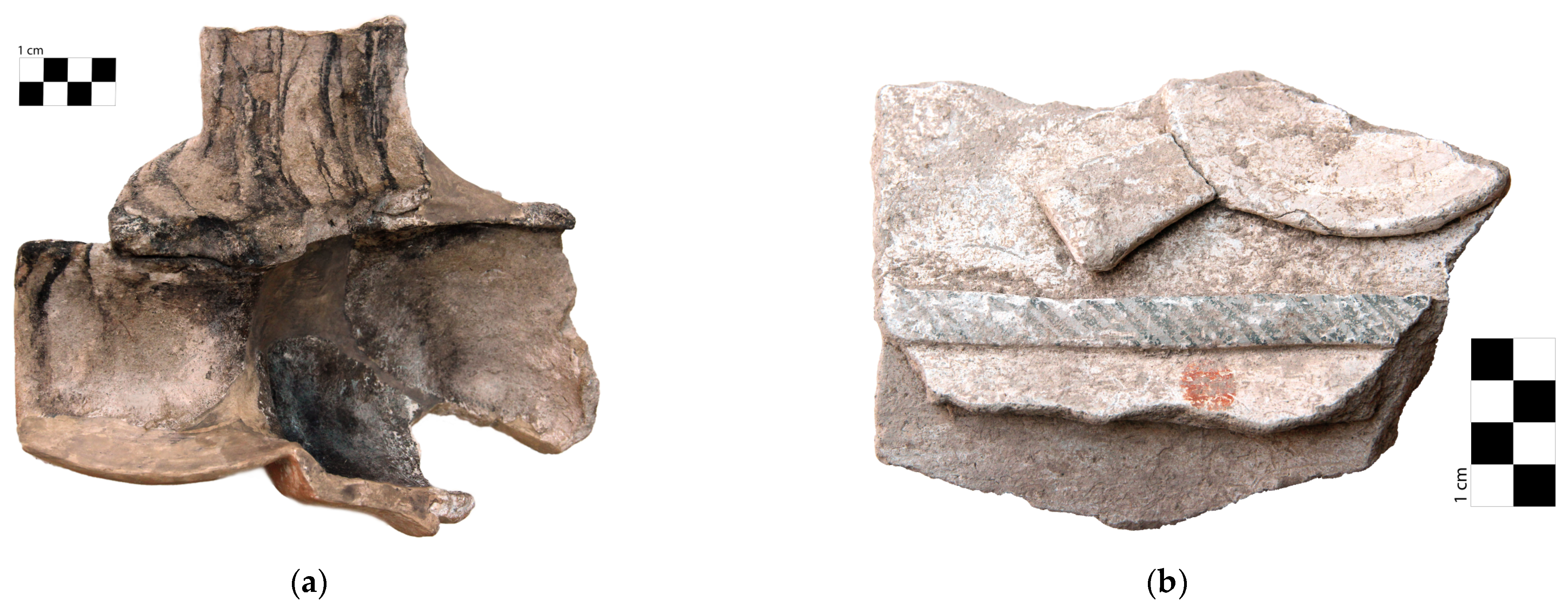
3.3.1. Black and White
3.3.2. Red, Orange, and Yellow
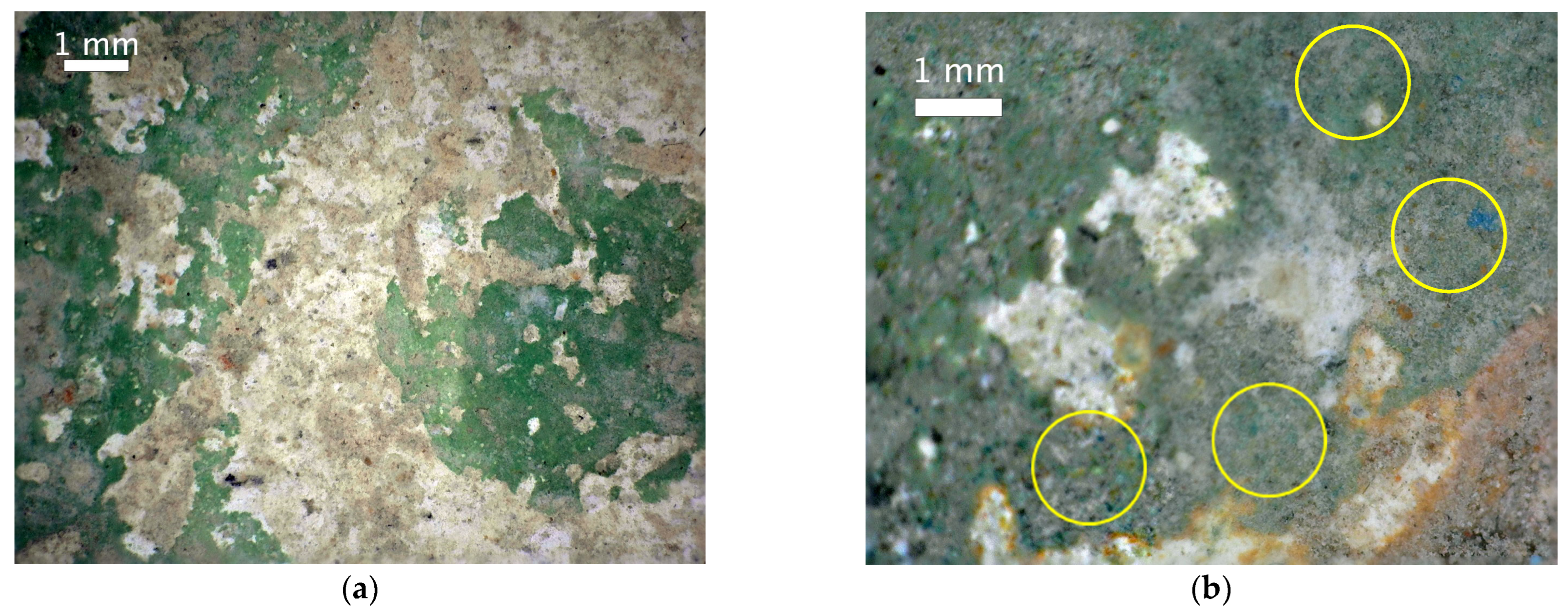
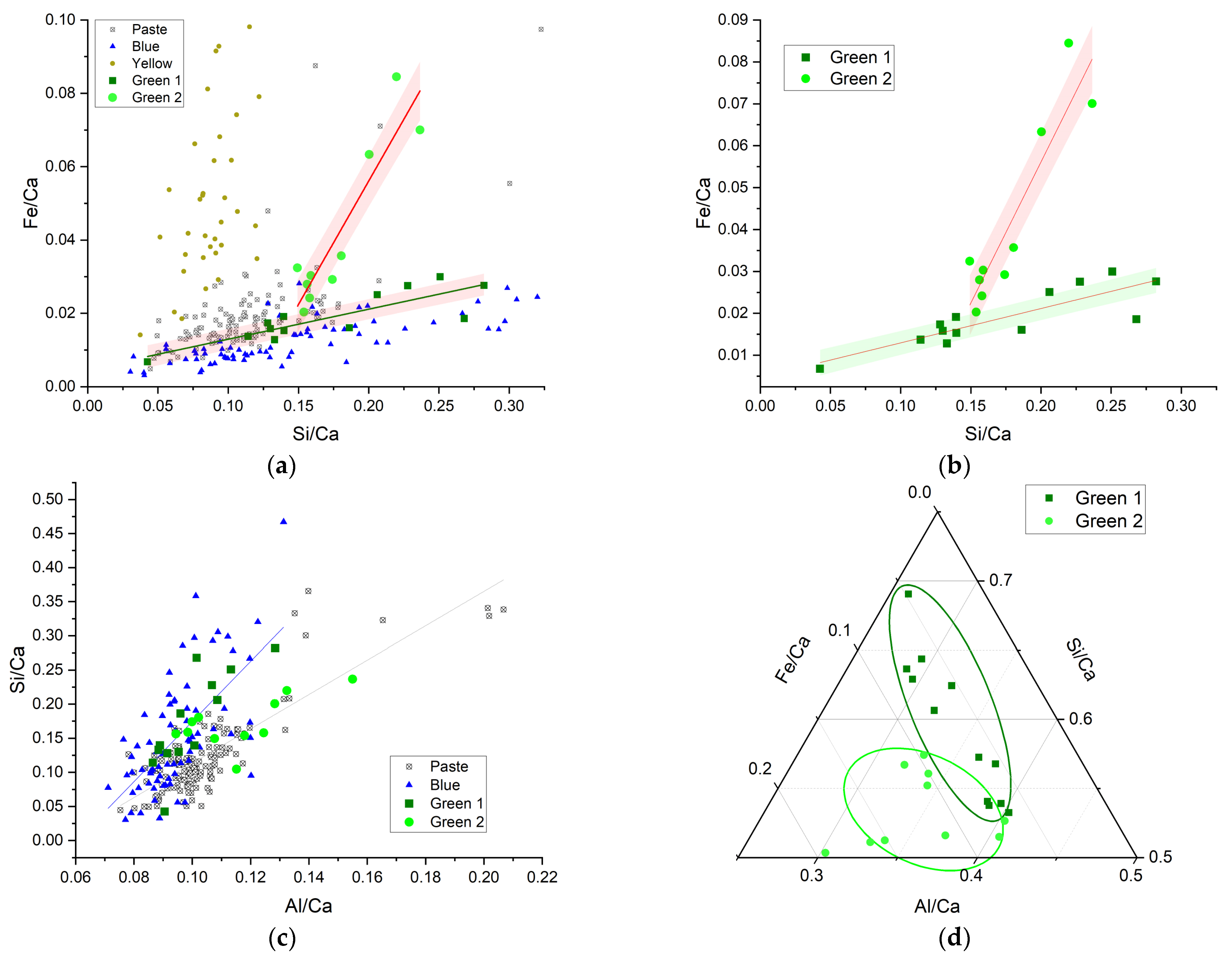
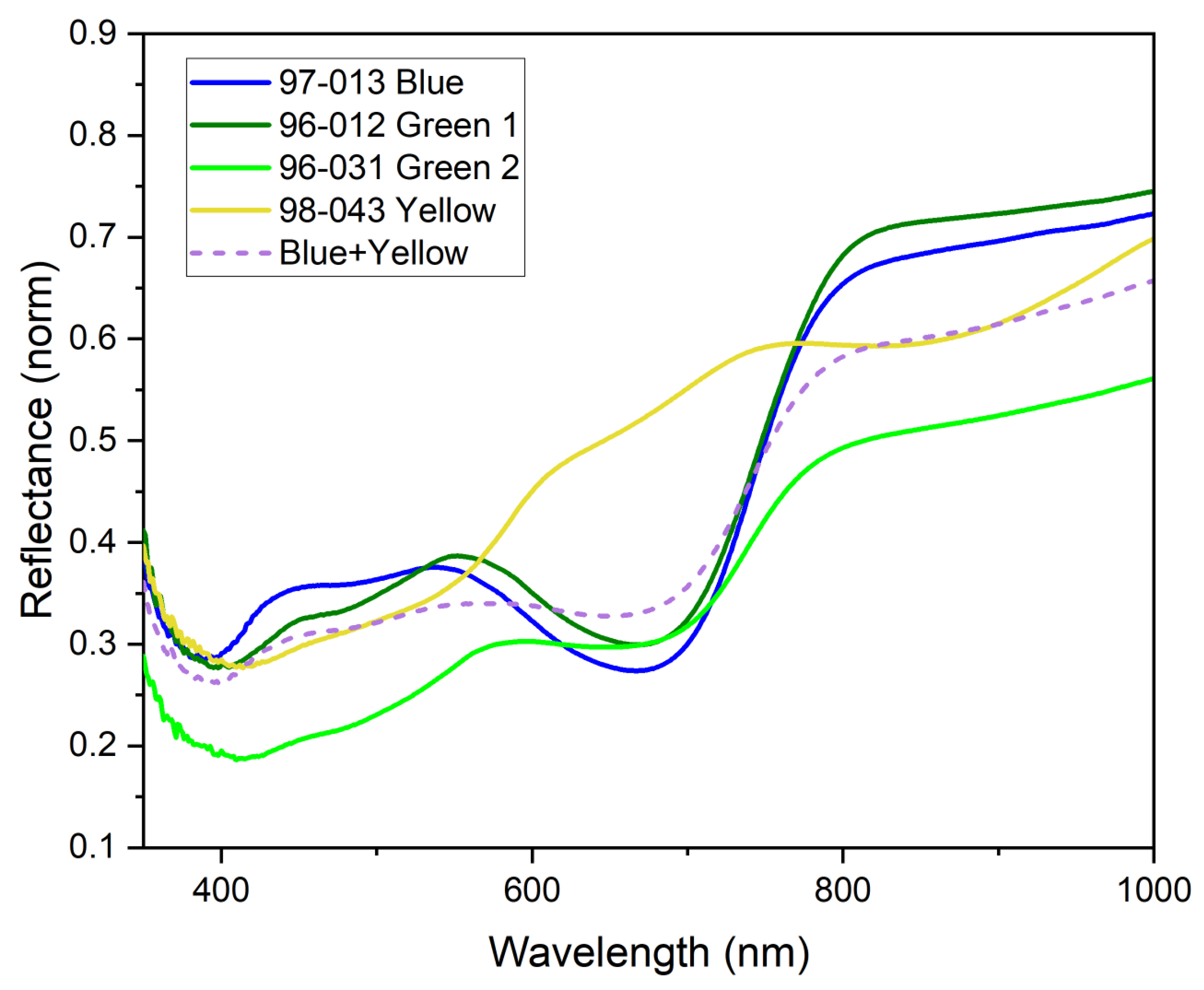
3.3.3. Blue and Green
3.3.4. Microscopy of Green Regions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pollock, H.E.D. Introduction. In Mayapan, Yucatan, Mexico; Pollock, H.E.D., Roys, R.L., Proskouriakoff, T., Ledyard, A., Eds.; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.L. Residential and Associated Structures at Mayapan. In Mayapan, Yucatan, Mexico; Pollock, H.E.D., Roys, R.L., Proskouriakoff, T., Ledyard, A., Eds.; Carnegie Institution of Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; pp. 165–320. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, B.W. Postclassic Maya Settlement on the Rural-Urban Fringe of Mayapán, Yucatán, Mexico. Doctoral Dissertation, Department of Anthropology, University at Albany, New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Haviland, W.A. The Book of Chilam Balam of Chumayel. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1967, 27, 402–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonson, M.S. The Ancient Future of the Itza. In The Book of Chilam Balam of Tizimin; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Alcalá, E.S. Códice Pérez: Traducción Libre Del Maya al Castellano; Edición de la Liga de Acción Social: Mérida Yucatán, México, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- De Landa, D. Relación de Las Cosas de Yucatán, 8th ed.; Editorial Porrúa, S. A.: México City, México, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.E. The Pottery of Mayapan Including Studies of Ceramic Material from Uxmal, Kabah, and Chichen Itza; Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Milbrath, S.; Lope, C.P. Mayapán’s Chen Mul Modeled Effigy Censers. In Ancient Maya Pottery; University Press of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 203–225. [Google Scholar]
- Milbrath, S.; Aimer, J.; Peraza Lope, C.; Florey-Folan, L. Effigy Censers of the Chen Mul Modeled Ceramic System and Their Implications for Late Postclassic Maya Interregional Interaction. Mexicon 2008, 30, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Milbrath, S. Los Incensarios Efigie de Mayapán: Iconografía, Contexto y Conexiones Externas. Famsi 2007, 2, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Peraza Lope, C.; Masson, M.A.; Cruz Alvarado, W.; Russell, B.W. Effigy Censer and Figurine Production at the Postclassic Maya City of Mayapan, Mexico. Anc. Mesoam. 2023, 34, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, M.A.; Peraza Lope, C. Kukulcan’s Realm; Universty Press of Colorado: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peraza Lope, C.; Masson, M.A.; Hare, T.S.; Cruz Alvarado, W.; Flores Coba, L. Pottery Assemblage Variation at Mayapán Residences. In Settlement, Economy and Society at Mayapan, Yucatan, Mexico; Masson, M.A., Hare, T.S., Peraza Lope, C., Rusell, B.W., Eds.; University of Pittsburg Center for Comparative Archaeology: Pittsburg, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 223–254. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, M.; Arroyo-Lemus, E.; Ruvalcaba-Sil, J.L.; Mitrani, A.; Maynez-Rojas, M.A.; de Lucio, O.G. Technical Non-Invasive Study of the Novo-Hispanic Painting the Pentecost by Baltasar de Echave Orio by Spectroscopic Techniques and Hyperspectral Imaging: In Quest for the Painter’s Hand. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 250, 119225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, M.; Cano, N.; Ruvalcaba-Sil, J.L.; Mitrani, A.; de Lucio, O.G. Technical Non-Invasive Study of an 18th Century Novo-Hispanic Panel Painting. Heritage 2021, 4, 3676–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.A.; Berman, M.; Switzer, P.; Craig, M.D. A Transformation for Ordering Multispectral Data in Terms of Image Quality with Implications for Noise Removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veganzones, M.A.; Graña, M. Endmember Extraction Methods: A Short Review. In Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, K.V.; Solankar, M.M.; Nalawade, D.B. Hyperspectral Endmember Extraction Techniques. In Processing and Analysis of Hyperspectral Data; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; Volume I, p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Foglini, F.; Grande, V.; Marchese, F.; Bracchi, V.A.; Prampolini, M.; Angeletti, L.; Castellan, G.; Chimienti, G.; Hansen, I.M.; Gudmundsen, M.; et al. Application of Hyperspectral Imaging to Underwater Habitat Mapping, Southern Adriatic Sea. Sensors 2019, 19, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Hong, H.; Zhao, L.; Kukolich, S.; Yin, K.; Wang, C. Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy for Investigating Soil Mineralogy: A Review. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 2018, 3168974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayem-Ghez, A.; Ravaud, E.; Boust, C.; Bastian, G.; Menu, M.; Brodie-Linder, N. Characterizing Pigments with Hyperspectral Imaging Variable False-Color Composites. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2015, 121, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvalcaba Sil, J.L.; Ramírez Miranda, D.; Aguilar Melo, V.; Picazo, F. SANDRA: A Portable XRF System for the Study of Mexican Cultural Heritage. X-ray Spectrom. 2010, 39, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, V.A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.; Walter, P.; Susini, J. A Multiplatform Code for the Analysis of Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectra. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báscones, A.; Suárez, M.; Ferrer-Julià, M.; García-Meléndez, E.; Colmenero-Hidalgo, E.; Quirós, A. Characterization of Clay Minerals and Fe Oxides through Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (VNIR-SWIR). Rev. Teledetección 2020, 2020, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L. Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy Laboratory Spectra of Geologic Materials. In Remote Compositional Analysis: Techniques for Understanding Spectroscopy, Mineralogy, and Geochemistry of Planetary Surfaces; Bishop, J.L., Bell, J.F., III, Moersch, J.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 68–101. ISBN 9781316888872. [Google Scholar]
- ASD Inc. TerraSpec Starter Pack: Practical Applications Guide to Using the TerraSpec in Exploration and Mining; AusSpec International Ltd.: Queenstown, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, G.T.; Amdt, R.E. Mineral Resources Data System (MRDS): USGS Data Series 20; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, J.; Barrón, V. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy of Iron Oxides. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 1438–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Leona, M.; Casadio, F.; Bacci, M.; Picollo, M. Identification of the Pre-Columbian Pigment Maya Blue on Works of Art by Noninvasive UV-Vis and Raman Spectroscopic Techniques. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 2004, 43, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazia, C.; Buti, D.; Amat, A.; Rosi, F.; Romani, A.; Domenici, D.; Sgamellotti, A.; Miliani, C. Shades of Blue: Non-Invasive Spectroscopic Investigations of Maya Blue Pigments. From Laboratory Mock-Ups to Mesoamerican Codices. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejoie, C.; Dooryhee, E.; Martinetto, P.; Blanc, S.; Bordat, P.; Brown, R.; Porcher, F.; Del Rio, M.S.; Strobel, P.; Anne, M.; et al. Revisiting Maya Blue and Designing Hybrid Pigments by Archaeomimetism. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1007.0818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, M.; Agostino, A.; Fenoglio, G.; Idone, A.; Gulmini, M.; Picollo, M.; Ricciardi, P.; Delaney, J.K. Characterisation of Colourants on Illuminated Manuscripts by Portable Fibre Optic UV-Visible-NIR Reflectance Spectrophotometry. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




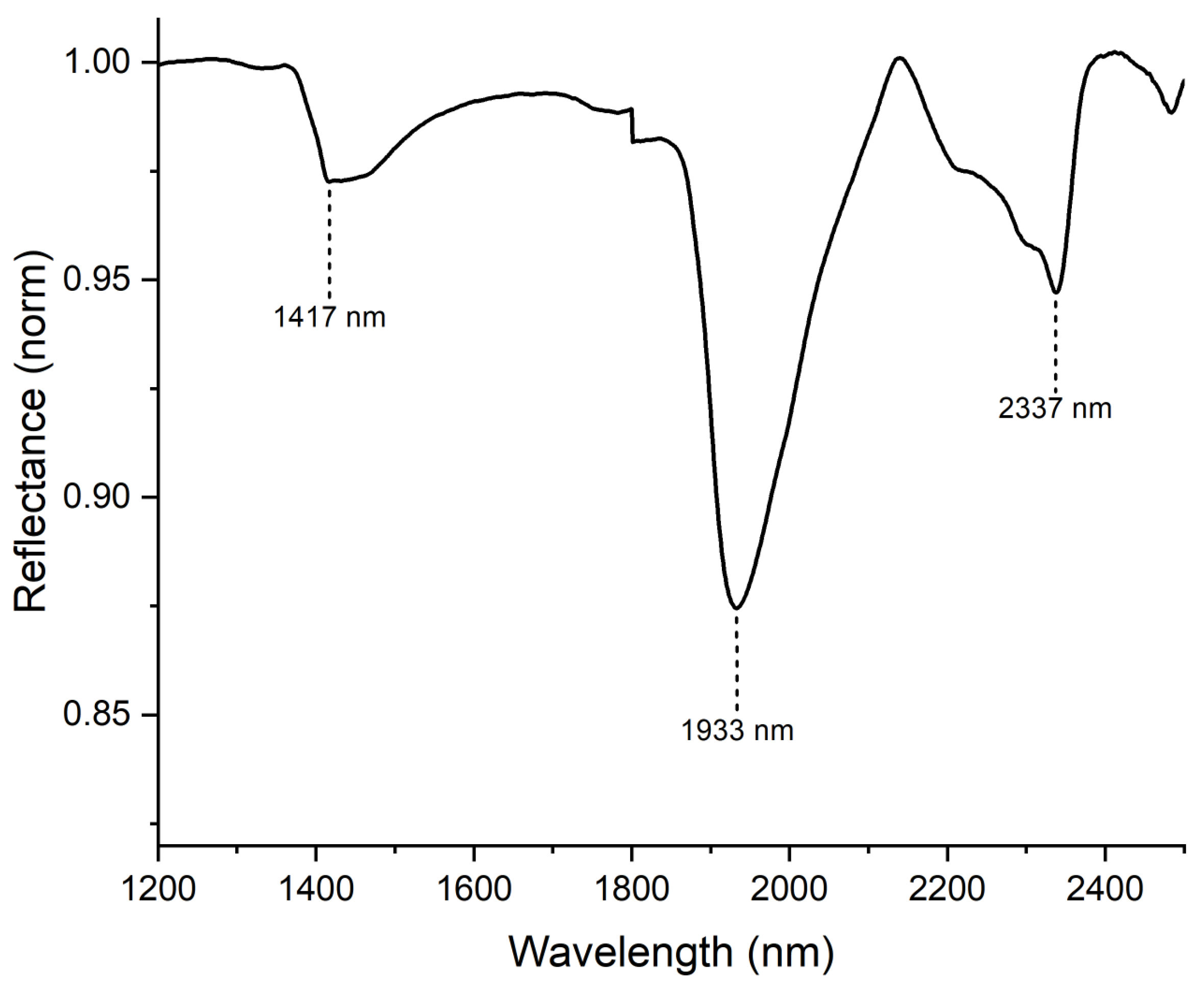

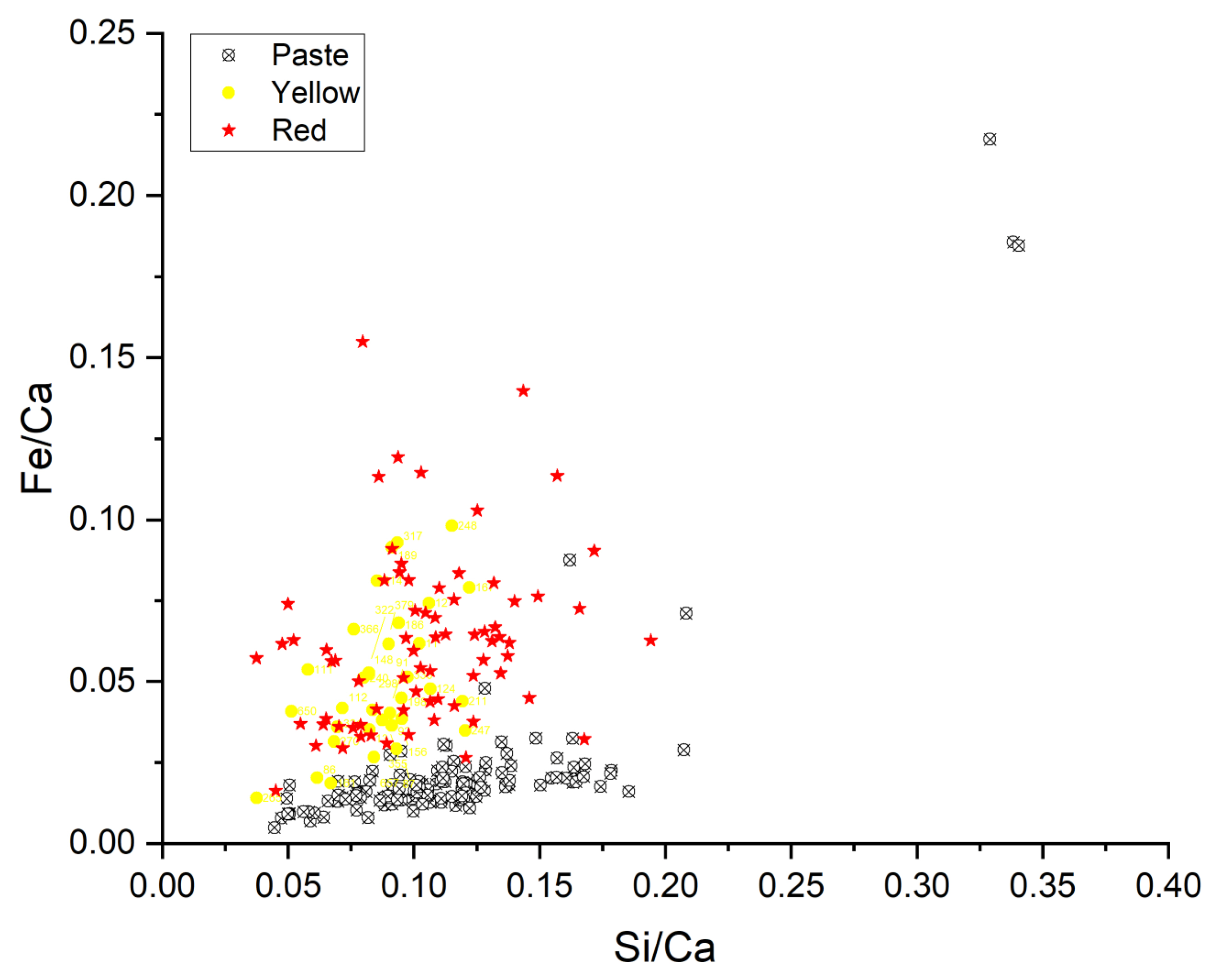
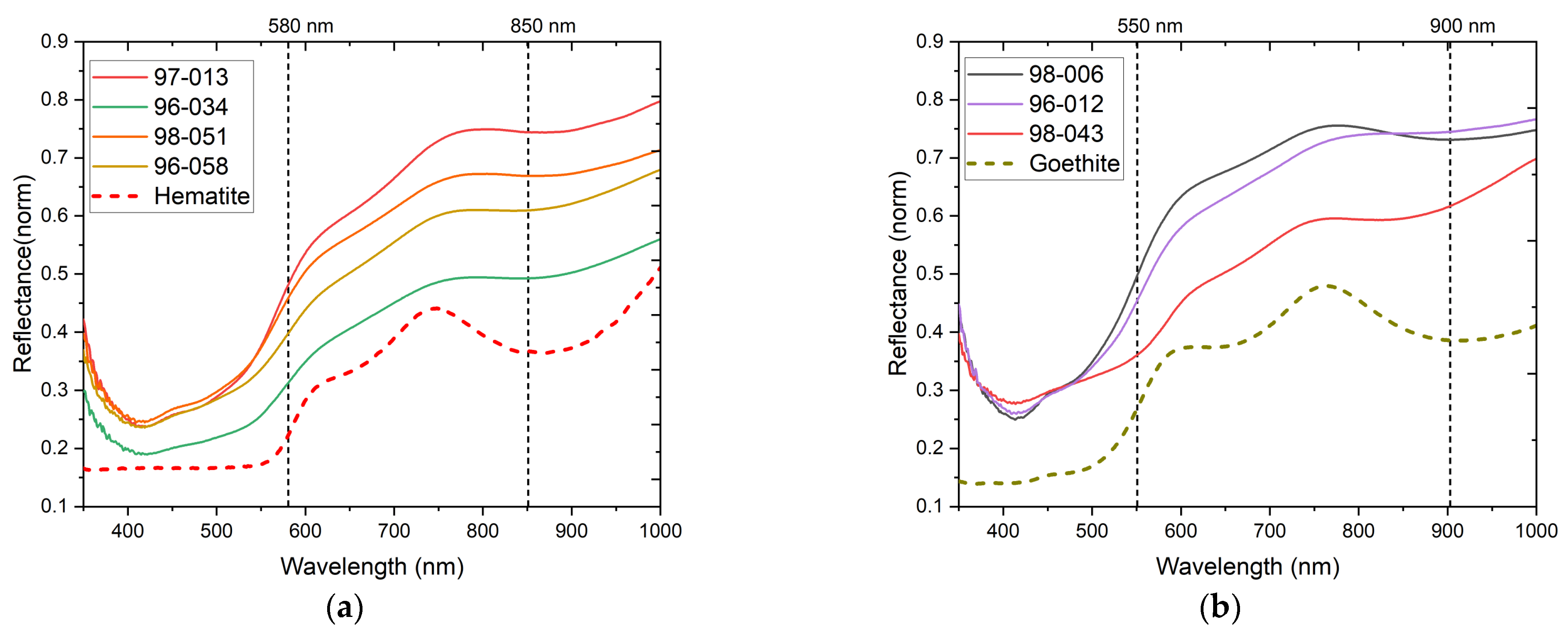
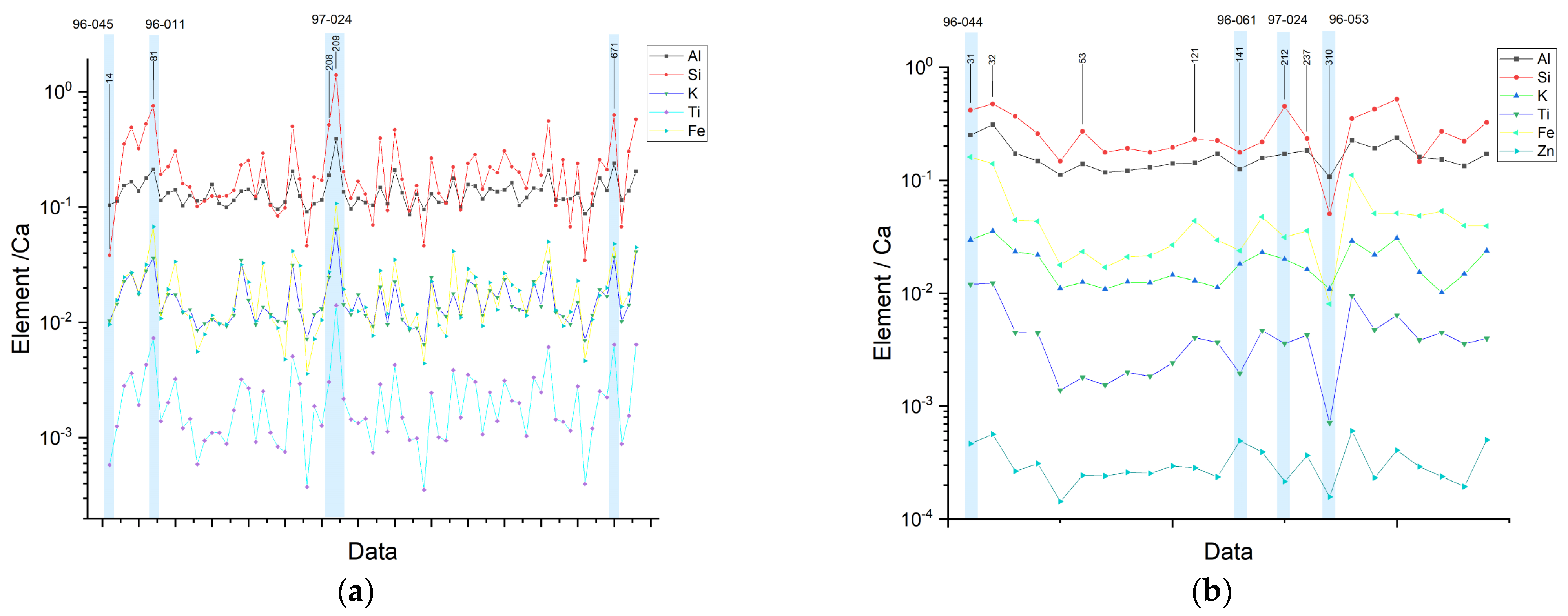

| Related Material | Chemical Composition | XRF | FORS | HSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite | CaCO3 | Ca | SWIR 2337 nm | |
| Soil minerals | Fe, Ti, Al | |||
| Aluminosilicate | Al2O5Si | Si, Al | SWIR 2200 nm–2332 nm | |
| Hematite | α-Fe2O3 | Fe | Vis 850 nm | Yes |
| Goethite | α-FeOOH | Fe | Vis 900 nm | Yes |
| Maya blue | Si, Al | Vis-SWIR 2221 nm, 2253 nm | Yes | |
| Green 1 | Si, Al | Vis-SWIR 659 nm, 2253 nm | Yes | |
| Green 2 | Si, Al, Fe | Vis-SWIR 647 nm, 2253 nm | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez, M.; de Lucio, O.G.; Mitrani, A.; Peraza Lope, C.; Cruz Alvarado, W.; Ortiz Ruiz, S. Material Characterization of Mayapán’s Effigy Censers’ Sherds. Minerals 2023, 13, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070974
Pérez M, de Lucio OG, Mitrani A, Peraza Lope C, Cruz Alvarado W, Ortiz Ruiz S. Material Characterization of Mayapán’s Effigy Censers’ Sherds. Minerals. 2023; 13(7):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070974
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez, Miguel, Oscar G. de Lucio, Alejandro Mitrani, Carlos Peraza Lope, Wilberth Cruz Alvarado, and Soledad Ortiz Ruiz. 2023. "Material Characterization of Mayapán’s Effigy Censers’ Sherds" Minerals 13, no. 7: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070974
APA StylePérez, M., de Lucio, O. G., Mitrani, A., Peraza Lope, C., Cruz Alvarado, W., & Ortiz Ruiz, S. (2023). Material Characterization of Mayapán’s Effigy Censers’ Sherds. Minerals, 13(7), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13070974









