Contraints on Petrogenesis and Fe Fertility of Intrusive Complexes in the Han–Xing Region, North China Craton from Apatite Geochemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
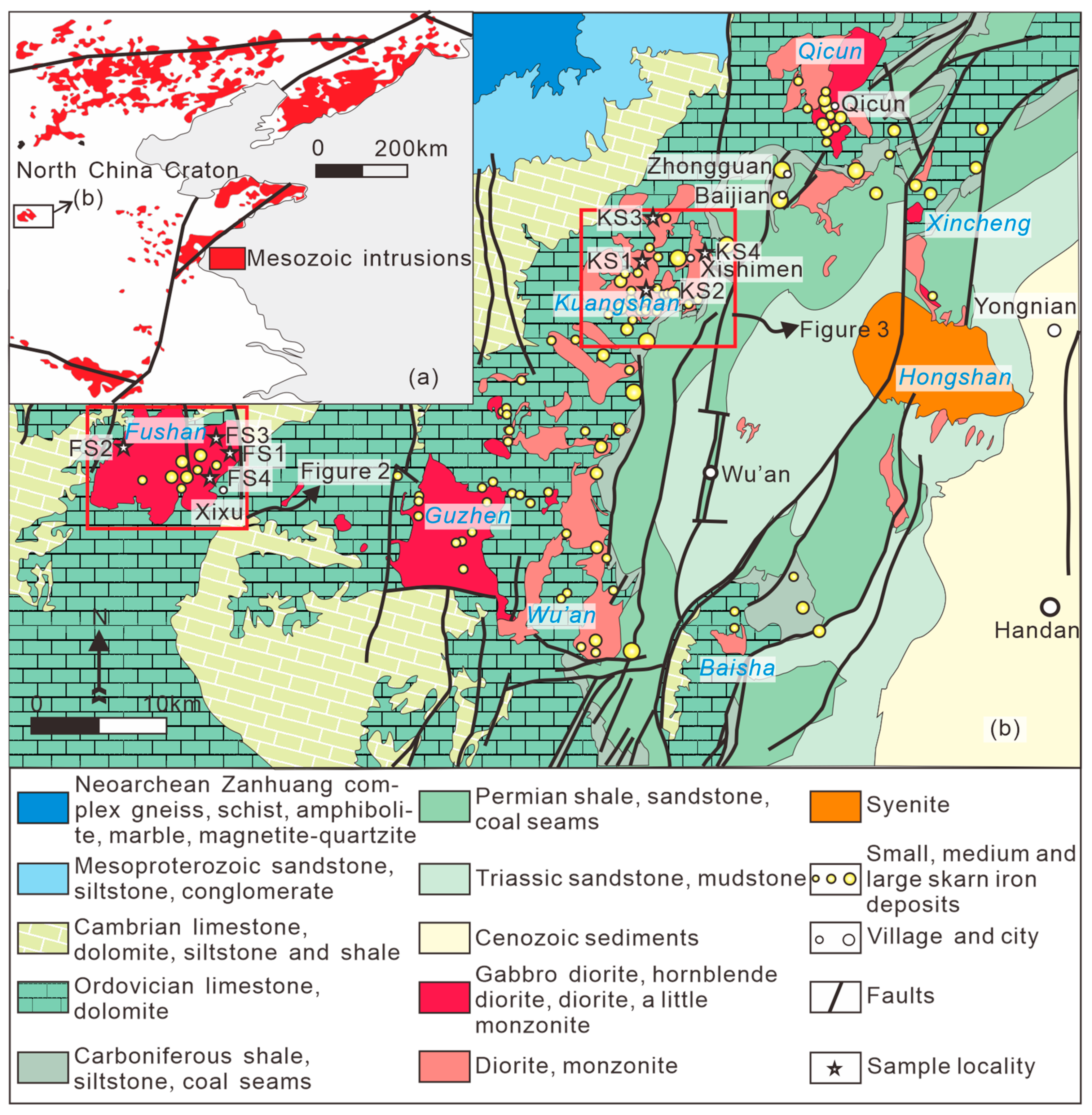
2. Geological Setting
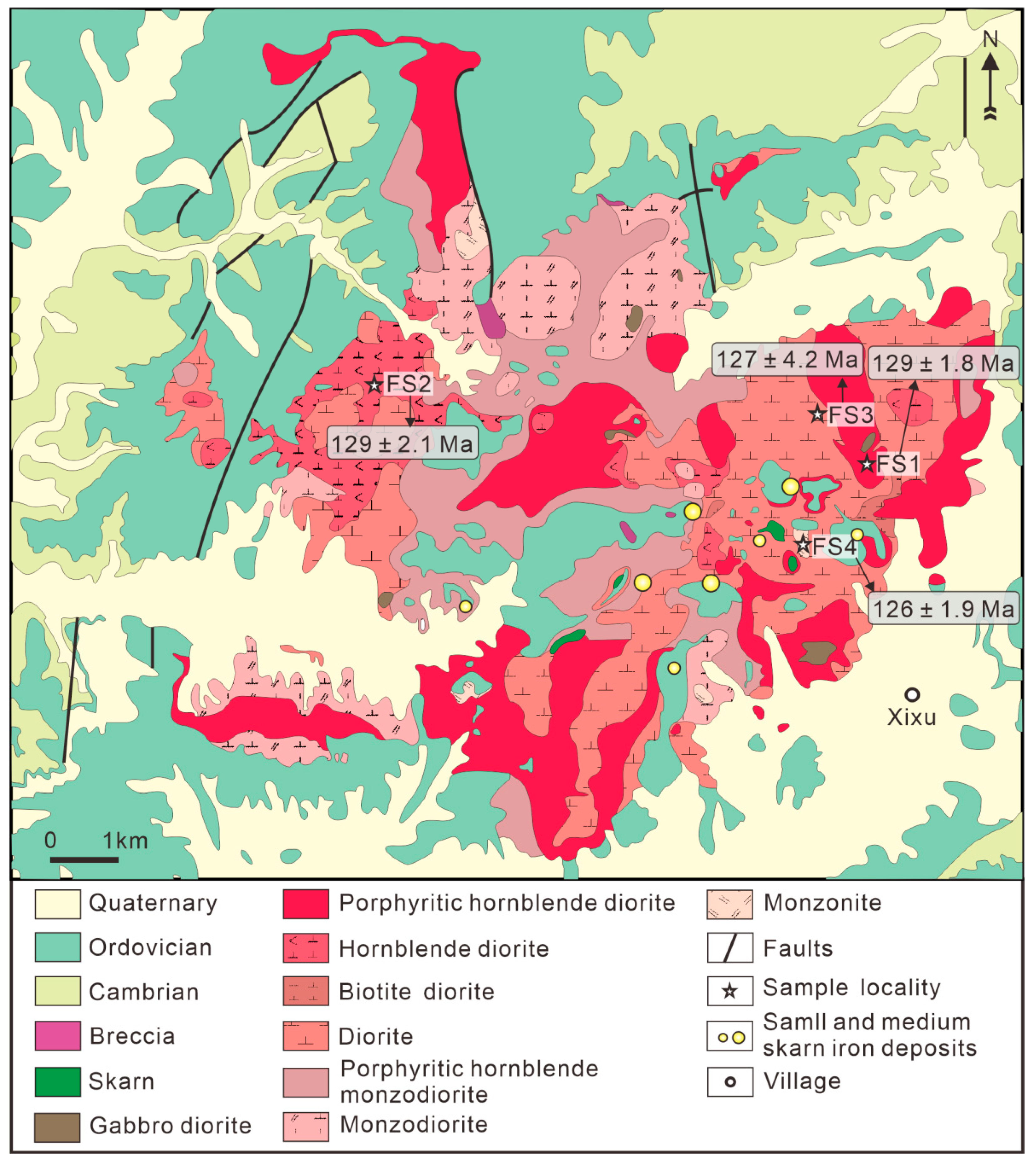
2.1. Geology of the Fushan Complex and Related Fe Deposits
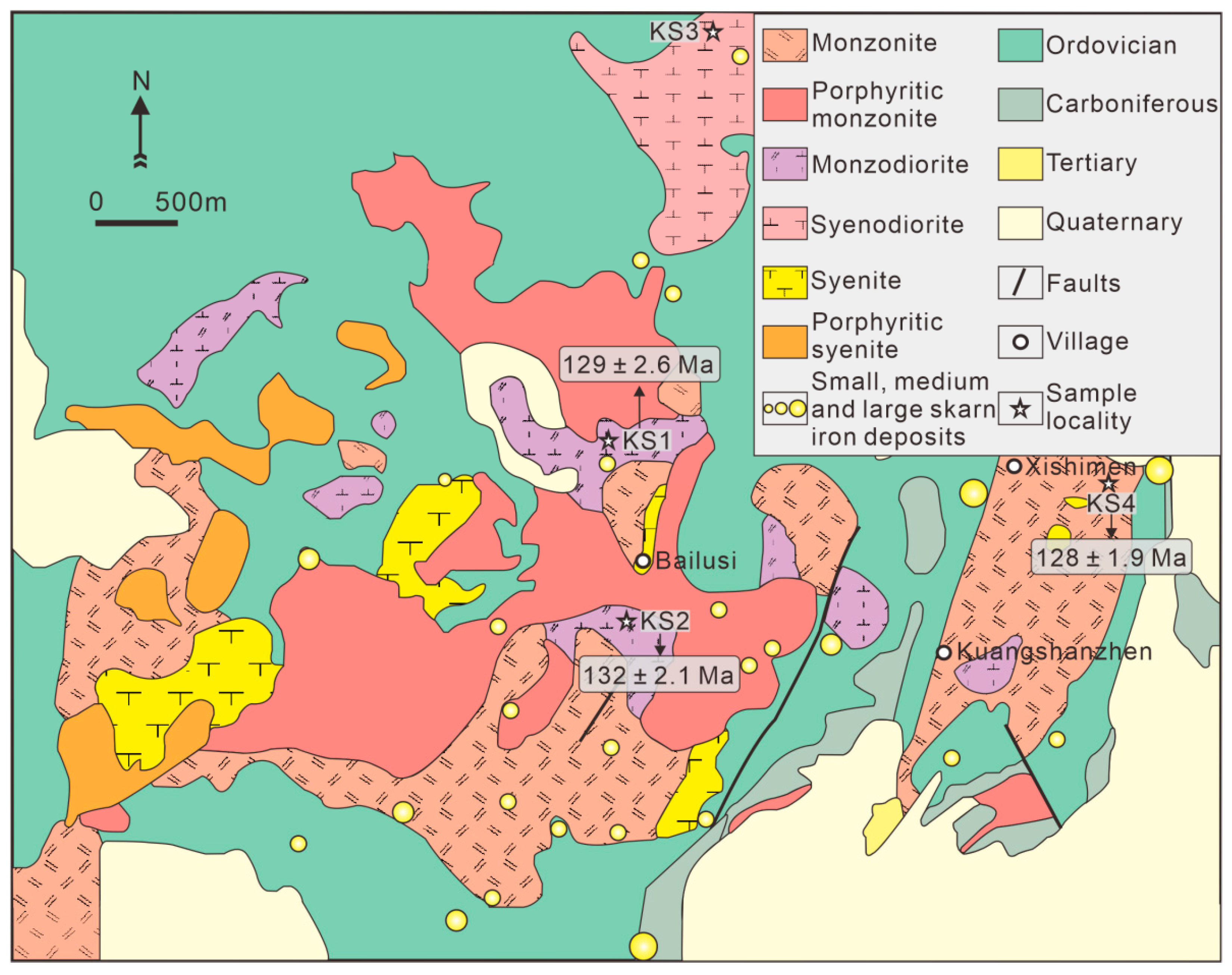
2.2. Geology of the Kuangshan Complex and Related Fe Deposits
3. Sampling and Analytical Methods
3.1. Sample Descriptions
3.2. Analytical Methods
4. Results
4.1. Major Elements of Apatite
4.2. Trace Elements of Apatite
5. Discussion
5.1. Magmatic Evolution Recorded by Apatite
5.2. Indication of Oxygen Fugacity of Apatite
5.3. Evolution Process of Magmatic Volatiles Reflected by Apatite
5.4. Contrast of the Iron-Bearing Complex and the Barren Complex
5.5. Preliminary Study on Favorable Ore-Forming Lithology of Skarn Iron Deposit Boarding Complex
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouzari, F.; Hart, C.J.R.; Bissig, T.; Barker, S. Hydrothermal Alteration Revealed by Apatite Luminescence and Chemistry: A Potential Indicator Mineral for Exploring Covered Porphyry Copper Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Rukhlov, A.S.; Rowins, S.M.; Spence, J.; Coogan, L.A. Apatite trace element compositions: A robust new tool for mineral exploration*. Econ. Geol. 2016, 111, 1187–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parat, F.; Holtz, F.; Klügel, A. S-rich apatite-hosted glass inclusions in xenoliths from La Palma: Constraints on the volatile partitioning in evolved alkaline magmas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2011, 162, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hermann, J. Chlorine and fluorine partitioning between apatite and sediment melt at 2.5 GPa, 800 °C: A new experimentally derived thermodynamic model. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Luhr, J.F.; Mcgee, J.J. Factors controlling sulfur concentrations in volcanic apatite. Am. Mineral. 1997, 82, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.D.; Piccoli, P.M. Magmatic Apatite: A Powerful, Yet Deceptive, Mineral. Elements 2015, 11, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, C.L.; Loader, M.A.; Wilkinson, J.J.; Buret, Y.; Sievwright, R.H.; Hollings, P. Multi-stage arc magma evolution recorded by apatite in volcanic rocks. Geology 2020, 48, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wen, G.; Li, J.; Jiang, S.; Hu, H.; Deng, X.; Zhao, X.; Yan, D.; Wei, K.; Cai, H.; et al. Apatite chemistry as a petrogenetic–metallogenic indicator for skarn ore-related granitoids: An example from the Daye Fe–Cu–(Au–Mo–W) district, Eastern China. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2022, 177, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhu, J.; Bi, X.; Xu, L.; Xu, Y. Low magmatic Cl contents in giant porphyry Cu deposits caused by early fluid exsolution: A case study of the Yulong belt and implication for exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Jiang, S. Using apatite to discriminate synchronous ore-associated and barren granitoid rocks: A case study from the Edong metallogenic district, South China. Lithos 2018, 310–311, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Jiang, S.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, J. Chlorine and sulfur evolution in magmatic rocks: A record from amphibole and apatite in the Tonglvshan Cu-Fe (Au) skarn deposit in Hubei Province, south China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 137, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, F.; Hao, J. Apatite and zircon compositions for Miocene mineralizing and barren intrusions in the Gangdese porphyry copper belt of southern Tibet: Implication for ore control. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, J.; Bi, X.; Fu, S.; Lu, Z.; Wu, L.; Hu, R. Increasing sulfur and chlorine contents in ore-forming magmas: The key to Pulang porphyry Cu-Au formation, SW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hou, Z.; Griffin, W.L.; Lu, Y.; Belousova, E.; Xu, J.; O’Reilly, S.Y. Recycled volatiles determine fertility of porphyry deposits in collisional settings. Am. Mineral. 2021, 106, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Richards, J.P.; Rees, C.; Creaser, R.; Dufrane, S.A.; Locock, A.; Petrus, J.A.; Lang, J. Elevated Magmatic Sulfur and Chlorine Contents in Ore-Forming Magmas at the Red Chris Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit, Northern British Columbia, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 1047–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Avila, L.A.; Hammerli, J.; Kemp, A.I.S.; Rohrlach, B.; Loucks, R.; Lu, Y.; Williams, I.S.; Martin, L.; Roberts, M.P.; Fiorentini, M.L. The long-lived fertility signature of Cu–Au porphyry systems: Insights from apatite and zircon at Tampakan, Philippines. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2022, 177, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhou, T. Apatite geochemistry as an indicator of petrogenesis and uranium fertility of granites: A case study from the Zhuguangshan batholith, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 128, 103886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Li, G.; Qin, K.; Seitmuratova, E.Y.; Liu, Y. Major and Trace Element Characteristics of Apatites in Granitoids from Central Kazakhstan: Implications for Petrogenesis and Mineralization. Resour. Geol. 2012, 62, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, A.; Listanco, E.L.; Fujii, T. Petrologic and sulfur isotopic significance of highly oxidized and sulfur-rich magma of Mt. Pinatubo, Philippines. Geology 1993, 21, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, M.; Su, S.; Chen, X. Contrasting Geochemistry of Apatite from Peridotites and Sulfide Ores of the Jinchuan Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposit, NW China. Econ. Geol. 2021, 116, 1073–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Graham, C.M.; Hawkesworth, C.J.; Gillespie, M.R.; Hinton, R.W.; Bromiley, G.D. Apatite: A new redox proxy for silicic magmas? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 132, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Hu, R.; Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, C. Apatite trace element and halogen compositions as petrogenetic-metallogenic indicators: Examples from four granite plutons in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Lithos 2016, 254–255, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parat, F.; Holtz, F. Sulfur partitioning between apatite and melt and effect of sulfur on apatite solubility at oxidizing conditions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2004, 147, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Yang, X.; Lu, S.; Lee, I.; Kim, Y. Petrogenetic and metallogenic implications of the Late Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Xuancheng ore district, eastern China: Insight from in situ analysis of apatite. Geosci. J. 2022, 26, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Shu, Q.; Lentz, D.R.; Wang, F. Zircon and apatite geochemical constraints on the formation of the Huojihe porphyry Mo deposit in the Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China. Am. Mineral. 2020, 105, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; He, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, X. Melt volatile budgets and magma evolution revealed by diverse apatite halogen and trace elements compositions: A case study at Pulang porphyry Cu-Au deposit, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 139, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Yang, Z.; Hou, Z.; White, N.C.; Yu, C. Contrasting porphyry Cu fertilities in the Yidun arc, eastern Tibet: Insights from zircon and apatite compositions and implications for exploration. Seg. Spec. Publ. 2021, 24, 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Luo, C.; Xia, W.; He, W.; Liu, B.; Huang, M.; Hou, Z.; Zhu, D. Role of alkaline magmatism in formation of porphyry deposits in nonarc settings: Gangdese and Sanjiang metallogenic belts. Seg. Spec. Publ. 2021, 24, 205–229. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Yang, Z.; White, N.C.; Hou, Z. Generation of the Giant Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit by Repeated Recharge of Mafic Magmas at Pulang in Eastern Tibet. Econ. Geol. 2022, 117, 57–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Santosh, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Yin, N.; Dong, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, G.; Yu, H. The Beiminghe skarn iron deposit, eastern China: Geochronology, isotope geochemistry and implications for the destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos 2013, 156–159, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, J.; Wen, G. U-Pb Geochronology of Hydrothermal Zircons from the Early Cretaceous Iron Skarn Deposits in the Handan-Xingtai District, North China Craton. Econ. Geol. 2015, 110, 2159–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhan, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhu, D.; Huang, W.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Y. Petrogenesis of the Kuangshancun and Hongshan intrusive complexes from the Handan–Xingtai district: Implications for iron mineralization associated with Mesozoic magmatism in the North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 1162–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; Santosh, M.; Han, L. Genetic relationship of high-Mg dioritic pluton to iron mineralization: A case study from the Jinling skarn-type iron deposit in the North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Mineral chemistry of high-Mg diorites and skarn in the Han–Xing Iron deposits of South Taihang Mountains, China: Constraints on mineralization process. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, T.; Xiao, L.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Y. U-Pb ages, Hf-O isotopes and trace elements of zircons from the ore-bearing and ore-barren adakitic rocks in the Handan-Xingtai district: Implications for petrogenesis and iron mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 104, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, T.; Xiao, L.; Bai, M.; Zhang, Y. Contrasting mineralogical-geochemical compositions of ore-bearing and ore-barren intrusive complexes in the Handan-Xingtai district, North China Craton: Implications for the iron mineralization. Lithos 2019, 350–351, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; Santosh, M.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Wang, D.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Tracing the genesis of skarn-type iron deposit in central North China Craton: Insights from mineral zoning textures in ore-forming intrusion. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 6280–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Li, J.; Hofstra, A.H.; Koenig, A.E.; Cui, B. Textures and compositions of clinopyroxene in an Fe skarn with implications for ore-fluid evolution and mineral-fluid REE partitioning. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 290, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S. World skarn deposits. In One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Hedenquist, J.W., Thompson, J.F.H., Goldfarb, R.J., Richards, J.P., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Xishimen Skarn Iron Deposit in Handan. Master’s Thesis, Shijiazhuang University of Economics, Shijiazhuang, China, 2011. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qi, T. The Large-Scale Metallogentic Process of Iron in the Cihai Giant Iron District, Xinjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H. Mineralogical, Geochemical, and Geochornological Constrains on the Genesis of Iron Deposits in the Daye District, Eastern China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2014. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C. Skarn mineral characteristics and zonation of the Makeng Fe-Mo deposit in Fujian Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1339–1354, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W. Characteristics and Origin of Magnetite in Fushan Iron Deposit, Shexian Country, Hebei Province. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabi, B.; Ghasemi Siani, M.; Zhang, R.; Neubauer, F.; Lentz, D.R.; Fazel, E.T.; Shahraki, B.K. Mineralogy, petrochronology, geochemistry, and fluid inclusion characteristics of the Dardvay skarn iron deposit, Sangan mining district, NE Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 134, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Hermann, J. Formation of High-Mg Diorites through Assimilation of Peridotite by Monzodiorite Magma at Crustal Depths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 1381–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jahn, B.M.; Arakawa, Y.; Zhai, M.G. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic intrusive complexes from the southern Taihang Orogen, North China Craton: Elemental and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic constraints. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2004, 148, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Tian, W.; Jahn, B.M.; Chen, Z.C. Zircon SHRIMP U–Pb ages and in-situ Hf isotopic analysis for the Mesozoic intrusions in South Taihang, North China craton: Evidence for hybridization between mantle-derived magmas and crustal components. Lithos 2008, 102, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhang, H.; Peng, T. Early Cretaceous gabbroic rocks from the Taihang Mountains: Implications for a paleosubduction-related lithospheric mantle beneath the central North China Craton. Lithos 2006, 86, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, D.; Gao, S.; Pei, F.; Yu, Y. Geochemistry of peridotite xenoliths in Early Cretaceous high-Mg# diorites from the Central Orogenic Block of the North China Craton: The nature of Mesozoic lithospheric mantle and constraints on lithospheric thinning. Chem. Geol. 2010, 270, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Su, S.; Yang, Y.; Gu, D. The evidence for lithospheric thinning of Mesozoic North China Craton: Taking Guzhen intrusion complex as an example. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 989–1014, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wilde, S.A.; Walker, R.J. Destruction of the North China Craton in the Mesozoic. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 47, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Zhang, H.; Shen, J.; Dong, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Inhomogeneous lithospheric thinning in the central North China Craton: Zircon U–Pb and S–He–Ar isotopic record from magmatism and metallogeny in the Taihang Mountains. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Yang, J.; Wu, F. Timing of destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos 2012, 149, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Dong, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Z. Zircon U–Pb geochronology of the basement rocks and dioritic intrusion associated with the Fushan skarn iron deposit, southern Taihang Mountains, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 113, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 376–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; Santosh, M.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, M. Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China: An overview. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Mesozoic Magmatism Time Limit of the South Taihang and Its Tectonic Significance. Master’s Thesis, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Guo, F.; Peng, B. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology of the diorites for southern Taihang Mountains in the North China Interior and its petrogenesis. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 5, 264–273, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. The Characteristics of Fushan Iron Deposit, Handan, Hebei Province, China, and Its Implication to the North China Craton Evolution. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Yang, D.; Pei, F.; Yu, Y. Petrogenesis of Fushan high-Mg# diorites from the southern Taihang Mts. in the central North Craton: Resulting from interaction of peridotite-melt derived from partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2009, 25, 1947–1961, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. Petrogenesis and Mineralization of the Early Cretaceous Intrusive Rocks in Handan-Xingtai Area, Hebei Province, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2016. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Guo, S.; Gao, X.; Li, G. 40Ar-39Ar dating of phologopite from the Xishimen skarn iron deposit in the Handan-Xingtai area, southern Hebei, and its implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2007, 10, 2513–2518, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Su, S.; Cui, X.; Liu, L.; Meng, W.; Wang, J. The processes and mechanism of lithospheric thinning in eastern North China Craton during Early Cretaceous: Evidence from Xishimen Complex, Hebei Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2020, 36, 356–390, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jurek, K.; Hulínský, V. The use and accuracy of the ZAF correction procedure for the microanalysis of glasses. Microchim. Acta. 1980, 73, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ge, C.; Ning, S.; Nie, L.; Zhong, G.; White, N.C. A new approach to LA-ICP-MS mapping and application in geology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3422–3436, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Chen, H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Ba, T.; Meng, X. CorelKit: An Extensible CorelDraw VBA Program for Geoscience Drawing. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 1–23. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1788.P.20221208.1416.002.html (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Piccoli, P.M.; Candela, P.A.; Kohn, M.J.; Rakovan, J.; Hughes, J.M. Apatite in igneous systems. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2002, 48, 255–292. Available online: https://go.exlibris.link/mv7WkDtP (accessed on 15 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Costa, F. A thermodynamic model for F-Cl-OH partitioning between silicate melts and apatite including non-ideal mixing with application to constraining melt volatile budgets. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 269, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Typomorphism and Significance of Apatite from the Granite in the Jiaodong and Xiaoqinling Regions. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.S.; Mcdonough, W.F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Bai, M.; Lu, J.; Wei, H.; Nie, X.; Liu, H. The genetic mineralogical study of magnetite in Baijian and Xishimen skarn type of iron deposit, southern Hebei Province. Earth Sci. Front. 2013, 20, 76–87, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müntener, O.; Kelemen, P.B.; Grove, T.L. The role of H2O during crystallization of primitive arc magmas under uppermost mantle conditions and genesis of igneous pyroxenites: An experimental study. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2001, 141, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, M. Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: An Earth scale perspective. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, M.; Caricchi, L. Stochastic modelling of deep magmatic controls on porphyry copper deposit endowment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekhova, E.; Blundy, J.; Robertson, R.; Humphreys, M.C.S. Experimental Evidence for Polybaric Differentiation of Primitive Arc Basalt beneath St. Vincent, Lesser Antilles. J. Petrol. 2015, 56, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X. Calculation of Oxygen Fugacity of Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks in Han–Xing Region, Southern Hebei Province and Their Geological Significances. Master’s Thesis, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F.; Jin, Y.; Fan, L.; Tang, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, J. Genetic mineralogical study of Ziquan diroite intrusion in the eastern of Handan-Xingtai region, Hebei province. J. Hebei GEO Univ. 2021, 44, 1–7, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, W.; Li, Q.; Bai, F.; Jin, Y.; Fan, L. Genetic mineralogy of apatite in Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Handan-Xingtai Region, Hebei Province. Geol. Explor. 2020, 56, 969–984, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xing, K.; Shu, Q. Applications of apatite in study of ore deposits: A review. Miner. Depos. 2021, 40, 189–205, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Burnham, A.D.; Berry, A.J. The effect of oxygen fugacity, melt composition, temperature and pressure on the oxidation state of cerium in silicate melts. Chem. Geol. 2014, 366, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smythe, D.J.; Brenan, J.M. Cerium oxidation state in silicate melts: Combined fO2, temperature and compositional effects. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 170, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, A. Variation of Cl and SO3 Contents of Microphenocrystic Apatite in Intermediate to Silicic Igneous Rocks of Cenozoic Japanese Island Arcs: Implications for Porphyry Cu Metallogenesis in the Western Pacific Island Arcs. Resour. Geol. 2004, 54, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelle-Michou, C.; Chiaradia, M. Amphibole and apatite insights into the evolution and mass balance of Cl and S in magmas associated with porphyry copper deposits. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2017, 172, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.; Zajacz, Z.; Ulmer, P.; Heinrich, C.A. Chlorine partitioning between granitic melt and H2O-CO2-NaCl fluids in the Earth’s upper crust and implications for magmatic-hydrothermal ore genesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 261, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L. The Study of Genetic Mineralogical of Amphibole in Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks in Han–Xing Area, Southern Hebei Province. Master’s Thesis, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2022. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
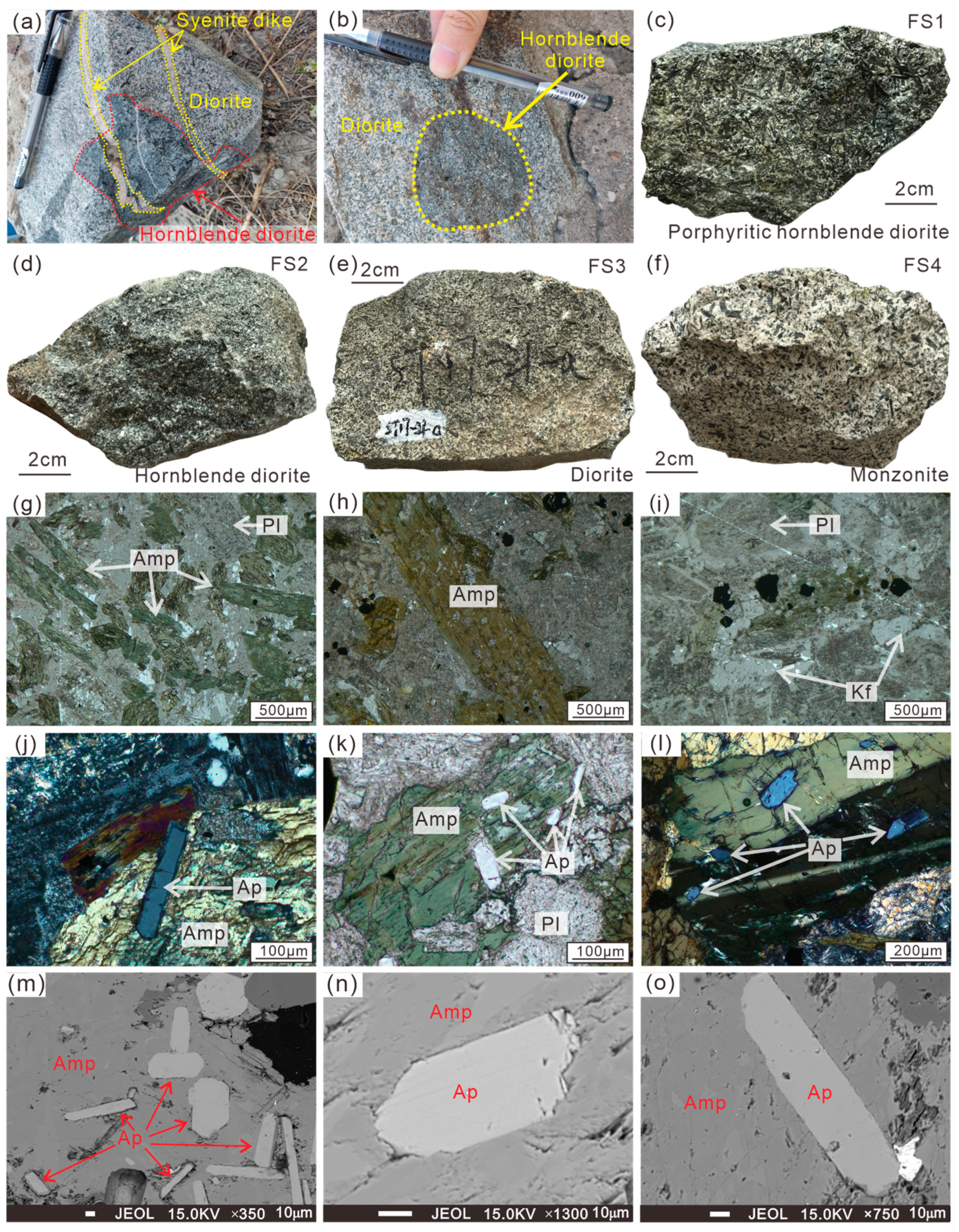
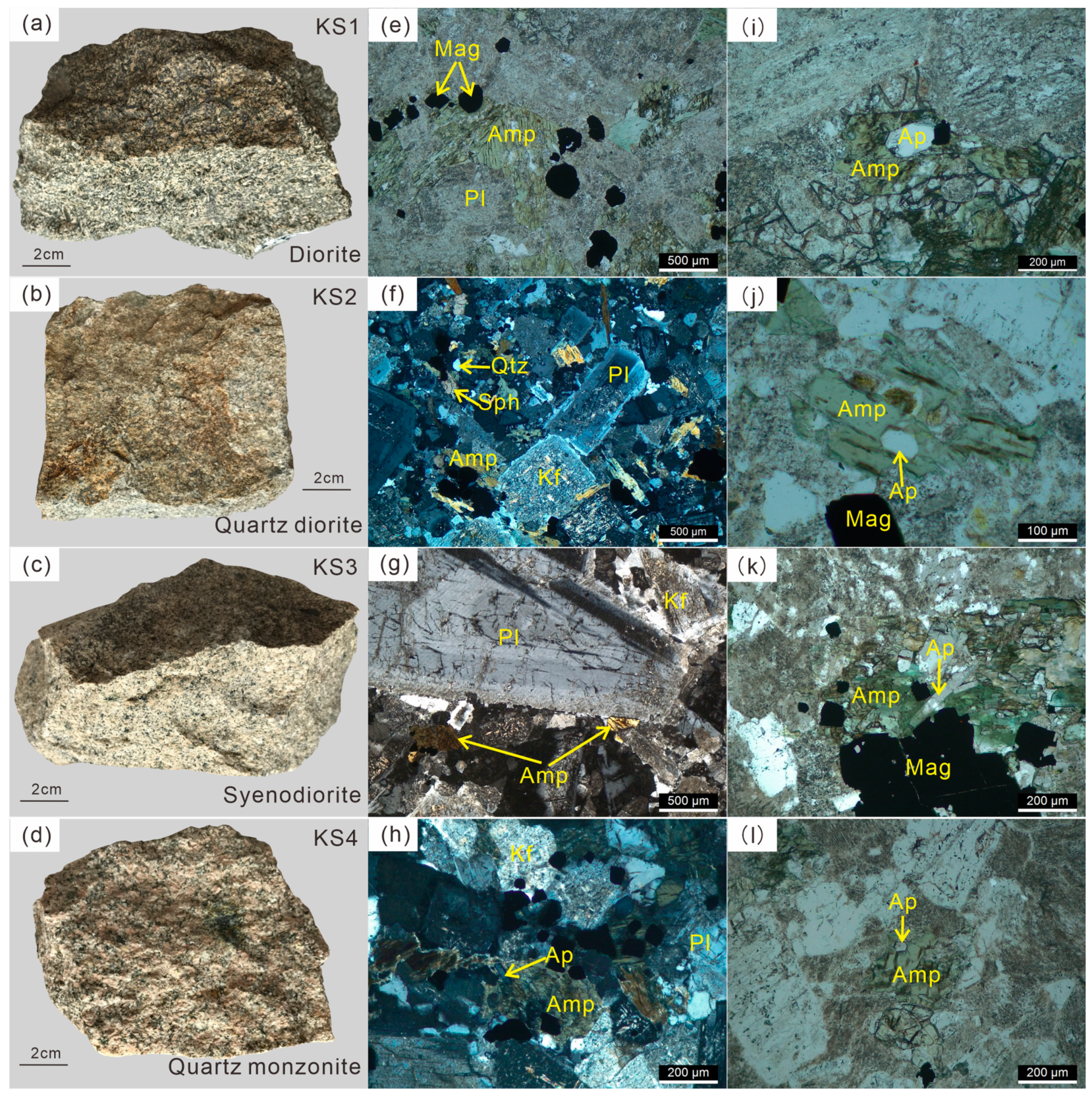
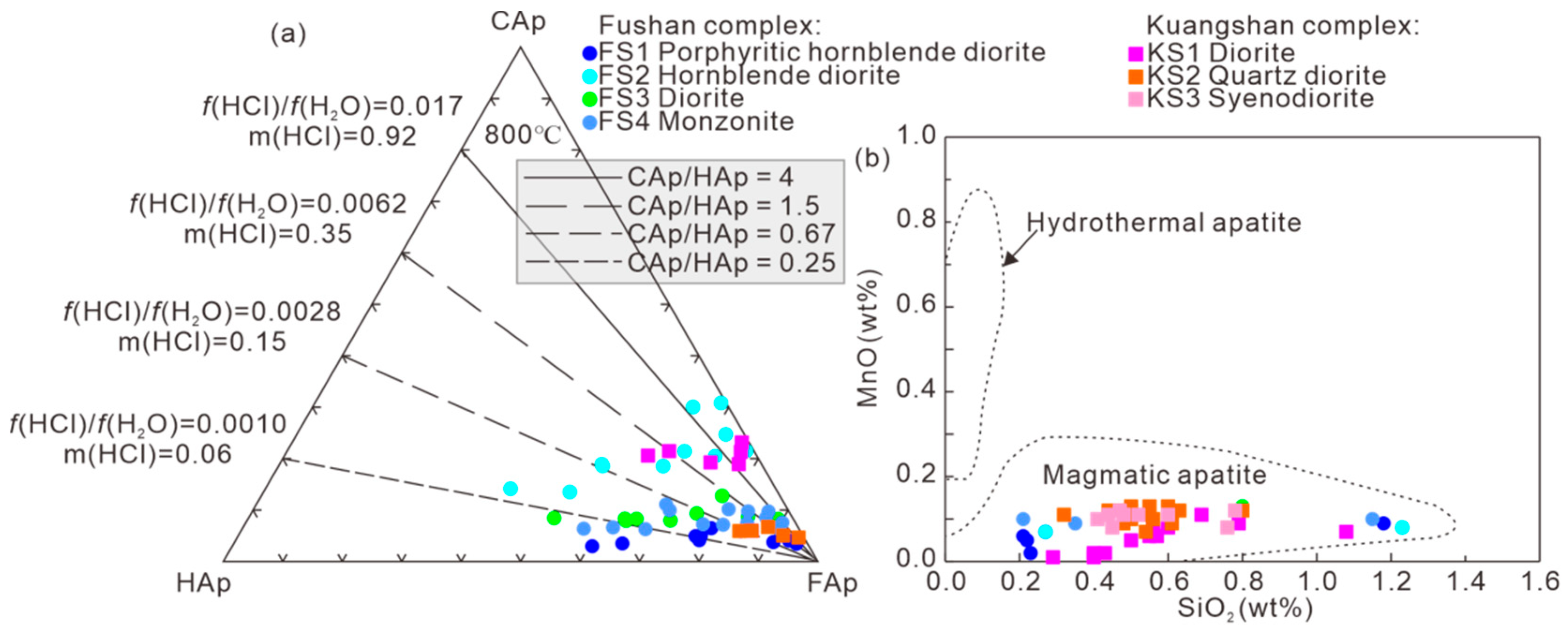
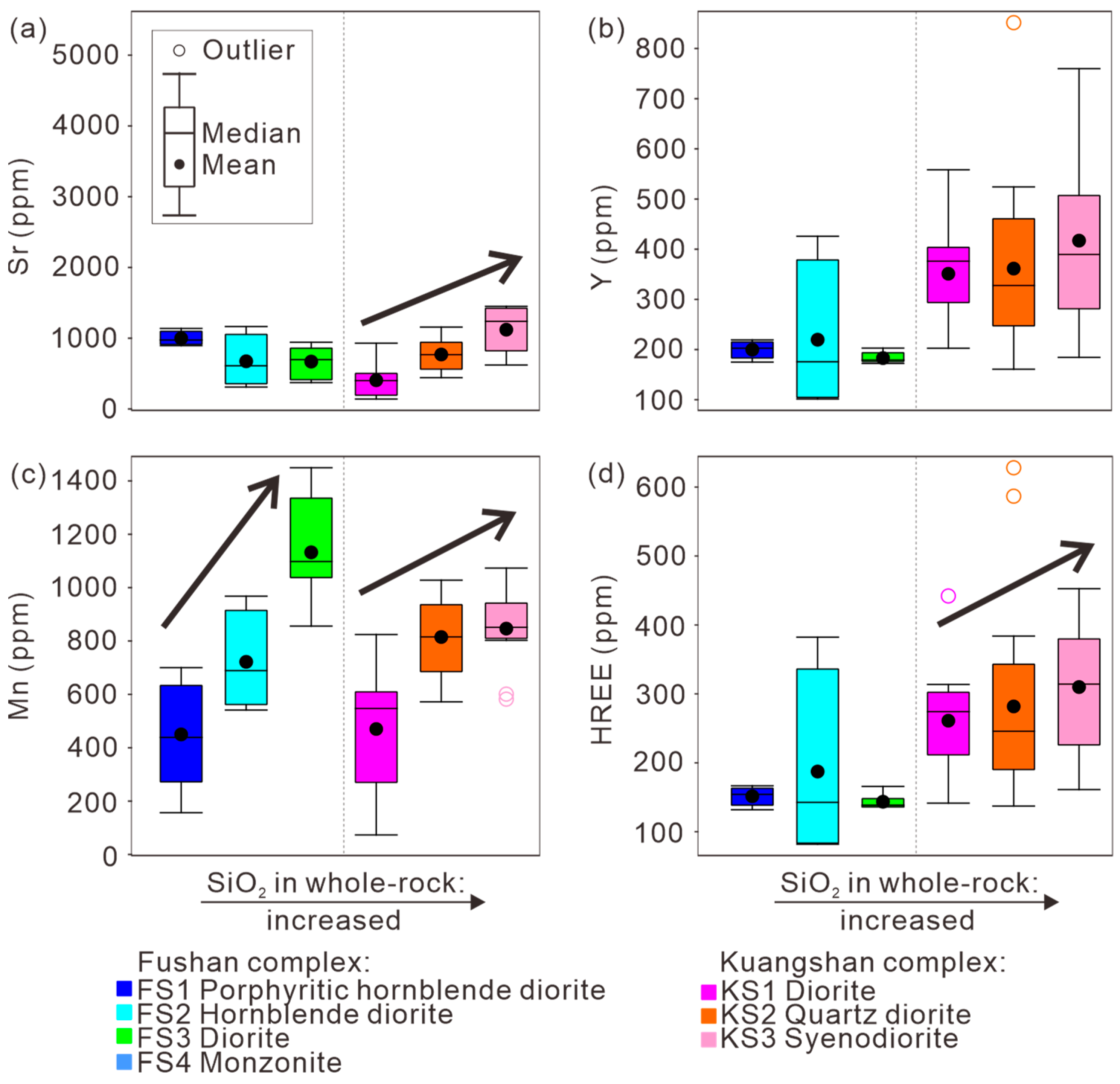
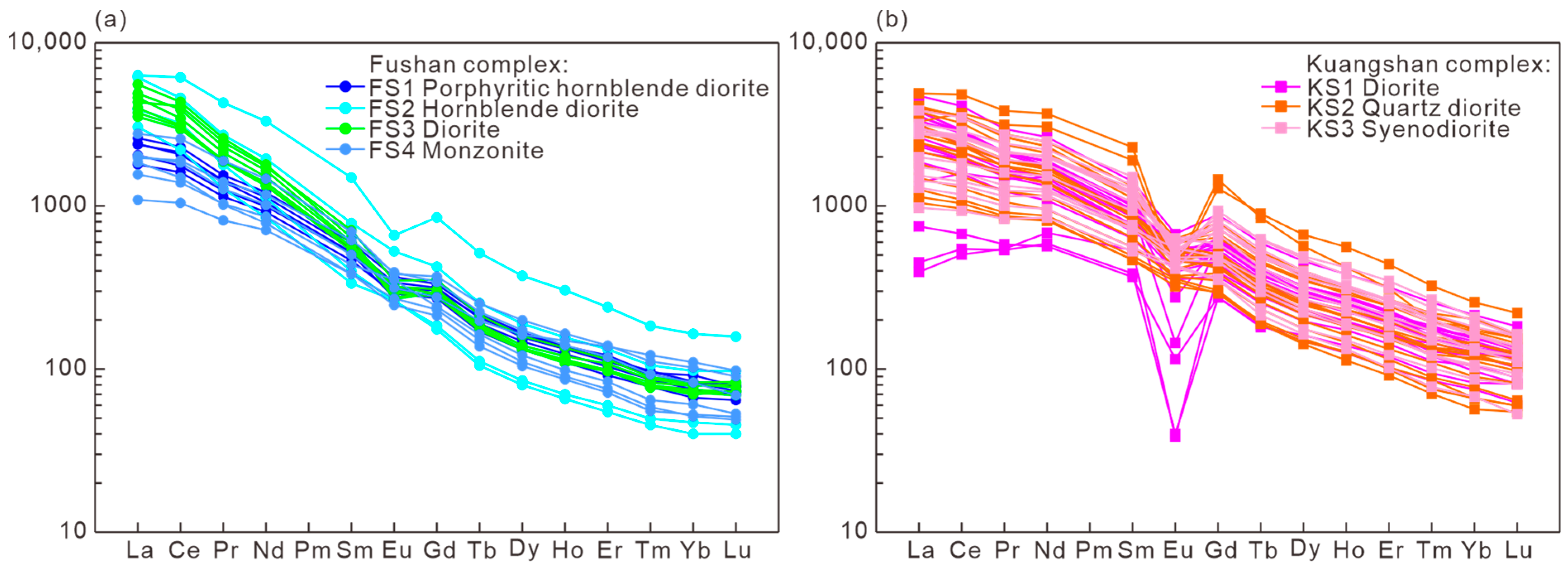
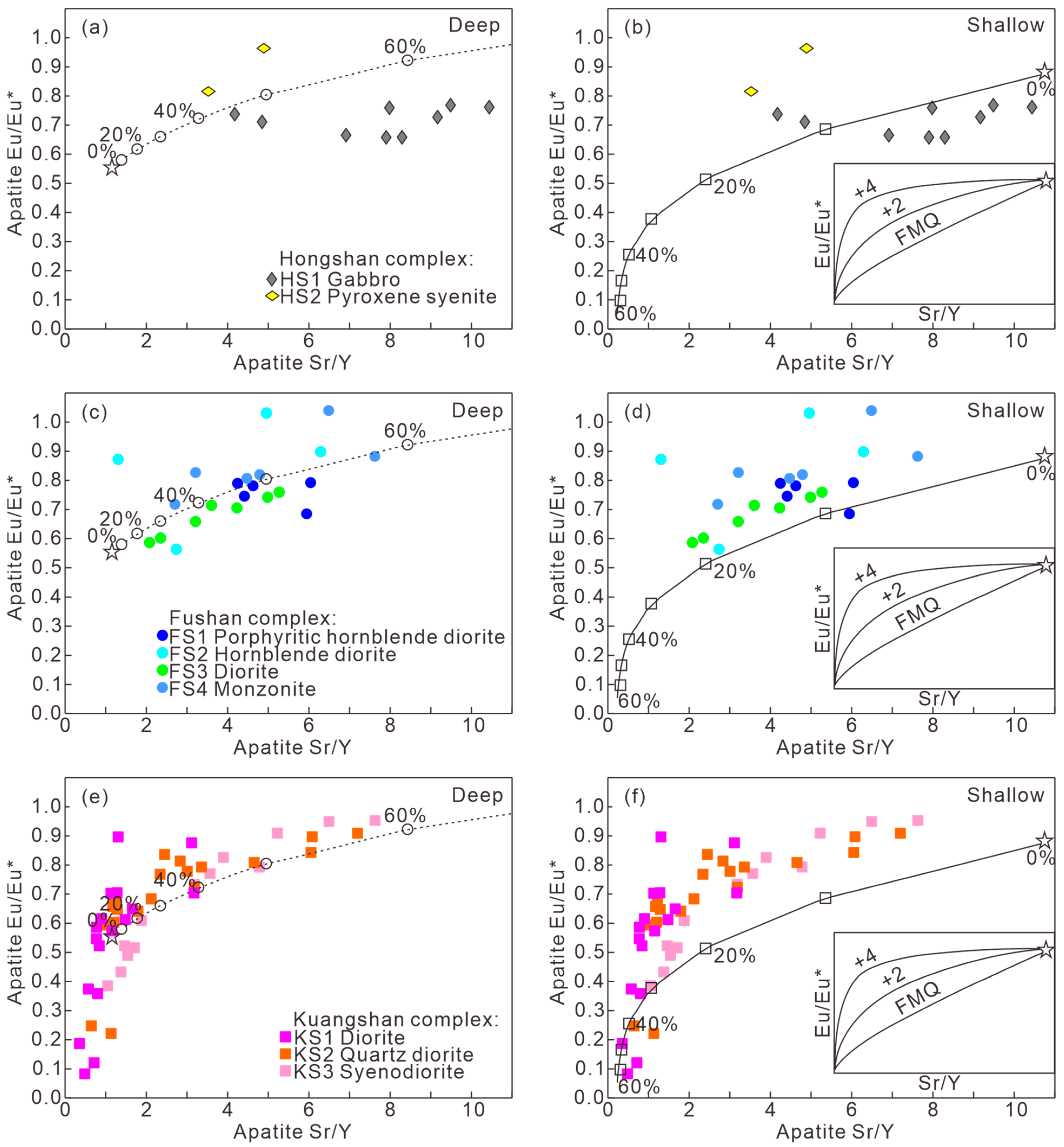
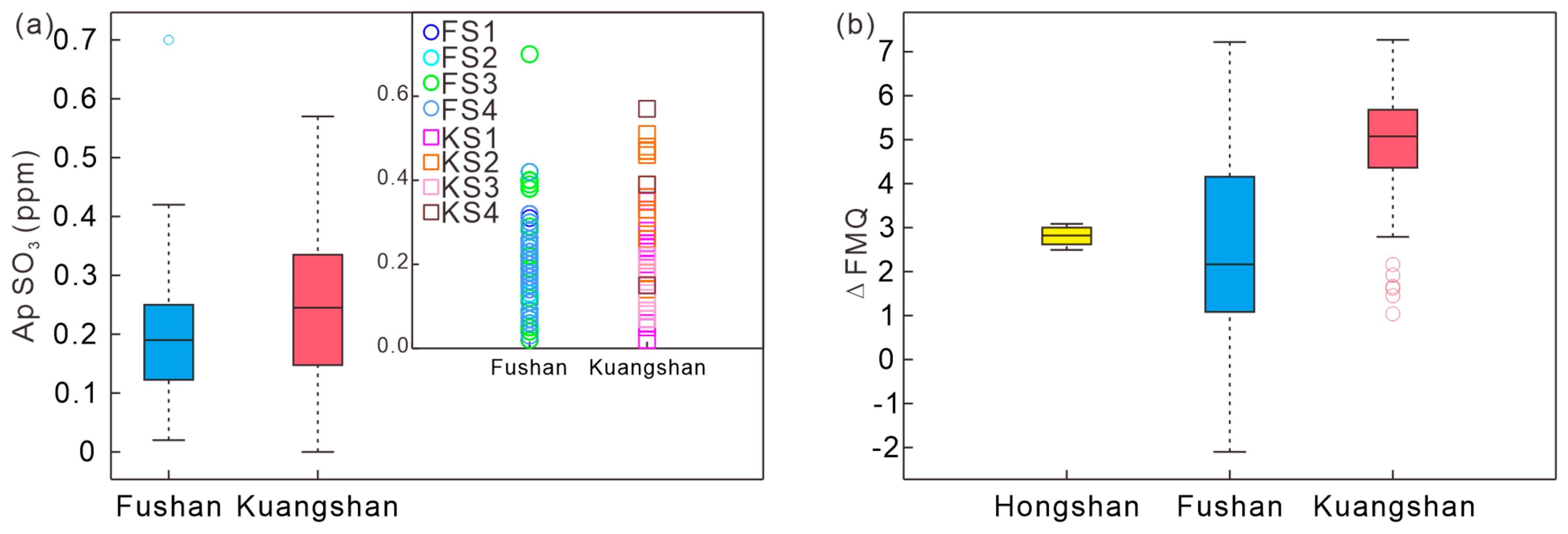
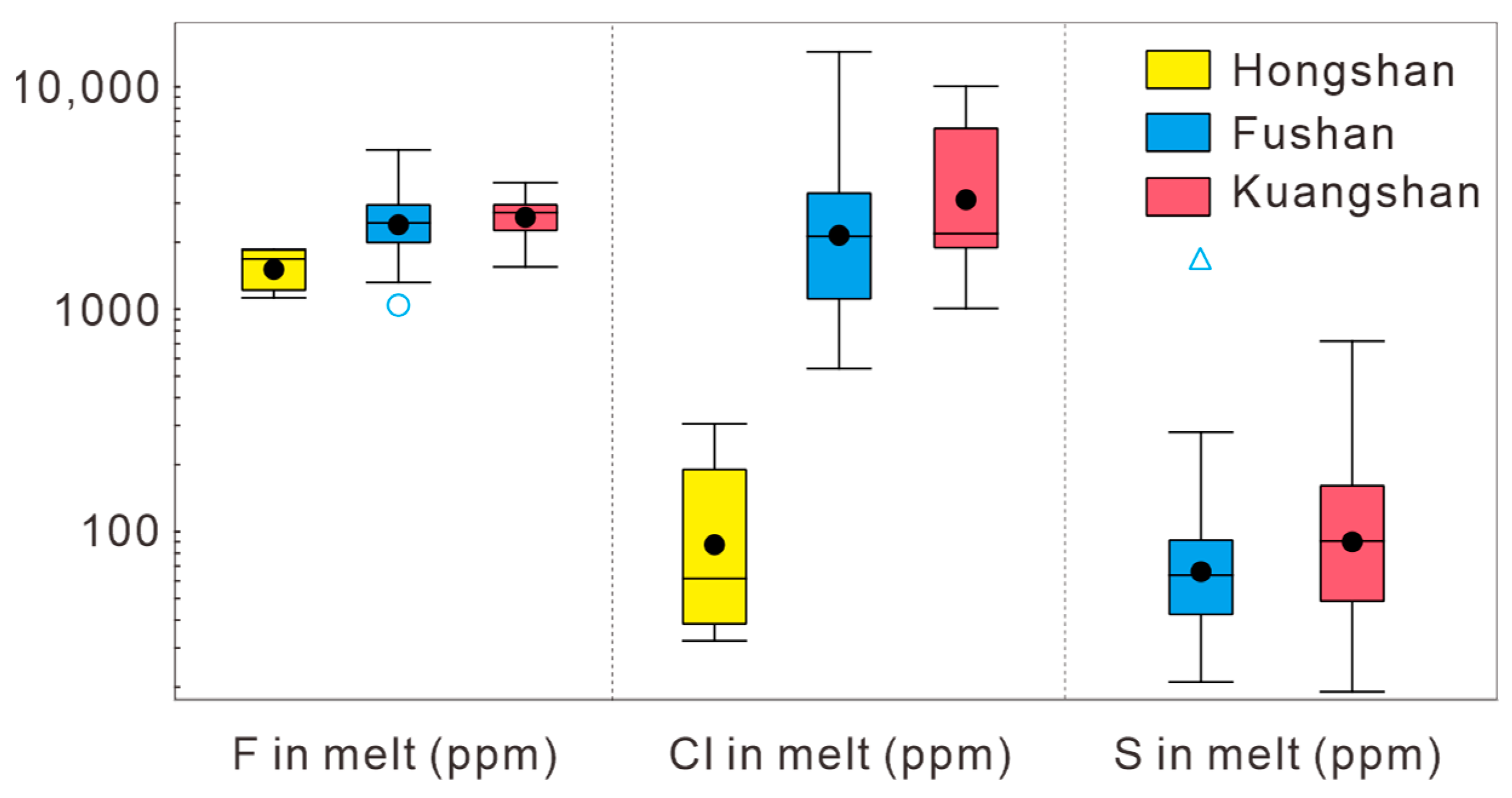
| Sample No. | Complex | Lithology | Texture | Main Mineral | Accessory Mineral | U-Pb Dating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS1 | Fushan | Porphyritic hornblende diorite | Porphyritic texture | Pl(60%) + Amp(35%) + Cpx(5%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn + Sph | 129 ± 1.8 Ma |
| FS2 | Fushan | Hornblende diorite | Hypidiomorphic-granual texture | Pl(60%) + Amp(40%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn | 129 ± 2.1 Ma |
| FS3 | Fushan | Diorite | Hypidiomorphic-granual texture | Pl(75%) + Amp(25%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn | 127 ± 4.2 Ma |
| FS4 | Fushan | Monzonite | Hypidiomorphic-granual texture | Pl(50%) + Amp(15%) + Kf(35%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn + Sph | 126 ± 1.9 Ma |
| KS1 | Kuangshan | Diorite | Medium-fine grained texture | Pl(65%) + Amp(30%) + Kf(5%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn + Sph | 129 ± 2.6 Ma |
| KS2 | Kuangshan | Quartz diorite | Medium-fine grained texture | Pl(70%) + Amp(20%) + Q(10%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn + Sph | 132 ± 2.1 Ma |
| KS3 | Kuangshan | Syenodiorite | Medium-fine grained texture | Pl(60%) + Amp(10%) + Kf(30%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn + Sph | – |
| KS4 | Kuangshan | Quartz monzonite | Medium-coarse grained texture | Pl(40%) + Amp(10%) + Kf(40%) + Q(10%) | Ap + Mag + Zrn + Sph | 128 ± 1.9 Ma |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Contraints on Petrogenesis and Fe Fertility of Intrusive Complexes in the Han–Xing Region, North China Craton from Apatite Geochemistry. Minerals 2023, 13, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040469
Liang X, Wang F, Zhang J, Zhang L, Zhang J, Wang J. Contraints on Petrogenesis and Fe Fertility of Intrusive Complexes in the Han–Xing Region, North China Craton from Apatite Geochemistry. Minerals. 2023; 13(4):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040469
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Xian, Fangyue Wang, Juquan Zhang, Long Zhang, Junwu Zhang, and Jingui Wang. 2023. "Contraints on Petrogenesis and Fe Fertility of Intrusive Complexes in the Han–Xing Region, North China Craton from Apatite Geochemistry" Minerals 13, no. 4: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040469
APA StyleLiang, X., Wang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., & Wang, J. (2023). Contraints on Petrogenesis and Fe Fertility of Intrusive Complexes in the Han–Xing Region, North China Craton from Apatite Geochemistry. Minerals, 13(4), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13040469