MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Subsampling Preparation
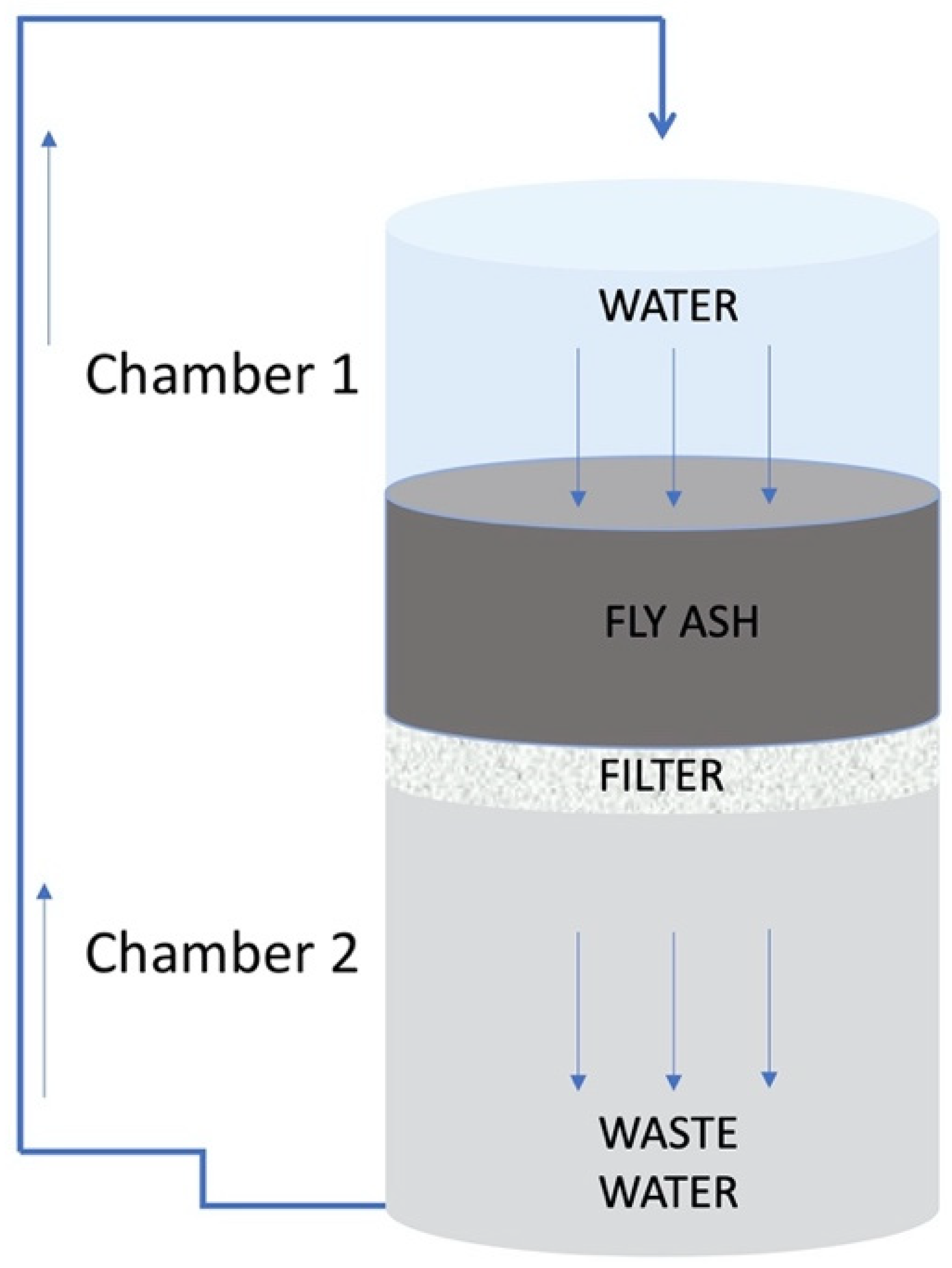
2.2. Falling Head Water Washing Implementation
2.3. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
2.4. Washing and Leaching Tests
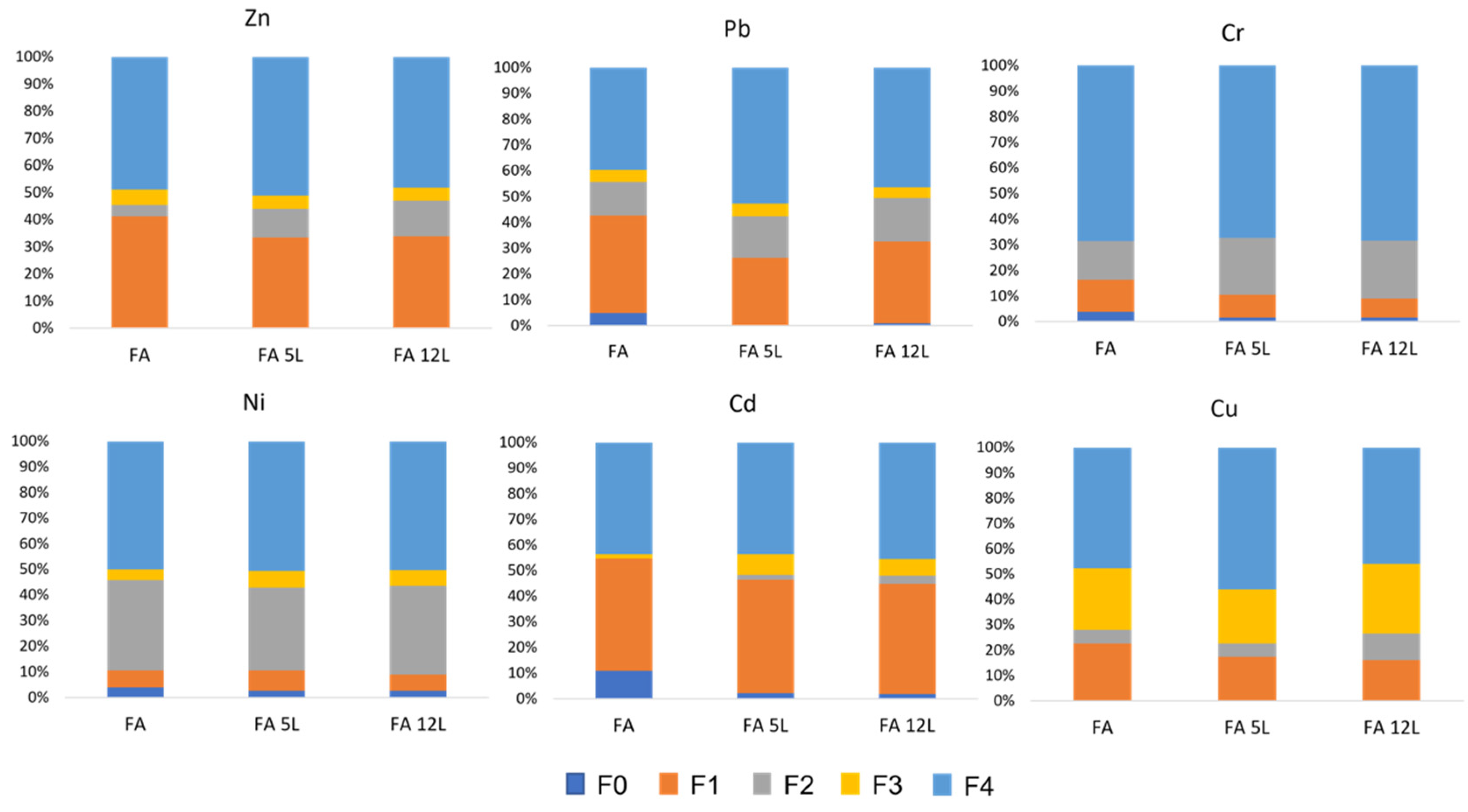
2.5. Sequential Extraction Method
3. Results
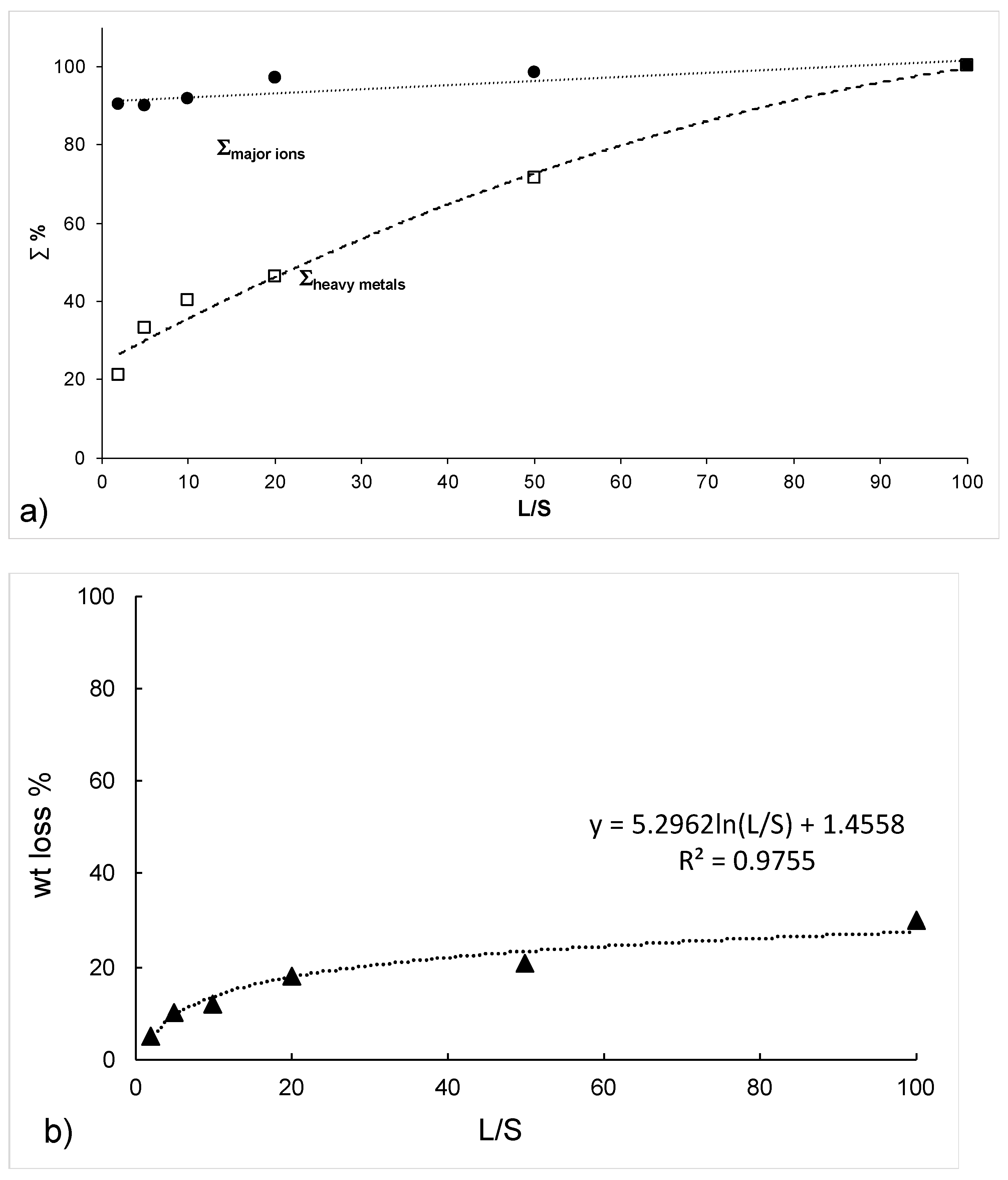
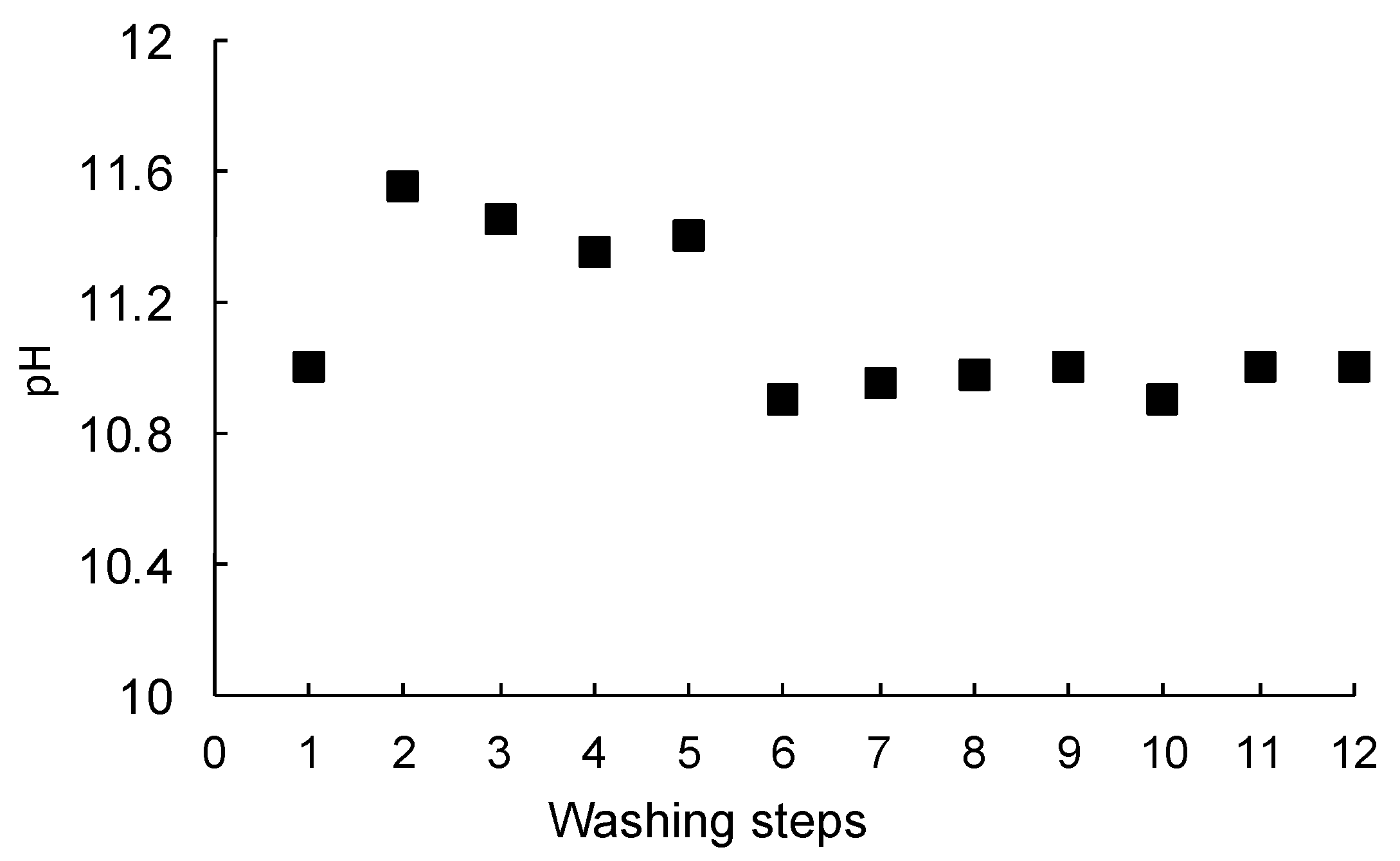
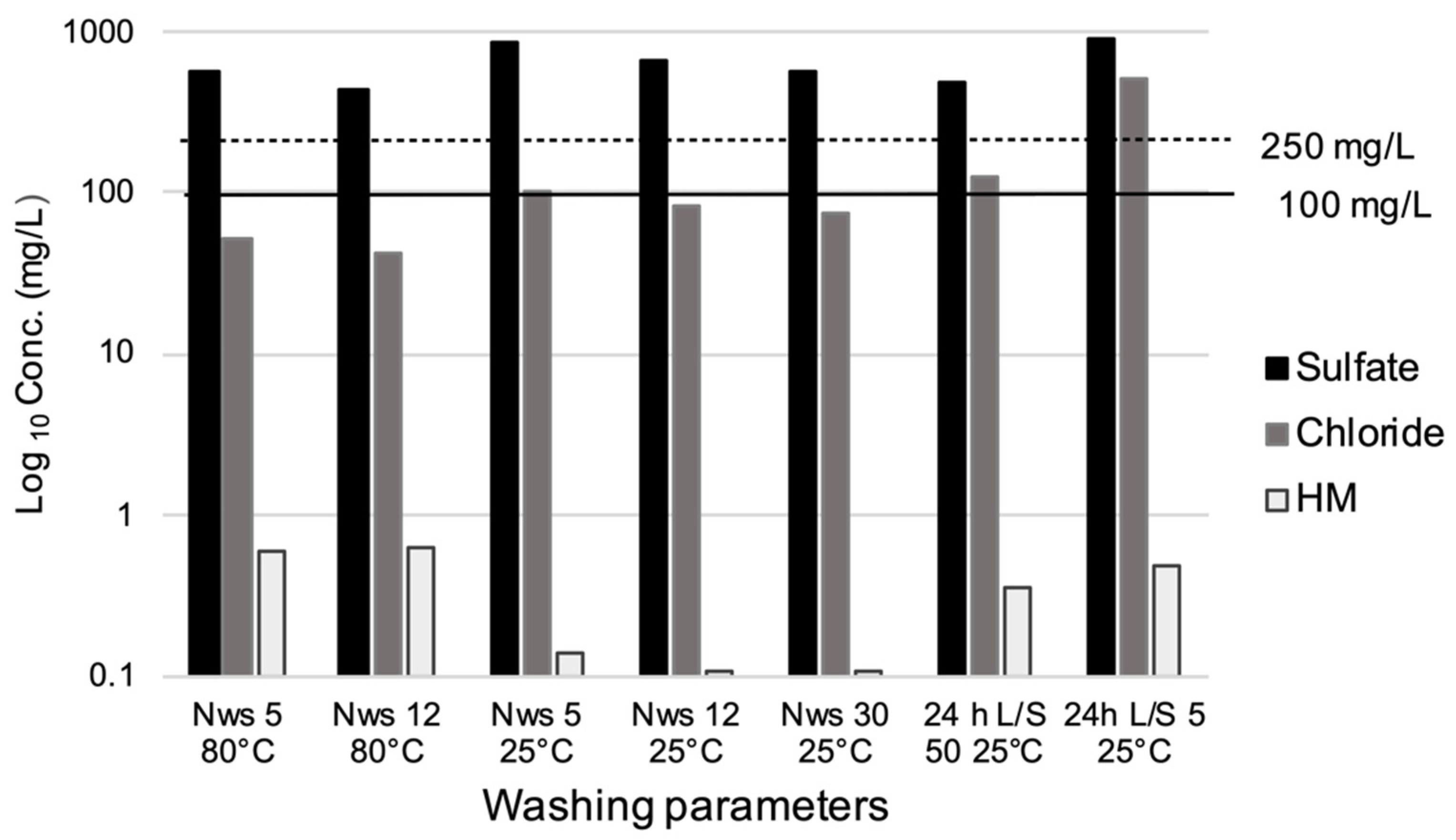
3.1. Washing Tests
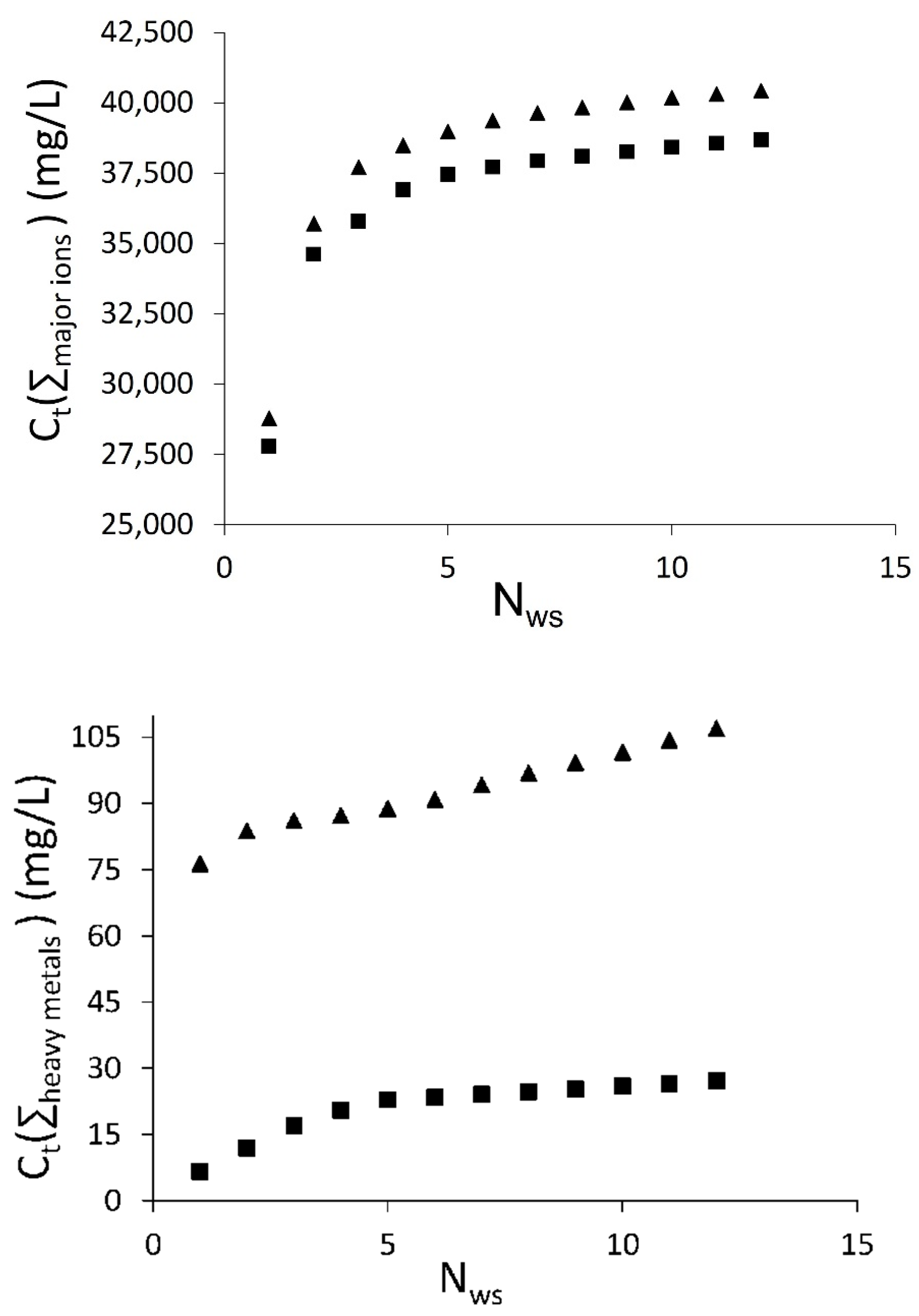
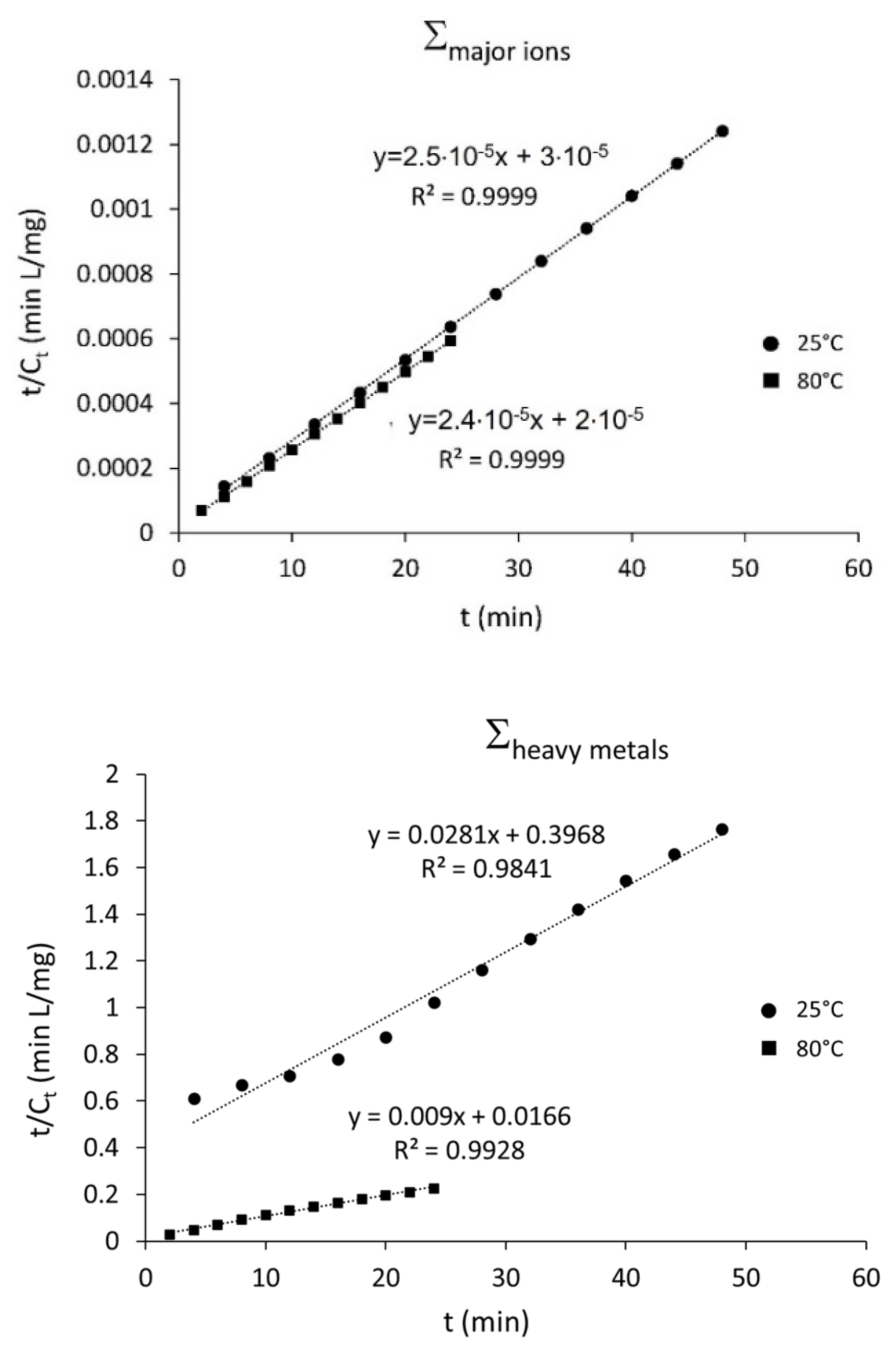
3.2. Falling Head Water Washing (FH-WW)
3.3. Leaching Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quina, M.J.; Bontempi, E.; Bogush, A.; Schlumberger, S.; Weibel, G.; Braga RFunari, V.; Hyks, J.; Rasmussen, E.; Lederer, J. Technologies for the management of MSW incineration ashes from gas cleaning: New perspectives on recovery of secondary raw materials and circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, C.K.; Das, P.; Samanta, S.; Ganguly, A.; Chatterjee, P.K. Municipal Solid Wastes—A Promising Sustainable Source of Energy: A Review on Different Waste-to-Energy Conversion Technologies. In Energy Recovery Processes from Wastes; Ghosh, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.M.; Snellings, R.; Van den Heede, P.; Matthys, S.; De Belie, N. The Use of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Ash in Various Building Materials: A Belgian Point of View. Materials 2018, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.H.; Ip, A.W.; Barford, J.P.; McKay, G. Use of incineration MSW ash: A review. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1943–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02008L0098-20180705 (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Dontriros, S.; Likitlersuang, S.; Janjaroen, D. Mechanisms of chloride and sulfate removal from municipal-solid-waste-incineration fly ash (MSWI FA): Effect of acid-base solutions. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y. Chlorine removal from MSWI fly ash by thermal treatment: Effects of iron/aluminum additives. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Xiong, Z.; Tian, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Influence of carbonation under oxy-fuel combustion flue gas on the leachability of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, W.Q.; Luo, G.Q.; Li, A.J.; Lu, Z.L.; Yao, H. Comparison of CaO’s effect on the fate of heavy metals during thermal treatment of two typical types of MSWI fly ashes in China. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikravan, M.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Maknoon, R. Study on physiochemical properties and leaching behavior of residual ash fractions from a municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, E.; Proskurnin, M.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash composition analysis: A case study of combined chelatant-based washing treatment efficiency. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, D.; Caviglia, C.; Destefanis, E.; Agostino, A.; Boero, R.; Marinoni, N.; Bonadiman, C.; Pavese, A. Influence of speciation distribution and particle size on heavy metal leaching from MSWI fly ash. Waste Manag. 2022, 138, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginés, O.; Chimenos, J.M.; Vizcarro, A.; Formosa, J.; Rosell, J.R. Combined use of MSWI bottom ash and fly ash as aggregate in concrete formulation: Environmental and mechanical considerations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, F.; Messina, F.; Cioffi, R. Recycling of MSWI fly ash by means of cementitious double step cold bonding pelletization: Technological assessment for the production of lightweight artificial aggregates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakubu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ping, D.; Shu, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of pH dynamics on solidification/stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, A.; Farina, I.; Race, M.; Colangelo, F.; Cioffi, R.; Fabbricino, M. Pre-treatments of MSWI fly-ashes: A comprehensive review to determine optimal conditions for their reuse and/or environmentally sustainable disposal. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gencturk, B.; Willam, K.; Attar, A. Carbonation-induced and chloride-induced corrosion in reinforced concrete structures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.H.; Nam, B.H.; An, J.; Youn, H. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Ashes as Construction Materials—A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhong, P.; Yan, J. Review of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2020, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Bilo, F.; Zanoletti, A.; Ponti, J.; Valsesia, A.; La Spina, R.; Zacco, A.; Bontempi, E. Zero-waste approach in municipal solid waste incineration: Reuse of bottom ash to stabilize fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Ahamed, A.; Lisak, G. Environmental perspectives of recycling various combustion ashes in cement production—A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Klupsch, E.; Kirkelund, G.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Dias-Ferreira, C. Recycling of MSWI fly ash in clay bricks-effect of washing and electrodialytic treatment. In WASTES—Solutions, Treatments and Opportunities II; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Son, J.; Yoo, Y.; Park, S.; Huh, I.-S.; Park, J. Heavy-metal reduction and solidification in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using water, NaOH, KOH, and NH4OH in combination with CO2 uptake procedure. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmark, D.; Lagerkvist, A. Controlling the mobility of chromium and molybdenum in MSWI fly ash in a washing process. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Chlorides Removal and Control through Water-washing Process on MSWI Fly Ash. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Blasenbauer, D.; Mallow, O.; Lederer, J.; Winter, F.; Fellner, J. Thermal co-treatment of combustible hazardous waste and waste incineration fly ash in a rotary kiln. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Funari, V.; Ferrari, R. Bioleaching for resource recovery from low-grade wastes like fly and bottom ashes from municipal incinerators: A SWOT analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkelund, G.M.; Skevi, L.; Ottosen, L.M. Electrodialytically treated MSWI fly ash use in clay bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhou, L.; Liu, L.; Xia, M. Ultrasound-enhanced electrokinetic remediation for removal of Zn, Pb, Cu and Cd in municipal solid waste incineration fly ashes. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boom, A.; Aubert, J.E.; Degrez, M. Carbonation of municipal solid waste incineration electrostatic precipitator fly ashes in solution. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Yang, L.; Bai, J. Enhanced geopolymeric co-disposal efficiency of heavy metals from MSWI fly ash and electrolytic manganese residue using complex alkaline and calcining pre-treatment. Waste Manag. 2019, 98, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, X. Immobilization of MSWI fly ash through geopolymerization: Effects of water-wash. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, Z.; Giannis, A.; Dong, Z.L.; Lisak, G.; Ng, W.J. Characteristics of incineration ash for sustainable treatment and reutilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16974–16997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhar, A.H.; Chen, S.; Wang, F. Incineration Fly Ash and its treatment to possible utilization: A review. Energies 2020, 13, 6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Steefel, C.I.; Yang, L. Scale dependence of mineral dissolution rates within single pores and fractures. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, A. Chapter 2: Principle of Groundwater Flow. In Fractional Operators with Constant and Variable Order with Application to Geo-Hydrology; Atangana, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 15–47. ISBN 9780128096703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Kang, Q.; Viswanathan, H.S.; Tao, W.Q. Pore-scale study of dissolution-induced changes in hydrologic properties of rocks with binary minerals. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 9343–9365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H.; Van Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Cryst. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder-Hubscher, V.; Lagarde, F.; Leroy, M.J.F.; Coughanowr, C.; Enguehard, F. 523 Application of a sequential extraction procedure to study the release of elements from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 451, 285–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerial Decree n. 186 Dated 5 April 2006. Regulatory That Modified Ministerial Decree Dated 5 February 1998. Official Gazette n. 115. 19 May 2006. Available online: http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/gu/2010/12/01/281/sg/pdf (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- G.U. Ministerial Decree 27/09/2010-Definition of the Criteria of Admissibility of Landfill Waste. Serie Generale n-281. 1 December 2010. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/id/2010/12/01/10A14538/sg (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Gharabaghi, M.; Irannajad, M.; Azadmehr, A. Leaching kinetics of nickel extraction from hazardous waste by sulphuric acid and optimization dissolution conditions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.D.; Pina, P.S.; Lima, E.V.O.; da Silva, C.A.; Leão, V.A. Kinetics of sulphuric acid leaching of a zinc silicate calcine. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Chern, J.M. Extraction kinetics of heavy metal-containing sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakultung, S.; Pruksathorn, K.; Hunsom, M. Simultaneous recovery of valuable metals from spent mobile phone battery by an acid leaching process. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 24, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Harouna-Oumarou, H.A.; Fauduet, H.; Porte, C. Kinetics and model building of leaching of water-soluble compounds of Tilia sapwood. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbogoro, M.; Snowden, E.; Edwards, M.; Peruffo, M.; Unwin, P. Intrinsic Kinetics of Gypsum and Calcium Sulfate Anhydrite Dissolution: Surface Selective Studies under Hydrodynamic Control and the Effect of Additives. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 10147–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Z.; Namioka, T.; Yamada, N.; Ninomiya, Y. Study on the species of heavy metals in MSW incineration fly ash and their leaching behavior. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 152, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funatsuki, A.; Takaoka, M.; Oshita, K.; Takeda, N. Methods of determining lead speciation in fly ash by X-ray absorption fine-structure spectroscopy and a sequential extraction procedure. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Cetin, B.; Likos, W.J.; Edil, T.B. Impacts of pH on leaching potential of elements from MSW incineration fly ash. Fuel 2016, 184, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| wt% | Bulk Fly Ash | Res.L/S 2 | Res.L/S 5 | Res.L/S 10 | Res.L/S 20 | Res.L/S 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halite | 12 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Sylvite | 8 | 2 | ||||
| Calcite | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| Syngenite | 7 | 5 | 2 | |||
| Anhydrite | 10 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 14 |
| Quartz | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| Bassanite | 8 | |||||
| Gypsum | 11 | 12 | 10 | 12 | ||
| Gehlenite | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Amorphous | 51 | 54 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 55 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | Not Reactive [40] | Non Hazardous [40] | Hazardous | Reuse [41] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E.Cond. (μs/cm) | 1650 | 1037 | 1858 | 1500 | 1340 | 1400 | 3160 | ||||
| pH | 9.6 | 9.6 | 9.7 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.1 | 9.4 | 5.5–12 | |||
| Na (mg/L) | 36 | 15 | 45 | 25 | 20 | 41 | 167 | ||||
| K(mg/L) | 37 | 31 | 58 | 15 | 9 | 31 | 159 | ||||
| Ca (mg/L) | 440 | 240 | 409 | 329 | 311 | 273 | 365 | ||||
| Mg (mg/L) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 7 | ||||
| Chloride (mg/L) | 51 | 43 | 100 | 83 | 73 | 125 | 500 | 80 | 2500 | 2500 | 100 |
| Bromides (mg/L) | 0.5 | n.d. | 3.4 | 2.8 | n.d. | 1.1 | n.d. | ||||
| Fluorides (mg/L) | n.d. | 1.1 | 1.7 | 2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | n.d. | 1 | 15 | 50 | 1.5 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 574 | 431 | 860 | 662 | 578 | 475 | 920 | 100 | 5000 | 5000 | 250 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 0.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.8 | n.d. | 1.3 | n.d. | 50 | |||
| Cr (mg/L) | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 1 | 7 | 0.05 |
| Ni (mg/L) | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.02 | n.d. | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 1 | 4 | 0.01 |
| Cu (mg/L) | 0.04 | 0.05 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.2 | 5 | 10 | 0.05 |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.1 | 0.2 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 4 | 5 | 20 | 3 |
| Cd (mg/L) | 0.02 | 0.02 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.004 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.005 |
| Ba (mg/L) | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 2 | 10 | 30 | 1 |
| Pb (mg/L) | 0.04 | 0.05 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.005 | n.d. | 0.05 | 1 | 5 | 0.05 |
| Temperature (°C) | R2 (R) | R2 (D) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σheavy metals | 25 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| 80 | 0.91 | 0.93 | |
| Σmajor ions | 25 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| 80 | 0.92 | 0.94 |
| Cs (mg/L) | k (L mg−1 min−1) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σheavy metals | 35.71 | 3.2 × 103 | 0.9841 |
| 111.11 | 7.4 × 105 | 0.9982 | |
| Σmajor ions | 40,000 | 5.3 × 1013 | 0.9999 |
| 42,478 | 7.2 × 1013 | 0.9999 |
| lnk | 1/T (K−1) | Ea (KJ/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Σheavy metals | 8.075 | 3.2 × 10−3 | 1.25 |
| 13.52 | 2.8 × 10−3 | ||
| Σmajor ions | 31.6 | 3.2 × 10−3 | 0.104 |
| 31.9 | 2.8 × 10−3 |
| wt% | 5-Step at 25 °C | 12-Step at 25 °C | 5-Step at 80 °C | 12-Step at 80 °C | 30-Step |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcite | 8 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 6 |
| Anhydrite | 15 | 14 | 17 | 16 | 13 |
| Quartz | 8 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 10 |
| Gehlenite | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| Amorphous | 62 | 61 | 60 | 59 | 62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caviglia, C.; Destefanis, E.; Pastero, L.; Bernasconi, D.; Bonadiman, C.; Pavese, A. MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution. Minerals 2022, 12, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742
Caviglia C, Destefanis E, Pastero L, Bernasconi D, Bonadiman C, Pavese A. MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution. Minerals. 2022; 12(6):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaviglia, Caterina, Enrico Destefanis, Linda Pastero, Davide Bernasconi, Costanza Bonadiman, and Alessandro Pavese. 2022. "MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution" Minerals 12, no. 6: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742
APA StyleCaviglia, C., Destefanis, E., Pastero, L., Bernasconi, D., Bonadiman, C., & Pavese, A. (2022). MSWI Fly Ash Multiple Washing: Kinetics of Dissolution in Water, as Function of Time, Temperature and Dilution. Minerals, 12(6), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12060742






