Metallogenic Mechanism and Geodynamic Background of the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo Deposit in Southern Ailaoshan Tectonic Belt: New Evidence from Garnet U-Pb Dating and In-Situ S Isotope
Abstract
1. Introduction
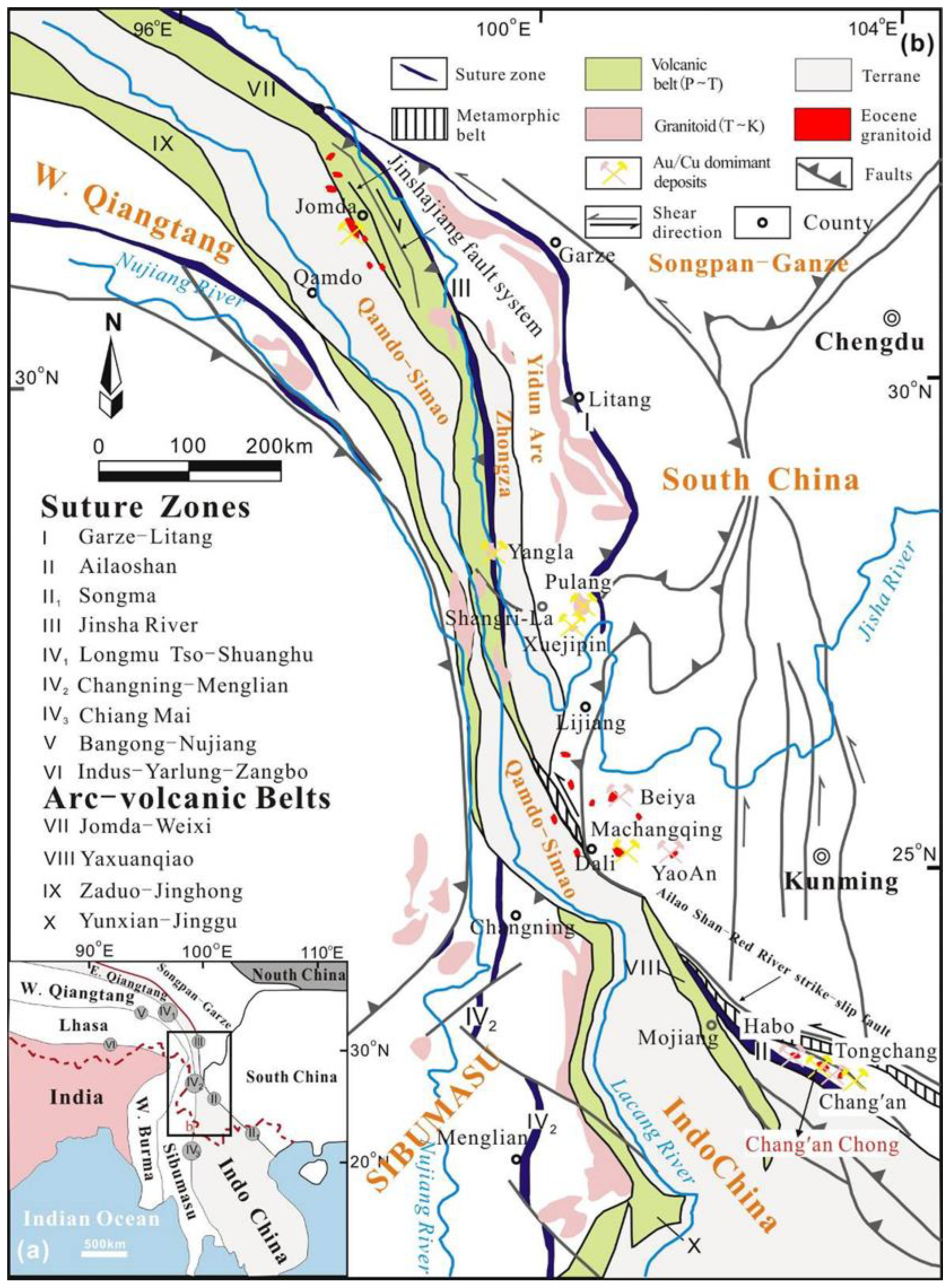
2. Regional Geological Setting
3. Ore Deposit Geology
3.1. Geological Characteristics of Intrusive Bodies
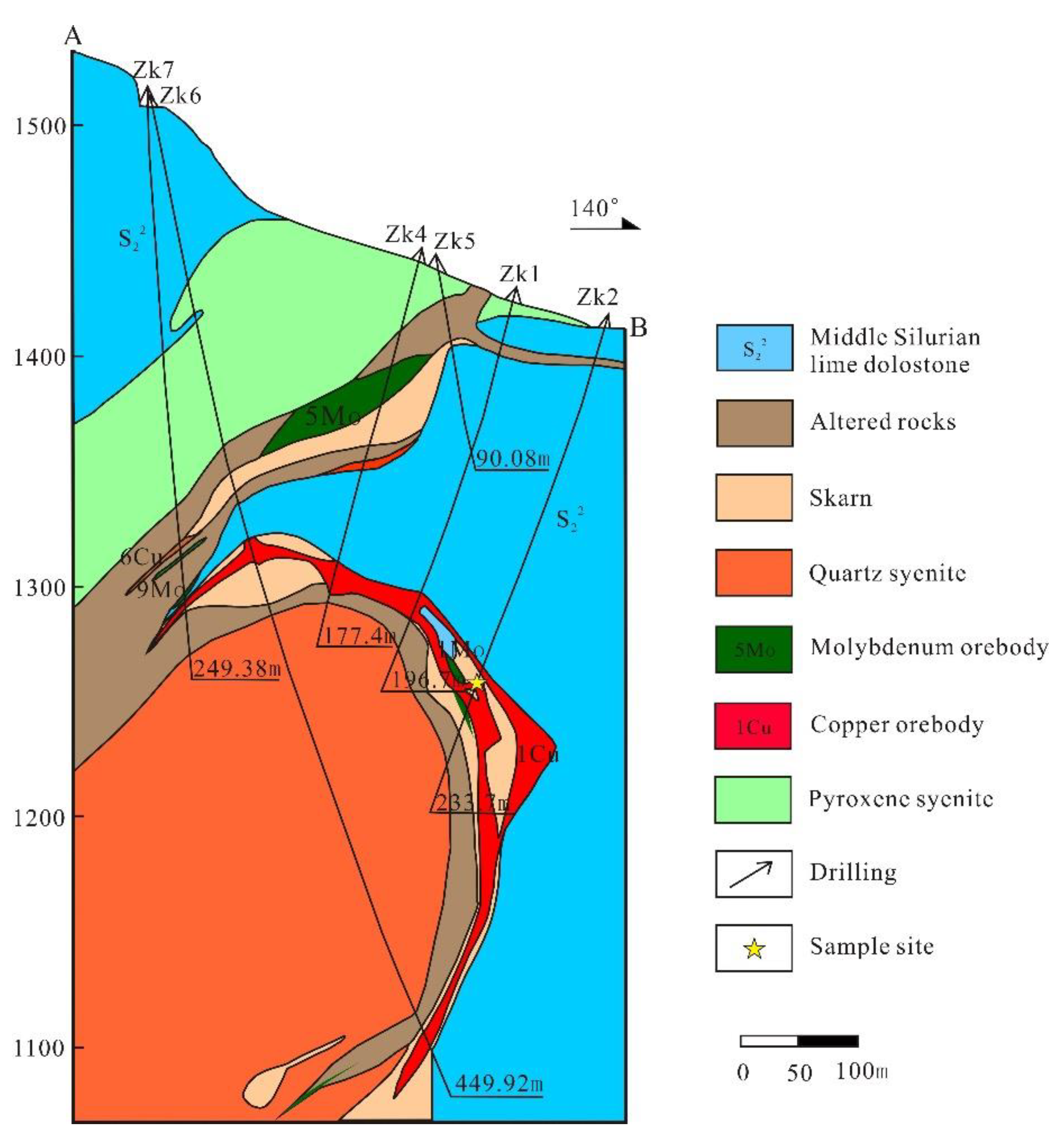
3.2. Orebody Geological Characteristics
3.3. Country Rock Alteration
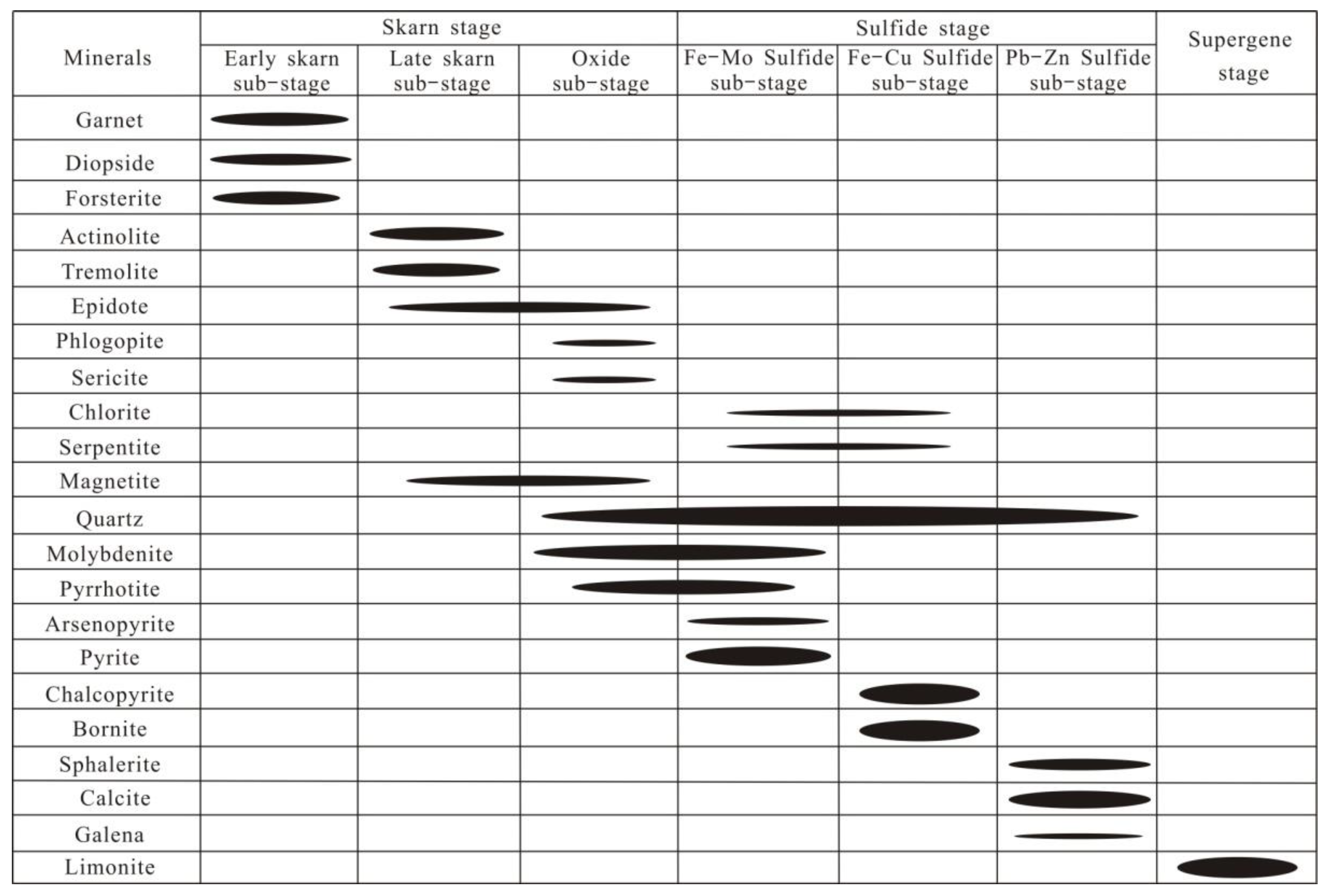
3.4. Mineralization Stages
4. Samples and Analytical Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Analytical Methods
5. Results
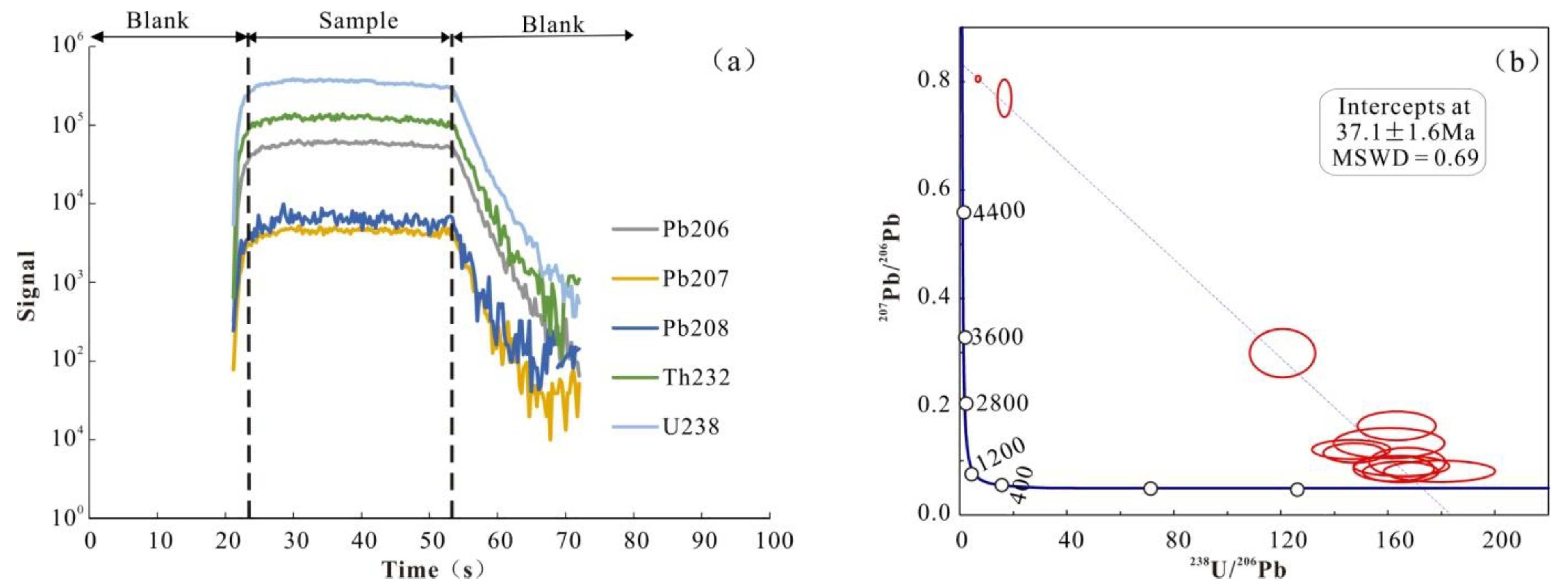
5.1. U-Pb Dating of Garnet
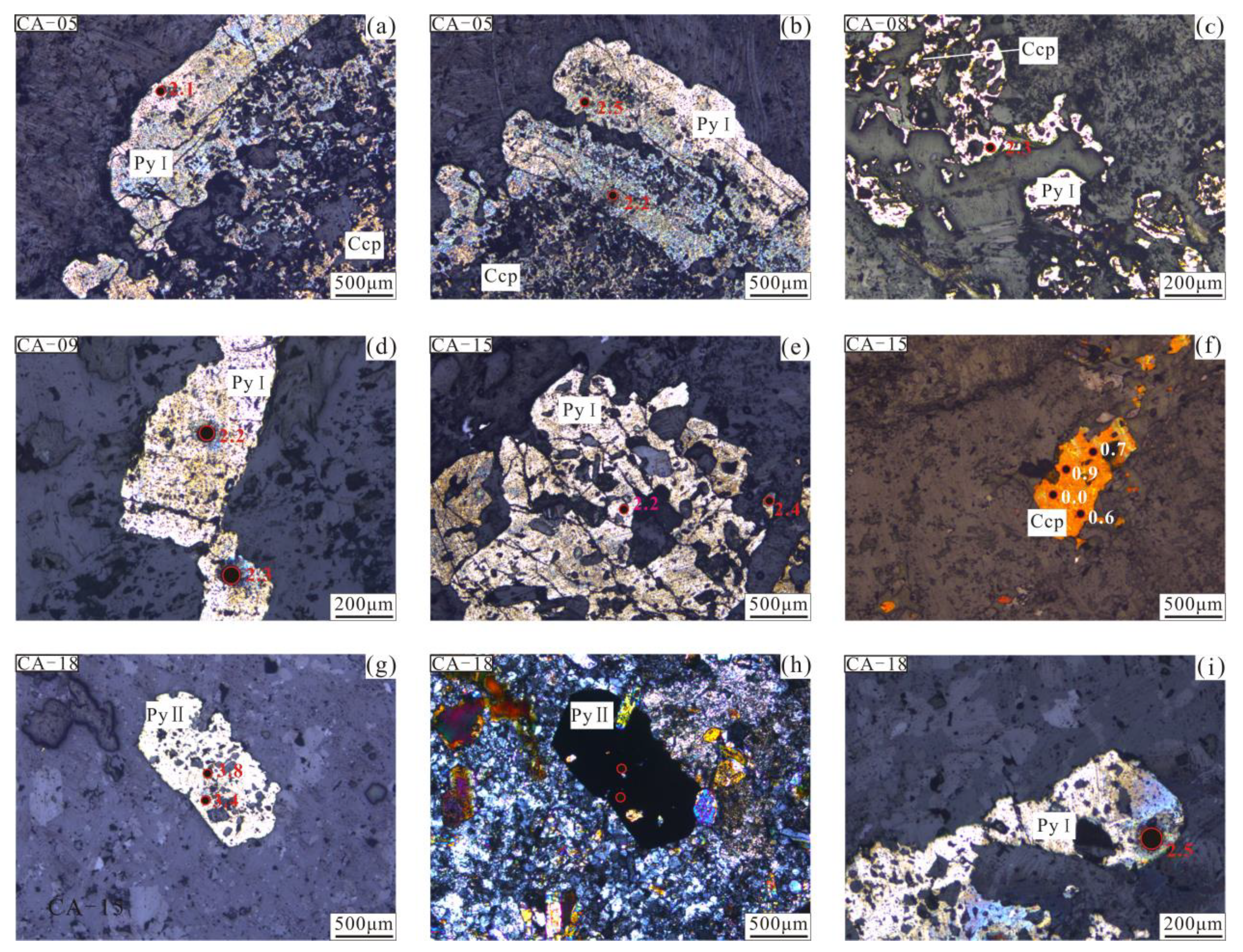
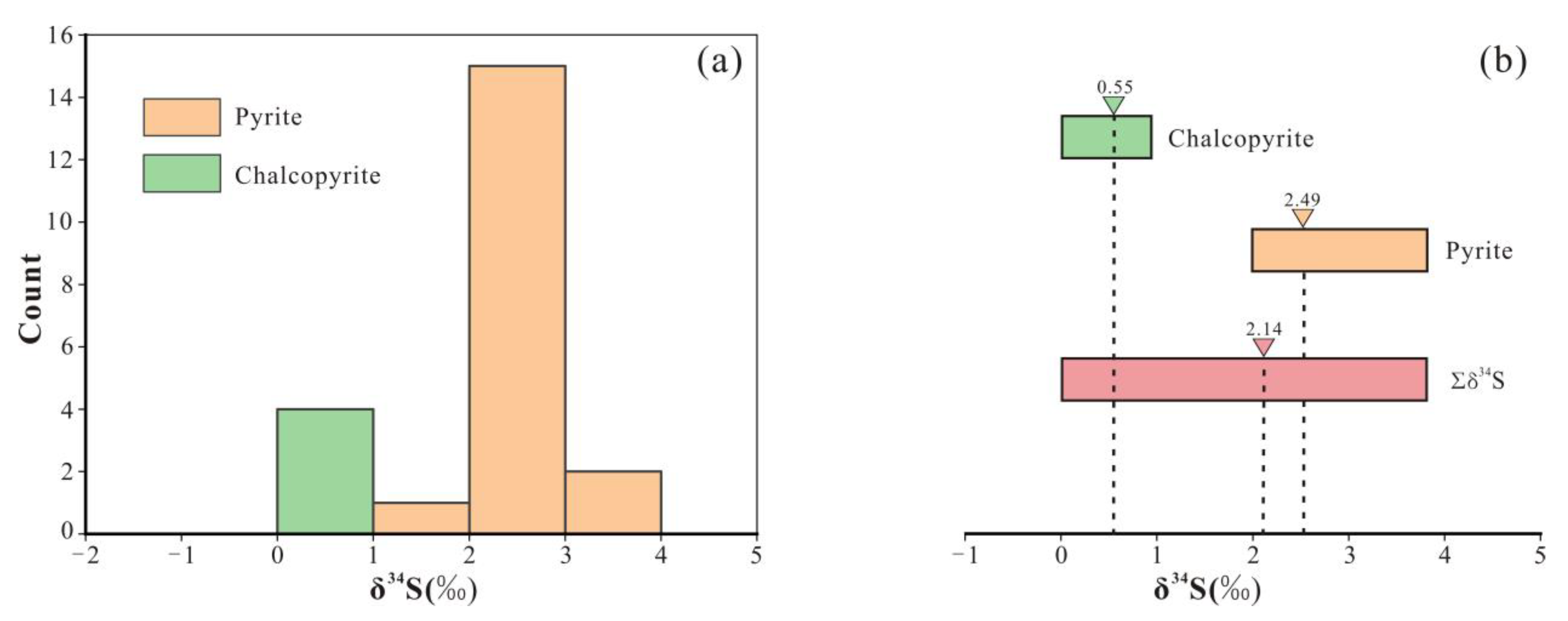
5.2. In-Situ S Isotopes
6. Discussion
6.1. Constraints on the Timing of Skarn Formation and Mineralization
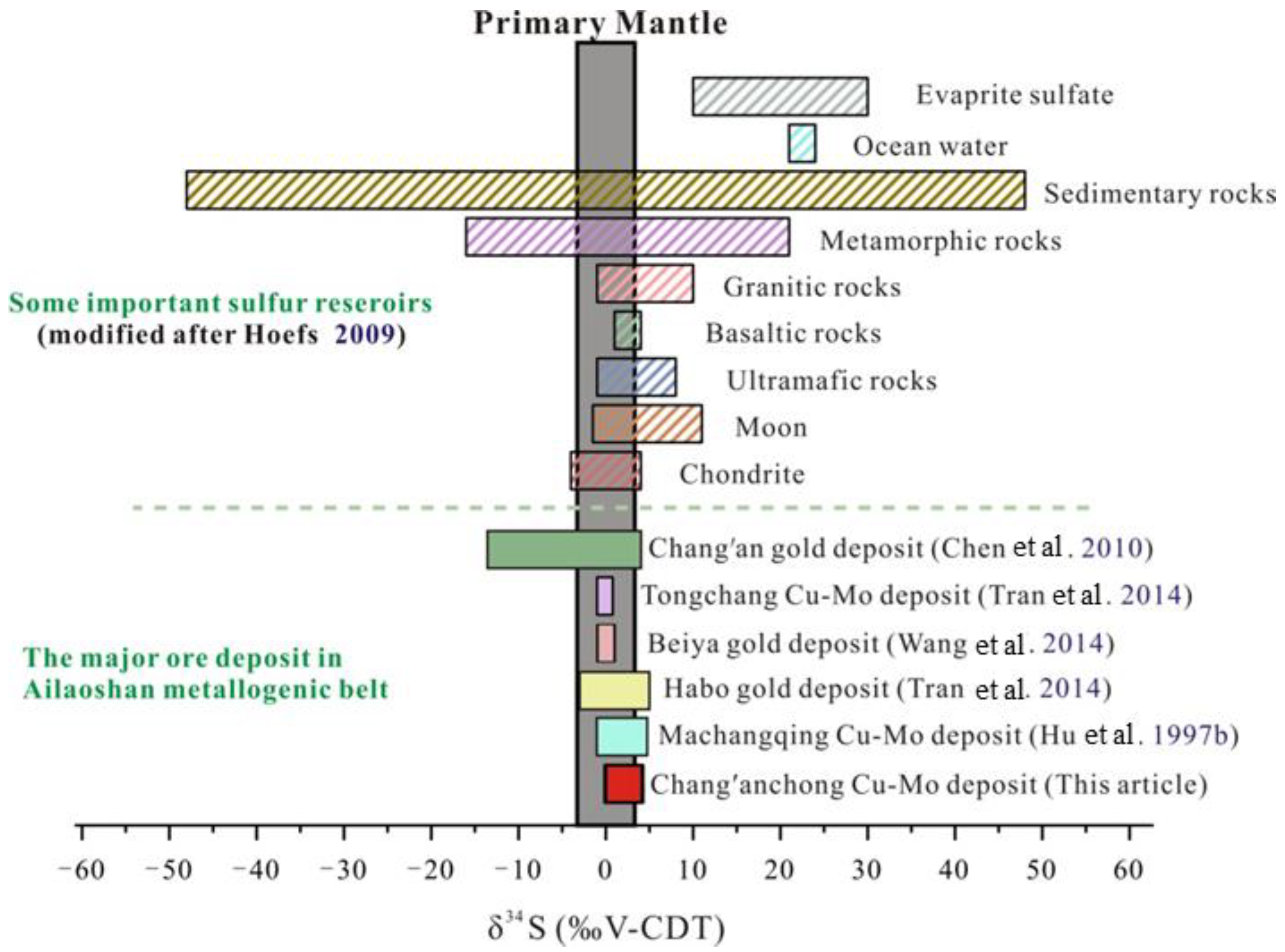
6.2. Ore-Forming Material Sources
6.3. Metallogenic Mechanism and Geodynamic Background
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- The U-Pb dating of garnet in the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo deposit is 37.1 ± 1.6 Ma, showing that the age of skarn was formed in the Late Eocene. There is no doubt that the mineralization stage is nearly consistent with skarn. It can represent an ore-forming state.
- (2)
- The δ34S value of sulfide in the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo deposit ranges from 0.0‰ to 3.8‰, indicating that the ore-forming materials are mainly mantle-derived.
- (3)
- The Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo deposit was formed in the intracontinental strike-slip environment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Xie, Y.W. Chronology and Nd-Sr isotopic characteristics of alkali-rich intrusive bodies in Ailaoshan- Jinshajiang. Sci. China Earth Sci. 1997, 27, 289–293, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M.; Grove, M.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xie, G.H. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 88, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Qu, W.J.; Li, Z.W.; Ying, H.L.; Chen, Y.C. Metallogenic Concentration Period of Porphyry Copper-Molybdenum Deposits in Jinshajiang-Red River Metallogenic Belt: Re-Os Isotopic Dating. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2004, 34, 345–349, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhong, D.L.; Guo, L. Strain and kinematic vorticity analysis: An indicator for sinistral transpressional strain-partitioning along the Lancangjiang shear zone, western Yunnan, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 602–618, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.X.; Sang, L.K. Petrology; Beijing Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 1–399. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.S.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.; Wen, Y.; He, W.Y.; Li, M.M. Geochemical discrimination between fertile and barren Eocene potassic porphyries in the Jinshajiang Cu-Au-Mo metallogenic belt, SW China: Implications for petrogenesis and metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 116, 103258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Zhong, D.L.; Deng, W.M. The tectonic model of the porphyry Cu-Mo-Au metallogenic belt in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. China Geol. 2004, 31, 1–14, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Qi, X.X.; Tang, G.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, F.B. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating for the alkaline porphyries and its constraint on the mineralization in Chang’an Cu-Mo-Au ore-concentrated region, Ailaoshan orogenic belt, western Yunnan. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2204–2216, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.F. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo Deposit, Jinping County, Yunnan Province. Master′s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mezger, K.; Hanson, G.N.; Bohlen, S.R. U-Pb systematics of garnet: Dating the growth of garnet in the late Archean Pikwitonei granulite domain at Cauchon and Natawahunan Lakes, Manitoba, Canada. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1989, 101, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, C.T. U-Pb Garnet and Titanite Age for the Bristol Township Lamprophyre Suite, Western Abitibi Subprovince, Canada. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1990, 27, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, K.W.; O’Nions, R.K. High-Resolution Garnet Chronometry and the Rates of Metamorphic Processes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 107, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.W.; Gao, J.F.; Lan, T.G.; Cui, K.; Han, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.W. In situ low-U garnet U-Pb dating by LA-SF-ICP-MS and its application in constraining the origin of Anji skarn system combined with Ar-Ar dating and Pb isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 130, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.D.; Li, J.W.; Luo, T.; Wang, H.Q. Dating magmatic and hydrothermal processes using andradite-rich garnet U–Pb geochronometry. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2017, 172, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.D.; Luo, T.; Li, J.W.; Hu, Z.C. Direct dating of hydrothermal tungsten mineralization using in situ wolframite U–Pb chronology by laser ablation ICP-MS. Chem. Geol. 2019, 515, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seman, S.; Stockli, D.F.; Mclean, N.M. U-Pb geochronology of grossular-andradite garnet. Chem. Geol. 2017, 460, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafforn, S.; Seman, S.; Kyle, J.R.; Stockli, D.; Leys, C. Andradite garnet U-Pb geochronology of the big Gossan skarn, Ertsberg-Grasberg mining district, Indonesia. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, X.M.; Li, D.F.; Lin, H. U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry of U-rich Garnet from the Giant Beiya Gold-Polymetallic Deposit in SW China: Constraints on Skarn Mineralization Process. Minerals 2018, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevedon, M.; Seman, S.; Barnes, J.D.; Lackey, J.S.; Stockli, D.F. Unraveling histories of hydrothermal systems via U-Pb laser ablation dating of skarn garnet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 498, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Mitchell, R.H.; Xie, L.W.; Huang, C.; Ma, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H. U-Pb age determination of schorlomite garnet by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Tan, C.Y.; Miao, F.Y.; Liu, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.M. Initiation of Zn-Pb mineralization in the Pingbao Pb-Zn skarn district, South China: Constraints from U-Pb dating of grossular-rich garnet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 107, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Deng, X.D.; Li, J.W.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, J.F. U-Pb geochronology of wolframite by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2019, 34, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.J.; Dong, L.L.; Liu, W.; Zhao, H.; Wan, B. Garnet U-Pb and O isotopic determinations reveal a shear-zone induced hydrothermal system. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Gleeson, S.A.; Gao, W.S.; Wang, F.Y.; Li, J.W. Garnet U-Pb dating of the Yinan Au-Cu skarn deposit, Luxi District, North China Craton: Implications for district-wide coeval Au-Cu and Fe skarn mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 118, 103310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kong, Z.G.; Chen, G.; Shao, F.L.; Tang, Y.W.; Sun, B.; Yang, G.S.; Cai, J.D. In-situ LA-SF-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of garnet from Guanfang tungsten deposit in southeastern Yunnan Province and its geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 847–864, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.C.; Lu, X.B.; Gao, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Yang, E.L. Dissolution and migration of Au in hydrothermal ore deposit: A review. Adv. Earth Sci. 2012, 27, 847–856, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lu, X.B.; Li, C.C.; Liu, G.; Shang, S.C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Mao, R.W. Metallogenic conditions and ore-searching prospect an depth of the Jincheng Au ore deposit in luoshan county, Hunan. Geol. Explor. 2013, 49, 265–273, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.Q.; Chen, G.M.; Chen, B.W. Preliminary analysis of the Tethys Himalayan tectonic domain. Acta Geol. Sin. 1984, 1, 1–17, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tapponnier, P.; Peltzer, G.; Le Dain, A.Y.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leloup, P.H.; Lacassin, R.; Tapponnier, P.; Schärer, U.; Zhong, D.L.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, L.S.; Ji, S.C.; Trinh, P.T. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina. Tectonophysics 1995, 251, 3–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Arnaud, N.; Liu, J. Post-collision, shoshonitic volcanism on the Tibet Plateau: Implications for connective thinning of the lithosphere and the source of ocean island basalts. J. Petrol. 1996, 37, 45–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Xu, J.F.; Wang, B.D.; Yang, Z.M.; Ren, J.B.; Yu, H.F.; Liu, H.F.; Feng, Y.X. Geochemical differences between subduction- and collision-related copper-bearing porphyries and implications for metallogenesis. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.L.; Niu, Y.L.; Xu, Y.G.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, Q.J. Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic rocks from western Yunnan, SW China. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 1617–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.J.; Qin, K.Z.; Li, G.M.; Jin, L.Y.; Evans, N.J.; Yang, X.R. Baogutu: An example of reduced porphyry Cu deposit in western Junggar. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.J.; Qin, K.Z.; Li, G.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Evans, N.J.; Zhang, R.; Jin, L.Y. Magmatic process recorded in plagioclase at the Baogutu reduced porphyry Cu deposit, western Junggar, NW-China. Asian J. Earth Sci. 2014, 82, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Subduction and closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in Ailaoshan: Clastic sedimentary and magmatic records. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe, I. Palaeozoic and Mesozoic tectonic evolution and palaeogeography of East Asian crustal fragments: The Korean Peninsula in context. Gondwana Res. 2006, 9, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 66, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.F.; Li, G.J.; Li, C.S.; Wang, C.M. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Res. 2014, 26, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.W.; Cui, K.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, J.F.; Han, J.J.; Yang, J.H.; Liu, L. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of wolframite by combining NIST series and common lead-bearing MTM as the primary reference material: Implications for metallogenesis of South China. Gondwana Res. 2020, 83, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, M.; Allé, P.; Corfu, F.; Griffin, W.L.; Meier, M.; Oberli, F.; Quadt, A.V.; Roddick, J.C.; Spiegel, W. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1995, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.H.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.L. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Hu, Z.C. Calibration and correction of LA-ICP-MS and LA-MC-ICP-MS analyses for element contents and isotopic ratios. Solid Earth Sci. 2016, 1, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 4.5, a geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronol. Cent. Spec. Publ. 2012, 4, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Zhao, X.F.; Lin, Z.W.; Zhao, S.R. In Situ Trace Elements and Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Pyrite from Jinchiling Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Region: Implications for Ore Genesis. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 945–959, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.Y.; Xie, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Campbell, I. Formation and evolution of potassium-rich alkaline intrusive body restrict copper mineralization-Take Machangqing Cu deposit as an example. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2004, 14, 116–120, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Liang, H.Y.; Mo, J.H.; Xie, Y.W. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Age of the Jinping-Tongchang Porphyry Associated with Cu-Mo Mineralization and its Geological Implication. Geotecton. Metallog. 2009, 33, 598–602, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Geological Characteristics and Metallogenic Model of the Chang’an Gold Deposit in Jinping County, Yunnan Province; Postdoctoral work report; Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 1–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.L.; Bi, X.W.; Tang, Y.Y. The metallogenic chronology and geological significance of the porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit in the southern part of the Jinshajiang-Red River metallogenic belt. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 25–526, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H.; Rye, R.O. Isotope of sulfur and carbon. In Geochem. Hydrotherm. Ore Depos, 3rd ed.; Barnes, H.L., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Xu, B.L.; Zhou, G.T. Geochemical studies of stable isotopes in minerals. Geosci. Front. 2000, 7, 299–321, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.G.; Xia, J.S.; Chen, C.Y. Geochemical features of alkali-rich porphyry and analysis of Au (polymetallic)deposits in western Yunnan. Geotecton. Metallog. 2000, S1, 44–51, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Tran, M.D.; Li, Y.C.; Bing, M.M. Regional Metallogenesis of the Chang'an Gold Ore Deposit in Western Yunnan:Evidences from Fluid Inclusions and Stable Isotopes. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.). 2010, 84, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, M.D.; Liu, J.L.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Song, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhao, Z.D. Cenozoic high-K alkaline magmatism and associated Cu–Mo–Au mineralization in the Jinping–Fan Si Pan region, southeastern Ailao Shan–Red River shear zone, southwestern China–northwestern Vietnam. J Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H. Study on the Beiya Au polymetallic mineralization system of alkali-rich porphyry in heqing County, western Yunnan Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2017. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.Z.; Huang, Z. The petrology and petrogensis of the Yangtze plantfrom western margins alkali-rich granite porphyry. Geotecton. Metallog. 1997, 21, 173–180, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Mo, X.X.; Yang, Z.M.; Wang, A.J.; Pan, G.T.; Qu, X.M.; Nie, F.J. Metallogeneses in the collisional orogen of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Tectonic setting, tempo-spatial distribution and ore deposit types. China Geol. 2006, 33, 340–351, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.S.; Xu, W.Y.; Mo, X.X.; Ding, L.; Gao, Y.F.; Dong, F.L.; Li, G.M.; Qu, X.M.; Li, G.M.; et al. Metallogenesis in Tibetan collisional orogenic belt: I. Mineralization in the main collisional orogenic setting. Miner. Depos. 2006, 25, 337–358, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Pan, G.T.; Wang, A.J.; Mo, X.X.; Tian, S.H.; Sun, X.M.; Ding, L.; Wang, E.Q.; Gao, Y.F.; Xie, Y.L.; et al. Metallogenesis in Tibetan collisional orogenic belt: II. Mineralization in late-collisional transformation setting. Miner. Depos. 2006, 25, 521–543, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Qu, X.M.; Yang, Z.S.; Meng, X.J.; Li, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Zhen, M.P.; Zhen, Y.Y.; Nie, F.J.; Gao, Y.F.; et al. Metallogenesis in Tibetan collisional belt: III. Mineralization in post-collisional extension setting. Miner. Depos. 2006, 25, 629–651, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.P. Geological Characteristics and Metallogenesis in Habo Porphyry Cu-Mo-Au Deposit, Yunnan, China. Ph.D. Thesis, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Mo, X.X.; Gao, Y.F.; Qu, X.M.; Meng, X.J. Adakite, possible host rock for porphyry copper deposits: Case studies of porphyry copper belts in Tibetan and northern Chile. Miner. Depos. 2003, 22, 1–12, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.W.; Hu, R.Z.; Hanley, J.J.; Mungall, J.E.; Peng, J.T.; Shang, L.B.; Wu, K.X.; Suang, Y.; Li, H.L.; Hu, X.Y. Crystallisation conditions (T, P, fO2) from mineral chemistry of Cu-and Au-mineralised alkaline intrusions in the Red River-Jinshajiang alkaline igneous belt, western Yunnan Province, China. Mineral. Petrol. 2009, 96, 43–58. [Google Scholar]


| Sample No. | ppm | Th/U | Isotope Ratio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Th | U | 207Pb/206Pb | 1 Sigma | 207Pb/235U | 1 Sigma | 206Pb/238U | 1 Sigma | ||
| CA05-01 | 0.06 | 1.09 | 4.89 | 0.22 | 0.1202 | 0.0263 | 0.0620 | 0.0111 | 0.0056 | 0.0004 |
| CA05-02 | 0.08 | 0.96 | 5.10 | 0.19 | 0.1502 | 0.0239 | 0.1070 | 0.0123 | 0.0068 | 0.0004 |
| CA05-03 | 0.07 | 1.19 | 5.36 | 0.22 | 0.0705 | 0.0126 | 0.0664 | 0.0112 | 0.0061 | 0.0003 |
| CA05-05 | 0.13 | 1.29 | 5.92 | 0.22 | 0.3394 | 0.0508 | 0.3414 | 0.0407 | 0.0083 | 0.0006 |
| CA05-06 | 0.07 | 1.40 | 4.88 | 0.29 | 0.1381 | 0.0323 | 0.0754 | 0.0117 | 0.0061 | 0.0004 |
| CA05-07 | 0.08 | 1.50 | 5.17 | 0.29 | 0.1826 | 0.0289 | 0.1389 | 0.0169 | 0.0061 | 0.0004 |
| CA05-08 | 0.09 | 1.34 | 5.18 | 0.26 | 0.1526 | 0.0237 | 0.1137 | 0.0134 | 0.0068 | 0.0005 |
| CA05-09 | 1.18 | 1.63 | 5.20 | 0.31 | 0.7521 | 0.0347 | 6.3694 | 0.6847 | 0.0600 | 0.0062 |
| CA05-10 | 2.63 | 0.82 | 4.70 | 0.18 | 0.8023 | 0.0270 | 16.3023 | 1.4166 | 0.1468 | 0.0127 |
| CA05-11 | 0.24 | 1.69 | 4.30 | 0.39 | 0.1180 | 0.0233 | 0.0803 | 0.0152 | 0.0060 | 0.0003 |
| CA05-12 | 0.20 | 1.84 | 4.45 | 0.41 | 0.1208 | 0.0317 | 0.0727 | 0.0139 | 0.0062 | 0.0004 |
| CA05-14 | 0.33 | 1.03 | 2.87 | 0.36 | 0.1367 | 0.0281 | 0.0968 | 0.0146 | 0.0079 | 0.0006 |
| CA05-15 | 0.37 | 1.39 | 2.90 | 0.48 | 0.1365 | 0.0253 | 0.1286 | 0.0178 | 0.0074 | 0.0005 |
| CA05-16 | 0.33 | 1.02 | 3.00 | 0.34 | 0.1653 | 0.0412 | 0.1138 | 0.0186 | 0.0062 | 0.0005 |
| CA05-18 | 0.43 | 0.75 | 2.97 | 0.25 | 0.1435 | 0.0243 | 0.1285 | 0.0167 | 0.0074 | 0.0004 |
| Sample No. | Mineral | Stage | 34SV-CDT‰ | Sample No. | Mineral | Stage | 34SV-CDT‰ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA-05-1 | pyrite | PyI | 2.1 | CA-15-1 | pyrite | PyI | 1.9 |
| CA-05-2 | pyrite | PyI | 2.5 | CA-15-2 | pyrite | PyI | 2.2 |
| CA-05-3 | pyrite | PyI | 2.2 | CA-15-3 | pyrite | PyI | 2.4 |
| CA-08-1 | pyrite | PyI | 2.2 | CA-15-4 | pyrite | PyI | 2.5 |
| CA-08-2 | pyrite | PyI | 2.3 | CA-18-1 | pyrite | PyⅡ | 3.8 |
| CA-08-3 | pyrite | PyI | 2.4 | CA-18-2 | pyrite | PyⅡ | 3.4 |
| CA-08-4 | pyrite | PyI | 2.5 | CA-18-3 | pyrite | PyI | 2.5 |
| CA-09-1 | pyrite | PyI | 2.6 | CA-15-5 | chalcopyrite | main mineralization period | 0.6 |
| CA-09-2 | pyrite | PyI | 2.2 | CA-15-6 | chalcopyrite | main mineralization period | 0.0 |
| CA-09-3 | pyrite | PyI | 2.9 | CA-15-7 | chalcopyrite | main mineralization period | 0.9 |
| CA-09-4 | pyrite | PyI | 2.3 | CA-15-8 | chalcopyrite | main mineralization period | 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ye, L.; Chen, G. Metallogenic Mechanism and Geodynamic Background of the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo Deposit in Southern Ailaoshan Tectonic Belt: New Evidence from Garnet U-Pb Dating and In-Situ S Isotope. Minerals 2022, 12, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111389
Sun B, Liu Y, Yan Y, Ye L, Chen G. Metallogenic Mechanism and Geodynamic Background of the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo Deposit in Southern Ailaoshan Tectonic Belt: New Evidence from Garnet U-Pb Dating and In-Situ S Isotope. Minerals. 2022; 12(11):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111389
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Bin, Yi Liu, Yongfeng Yan, Lei Ye, and Gang Chen. 2022. "Metallogenic Mechanism and Geodynamic Background of the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo Deposit in Southern Ailaoshan Tectonic Belt: New Evidence from Garnet U-Pb Dating and In-Situ S Isotope" Minerals 12, no. 11: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111389
APA StyleSun, B., Liu, Y., Yan, Y., Ye, L., & Chen, G. (2022). Metallogenic Mechanism and Geodynamic Background of the Chang’an Chong Cu-Mo Deposit in Southern Ailaoshan Tectonic Belt: New Evidence from Garnet U-Pb Dating and In-Situ S Isotope. Minerals, 12(11), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111389








