Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Shear Strength and Splash Erosion of Clay–Sand Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Samples and Preparation
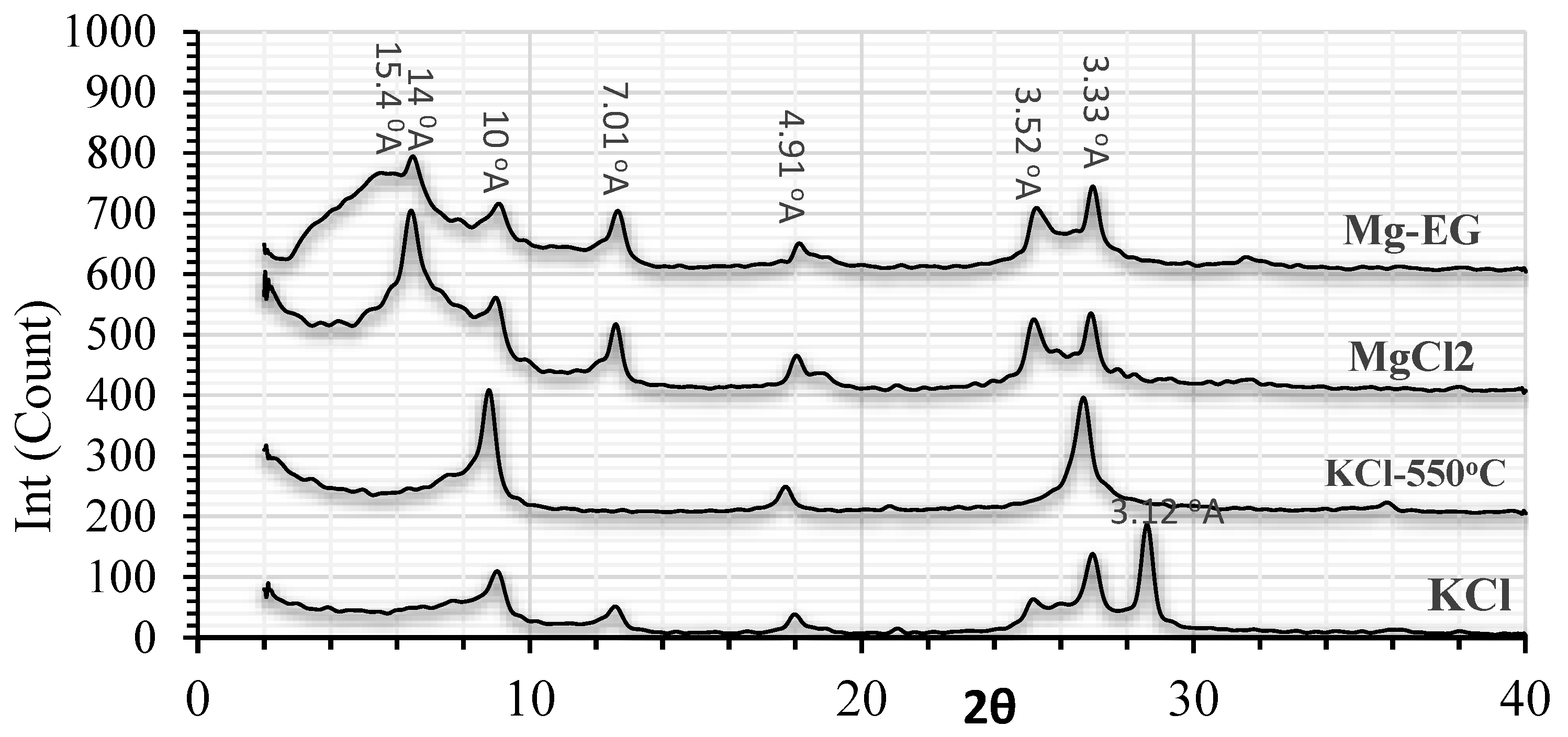
2.2. Laboratory Analyses
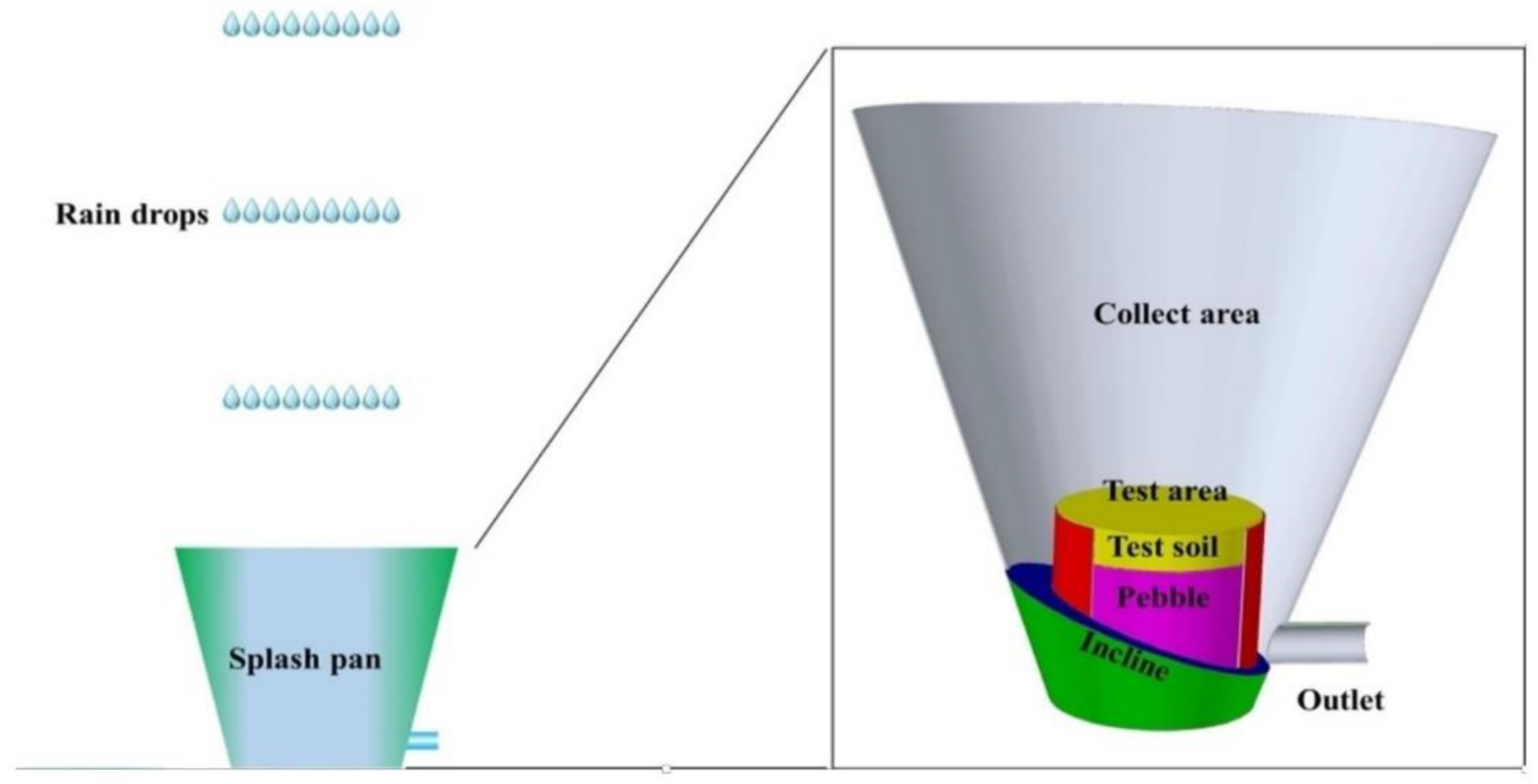
2.3. Splash Erosion Experiment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
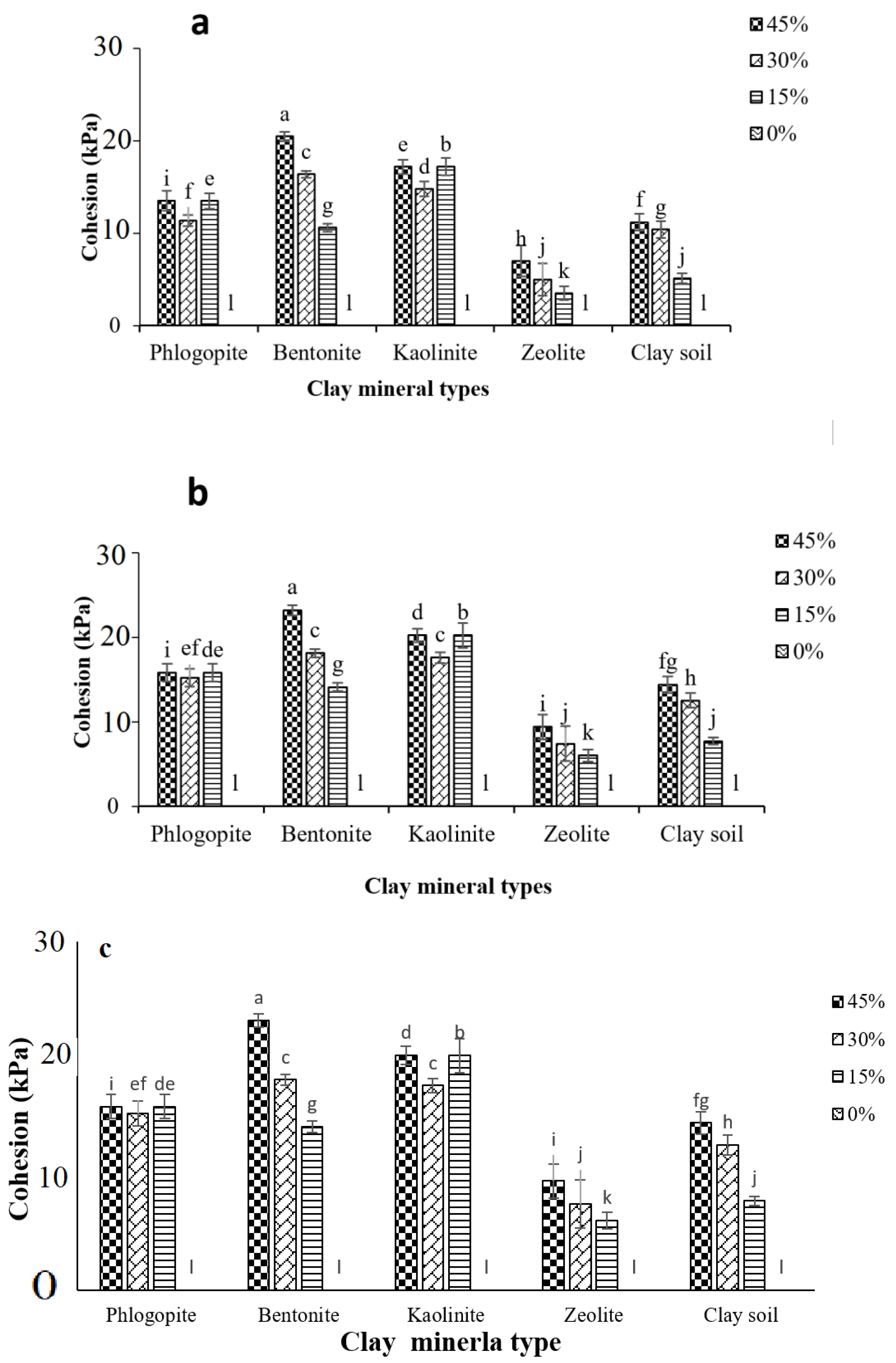
3.2. Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Cohesion at Various Water Contents and W&D Cycles
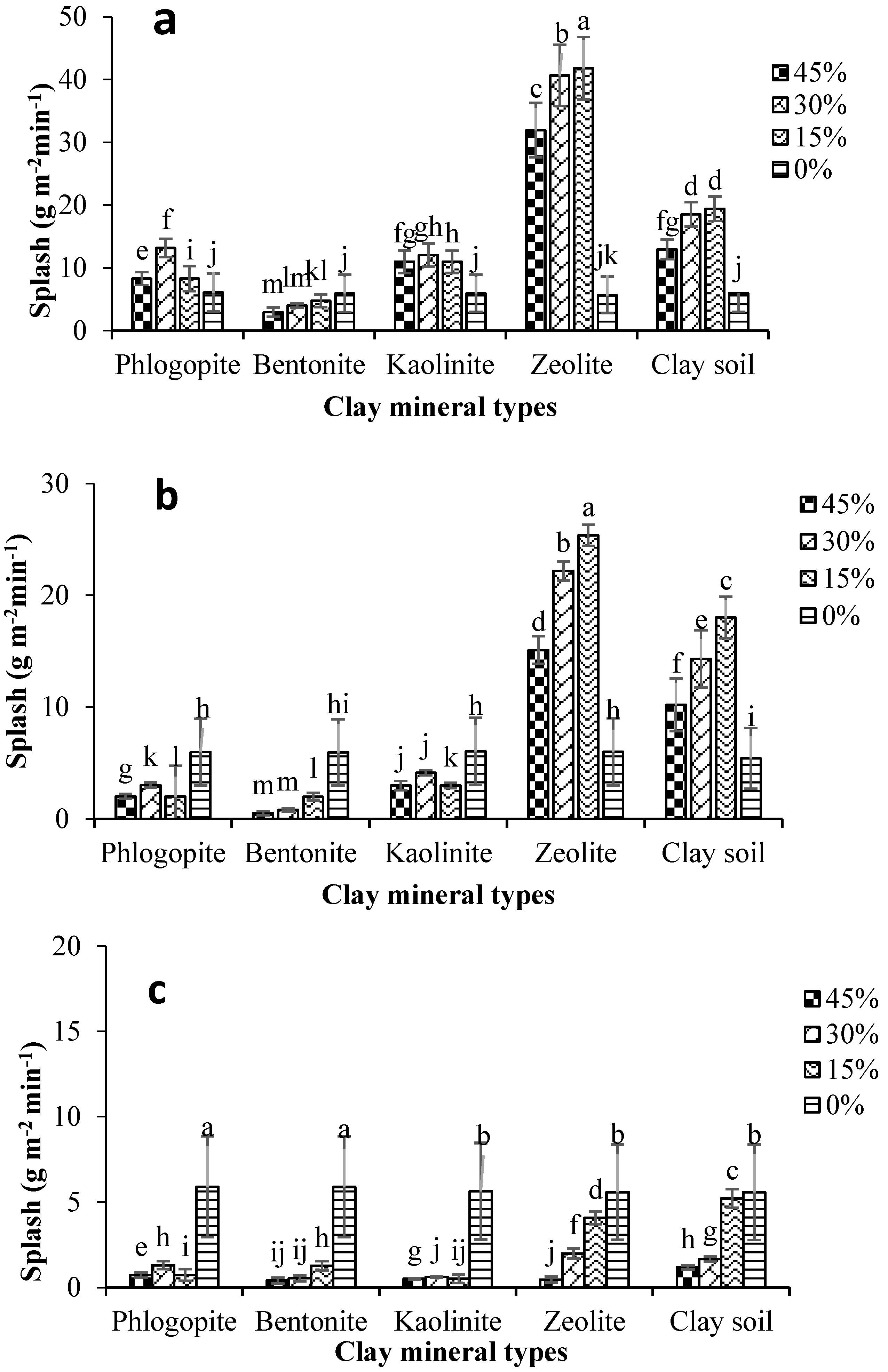
3.3. Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Splash Erosion at Various Water Contents and W&D Cycles
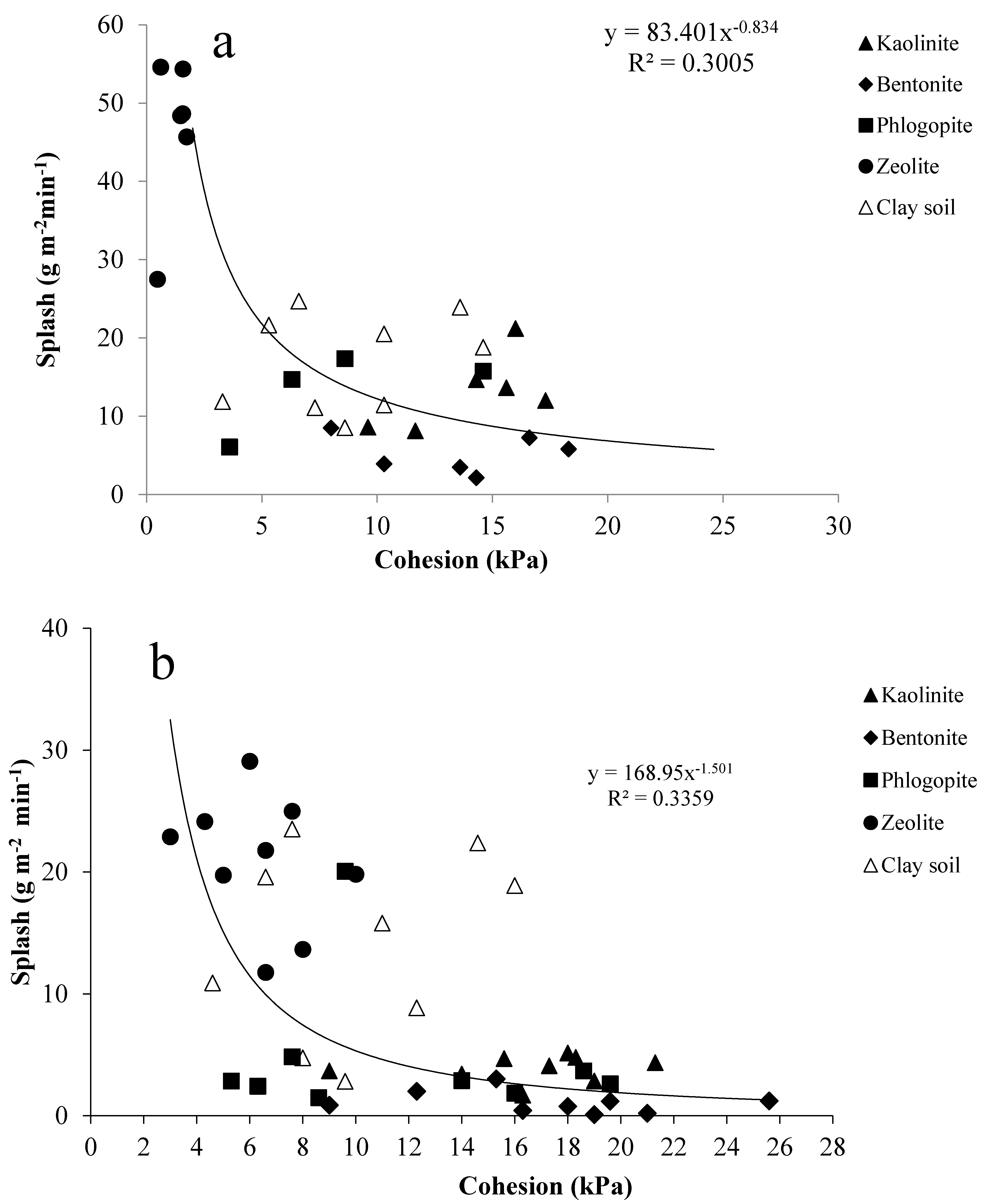
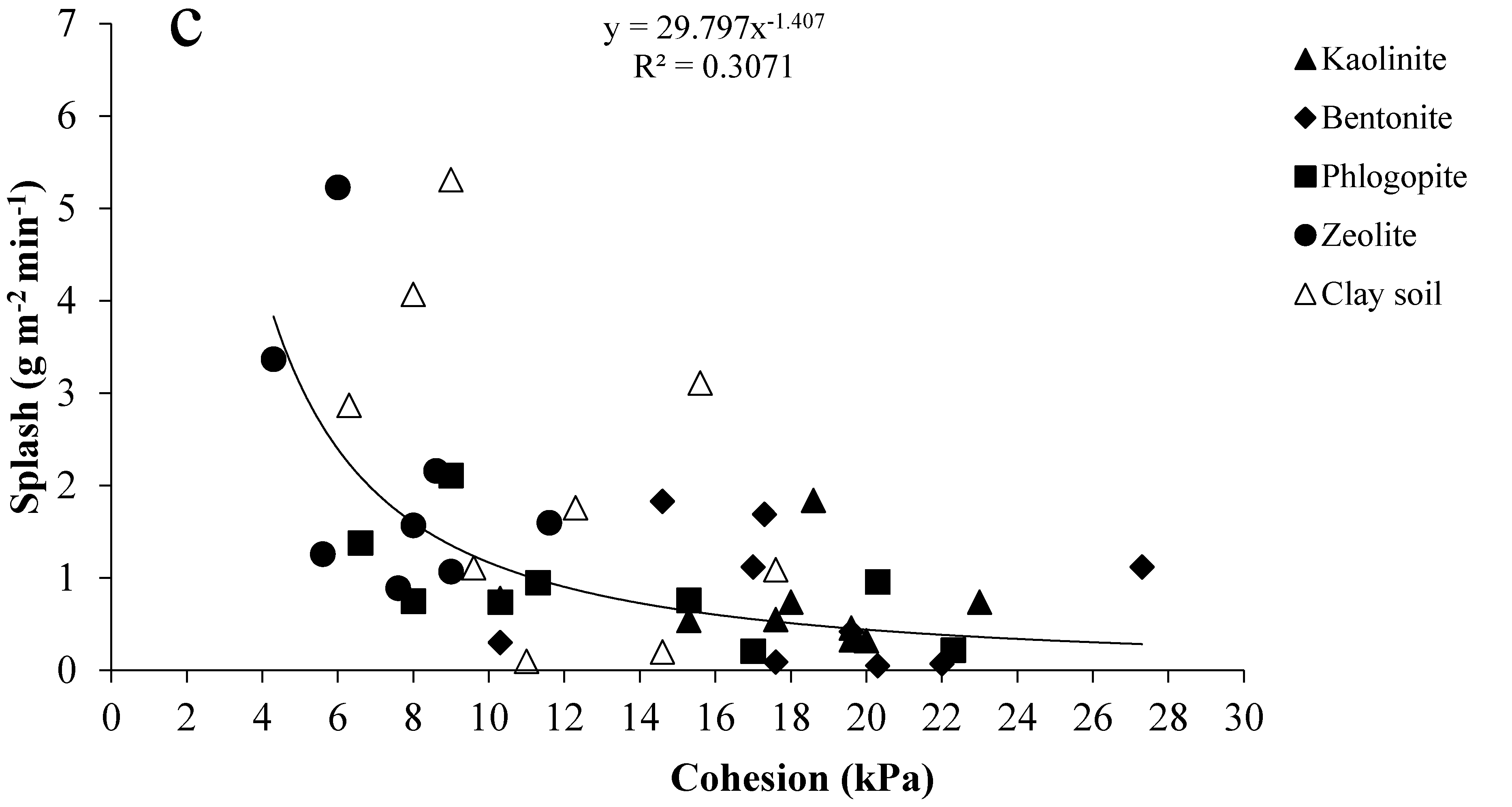
3.4. Relationships between Splash Erosion and Shear Strength
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The impacts of clay percent and clay type on the cohesion and splash erosion of clay–sand mixtures were studied at different initial water states in comparison with a clay soil under controlled conditions. The results revealed that the highest values of splash erosion were observed in the samples without the wetting and drying cycle. Furthermore, the splash erosion rate decreased following the drying and wetting cycles.
- (2)
- The lowest splash erosion rate was observed at an intermediate water content (i.e., plastic limit) compared with lower (air-dry) and higher (liquid limit) water statuses. Increases in the clay content led to decreases splash erosion due to structure formation in the clay–sand mixtures.
- (3)
- The shear strength of the clay–sand mixtures significantly increased following the wetting and drying cycles. The cohesion showed the following order for the clay–sand mixtures: bentonite > kaolinite > phlogopite > clay soil > zeolite. However, splash erosion showed the following order for the studied clay–sand mixtures: zeolite > clay soil > phlogopite > kaolinite > bentonite. These results show that splash erosion is not solely controlled by shear strength.
- (4)
- Nonlinear power relations were obtained between splash erosion and cohesion, showing that shear strength could explain about 30–33% of the splash erosion variability in the studied clay–sand mixtures.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbaszadeh Afshar, F.; Ayoubi, S.; Jalalian, A. Soil redistribution rate and its relationship with soil organic carbon and total nitrogen using 137Cs technique in a cultivated complex hillslope in western Iran. J. Environ. Radioact. 2010, 101, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Moghadam, B.; Jabarifar, M.; Bagheri, M.; Shahbazi, E. Effects of land use change on soil splash erosion in the semi-arid region of Iran. Geoderma 2015, 241–242, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legout, C.; Leguedois, S.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Issa, O.M. Splash distance and size distribution for various soils. Geoderma 2005, 124, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Cai, C. Splash erosion of clay-sand mixtures and its relationship with soil physical properties: The effects of particle size distribution on soil structure. Catena 2015, 135, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Erosion and Conservation, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2005; 303p.
- Angulo-Martinez, M.; Begueria, S.; Navas, A.; Machin, J. Splash erosion under natural rainfall on three soil types in NE Spain. Geomorphology 2010, 175–176, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Z.; Wei, M. Soil detachment by overland flow on steep cropland in the subtropical region of China. Hydrol. Process. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisal, F. The effect of raindrop size and impact velocity on sand splash. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1960, 40, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ellison, W.D. Studies of raindrop size erosion. Agric. Eng. 1944, 25, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, M.; Chenghu, Z.; Tongxin, Z.; Qiangguo, C. Modeling raindrop impact and splash erosion processes within a spatial cell: A stochastic approach. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 712–723. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Raindrop-impact-induced erosion processes and prediction: A review. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 2815–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Fraile, R.; Keizer, J.J.; Tiejiero, M.E.V.; Castro, A.; Palencia, C.; Calvo, I.; Ghahramani, A.; Ishikawa, Y.; Gomi, T.; et al. Effect of ground cover on splash and sheetwash erosion over a steep forested hillslope: A plot-scale study. Catena 2011, 85, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Saedi, T.; Shorafa, M.; Gorji, M.; KhaliliMoghadam, B. Indirect and direct effects of soil properties on soil splash erosion rate in calcareous soils of the central Zagross, Iran: A laboratory study. Geoderma 2016, 271, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwue, E.I. The effects of soil organic matter content. Rainfall duration and aggregate size on soil detachment. Soil Technol. 1991, 4, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Brovelli, A.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.Y.; Heng, B.C.P.; Tromp-van Meerveld, H.J. Effect of raindrop splash and transversal width on soil erosion: Laboratory flume experiments and analysis with the Hairsine-Rose model. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinjuan, C.H.; Qiangguo, C.; Wenjun, M.A. Comparative study on rain splash erosion of representative soils in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Planchon, O.; Esteves, M.; Silvera, N.; Lapetite, J.M. Raindrop erosion of tillage induced microrelief: Possible use of the diffusion equation. Soil Tillage Res. 2000, 56, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, S.; Mokhtari, J.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Zeraatpisheh, M. Erodibility of calcareous soils as influenced by land use and intrinsic soil properties in a semiarid region of central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shayea, N.A. The combined effect of clay and moisture content on the behavior of remolded unsaturated soils. Eng. Geol. 2001, 62, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedov, A.I.; Huang, C.; Levy, G.J. Antecedent moisture content and aging duration effects on seal formation and erosion in smectitic soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; El-Swaify, S.A.; Sutherland, R.A. Partitioning interrill splash and wash dynamics: A novel laboratory approach. Soil Technol. 1996, 9, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.; Kacevas, A.; Fiori, H. Soil erodibility assesments with simulated rainfall and with the USLE nomograph in soil from Uruguay. In Proceedings of the 16th World Congress Soil Science, Montpellier, France, 20–26 August 1998; p. 1041. [Google Scholar]
- Piccarreta, M.; Faulkner, H.; Bentivenga, M.; Capolongo, D. The influence of physic-chemical material properties of erosion process in the badlands of Basilicata, Southern Italy. Geology 2006, 29, 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Poesen, J. An improved splash transport model. Geology 1985, 29, 193–211. [Google Scholar]
- Torri, D.; Sfalanga, M.; Delsette, M. Splash detachment: Runoff depth and soil cohesion. Catena 1987, 14, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuddivira, M.N.; Stone, R.J.; Ekwue, E.I. Clay, Organic Matter, and Wetting Effects on Splash Detachment and Aggregate Breakdown under Intense Rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lin, L.; Ding, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, K.; Zhao, Y. Characteristics of Soil Erodibility K Value and Its Influencing Factors in the Changyan Watershed, Southwest Hubei, China. Land 2022, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.T.; Guo, W.; Hu, F.N.; Xu, C.Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.W.; Zheng, F.L. Effects of soil internal forces on splash detachment and transport of aggregate fragments in Mollisols of Northeast China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, N.; Johannsen, L.L.; Strauss, P.; Dostal, T.; Zumr, D.; Cochrane, T.A.; Klik, A. Splash erosion affected by initial soil moisture and surface conditions under simulated rainfall. Catena 2021, 196, 104827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, H.; Zhao, S. Soil internal forces initiate aggregate breakdown and splash erosion. Geoderma 2018, 320, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spera, S.T.; Denardin, J.E.; Escosteguy, P.A.V.; Santos, H.P.; Figueroa, E.A. Clay dispersion in microaggregates of soil incubated with limestone. Rev. Bras. De Ciência Do Solo 2008, 32, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, A.; Rengasamy, P.; McNeill, A.; Kumar, A. Nature of the clay-cation bond affects soil structure as verified by X-ray computed tomography. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Xia, J.; Miller, G.A.; Cai, C.; Guo, Z.; Arash, H. The effect of water content on the shear strength characteristics of granitic soils in South China. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 187, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kittrick, J.A.; Hope, E.W. A procedure for the particle size separation of soils for X-ray diffraction analysis. Soil Sci. 1963, 96, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C., Jr. X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- BSI (British Standards Institution). British Standards Institution). British Standard Methods of Test for Soils for Civil Engineering Campbell, D.J. 2001. Liquid and plastic limits. In Soil and Environmental Analysis-Physical Methods; Smith, K.A., Mullins, C.E., Eds.; Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 349–375. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, W.D. Soil erosion studies-part 2: Soil detachment hazard by raindrop splash. Agric. Eng. 1947, 28, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, M.; Modarres, R. Dry spell trend analysis of Isfahan Province, Iran. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 29, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Field studies of rainsplash erosion. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 1978, 3, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, L.P. Spatial variability: Its documentation, accommodation and implica tion to soil surveys. In Soil Spatial Variability; Nielsen, D.R., Bouma, J., Eds.; Pudoc: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 166–194. [Google Scholar]
- Rajarama, G.; Erbach, D.C. Effect of wetting and drying on soil physical properties. J. Terramech. 1999, 36, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.; Kroesbergen, B.; Kuipers, H. Some mechanical properties of aggregates of top soils from the IJsselmeerpolders. 2. Remoulded soil aggregates and the effects of wetting and drying cycles. Neth. J. Agri. Sci. 1984, 32, 215–227. [Google Scholar]
- Mouzai, L.; Bouhadef, M. Shear strength of compacted soil: Effects on splash erosion by single water drops. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2011, 36, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.; Ali, F.; Hashim, S.; Huat, B. Relationship between shear strength and soil water characteristic curve of an unsaturated granitic residual soil. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 2, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, B.H.; Miller, G.A. A constitutive model for unsaturated soil interfaces. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Met. 2008, 32, 1693–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Shanyoug, W.; Chan, D. Experimental study of the fines content on dynamic compaction grouting in completely decomposed grantie of Hong Kong. Cons. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, B.; Marui, H. A new method for the correlation of residual shear strength of soil with mineralogical composition. Geothech. Geoenviron. Eng. J. 2005, 131, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domitrović, D.; Kovačević Zelić, B. The relationship between swelling and shear strength properties of bentonites. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris, France, 2–6 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Vonmoos, M.; Løken, T. The shearing behaviour of clays. Appl. Clay Sci. 1989, 4, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, L.E.; Mawby, R. Porosity influence on the shear strength of granular material–clay mixtures. Eng. Geol. 2000, 58, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, H. Influence of gradation and proportion of sand on stress–strain behavior of clay-sand mixtures. Int. J. Geo. Eng. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.E.; Alam, M.J. Effect of nonplastic silt content on undrained shear strength of sand–silt mixtures. Int. J. Geo. Eng. 2017, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.; Dexter, A. Dynamics of soil aggregation in an irrigated desert loess. Soil Tillage Res. 1989, 13, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, E.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Mahboubi, A.A.; Dexter, A.R. Prediction of soil hard-setting and physical quality using water retention data. Geoderma 2019, 338, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quansah, C. The effect of soil type, slope, rain intensity and their interactions on splash detachment and transport. Soil Sci. J. 1981, 32, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Raga, M.; Palencia, C.; Keesstra, S.; Jordan, A.; Fraile, R.; Angulo-Martinez, M.; Cerda, A. Splash erosion: A review with unanswered questions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, S. Effect of soil properties on erosion by wash and splash. Earth Surf. Process. 1979, 4, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G.J.; Mamedov, A.I.; Goldstein, D. Sodicity and water quality effects on slaking of aggregates from semi-arid soils. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, H.; Caron, J. Aggregate slaking during rapid wetting: Hydrophobicity and pore occlusion. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuddivira, M.N.; Stone, R.J.; Ekwue, E.I. Influence of cohesive and disruptive forces on strength and erodibility of tropical soils. Soil Till. Res. 2013, 133, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Soil mineralogy effects on seal formation, runoff and soil loss. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 24, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.; Paustian, K. Soil structure and soil organic matter II. A normalized stability index and the effect of mineralogy. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.; Çelik, I.; Kapur, S.; Ryan, J. Clay minerals, Ca/Mg ratio and Fe-Al-oxides in relation to structural stability, hydraulic conductivity and soil erosion in southeastern Turkey. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2005, 29, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Rachman, A.; Anderson, S.H.; Gantzer, C.J.; Thompson, A.L. Influence of long term cropping systems on soil physical properties related to soil erosibility. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Bradford, J.M. Single water drop splash detachment and mechanical properties of soils. Soil Sci. Am. J. 1985, 49, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clay (kg 100 kg−1) | Water Content (kg 100 kg−1) | Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite | Bentonite | Phlogopite | Zeolite | Clay Soil | ||
| 45 | PL | 22.4 | 27.6 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 12 |
| LL | 69.8 | 134.9 | 22.7 | 23.2 | 25 | |
| 30 | PL | 15.4 | 22.9 | 4.9 | 6.3 | 9 |
| LL | 48.1 | 119.2 | 15.2 | 19.7 | 18.7 | |
| 15 | PL | 9.3 | 14.3 | 4.6 | 5.8 | 8.2 |
| LL | 29.1 | 74.9 | 14.3 | 18.2 | 17 | |
| Treatments | Min | Max | Range | Mean | SD | CV % | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without W&D | |||||||
| Air-dry | 0.321 | 5.472 | 5.151 | 2.155 | 1.565 | 72.66 | 1.13 |
| PL | 0.065 | 2.27 | 2.205 | 0.915 | 0.701 | 76.6 | 0.79 |
| LL | 0.193 | 5.52 | 5.327 | 1.91 | 1.438 | 75.3 | 1.23 |
| 45 | 0.065 | 4.952 | 4.887 | 1.342 | 1.19 | 88.7 | 1.74 |
| 30 | 0.101 | 5.472 | 5.371 | 1.768 | 1.456 | 82.3 | 1.38 |
| 15 | 0.165 | 5.52 | 5.355 | 1.87 | 1.482 | 79.2 | 1.33 |
| One cycle of W&D | |||||||
| Air-dry | 0.074 | 2.53 | 2.456 | 1.062 | 0.93 | 87.5 | 0.45 |
| PL | 0.001 | 2.31 | 2.309 | 0.6 | 0.696 | 116 | 1.46 |
| LL | 0.018 | 2.95 | 2.923 | 1.025 | 0.94 | 91.7 | 0.67 |
| 45 | 0.001 | 201.7 | 2.016 | 0.615 | 0.661 | 107.4 | 1.07 |
| 30 | 0.016 | 2.53 | 2.514 | 0.888 | 0.891 | 100.3 | 0.79 |
| 15 | 0.059 | 2.95 | 2.891 | 1.183 | 0.986 | 83.4 | 0.43 |
| Two cycles of W&D | |||||||
| Air-dry | 0.058 | 5.04 | 0.482 | 0.201 | 0.125 | 62.5 | 1.28 |
| PL | 0.002 | 0.392 | 0.39 | 0.093 | 0.098 | 105.7 | 1.62 |
| LL | 0.002 | 0.73 | 0.728 | 0.187 | 0.197 | 105.3 | 1.53 |
| 45 | 0.002 | 0.2 | 0.198 | 0.066 | 0.05 | 75.3 | 0.51 |
| 30 | 0.002 | 0.318 | 0.316 | 0.122 | 0.081 | 65.9 | 0.79 |
| 15 | 0.018 | 0.73 | 0.712 | 0.293 | 0.185 | 63 | 0.68 |
| Treatments | Min | Max | Range | Mean | SD | CV % | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without W&D | |||||||
| Air-dry | 3.0 | 20 | 17 | 11.3 | 4.9 | 43.60 | 0.01 |
| PL | 5.0 | 25 | 20 | 13.8 | 5.6 | 40.60 | −0.05 |
| LL | 2.0 | 18 | 16 | 8.0 | 4.5 | 56.1 | 0.56 |
| 45 | 5.0 | 25 | 20 | 13.9 | 5.6 | 40.5 | 0.09 |
| 30 | 3.0 | 19 | 16 | 11.6 | 4.9 | 42.7 | −0.30 |
| 15 | 1.0 | 16 | 14 | 7.7 | 4.2 | 54.5 | 0.55 |
| One cycle of W&D | |||||||
| Air-dry | 4.0 | 21 | 17 | 12.6 | 5.0 | 39.9 | −0.05 |
| PL | 6.0 | 26 | 20 | 15.2 | 5.6 | 37.4 | −0.12 |
| LL | 3.0 | 19 | 16 | 9.4 | 4.7 | 50.0 | 0.72 |
| 45 | 6.0 | 26 | 20 | 15 | 5.6 | 36.9 | 0.01 |
| 30 | 5.0 | 20 | 15 | 13 | 5.0 | 38.6 | −0.28 |
| 15 | 3.0 | 18 | 15 | 8.9 | 4.4 | 49.4 | 0.70 |
| Two cycles of W&D | |||||||
| Air-dry | 6.0 | 22 | 16 | 14.1 | 5.0 | 35.5 | −0.14 |
| PL | 7.0 | 28 | 16.5 | 16.5 | 5.8 | 35.4 | −0.04 |
| LL | 4.0 | 21 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 4.7 | 44.3 | 0.68 |
| 45 | 7.0 | 28 | 21 | 16.6 | 5.6 | 33.8 | 0.01 |
| 30 | 5.0 | 23 | 18 | 14.2 | 5.1 | 36.6 | −0.12 |
| 15 | 4.0 | 20 | 16 | 10.6 | 4.7 | 44.4 | 0.74 |
| Without W&D Cycle | After One W&D Cycle | After Three W&D Cycles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay type | |||
| Phlogopite | 7.8 c | 8.8 c | 10.0 b |
| Bentonite | 11.9 a | 13.0 a | 13.8 a |
| Kaolinite | 11.3 b | 12.4 b | 13.5 a |
| Zeolite | 3.8 e | 4.7 e | 5.8 d |
| Clay soil | 6.6 d | 7.5 d | 8.6 c |
| Clay content (kg 100 kg−1) | |||
| 45 | 13.9 a | 15.2 a | 16.6 a |
| 30 | 7.7 c | 8.9 c | 10.6 c |
| 15 | 11.6 b | 13.0 b | 14.2 b |
| Water status | |||
| Air-dry | 8.5 b | 9.5 b | 10.6 b |
| PL | 10.4 a | 11.4 a | 12.4 a |
| LL | 6.0 c | 7.0 c | 8.0 c |
| Without W&D Cycle | After One W&D Cycle | After Three W&D Cycles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay type | |||
| Phlogopite | 10.60 c | 5.06 c | 2.58 c |
| Bentonite | 4.41 d | 2.30 e | 2.03 d |
| Kaolinite | 10.42 c | 4.40 d | 2.11 d |
| Zeolite | 30.01 a | 17.16 a | 3.41 a |
| Clay soil | 14.21 b | 11.98 b | 3.03 b |
| Clay content (kg 100 kg−1) | |||
| 45% | 13.42 c | 6.15 c | 1.22 c |
| 30% | 18.70 a | 11.83 a | 5.72 a |
| 15% | 17.68 b | 8.88 b | 2.93 b |
| Water status | |||
| Air-dry | 17.31 a | 9.24 b | 1.76 b |
| PL | 6.86 b | 4.50 c | 0.70 c |
| LL | 17.61 a | 10.81 a | 5.45 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayoubi, S.; Milikian, A.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Zhao, S. Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Shear Strength and Splash Erosion of Clay–Sand Mixtures. Minerals 2022, 12, 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111339
Ayoubi S, Milikian A, Mosaddeghi MR, Zeraatpisheh M, Zhao S. Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Shear Strength and Splash Erosion of Clay–Sand Mixtures. Minerals. 2022; 12(11):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111339
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyoubi, Shamsollah, Anashia Milikian, Mohammad Reza Mosaddeghi, Mojtaba Zeraatpisheh, and Shuai Zhao. 2022. "Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Shear Strength and Splash Erosion of Clay–Sand Mixtures" Minerals 12, no. 11: 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111339
APA StyleAyoubi, S., Milikian, A., Mosaddeghi, M. R., Zeraatpisheh, M., & Zhao, S. (2022). Impacts of Clay Content and Type on Shear Strength and Splash Erosion of Clay–Sand Mixtures. Minerals, 12(11), 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12111339








