The Mesozoic Tectonic Transition from Compression to Extension in the South China Block: Insight from Structural Deformation of the Lushan Massif, SE China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
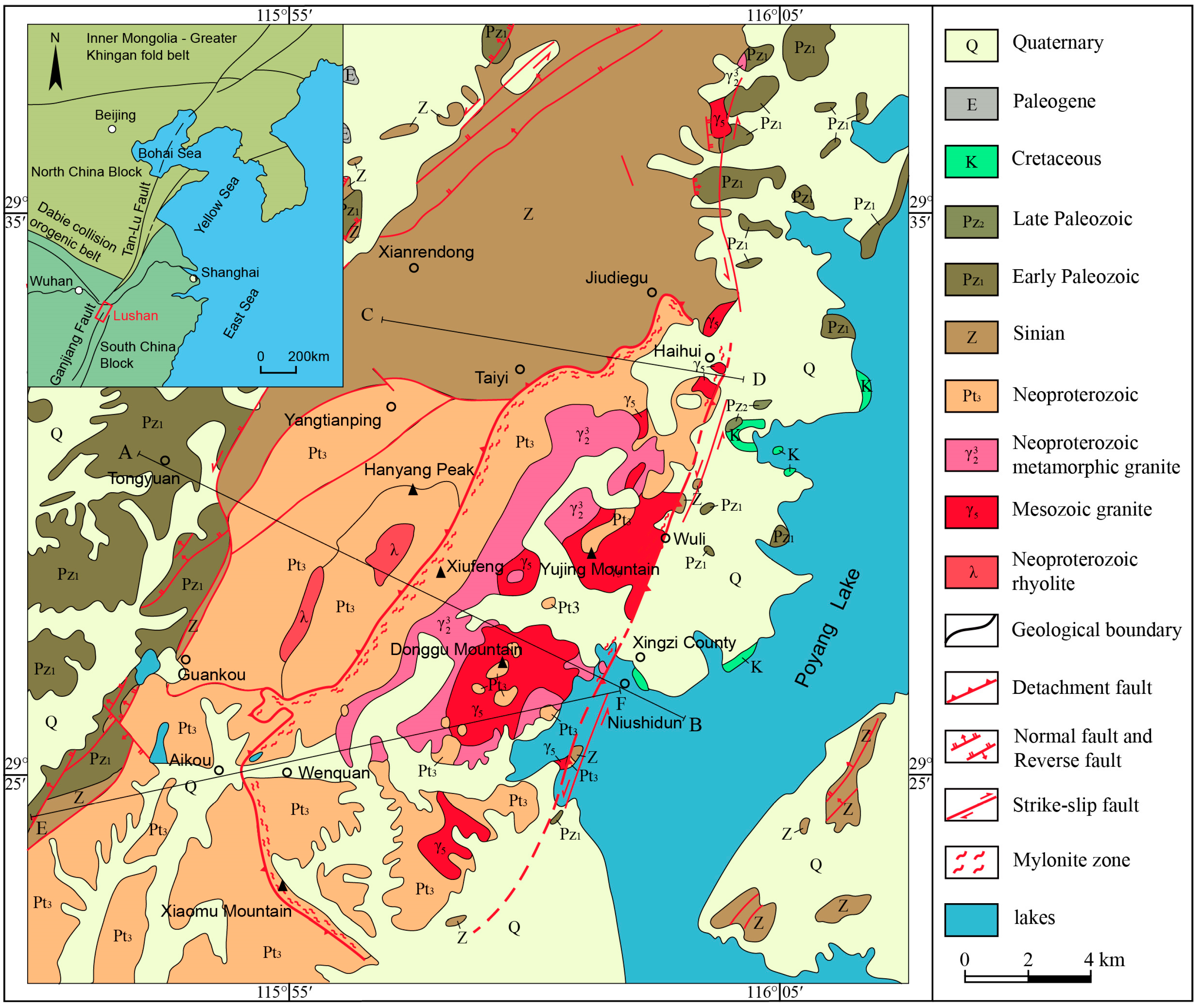
2. Geological Setting
3. Two Phases of Deformation of the Lushan Massif
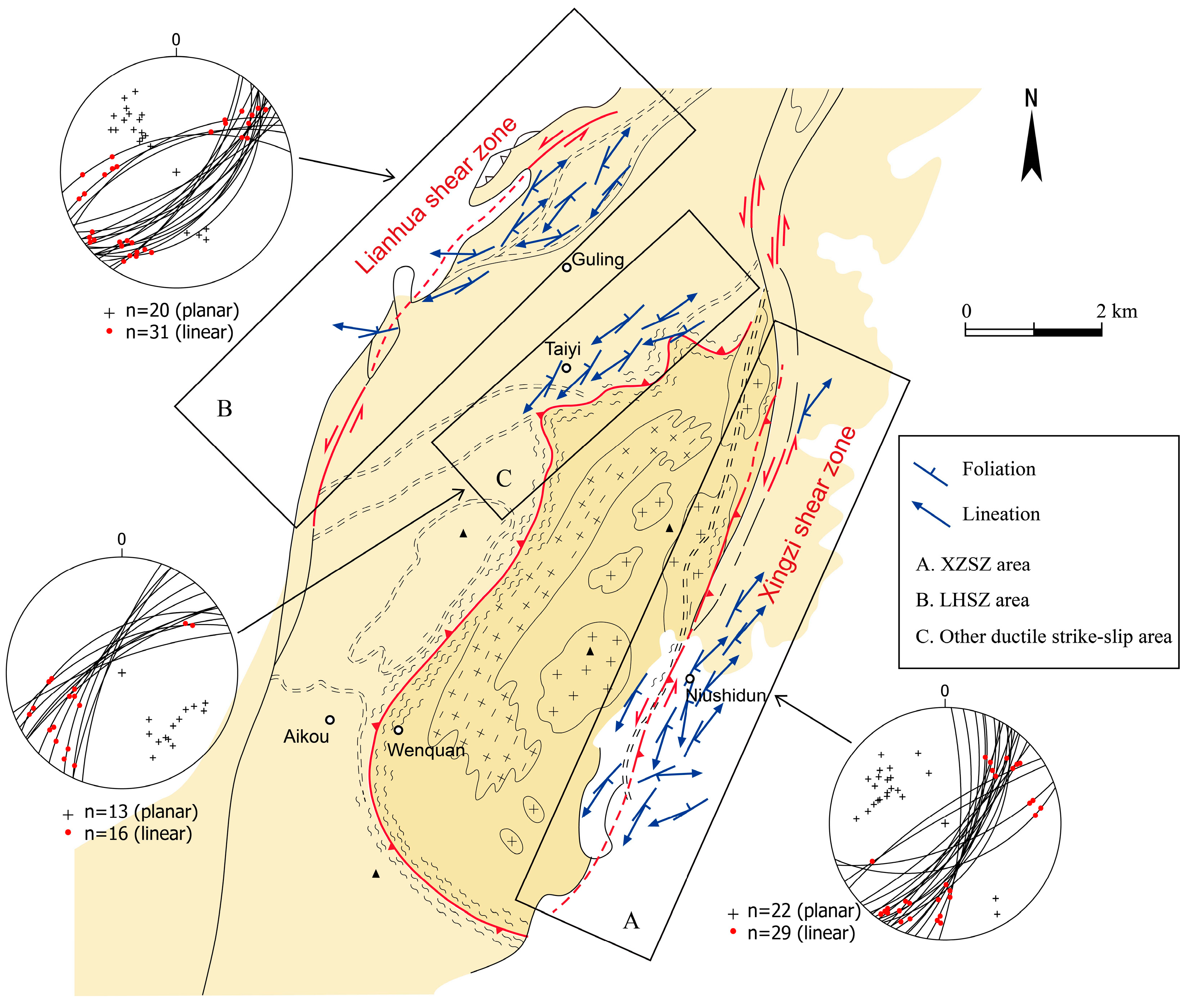
3.1. Transpressional Deformation (D1)
3.1.1. Xingzi Shear Zone (XZSZ)
3.1.2. Lianhua Shear Zone (LHSZ)
3.1.3. Other Ductile Strike-Slip Structures
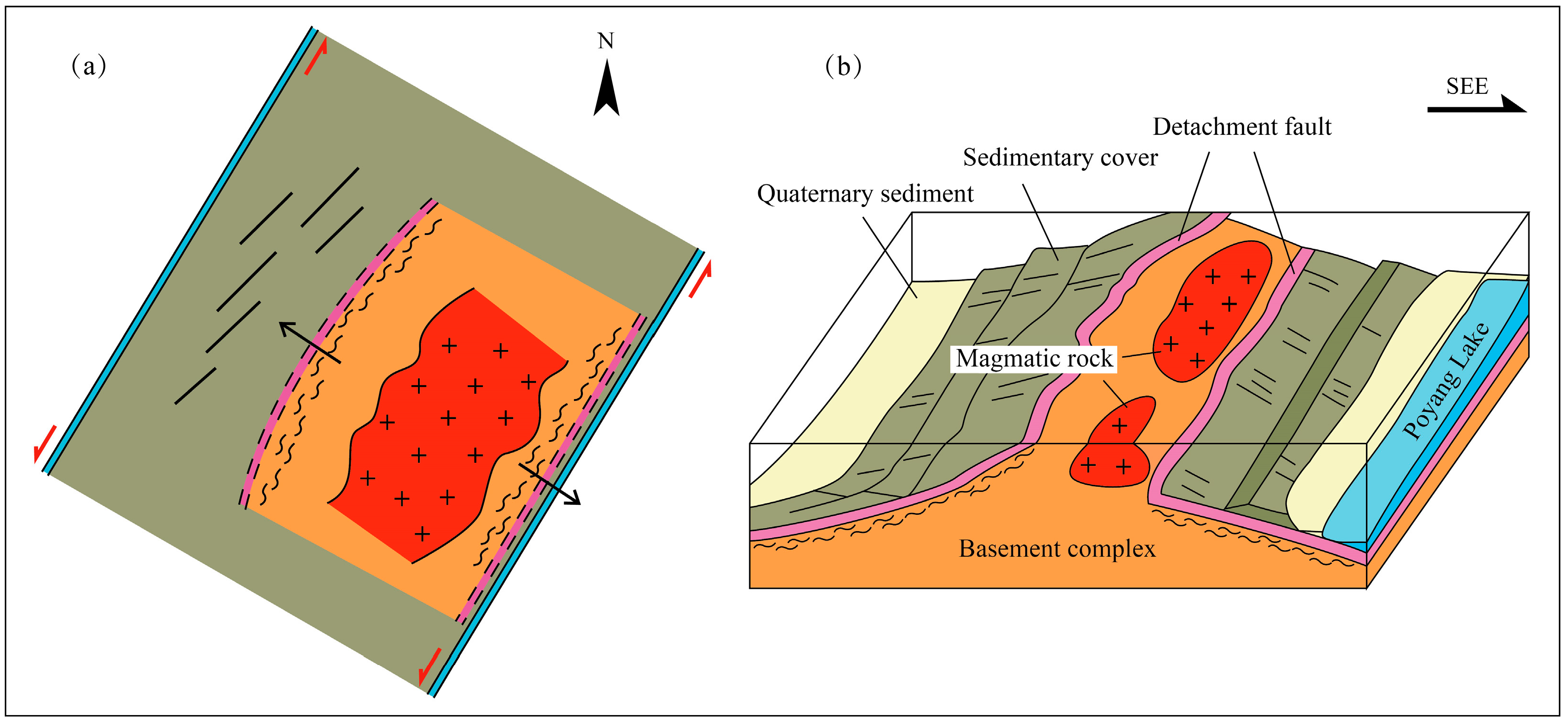
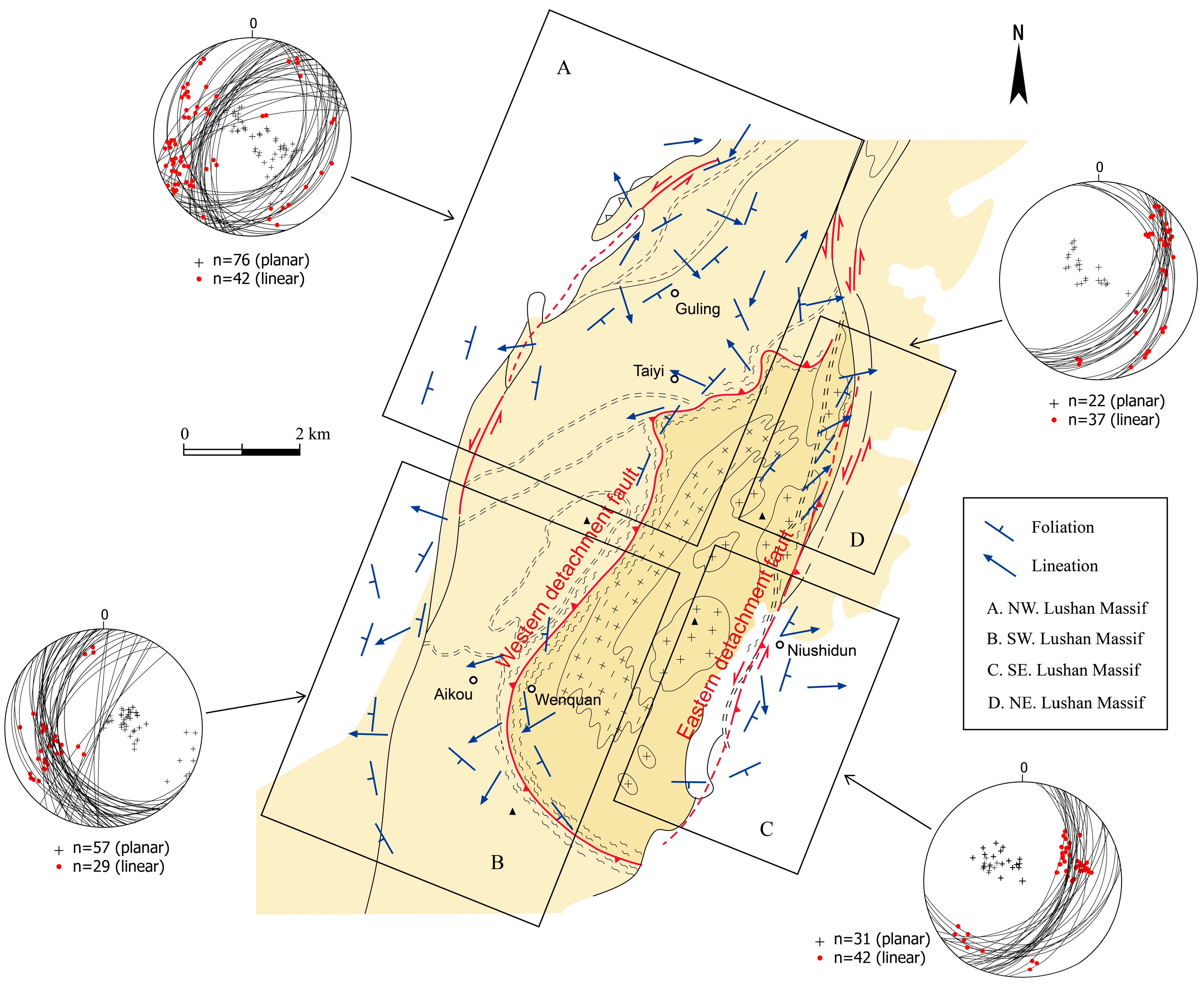
3.2. Extensional Deformation (D2)
3.2.1. Identification of the EDF
3.2.2. The WDF
4. Zircon U-Pb and Mica Ar-Ar Geochronology
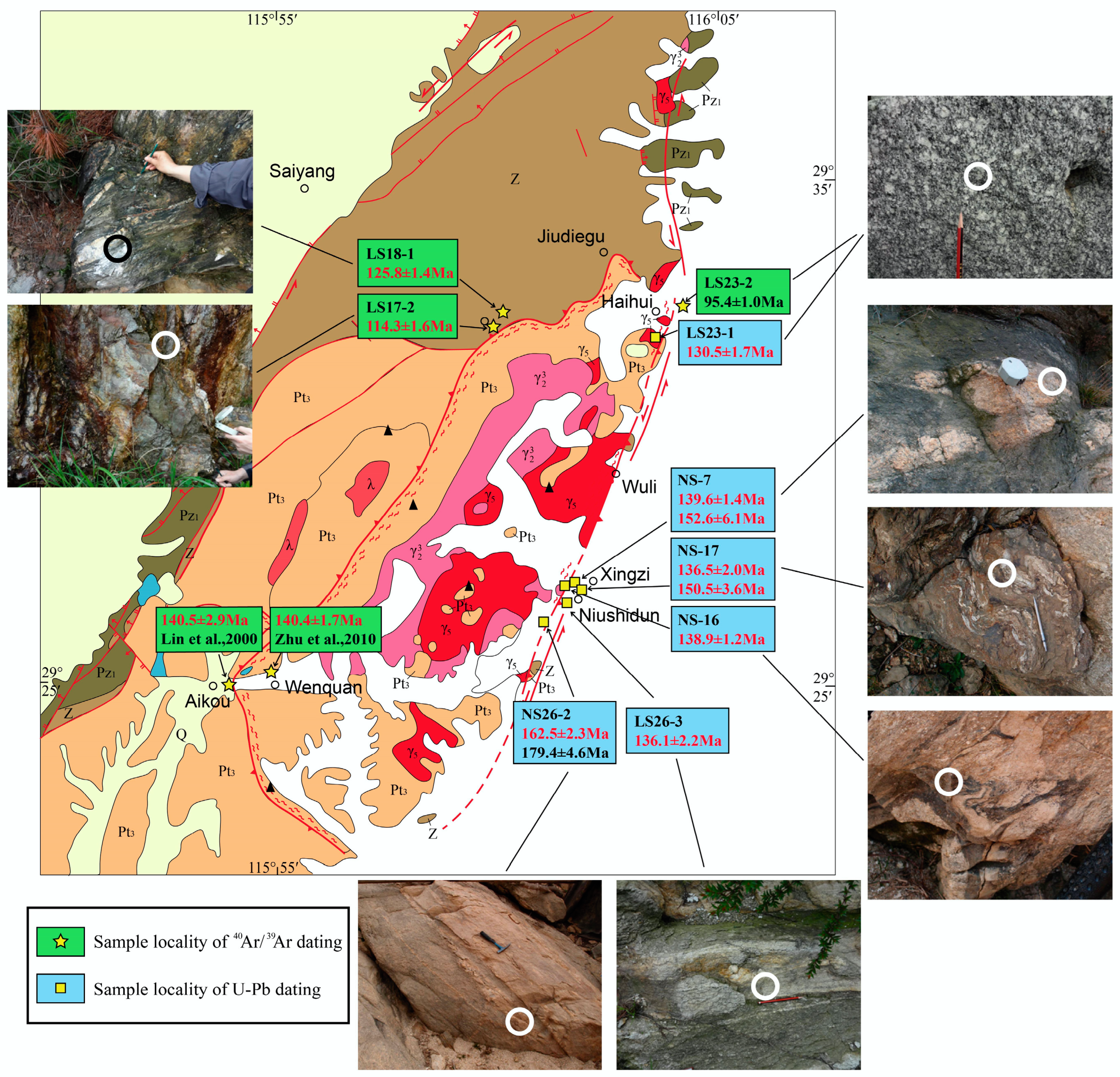
4.1. Sample Description
4.2. Analytical Techniques
4.2.1. Zircon U-Pb
4.2.2. Mica Ar-Ar
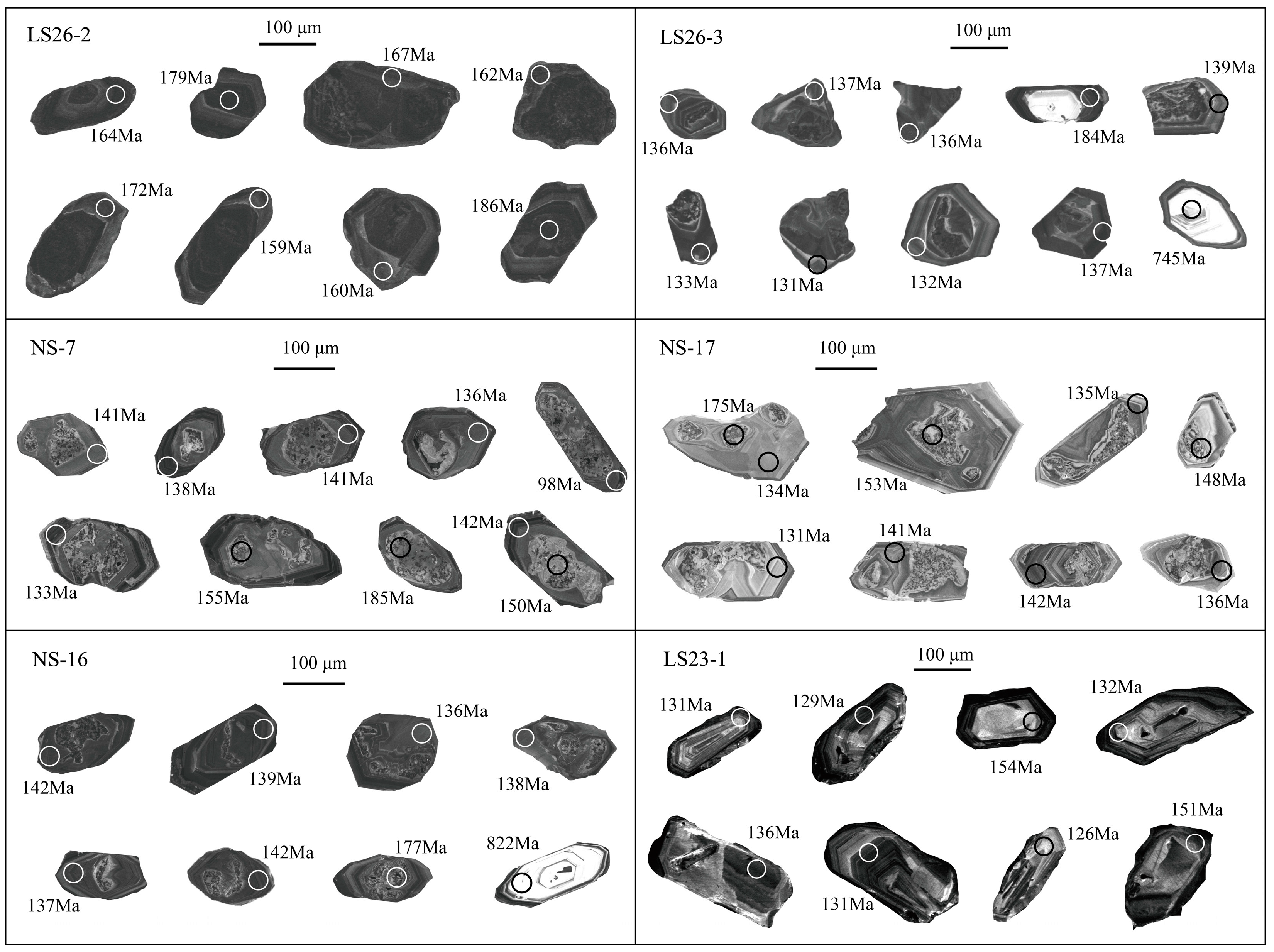
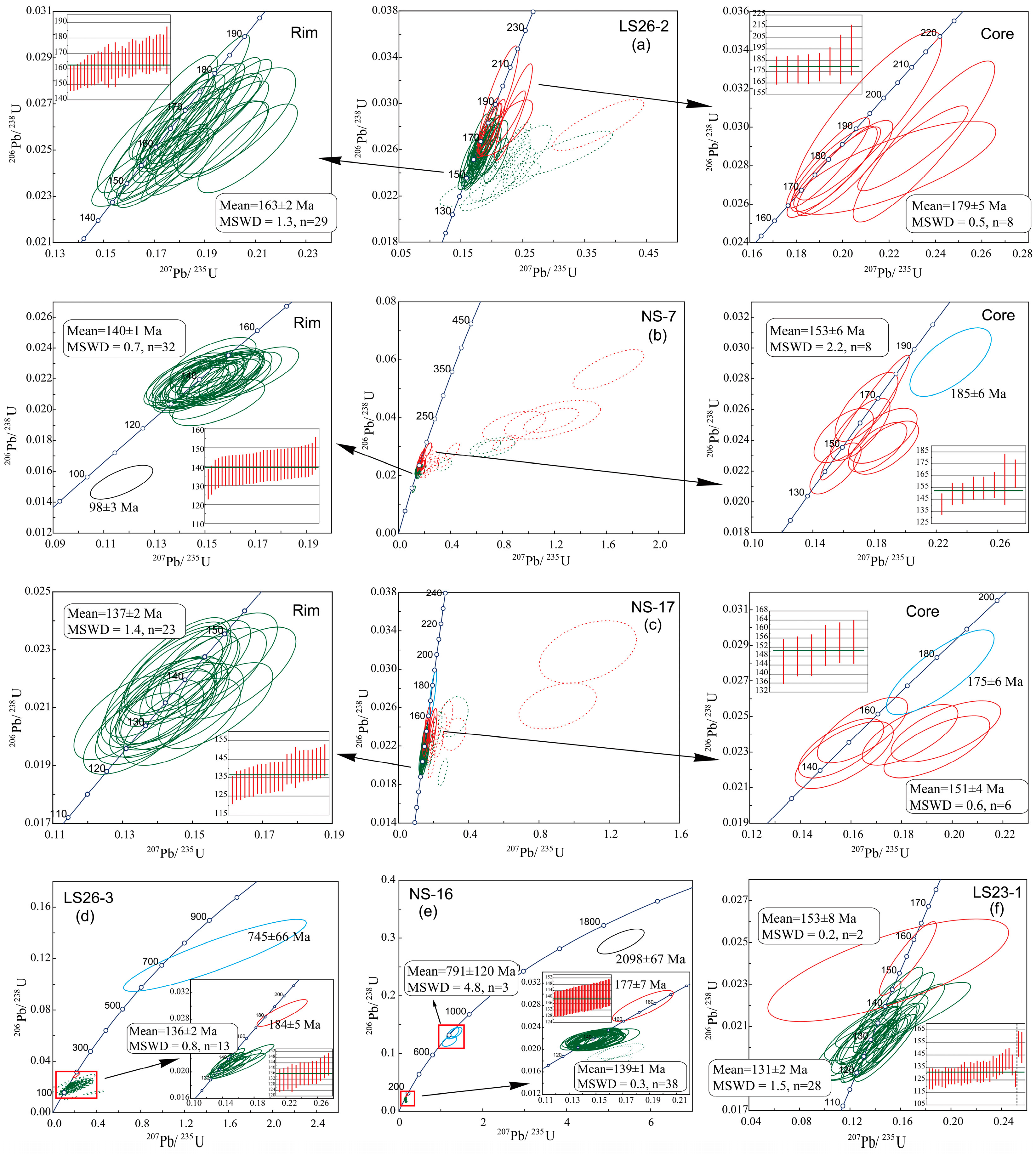
4.3. Analytical Results
4.3.1. U-Pb Dating of Zircon
4.3.2. Ar-Ar Dating of Mica
5. Discussion and Interpretation
5.1. Formation Mechanism of the Detachment Fault
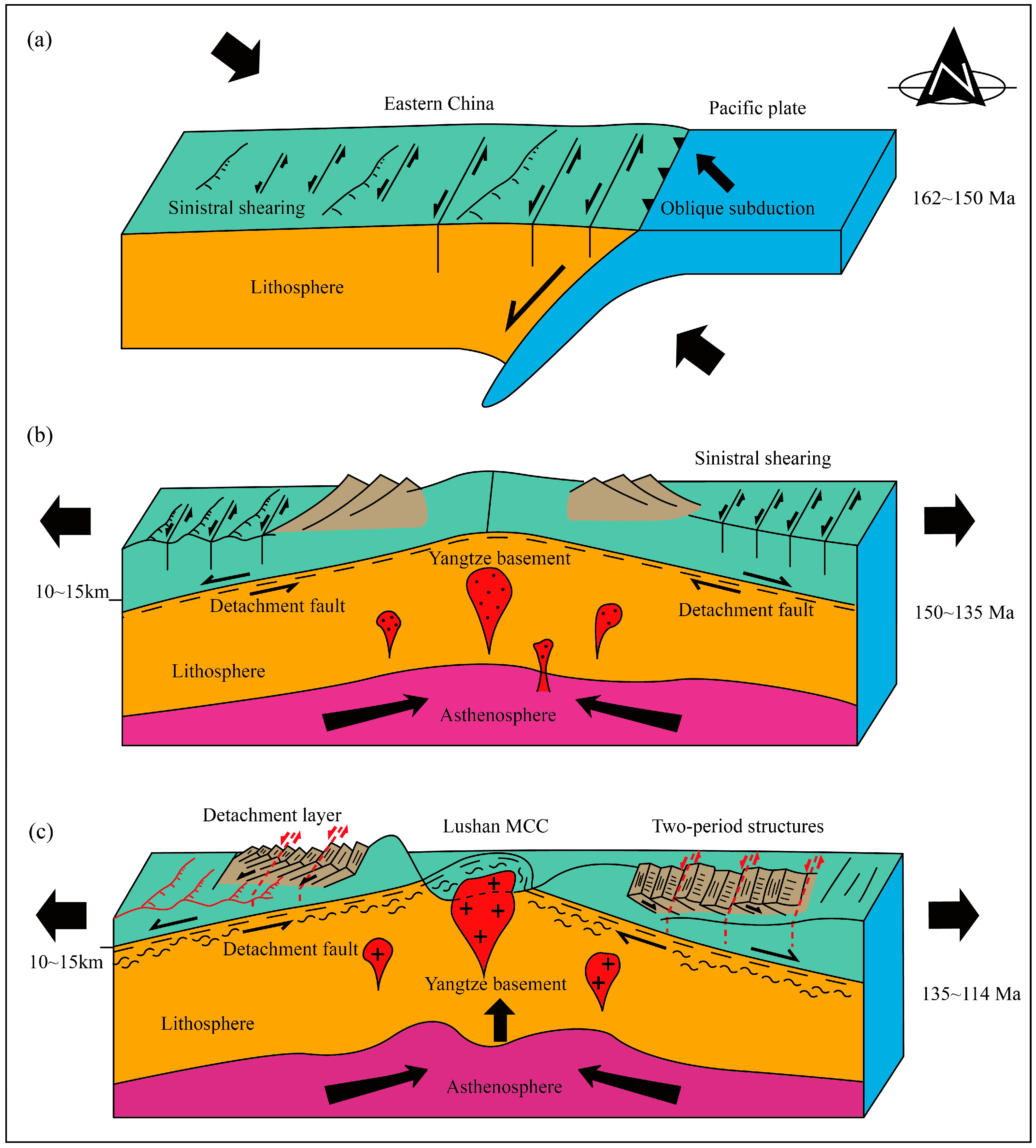
5.2. Tectonic Transition from Compression to Extension
5.2.1. Geodynamic Setting
5.2.2. Tectonic Evolution Sequence
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, W.; Menzies, M. Destruction of aged lower lithosphere and accretion of asthenosphere mantle beneath eastern China. Geotecton. Metallog. 1992, 16, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Song, C.; Hou, Q.L.; Chen, Y.; Faure, M.; Yan, Q.R.; Liu, Q.; Sun, J.F.; Zhu, H.F. The Late Jurassic extensional event in the central part of the South China Block—Evidence from the Laoshan’ao shear zone and Xiangdong Tungsten deposit (Hunan, SE China). Int. Geol. Rev. 2018, 60, 1644–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.T.; Chu, Y.; Wei, W.; Lin, W.; Xin, G.Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H.B.; Ren, Z.H. Splitting a large pluton by Cretaceous crustal extension: Evolution of the Ziyuan Detachment and crustal thinning of the South China Block. Tectonophysics 2022, 838, 229481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Unsworth, M.J.; Hu, X.Y.; Mooney, W.D. Magnetotelluric evidence for asymmetric simple shear extension and lithospheric thinning in South China. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.H.; Cawood, P.A.; Ratschbacher, L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dong, S.W.; Xin, Y.J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, P.X. Building Southeast China in the late Mesozoic: Insights from alternating episodes of shortening and extension along the Lianhuashan fault zone. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. Flat mantle reflectors in Eastern China: Possible evidence of lithospheric thinning. Tectonophysics 2003, 369, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Lin, W.; Faure, M.; Xue, Z.H.; Ji, W.B.; Feng, Z.T. Cretaceous Episodic Extension in the South China Block, East Asia: Evidence from the Yuechengling Massif of Central South China. Tectonics 2019, 38, 3675–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Tang, S.; Lin, S.F. Paleostress inversion of fault-slip data from the Jurassic to Cretaceous Huangshan Basin and implications for the tectonic evolution of southeastern China. J. Geodyn. 2016, 98, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Liang, C.H.; Xu, Y.D. Kinematic analysis of fault-slip data in the Nanling Tectonic Belt and Cretaceous to Paleogene tectonic evolution of the Central South China Block. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 221, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.G. Roles of thermo-mechanic and chemical erosion in continental lithospheric thinning. Bull. Miner. Petrol. Geochem. 1999, 18, 3–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.X.; Zheng, J.P.; Li, W.P.; Chen, M.H.; Cheng, Z.M. The main evolution pattern of phanerozoic mantle in the eastern China: The “mushroom cloud” model. Earth Sci. Front. 2000, 7, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Monnerau, M.; Rabinowicz, M.; Arquis, E. Mechanical erosion and reheating of the lithsphere: A numerical model for hoptspot swells. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.L. Generation and evolution of basaltic magmas: Some basic concepts and a new view on the origin of mesozoic-cenozoic basaltic volcanism in eastern China. Geol. J. China Univ. 2005, 11, 9–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.P.; Griffin, W.L.; O’Reilly, S.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Li, T.F.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.Y.; Liou, J.G. Mineral Chemistry of Peridotites from Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lithosphere: Constraints on Mantle Evolution beneath Eastern China. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 2233–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2000, 18, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Chen, Z.G.; Liu, D.Y.; Li, W.X. Jurassic gabbro-granite-syenite suites from Southern Jiangxi province, SE China: Age, origin, and tectonic significance. Int. Geol. Rev. 2003, 45, 898–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, B.R.; Jin, Z.M.; Kern, H.; Luo, T.C.; Zhao, Z.D. How mafic is the lower continental crust? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1998, 161, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhang, G.L.; Ren, X.W. Deep geodynamics of yanshain movement. Geol. J. China Univ. 2000, 6, 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Y.; Ge, W.C.; Sun, D.Y.; Guo, C.L. Discussions on the lithospheric thinning in eastern China. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 51–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Guo, F.; Peng, T.P.; Li, C.W. Geochemistry of Mesozoic Mafic Rocks Adjacent to the Chenzhou-Linwu fault, South China: Implications for the Lithospheric Boundary between the Yangtze and Cathaysia Blocks. Int. Geol. Rev. 2003, 45, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Rudnick, R.L.; Yuan, H.L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Ling, W.L.; Ayers, J.C.; Wang, X.C.; Wang, Q.H. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature 2004, 432, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.F.; Mo, X.X.; Zhao, H.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Su, S.G. A new model for the dynamic evolution of Chinese lithosphere: Continental rootsplume tectonics. Earth Sci. Rev. 2004, 65, 223–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.Q.; Hu, R.Z.; Zhao, J.H.; Jiang, G.H. Mantle plume and the relationship between it and Mesozoic large-scale metallogenesis in Southeastern China: A preliminary discussion. Geotecton. Metallog. 2001, 25, 179–186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hsü, K.J.; Li, J.L.; Chen, H.H.; Wang, Q.C.; Sun, S.; Sengör, A.M.C. Tectonics of South China: Key to understanding West Pacific geology. Tectonophysics 1990, 183, 9–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.S.; Xu, X.S.; Wang, X.J.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.X.; Huang, B.; Huang, F. Geochemical evidence for the Paleo-Pacific plate subduction at ~125 Ma in Eastern China. Lithos 2021, 398–399, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.S. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block. Geol. Bull. China 2012, 31, 1035–1053. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.R.; Ye, H.M.; Liu, K.; Li, Z.L.; Takahashi, Y.; Zhao, X.L.; Kee, W.S. The Indosinian collision–extension event between the South China Block and the Palaeo-Pacific plate: Evidence from Indosinian alkaline granitic rocks in Dashuang, eastern Zhejiang, South China. Lithos 2013, 172–173, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Chen, Y.J. Evidence of lateral asthenosphere flow beneath the South China craton driven by both Pacific plate subduction and the India–Eurasia continental collision. Terra Nova 2014, 26, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Zang, Y.B.; Wang, P.C.; Suo, Y.H.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Liu, X.G.; Wang, Q. Mesozoic tectonic transition in South China and initiation of Palaeo-Pacific subduction. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 213–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.B.; Lin, W.; Faure, M.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Y.; Xue, Z.H. Origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous peraluminous granitoids in the northeastern Hunan province (middle Yangtze region), South China: Geodynamic implications for the Paleo-Pacific subduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 141, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.B.; Ding, X.; Ling, M.X.; Li, C.Y.; Harlov, D.E.; Sun, W.D. Three late-Mesozoic fluorite deposit belts in southeast China and links to subduction of the (paleo-) Pacific plate. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 129, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.B.; Chen, H.; Xia, Q.K.; Liu, J.; Zhu, K.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Markhand, A.H. Influence of the subduction of the Pacific plate on the mantle characteristics of South China: Constraints from the temporal geochemical evolution of the Mesozoic basalts in the Jitai Basin. Lithos 2020, 352–353, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Kensaku, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Late mesozoic and cenozoic rifting and its dynamic setting in Eastern China and adjacent areas. Tectonophysics 2002, 344, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.R. What drove late mesozoic extension of the northern China–Mongolia tract? Tectonophysics 2003, 369, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Lin, J.Q.; Wilde, S.A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.H. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 233, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.Z.; Lin, S.F.; Zhou, T.F.; Yan, J.; Ren, S.L.; Li, J.H.; Tu, W.C.; Zhang, Y. Mesozoic tectonic regime transition of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River and its adjacent area. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2010, 26, 2835–2849. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Ji, W.B.; Faure, M.; Wu, L.; Li, Q.L.; Shi, Y.H.; Scharer, U.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.C. Early Cretaceous extensional reworking of the Triassic HP–UHP metamorphic orogen in Eastern China. Tectonophysics 2015, 662, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Shu, L.S.; Jia, D. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the sheared metamorphic rocks in the Wuyishan: Constraints on the timing of Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic tectono-thermal events in SE China. Tectonophysics 2011, 501, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Fan, H.R.; Santoshi, M.; Hu, F.F.; Yang, K.F.; Li, Q.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, Y.S. Remelting of Neoproterozoic relict volcanic arcs in the Middle Jurassic: Implication for the formation of the Dexing porphyry copper deposit, Southeastern China. Lithos 2012, 150, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Ni, P.; Zhao, K.D.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Jiang, S.Y.; Chen, H. Petrogenesis of the Middle Jurassic Yinshan volcanic-intrusive complex, SE China: Implications for tectonic evolution and Cu-Au mineralization. Lithos 2012, 150, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Zhou, J.; Mao, J.R.; Santosh, M.; Yu, M.G.; Li, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.Z.; Langmuir, C.H.; Chen, Z.X.; Cai, X.X.; et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of two episodes of granitoids from the northwestern Zhejiang Province, SE China: Implication for magmatic evolution and tectonic transition. Lithos 2013, 179, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.R.; Li, Z.L.; Ye, H.M. Mesozoic tectono-magmatic activities in South China: Retrospect and prospect. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2853–2877. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Zhao, X.F.; Zhou, M.F.; Ma, C.Q.; De Souza, Z.S.; Vasconcelos, P.M. Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Daye region, eastern China: U-Pb ages, petrogenesis, and geodynamic implications. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 2009, 157, 383–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.S.; Xie, G.G. Extensional structure and the Xingzi metamorphic core complex in the Lushan area. Jiangxi Reg. Geol. China 1996, 8, 17–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.F.; Liu, C.Q. Trace element geochemistry during metamorphic dehy dration: A case study from the Xingzi Group of Lushan, southeast China. Geochem. J. 2002, 36, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.K.; Xu, J.H.; Ma, C.X. Preliminary study on the structure of the metamorphic nucleus complex in Lushan. J. East China Geol. Inst. 1994, 17, 11–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Alle, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Oberli, F.; Vonquadt, A.; Roddick, J.C.; Speigel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U–Th–Pb, Lu–Hf, trace-element and REE analyses. Geostand. Newslett 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, C.G.; Zong, K.Q.; Wang, D.B. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, C.G.; Gao, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.H. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem. Geol. 2002, 192, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot/Ex, Version 3.00, A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Song, C.Z.; Ren, S.L.; Li, J.H.; Li, H.L. Metamorphism P-T conditions and active age of the detachment belt in the Lushan metamorphic core complex. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 979–992. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hacker, B.R.; Wang, Q. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism in central China. Tectonics 1995, 14, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, W.J. Neocrystallization of cooling: 40Ar/39Ar ages of white mica of low-grade mylonites. Chem. Geol. 1997, 143, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Zhou, X.M.; Li, X.H.; Xie, G.G.; Li, J.H. Zircon U-Pb dating of pegmatite from Xingzi metamorphic core complex of Lushan mountain and its geological implication. Earth Sci. 2001, 26, 491–495. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dokka, R.K. Original dip and subsequent modification of a Cordilleran detachment fault, Mojave extensional belt, California. Geology 1993, 21, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livaccari, R.F.; Geissman, J.W.; Reynolds, S.J. Palaeomagnetic evidence for large-magnitude, low-angle normal faulting in a metamorphic core complex. Nature 1993, 361, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livaccari, R.F.; Geissman, J.W. Large-magnitude extension along metamorphic core complexes of western Arizona and southeastern California: Evaluation with paleomagnetism. Tectonics 2001, 20, 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.D.; Wang, T.; Ma, M.B.; Davis, G.A. Maximum effective moment criterion and the origin of low-angle normal faults. J. Struct. Geol. 2004, 26, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Fan, W.M.; Zhang, G.W.; Zhang, Y.H. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block: Key observations and controversies. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1273–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, F.Q.; Cui, J.J.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Miao, L.C.; Li, J.H.; Shi, W.; Li, Z.H.; et al. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous continental convergence and intracontinental orogenesis in East Asia: A synthesis of the Yanshan Revolution. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 114, 750–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engebretson, D.C.; Cox, A.; Gordon, R.G. Relative Motion Between Oceanic and Continental Plates in the Pacific Basin. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 1985, 206, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Ding, X.; Hu, Y.H.; Li, X.H. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 262, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Son, M.; Cheon, Y.; Sohn, Y.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, H.C. Evolution of the Late Cretaceous Dadaepo Basin, SE Korea, in response to oblique subduction of the proto-Pacific (Izanagi/Kula) or Pacific plate. Gondwana Res. 2016, 39, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W. The Tancheng-Lujiang Wrench Fault System; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1993; pp. 17–149. [Google Scholar]
- Chough, S.K.; Kwon, S.T.; Ree, J.H.; Choi, D.K. Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of the Korean Peninsula: A review and new view. Earth–Sci. Rev. 2000, 52, 175–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.D.; Hao, T.Y.; Dong, S.W.; Chen, X.H.; Cui, J.J.; Yang, X.Y.; Liu, C.Z.; Li, T.J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. The structural and tectonic relationships of the major fault systems of the Tan-Lu fault zone, with a focus on the segments within the North China region. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 110, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Faure, M.; Monié, P.; Schärer, U.; Zhang, L.S.; Sun, Y. Tectonics of SE China: New insights from the Lushan massif (Jiangxi Province). Tectonics 2000, 19, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.B.; Yang, K.G.; Wang, Y. Extensional detachment and magmatism of the Lushan metamorphic core complex: Constraints from 40Ar/39Ar and U-Pb geochronology. Geotecton. Metallog. 2010, 34, 391–401. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.B.; Faure, M.; Lin, W.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Y.; Xue, Z.H. Multiple emplacement and exhumation history of the Late Mesozoic Dayunshan-Mufushan Batholith in Southeast China and its tectonic significance: 1. Structural analysis and geochronological constraints. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 113, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, W.B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Wei, W.; Faure, M.; Lin, W. Multiple emplacement and exhumation history of the Late Mesozoic Dayunshan-Mufushan Batholith in Southeast China and its tectonic significance: 2. Magnetic fabrics and gravity survey. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Xie, C.L.; Chen, W.; Xiang, B.W.; Hu, Z.Q. Evolution of the Hongzhen metamorphic core complex: Evidence for Early Cretaceous extension in the eastern Yangtze craton, eastern China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2010, 122, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dong, S.W.; Johnston, S.T. Cretaceous tectonic evolution of South China: A preliminary synthesis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 134, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dong, S.W.; Ma, Z.L. Thermal evolution of the Hengshan extensional dome in central South China and its tectonic implications: New insights into low-angle detachment formation. Gondwana Res. 2016, 35, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



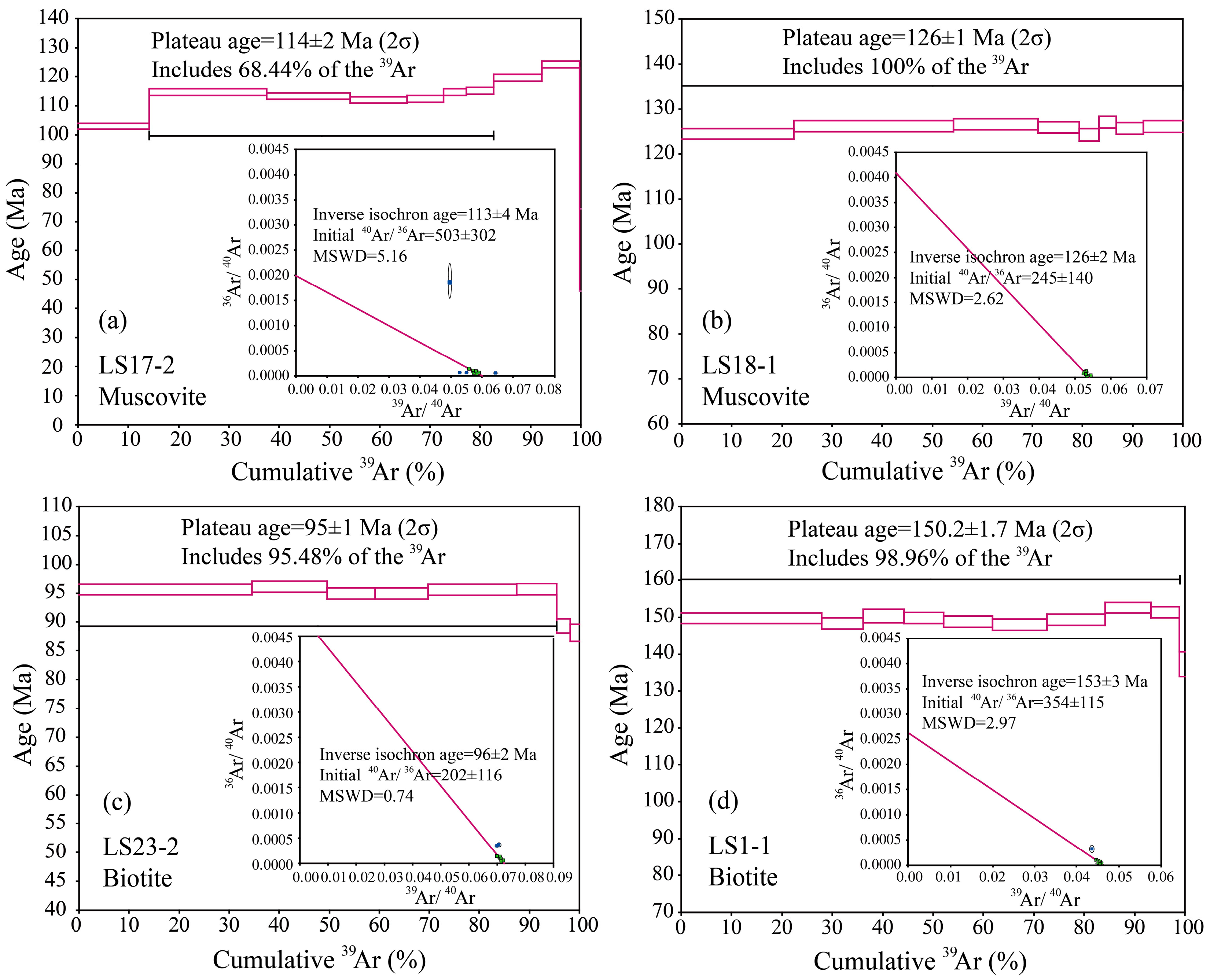


| T | 40Ar(r)/39Ar(k) | 40Ar/39Ar | 37Ar/39Ar | 36Ar/39Ar | 40Ar(r) (%) | 39Ar(k) (%) | Age (Ma) | ±2σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS17-2, muscovite, J = 0.0038585, tp = 114 ± 2Ma | ||||||||
| 750 ℃ | 15.2843 | 15.5315 | 0.0687 | 0.0008 | 98.40 | 14.20 | 103.6 | 1.0 |
| 810 ℃ | 17.0664 | 17.4189 | 0.0890 | 0.0012 | 97.97 | 23.31 | 115.3 | 1.1 |
| 850 ℃ | 16.8543 | 17.1123 | 0.0910 | 0.0009 | 98.49 | 16.65 | 113.9 | 1.1 |
| 890 ℃ | 16.6622 | 16.9887 | 0.1226 | 0.0011 | 98.07 | 11.23 | 112.7 | 1.1 |
| 930 ℃ | 16.7065 | 17.1710 | 0.1344 | 0.0016 | 97.29 | 7.27 | 113.0 | 1.1 |
| 970 ℃ | 17.0712 | 17.4879 | 0.0458 | 0.0014 | 97.61 | 4.60 | 115.4 | 1.1 |
| 1030 ℃ | 17.1368 | 17.8199 | 0.2122 | 0.0024 | 96.15 | 5.39 | 115.8 | 1.2 |
| 1090 ℃ | 17.8311 | 18.1594 | 0.0827 | 0.0011 | 98.19 | 9.57 | 120.3 | 1.2 |
| 1150 ℃ | 18.5431 | 18.9096 | 0.1334 | 0.0013 | 98.05 | 7.59 | 125.0 | 1.2 |
| 1220 ℃ | 8.8784 | 20.1213 | 2.1772 | 0.0387 | 44.06 | 0.19 | 60.9 | 14.2 |
| LS18-1, muscovite, J = 0.0038975, tp = 126 ± 1Ma | ||||||||
| 750 ℃ | 18.2825 | 18.4367 | 0.1018 | 0.0005 | 99.16 | 22.42 | 124.5 | 1.2 |
| 810 ℃ | 18.5480 | 18.7039 | 0.0869 | 0.0005 | 99.16 | 31.86 | 126.2 | 1.2 |
| 850 ℃ | 18.6073 | 18.7520 | 0.0954 | 0.0005 | 99.22 | 16.84 | 126.6 | 1.2 |
| 890 ℃ | 18.4905 | 18.7956 | 0.0547 | 0.0010 | 98.37 | 8.25 | 125.8 | 1.2 |
| 930 ℃ | 18.2512 | 18.8442 | 0.0149 | 0.0020 | 96.85 | 3.90 | 124.3 | 1.3 |
| 980 ℃ | 18.6717 | 19.0520 | 0.1441 | 0.0013 | 97.99 | 3.41 | 127.0 | 1.3 |
| 1040 ℃ | 18.4606 | 19.0092 | 0.0151 | 0.0018 | 97.11 | 5.45 | 125.6 | 1.3 |
| 1100 ℃ | 18.5330 | 18.9855 | 0.1389 | 0.0015 | 97.61 | 7.89 | 126.1 | 1.3 |
| LS23-2, biotite, J = 0.0039567, tp = 95 ± 1Ma | ||||||||
| 750 ℃ | 13.7225 | 13.9210 | 0.0539 | 0.0007 | 98.57 | 34.60 | 95.6 | 0.9 |
| 810 ℃ | 13.7904 | 13.9852 | 0.0452 | 0.0006 | 98.60 | 14.98 | 96.1 | 0.9 |
| 850 ℃ | 13.6165 | 14.0525 | 0.1206 | 0.0015 | 96.89 | 9.63 | 94.9 | 1.0 |
| 890 ℃ | 13.6098 | 14.0682 | 0.0949 | 0.0016 | 96.74 | 10.59 | 94.8 | 1.0 |
| 930 ℃ | 13.7114 | 14.0360 | 0.0790 | 0.0011 | 97.68 | 17.62 | 95.5 | 1.0 |
| 970 ℃ | 13.7238 | 14.2435 | 0.1181 | 0.0018 | 96.34 | 8.05 | 95.6 | 1.0 |
| 1030 ℃ | 12.7975 | 14.2967 | 0.2741 | 0.0051 | 89.50 | 2.66 | 89.3 | 1.2 |
| 1130 ℃ | 12.6159 | 14.1595 | 0.6516 | 0.0054 | 89.06 | 1.87 | 88.1 | 1.5 |
| LS1-1, biotite, J = 0.0039929, tp = 150 ± 2Ma | ||||||||
| 750 ℃ | 21.6873 | 21.9054 | 0.0611 | 0.0007 | 99.00 | 27.83 | 150.2 | 1.4 |
| 800 ℃ | 21.4805 | 21.7656 | 0.0352 | 0.0009 | 98.69 | 8.32 | 148.8 | 1.5 |
| 840 ℃ | 21.7771 | 22.1024 | 0.0595 | 0.0011 | 98.52 | 8.02 | 150.8 | 1.8 |
| 880 ℃ | 21.7082 | 21.9364 | 0.0015 | 0.0007 | 98.96 | 7.95 | 150.3 | 1.5 |
| 920 ℃ | 21.5608 | 21.9640 | 0.0995 | 0.0014 | 98.16 | 9.68 | 149.3 | 1.5 |
| 960 ℃ | 21.4296 | 21.8702 | 0.0816 | 0.0015 | 97.98 | 10.78 | 148.5 | 1.5 |
| 1000 ℃ | 21.6255 | 22.0163 | 0.0434 | 0.0013 | 98.22 | 11.54 | 149.8 | 1.5 |
| 1040 ℃ | 22.1215 | 22.3006 | 0.0889 | 0.0006 | 99.19 | 9.06 | 153.1 | 1.5 |
| 1100 ℃ | 21.9309 | 22.2863 | 0.0377 | 0.0012 | 98.40 | 5.76 | 151.8 | 1.5 |
| 1400 ℃ | 19.8178 | 22.1054 | 0.4854 | 0.0079 | 89.62 | 1.04 | 137.7 | 3.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Song, C.; Ren, S.; Ji, M. The Mesozoic Tectonic Transition from Compression to Extension in the South China Block: Insight from Structural Deformation of the Lushan Massif, SE China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121531
Yang F, Song C, Ren S, Ji M. The Mesozoic Tectonic Transition from Compression to Extension in the South China Block: Insight from Structural Deformation of the Lushan Massif, SE China. Minerals. 2022; 12(12):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121531
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fan, Chuanzhong Song, Shenglian Ren, and Meihua Ji. 2022. "The Mesozoic Tectonic Transition from Compression to Extension in the South China Block: Insight from Structural Deformation of the Lushan Massif, SE China" Minerals 12, no. 12: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121531
APA StyleYang, F., Song, C., Ren, S., & Ji, M. (2022). The Mesozoic Tectonic Transition from Compression to Extension in the South China Block: Insight from Structural Deformation of the Lushan Massif, SE China. Minerals, 12(12), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12121531




