A New Route of Roasting-Flotation-Leaching for the Beneficiation of Ti-Bearing Minerals from Altered Vanadium Titanomagnetite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Ore Sample
2.1.2. Reagents
2.2. Experimental Methods
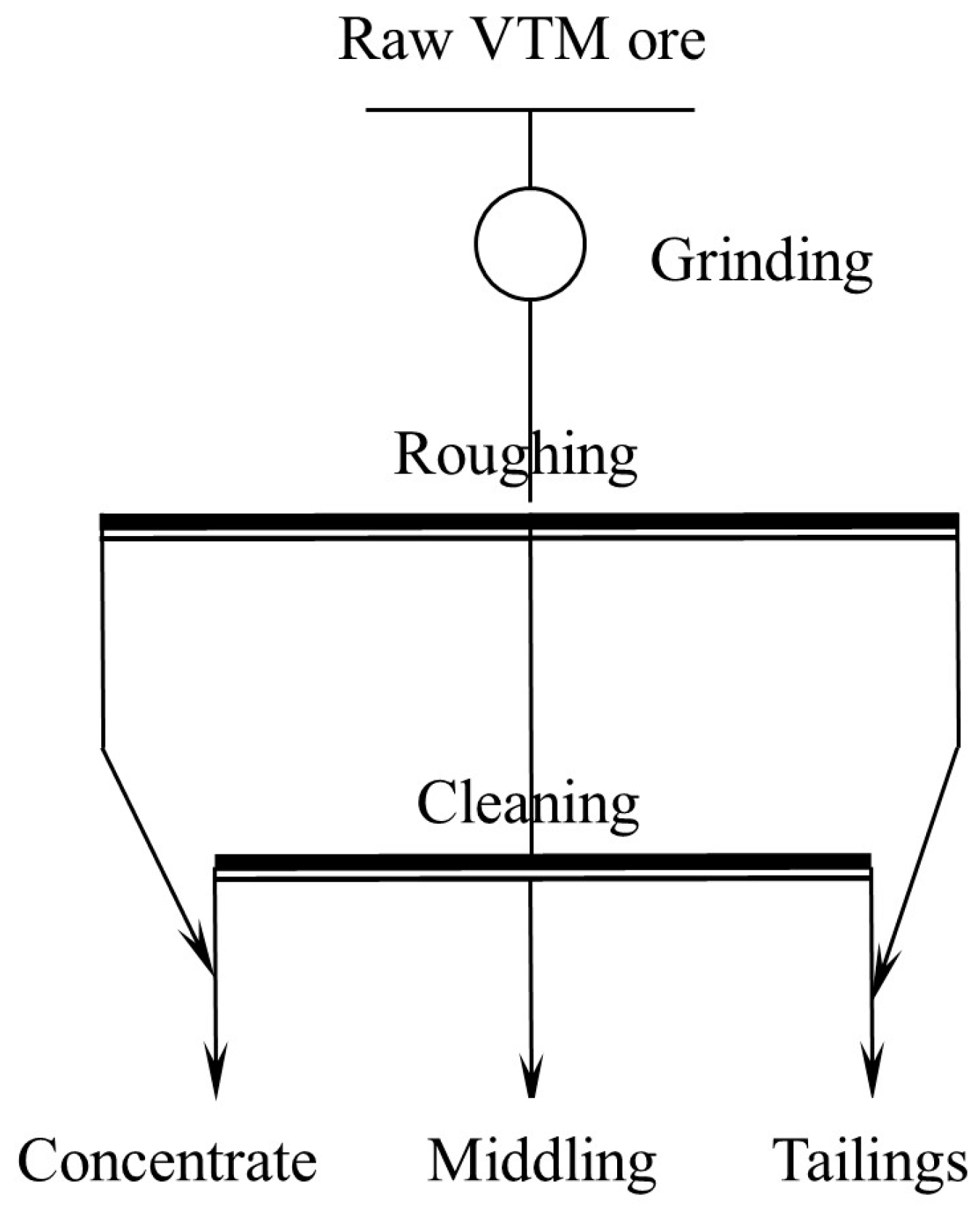
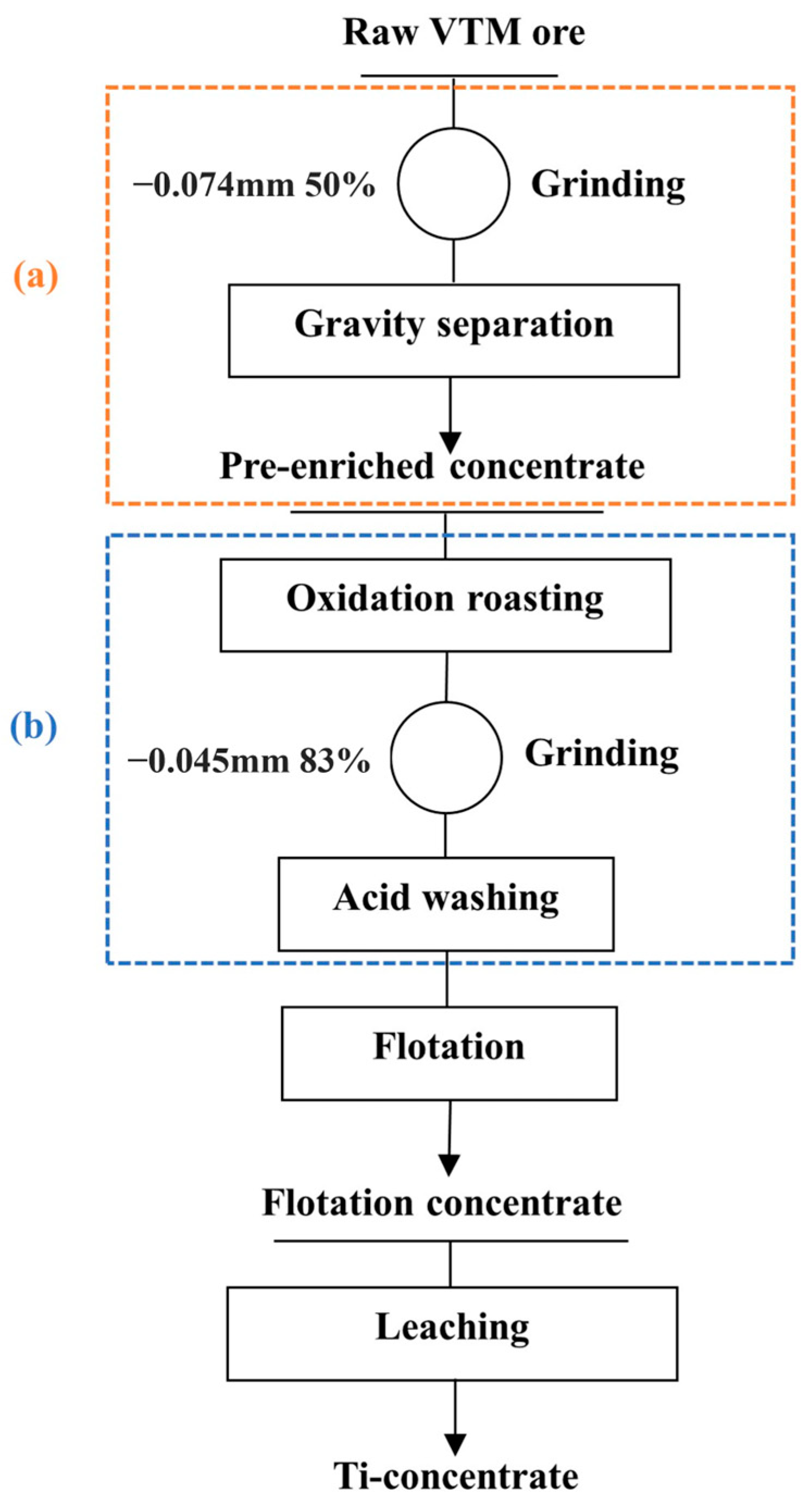
2.2.1. Pre-Concentration
Magnetic Separation
Gravity Separation
2.2.2. Pretreatment
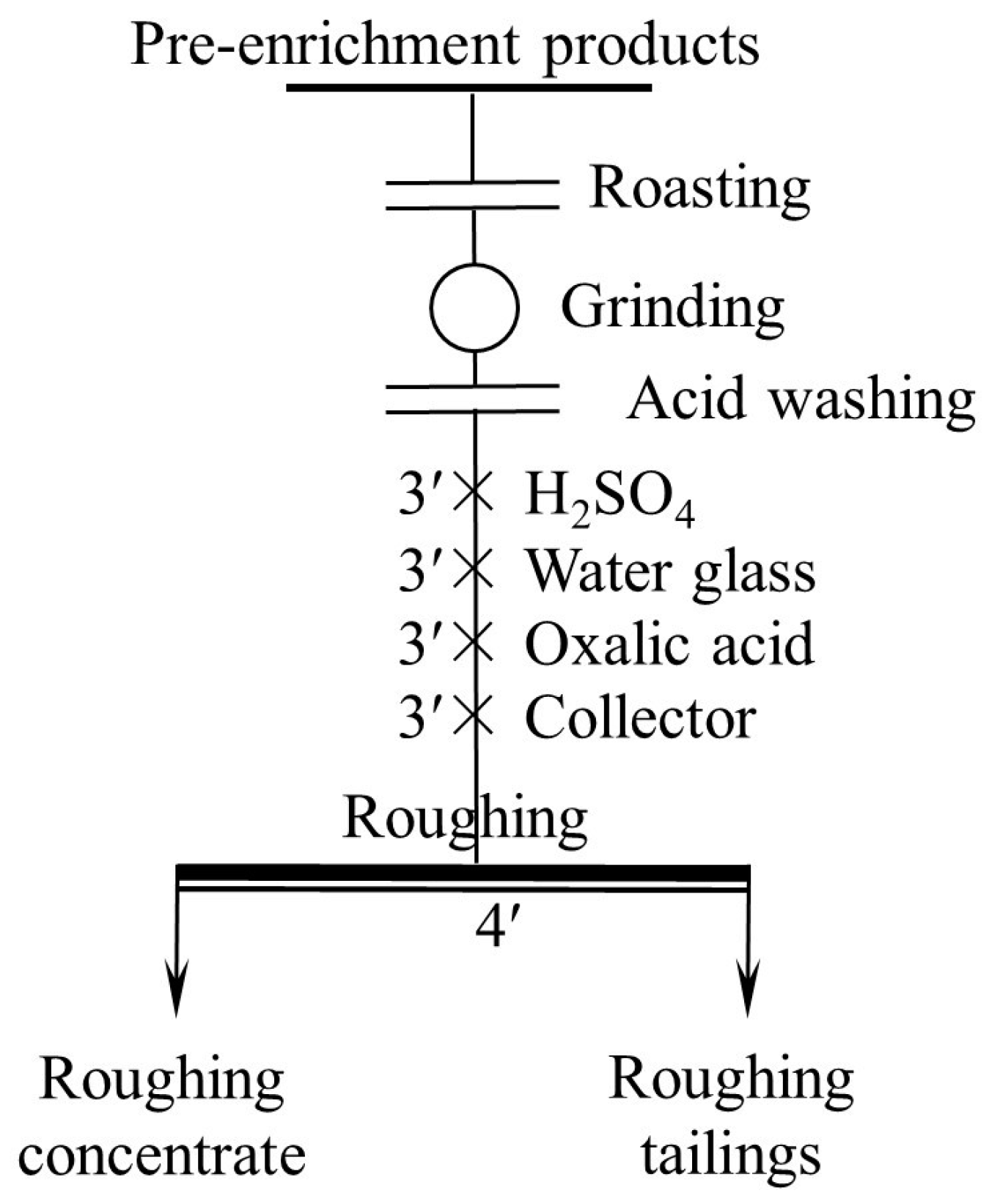
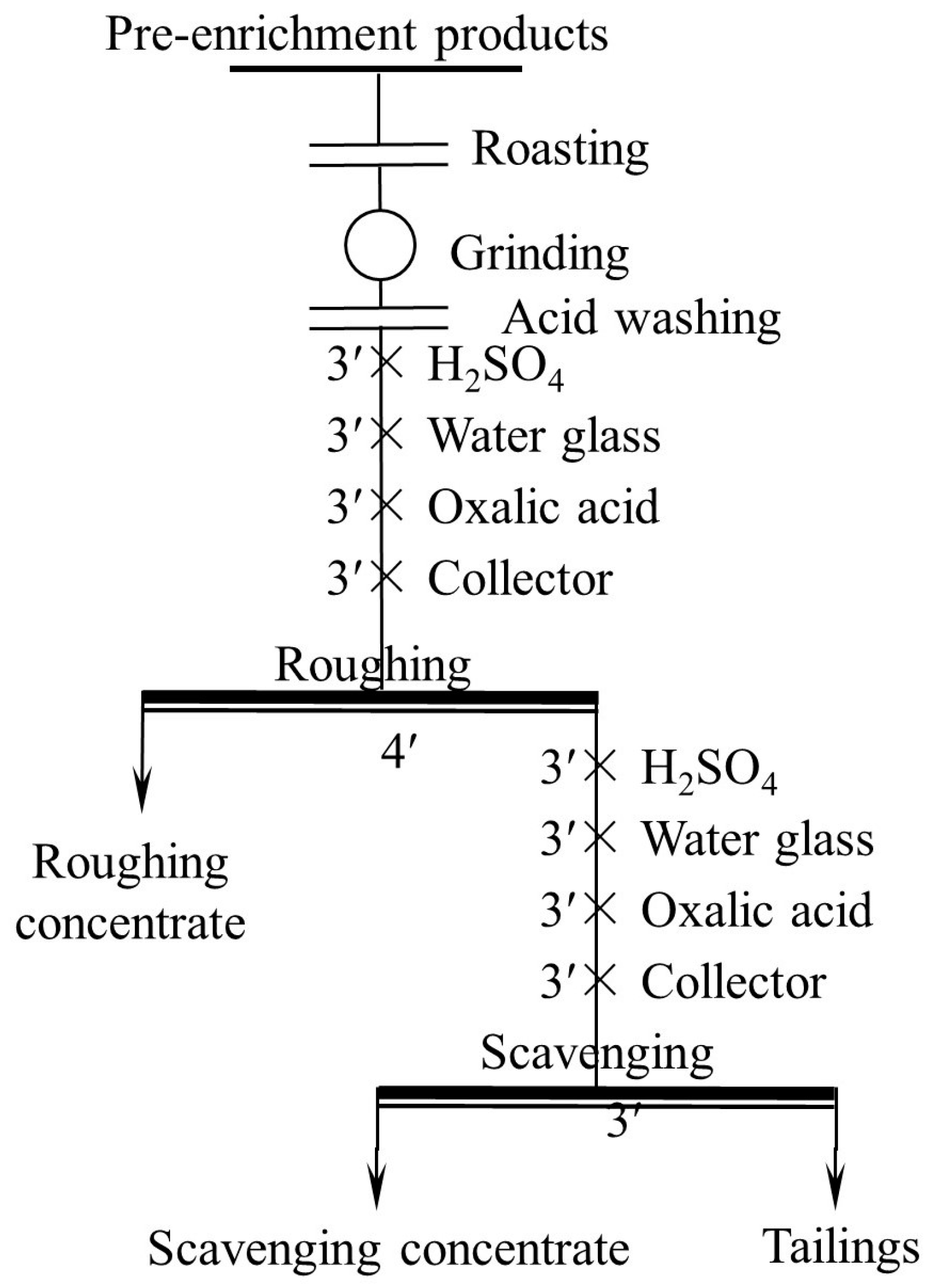
2.2.3. Flotation Tests
2.2.4. Acid Leaching Test
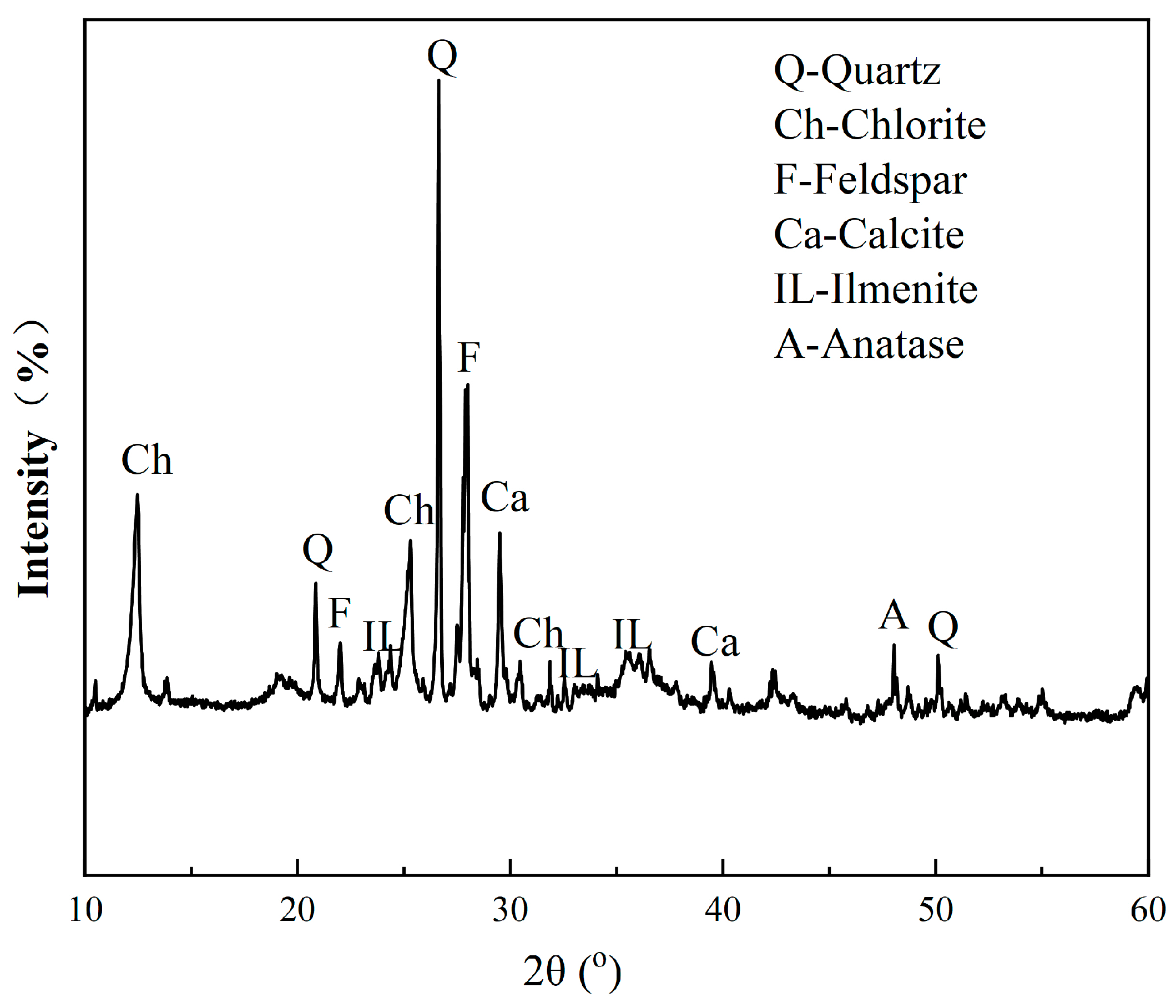
2.2.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3. Results
3.1. Titanium Pre-Concentration Experiments
3.1.1. Magnetic Separation
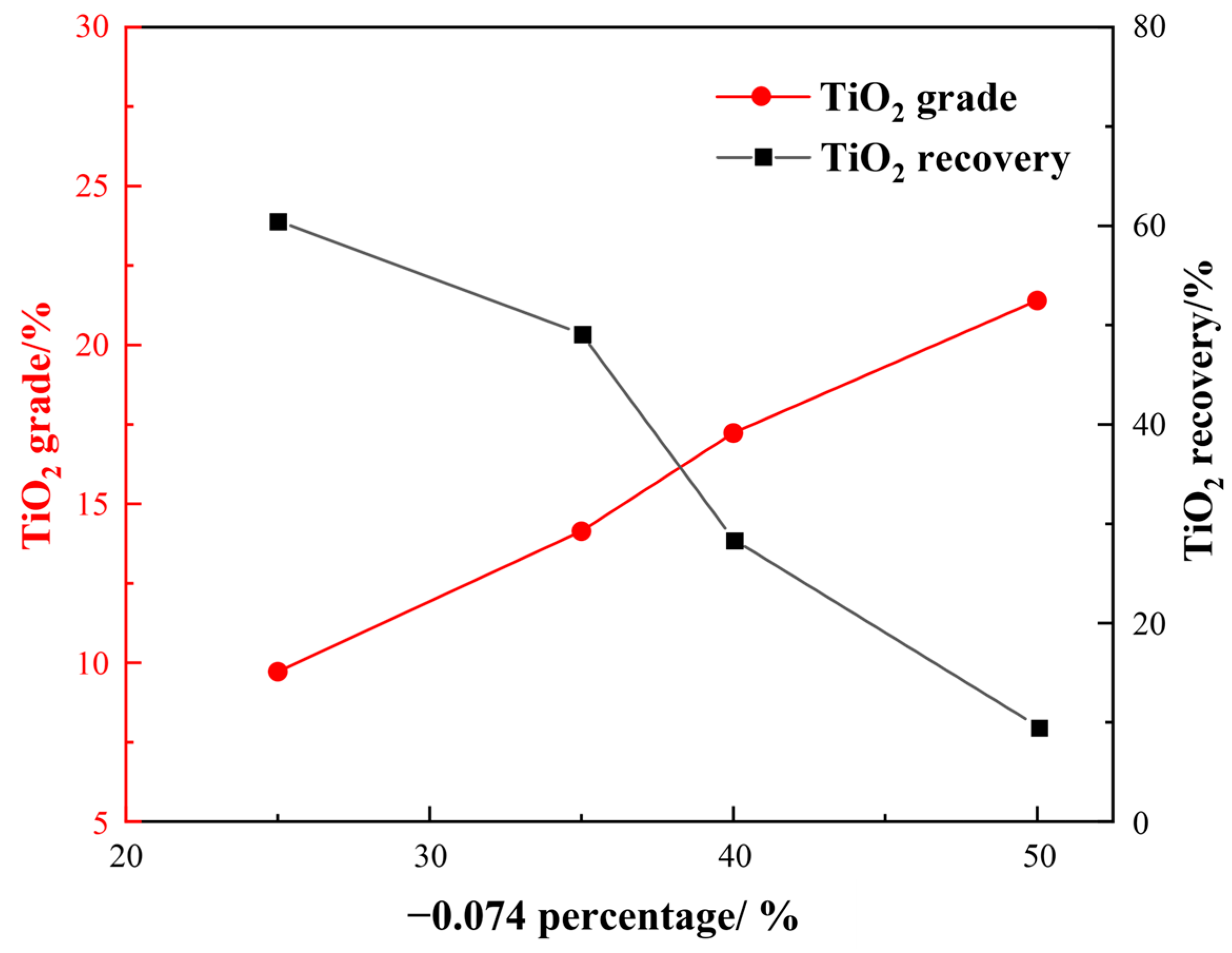
3.1.2. Gravity Separation
3.2. Pretreatment Experiments
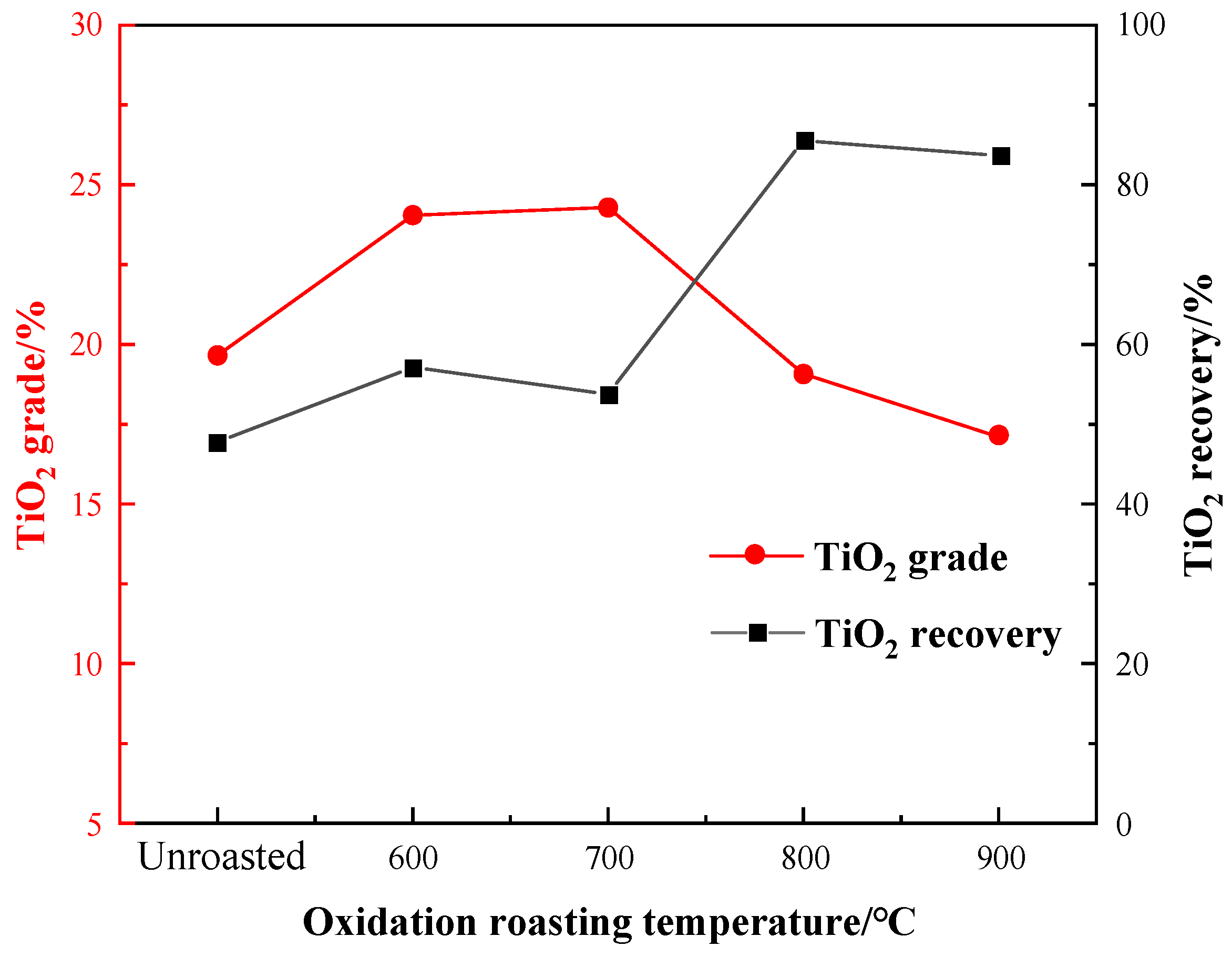
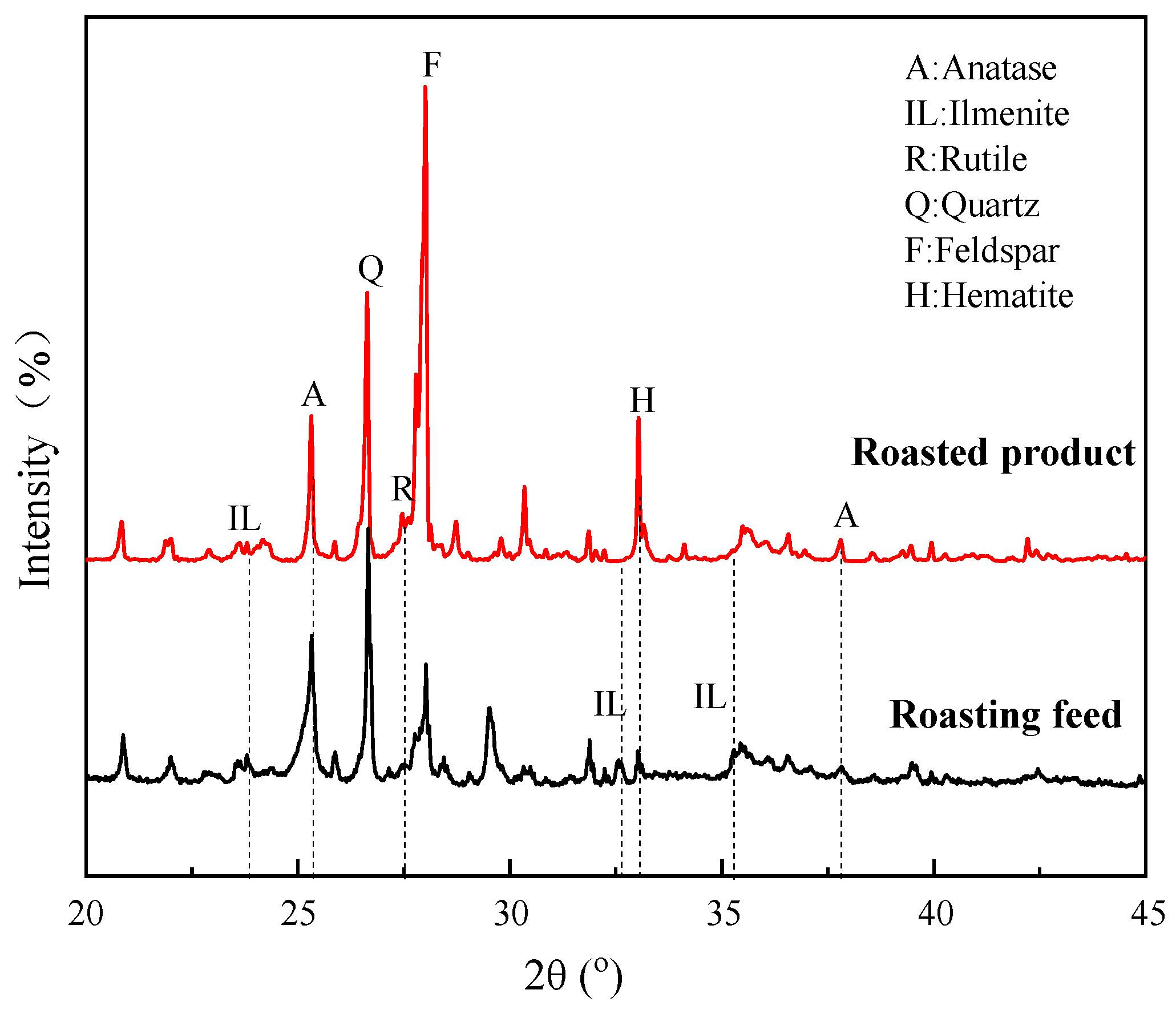
3.2.1. Oxidation Roasting Temperature Experiment
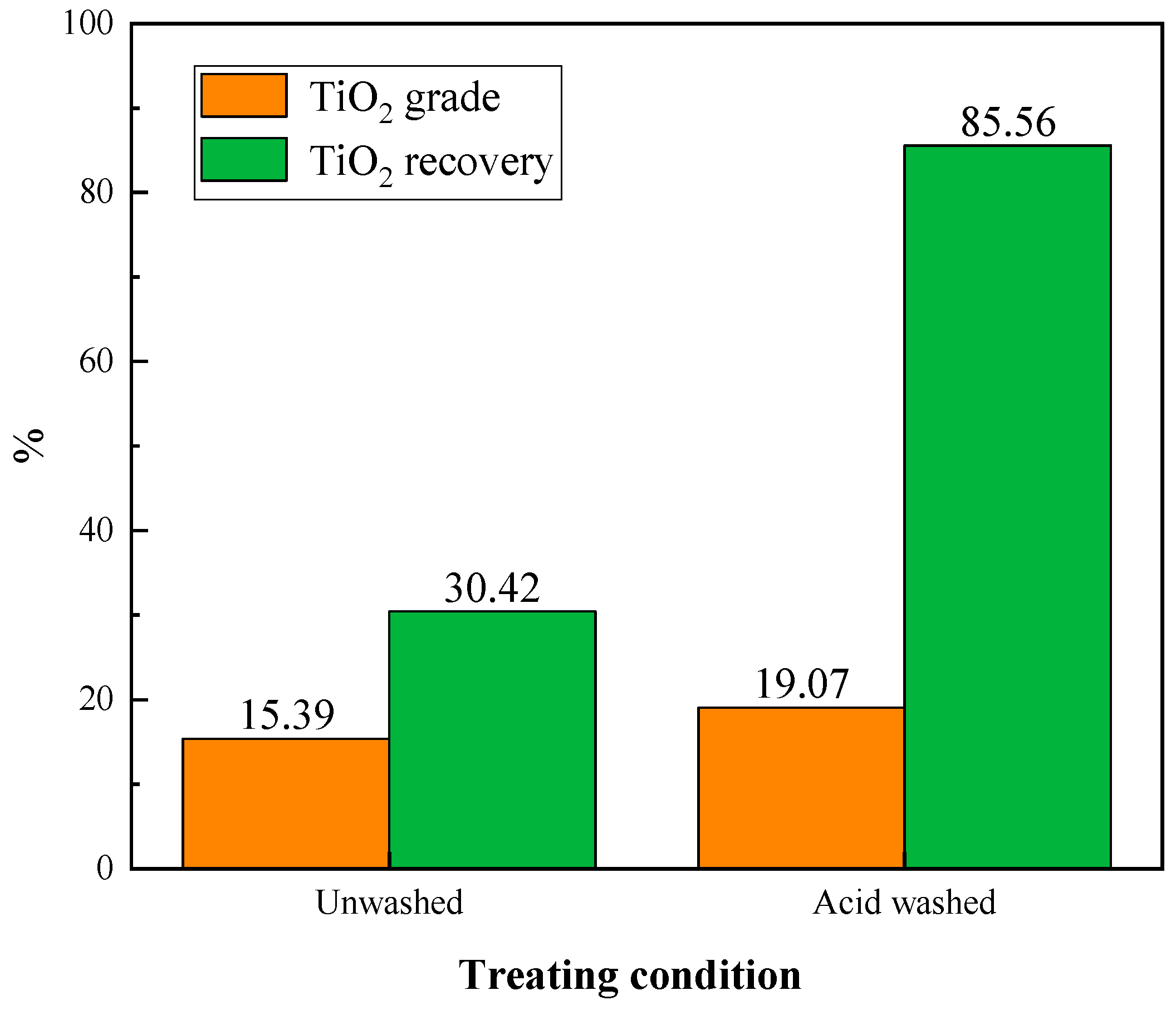
3.2.2. Acid Washing Experiment
3.3. Flotation Tests
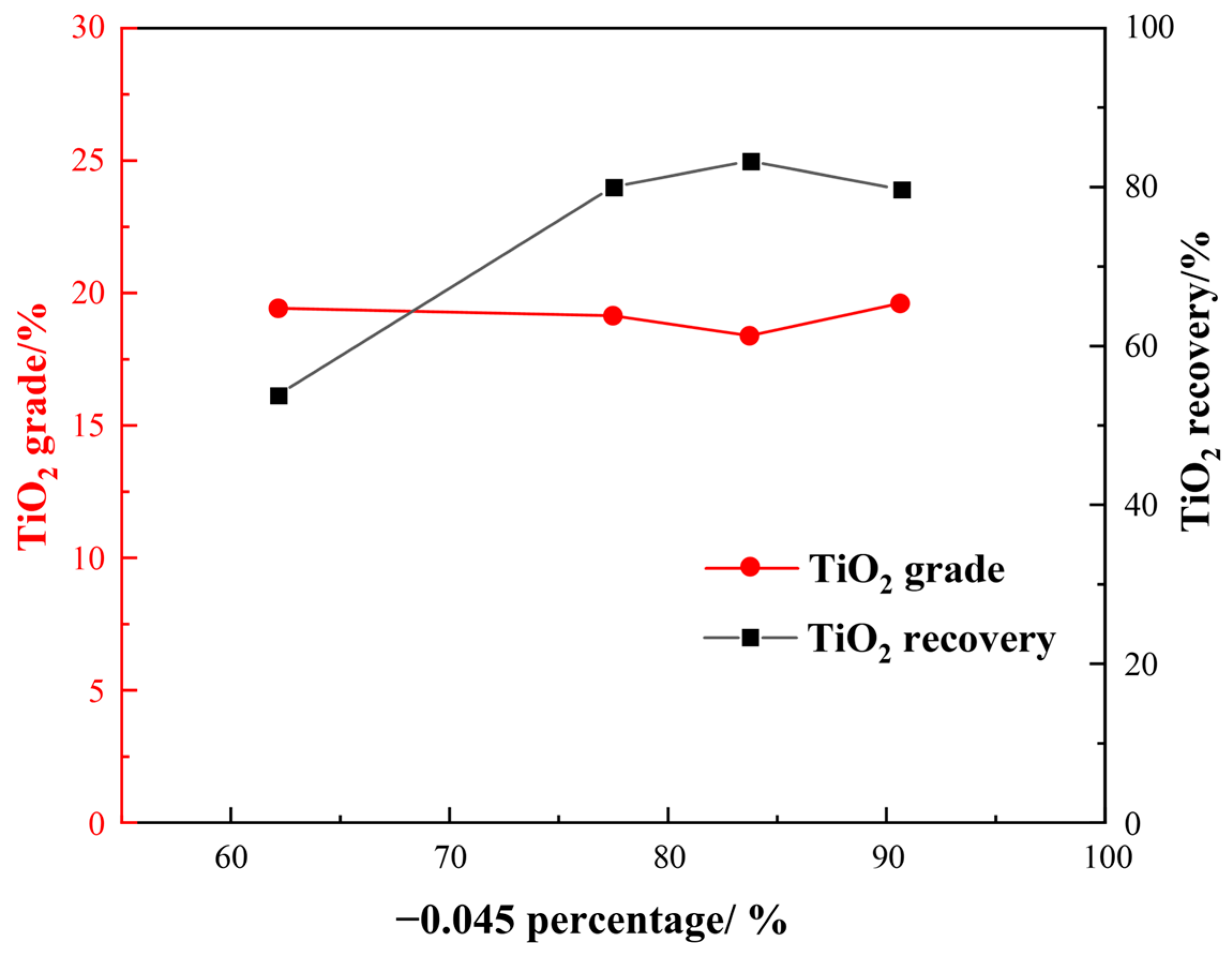
3.3.1. Effect of Grinding Fineness
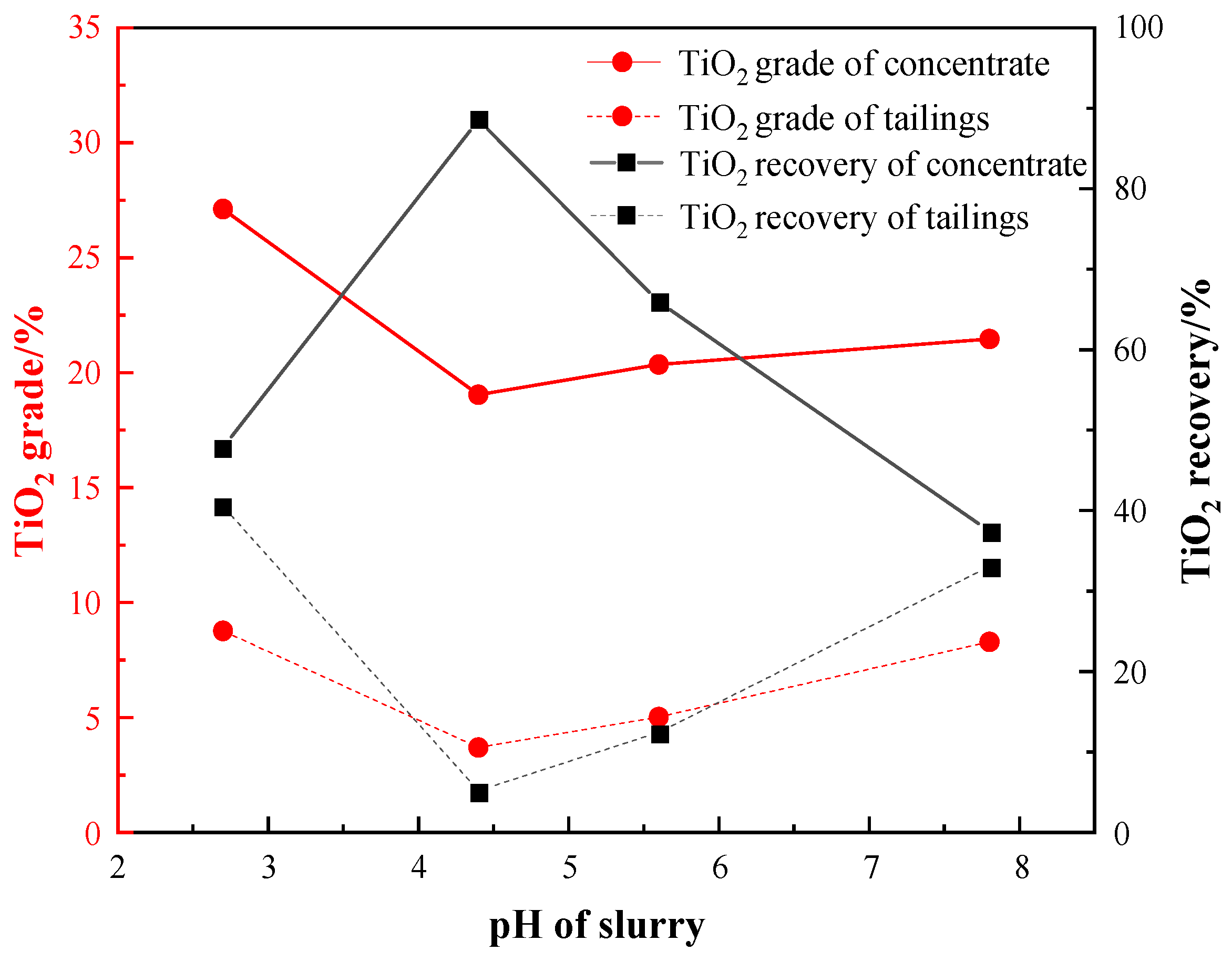
3.3.2. Effect of pH Condition
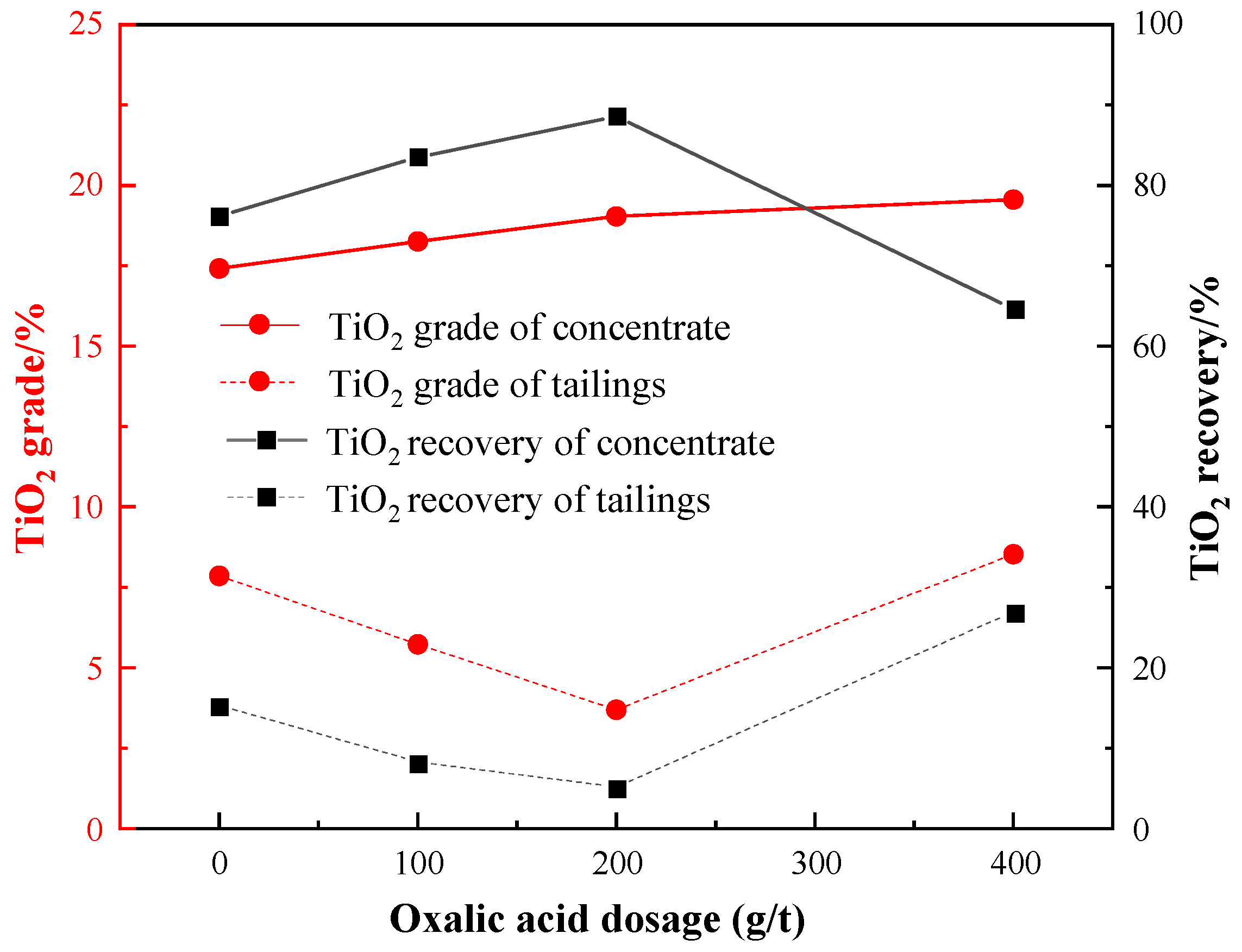
3.3.3. Effect of Depressants Dosage
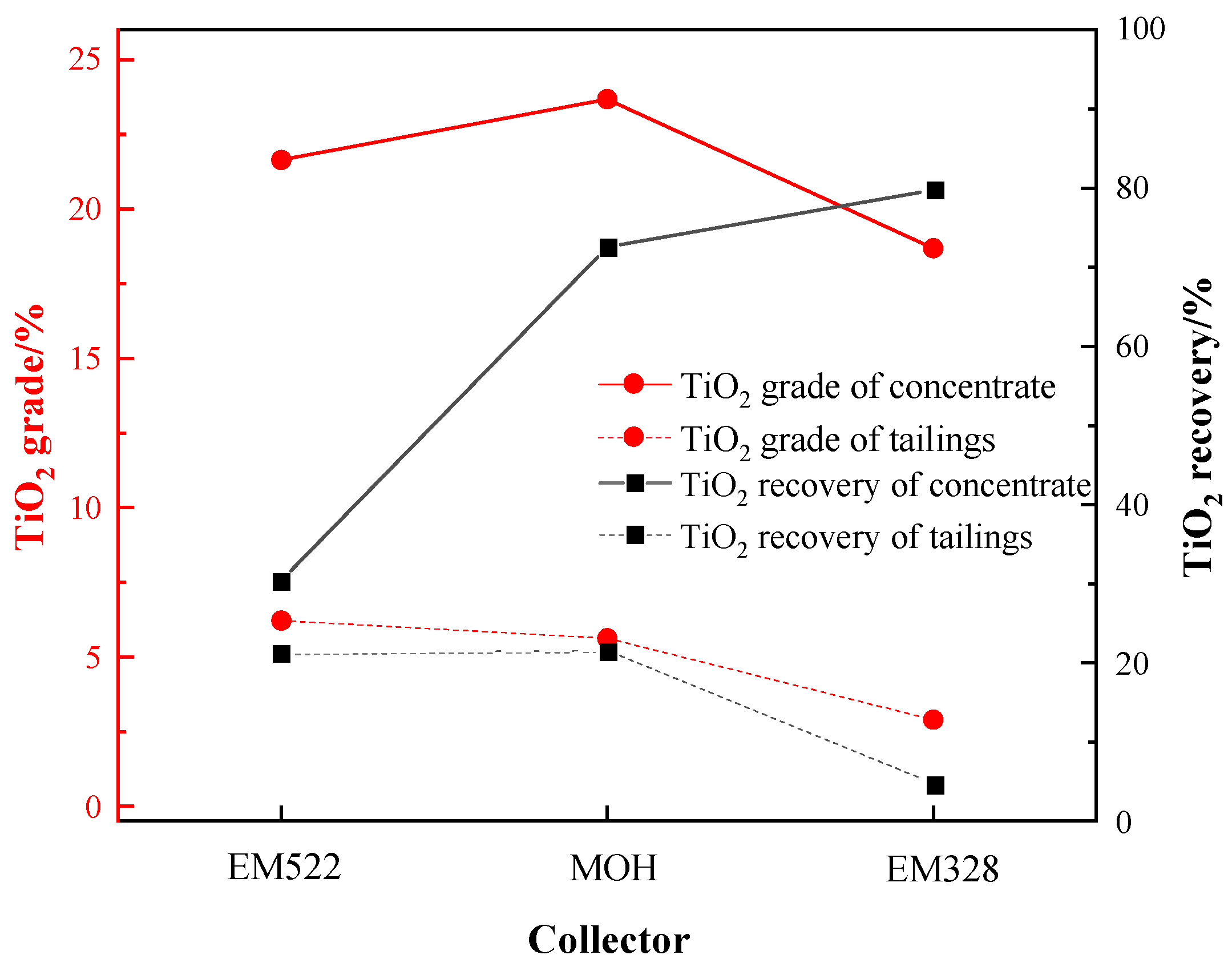
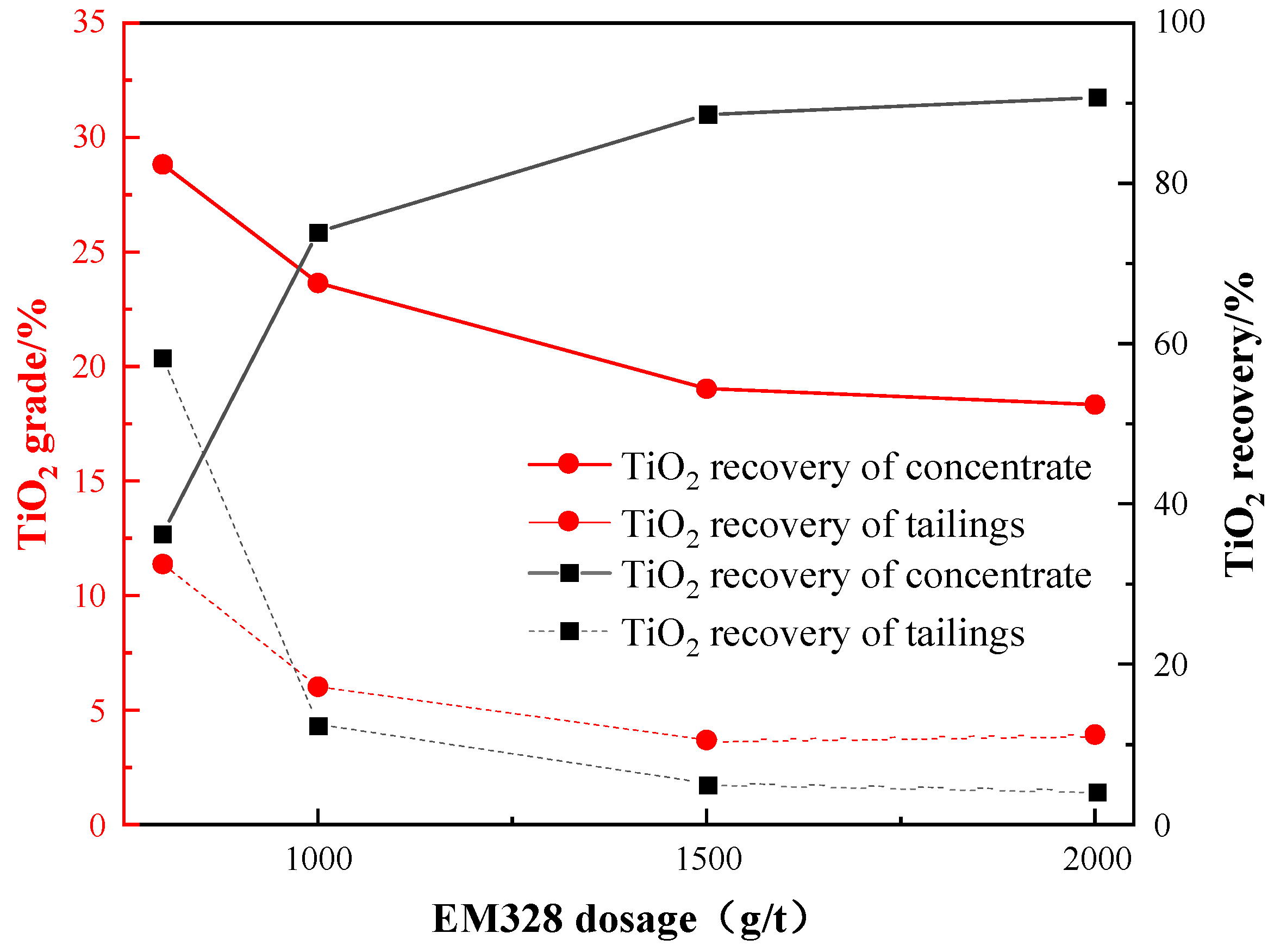
3.3.4. Effect of Collector Species and Dosage
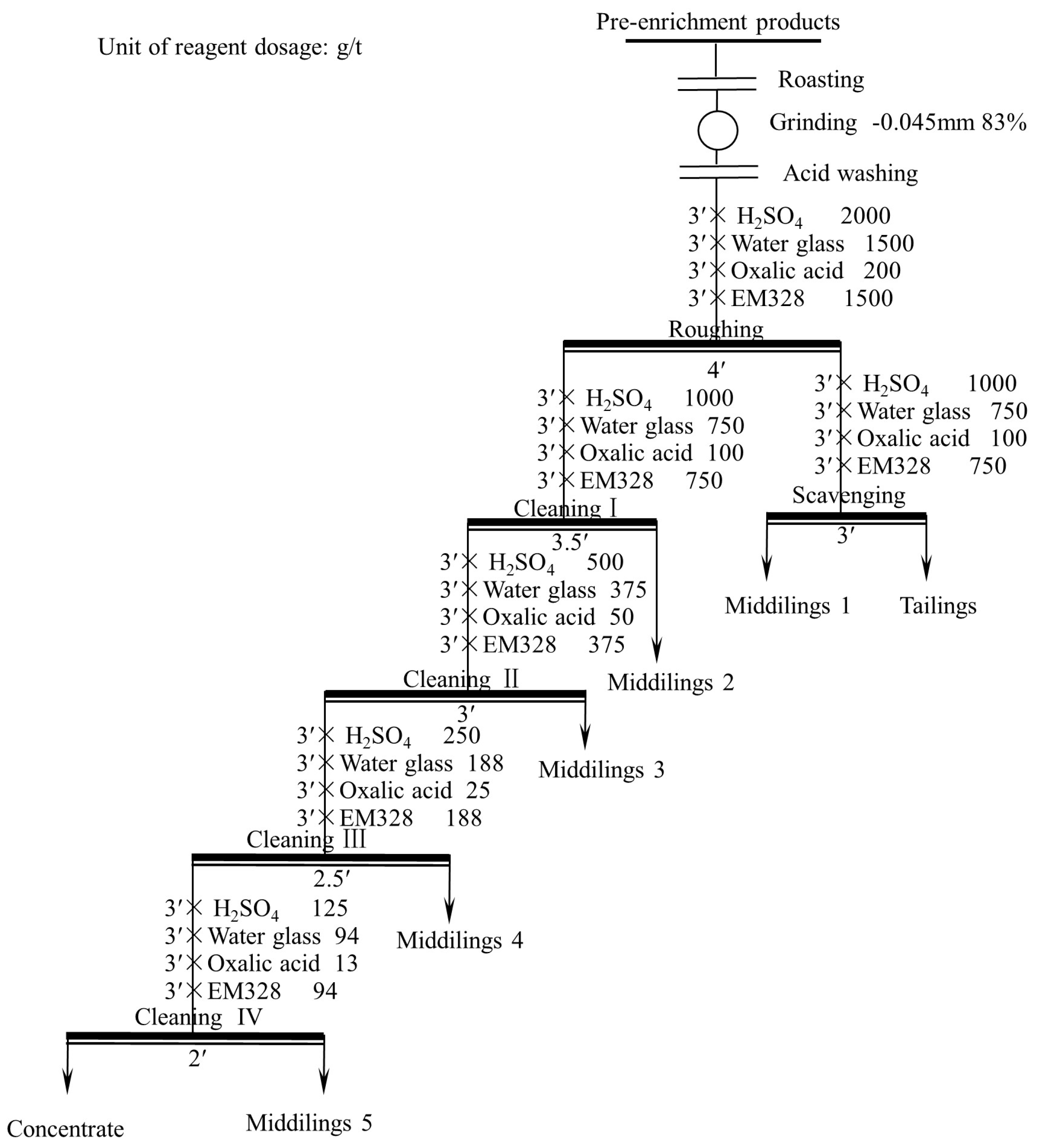
3.3.5. Open Flotation Circuit Test
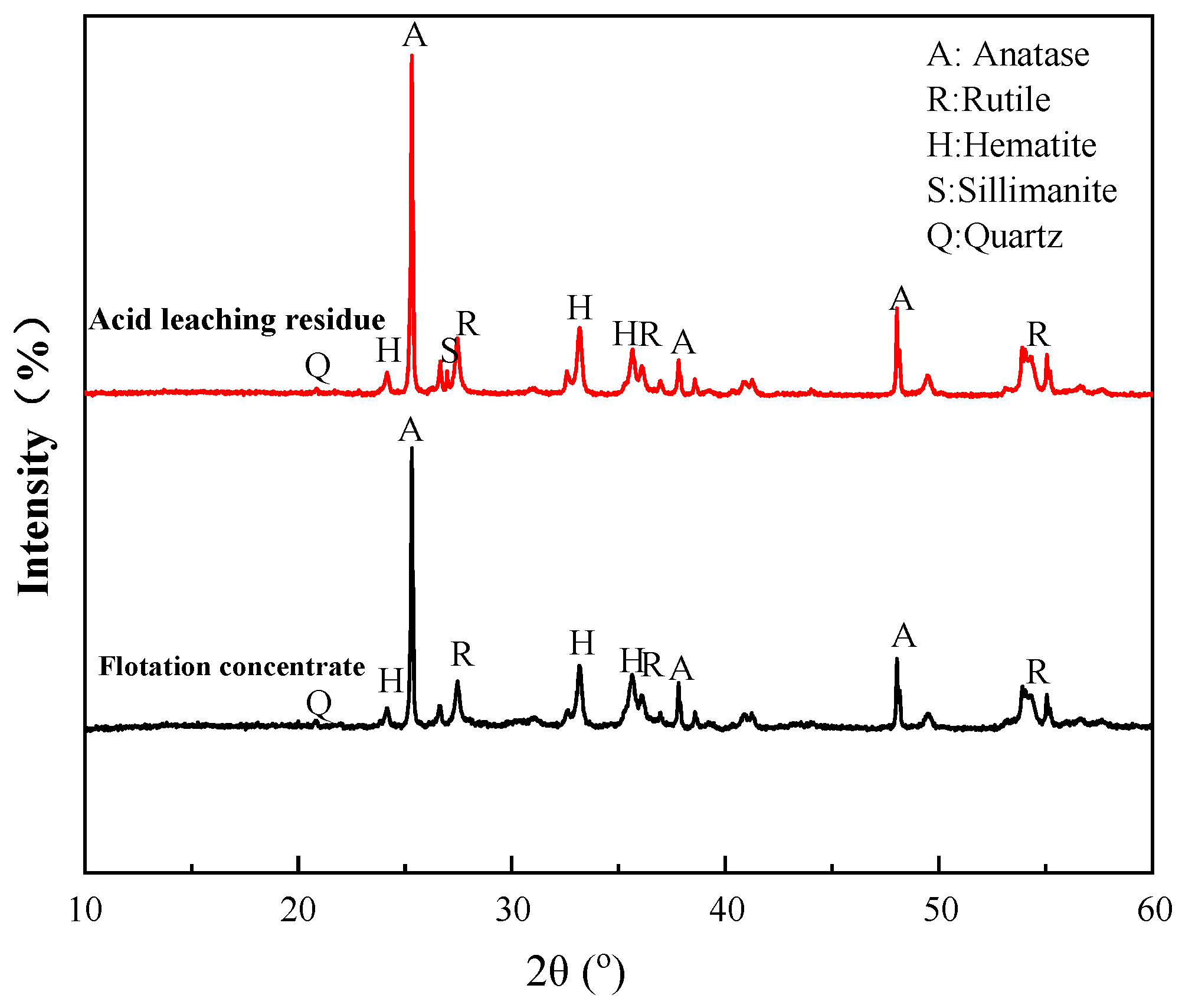
3.4. Leaching Exploration Test of Flotation Concentrate
4. Discussions
4.1. Strengthening Mechanism of Roasting Pretreatment
4.2. Mechanism of Acid Leaching
4.3. Route of Ti-Concentrate Production from Altered VTM Ore
5. Conclusions
- The study of VTM ore sample’s character showed that the TFe and TiO2 contents were 14.40% and 7.15%, respectively, with a high degree of alteration. Ti-bearing minerals, ilmenite and anatase, were considered to recover as composite mineral.
- Comparative titanium pre-concentration experiments showed that the gravity separation method achieved a better result, improving the TiO2 grade by approximately 7% at a grinding fineness of −0.074 mm, accounting for 35%.
- The oxidation roasting and acid washing pretreatments increased the flotation indexes obviously. Compared to the unroasted sample, the TiO2 recovery of the flotation concentrate rose from 47.78% to 85.56% at 800 °C roasting. Compared to the flotation concentrate obtained from the untreated sample, the TiO2 grade and recovery of that from acid-washed sample were enhanced to 3.68% and 55.14%, respectively.
- Flotation condition tests showed that the optimal conditions were a grinding fineness of −0.045 mm 83%, a sulfuric acid dosage of 2000 g/t, a water glass dosage of 1500 g/t, an oxalic acid dosage of 200 g/t, and an EM328 dosage of 1500 g/t. Open flotation circuit tests resulted in a TiO2 grade and recovery of 38.30% and 25.99%, respectively, in the flotation concentrate. A leaching exploration test showed that the TiO2 grade of the flotation concentrate could be improved to 53.90%, and the recovery was 91.05% (relative to flotation concentrate).
- XRD revealed that ilmenite in the VTM ore was converted into anatase and rutile during the roasting process at 600–800 °C, but pseudobrookite began to form by combining hematite, anatase, and rutile at 900 °C, which is harmful to flotation. Compared to the flotation concentrate, the content of Ti-bearing minerals was significantly increased in the acid leaching residue.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, E.; Gao, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, C.; Wen, J.; Gao, Y.; Huang, G.; Xu, S. Sustainable recovery of titanium from secondary resources: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Kim, S.; Kim, R.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Jung, H.-Y.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, H.-T. A review of vanadium electrolytes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K.; Wierzbicki, T. Determination of vanadium species in environmental samples. Talanta 2004, 64, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilligan, R.; Nikoloski, A.N. The extraction of vanadium from titanomagnetites and other sources. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphutha, M.; Ramaili, M.; Sitefane, M.; Goso, X. The effect of magnesia and alumina crucible wear on the smelting characteristics of titaniferous magnetite. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2017, 117, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.-N.; Zhang, L.; Sui, Z.-T.; Tu, G.-F. Selective enrichment of TiO2 and precipitation behavior of perovskite phase in titania bearing slag. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Bai, S. Upgrading of raw vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2019, 119, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-H.; Kou, J.; Sun, T.-C.; Wu, S.-C.; Zhao, Y.-Q. Effects of calcium compounds on the carbothermic reduction of vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Ma, Z.; Gao, G.; Qiu, K.; Peng, W. Process Mineralogy of Vanadium Titanomagnetite Ore in Panzhihua, China. Separations 2023, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Yang, J.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J. Impact of urbanization and industrialization upon surface water quality: A pilot study of Panzhihua mining town. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 22, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, T.; Ikuo, K. Titanomaghemite in igneous rocks. Am. Mineral. 1961, 46, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Shau, Y.H.; Torii, M.; Horng, C.S.; Peacor, D. Subsolidus evolution and alteration of titanomagnetite in ocean ridge basalts from Deep Sea Drilling Project/Ocean Drilling Program Hole 504B9 Leg 83: Implications for the timing of magnetization. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 23635–23649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, R. Alteration of detrital Fe-Ti oxides in Miocene fluvial deposits, central Jutland, Denmark. Bull. Geol. Soc. Den. 2003, 50, 141–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gruenewaldt, G.; Klemm, D.D.; Henckel, J.; Dehm, R.M. Exsolution features in titanomagnetites from massive magnetite layers and their host rocks of the upper zone, eastern Bushveld Complex. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, V.E. A Study of Titanium-Bearing Oxides in Heavy Mineral Deposits Along the East Coast of South Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.; Kanazawa, Y.; Sato, N.; Galtchandmani, P.; Jha, M.K.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. Beneficiation of Low-Grade Rare Earth Ore from Khalzan Buregtei Deposit (Mongolia) by Magnetic Separation. Minerals 2021, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbayoğlu, G.; Ümit Atalay, M. Beneficiation of bastnaesite by a multi-gravity separator. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 303–304, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Wang, W.P.; Yang, J.; You, J.G. Beneficiation of a low grade titanomagnetite ore in mining engineering. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 577, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, J. Characterization and pre-concentration of low-grade vanadium-titanium magnetite ore. Minerals 2017, 7, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y. Flotation separation of ilmenite from titanaugite using mixed collectors. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fang, S.; Shu, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Selective flotation and adsorption of ilmenite from titanaugite by a novel method: Ultrasonic treatment. Powder Technol. 2020, 363, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W. Flotability Improvement of Ilmenite Using Attrition-Scrubbing as a Pretreatment Method. Minerals 2017, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S. Kaolin Flotation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 256, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, K.R.; McDonald, R.G.; Pownceby, M.I.; Sparrow, G.J.; Zhang, W. Processing anatase ores for pigment production. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasomo, R.M.; Li, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Q.; Weng, X.; Mwangi, A.D.; Kiamba, E.; Song, S. Depression of the selective separation of rutile from almandine by Sodium Hexametaphosphate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 593, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapari, P.S.; Irannajad, M.; Mehdilo, A. Modification of ilmenite surface properties by superficial dissolution method. Miner. Eng. 2016, 92, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Waters, K.E.; Rowson, N.A.; Parker, D.J. Modification of ilmenite surface chemistry for enhancing surfactants adsorption and bubble attachment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdilo, A.; Irannajad, M. Comparison of microwave irradiation and oxidation roasting as pretreatment methods for modification of ilmenite physicochemical properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdilo, A.; Irannajad, M.; Rezai, B. Effect of oxidation roasting on ilmenite flotation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2014, 50, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Souza, R.F.M.; Aguilera, L.S.; de Campos, J.B.; Brocchi, E.A. Upgrade of titanium content in a vanadiferous titanomagnetite waste: Design of a roast-leach route based on thermodynamics simulations. Miner. Eng. 2022, 179, 107460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Deng, J. Influence of particle size on flotation separation of ilmenite, olivine, and pyroxene. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2021, 57, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xu, L.H.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.B.; Deng, W. Selective flotation separation of ilmenite from titanaugite using mixed anionic/cationic collectors. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 166, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.H.; Nagaraj, D.R.; Wang, S.S.; Hildebrand, T.M. Beneficiation of kaolin clay by froth flotation using hydroxamate collectors. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.P.; Wu, H.Q.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Shu, K.Q.; Xu, Y.B.; Yan, W.P.; Xu, L.H. Effects of microwave pre-treatment on the flotation of ilmenite and titanaugite. Miner. Eng. 2020, 155, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.F.; Zhang, R.L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.X.; Li, C.; Zeng, J. Kinetics Study on the Leaching of Copper from Calcification Roasting Copper Refining Slag Using Waste Acid. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.Q.; Cheng, M. Experimental study on preparation of titanium-rich material by pressure leaching of titanium concentrate from titanium dioxide waste acid. Ferroelectrics 2021, 581, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element (Compound) | TFe | TiO2 | V2O5 | Cr2O3 | P2O5 | S | K2O | Na2O |
| Content | 14.40 | 7.15 | 0.044 | 0.026 | 1.04 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 2.04 |
| Element (Compound) | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | MnO | Sr | Sc2O3 1 | |
| Content | 36.61 | 13.65 | 6.17 | 3.05 | 0.32 | 0.034 | 28.45 |
| Mineral | Titanomagnetite | Ilmenite | Anatase | Anatase-Chlorite Transition Phase | Chlorite | Feldspar |
| Content | 1.00 | 2.71 | 4.21 | 1.53 | 41.13 | 25.16 |
| Mineral | Quartz | Calcite | Titanite | Hornblende, Pyroxene | Apatite | Zoisite |
| Content | 10.71 | 5.45 | 1.33 | 4.15 | 2.01 | 0.61 |
| Product | Yield (%) | TiO2 Grade (%) | TiO2 Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic components | 7.56 | 6.71 | 7.41 |
| Concentrate | 17.66 | 10.43 | 26.94 |
| Tailings I | 37.73 | 4.66 | 25.71 |
| Tailings II | 37.05 | 7.37 | 39.93 |
| Feed | 100.00 | 6.84 | 100.00 |
| Product | Yield | TiO2 Grade | TiO2 Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrate | 10.10 | 38.30 | 25.99 |
| Middling 5 | 1.91 | 28.81 | 3.69 |
| Middling 4 | 2.61 | 21.64 | 3.79 |
| Middling 3 | 11.87 | 21.69 | 17.30 |
| Middling 2 | 34.19 | 15.04 | 34.55 |
| Middling 1 | 8.63 | 12.12 | 7.03 |
| Tailings | 30.69 | 3.71 | 7.65 |
| Feed | 100.00 | 14.88 | 100.00 |
| Product | Yield | TiO2 Grade | TiO2 Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaching residue | 64.70 | 53.90 | 91.05 |
| Flotation concentrate | 100.00 | 38.30 | 100.00 |
| Content | TFe | TiO2 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | P | Na2O | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaching residue | 22.88 | 53.90 | 6.38 | 2.33 | 0.37 | 0.84 | 0.009 | 0.07 | 0.02 |
| Flotation concentrate | 24.96 | 38.30 | 12.48 | 7.72 | 1.01 | 2.11 | 0.026 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Deng, W.; Liu, F. A New Route of Roasting-Flotation-Leaching for the Beneficiation of Ti-Bearing Minerals from Altered Vanadium Titanomagnetite. Minerals 2023, 13, 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121472
Xu Y, Chen C, Yang Y, Deng W, Liu F. A New Route of Roasting-Flotation-Leaching for the Beneficiation of Ti-Bearing Minerals from Altered Vanadium Titanomagnetite. Minerals. 2023; 13(12):1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121472
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yanbo, Chao Chen, Yaohui Yang, Wei Deng, and Feiyan Liu. 2023. "A New Route of Roasting-Flotation-Leaching for the Beneficiation of Ti-Bearing Minerals from Altered Vanadium Titanomagnetite" Minerals 13, no. 12: 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121472
APA StyleXu, Y., Chen, C., Yang, Y., Deng, W., & Liu, F. (2023). A New Route of Roasting-Flotation-Leaching for the Beneficiation of Ti-Bearing Minerals from Altered Vanadium Titanomagnetite. Minerals, 13(12), 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13121472





