Structural and Surface Modification of Oxalic-Acid-Activated Bentonites in Various Acid Concentrations for Bleaching Earth Synthesis—A Comparative Study †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Raw Materials
3.1.1. Chemical Analysis of Raw Materials
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction of Raw Materials
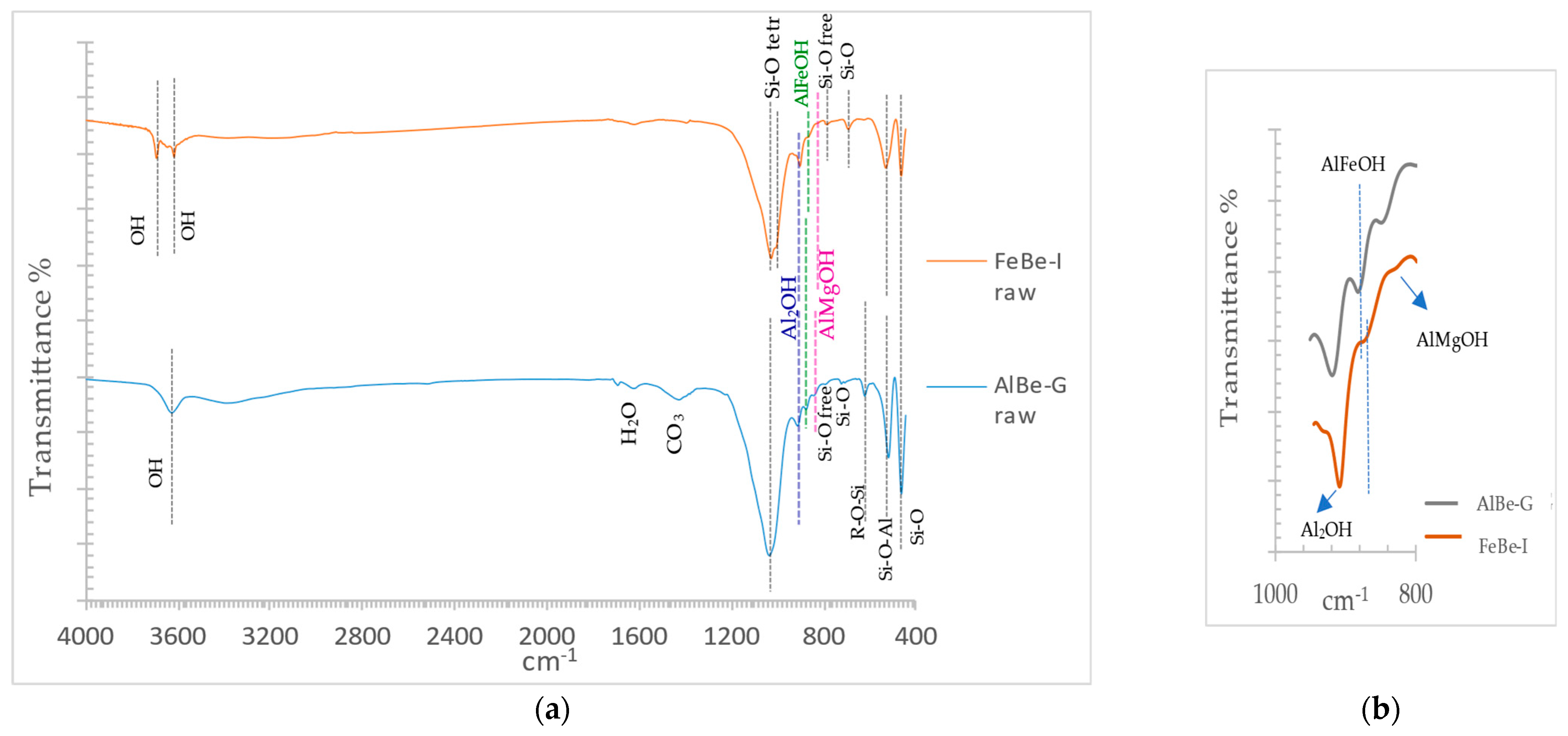
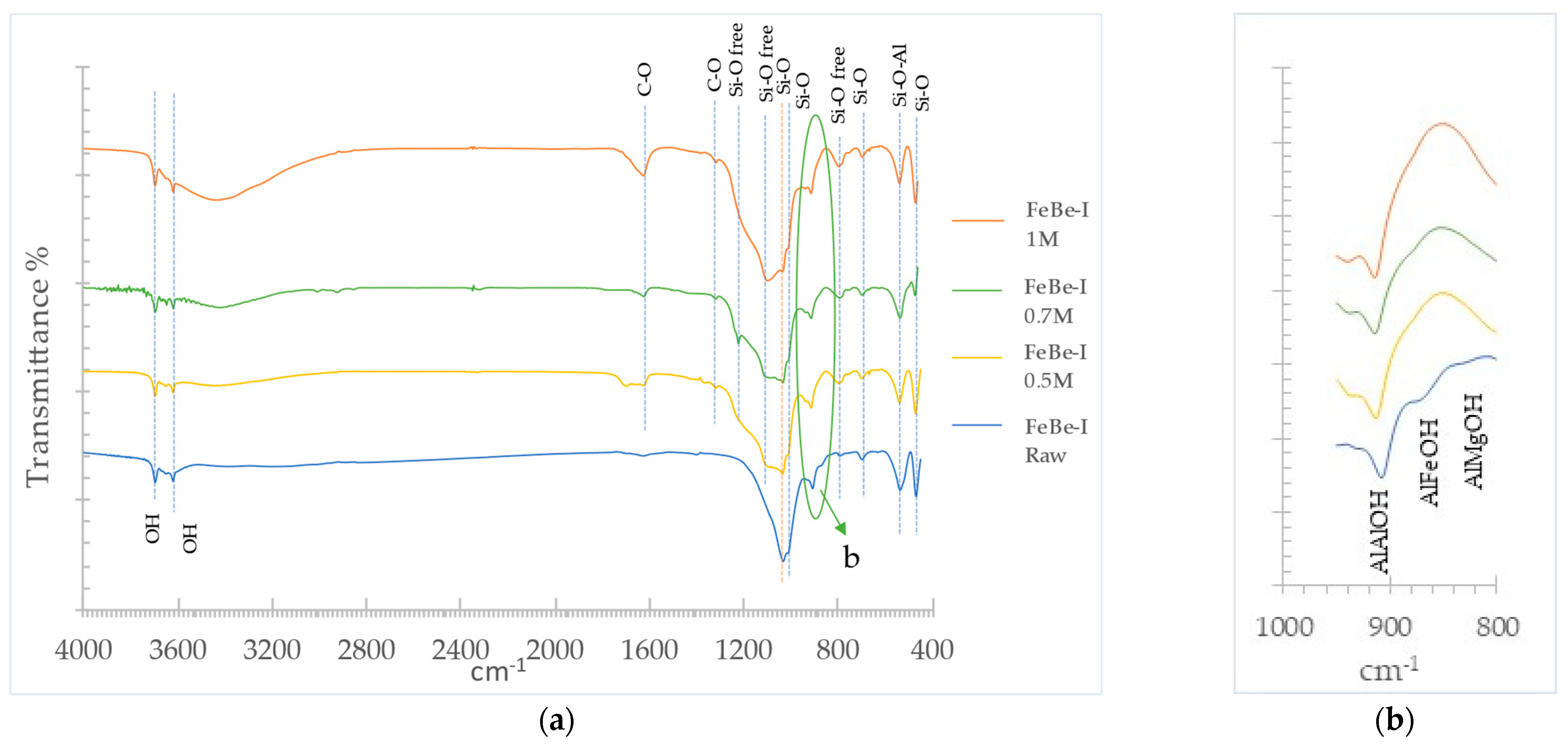
3.1.3. Infrared Spectroscopy of Raw Materials
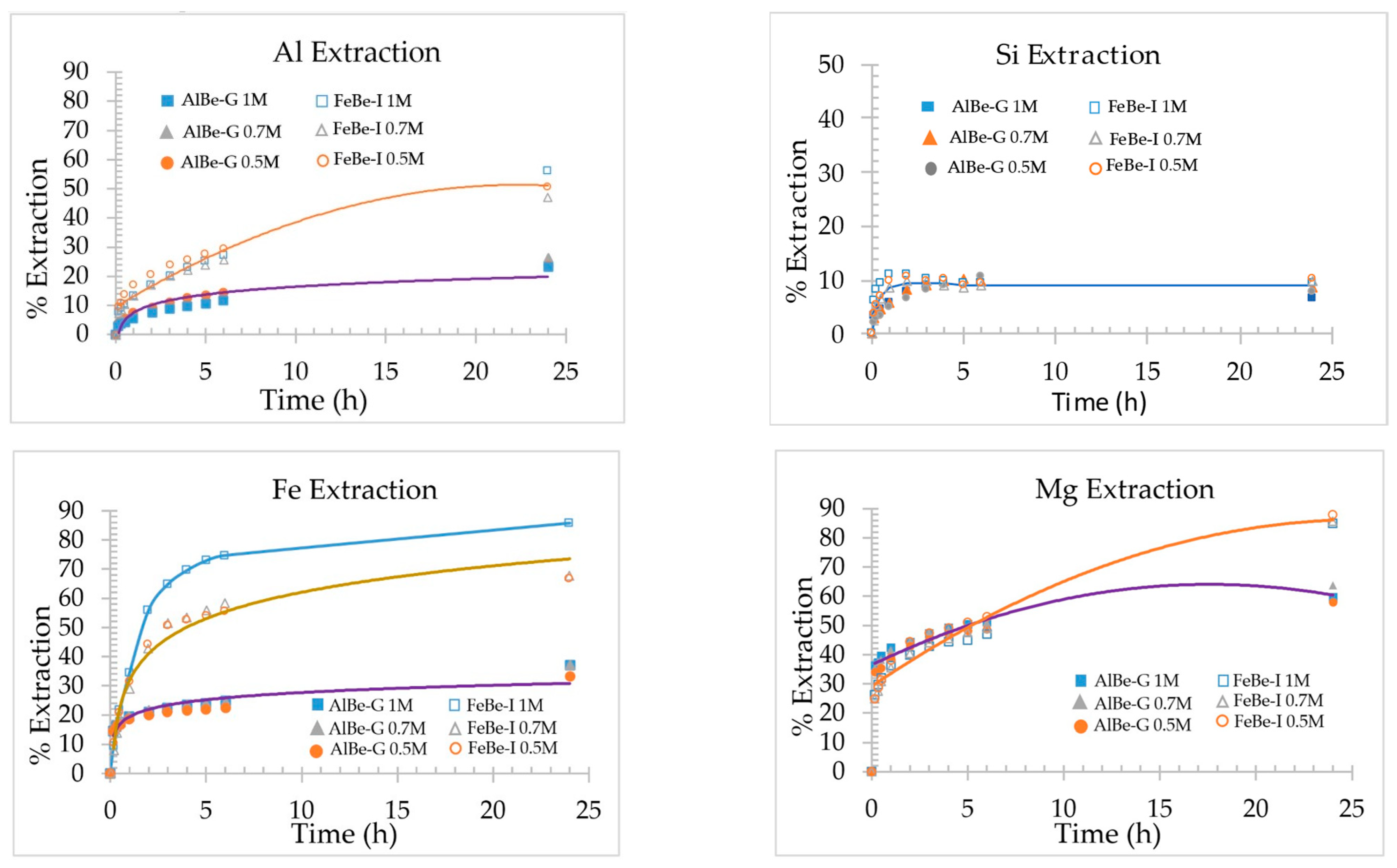
3.2. Metals’ Extraction during Acid Activation of Samples
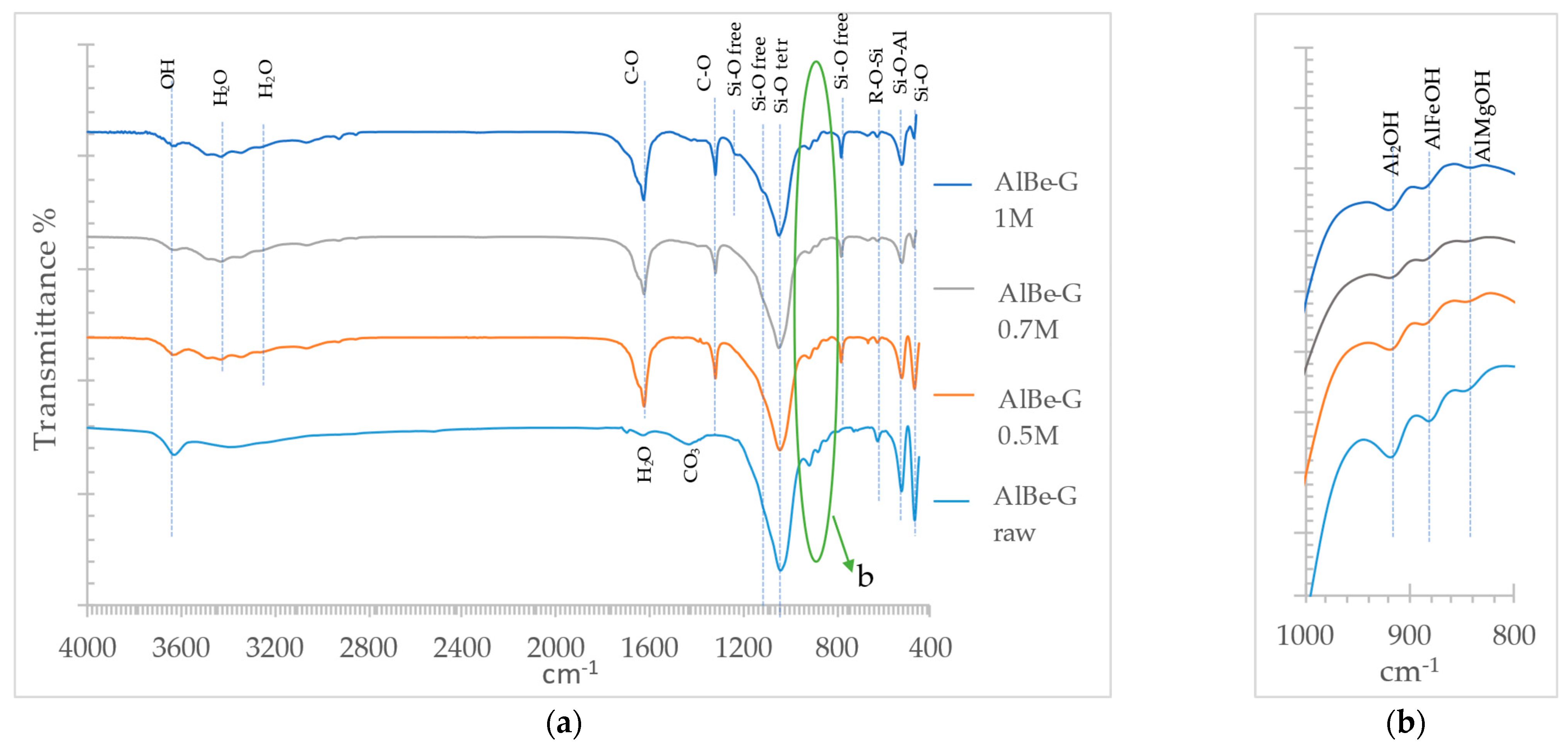
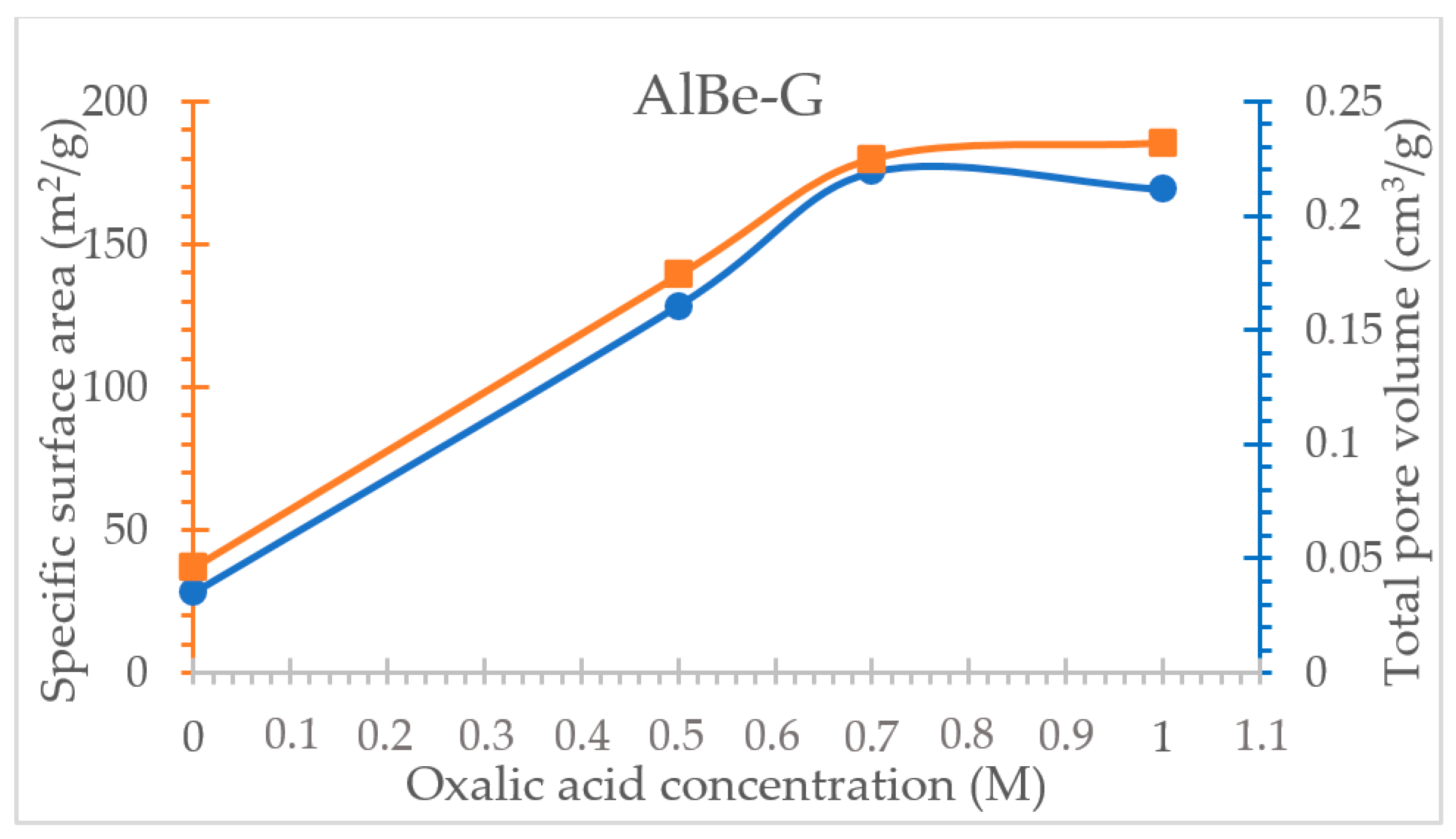
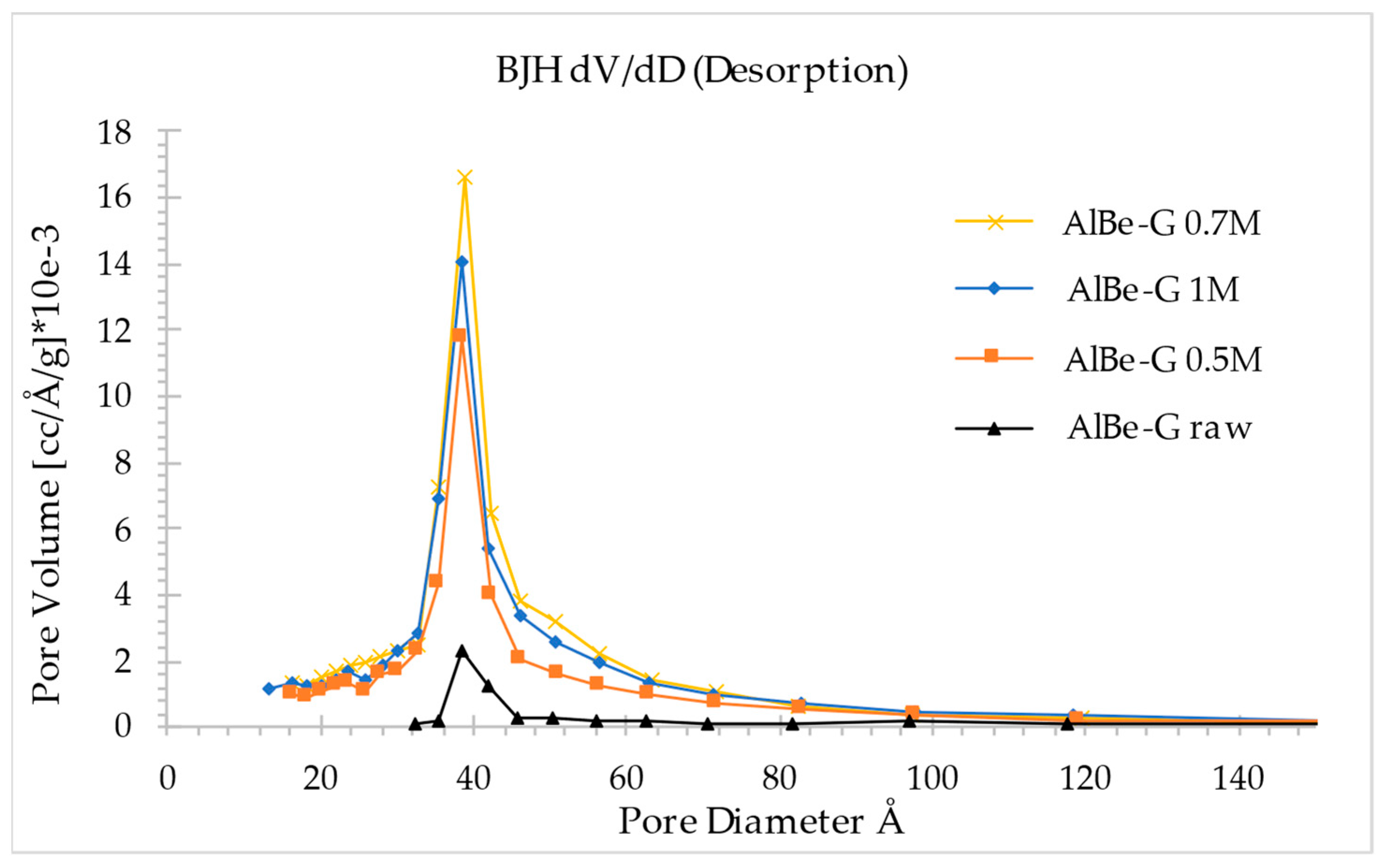
3.3. Oxalic Acid Activated Aluminum Smectite
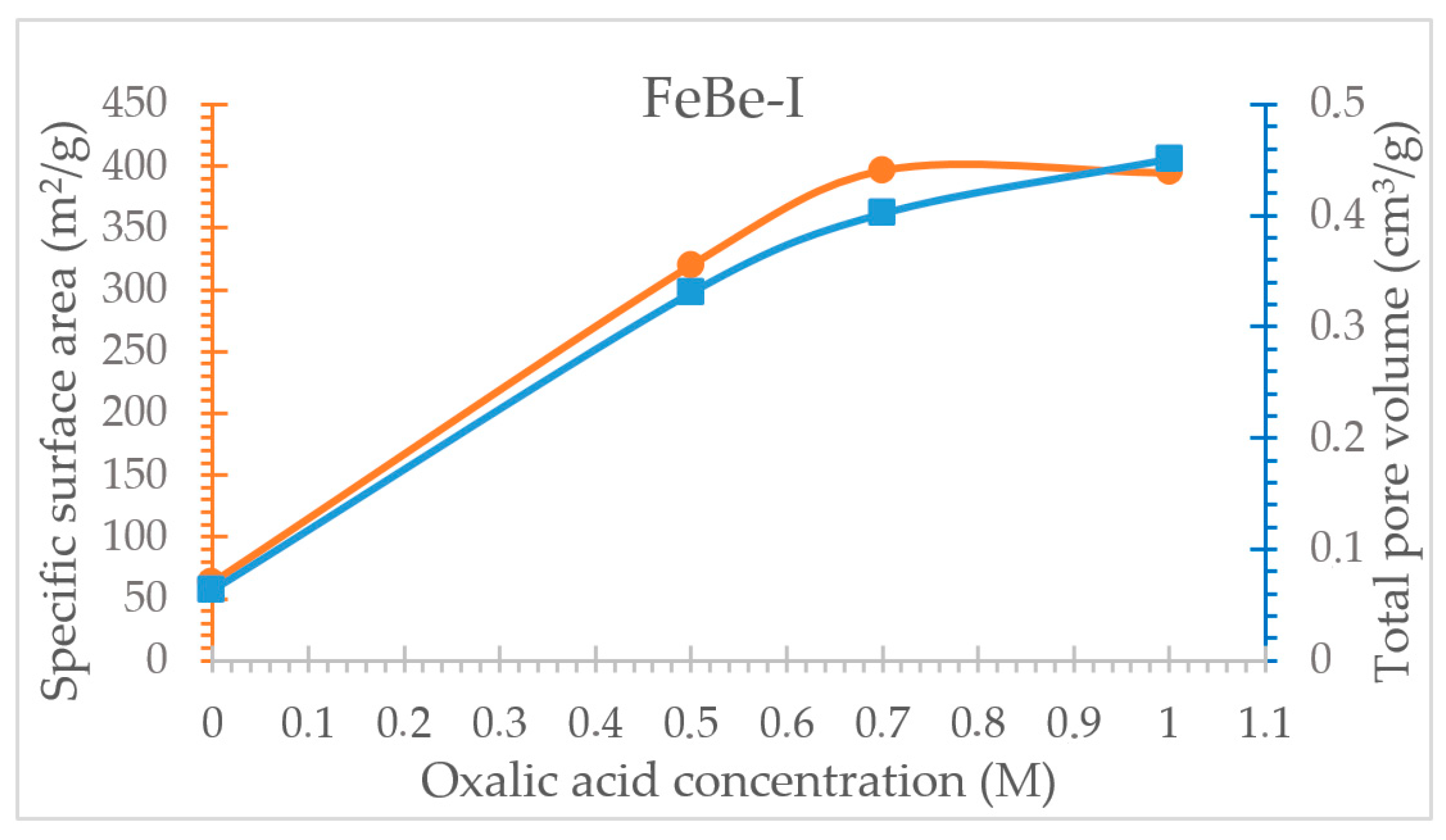
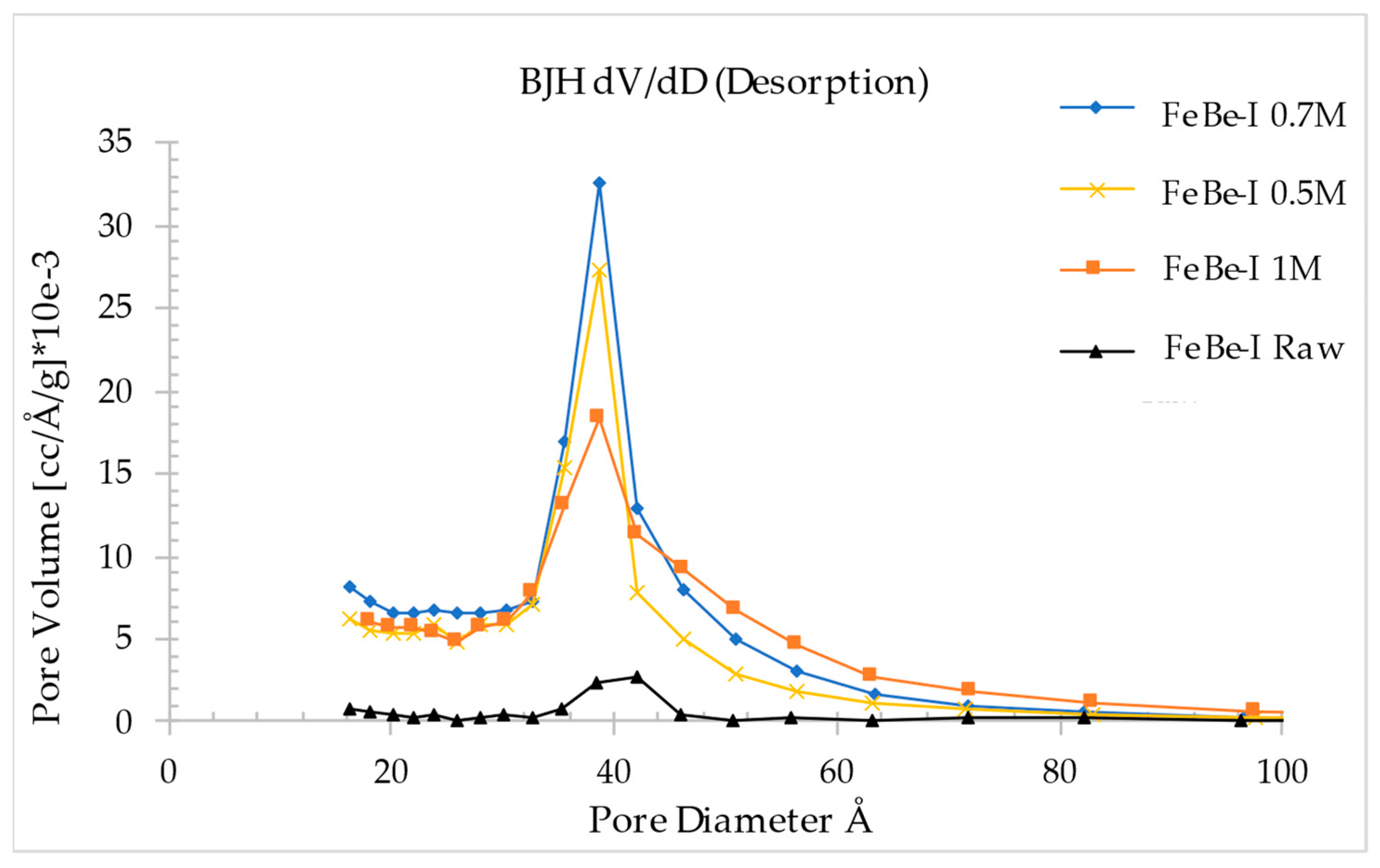
3.4. Oxalic Acid Activated Ferruginous Smectite
3.5. Bleaching Efficiency of Oxalic Acid Activated Bentonites
3.6. Comparison of Acid-Activated AlBe-G and FeBe-I Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergaya, F.; Theng, B.K.G.; Lagaly, G. Handbook of Clay Science, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 263. [Google Scholar]
- Hussin, F.; Aroua, M.K.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Textural characteristics, surface chemistry and activation of bleaching earth: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.E.; Scott, P.W.; Dunham, A.C. Acid activation and bleaching capacity of bentonites from the islands of Milos and Chios, Aegean, Greece. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.; Sarikaya, Y.; Alemdaroğlul, T.; Bozdoğan, I. The effect of acid activation on some physicochemical properties of a bentonite. Turk. J. Chem. 2002, 26, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Tomić, Z.P.; Logar, V.P.; Babic, B.M.; Rogan, J.R.; Makreski, P. Comparison of structural, textural and thermal characteristics of pure and acid trated bentonites from Aleksinac and Petrovac (Serbia). Spectrochim. Acta A 2011, 82, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Jasra, R.V.; Bhat, T.S.G. Evolution of porosity and surface acidity in montmorillonite clay on acid activation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesquera, C.; González, F.; Benito, I.; Blanco, C.; Mendioroz, S.; Pajares, J. Passivation of a montmorillonite by the silica created in acid activation. J. Mater. Chem. 1992, 2, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, W.P.; Anderson, J.S.; Raven, M.D.; Churchman, G.J. Mineralogy of a bentonite from Miles, Queensland, Australia and characterisation of its acid activation products. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 20, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J.; Bujdák, J.; Janek, M.; Komadel, P. Comparative FT-IR study of structural modifications during acid treatment of dioctahedral smectites and hectorite. Spectrochim. Acta A 1998, 54, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaki, H.; Salem, A.; Jafarizad, A. Kinetic model for the isothermal activation of bentonite by sulfuric acid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 108, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Chudasama, C.D.; Jasra, R.V. Determination of structural modification in acid activated montmorillonite clay by FT-IR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A 2006, 64, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, S.A.; Ullman, W.J. Feldspar dissolution in acidic and organic solutions: Compositional and pH dependence of dissolution rate. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cama, J.; Ganor, J. The effects of organic acids on the dissolution of silicate minerals: A case study of oxalate catalysis of kaolinite dissolution. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozalen, M.; Huertas, F.J. Comparative effect of chrysotile leaching in nitric, sulfuric and oxalic acids at room temperature. Chem. Geol. 2013, 352, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, M.K. Effects of oxalic and citric acids on three clay minerals after incubation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 99, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, S.; Samsuri, A. A study of iron removal from Sabah montmorillonite by extracting with organic acid. In Proceedings of the Regional Conference for Young Chemists USM, Penang, Malaysia, 13–14 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Naqvi, S.H.J.; Kazmi, M.A.; Ashraf, Z. Surface activation of fuller’s earth (bentonite clay) using organic acids. Sci. Int. 2015, 27, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Taxiarchou, M.; Douni, I. The effect of oxalic acid activation on the bleaching properties of a bentonite from Milos Island, Greece. Clay Miner. 2014, 49, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.E.; Garcia-Palma, S.; Rozalen, M.; Johnston, C.T.; Huertas, F.J. Kinetics of montmorillonite dissolution, an experimental study of the effect of oxalate. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.E.; Emiroglu, C.; García, D.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I.; Huertas, F.J. Modeling the Adsorption of Oxalate onto Montmorillonite. Langmuir 2015, 31, 11825–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K. Practical Guide to Vegetable Oil Processing, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK; AOCS Press: London, UK, 2017; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Balestri, S.; Beretta, S. Poverty Eradication: Access to Land, Access to Food; EduCatt: Milan, Italy, 2015; pp. 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F. Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products, 6th ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volumes 1–6, pp. 285–339. [Google Scholar]
- Noyan, H.; Önal, M.; Sarikaya, Y. The effect of sulphuric acid activation on the crystallinity, surface area, porosity, surface acidity, and bleaching power of a bentonite. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didi, M.A.; Makhoukhi, B.; Azzouz, A.; Villemin, D. Colza oil bleaching through optimized acid activation of bentonite. A comparative study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 42, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagüzel, C.; Çetinel, T.; Boylu, F.; Çinku, K.; Çelik, M.S. Activation of (Na, Ca)-bentonites with soda and MgO and their utilization as drilling mud. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liua, Y.; Meib, Y.; Liuc, H.; Xu, D.; Peng, C. Identification and Assessment of Natural Sodium Bentonite. Key Eng. Mater. 2015, 633, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Środoń, J. Quantitative X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Clay-Bearing Rocks from Random Preparations. Clays Clay Miner. 2001, 49, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, H.M.; Ehrlicher, U.; Gilg, H.A.; Jordan, R.; Murad, E.; Onnich, K. Mineralogical and chemical characteristics of five nontronites and Fe-rich smectites. Clay Miner. 1999, 34, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temuujin, J.; Jadambaa, T.; Burmaa, G.; Erdenechimeg, S.; Amarsanaa, J.; MacKenzie, K.J.D. Characterisation of acid activated montmorillonite clay from Tuulant (Mongolia). Ceram. Int. 2004, 30, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, A.; Afsin, B.; Caglar, B.; Koksal, E. Characterization and pillaring of a Turkish bentonite (Resadiye). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, B.A. A Mössbauer and I.R. Spectroscopic Study of the Structure of Nontronite. Clays Clay Miner. 1976, 24, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Ding, Z. Near-infrared spectroscopic study of nontronites and ferruginous smectite. Spectrochim. Acta A 2002, 58, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Meena, S.K.; Kusurkar, T.S.; Singh, S.K.; Sethy, N.K.; Bhargava, K.; Sarkar, S.; Das, M. Carbondioxide gating in silk cocoon. Biointerphases. 2012, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouqérol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, R.; Díaz, V.; Santos, P.S. Studies on the acid activation of Brazilian smectitic clays. Quim. Nova 2001, 24, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Sarioğlan, Ş.; Yüzer, H.; Koral, M. Acid Activation and Bleaching Performance of Turkish (Somas) Bentonite in Crude Soybean Oil. Part. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokaya, R.; Jones, W.; Davies, M.E.; Whittle, M.E. Chlorophyll adsorption by alumina-pillared acid-activated clays. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1993, 70, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinney, G.; Chichester, C.O. The Color Problem in Foods. In Advances in Food Research, 1st ed.; Mrak, E.M., Stewart, G.F., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1954; Volume 5, pp. 301–351. [Google Scholar]
- Boki, K.; Kubo, M.; Kawasaki, N.; Mori, H. Adsorption Isotherms of Pigments from Alkali Refined Vegetable Oils with Clay Minerals. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henache, Z.; Boukerroui, A.; Kashi, I. Modeling of the soybean oil bleaching and optimization of its conditions in the refining process for environmental interest. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2018, 17, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Oxides (wt.%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | L.O.I. | Total | |
| AlBe-G | 48.28 | 17.25 | 3.68 | 5.28 | 9.01 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.71 | 15.10 | 100.00 |
| FeBe-I | 46.96 | 17.66 | 19.32 | 2.80 | 1.75 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 1.39 | 9.05 | 100.00 |
| AlBe-G Raw | AlBe-G 0.5 M | AlBe-G 0.7 M | AlBe-G 1 M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 28.11 | 128.37 | 175.04 | 169.13 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 65.98 | 54.10 | 51.41 | 54.84 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.046 | 0.174 | 0.225 | 0.232 |
| FeBe-I Raw | FeBe-I 0.5 M | FeBe-I 0.7 M | FeBe-I 1 M | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 63.21 | 320.16 | 396.84 | 394.87 |
| Average pore diameter (Å) | 40.20 | 41.31 | 40.54 | 45.72 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.064 | 0.331 | 0.402 | 0.451 |
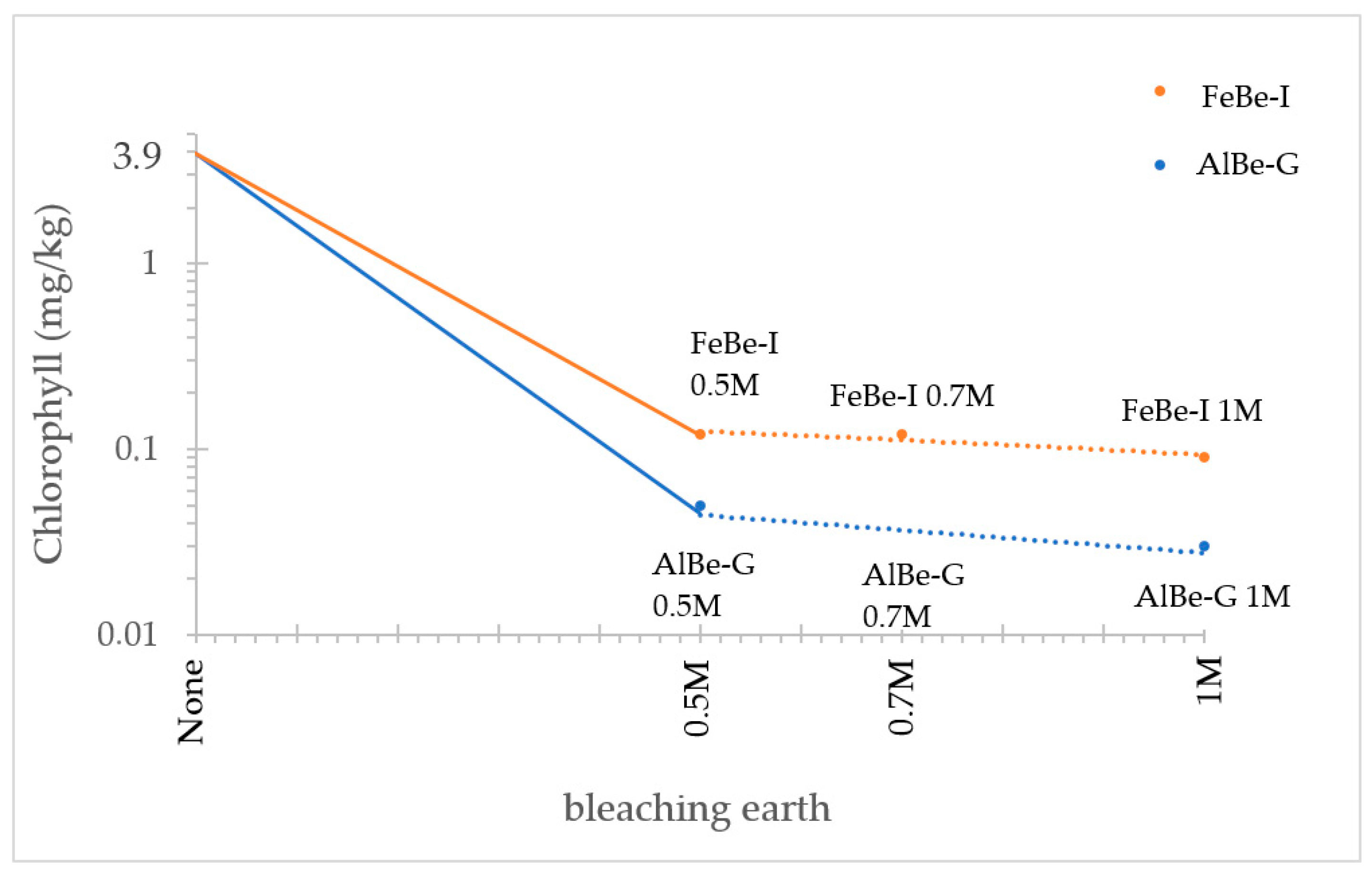
| Bleaching Earth | Chlorophyll (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| None | 3.90 |
| Tonsil | <0.01 |
| AlBe-G 0.5 M | 0.05 |
| AlBe-G 0.7 M | 0.03 |
| AlBe-G 1 M | 0.03 |
| FeBe-I 0.5 M | 0.12 |
| FeBe-I 0.7 M | 0.12 |
| FeBe-I 1 M | 0.09 |
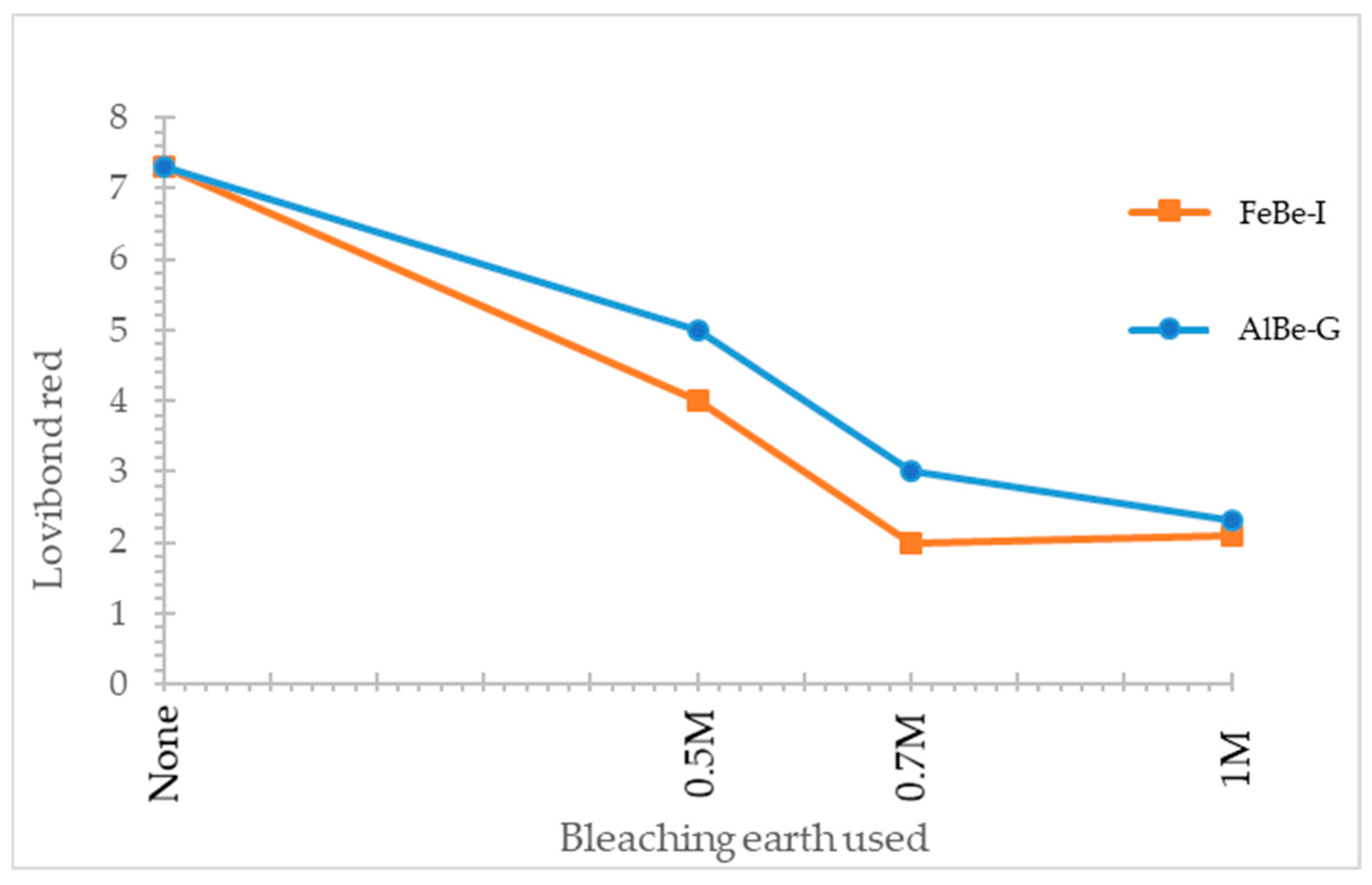
| Bleaching Earth | Lovibond Red | Lovibond Yellow |
|---|---|---|
| None | 7.3 | 40.0 |
| Tonsil | 4.0 | 30.0 |
| AlBe-G 0.5 M | 5.0 | 30.0 |
| AlBe-G 0.7 M | 3.0 | 30.0 |
| AlBe-G 1 M | 2.3 | 30.0 |
| FeBe-I 0.5 M | 4.0 | 40.0 |
| FeBe-I 0.7 M | 2.0 | 40.0 |
| FeBe-I 1 M | 2.1 | 30.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsakiri, D.; Douni, I.; Taxiarchou, M. Structural and Surface Modification of Oxalic-Acid-Activated Bentonites in Various Acid Concentrations for Bleaching Earth Synthesis—A Comparative Study. Minerals 2022, 12, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060764
Tsakiri D, Douni I, Taxiarchou M. Structural and Surface Modification of Oxalic-Acid-Activated Bentonites in Various Acid Concentrations for Bleaching Earth Synthesis—A Comparative Study. Minerals. 2022; 12(6):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060764
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsakiri, Danai, Iliana Douni, and Maria Taxiarchou. 2022. "Structural and Surface Modification of Oxalic-Acid-Activated Bentonites in Various Acid Concentrations for Bleaching Earth Synthesis—A Comparative Study" Minerals 12, no. 6: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060764
APA StyleTsakiri, D., Douni, I., & Taxiarchou, M. (2022). Structural and Surface Modification of Oxalic-Acid-Activated Bentonites in Various Acid Concentrations for Bleaching Earth Synthesis—A Comparative Study. Minerals, 12(6), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060764






