Structural Study and Detrital Zircon Provenance Analysis of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit Rocks from Iraklia Island: From the Paleozoic Basement Unroofing to the Cenozoic Exhumation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
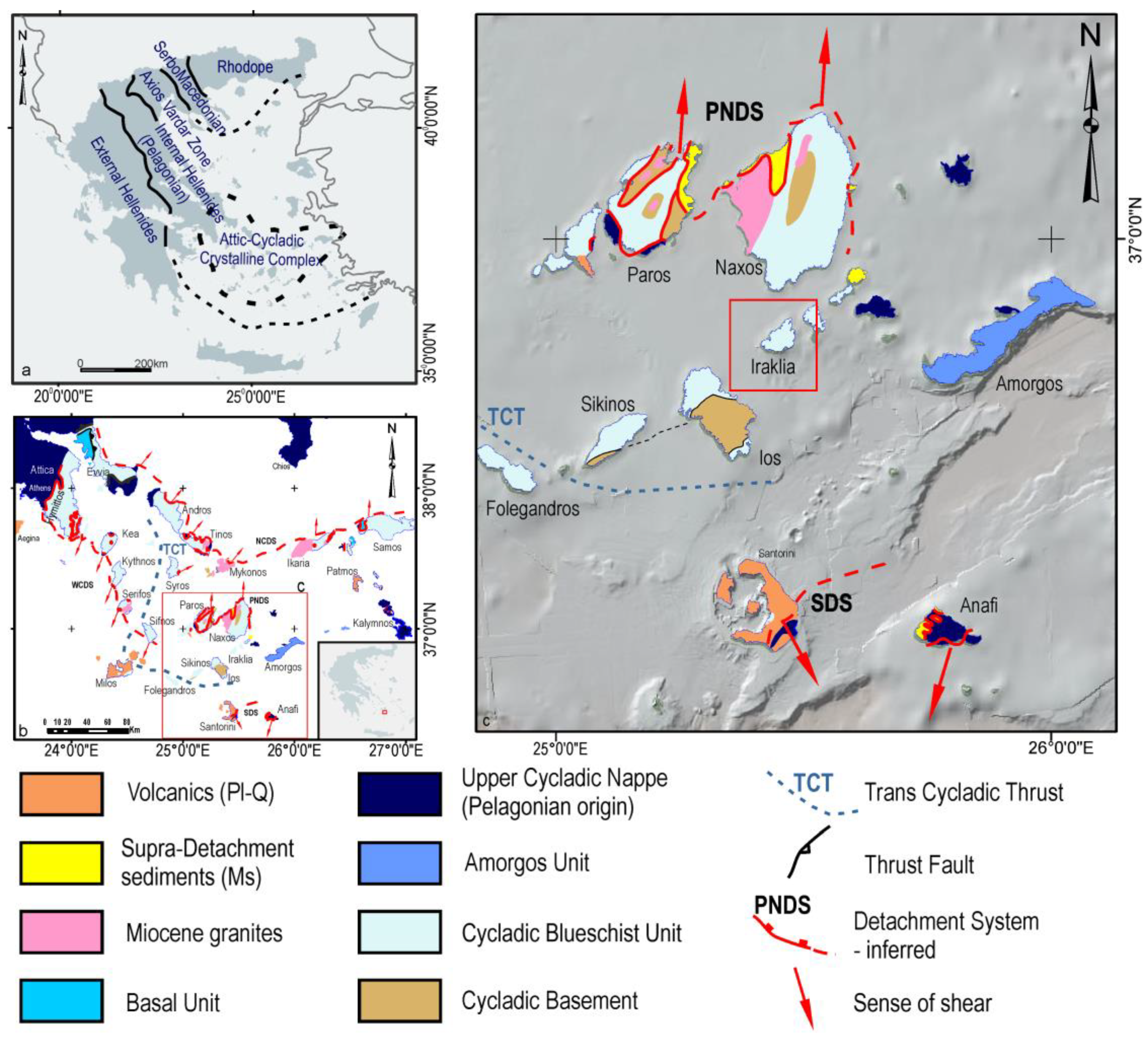
2. Geological Setting
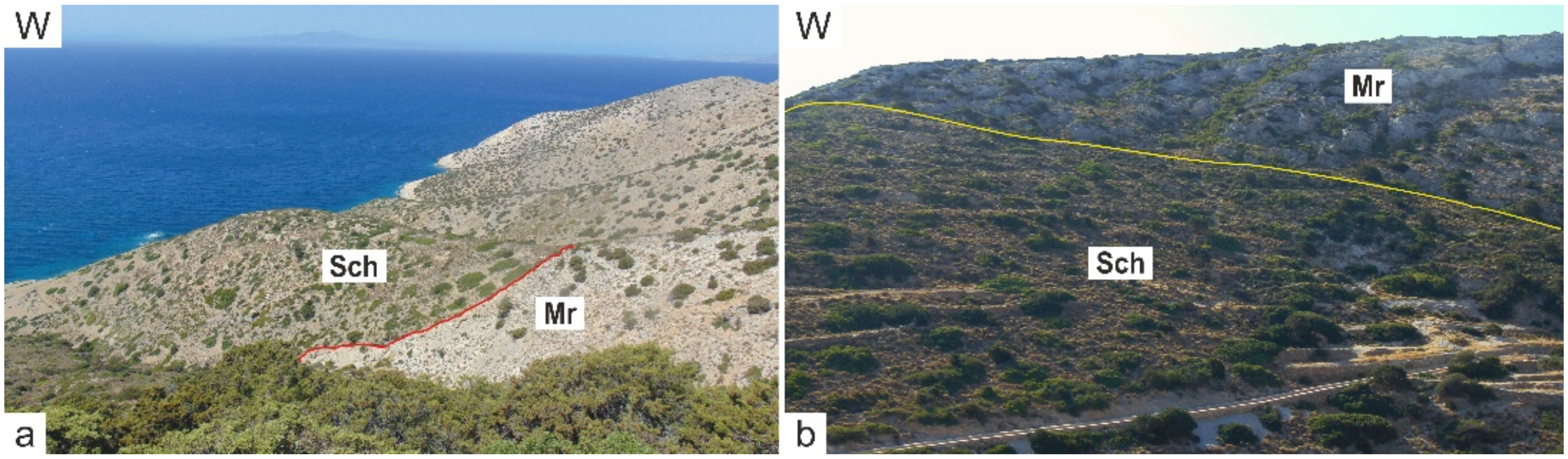
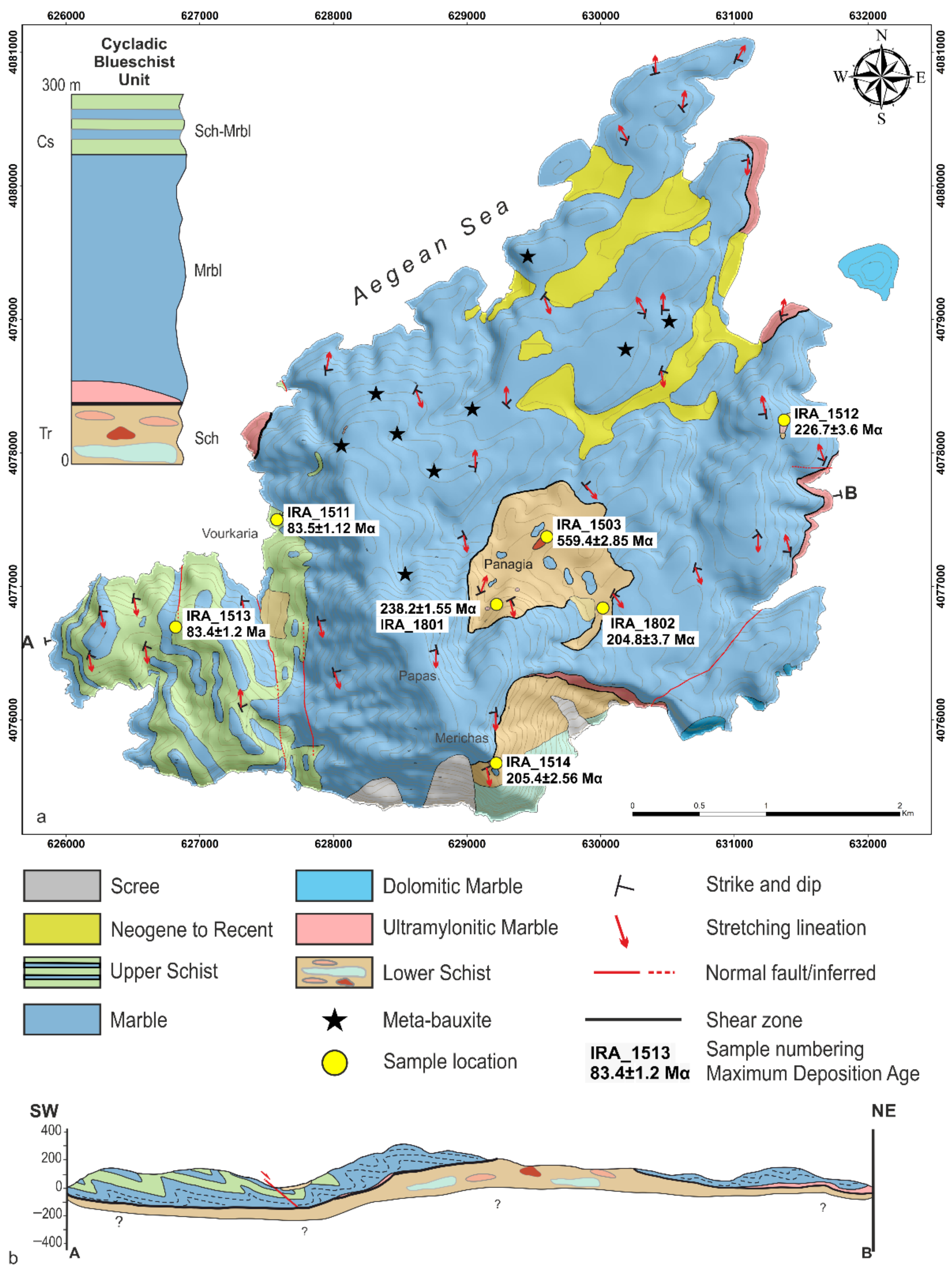
3. A New Geological Map of Iraklia
3.1. Lithostratigraphic Subdivision
3.2. Structures
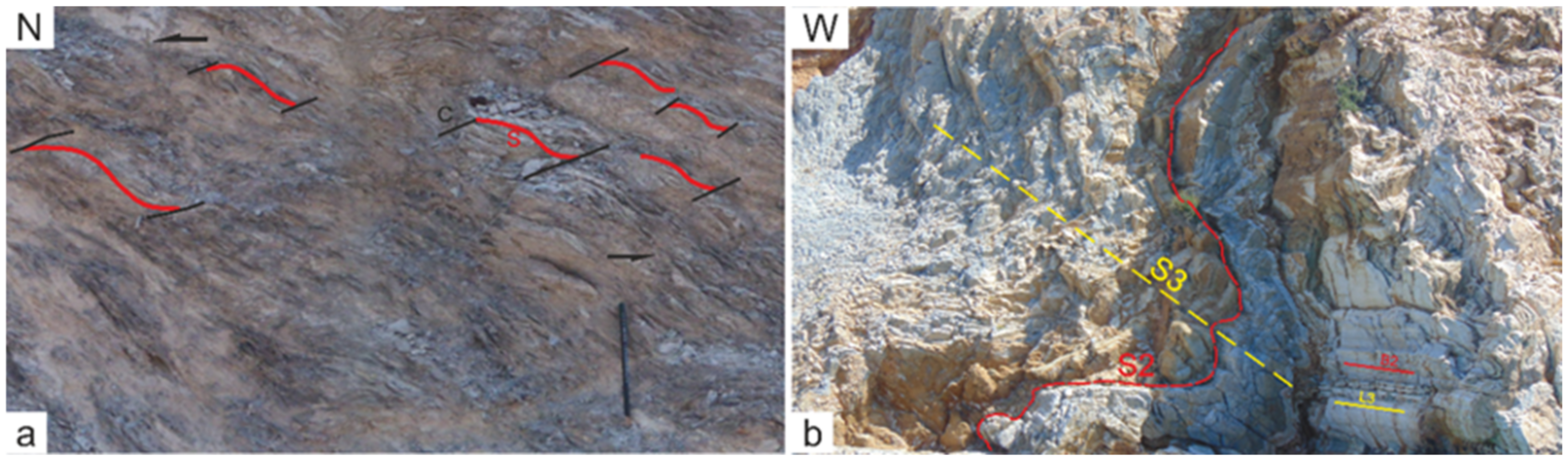
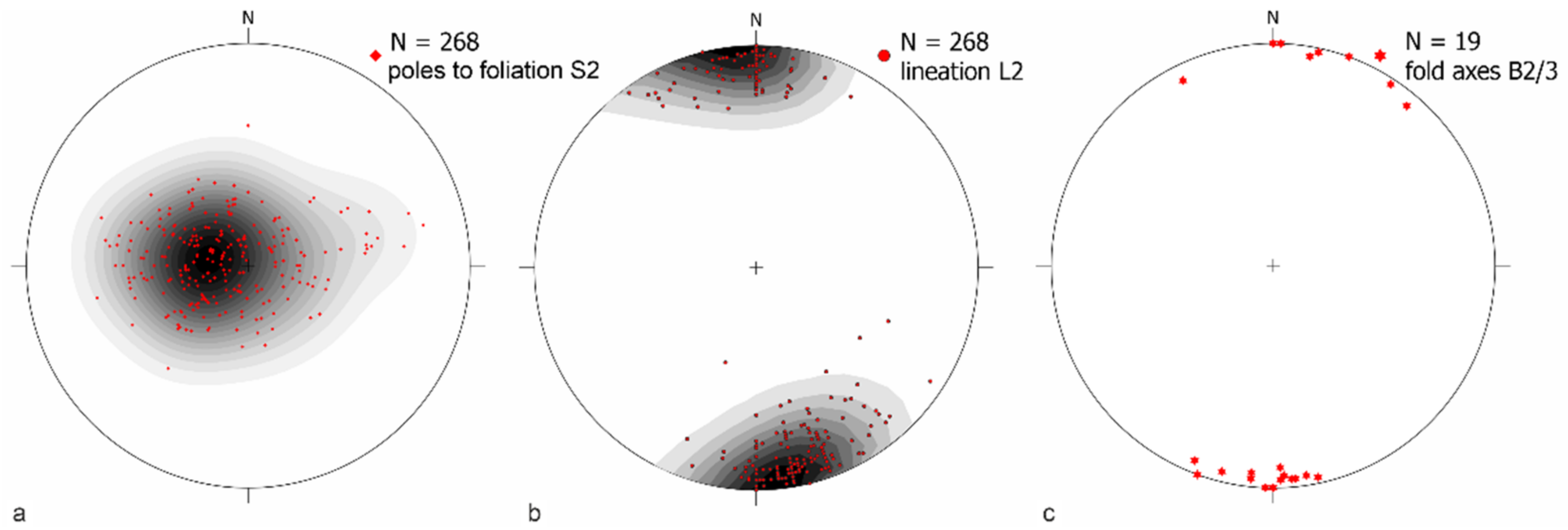
3.2.1. D1 Syn-Blueschist Facies Structures
3.2.2. D2 Ductile to Brittle Deformation
3.2.3. D3 Late Brittle Deformation
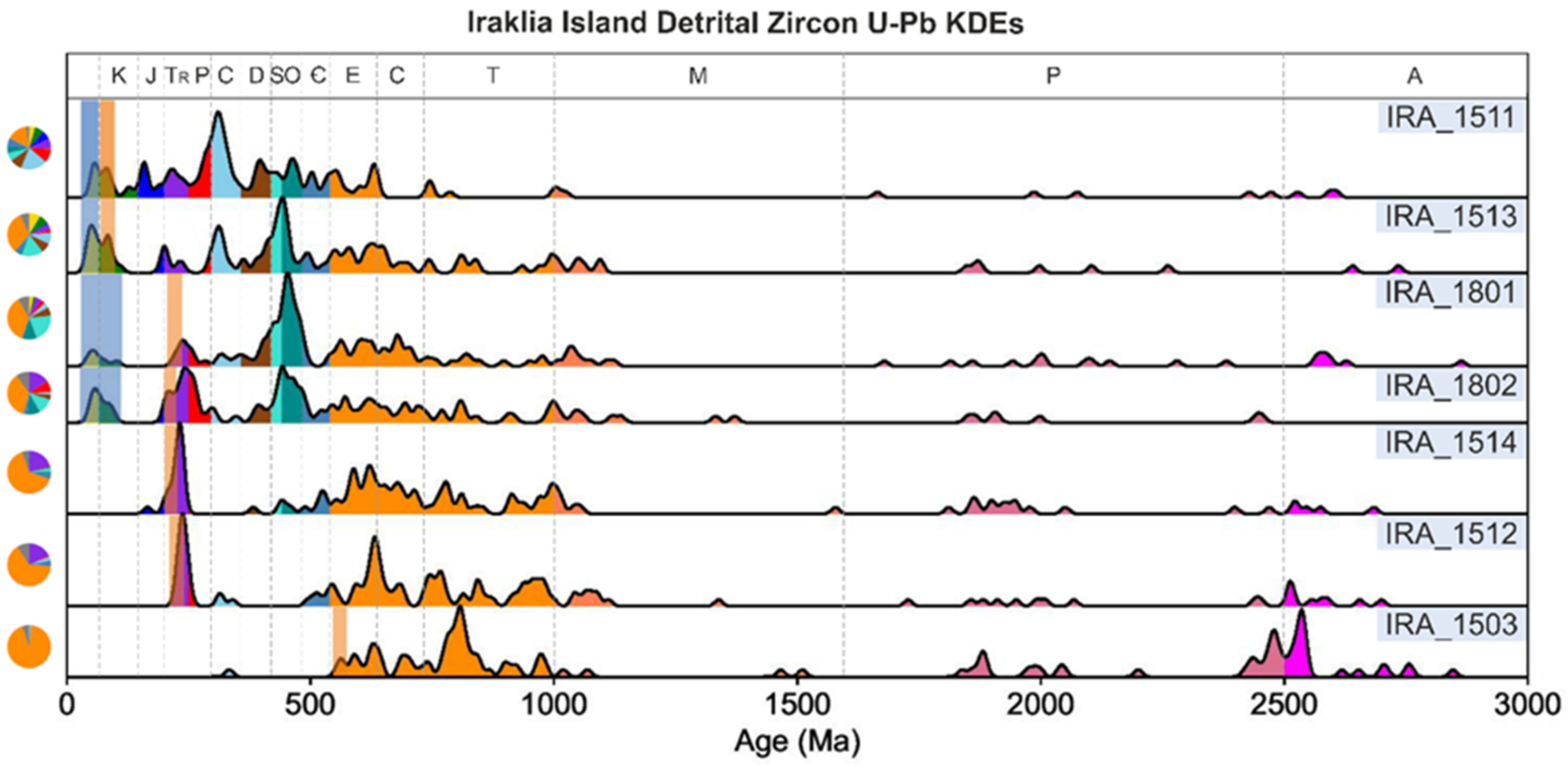
4. Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Results
4.1. Methodology
4.2. U-Pb Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Review of the Lithostratigraphy of Iraklia
5.2. Structures and Metamorphism
5.3. Provenance of Detrital Zircons
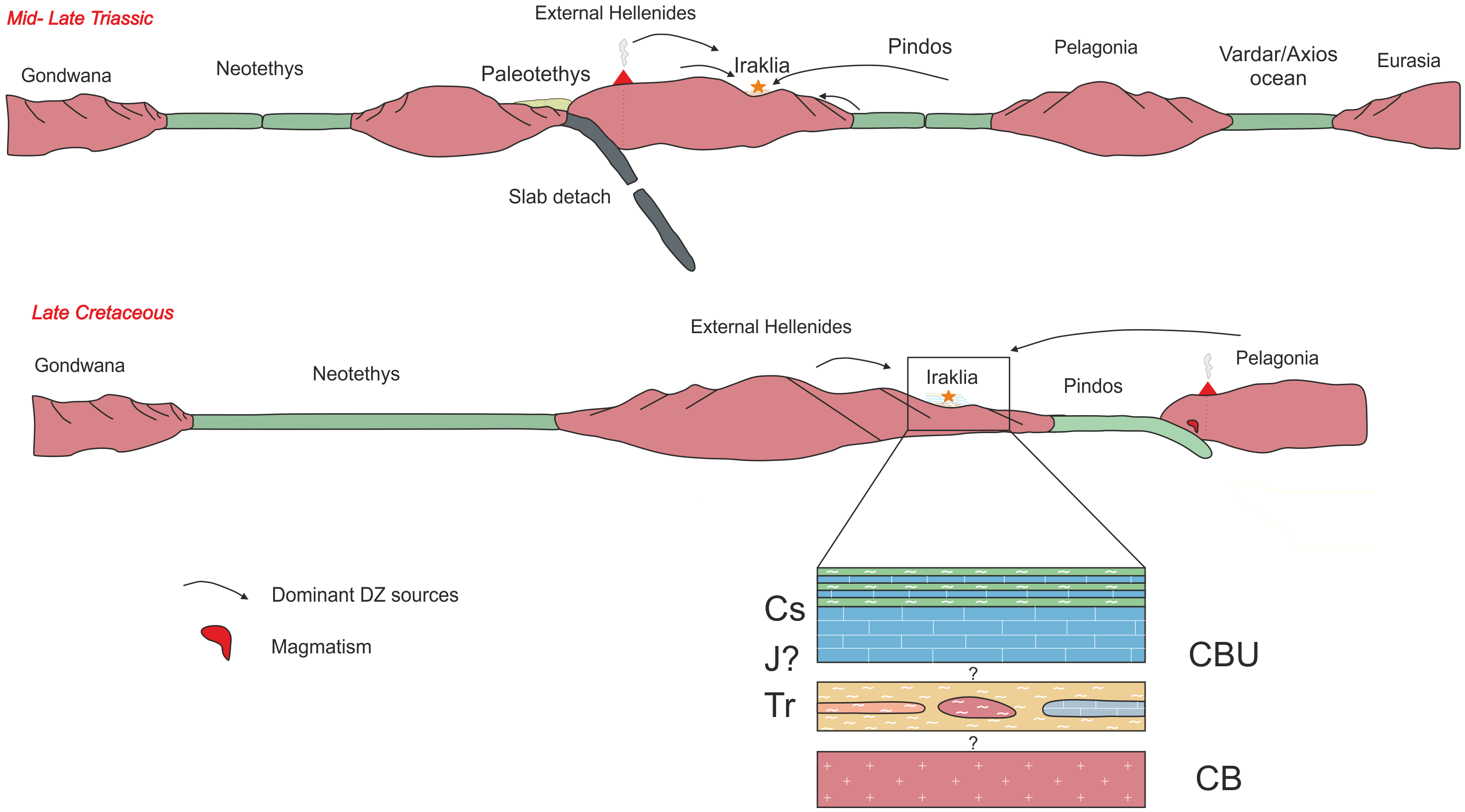
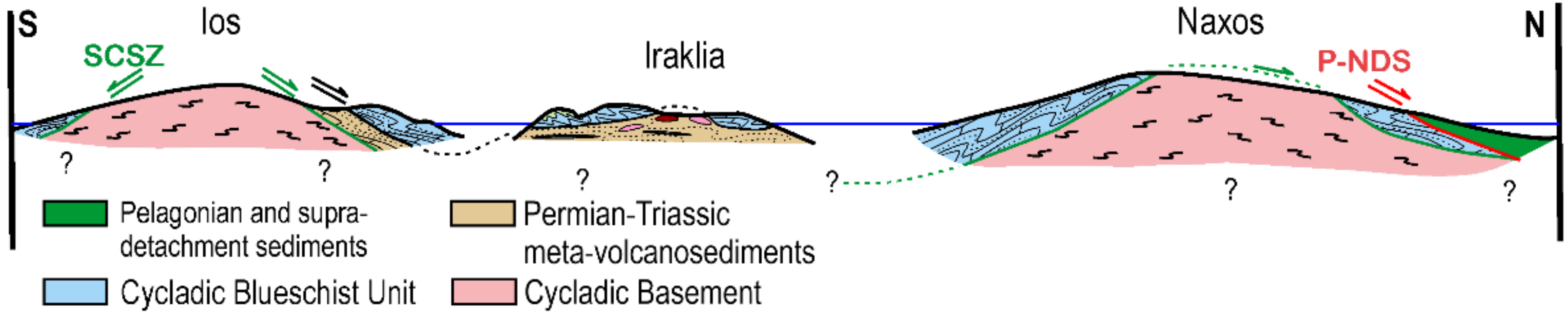
5.4. Regional Implications
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lister, G.S.; Banga, G.; Feenstra, A. Metamorphic core complexes of Cordilleran type in the Cyclades Aegean Sea, Greece. Geology 1984, 12, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröcker, M.; Kreuzer, H.; Matthews, A.; Okrusch, M. 40Ar/39Ar and oxygen isotope studies of polymetamorphism from Tinos Island, Cycladic blueschist belt, Greece. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1993, 11, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, P.; Brun, J.P.; Jolivet, L. Structure and kinematics of Upper Cenozoic extensional detachment on Naxos and Paros (Cyclades Islands, Greece). Tectonics 1993, 12, 1180–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröcker, M.; Franz, L. Rb–Sr isotope studies on Tinos Island (Cyclades, Greece): Additional time constraints for metamorphism, extent of infiltration-controlled overprinting and deformational activity. Geol. Mag. 1998, 135, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichau, S.; Ring, U.; Carter, A.; Monié, P.; Bolhar, R.; Stockli, D.; Brunel, M. Extensional faulting on Tinos Island, Aegean Sea, Greece: How many detachments? Tectonics 2007, 26, TC4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolivet, L.; Brun, J.P. Cenozoic geodynamic evolution of the Aegean. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 99, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, L.; Lecomte, E.; Huet, B.; Denèle, Y.; Lacombe, O.; Labrousse, L.; Le Pourhiet, L.; Mehl, C. The North Cycladic detachment system. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ring, U.; Glodny, J.; Will, T.; Thomson, S. The Hellenic Subduction System: High-Pressure Metamorphism, Exhumation, Normal Faulting, and Large-Scale Extension. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 45–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasemann, B.; Schneider, D.A.; Stockli, D.F.; Iglseder, C. Miocene bivergent crustal extension in the Aegean: Evidence from the western Cyclades (Greece). Lithosphere 2012, 4, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soukis, K.; Stockli, D.F. Structural and thermochronometric evidence for multi-stage exhumation of southern Syros, Cycladic islands, Greece. Tectonophysics 2013, 595, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, B.; Labrousse, L.; Monjé, P.; Malvoisin, B.; Jolivet, L. Coupled phengite 40Ar-39Ar geochronology and thermobarometry: PTt evolution of Andros Island (Cyclades, Greece). Geol. Mag. 2014, 152, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandri, C.; Soukis, K.; Maffione, M.; Özkaptan, M.; Vassilakis, E.; Lozios, S.; Van Hinsbergen, D.J. Vertical-axis rotations accommodated along the Mid-Cycladic lineament on Paros Island in the extensional heart of the Aegean orocline (Greece). Lithosphere 2017, 9, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, D.A.; Grasemann, B.; Lion, A.; Soukis, K.; Draganits, E. Geodynamic significance of the Santorini Detachment System (Cyclades, Greece). Terra Nova 2018, 30, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flansburg, M.E.; Stockli, D.F.; Poulaki, E.M.; Soukis, K. Tectono-magmatic and stratigraphic evolution of the Cycladic Basement, Ios Island, Greece. Tectonics 2019, 38, 2291–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulaki, E.M.; Stockli, D.F.; Flansburg, M.E.; Soukis, K. Zircon U-Pb chronostratigraphy and provenance of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit and Cycladic Basement on Sikinos and Ios Islands, Greece. Tectonics 2019, 38, 2291–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdis, V.; Triantaphyllis, M. Geological Map, Sheets Iraklia and Schinoussa, Scale 1: 50,000; Department of Geology and Geological Mapping: Athens, Greece, 1994.
- Behrmann, J.H.; Seckel, C. Structures, flow stresses, and estimated strain rates in metamorphic rocks of the Small Cyclades Islands Iraklia and Schinoussa (Aegean Sea, Greece). Geotecton. Res. 2007, 95, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, D. Tectonic evolution of the Cycladic blueschist belt (Aegean Sea, Greece). In Chemical Transport in Metasomatic Processes; Helgeson, H.C., Ed.; D. Reidel Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 429–450. [Google Scholar]
- Henjes-Kunst, F.; Kreuzer, H. Isotopic dating of pre-alpidic rocks from the island of Ios (Cyclades, Greece). Contr. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 80, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keay, S.; Lister, G. African provenance for the metasediments and meta-igneous rocks of the Cyclades, Aegean Sea, Greece. Geology 2002, 30, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröcker, M.; Pidgeon, R.T. Protolith Ages of Meta-igneous and Metatuffaceous Rocks from the Cycladic Blueschist Unit, Greece: Results of a Reconnaissance U-Pb Zircon Study. J. Geol. 2007, 115, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwen, K.; Bröcker, M.; Berndt, J. Depositional ages of clastic metasediments from Samos and Syros, Greece: Results of a detrital zircon study. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 104, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröcker, M.; Huyskens, M.; Berndt, J. U–Pb dating of detrital zircons from Andros, Greece: Constraints for the time of sediment accumulation in the northern part of the Cycladic blueschist belt. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsken, T.; Bröcker, M.; Berndt, J.; Gärtner, C. Maximum sedimentation ages and provenance of metasedimentary rocks from Tinos Island, Cycladic blueschist belt, Greece. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 105, 1923–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seman, S.; Stockli, D.F.; Soukis, K. The provenance and internal structure of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit revealed by detrital zircon geochronology, Western Cyclades, Greece. Tectonics 2017, 36, 1407–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasemann, B.; Huet, B.; Schneider, D.A.; Rice, A.H.N.; Lemonnier, N.; Tschegg, C. Miocene postorogenic extension of the Eocene synorogenic imbricated Hellenic subduction channel: New constraints from Milos (Cyclades, Greece). GSA Bull. 2018, 130, 238–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pe-Piper, G.; Piper, D.J.W. The igneous rocks of Greece. In The Anatomy of an Orogen; Gebruder Borntraeger: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 1–573. [Google Scholar]
- Soukis, K.; Papanikolaou, D. Contrasting geometry between Alpine and late- to post-Alpine tectonic structures in Anafi Island (Cyclades). Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2004, 36, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lekkas, S.; Skourtsos, E.; Soukis, K.; Kranis, H.; Lozios, S.G.; Alexopoulos, A.; Koutsovitis, P. Late Miocene detachment faulting and crustal extension in SE Attica (Greece). Geoph. Res. Abstr. 2011, 13, EGU2011–EGU13016. [Google Scholar]
- Grasemann, B.; Schneider, D.A.; Soukis, K.; Roche, V.; Hubmann, B. Paleogeographic position of the central Dodecanese Islands, southeastern Greece: The push-pull of Pelagonia. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royden, L.H. Evolution of retreating subduction boundaries formed during continental collision. Tectonics 1993, 12, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürr, S.; Altherr, R.; Keller, J.; Okrusch, M.; Seidel, E. The Median Aegean Crystalline Belt: Stratigraphy, structure, metamorphism, magmatism. In Alps, Apennines, Hellenides; Closs, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; Volume 38, pp. 455–477. [Google Scholar]
- Böger, H. Stratigraphische und tektonische Verknuepfungen kontinentaler Sedimente des Neogens im Aegais-Raum. Geol. Rundsch. 1983, 72, 771–813. [Google Scholar]
- Menant, A.; Jolivet, L.; Vrielynck, B. Kinematic reconstructions and magmatic evolution illuminating crustal and mantle dynamics of the eastern Mediterranean region since the late Cretaceous. Tectonophysics 2016, 675, 103–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jansen, J.B.H. Metamorphism on Naxos, Greece. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Stouraiti, C.; Pantziris, I.; Vasilatos, C.; Kanellopoulos, C.; Mitropoulos, P.; Pomonis, P.; Chiaradia, M. Ophiolitic remnants from the upper and intermediate structural unit of the Attic-Cycladic Crystalline Belt (Aegean, Greece): Fingerprinting geochemical affinities of magmatic precursors. Geosciences 2017, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavrogonatos, C.; Magganas, A.; Kati, M.; Brocker, M.; Voudouris, P. Ophicalcites from the Upper Tectonic Unit on Tinos, Cyclades, Greece: Mineralogical, geochemical and isotope evidence for their origin and evolution. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 110, 809–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, D.J. Contribution to the geology of Aegean Sea. The Island of Andros. Ann. Géol. Pays Hellén. 1978, 29, 477–553. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, M.C.; Geyssant, J.; Kienast, J.R.; Lepvrier, C.; Maluski, H.; Papanikolaou, D. A geologic reconnaissance of the Cycladic Blueschist Belt, Greece. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1981, 92, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröcker, M. Die Blauschiefer-Grünschiefer-Assoziation der Insel Tinos (Kykladen, Griechenland) und ihre kontaktmetamorphe Überprägung. Geotekton. Forsch. 1990, 74, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Keiter, M.; Ballhaus, C.; Tomaschek, F. A New Geological Map of the Island of Syros (Aegean Sea, Greece): Implications for Lithostratigraphy and Structural History of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2011, 2011, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, M.; Barnes, J.D.; Behr, W.M.; Kotowski, A.J.; Stockli, D.F.; Soukis, K. Insights from elastic thermobarometry into exhumation of high-pressure metamorphic rocks from Syros, Greece. Solid Earth 2021, 12, 1335–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, M.; Kienast, J.R. Subduction, collision et schistes bleus; l’exemple de l’Egee (Grece). Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 1982, 7, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijbrans, J.R.; McDougall, I. Metamorphic evolution of the Attic Cycladic Metamorphic belt on Naxos (Cyclades, Greece) utilizing 40Ar/39Ar age spectrum measurements. J. Metamorph. Geol. 1988, 6, 571–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, M.; Scherer, E.E.; Tomaschek, F.; Münker, C.; Keiter, M.; Berndt, J.; Ballhaus, C. High precision Lu–Hf geochronology of Eocene eclogite-facies rocks from Syros, Cyclades, Greece. Chem. Geol. 2007, 243, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowski, A.J.; Behr, W.M.; Cisneros, M.; Stockli, D.F.; Soukis, K.; Barnes, J.; Ortega-Arroyo, D. Subduction, underplating, and return flow recorded in the Cycladic Blueschist Unit exposed on Syros Island, Greece. In Earth and Space Science Open Archive; ESSOAr: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ring, U.; Pantazides, H.; Glodny, J.; Skelton, A. Forced return flow deep in the subduction channel, Syros, Greece. Tectonics 2020, 39, e2019TC005768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keay, S.; Lister, G.; Buick, I. The timing of partial melting, Barrovian metamorphism and granite intrusion in the Naxos metamorphic core complex Cyclades, Aegean Sea, Greece. Tectonophysics 2001, 342, 275–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denèle, Y.; Lecomte, E.; Jolivet, L.; Lacombe, O.; Labrousse, L.; Huet, B.; Le Pourhiet, L. Granite intrusion in a metamorphic core complex: The example of the Mykonos laccolith (Cyclades, Greece). Tectonophysics 2011, 501, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaudoin, A.; Laurent, V.; Augier, R.; Jolivet, L.; Lahfid, A.; Arbaret, L.; Rabillard, A.; Menant, A. The Ikaria high-temperature metamorphic core complex (Cyclades, Greece): Geometry, kinematics and thermal structure. J. Geodyn. 2015, 92, 18–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurent, V.; Beaudoin, A.; Jolivet, L.; Arbaret, L.; Augier, R.; Rabillard, A.; Menant, A. Interrelations between extensional shear zones and synkinematic intrusions: The example of Ikaria Island (NE Cyclades, Greece). Tectonophysics 2015, 651, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.Y.; Neubauer, F.; Bernroider, F.; Genser, J.; Liu, J.; Friedl, G. Low-grade retrogression of a high-temperature metamorphic core complex: Naxos, Cyclades, Greece. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2017, 129, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peillod, A.; Ring, U.; Glodny, J.; Skelton, A. An Eocene/Oligocene blueschist−/greenschist-facies P-T loop from the Cycladic Blueschist unit on Naxos island, Greece: Deformation-related reequilibration vs thermal relaxation. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2017, 35, 805–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, U.; Glodny, J.; Pelliod, A.; Skelton, A. The timing of high-temperature conditions and ductile shearing in the footwall of the Naxos extensional fault system, Aegean Sea, Greece. Tectonophysics 2018, 700, 108–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, U.; Thompson, S.; Brocker, M. Fast extension but little exhumation: The Vari detachment in the Cyclades, Greece. Geol. Mag. 2003, 140, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xypolias, P.; Kokkalas, S.; Skourlis, K. Upward extrusion and subsequent transpression as a possible mechanism for the exhumation of HP/LT rocks in Evia Island (Aegean Sea, Greece). J. Geodyn. 2003, 35, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, V.; Laurent, V.; Cardello, G.L.; Jolivet, L.; Scaillet, S. Anatomy of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit on Sifnos Island (Cyclades, Greece). J. Geodyn. 2016, 97, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huet, B.; Labrousse, L.; Jolivet, L. Thrust or detachment? Exhumation processes in the Aegean: Insight from a field study on Ios (Cyclades, Greece). Tectonics 2009, 28, TC3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xypolias, P.; Iliopoulos, I.; Chatzaras, V.; Kokkalas, S. Subduction- and exhumation-related structures in the Cycladic Blueschists: Insights from south Evia Island (Aegean region, Greece). Tectonics 2012, 31, TC2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargnesi, E.A.; Stockli, D.F.; Mancktelow, N.; Soukis, K. Miocene core complex development and coeval supradetachment basin evolution of Paros, Greece, insights from (U–Th)/He thermochronometry. Tectonophysics 2013, 595, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.C.; Lister, G.S. Structural analysis of basement tectonites from the Aegean metamorphic core complex of Ios, Cyclades, Greece. J. Struct. Geol. 1996, 18, 1437–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippon, M.; Brun, J.P.; Gueydan, F. Deciphering subduction from exhumation in the segmented Cycladic Blueschist unit (Central Aegean, Greece). Tectonophysics 2012, 524, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, M.; Behrmann, J.H. Strain and flow in the metamorphic core complex of Ios Island (Cyclades, Greece). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 105, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.; Dubosq, R.; Schneider, D.A.; Grasemann, B.; Soukis, K. Along-strike consistency of an extensional detachment system, West Cyclades, Greece. Terra Nova 2019, 31, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.J.; Schneider, D.A.; Grasemann, B.; Soukis, K.; Lozios, S.; Hollinetz, M.S. Lateral Termination of a Cycladic-Style Detachment System (Hymittos, Greece). Tectonics 2020, 39, e2020TC006128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altherr, R.; Kreuzer, H.; Lenz, H.; Wendt, I.; Harre, W.; Dürr, S. Further evidence for a Late Cretaceous low-pressure/high-temperature terrane in the Cyclades, Greece. Chem. Erde 1994, 54, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhar, R.; Ring, U.; Allen, C.M. An integrated zircon geochronological and geochemical investigation into the Miocene plutonic evolution of the Cyclades, Aegean Sea, Greece: Part 1: Geochronology. Contr. Miner. Petrol. 2010, 160, 719–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouraiti, C.; Mitropoulos, P.; Tarney, J.; Barreiro, B.; McGrath, A.M.; Baltatzis, E. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of late Miocene granitoids, Cyclades, southern Aegean: Nature of source components. Lithos 2010, 114, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouraiti, C.; Baziotis, I.; Asimow, P.D.; Downes, H. Geochemistry of the Serifos calc-alkaline granodiorite pluton, Greece: Constraining the crust and mantle contributions to I-type granitoids. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 1657–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, D.J. On the structural geology and tectonics of Paros Island (Aegean Sea). Ann. Geol. Pays Hellén. 1977, 28, 450–464. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, D.J. Contribution to the geology of Aegean Sea. The island of Paros. Ann. Géol. Pays Hellén. 1980, 30, 65–96. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Maar, P.A. Metamorphism on Ios and the Geological History of the Southern Cyclades, Greece. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Andriessen, P.A.M.; Banga, G.; Hebeda, E.H. Isotopic age study of pre-Alpine rocks in the basal units on Naxos, Sikinos and Ios, Greek Cyclades. Geol. Mijnb. 1987, 66, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, M.; Reischmann, T. Single zircon geochronology of orthogneisses from Paros, Greece. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 1998, 32, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Reischmann, T. Pre alpine origin of tectonic units from the metamorphic complex of Naxos, Greece, identified by single zircon Pb/Pb dating. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 1998, 32, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zlatkin, O.; Avigad, D.; Gerdes, A. New Detrital Zircon Geochronology from the Cycladic Basement (Greece): Implications for the Paleozoic Accretion of Peri-Gondwanan Terranes to Laurussia. Tectonics 2018, 37, 4679–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, A.; Stouraiti, C.; Windley, B. Geochemistry of mylonitic gneisses from the Cycladic Basement Unit (Paros and Serifos, Aegean Sea): Implications for protoliths of the high-grade gneisses. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 106, 2067–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.A.; Lister, G.S. Detachment faults in the Aegean core complex of Ios, Cyclades, Greece. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1999, 154, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.; Lister, G. Core-complex-related extension of the Aegean lithosphere initiated at the Eocene-Oligocene transition. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, B02401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.N.; Ring, U.; Brichau, S.; Glodny, J.; Will, T.M. Timing and nature of formation of the Ios metamorphic core complex, southern Cyclades, Greece. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2009, 321, 139–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augier, R.; Jolivet, L.; Gadenne, L.; Lahfid, A.; Driussi, O. Exhumation kinematics of the Cycladic Blueschists unit and back-arc extension, insight from the Southern Cyclades (Sikinos and Folegandros Islands, Greece). Tectonics 2014, 34, 152–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keay, S. The Geological Evolution of the Cyclades, Greece: Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb Geochronology. Ph.D. Thesis, Research School of Earth Science, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulaki, E.M.; Stockli, D.F.; Flansburg, M.E.; Gevedon, M.L.; Stockli, L.D.; Barnes, J.D.; Soukis, K.; Kitajima, K.; Valley, J.W. Zircon U-Pb and geochemical signatures in high-pressure, low-temperature metamorphic rocks as recorders of subduction zone processes, Sikinos and Ios islands, Greece. Chem. Geol. 2021, 582, 120447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, T.; Altherr, R.; Hartung, B.; Hatzipanagiotou, K.; Kreuzer, H.; Harre, W.; Klein, H.; Keller, J.; Geenen, E.; Böger, H. Remnants of a late Cretaceous high temperature belt on the island of Anafi (Cyclades, Greece). Neues J. Miner. Abh. 1982, 145, 157–182. [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau, M. Correlation of the Hellenic nappes in the south-east Aegean and their tectonic reconstruction. In The Geological Evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean. Special Publication of the Geological Society of London; Dixon, J.E., Robertson, A.H.F., Eds.; Blackwell Science Publishing: Oxford, UK, 1984; pp. 517–527. [Google Scholar]
- Papanikolaou, D. The Geology of Greece; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brodhag, S.; Gracia-Calvo, M.; Schiwek, P. Geologie und Tektonik der Insel Iraklia/Kykladen (Griechenland)—Unpubl.nMapping Report; University of Freiburg: Freiburg, Germany, 2003; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.H.; Stockli, D.F. Zircon U-Pb and trace element zoning characteristics in an anatectic granulite domain: Insights from LASS-ICP-MS depth profiling. Lithos 2015, 239, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.E.; Pearson, N.J.; Griffin, W.L.; Belousova, E.A. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem. Geol. 2004, 211, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sláma, J.; Košler, J.; Condon, D.J.; Crowley, J.L.; Gerdes, A.; Hanchar, J.M.; Schaltegger, U. Plešovice zircon—A new natural reference material for U–Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.; Woodhead, J.D.; Hellstrom, J.C.; Hergt, J.M.; Greig, A.; Maas, R. Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust downhole fractionation correction. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2010, 11, Q0AA06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrus, J.A.; Kamber, B.S. VizualAge: A novel approach to laser ablation ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology data reduction. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2012, 36, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, G.R.; Sharman, J.P.; Sylvester, Z. DetritalPy: A Python-based toolset for visualizing and analysing detrital geo-thermochronologic data. Depos. Rec. 2018, 4, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubatto, D. Zircon trace element geochemistry: Partitioning with garnet and link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism. Chem. Geol. 2002, 184, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnemann, U.; Ouzegane, K.; Drareni, A.; Hofmann, M.; Becker, S.; Gärtner, A.; Sagawe, A. Sands of West Gondwana: An archive of secular magmatism and plate interactions—A case study from the Cambro-Ordovician section of the Tassili Ouan Ahaggar (Algerian Sahara) using U–Pb–LA-ICP-MS detrital zircon ages. Lithos 2011, 123, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.O.; Schaltegger, U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, W.R.; Gehrels, G.E. Use of U-Pb ages of detrital zircons to infer maximum depositional ages of strata: A test against a Colorado Plateau Mesozoic database. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 288, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoux, L. Stratigraphie, Structure et Métamorphisme de l’île d’Amorgos (Cyclades, Grèce). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Dürr, S. Geological Map of Greece, 1:50.000, Amorgos–Donousa Sheet; Institute of Geological and Mining Research: Athens, Greece, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Laskou, M.; Economou, M. Platinum group element and gold concentrations in Greek bauxites. Geol. Balc. 1990, 21, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ring, U.; Layer, P.W. High-pressure metamorphism in the Aegean, eastern Mediterranean: Underplating and exhumation from the Late Cretaceous until the Miocene to Recent above the retreating Hellenic subduction zone. Tectonics 2003, 22, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaschek, F.; Kennedy, A.K.; Villa, I.M.; Lagos, M.; Ballhaus, C. Zircons from Syros, Cyclades, Greece—Recrystallization and mobilization of zircon during high pressure metamorphism. J. Petrol. 2003, 44, 1977–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forster, M.A.; Lister, G.S. Several distinct tectono-metamorphic slices in the Cycladic eclogite–blueschist belt, Greece. Contr. Miner. Petrol. 2005, 150, 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putlitz, B.; Cosca, M.A.; Schumacher, J.C. Prograde mica 40Ar/39Ar growth ages recorded in high pressure rocks (Syros, Cyclades, Greece). Chem. Geol. 2005, 214, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, G.S.; Forster, M.A. White mica 40Ar/39Ar age spectra and the timing of multiple episodes of high-P metamorphic mineral growth in the Cycladic eclogite–blueschist belt, Syros, Aegean Sea, Greece. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2016, 34, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, V.; Lanari, P.; Naïr, I.; Augier, R.; Lahfid, A.; Jolivet, L. Exhumation of eclogite and blueschist (Cyclades, Greece): Pressure-temperature evolution determined by thermobarometry and garnet equilibrium modelling. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2018, 36, 769–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Maar, P.A.; Jansen, J.B.H. The geology of the polymetamorphic complex of Ios, Cyclades, Greece and its significance for the Cycladic Massif. Int. J. Earth Sci. 1983, 72, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, S.L. Contrasting PTt histories for blueschists from the western Baja Terrane and the Aegean: Effects of synsubduction exhumation and backarc extension. Wash. Am. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 1996, 96, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Avigad, D. High-pressure metamorphism and cooling on SE Naxos (Cyclades, Greece). Eur. J. Miner. 1998, 10, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.B.H.; Schuiling, R.D. Metamorphism on Naxos: Petrology and geothermal gradients. Am. J. Sci. 1976, 276, 1225–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buick, I.S.; Holland, T.J.B. The P-T-t path associated with crustal extension, Naxos, Cyclades. In The Evolution of Metamorphic Belts; Daly, J.S., Cliff, R.A., Yardley, B.W.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 1989; Volume 40, pp. 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Duchene, S.; Aissa, R.; Vanderhaeghe, O. Pressure-temperature-time evolution of metamorphic rocks from Naxos (Cyclades, Greece): Constraints from thermobarometry and Rb/Sr dating. Geodin. Acta 2006, 19, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, L.; Duchêne, S.; Deloule, E.; Vanderhaeghe, O. The isotopic composition of zircon and garnet: A record of the metamorphic history of Naxos, Greece. Lithos 2006, 87, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.A.; Duchêne, S.; Deloule, E.; Vanderhaeghe, O. Mobility of trace elements and oxygen in zircon during metamorphism: Consequences for geochemical tracing. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 267, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, V.; Jolivet, L.; Roche, V.; Augier, R.; Scaillet, S.; Cardello, G.L. Strain localization in a fossilized subduction channel: Insights from the Cycladic Blueschist Unit (Syros, Greece). Tectonophysics 2016, 672, 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vavassis, I.; De Bono, A.; Stampfli, G.M.; Giorgis, D.; Valloton, A.; Amelin, Y. U–Pb and Ar–Ar geochronological data from Pelagonian basement in Evia (Greece): Geodynamic implications for the evolution of the Paleotethys. Schw. Miner. Petrograph. Mitteil. 2000, 80, 21–43. [Google Scholar]
- Avigad, D.; Gerdes, A.; Morag, N.; Bechstadt, T. Coupled U–Pb– Hf of detrital zircons of Cambrian sandstones from Morocco and Sardinia: Implications for provenance and Precambrian crustal evolution of north Gondwana. Gondwana Res. 2012, 21, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinhold, G.; Morton, A.C.; Avigad, D. New insights into peri-Gondwana paleogeography and the Gondwana super-fan system from detrital zircon U–Pb ages. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xypolias, P.; Dörr, W.; Zulauf, G. Late Carboniferous plutonism within the pre-Alpine basement of the External Hellenides (Kithira, Greece): Evidence from U–Pb zircon dating. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 2006, 163, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydonakis, K.; Gallagher, K.; Brun, J.P.; Jolivet, M.; Gueydan, F.; Kostopoulos, D. Upper Cretaceous exhumation of the western Rhodope Metamorphic Province (Chalkidiki Peninsula, northern Greece). Tectonics 2014, 33, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dörr, W.; Zulauf, G.; Gerdes, A.; Lahaye, J.; Kowalczyk, G. A hidden Tonian basement in the eastern Mediterranean: Age constraints from U–Pb data of magmatic and detrital zircons of the External Hellenides (Crete and Peloponnesus). Precambrian Res. 2015, 258, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulauf, G.; Dörr, W.; Fisher-Spurlock, S.C.; Gerdes, A.; Chatzaras, V.; Xypolias, P. Closure of the Paleo-Tethys in the External Hellenides: Constraints from U-Pb ages of magmatic and detrital zircons (Crete). Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 642–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulauf, G.; Dörr, W.; Marko, L.; Krahl, J. The late Eo-Cimmerian evolution of the external Hellenides: Constraints from microfabrics and U–Pb detrital zircon ages of Upper Triassic (meta)sediments (Crete, Greece). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 2859–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, U.; Laws, S.; Bernet, M. Structural analysis of a complex nappe sequence and late-orogenic basins from the Aegean Island of Samos, Greece. J. Struct. Geol. 1999, 21, 1575–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaschek, F.; Kennedy, A.; Keay, S.; Ballhaus, C. Geochronological constraints on Carboniferous and Triassic magmatism in the Cyclades: SHRIMP U–Pb ages of zircons from Syros, Greece. J. Confer. Abstr. 2001, 6, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Reischmann, T.; Kostopoulos, D.K.; Loos, S.; Anders, B.; Avgerinas, A.; Sklavounos, S.A. Late Palaeozoic magmatism in the basement rocks southwest of Mt. Olympos, Central Pelagonian Zone, Greece: Remnants of a Permo-Carboniferous magmatic arc. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2001, 34, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, B.; Reischmann, T.; Kostopoulos, D. Zircon geochronology of basement rocks from the Pelagonian Zone, Greece: Constraints on the pre-Alpine evolution of the westernmost Internal Hellenides. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 639–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.H.F.; Clift, P.D.; Degnan, P.J.; Jones, G. Palaeogeographic and palaeotectonic evolution of the Eastern Mediterranean Neotethys. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 1991, 87, 289–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.H.F.; Dixon, J.E.; Brown, S.; Collins, A.; Morris, A.; Pickett, E.A.; Sharp, I.; Ustaömer, T. Alternative tectonic models for the Late Palaeozoic–Early Tertiary development of Tethys in the Eastern Mediterranean region. In Palaeomagnetism and Tectonics of the Μediterranean Region; Morris, A., Tarling, D.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; Volume 105, pp. 239–263. [Google Scholar]
- Stampfli, G.M.; Borel, G.D. A plate tectonic model for the Paleozoic and Mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrons. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 196, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.H.F. Sedimentary evidence from the south Mediterranean region (Sicily, Crete, Peloponnese, Evia) used to test alternative models for the regional tectonic setting of Tethys during Late Palaeozoic–Early Mesozoic time. In Tectonic Development of the Eastern Mediterranean Region; Robertson, A.H.F., Mountrakis, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; Volume 260, pp. 91–154. [Google Scholar]
- Buick, I.S. The late Alpine evolution of an extensional shear zone, Naxos, Greece. J. Geol. Soc. 1991, 148, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubouin, J.; Bonneau, M.; Celet, P. Contribution à la Géologie des Hellènides: Le Gavrovo, le Pinde et la Zone Ophiolique Subpélagonienne. Ann. Soc. Géol. Nord 1970, 90, 277–306. [Google Scholar]
- Fleury, J.J. Evolution d’une platforme et d’un bassin dans leur cadre alpin: Les zones de Gavrovo-Tripolitza et du Pinde-Olonos. Soc. Géol. Nord. Spec. Publ. 1980, 4, 651. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, S.L.; Lister, G.S. Thermochronology of the South Cyclades Shear Zone, Ios, Greece: Effects of ductile shear in the argon partial retention zone. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 7315–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeesch, P. IsoplotR: A free and open toolbox for geochronology. Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laskari, S.; Soukis, K.; Lozios, S.; Stockli, D.F.; Poulaki, E.M.; Stouraiti, C. Structural Study and Detrital Zircon Provenance Analysis of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit Rocks from Iraklia Island: From the Paleozoic Basement Unroofing to the Cenozoic Exhumation. Minerals 2022, 12, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010083
Laskari S, Soukis K, Lozios S, Stockli DF, Poulaki EM, Stouraiti C. Structural Study and Detrital Zircon Provenance Analysis of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit Rocks from Iraklia Island: From the Paleozoic Basement Unroofing to the Cenozoic Exhumation. Minerals. 2022; 12(1):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010083
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaskari, Sofia, Konstantinos Soukis, Stylianos Lozios, Daniel F. Stockli, Eirini M. Poulaki, and Christina Stouraiti. 2022. "Structural Study and Detrital Zircon Provenance Analysis of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit Rocks from Iraklia Island: From the Paleozoic Basement Unroofing to the Cenozoic Exhumation" Minerals 12, no. 1: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010083
APA StyleLaskari, S., Soukis, K., Lozios, S., Stockli, D. F., Poulaki, E. M., & Stouraiti, C. (2022). Structural Study and Detrital Zircon Provenance Analysis of the Cycladic Blueschist Unit Rocks from Iraklia Island: From the Paleozoic Basement Unroofing to the Cenozoic Exhumation. Minerals, 12(1), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010083








